#Consumer Data Analytics
Text
Accelerate Your Feasibility Study in Focus Groups in UAE

In summing up, Researchers is your one-stop solution for doing all-encompassing feasibility studies. We have the knowledge and experience to assist you in achieving success, regardless of whether you are a startup operating in the web3 domain or any other breakthrough technology.
#Brand awareness surveys UAE#Competitive analysis Dubai#Competitive analysis UAE#Consumer insights Dubai#Data analytics Abu Dhabi
2 notes
·
View notes
Photo

In this digital world, companies rely on survey data to gather information about their targeted audience and their preferences. Businesses employ different methods to collect the survey data and analyze it. There are various mediums used to collect opinions and feedback from customers. While conducting a survey, researchers often choose multiple sources to collect data. KnowledgeHound shares the different methods used to collect the data.,,Learn more
#survey data#survey tools#knowledgehound#research analysis#survey analysis#database management#data management#data insights#longitudinal data#data exploration#database tool#analytics solution#consumer data#data sharing
1 note
·
View note
Text
Why Every Business Needs India Location Analysis in 2024
In today’s data-driven business environment, sales prediction is more critical than ever. Accurate forecasts can provide companies with a competitive edge, enabling them to allocate resources more effectively, manage supply chains, and make informed strategic decisions. However, sales prediction is fraught with challenges, and even small errors can lead to significant consequences. In this article, we explore the ten most common mistakes in sales prediction and provide actionable insights on how to avoid them.
1. Over-Reliance on Historical Data
While historical data is a valuable asset in sales prediction, relying solely on it can be misleading. Markets are dynamic, and past trends do not always predict future behavior. Companies must integrate real-time data and consider external factors such as economic shifts, changes in consumer behavior, and industry disruptions to enhance the accuracy of their forecasts.
2. Ignoring Market Conditions
Market conditions play a pivotal role in shaping sales outcomes. Failing to account for changes in the competitive landscape, regulatory shifts, or macroeconomic factors can lead to inaccurate predictions. Regularly updating prediction models to reflect the current market conditions is crucial for maintaining the relevance and accuracy of sales forecasts.
3. Poor Data Quality
One of the most significant challenges in sales prediction is the use of poor-quality data. Inaccurate, incomplete, or outdated data can skew results and lead to misguided decisions. To mitigate this risk, companies should implement robust data governance practices, including regular data cleansing, validation, and the use of reliable data sources.
4. Lack of Collaboration Between Departments
Sales prediction is not solely the responsibility of the sales team. Effective forecasting requires input from various departments, including marketing, finance, and operations. A lack of collaboration can result in siloed data and incomplete insights. Cross-functional teams should work together to share knowledge and data, ensuring a holistic view of the factors influencing sales performance.
Also Read: Sales Prediction for Small Businesses: Tips and Tricks
5. Underestimating the Impact of Seasonality
Seasonality is a critical factor in many industries, yet it is often overlooked in sales predictions. Failing to account for seasonal fluctuations can lead to inaccurate forecasts and misaligned resources. Companies should analyze historical sales data with a focus on seasonal patterns and adjust their predictions accordingly.
6. Inadequate Use of Predictive Analytics Tools
Predictive analytics tools have revolutionized sales forecasting, offering advanced algorithms and machine learning capabilities to enhance prediction accuracy. However, many companies fail to fully leverage these tools, either due to a lack of understanding or insufficient training. Investing in the right tools and training staff to use them effectively can significantly improve sales predictions.
7. Overcomplicating the Prediction Model
While complex models may seem more accurate, they can often lead to confusion and misinterpretation of results. Overcomplicating the prediction model with too many variables or advanced techniques can make it difficult to understand and act upon the insights generated. It is essential to strike a balance between model complexity and usability, focusing on the most relevant factors and ensuring that the model is accessible to all stakeholders.
8. Failing to Adjust for Uncertainty
No prediction model is perfect, and uncertainty is an inherent part of any forecast. However, many companies fail to account for this uncertainty in their predictions, leading to overconfidence in the results. To address this, companies should incorporate scenario planning and sensitivity analysis into their forecasting process, allowing them to prepare for a range of potential outcomes.
