#CommandLineTools
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Whisper on Older Machines

youtube
With so many paid AI-powered services around these days, has anyone ever wondered if one can do these things locally on their own machine without the use of paid services to do this deal? Well, I thought I’d give it a go on my own setup. A few months ago I did the same thing with SoVITS, which is a standalone program for cloning your voice or other voices, locally on one’s own machine with no paid services needed. While I got mixed results due to my own hardware limitations and age of that hardware I did get it to work and that was the mission of those experiments. Just to see if I could get it working based on my current hardware setup and its limitations. For this experiment we are work with transcribing audio to text, I thought this process would be much easier for my system to handle and I wasn’t wrong. However, I did run into several challenges that hindered my computer’s ability to properly install the software and all its dependencies properly without errors. I did several workarounds and I did eventually get it working to the level I wanted it to work at. For me it was about quality, speed and accuracy. I now feel confident that if in the future I need an audio file that has the majority of that audio file as spoken word dialog/conversation and have my computer transcribe that and dump it into a very easy to manipulate text file that I can copy/paste/edit said text. Below is my explanation along with the methodologies I used to get it working with all the proper commands and explanation of those commands.
First let’s talk about Whisper and what it is…
Whisper is an advanced automatic speech recognition (ASR) system developed by OpenAI. OpenAI is the same company that develops ChatGPT. It is designed to transcribe spoken language into written text. The program is capable of processing a variety of audio files containing speech. Examples would be MP3, WMA, ACC, AIFF, PCM, WAV, Ogg, FLAC and many others. Whisper's practicality comes from its ability to transcribe audio files into text, making it highly useful for a range of tasks, such as:
Transcribing Conversations or Meetings:
If you recorded a conversation or a meeting, Whisper can take that audio and turn it into a readable text formatted document. This could be helpful for keeping a written record of important discussions, or for reference in the future.
Content Creation:
For creators, podcasts, YouTube videos, or interviews, Whisper can convert spoken words into text, which could then be used for captions, subtitles, or blog posts.
Accessibility:
It provides a way for individuals who are deaf or hard of hearing to have access to content that is spoken. This is especially useful for video content, meetings, or any form of multimedia.
Research or Note-Taking:
Researchers or students can use Whisper to transcribe lectures, interviews, or audio notes, making it easier to analyze and reference the material in written form.
Whisper doesn't come with a typical graphical interface (GUI) for easier usage that one might expect from most software. Instead, it uses a command-line interface (CLI), where you type in text-based commands in programs like CMD, PowerShell, or Python. While this might sound complicated, there are a few practical reasons why Whisper is designed this way, especially for its intended audience. A GUI requires more system resources, like memory and processing power, because it needs to display visuals and handle user interactions. The basic functionality in a command-line tool is much lighter on resources, meaning Whisper can focus all its energy on doing the heavy work of transcribing or processing audio. This is especially important for Whisper, which can handle long audio files or large amounts of data—something that could slow down if it had to display a graphical interface as well.
Another reason is that Whisper is mainly aimed at developers, researchers, and people with some technical background who need a lot of control over how the program works. With a command-line tool, users can easily adjust things, like the model it uses, whether to process the audio with a computer's CPU or in some cases a more powerful GPU, and what kind of output file they want. These things might not be easy to do with a GUI, and people who are comfortable with coding often prefer to have this level of control. Whisper also needs to be able to run on a variety of systems, from personal computers to powerful cloud servers. A command-line interface is more flexible and can be used in many different environments, whether on a personal desktop or remotely via the internet. GUIs are harder to set up and maintain across different systems, making the CLI a better choice for Whisper's developers, who want to keep it simple and efficient.
Since Whisper is open-source software, it’s also built to be transparent and modifiable. Advanced users can dive into the code and customize how it works or integrate it into larger projects. This wouldn’t be as easy to do if there were a GUI, which would hide much of the underlying functionality. The people who use Whisper are usually looking to get fast results, not spend time navigating through menus, settings and buttons. The command-line interface allows them to quickly type commands and get the task done, whether they are transcribing an audio file or running batch processes for many files at once. While a graphical interface might make Whisper look more user-friendly, the command-line design actually gives users more power, speed, and control. It's a tool made for people who know how to work with it on a deeper level, and it allows Whisper to run efficiently and be used in a wide range of setups and environments.
Fear not though. One can and probably should, as I did, use ChatGPT to help with making the setup more logical and help with the actual commands. I know next to nothing on how Python, Python’s venv (virtual workspace on your computer), PowerShell actually work; and I only have moderate knowledge on how CMD works. At least it isn’t a foreign language for me. You do not have to be an advanced programmer for this. My attempt here is to make this essay-style tutorial be as easy as possible to follow along. I am not saying this will work for ALL novice Windows-based computer users, but it should work for most of you. If I can get this working on a 15-year old, low-end gaming machine, built for video editing, then it’s likely one can make it work on their newer system that was more/less built for advanced office-style duties. The hardest parts here is installing Whisper and all its support software correctly, in the correct order, paths, with the correct versions of those dependences, depending on one’s computer hardware specifications. That is the key here; because everyone’s computer setup, whether or not it’s a Dell or an HP or whatever, is all configured, setup and has different types of hardware profiles inside the chassis. It is all uniquely different. Just like human-beings…
So, how exactly does Whisper work?
Once the Whisper program is properly set up on your computer it can process an audio file, (like an MP3 or WAV), that contains speech. Whisper then transcribes the speech into text and outputs it as a .txt file, which is one of the most basic and universally supported text file formats in the digital world. This text file can be opened and used across virtually all devices, operating systems, and software programs in the world. A real-world practical example; imagine you recorded a conversation between you, and say, your ex, and for legal reasons you need to have a written record of that conversation for your lawyer. Whisper can transcribe the spoken words into a simple text file, which you can then edit, share, or use as needed. Whisper is a tool that allows you to turn speech into text, making audio content more accessible and usable for various purposes. Once set up, it becomes a simple and practical tool for converting spoken word into a written form and it’s on your computer, free to use. So after all that sale’s pitch and definition nonsense let’s try to install this puppy…
Tutorial 1: Installing Whisper Without Virtual Environment on Windows 10:
Our first tutorial here will be on trying to install everything just using Windows 10 Pro’s CMD and the basic Python setup as the installation bed. Most recommendations had said it is way easier to install/setup/configure Whisper inside a Python venv (virtual environment). This will be explained a little later, but this was a good lesson on at least learning the programming language, commands and philosophy as to how this stuff works. If one is on a much newer machine than mine, perhaps a brand new one, one may not have to go through all the virtual setups for this as I did. Although this method did not work on my system, it can work on modern machines with s more up-to-date hardware package.
First we may need to download and install the Python system on the machine that is going to use Whisper. One might already have it, but if it is a brand new machine it is likely one would have to download and install it. Now before we get started it should be noted that there are multiple ways to download, install, configure programming language software on your computer. The method I used here was more/less due to my inexperience using CLI software like this and my older, out-of-date, hardware profile.
