#Clean Renewable Energy
Text

TL/DR: Vote like your life depends on it. Cuz it does.
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
Commercial heating systems for public and private sector. A range of fully scalable air source and ground source heat pumps and biomass boilers are available.
#commercial heating systems#commercial air source heat pump#commercial ground source heat pump#commercial biomass boilers#Clean Renewable Energy#Portsmouth#UK
0 notes
Text
"It is 70 years since AT&T’s Bell Labs unveiled a new technology for turning sunlight into power. The phone company hoped it could replace the batteries that run equipment in out-of-the-way places. It also realised that powering devices with light alone showed how science could make the future seem wonderful; hence a press event at which sunshine kept a toy Ferris wheel spinning round and round.
Today solar power is long past the toy phase. Panels now occupy an area around half that of Wales, and this year they will provide the world with about 6% of its electricity—which is almost three times as much electrical energy as America consumed back in 1954. Yet this historic growth is only the second-most-remarkable thing about the rise of solar power. The most remarkable is that it is nowhere near over.
To call solar power’s rise exponential is not hyperbole, but a statement of fact. Installed solar capacity doubles roughly every three years, and so grows ten-fold each decade. Such sustained growth is seldom seen in anything that matters. That makes it hard for people to get their heads round what is going on. When it was a tenth of its current size ten years ago, solar power was still seen as marginal even by experts who knew how fast it had grown. The next ten-fold increase will be equivalent to multiplying the world’s entire fleet of nuclear reactors by eight in less than the time it typically takes to build just a single one of them.
Solar cells will in all likelihood be the single biggest source of electrical power on the planet by the mid 2030s. By the 2040s they may be the largest source not just of electricity but of all energy. On current trends, the all-in cost of the electricity they produce promises to be less than half as expensive as the cheapest available today. This will not stop climate change, but could slow it a lot faster. Much of the world—including Africa, where 600m people still cannot light their homes—will begin to feel energy-rich. That feeling will be a new and transformational one for humankind.
To grasp that this is not some environmentalist fever dream, consider solar economics. As the cumulative production of a manufactured good increases, costs go down. As costs go down, demand goes up. As demand goes up, production increases—and costs go down further. This cannot go on for ever; production, demand or both always become constrained. In earlier energy transitions—from wood to coal, coal to oil or oil to gas—the efficiency of extraction grew, but it was eventually offset by the cost of finding ever more fuel.
As our essay this week explains, solar power faces no such constraint. The resources needed to produce solar cells and plant them on solar farms are silicon-rich sand, sunny places and human ingenuity, all three of which are abundant. Making cells also takes energy, but solar power is fast making that abundant, too. As for demand, it is both huge and elastic—if you make electricity cheaper, people will find uses for it. The result is that, in contrast to earlier energy sources, solar power has routinely become cheaper and will continue to do so.
Other constraints do exist. Given people’s proclivity for living outside daylight hours, solar power needs to be complemented with storage and supplemented by other technologies. Heavy industry and aviation and freight have been hard to electrify. Fortunately, these problems may be solved as batteries and fuels created by electrolysis gradually become cheaper...
The aim should be for the virtuous circle of solar-power production to turn as fast as possible. That is because it offers the prize of cheaper energy. The benefits start with a boost to productivity. Anything that people use energy for today will cost less—and that includes pretty much everything. Then come the things cheap energy will make possible. People who could never afford to will start lighting their houses or driving a car. Cheap energy can purify water, and even desalinate it. It can drive the hungry machinery of artificial intelligence. It can make billions of homes and offices more bearable in summers that will, for decades to come, be getting hotter.
But it is the things that nobody has yet thought of that will be most consequential. In its radical abundance, cheaper energy will free the imagination, setting tiny Ferris wheels of the mind spinning with excitement and new possibilities.
This week marks the summer solstice in the northern hemisphere. The Sun rising to its highest point in the sky will in decades to come shine down on a world where nobody need go without the blessings of electricity and where the access to energy invigorates all those it touches."
-via The Economist, June 20, 2024
#solar#solar power#solarpunk#hopepunk#humanity#electricity#clean energy#solar age#renewables#green energy#solar energy#renewable energy#solar panels#fossil fuels#good news#hope#climate change#climate hope
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Previous similar drops in emissions were due to periods of economic stagnation or recession--this is the first significant drop in emissions that has coincided with GDP growth.
The majority of this decline is due to changes in energy use and generation. Coal demand has dropped nearly to 1900s levels, while use of renewables grows significantly--for the first time renewables accounted for half of the energy generated in "advanced economies" included in this analysis.