9. Inconsistent Forecasting Methods
Consistency in forecasting methods is key to ensuring reliable predictions. Using different models or methods across departments or over time can result in inconsistent forecasts, making it difficult to track performance and identify trends. Companies should establish standardized forecasting procedures and ensure that all relevant teams are aligned in their approach.
10. Neglecting Post-Forecast Analysis
Once a sales prediction has been made, the work is not over. Neglecting post-forecast analysis is a common mistake that can prevent companies from learning from their predictions and improving future forecasts. Regularly reviewing forecast accuracy, analyzing discrepancies, and incorporating lessons learned into the next forecasting cycle are essential steps in refining the prediction process.
Also Read: Top 10 Secrets to Understanding Purchase Behavior
Conclusion
Accurate sales prediction is both an art and a science, requiring a careful balance of data analysis, market understanding, and strategic thinking. By avoiding these common mistakes, companies can improve the reliability of their forecasts and make better-informed decisions that drive growth and success.
0 notes
Text
Consumer Behavior Analysis: Insights from Sikkim Manipal University
Hello, curious brains and fans of marketing! Have you ever wondered why you consistently eat the same sort of cereal or why you can’t resist purchasing the newest technology? It is primarily the subject of consumer behavior analysis, and Sikkim Manipal University (SMU) is researching this fascinating subject. Let’s examine some intriguing results from studies and research on consumer behavior…
#Behavioral Analysis#Business Growth#Business Intelligence#Consumer Behavior#Consumer Insights#Consumer Psychology#Customer Experience#Data-Driven#Digital Marketing#Market Research#Market Trends#Marketing Analytics#Marketing Strategy#Marketing Trends#Sikkim Manipal Distance MBA#Strategic Marketing
0 notes
Text
XLRI Hosts ReEnvision 3.0: Digital Transformation Conclave
Experts discuss data-driven consumer strategies at XLRI’s Digital Transformation event
The conclave explored India’s data-driven digital transformation across various consumer sectors, featuring insights from industry leaders.
JAMSHEDPUR – XLRI’s PGDM (GM) Batch 2024-25 organized ReEnvision 3.0, a Digital Transformation Conclave centered on data-driven consumer world strategies.
The event…
#AI in consumer engagement#शिक्षा#business technology integration#consumer analytics#data-driven strategies#Digital Transformation Conclave#e-commerce trends#education#industry experts panel#Marketing Innovation#ReEnvision 3.0#XLRI Jamshedpur
0 notes
Text
One of the major sellers of detailed driver behavioral data is shutting down | Ars Technica
0 notes
Text
Overcoming the 60% Struggle with ML Adoption: Key Insights

In the race to stay competitive, companies are turning to machine learning (ML) to unlock new levels of efficiency and innovation. But what does it take to successfully adopt ML?
Machine learning (ML) is a transformative technology offering personalized customer experiences, predictive analytics, operational efficiency, fraud detection, and enhanced decision-making. Despite its potential, many companies struggle with ML adoption due to data quality challenges, a lack of skilled talent, high costs, and resistance to change.
Effective ML implementation requires robust data management practices, investment in training, and a culture that embraces innovation. Intelisync provides comprehensive ML services, including strategy development, model building, deployment, and integration, helping companies overcome these hurdles and leverage ML for success.
Overcoming data quality and availability challenges is crucial for building effective ML models. Implementing robust data management practices, including data cleaning and governance, ensures consistency and accuracy, leading to reliable ML models and better decision-making. Addressing the talent gap through training programs and partnerships with experts like Intelisync can accelerate ML project implementation. Intelisync’s end-to-end ML solutions help businesses navigate the complexities of ML adoption, ensuring seamless integration with existing systems and maximizing efficiency. Fostering a culture of innovation and providing clear communication and leadership support are vital to overcoming resistance and promoting successful ML adoption.
Successful ML adoption involves careful planning, strategic execution, and continuous improvement. Companies must perform detailed cost-benefit analyses, start with manageable pilot projects, and regularly review and optimize their AI processes. Leadership support and clear communication are crucial to fostering a culture that values technological advancement. With Intelisync’s expert guidance, businesses can bridge the talent gap, ensure smooth integration, and unlock the full potential of machine learning for their growth and success. Transform your business with Intelisync’s comprehensive ML services and stay ahead in the competitive Learn more....