Download and install Python from the official Python.org/downloads/windows/. Download the newest version. At the time of this writing the newest version is 3.13.2. It should be noted that due to my machine’s age I needed a far older version (3.9.6), which will be explained later in this essay. While installing if there is an option to check a box to add Python to the system PATH during installation, do so. If there isn’t, once Python is installed we will need to ad it manually. I had to.
The Python executables or the actual file that opens the program is not installed in the normal places one installs software for their computer, where Windows will put a shortcut to it either on your desktop top or in your Windows Taskbar or Windows Start Menu. It stores it in a folder that tends to be hidden in Windows by Default in your main Libraries folder. This is the folder where your main folders for your profile on the Operating System are stored: Documents, Pictures, Videos, etc. This folder usually has the name you labeled it as when you setup your computer initially. The folder we need to access is also here, but might be hidden. So we need to tell Windows to show these folders in the Librarie’s directory. Navigate to your main Library’s folder and click view at the top. There should be a checkbox that says hidden items.Make sure that is checked. There should be a folder there named APPDATA. Open it. Open the folder named Local. Open the folder named Programs. Open the folder named Python. If you have a single version of Python you should see the folder there. For this installation attempt we are using Python313. Open the folder named Python313.What we want to do here is copy the file path of this folder. Go into the address, highlight and copy the entire address string for this directory. It should look something like this: C:\Users\Your-Library-Folder-Name\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python313\ - We are going to want to copy this. We are then going to paste this path into our System Properties – Environmental Variables Settings. Go into your Windows search and type in Environmental Variables and click the option that says: Edit environment variables for your account. This should open a little Window that says: SystemProperties. At the bottom select button that says: Environmental Variables. Under System Variables scroll through the variables to Path. Click Edit. Click New. Scroll to the bottom of the list and paste your Python installation here: C:\Users\Your-Library-Folder-Name\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python313\ - Once that is done you will need to click the OK button three times to get out of the System Environmental Settings. We now want to confirm Python’s installation and access. We are going to want to open your Command Prompt or CMD, but we are going to want to open this in Administrator Mode. This will by-pass any permission issues we might run into while downloading, installing and setting up the proper software packages into the Windows OS Environment. In the Windows Search type CMD, you should see it on the left but on the right it should say Run As Administrator.You can also right click on the CMD and choose to Run As Administrator from the right-click menu. Once CMD is open type: python --version – This will show you the version number of Python. Mine says Python 3.13.2. I never ran into an error here. So if you did either try the process again after a reboot, check Google and/or ChatGPT or consult a friend who has advanced IT skills.
Next we need to start the process of downloading and installing the required dependencies. In your CMD install pip, numpy, and other dependencies:
In CMD type/copy/paste these commands separately so that we know each one is installed correctly. Doing batch-style commands here gave me issues.
First Command:
Python -m pip install --upgrade pip
Second Command:
Python -m pip install numpy
Third Command:
Python -m pip install torch torchvision torchaudio
Now it is time to install Whisper itself. Type this command:
pip install openai-whisper
If everything worked correctly one could try to test it with a file to see if it is working. For this tutorial we are just going to use a generic audio file that has dialog on it that we popped into the directory.
This would be the command one would use to do this:
whisper "C:\path\to\your\audiofile.mp3"
This is where we ran into issues. I never could get past the installation step of Whisper on my system under this type of configuration. It was recommended to attempt to download an older version of Whisper, which I tried, that also failed. Whisper did not work in this setup due to hardware limitations and conflicts between software versions (such as NumPy version issues). Why It Failed is probably closer to the lack of a virtual environment resulting in version conflicts between the System, Python, and Packages, especially with NumPy. The solution here was to move to the next method using a virtual environment (venv) to isolate the setup. On a modern system the steps should work without modification. Newer hardware can follow the standard installation process without these issues.
Tutorial 2: Installing Whisper Using a Virtual Environment (venv) with CPU:
This method involved setting up a virtual environment (venv) to avoid conflicts with system-level Python packages and dependency conflicts. A Python virtual environment (venv) is like creating a separate, contained workspace on your computer where you can install and manage specific tools and libraries for a particular project without affecting the rest of your system. Imagine it like a special, isolated folder that has everything needed for a specific project. Inside this folder, you can install Python packages, like Whisper, and only those packages will be available for that project. Other projects or programs on your computer won’t be impacted by these installations and configurations. This is especially useful when you're working on different projects that might need different versions of Python or specific libraries that could be in conflict with each other. By using a virtual environment, you ensure that each project has its own set of tools, rules for those tools and your main system stays clean and organized. A venv keeps things tidy, avoids conflicts, and makes it easier to manage dependencies for projects like Whisper or any other Python-based projects one is using.
We will skipped a lot of the specifics within the details that I have already outlined above. Much of these commands are the same. It is just the initial settings where things tend to be different. After trying much of the same processes rom above I ran into more conflicts and system setup errors. This is where we downloaded an older version of Python for my setup. Your setup could literally be the same as the one above except one would be using the venv for that setup over this one. This is one is identical except we are using an older version of Python. I will talk about this because it is still likely enough one might have to use an older version of Python, but not all or even most, just some.
To download, install, and ad path to the System Properties Environmental Settings follow the same process above except download and install Python 3.9.6 using this link:
python.org/downloads/release/python-396/
In the C:\Users\Your-Library-Folder-Name\AppData\Local\Programs directory you will now see multiple Python folders. Open the folder Python39 and copy the address:
C:\Users\Your-Library-Folder-Name\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python39\
When you go into the Environmental Settings to edit the Path you will ad this path beneath the path that say:
C:\Users\Your-Library-Folder-Name\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python313\
This essential tells Windows that your primary version is 3.13.2 but if you designate it to use 3.9.6 that Windows will recognize it and use it. We have to tell our OS that in the CMD, but this is the first leg of those steps.
We are now going to create the venv using this older version Python. For users that want to simply use the venv setup using the newest version of Python, both setups for that venv will be listed here. For this to work it is always easier to make Windows do less. So the placement of your venv should be in the most easiest, basic spot on your computer. The C-Drive. In theory you can place it anywhere but the more jumps the more resource-intensive the process becomes. I created a folder on my C-drive and just named it ‘whisperabc.’ No caps, no quotes just whisperabc – the directory should be: C:\whisperabc
Open your CMD in Run As Administrator mode.
We want to navigate to this directory:
cd C:\whisperabc
This will make sure you are in the C-drive in the whisperabc folder. We now want to run this command in CMD:
C:\Users\Your-Library-Folder-Name\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python39\python.exe -m venv whisperabc-env
What this means is you are telling CMD to use the Python executable from that specific location on your computer. The Usual way would be just to type the command:
python3.9 -m venv whisper-env but that command did not work for my system. I had to include the entire file path in order for Windows to recognize that I wanted to specifically use Python 3.9.6 for this venv installation. It should also be noted here we are using the CPU for the processing and not the GPU. We will have a tutorial for swapping out the CPU for the GPU in our final tutorial on Whisper. Once we have our venv created we want to navigate back to the folder in Windows. Go to your C:\whisperabc and open the folder whisperabc-env. Then open the folder Scripts. Copy the file address and go back to your CMD to navigate to this directory with the command:
cd C:\whisperabc\whisperabc-env\Scripts
This will tell CMD to go to this folder. Once there type the command:
activate and press enter.