#good news#hope#ecoanxiety#ecogrief#climate anxiety#climate grief#climate change#global warming#renewable energy#green energy#clean energy#coal#solar#wind energy
912 notes
·
View notes
Text

#free congo#don't forget about the congo#tesla#glencore#cobalt#nickel#human rights abuses#allegations#mining industry#renewable energy#clean energy#environmental impact#worker mistreatment#corruption#ethical sourcing#global supply chain#corporate responsibility#renewable energy transition#accountability
333 notes
·
View notes
Text
I really hope they can work the bugs out of this solution, because if it's done right, it'll really be a win-win situation. Less evaporation of water, and solar power being generated every day? Yes, please. We are smart, resourceful beings, and this is far from the most difficult problem we've had to address.
This is also a great example of how we can go back and fix mistakes of the past. We very, very rarely ever come up with technological solutions that take long-term effects on the environment into consideration, and so the way many things are designed often leads to some sort of damage, whether through manufacture, use, disposal, or all of the above. Retrofitting canals (which have been used in agriculture for thousands of years) will have benefits not only in the ways mentioned above, but also gets people thinking more about the impacts we make.
I'm hoping that this will lead to more new technology being developed in ways that already anticipate and account for negative impacts so that they avoid them in the first place, rather than having to engineer new solution many years down the line.
#solar power#solar panels#renewable energy#water#environment#irrigation#agriculture#green energy#conservation#technology#clean energy#science#solarpunk#hopepunk
697 notes
·
View notes
Text
California used 100% renewable energy for 25 out of the last 32 days.
69 notes
·
View notes
Text
From Lexi Drumonde's video on Hopepunk.

#hopepunk#hope punk#solar punk#solarpunk#futurism#misinformation#clean energy#renewable energy#nihilsm#nihilizm#climate and environment#climate hope#climate action#climate doom#doomerism
155 notes
·
View notes
Text
45 notes
·
View notes
Text
"There is a small panel of regulators in every state that holds a similar power over electricity generation and, by extension, an enormous segment of the United States’ greenhouse gas emissions that are warming the planet. By setting electricity prices, they also have a substantial impact on most people’s lives and pocketbooks. Yet, in Georgia and elsewhere, these groups — known as public service or public utility commissions — get little attention or scrutiny outside of energy wonk circles. Their hearings and documents tend to be long and jargon-heavy, covered in the media by a small group of specialized reporters, making it hard to engage with the process.
This year, Grist and WABE will try to demystify energy regulation in Georgia and beyond. We’ll bring you stories on not only how your power gets made, but how those decisions happen — and how residents who vote and pay electricity bills can get involved."
-via Grist, March 5, 2024. See link for more details (especially in Georgia) and more ways to get involved.
#clean energy#green energy#renewable energy#climate crisis#fossil fuels#elected officials#2024 elections#us election#united states#us politics#state politics#georgia#solar power#wind power#utilities#activism#climate activism#organizing#action post#hope
22 notes
·
View notes
Text
If there is anyone in Pennsylvania who is undecided please send this to them. Or anyone who think that renewable energy is inherently bad for “the economy”.
Would it help if I pointed out Taylor Swift was born in Pennsylvania? 🙄
#pennsylvania#please vote#election 2024#2024 elections#trump vance 2024#politics#political#go green#reduce reuse recycle#green energy#renewable energy#climate crisis#climate change#climate news#climate action#climate justice#climate solutions#climate and environment#climate chaos#climate catastrophe#climate collapse#global warming#environmentalism#environmentalist#PA#clean energy#fuck donald trump#donald trump#build back better#inflation reduction act
9 notes
·
View notes
Text

#photo#my photos#photooftheday#picture#photoshop#photographer#photoshoot#photography#photograph#nature art#nature aesthetic#nature hikes#nature lovers#nature photography#nature images#sky#sky photography#clouds#skyscape#blue sky#green energy#wind turbines#windmill#windmills#renewable energy#clean energy#wind power#green energy solutions#sweden#climate
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
UK homeowners get renewable energy finance now! RHI Scheme, Green Homes Grant or regular financing for a biomass boiler, solar panels or heat pumps. Free advice.
#UK homeowners#renewable energy finance#RHI Scheme#Green Homes Grant#regular financing for a biomass boiler#regular financing for solar panels#regular financing for heat pumps#air source heat pump finance#Clean Renewable Energy#Portsmouth#UK
0 notes
Text
"A 1-megawatt sand battery that can store up to 100 megawatt hours of thermal energy will be 10 times larger than a prototype already in use.
The new sand battery will eliminate the need for oil-based energy consumption for the entire town of town of Pornainen, Finland.
Sand gets charged with clean electricity and stored for use within a local grid.
Finland is doing sand batteries big. Polar Night Energy already showed off an early commercialized version of a sand battery in Kankaanpää in 2022, but a new sand battery 10 times that size is about to fully rid the town of Pornainen, Finland of its need for oil-based energy.