#5 Top Reasons Companies Struggle with Machine Learning Adoption#Boost your business efficiency and innovation with Intelisync’s expert ML solutions#Change Management and Organizational Resistance#Data Quality and Availability Challenges#Developing an ML Strategy for Your Business#High Costs and Resource Allocation#How can companies measure the ROI of their ML projects?#Machine learning#ML adoption#Personalized Customer Experiences#Predictive Analytics#Time-Consuming Implementation#What are some common misconceptions about machine learning adoption?#What are the benefits of partnering with a machine learning service provider?#What are the benefits of starting with pilot projects for ML adoption?#What are the main challenges companies face when adopting machine learning (ML)#What is Machine Learning?#Why Is ML Important for Companies?#Why Do 60% of Companies Struggle with ML Adoption?
0 notes
Text
5 Strategies for Understanding Consumer Behavior Insights to Drive Sales Growth
Understanding consumer behavior is crucial for any business aiming to drive sales growth. By comprehensively analyzing how and why consumers make purchasing decisions, businesses can tailor their strategies to better meet customer needs, ultimately leading to increased sales and customer loyalty. In this blog, we will explore five effective strategies to gain consumer behavior insights and leverage them for sales growth.
1. Utilize Market Segmentation
Market segmentation is the process of dividing a broad consumer market into sub-groups of consumers with common needs and characteristics. This strategy allows businesses to target specific segments with tailored marketing efforts, which can result in more effective communication and increased sales.
Types of Market Segmentation:
Demographic Segmentation: Dividing the market based on variables such as age, gender, income, education, and family size.
Psychographic Segmentation: Segmenting the market based on lifestyle, values, interests, and attitudes.
Behavioral Segmentation: Dividing the market based on consumer behavior, including purchasing patterns, usage rates, and brand loyalty.
Geographic Segmentation: Segmenting the market based on geographical location, such as country, region, city, or neighborhood.
Steps to Implement Market Segmentation:
Conduct Market Research: Gather data on potential customers using surveys, interviews, and focus groups.
Identify Segmentation Criteria: Choose the variables that best represent the target market.
Segment the Market: Divide the market into distinct groups based on the selected criteria.
Analyze Each Segment: Evaluate the size, potential, and unique characteristics of each segment.
Develop Targeted Marketing Strategies: Create marketing campaigns tailored to the specific needs and preferences of each segment.
Benefits of Market Segmentation:
Improved customer satisfaction due to personalized marketing.
Increased efficiency in marketing efforts.
Enhanced ability to identify and target high-value customers.
Better allocation of marketing resources.
By understanding the specific needs and preferences of different market segments, businesses can develop targeted marketing strategies that resonate with consumers, leading to higher engagement and sales.
2. Leverage Data Analytics
Data analytics involves the process of examining large sets of data to uncover patterns, correlations, and insights that can inform business decisions. In the context of consumer behavior, data analytics can provide valuable insights into how consumers interact with products and services, enabling businesses to make informed decisions that drive sales growth.
Types of Data Analytics:
Descriptive Analytics: Summarizes historical data to identify trends and patterns.
Diagnostic Analytics: Examines data to determine the causes of past performance.
Predictive Analytics: Uses statistical models and machine learning techniques to forecast future consumer behavior.
Prescriptive Analytics: Provides recommendations for actions based on predictive and descriptive analyses.
Steps to Implement Data Analytics:
Collect Data: Gather data from various sources, such as customer surveys, transaction records, social media, and website analytics.
Clean and Organize Data: Ensure data is accurate, complete, and formatted correctly for analysis.
Analyze Data: Use analytical tools and techniques to uncover insights and patterns.
Interpret Results: Translate analytical findings into actionable insights.
Implement Strategies: Apply insights to develop strategies that enhance customer experience and drive sales.
Benefits of Data Analytics:
Improved understanding of consumer preferences and behaviors.
Enhanced ability to predict future trends and consumer needs.
More effective marketing and sales strategies.
Increased customer satisfaction and loyalty.
By leveraging data analytics, businesses can gain a deeper understanding of consumer behavior, allowing them to make data-driven decisions that boost sales and improve overall performance.