At this point you should be inside your virtual environment by seeing the prompt with parenthesis around it followed by the directory you are currently in: (whisperabc-env) C:\whisperabc\whisperabc-env\Scripts> and now it is time to start installing dependencies.
First Command:
Python -m pip install --upgrade pip
Second Command:
Python -m pip install numpy
Third Command:
Python -m pip install torch torchvision torchaudio
Now it is time to install Whisper itself. This time we are going to download an older version for this configuration because others also failed on my system even in the venv. One would use the command in the above tutorial over this one below.
Type this command:
pip install openai-whisper==20230918
This tells our pip configuration tool to download and install Open Ai’s Whisper, Version released on 09/18/2023. On a newer machine one would not need this version but it may be noteworthy that one can download earlier versions if the newest version is not working with your hardware configuration. A test is in order with the generic audio file we had from earlier. Let’s verify the installation first to make sure we have it installed properly.
Verify Installed Version:
Usually one would use the standard command of whisper --version but because we are using an older version we may want to run the pip show openai-whisper command. This will also display the version number.
The command you are going to want to use is:
"C:\whisperabc\whisperabc-env\Scripts\python.exe" -m whisper "C:\whisperabc\audio123.mp3" --model large --output_dir "C:\whisperabc" --output_format txt --language English
This tells your venv that you want to use your old python 3.9.6 by pointing to it in your venv scripts. You want to use whisper here and to transcribe the mp3 in that directory using the large model, which is the more accurate than the small model, just takes a little bit longer to process. The command then is saying to export the transcribed text into text format with the .txt file extension in the English language. This skips the system checks for these output procedures which quickens the process.
Now you can go back to your C:\whisperabc folder and there should be a text file there called audio123.txt. If you open it –it will have your transcribed text in a simple basic format. You can then copy/paste this text into a document for whatever purpose you need it for.
Tutorial 3: Installing Whisper Using Virtual Environment (venv) with GPU:
Next we are going to try install this again but instead of using our computer’s CPU we are going to make it use the GPU. The GPU is the CPU for the Graphics Card. If one has an exterior graphics card independent from the motherboard it is called a GPU. The CPU is like a single smart, multi-tasking tool that handles a variety of tasks efficiently, but only has a few resources. It’s great for general work, but can get overwhelmed with heavy, repetitive calculations. The GPU is like a massive team of these specialized tools, plural, each handling a tiny part of a big job at the same time. Since transcribing audio with Whisper involves a ton of complex mathematical calculations, the GPU can break it down into smaller pieces and process them all at once—making it noticeably faster than a CPU for this kind of workload. While a CPU can do the job, a GPU does it much faster and efficiently because it's built for parallel processing. That’s why we want to set Whisper up to use your graphics card. In the case it is a NVIDIA GeForce GTX 750Ti. Since we are using an older system this becomes even more problematic because we still have to install this puppy using our older versions. It is very doable, but a little more complex a setup: The GPU (GTX 750 Ti) does not support CUDA 11+, which is required for the latest versions of PyTorch with GPU acceleration. OpenAI Whisper defaults to CPU unless explicitly told to use the system’s GPU.
We need to build another venv. Open your CMD in Run As Administrator mode.
We want to navigate to this directory again:
cd C:\whisperabc
This will make sure you are in the C-drive in the whisperabc folder. We now want to run this command in CMD:
C:\Users\David-PC\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python39\python.exe -m venv whisperabc-env
Like before; CMD uses Python from older the version’s location. Once we have our venv created we want to navigate back to the folder in Windows. Go to your C:\whisperabc and open the folder. Open the folder whisperabc-env. Then open the folder Scripts. Copy the file address and go back to your CMD to navigate to this directory with the command:
cd C:\whisperabc\whisperabc-env\Scripts
Once there type the command:
activate and press enter.
First Command:
At this point you should be inside your virtual environment and now it is time to start installing dependencies. Since Whisper uses PyTorch under the hood, you need to install the CUDA-compatible version of PyTorch. For NVIDIA GPUs, install a CUDA-supported version of PyTorch with this commend: pip install torch torchvision torchaudio --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu117
We are using an older GPU (GTX750Ti), CUDA 11+ is not supported, so installing an older CUDA version was recommended with this command but failed during the installation process. You want to use the version above this one: pip install torch==1.10.0+cu102 torchvision==0.11.1+cu102 torchaudio==0.10.1 -f https://download.pytorch.org/whl/torch_stable.html in the case one wants to try this hardware profile.
We have to do the same for numpy here. We have to download an older version that supports this older GPU. Through trial and error this version worked for me.
Second Command:
Python -m pip install numpy==1.23.5
We can verify the install with this command:
python -c "import numpy; print(numpy.__version__)"
Now it is time to install Whisper itself. Same as before; we are going to download the same older version for this configuration. For a regular installation on a newer machine, one would use the command in the first tutorial above over this one. The only real difference between this installation and the last one is we are forcing our system to use the GPU over the CPU, but other than that it is basically the same setup.
Type this command:
pip install openai-whisper==20230918
This tells our pip configuration tool to download and install that same version of Whisper that worked before.
Verify Installed Version:
You can either try the standard verification of whisper --version command but because of the older version the pip show openai-whisper command will display the version number a little easier.
We need to verify that PyTorch detects your GPU. We’ll need to activate Python inside our venv. Run this command: python You will see Python activate inside your venv as >>>
Run the following commands in the Python CLI:
First Command:
import torch press enter
The response should be another >>>
print(torch.cuda.is_available()) press enter
The response should be TRUE
print(torch.cuda.get_device_name(0) if torch.cuda.is_available() else "No GPU detected")
press enter.
The response should be NVIDIA GeForce GTX 750Ti
If the read outs for each come out as shown above then PyTorch detects your GPU. All we need to do now is Force Whisper to Use GPU. By default Whisper uses yours system’s CPU. We have to instruct Whisper to use the GPU inside our command prompt structure. The command will look something like this but we are not done just yet.
whisper "C:\whisperabc\audio123.mp3" --model large --device cuda
We are now ready to run our test of Whisper using our GPU with our, sort of, complicated hardware profile. As before, we are using the same mp3 in the C:\whisperabc. The command you are going to want to use is the same as the last tutorial, but with the added –device cuda tag to tell Whisper to use the GPU. We had to do this workaround to tell venv to utilize the GPU for the calculation processing that is why we could not just use the second tutorial and just adding the –device cuda tag to it. We would have gotten errors. Use this command:
"C:\whisperabc\whisperabc-env\Scripts\python.exe" -m whisper "C:\whisperabc\audio123.mp3" --model large --output_dir "C:\whisperabc" --output_format txt --language English --device cuda
We are again explicitly telling Whisper to:
Use Python inside your virtual environment
Run Whisper as a module
Use the large model
Process audio123.mp3 from the directory
Save the output to C:\whisperabc in TXT format (.txt)
Specify the language (English) instead of auto-detecting
Force GPU usage with --device cuda
If PyTorch is properly detecting your GPU (torch.cuda.is_available() returns True), which we verified above, then the command should run Whisper using the GPU instead of the CPU. When it’s done, go back to your C:\whisperabc and see if audio123.txt is there. Open the file and check the accuracy.