In cooperation with the local Finnish district heating company Loviisan Lämpö, Polar Night Energy will develop a 1-megawatt sand battery capable of storing up to 100 megawatt hours of thermal energy.
“With the sand battery,” Mikko Paajanen, CEO of Loviisan Lämpö, said in a statement, “we can significantly reduce energy produced by combustion and completely eliminate the use of oil.”
Polar Night Energy introduced the first commercial sand battery in 2022, with local energy utility Vatajankoski. “Its main purpose is to work as a high-power and high-capacity reservoir for excess wind and solar energy,” Markku Ylönen, Polar Nigh Energy’s co-founder and CTO, said in a statement at the time. “The energy is stored as heat, which can be used to heat homes, or to provide hot steam and high temperature process heat to industries that are often fossil-fuel dependent.” ...
Sand—a high-density, low-cost material that the construction industry discards [Note: 6/13/24: Turns out that's not true! See note at the bottom for more info.] —is a solid material that can heat to well above the boiling point of water and can store several times the amount of energy of a water tank. While sand doesn’t store electricity, it stores energy in the form of heat. To mine the heat, cool air blows through pipes, heating up as it passes through the unit. It can then be used to convert water into steam or heat water in an air-to-water heat exchanger. The heat can also be converted back to electricity, albeit with electricity losses, through the use of a turbine.
In Pornainen, Paajanen believes that—just by switching to a sand battery—the town can achieve a nearly 70 percent reduction in emissions from the district heating network and keep about 160 tons of carbon dioxide out of the atmosphere annually. In addition to eliminating the usage of oil, they expect to decrease woodchip combustion by about 60 percent.
The sand battery will arrive ready for use, about 42 feet tall and 49 feet wide. The new project’s thermal storage medium is largely comprised of soapstone, a byproduct of Tulikivi’s production of heat-retaining fireplaces. It should take about 13 months to get the new project online, but once it’s up and running, the Pornainen battery will provide thermal energy storage capacity capable of meeting almost one month of summer heat demand and one week of winter heat demand without recharging.
“We want to enable the growth of renewable energy,” Paajanen said. “The sand battery is designed to participate in all Fingrid’s reserve and balancing power markets. It helps to keep the electricity grid balanced as the share of wind and solar energy in the grid increases.”"
-via Popular Mechanics, March 13, 2024
--
Note: I've been keeping an eye on sand batteries for a while, and this is really exciting to see. We need alternatives to lithium batteries ASAP, due to the grave human rights abuses and environmental damage caused by lithium mining, and sand batteries look like a really good solution for grid-scale energy storage.
--
Note 6/13/24: Unfortunately, turns out there are substantial issues with sand batteries as well, due to sand scarcity. More details from a lovely asker here, sources on sand scarcity being a thing at the links: x, x, x, x, x
#sand#sand battery#lithium#lithium battery#batteries#technology news#renewable energy#clean energy#fossil fuels#renewables#finland#good news#hope#climate hope
1K notes
·
View notes
Link
“Experts are calling time on the fossil age as new analysis shows wind and solar power produced a record amount of the world’s electricity last year.The renewables generated 12 per cent of global electricity in 2022, up from 10 per cent the previous year, according to the report from clean energy think tank Ember.And while a small increase in coal burning pushed electricity emissions up to an all-time high, analysts predict this will be the peak of pollution.”
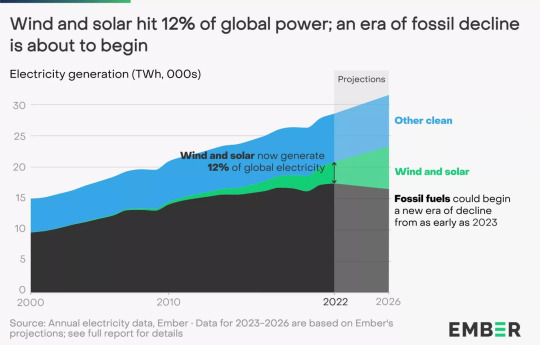
#clean energy#renewable energy#green energy#solar energy#wind energy#hope#good news#energy#environment#climate change#global warming#ecoanxiety#ecogrief#environmental grief#ecological grief#climate anxiety
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
A new government-commissioned report says Ontario should commit to achieving a clean energy economy by 2050.
An expert panel says in the report that the province should develop related policies and communicate its vision clearly to the public about a transition to electrification.
The report lays out a series of recommendations to the province, including providing clarity on the role of natural gas that should be aligned with a commitment to clean energy.
The panel also says the province should figure out how to find broad support to switch to clean technology such as electric vehicles, energy storage and heat pumps.
Continue Reading
Tagging @politicsofcanada
21 notes
·
View notes