3. Conduct Consumer Surveys and Focus Groups
Consumer surveys and focus groups are essential tools for gathering direct feedback from customers. These methods allow businesses to understand consumer opinions, preferences, and behaviors, providing valuable insights that can inform marketing and sales strategies.
Types of Consumer Surveys:
Online Surveys: Conducted via email or web-based platforms, offering convenience and wide reach.
Telephone Surveys: Conducted over the phone, allowing for more detailed responses.
Face-to-Face Surveys: Conducted in person, providing the opportunity for in-depth interaction.
Mail Surveys: Sent through postal mail, though less common in the digital age.
Steps to Conduct Consumer Surveys:
Define Objectives: Determine the goals of the survey and what information is needed.
Design the Survey: Create questions that are clear, concise, and relevant to the objectives.
Distribute the Survey: Choose the appropriate method for reaching the target audience.
Analyze Responses: Compile and analyze the data to identify trends and insights.
Implement Findings: Use the insights to inform business decisions and strategies.
Benefits of Consumer Surveys:
Direct feedback from customers.
Insights into consumer preferences and satisfaction levels.
Identification of areas for improvement.
Focus Groups:
Focus groups involve guided discussions with a small group of consumers to gather detailed insights into their attitudes, perceptions, and behaviors. These discussions are typically moderated by a facilitator who guides the conversation to cover specific topics of interest.
Steps to Conduct Focus Groups:
Define Objectives: Determine the goals of the focus group and the information needed.
Recruit Participants: Select a diverse group of participants that represents the target market.
Design the Discussion Guide: Create a list of topics and questions to be covered.
Conduct the Focus Group: Facilitate the discussion, encouraging open and honest feedback.
Analyze Findings: Review and analyze the discussion to identify key insights.
Implement Strategies: Apply the insights to develop marketing and sales strategies.
Benefits of Focus Groups:
In-depth understanding of consumer attitudes and behaviors.
Opportunity to explore complex topics in detail.
Immediate feedback on products, services, and marketing concepts.
By conducting consumer surveys and focus groups, businesses can gather valuable feedback directly from their customers, providing insights that can be used to improve products, services, and marketing strategies, ultimately driving sales growth.
4. Monitor Social Media and Online Reviews
Social media and online reviews are powerful sources of consumer insights. By monitoring these platforms, businesses can gain real-time feedback on their products and services, understand consumer sentiment, and identify emerging trends.
Strategies for Monitoring Social Media:
Social Listening: Use social listening tools to track mentions of the brand, products, and relevant keywords across social media platforms.
Engage with Customers: Respond to comments, questions, and complaints to build relationships and gather feedback.
Analyze Sentiment: Evaluate the tone and sentiment of social media mentions to understand how consumers feel about the brand.
Steps to Monitor Online Reviews:
Identify Review Platforms: Determine which platforms are most relevant to the industry, such as Yelp, Google Reviews, or industry-specific sites.
Monitor Reviews: Regularly check these platforms for new reviews.
Analyze Feedback: Look for common themes, trends, and areas of concern.
Respond to Reviews: Address negative reviews promptly and professionally, and thank customers for positive feedback.
Implement Changes: Use the insights gained from reviews to make improvements to products, services, and customer experiences.
Benefits of Monitoring Social Media and Online Reviews:
Real-time feedback from customers.
Insights into consumer sentiment and brand perception.
Identification of potential issues before they escalate.
Opportunities to engage with customers and build loyalty.
By actively monitoring social media and online reviews, businesses can stay attuned to consumer opinions and behaviors, allowing them to make timely adjustments and improvements that enhance customer satisfaction and drive sales growth.
5. Implement Customer Journey Mapping
Customer journey mapping is the process of creating a visual representation of the steps a customer takes when interacting with a brand, from initial awareness to post-purchase. This strategy helps businesses understand the customer experience, identify pain points, and uncover opportunities to improve the journey, leading to increased sales and customer loyalty.
Steps to Create a Customer Journey Map:
Define Objectives: Determine the goals of the journey mapping exercise and what insights are needed.
Identify Customer Personas: Develop detailed profiles of typical customers, including their needs, preferences, and behaviors.