Conclusion:
• Summary of Methodology: We first tried installing Whisper without a virtual environment, which caused issues due to package conflicts and our outdated hardware profile. We then used a virtual environment to isolate the installation and ensure proper compatibility with the required dependencies. Finally, we switched to using the GPU to take advantage of hardware acceleration, resolving issues with legacy dependencies.
• Lessons Learned: Isolating dependencies with a virtual environment is crucial to avoid conflicts. Additionally, ensuring that the correct versions of libraries (e.g., NumPy, PyTorch) are installed is key to getting Whisper to work on older hardware.
The purpose of this essay on the methodology I used here was to both learn how to use Whisper for my many projects and be able to do something technical, like, installing, configuring it on a machine that is considered vastly outdated by today’s standards. Specifically, using your personal computer to do high level, mostly, automated processes. These three tutorials now reflect the specific steps taken and could serve as a guide for others that have older rigs, wants a very basic but detailed version of the steps, what they are, why they exist, and want to do some neat stuff with open source programs like this. Most everyday computers could do this. The high level gaming machines of today would zip through this compared to my current setup here.
It took some trial and error, but that’s part of the fun, I guess—learning how to work with what you’ve got and making it do things it wasn’t necessarily built for. If you’ve got a modern machine, you’ll probably breeze through this setup without much hassle. But even if you’re working with older hardware like mine, this just proves that with the right tweaks, open-source tools like Whisper can still run just fine. The big takeaway? You don’t always need the latest and greatest tech to do cool stuff. A little problem-solving, the right software versions, and some patience can go a long way in getting powerful AI tools up and running, locally on your own machine and most important, FREE...
Whisper on Older Machines by David-Angelo Mineo 3/29/2025 5,068 Words
Full Text with commands in PDF format below:
https://mineofilms.me/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/Blog-164-Whisper-on-Older-Machines.pdf
#whisper#openai#aitranscription#speechtotext#transcribeaudio#whisperai#offlinetranscription#freetranscription#installwhisper#whispertutorial#whisperonwindows#whisperonoldermachines#pythonwhisper#automatictranscription#localai#aitools#commandlinetools#cmd#powershell#virtualenvironment#aiforwriters#writersandai#aiwriting#blogwriting#bloggers#bloggingtools#freesoftware#opensource#transcribemeetings#transcribelectures
0 notes
Text
Login to openshift cluster in different ways | openshift 4
There are several ways to log in to an OpenShift cluster, depending on your needs and preferences. Here are some of the most common ways to log in to an OpenShift 4 cluster: Using the Web Console: OpenShift provides a web-based console that you can use to manage your cluster and applications. To log in to the console, open your web browser and navigate to the URL for the console. You will be…

View On WordPress
#openshift openshift4 containerization openshiftonline openshiftcluster openshiftlogin webconsole commandlinetool Login to openshift#container platform#Introduction to openshift online cluster#openshift#openshift 4#Openshift architecture#openshift cli#openshift connector#openshift container platform#OpenShift development#openshift login#openshift login web console command line tool openshift 4.2#openshift online#openshift paas#openshift tutorial#red hat openshift#redhat openshift online#web application openshift online#what is openshift online
0 notes
Text
Mac OS: xcrun: error: invalid active developer path
Mac OS: xcrun: error: invalid active developer path
While watching one of the Microsoft Build 2021 sessions, I ran into the following error message while trying to clone a project from Github using the git clone command line on my Mac. The entire error message is below: xcrun: error: invalid active developer path (/Library/Developer/CommandLineTools), missing xcrun at: /Library/Developer/CommandLineTools/usr/bin/xcrun Thankfully, the fix for…
View On WordPress
1 note
·
View note
Link
In this tutorial, I have explained how to solve the problem of applications (Like: AltDeploy) that reports:-
- “AltDeploy.app” will damage your computer. You should move it to the Trash. - You do not have permission to open the application “AltDeploy.app”.
- Contact your computer or network administrator for assistance.
Also, how to solve:- - xcrun: error: invalid active developer path (/Library/Developer/CommandLineTools), missing xcrun at: /Library/Developer/CommandLineTools/usr/bin/xcrun /Users/sherifeid/Desktop/AltDeploy.app/Contents/MacOS/AltDeploy: the codesign_allocate helper tool cannot be found or used. - missing xcrun - xcrun: error - install Xcode command line tools - This problem can be solved using four different procedures described here on my channel, using theses videos: 1) https://youtu.be/DrNcsTcZvhg 2) https://youtu.be/dmNhKjHuhH0 3) https://youtu.be/_4WNUS_YQ-M 4) https://youtu.be/sWSySXfR17c Please Note: For your Mac safety, the applications like "AltDeploy" is downloaded from the internet and it may harm your Mac, so you have to make your own decision if you trust its developers :)
1 note
·
View note
Text
Creating New Android Studio Project using Command Line Tools
Creating New Android Studio Project using Command Line Tools - Once the SDK Tools are installed and its "tools", "platforms" and "platform-tools" directories are set in the Environment Variable named Path using SETX Command as above. Creating New Android Studio Project using Command Line Tools After that, we can also create our new Android project through Command Prompt using various Android Tools of Android SDK. For example, suppose we want to create our first Android project in the "E: Softwares AndroApps" folder. Therefore, first we have to reach this path in our Command Prompt, for which we use CD Command as follows: By reaching the Destination Folder of our project, now we first have to find out what target devices we can develop for our Android Project by executing the next command as follows. Able to develop Application for: We can see that by executing the command "android list targets" on Command Prompt, we get a long list of supported Android Targets. This list gives an indication of which platforms our current Android SDK Tools supports, on which we can compile our Android Application. The main thing to keep in mind here is that we should always compile our Android application only for the latest supported version platform, because if we will compile our application for the old version's Android platform, then our application is new devices. Read the full article
#CommandLineTools#CreatingNewAndroidStudioProject#CreatingNewAndroidStudioProjectusingCommandLineTools#CreatingNewProjectusingCommandLineTools#ProjectusingCommandLineTools
0 notes
Text
Windows 11-bèta maakt gebruik van Windows Terminal als opdrachtpromptalternatief
Microsoft heeft een nieuwe Insider Preview van Windows 11 vrijgegeven in het Dev Channel. De opvallendste wijziging daarin is dat de standaard commandlinetool nu is gewijzigd naar Windows Terminal. Command Prompt en PowerShell blijven wel bestaan. http://dlvr.it/SXF1M2
0 notes
Text
pyenv でpythonのインストールに失敗
pyenvをインストール後pythonをインストールしようとしたら下記のエラーがでた
//////////
****@MacBook-Pro ~ % pyenv install 3.8.3
python-build: use [email protected] from homebrew
python-build: use readline from homebrew
Downloading Python-3.8.3.tar.xz...