Map the Journey Stages: Outline the key stages of the customer journey, such as awareness, consideration, purchase, and post-purchase.
Gather Data: Collect data on customer interactions at each stage, using surveys, interviews, analytics, and other sources.
Visualize the Journey: Create a visual representation of the journey, highlighting key touchpoints and pain points.
Analyze and Improve: Review the journey map to identify areas for improvement and develop strategies to enhance the customer experience.
Benefits of Customer Journey Mapping:
Comprehensive understanding of the customer experience.
Identification of pain points and areas for improvement.
Enhanced ability to align marketing and sales efforts with customer needs.
Improved customer satisfaction and loyalty.
By implementing customer journey mapping, businesses can gain a holistic view of the customer experience, allowing them to make targeted improvements that enhance satisfaction and drive sales growth.
Conclusion
Understanding consumer behavior is essential for driving sales growth. By utilizing market segmentation, leveraging data analytics, conducting consumer surveys and focus groups, monitoring social media and online reviews, and implementing customer journey mapping, businesses can gain valuable insights into consumer preferences and behaviors. These insights enable businesses to develop targeted marketing and sales strategies that meet customer needs, enhance satisfaction, and ultimately boost sales.
Embracing these strategies will not only provide a deeper understanding of consumer behavior but also equip businesses with the tools needed to stay competitive in an ever-evolving market. By continually analyzing and adapting to consumer insights, businesses can foster long-term relationships with their customers and achieve sustained sales growth.
FAQs
1. What is market segmentation and why is it important for understanding consumer behavior?
Market segmentation is the process of dividing a broad consumer market into sub-groups of consumers with common needs and characteristics. It is important because it allows businesses to target specific segments with tailored marketing efforts, resulting in more effective communication and increased sales.
2. What types of market segmentation can businesses use?
Businesses can use several types of market segmentation:
Demographic Segmentation: Based on variables like age, gender, income, education, and family size.
Psychographic Segmentation: Based on lifestyle, values, interests, and attitudes.
Behavioral Segmentation: Based on purchasing patterns, usage rates, and brand loyalty.
Geographic Segmentation: Based on geographical location, such as country, region, city, or neighborhood.
3. How does data analytics help in understanding consumer behavior?
Data analytics involves examining large sets of data to uncover patterns, correlations, and insights. It helps businesses understand how consumers interact with products and services, enabling them to make informed decisions that drive sales growth. Types of data analytics include descriptive, diagnostic, predictive, and prescriptive analytics.
4. What are the steps to implement data analytics in a business?
Steps to implement data analytics include:
Collecting data from various sources.
Cleaning and organizing the data.
Analyzing the data using analytical tools and techniques.
Interpreting the results to gain actionable insights.
Implementing strategies based on these insights.
5. Why are consumer surveys and focus groups valuable for understanding consumer behavior?
Consumer surveys and focus groups provide direct feedback from customers, offering insights into their opinions, preferences, and behaviors. This feedback helps businesses understand customer needs and improve products, services, and marketing strategies.
6. What are the different types of consumer surveys?
Different types of consumer surveys include:
Online Surveys: Conducted via email or web-based platforms.
Telephone Surveys: Conducted over the phone for more detailed responses.
Face-to-Face Surveys: Conducted in person for in-depth interaction.
Mail Surveys: Sent through postal mail.
7. How can businesses effectively conduct focus groups?
To conduct focus groups, businesses should:
Define objectives for the focus group.
Recruit a diverse group of participants.
Design a discussion guide with specific topics and questions.
Facilitate the discussion to encourage open and honest feedback.
Analyze the findings to identify key insights.
Apply the insights to develop marketing and sales strategies.
8. What role do social media and online reviews play in understanding consumer behavior?
Social media and online reviews provide real-time feedback on products and services, helping businesses understand consumer sentiment and identify emerging trends. Monitoring these platforms allows businesses to address issues promptly and engage with customers.
9. What strategies can businesses use to monitor social media effectively?
Businesses can use the following strategies to monitor social media:
Social Listening: Track mentions of the brand and relevant keywords.
Engaging with Customers: Respond to comments, questions, and complaints.