-> https://www.python.org/ftp/python/3.8.3/Python-3.8.3.tar.xz
Installing Python-3.8.3...
python-build: use tcl-tk from homebrew
python-build: use readline from homebrew
BUILD FAILED (OS X 12.2 using python-build 20180424)
Inspect or clean up the working tree at /var/folders/44/32fwrzns4t1d214rhshxcdpc0000gn/T/python-build.20220204165713.18613
Results logged to /var/folders/44/32fwrzns4t1d214rhshxcdpc0000gn/T/python-build.20220204165713.18613.log
Last 10 log lines:
checking for --with-universal-archs... no
checking MACHDEP... "darwin"
checking for gcc... clang
checking whether the C compiler works... no
configure: error: in `/var/folders/44/32fwrzns4t1d214rhshxcdpc0000gn/T/python-build.20220204165713.18613/Python-3.8.3':
configure: error: C compiler cannot create executables
See `config.log' for more details
xcrun: error: active developer path ("/Applications/Xcode.app/Contents/Developer") does not exist
Use `sudo xcode-select --switch path/to/Xcode.app` to specify the Xcode that you wish to use for command line developer tools, or use `xcode-select --install` to install the standalone command line developer tools.
See `man xcode-select` for more details.
//////////
xcode-select のパスがあっていないようなので変更
下記を実行
% sudo xcode-select -switch /Library/Developer/CommandLineTools
これでうまく行ったと思いました。
0 notes
Text
Xcode 10.11

Question or issue on macOS:
Xcode 10 Download For Mac
Xcode For Macos High Sierra
Xcode 10.13
Xcode 10.11.6 Download
I am trying to update Command line tools on my mac osx.
All downloads are hosted by Apple. Links on this site take you directly to Apple’s download pages. This is not an official Apple website. Please consider donating to help maintain it. Xcode - Wikipedia has a complete compatibility listing for Xcode, what version works with which version of OS X. It also includes a listing of versions of Xcode’s support libraries for things like iOS and iWatch, for each version. I am searching for a proper IDE for iOS developement but MAC OS X version is 10.11.6 & because of this I am unable to install XCode. It says 'I should have MAC OS X 10.12+'. Developers who want to make use of the Xcode 8 SDKs from the command line must choose the SDK with xcode-select. Developers on OS X El Capitan who have installed versions of the Command Line Tools (OS X 10.11) for Xcode 8 Beta should install Command Line Tools (OS X 10.11) for Xcode 7.3.1.
1 Swift 5.5 is available as part of Xcode 13. 2 Swift 5.5 Windows 10 toolchain is provided by Saleem Abdulrasool.Saleem is the platform champion for the Windows port of Swift and this is an official build from the Swift project.
But when I run the update command, I get this error:
This doesn’t work either:
What is the exact string I should specify after sofwareupdate -i?
How to solve this problem?
Solution no. 1:
For future travelers, here’s a version-agnostic approach. First, run softwareupdate --list. This will probably take a couple of minutes. When it’s done, you’ll see a bulleted (with an asterisk) output like this:
Find the bullet that refers to the Xcode command line tools. Copy that entire line (except the asterisk…). In the above case, you would copy: Command Line Tools (macOS High Sierra version 10.13) for Xcode-10.1
Then, run the install command (as shown by Brendan Shanks) with what you copied inside quotes:
Solution no. 2:
I’m going to answer a slightly different question here, because this question came up when I searched for a solution to my problem. Hopefully it’ll help someone (and it’ll surely help me next time I run into the same issue).
I wanted to upgrade the command line tools from version 8 to 9. The App Store didn’t suggest this upgrade, and neither did softwareupdate --list.
installed the new version of the tools. But clang --version still gave 8.0.0 as the version number. xcode-select -r and rebooting didn’t solve this issue.
xcode-select -p returned /Applications/Xcode.app/Contents/Developer, and clang --version reported an installation directory under there. I thought I’d start over again.
deleted version 8 of the tools. But xcode-select --install said the command line tools were already installed.
Now, sudo xcode-select -p returns /Library/Developer/CommandLineTools/.
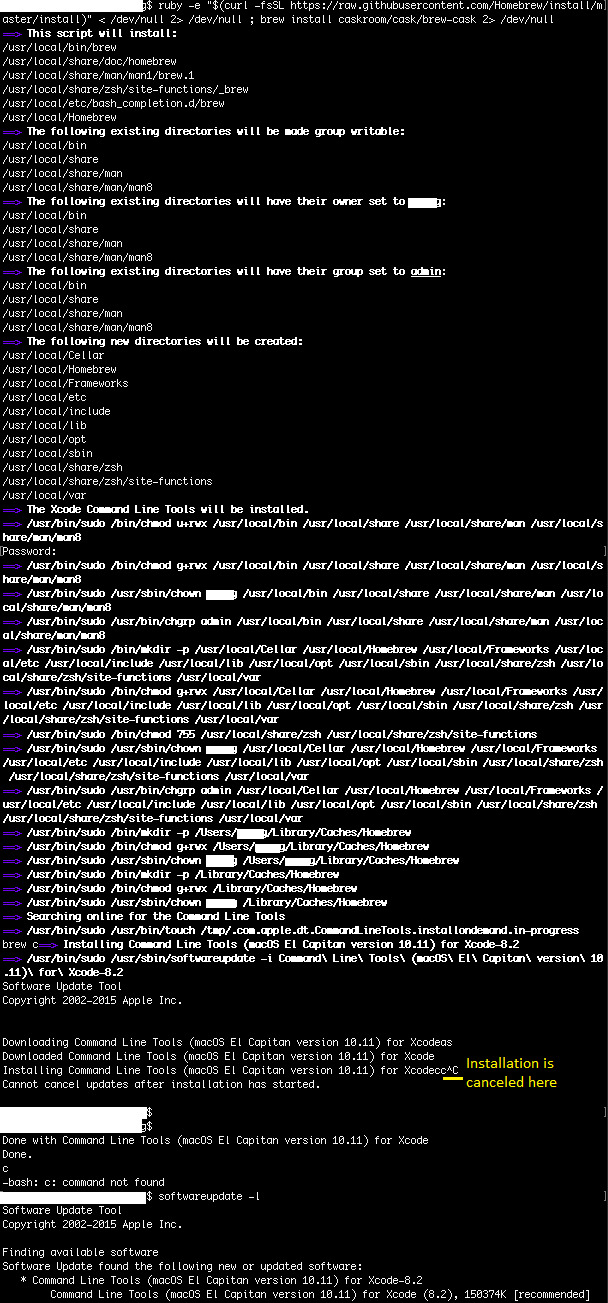
It seems that the problem was that the new version of the tools are installed to a different directory, and xcode-select -r is not clever enough to find the latest version.