Analyzing Sentiment: Evaluate the tone and sentiment of social media mentions.
10. How can businesses monitor and analyze online reviews?
To monitor and analyze online reviews, businesses should:
Identify relevant review platforms.
Regularly check these platforms for new reviews.
Analyze the feedback to identify common themes and trends.
Respond to reviews professionally.
Use insights from reviews to improve products and services.
#Social Media Online Reviews#Market Segmentation#Focus Group#Data Analytics#Customer Journey Mapping#Consumer Behavior
0 notes
Text
Brand Tracking Guide: Methods, Benefits, and a Case Study
Discover the essential methods and numerous benefits of brand tracking in our comprehensive guide. Learn how to effectively monitor brand performance and make informed decisions to enhance your brand's success.
#Brand tracking#Brand awareness#Brand perception#Brand equity#Market research#Consumer insights#Competitive analysis#Marketing strategy#Consumer behavior#Brand loyalty#Customer satisfaction#Market trends#Data analytics#Performance measurement#Brand positioning#Market intelligence#Tracking metrics#Brand health#Brand image#Brand recall#Purchase intent#Customer engagement#Social media monitoring#Online presence#Customer sentiment#Brand consistency#Trend analysis#Benchmarking#Perception gaps#Target audience
0 notes
Text
Prepaid Cards Revolutionize Cashless Dining in Food Courts

Introduction to Prepaid Cards
In today's fast-paced world, convenience is paramount, especially when it comes to dining out. Prepaid cards have emerged as a revolutionary solution, offering a seamless and efficient way to enjoy cashless dining experiences. The concept of prepaid cards is not new, but their integration into food courts has sparked a significant shift in consumer behavior.
Cashless Dining Trends
The global trend towards cashless transactions has gained momentum in recent years, driven by advancements in technology and changing consumer preferences. In food courts, where speed and convenience are key, the adoption of cashless payment methods has become increasingly prevalent.
Challenges in Traditional Payment Methods
Traditional payment methods, such as cash or credit/debit cards, pose several challenges in food court settings. Cash transactions can lead to long queues and delays, while credit/debit card payments may be inconvenient for both consumers and vendors due to processing fees and minimum purchase requirements.
The Emergence of Prepaid Cards in Food Courts
To address these challenges, food courts are embracing prepaid card systems, revolutionizing the way customers pay for their meals. By preloading funds onto a card, customers can enjoy quick and hassle-free transactions, eliminating the need for cash or physical cards.
How Prepaid Cards Work
Prepaid cards operate on a simple premise: customers load funds onto their cards either online or at designated kiosks within the food court. They can then use these funds to make purchases at any participating vendor within the food court.
Advantages of Prepaid Cards in Food Courts
The benefits of prepaid cards in food courts are manifold. For consumers, they offer unmatched convenience and speed, allowing them to make purchases with a simple tap or swipe. Additionally, prepaid cards provide consumers with greater control over their spending, helping them stick to their budgets more effectively.
For food court operators, prepaid cards streamline transaction processing, reducing wait times and enhancing overall efficiency. By centralizing payments through a single platform, vendors can also gain valuable insights into consumer behavior and preferences, enabling them to tailor their offerings accordingly.
Enhanced Customer Experience
One of the key advantages of prepaid cards in food courts is the enhanced customer experience they provide. By minimizing wait times and offering seamless transactions, prepaid cards ensure that customers spend less time queuing and more time enjoying their meals.
Moreover, prepaid cards enable food court operators to implement customized loyalty programs, rewarding customers for their continued patronage. By offering incentives such as discounts or freebies, operators can further enhance the overall dining experience and foster customer loyalty.
Security and Safety Measures
Security is a top priority in any payment system, and prepaid cards are no exception. With robust encryption protocols and built-in fraud detection mechanisms, prepaid card systems offer consumers peace of mind knowing that their financial information is safe and secure.
Additionally, prepaid cards eliminate the need for consumers to carry large amounts of cash, reducing the risk of theft or loss. In the event that a card is lost or stolen, most prepaid card providers offer 24/7 customer support and the ability to freeze or deactivate the card remotely.
Adoption and Acceptance
The adoption of prepaid cards in food courts is steadily increasing, driven by the growing demand for cashless payment options. As more consumers become accustomed to the convenience and benefits of prepaid cards, food court vendors are increasingly recognizing the need to offer these payment methods to remain competitive.
Impact on Business Operations
From a business perspective, the integration of prepaid card systems can have a transformative impact on operations. By automating transaction processing and streamlining administrative tasks, vendors can reduce overhead costs and improve overall efficiency.
Moreover, prepaid card systems provide vendors with valuable data insights, allowing them to track sales trends, identify popular menu items, and target specific customer demographics more effectively. This data-driven approach enables vendors to make informed decisions that drive business growth and profitability.
Future Trends and Innovations
Looking ahead, the future of prepaid cards in food courts looks promising, with continued advancements in technology driving innovation and customization. From mobile payment solutions to personalized loyalty programs, vendors are constantly seeking new ways to enhance the customer experience and stay ahead of the competition.
Challenges and Concerns
Despite the many benefits of prepaid cards, there are also challenges and concerns that must be addressed. Chief among these is the need to ensure consumer privacy and data security. As prepaid card systems become more sophisticated, it is essential for vendors to implement robust privacy policies and security measures to protect customer information.
Additionally, accessibility remains a concern for some consumers, particularly those who may not have access to smartphones or digital payment methods. To address this issue, food courts must ensure that alternative payment options are available to accommodate all customers.
Case Studies and Success Stories
Numerous food courts around the world have already embraced prepaid card systems with great success. From small-scale vendors to large multinational chains, businesses of all sizes have reported significant improvements in transaction processing times, customer satisfaction, and overall revenue.
For example, a recent case study conducted by a major food court operator found that the implementation of prepaid card systems resulted in a 30% increase in sales and a 20% reduction in wait times. These impressive results demonstrate the tangible benefits that prepaid cards can
offer to both consumers and businesses alike.
Consumer Education and Awareness
Despite the growing popularity of prepaid cards, there is still a need for consumer education and awareness. Many consumers may be unfamiliar with how prepaid cards work or may have misconceptions about their usage and benefits. As such, food courts must invest in educational campaigns to inform consumers about the advantages of prepaid cards and how to use them effectively.
Conclusion
In conclusion, prepaid cards are revolutionizing the way consumers pay for their meals in food courts. By offering unmatched convenience, speed, and security, prepaid cards are transforming the dining experience for both customers and vendors alike. As the adoption of prepaid cards continues to grow, food courts are poised to reap the benefits of improved efficiency, increased revenue, and enhanced customer satisfaction.
We hope you enjoyed reading our blog posts about food court billing solutions. If you want to learn more about how we can help you manage your food court business, please visit our website here. We are always happy to hear from you and answer any questions you may have.
You can reach us by phone at +91 9810078010 or by email at [email protected]. Thank you for your interest in our services.
FAQs
1. Are prepaid cards accepted at all vendors in the food court?
Yes, prepaid cards can typically be used at any participating vendor within the food court.
2. Can I reload funds onto my prepaid card?
Yes, most prepaid card systems allow users to reload funds either online or at designated kiosks within the food court.
3. Is my personal information secure when using a prepaid card?
Yes, prepaid card systems employ robust security measures to protect customer information and prevent unauthorized access.
4. Are there any fees associated with using a prepaid card?
Some prepaid card providers may charge nominal fees for certain services, such as reloading funds or replacing lost or stolen cards.
5. Can I earn rewards or loyalty points with a prepaid card?
Yes, many prepaid card systems offer rewards or loyalty programs that allow users to earn points or discounts on their purchases.
#prepaid cards#cashless dining#food courts#payment methods#prepaid card systems#consumer convenience#customer experience#cashless transactions#digital payments#financial security#loyalty programs#transaction processing#data analytics#customer education#privacy concerns#business efficiency#innovation#technology integration#consumer awareness#case studies#success stories#FAQs#blogging#digital trends#restaurant industry#financial technology#prepaid card benefits#prepaid card acceptance
0 notes
Text
Deciphering Consumer Behavior Online: Understanding the Digital Path to Purchase
Consumer behavior in the digital realm is a complex and ever-changing landscape, influenced by a myriad of factors ranging from personal preferences to external stimuli. As businesses strive to connect with their audience and drive conversions online, understanding the intricacies of consumer behavior has become paramount. Let's delve into the fascinating world of online consumer behavior and explore how businesses can leverage insights to enhance their digital marketing strategies.