Solution no. 3:
Run softwareupdate -i 'Command Line Tools (macOS El Capitan version 10.11) for Xcode-8.2'. The quotes are important.
Solution no. 4:
I faced similar problem on MacOS Mojave version 10.14.3 with Xcode 10.3 installed. The real problem was, when I installed the Xcode 10.3, I deleted the “Xcode-beta.app” first and then installed the new version. Therefore, when I tried installing CLion for C++ development and configuring it, CMake gave me error And Updating Command Line Tool didnt work for me:
and showed me this response in terminal
Then I tried to check the version of Clang using:
And the response lead me to the real problem i.e. Active Developer path was still pointing to Old version of Xcode that I had already deleted.
Therefore, I switched the active developer path to latest Xcode App installed using:
And everything worked like a charm automatically.
Solution no. 5:
Xcode 10 Download For Mac
I ran the same command with sudo and that did the trick.
sudo softwareupdate -i 'Command Line Tools (macOS El Capitan version 10.11) for Xcode-8.2'
Solution no. 6:
when upgrading to MacOS Catalina, Version 10.15.* you can install the command line tools for xcode 11.3 like this:
Hope this helps!
Xcode for Mac OS and iOS
With Xcode you can work inside one window, split windows, and even compare options side by side. Source and project code can be shared across both platforms.
MacOS app developer made simple and easy
Design great apps on either Mac, iPad, or iPhone using Xcode.
MacOS or iOS developers need look no further than the Xcode developer tool to design great apps.
Xcode featuresSwift UI, which offers up its own syntax. Easy to read and write, Swift UI will help keep your apps smaller and download faster by using less code.
Updated functionality now lets you code, test and debug all inside one window. Debugging is done via the Xcode IDE. This added plus can identify errors in syntax and logic, and often fix the code for you.
Newly introduced dark mode is built into Xcode. Interface builder allows you to switch between light and dark modes, or even view them side by side.
The drag and drop function helps you to make changes to visual UI elements, quickly and easily. For developers who prefer multiple editing panes, Xcode provides you with total control of your work area. You can view your design changes instantly in another window.
Use the devices window to simulate other environments. If your users have slow networks or run in extreme heat, you can test those conditions out before releasing your app. For ease of use, source and project code can be shared by Mac and iPad, allowing you to convert existing iPad apps into Mac apps. The changes will take effect across both platforms.
Where can you run this program?
You can run Xcode on OS X 10.8 Mountain Lion or iOS 7 and above.
Is there a better alternative?
With its solid functionality, multiple panes, and shared source code, there is no need to look at any alternatives when choosing an app development tool.
Our take
App development tools have come a long way. Xcode is the perfect tool for experienced developers. To be able to code, test, and debug inside the same window, this download will certainly save development time.
Should you download it?
Yes. You won't need another developer tool once you install Xcode. You can share code across OS or iOS.
Highs
Develop apps for any iOS platform
Bad code corrected by Xcode IDE
Code, test, and debug inside one window
Switch between light and dark mode
Simulate user environments for testing
Lows
Xcode For Macos High Sierra
May not be suitable for beginners
Apple developer membership required
Interface isn’t always easy to use
Xcode 10.13
Xcodefor Mac
Xcode 10.11.6 Download
12.5

0 notes
Text
Download Command Line Tools Mac

Mac Tool Et97 Update Software
Download Command Line Tools Mac Catalina
Download Command Line Tools (macos Mojave Version 10.14) For Xcode 10.3
Download from the Mac App Store. Additional Downloads. Get the latest beta and older versions of Xcode. To view downloads, simply sign in with your Apple ID. Command Line Tools & Older Versions of Xcode. See the latest advances in Xcode presented at WWDC and other events. Help and Support. Get step-by-step guidance. You can download the Xcode command-line tools in either of two ways: To install the necessary Xcode tools using Xcode on the Mac: Start Xcode on the Mac.
Command-line tools on macOS Catalina is essential to running of commands and development task. Just like with all new versions of macOS you have to install command-line tools to run commands.
Aqua Command-Line Tools provides point-and-click user interfaces for controlling the command-line tools shipped with Mac OS X. With Aqua Command-Line Tools, the layout of each tool's graphical interface makes it easy to quickly find and activate just the features you want.
$gh issue list
Showing 4 of 4 issues in cli/cli #16Improving interactions with protected branches #14PR commands on a detached head #13Support for GitHub Enterprise (enhancement) #8Add an easier upgrade command (bug)
gh pr status
Relevant pull requests in cli/cli Current branch There is no pull request associated with [fix-homepage-bug] Created by you You have no open pull requests Requesting a code review from you #100Fix footer on homepage[fix-homepage-footer] ✓ Checks passing- Review pending
gh pr checkout 12

remote: Enumerating objects: 66, done. remote: Counting objects: 100% (66/66), done. remote: Total 83 (delta 66), reused 66 (delta 66), pack-reused 17 Unpacking objects: 100% (83/83), done. From https://github.com/owner/repo * [new ref] refs/pull/8896/head -> patch-2 M README.md Switched to branch 'patch-2'
gh pr create
Creating pull request for feature-branch into main in ampinsk/test ? Title My new pull request ? Body [(e) to launch vim, enter to skip] ? What's next? Submit http://github.com/owner/repo/pull/1
gh pr checks
All checks were successful 1 failing, 3 successful, and 1 pending checks -CodeQL3m43shttps://github.com/cli/cli/runs/123 ✓build (macos-latest)4m18shttps://github.com/cli/cli/runs/123 ✓build (ubuntu-latest)1m23shttps://github.com/cli/cli/runs/123 ✓build (windows-latest)4m43shttps://github.com/cli/cli/runs/123 ×lint47shttps://github.com/cli/cli/runs/123
gh release create 1.0
? Title GitHub CLI 1.0 ? Release notes Write my own ? Is this a prerelease? No ? Submit? Publish release https://github.com/octocat/.github/releases/tag/1.0
gh repo view
cli/cli GitHub’s official command line tool GitHub CLI gh is GitHub on the command line. It brings pull requests, issues, and other GitHub concepts to the terminal next to where you are already working with git and your code. Image: screenshot of gh pr status →https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/98482/84171218-327e7a80-aa40-11ea-8cd1-5177fc2d0e72.png View this repository on GitHub: https://github.com/cli/cli
gh alias set bugs 'issue list --label='bugs'
- Adding alias for bugs: issue list --label='bugs' ✓ Added alias. $ gh bugs Showing 2 of 7 issues in cli/cli that match your search #19Pagination request returns empty JSON (bug) #21Error raised when passing valid parameters (bug)
Mac Tool Et97 Update Software
Mac users with macOS Mojave and macOS Catalina, and new operating systems in place can now install Command Line Tools from the Xcode IDE without needing to install the entire Xcode package, or opening an Apple developers account.
In this article, we cover how you can install this optional and highly useful Command Line Tools package.
X code 11. Credit: developerinsider
What is the Xcode Command Line Tools package?
For Mac power users — we wouldn't recommend downloading this unless you are comfortable with Terminal — the Xcode Command Line Tools package gives you a complete Unix toolkit accessible through Terminal. No developer account needed and you don't need to download the entire — and quite large Xcode package of executables.
Within the Xcode Command Line toolkit, Mac users gain access to numerous useful tools, utilities, and compilers, including make, GCC, clang, perl, svn, git, size, strip, strings, libtool, cpp, and many others. All of these commands are a default part of Linux systems and programs.
We recommend following these steps for those with the following operating systems running on a Mac: macOS 10.13 High Sierra, macOS 10.14 Mojave, and macOS 10.15 Catalia onward. It isn't always possible to download these Xcode Command Line Tools, following these steps, on Mac’s running older operating systems. Other ways to install command tools and gcc (without needing Xcode) is available through the Apple Developer website.
Here is how you install Xcode Command Line Tools.
How to install Xcode Command Line Tools?
Go to Terminal in /Applications/Utilities/.
Input the following command string in Terminal: xcode-select —install
In the same way when you are downloading new software and apps, a popup update window will appear asking you: “The xcode-select command requires the command line developer tools. Would you like to install the tools now?”
Select confirm by clicking Install.
Wait for the Xcode Command Line Tools package to install. It is around 130 MB and usually installs fairly quickly; although it depends on your connection.
Once everything is installed, the installer goes away and you should be able to any of the new commands that you’ve now got access to. Enjoy using your new Unix command line tools!
With this new download, you should have access to 61 Unix command line tools. For example, one of the advantages of having these tools is you can install new apps and software directly from the source code instead of needing to go through the package manager and usual download route.

To access or view everything you've now got, go to the following directory:
/Library/Developer/CommandLineTools/
Please note, this is the root /Library of your macOS/OS X, not the ~/Library directory.
All of these tools can also be found in: /Library/Developer/CommandLineTools/usr/bin/
What happens if I encounter problems downloading these?

If you get an error message that says “Can’t install the software because it is not currently available from the Software Update server”, it means you've already got the Xcode package on your Mac. Mac OS X 10.9 onward, Xcode was already installed, which is why you aren't able to download these tools. However, what you can do is uninstall the entire Xcode app if you'd prefer to only access these tools and not a whole load of software that isn’t going to be of much use.
Watch out for Xcode junk
The Xcode junk is one of those types of clutter that is keeps accumulating in remote places on your Mac. It could take up a few gigs of your space. The only app that seems to address this problem is CleanMyMac X by MacPaw. It’s loved by many Mac developers because it collects those specific types of development junk, like Xcode or outdated libraries.
Download Command Line Tools Mac Catalina
Once you launch the app, click on System Junk > Scan. Then, click “Review Details”
Download Command Line Tools (macos Mojave Version 10.14) For Xcode 10.3
CleanMyMac X is a powerful Mac performance improvement app. It makes your Mac as good as new. Let it scan your system and clear out any unwanted Xcode, development and system junk that is taking up too much space and cluttering up your Mac. In a few clicks, your Mac could be running smoother, quicker and more efficiently.

0 notes
Text
macOS 更新後無法使用 command line
當更新了 mac 後,有時候會遇到在終端機要下指定的時候噴出
xcrun: error: invalid active developer path (/Library/Developer/CommandLineTools), missing xcrun at: /Library/Developer/CommandLineTools/usr/bin/xcrun
這時候請在終端下
xcode-select --install
你的終端就會活過來了(遠目)
ref:
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/52522565/git-is-not-working-after-macos-update-xcrun-error-invalid-active-developer-pa
0 notes
Text
Mac OS: xcrun: error: invalid active developer path, missing xcrun
Mac OS: xcrun: error: invalid active developer path, missing xcrun
I ran into this error when I tried any git operation (like git clone and git pull) on a Mac. I had just upgraded to the latest OS (Catalina)to and suddenly my git broke!
$ git pull xcrun: error: invalid active developer path (/Library/Developer/CommandLineTools), missing xcrun at: /Library/Developer/CommandLineTools/usr/bin/xcrun
The fix, luckily, is pretty straight forward. Install the Xcode…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Video
youtube
Login to openshift cluster in different ways | openshift 4Openshift 4 is latest devops technology which can benefit the enterprise in a lot of ways. Build development and deployment can be automated using Openshift 4 platform. Features for autoscaling , microservices architecture and lot more features. So please like watch subscribe my channel for the latest videos. #openshift # openshift4 #containerization #cloud #online #container #kubernetes #redhatopenshift #openshifttutorial #openshiftonline #openshiftcluster #openshiftlogin #webconsole #commandlinetool , openshift,redhat openshift online,web application openshift online,openshift login,openshift development,online learning,openshift connector,online tutorial,openshift tutorial,openshift cli,red hat openshift,openshift 4,openshift paas,openshift architecture,free cloud hosting,container platform,openshift login web console command line tool openshift 4.2,Login to openshift cluster in different ways openshift 4 red hat openshift https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCnIp4tLcBJ0XbtKbE2ITrwA?sub_confirmation=1&app=desktop About: 00:00 Login to openshift cluster in different ways | openshift 4 | red hat openshift In this course we will learn about login to openshift / openshift 4 online cluster in different ways. First method is to use the webconsole to login to cluster. Second way is to login through OC openshift cluster command line tool for windows. Openshift/ Openshift4 a cloud based container to build deploy test our application on cloud. In the next videos we will explore Openshift4 in detail. https://www.facebook.com/codecraftshop/ https://t.me/codecraftshop/ Please do like and subscribe to my you tube channel "CODECRAFTSHOP" Follow us on facebook | instagram | twitter at @CODECRAFTSHOP . -~-~~-~~~-~~-~- Please watch: "Install hyperv on windows 10 - how to install, setup & enable hyper v on windows hyper-v" https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KooTCqf07wk -~-~~-~~~-~~-~-
#openshift#redhat openshift online#web application openshift online#openshift login#openshift development#online learning#openshift connector#online tutorial#openshift tutorial#openshift cli#red hat openshift#openshift 4#openshift paas#openshift architecture#free cloud hosting#container platform#openshift login web console command line tool openshift 4.2#Login to openshift cluster in different ways openshift 4 red hat openshift#open shift
0 notes
Text
VIM学习笔记 编译源码(Compile Code)-Python
Python作为一种解释型编程语言,需要解释器来编译并执行Python代码。
测试Python
对于Linux和Mac操作系统,均已预装Python。而在Windows下,可以使用安装包或者直接解压版zip文件。
使用以下命令,可以查看当前Python版本:
$ python --version
设置动态调用库
新版本的Vim已经默认支持Python。可以使用:version命令,确认是否包含“+python/dyn”和“+python3/dyn”特性。
其中dyn,即dynamic,表示可以通过'pythondll'和'pythonthreedll'选项动态调用Python库。
使用set pythonthreedll?命令,可以查看当前动态调用的Python库。以下为Fedora31下的默认设置:
set pythonthreedll=libpython3.7m.so.1.0
如果您的Vim不支持动态调用Python库,那么以上命令将会报错。
如果您仅是下载并解压程序包(而不是进行安装),那么同时需要设置pythonthreehome选项。例如以下命令,在Windows下设置Python3环境:
set pythonthreehome=C:\tools\Python3 set pythonthreedll=C:\tools\Python3\python38.dll
以下命令,可以在Mac下设置Python环境:
" for python 3.X set pythonthreehome=/Library/Developer/CommandLineTools/Library/Frameworks/Python3.framework/Versions/3.7 set pythonthreedll=/Library/Developer/CommandLineTools/Library/Frameworks/Python3.framework/Versions/3.7/lib/libpython3.7m.dylib " for python 2.X set pythonhome=/System/Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/2.7 set pythondll=/System/Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/2.7/Python
请注意,在您的环境中Python所处的路径可能会不同。请在操作系统中使用以下命令,查看Python系统路径:
$ python -c "import sys; print(sys.path)"
请使用以下命令,查看更多帮助信息:
:help python-dynamic :help 'pythonhome' :help 'pythonthreehome'
设置编译器
使用以下命令,设置'makeprg'选项为python3命令:
set makeprg=python3\ %
通过在vimrc文件中增加以下自动命令,可以为Python源码文件设置编译快捷键:
augroup make_python au! au FileType python set makeprg=python3\ % au FileType python map <buffer> <leader><space> :w<cr>:make<cr> augroup end
编译Python代码
使用以下命令,将根据'makeprg'选项编译并执行Python文件:
:make
如果编译出现错误,将在QuickFix中显示错误列表,并自动跳转到第一个错误处:
启用以下内置的编译器,再执行:make编译命令,报错信息将被整合为一行:
:compiler pyunit
如果希望在编译时保持当前光标位置不变,那么可以使用以下命令:
:make!
使用:cw命令,将���开quickfix窗口。使用:cp命令,跳转到上一个错误;使用:cn命令,跳转到下一个错误。关于QuickFix操作的更多信息,请参阅QuickFix章节。
在修复错误并成功编译之后,将显示命令输出:
使用以下命令,将解释执行当前文件:
:!python3 %
如果执行不带任何参数的python3命令,那么将进入交换模式的python shell,您可以在其中直接执行python命令:
:!python3
使用以下命令,可以退出交换模式的python shell:
import sys; sys.exit()
您也可以直接使用Vim内置的:python3命令来执行代码:
:py3 print('hello world')
Ver: 2.0 | YYQ<上一篇 | 目录 | 下一篇>
from Blogger https://ift.tt/2WH9i7q via IFTTT
0 notes
Text
Awesome #CommandLineTools https://t.co/s83FqfDNjh #CLITools https://t.co/BgVRCUjqL5
Awesome #CommandLineTools https://t.co/s83FqfDNjh #CLITools pic.twitter.com/BgVRCUjqL5
— Macronimous.com (@macronimous) January 23, 2020
from Twitter https://twitter.com/macronimous January 24, 2020 at 12:29AM via IFTTT
0 notes
Text
Error 127 Unable to compile a JNI program on mac
I want to install rJava in my Rstudio but it doesn’t work. When I am typing R CMD javareconf in the console I get the following error:
trying to compile and link a JNI program detected JNI cpp flags : -I$(JAVA_HOME)/include -I$(JAVA_HOME)/include/darwin detected JNI linker flags : -L$(JAVA_HOME)/lib/server -ljvm /usr/local/Cellar/gcc/9.2.0_2/bin/gcc-7 -I"/Library/Frameworks/R.framework/Resources/include"-DNDEBUG -I/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk-13.0.1.jdk/Contents/Home/include -I/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk-13.0.1.jdk/Contents/Home/include/darwin -isysroot /Library/Developer/CommandLineTools/SDKs/MacOSX.sdk -I/usr/local/include -fPIC -Wall -g -O2 -c conftest.c -o conftest.o /bin/sh: /usr/local/Cellar/gcc/9.2.0_2/bin/gcc-7: No such file or directory make: *** [conftest.o] Error 127 Unable to compile a JNI program JAVA_HOME : /Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk-13.0.1.jdk/Contents/Home Java library path: JNI cpp flags : JNI linker flags : Updating Java configuration in /Library/Frameworks/R.framework/Resources Done.
I know there are a lot of similar questions related to this in stackoverflow, such as this. and I have looked through all of the solutions, but still didn’t work. I have been spending hours trying to figure this out but still stuck here. (I have successfully download JDK, my java version is 13.0.1. And I have set JAVA_HOME)
Can anyone please help me with this question? Thank you so much.
Archive from: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/59064050/error-127-unable-to-compile-a-jni-program-on-mac
from https://knowledgewiki.org/error-127-unable-to-compile-a-jni-program-on-mac/
0 notes
Text
Windows Terminal gaat met tabs toegang geven tot PowerShell en Linux-subsysteem
Microsoft brengt half juni een nieuwe commandline-applicatie voor Windows met de naam Windows Terminal uit. De applicatie ondersteunt tabs en thema's en biedt toegang tot cmd, PowerShell en het vernieuwde Windows Subsystem for Linux.
Naast tabs en thema's biedt de Windows Terminal volgens Microsoft volledige ondersteuning voor Unicode waaronder voor emoji. Bovendien ondersteunt de terminal extensies en is er gpu-acceleratie voor het renderen van tekst. De commandlinetool breidt de functionaliteit van bestaande tools zoals cmd, PowerShell en Windows Subsystem for Linux uit en kan dienen als enkele terminal voor meerdere shells. Een preview van de Windows Terminal is per direct beschikbaar en de uiteindelijke release volgt half juni. De broncode van Windows Terminal staat op GitHub.
Het Windows Subsystem for Linux krijgt zelf een update naar versie 2. Deze is gebaseerd op Linux-kernel 4.19 die daarmee onderdeel wordt van Windows. De versie zou voor kortere boottijden van Linux en efficiënter geheugengebruik zorgen. Daarnaast verbetert Windows Subsystem for Linux 2 de i/o-prestaties van het bestandssysteem en kan dit standaard Docker-containers draaien zonder dat nog een virtuele machine nodig is. Een preview van WSL 2 verschijnt later dit jaar. Microsoft introduceerde het Linux-subsysteem in 2016 in Windows 10, met de komst van Bash naar het OS.
0 notes