The Digital Consumer Journey
The digital consumer journey encompasses the various stages that a consumer goes through before making a purchase online. It typically begins with awareness, where consumers become aware of a need or desire through various touchpoints such as social media, search engines, or word-of-mouth recommendations. This is followed by consideration, where consumers research and evaluate different options before making a decision. Finally, the journey culminates in the purchase stage, where consumers complete the transaction and potentially engage in post-purchase activities such as reviews and feedback.
Data-driven Insights
One of the key advantages of digital marketing is the abundance of data available to businesses, allowing them to gain valuable insights into consumer behavior. By analyzing data from website analytics, social media engagement, and online transactions, businesses can identify patterns and trends that provide valuable insights into consumer preferences, motivations, and pain points. This data-driven approach enables businesses to tailor their marketing strategies to better meet the needs of their target audience.
Personalization and Customization
Consumers today expect personalized experiences tailored to their individual preferences and interests. By leveraging data analytics and automation technologies, businesses can deliver targeted and relevant content to consumers at each stage of the buyer's journey. Personalization can take many forms, from personalized product recommendations based on past purchases to customized email campaigns addressing specific needs and preferences. By delivering personalized experiences, businesses can increase engagement, build trust, and drive conversions.
The Role of Social Proof
In the digital age, social proof plays a significant role in influencing consumer behavior. Social proof refers to the phenomenon where people look to the actions and opinions of others to guide their own behavior. This can take the form of online reviews, social media endorsements, or user-generated content. Positive social proof can help build credibility and trust in a brand, while negative social proof can have the opposite effect. By actively managing and leveraging social proof, businesses can enhance their reputation and influence purchasing decisions.
The Power of Emotion
Emotion plays a crucial role in driving consumer behavior online. Studies have shown that emotions have a significant impact on decision-making, often outweighing rational factors. By tapping into the emotional triggers of consumers, businesses can create more compelling and memorable experiences that resonate on a deeper level. Whether it's through storytelling, imagery, or user-generated content, evoking the right emotions can help businesses forge stronger connections with their audience and drive loyalty.
In conclusion, deciphering consumer behavior online is essential for businesses looking to succeed in today's digital landscape. By gaining insights into the digital consumer journey, leveraging data-driven analytics, personalizing experiences, harnessing the power of social proof, and tapping into the emotional triggers of consumers, businesses can create more effective digital marketing strategies that drive engagement, foster loyalty, and ultimately, lead to conversions.
#Digital Marketing#Consumer Behavior#Online Shopping#Data Analytics#Personalization#Social Proof#Emotional Marketing#recruitment
0 notes
Text
Consumer Loyalty in the Digital Marketplace Insights and Strategies
In the bustling digital marketplace, fostering consumer loyalty is akin to striking gold. It's no secret that acquiring a new customer can cost five times more than retaining an existing one. Yet, in the fast-paced, ever-evolving digital realm, securing customer loyalty requires more than just a quality product or service. It demands a deep understanding of consumer behaviour, tailored experiences, and, crucially, an ability to engage on a personal level. For brands looking to thrive, not just survive, nailing this balance is non-negotiable.
The digital age has transformed consumer expectations. Today's shoppers are savvy, informed, and, let's face it, a tad impatient. They demand convenience, value, and, above all, a seamless experience. Loyalty is no longer just about who offers the best price; it's about who makes shopping easy, enjoyable, and, importantly, personalised. In the UK's competitive market, understanding these shifting dynamics is key. Brands that adapt, offering a curated, frictionless shopping experience, are the ones that will keep customers coming back for more.
But here's the rub: in the digital world, personalisation is the name of the game. It's about recognising your customers as individuals, with unique preferences, needs, and desires. Leveraging data analytics to tailor marketing messages, recommend products, and even predict future purchases can make all the difference. It turns a transaction into an experience, and an experience into loyalty. If your brand isn't utilising data to personalise at every touchpoint, you're missing a trick, and crucially, risking being left behind.
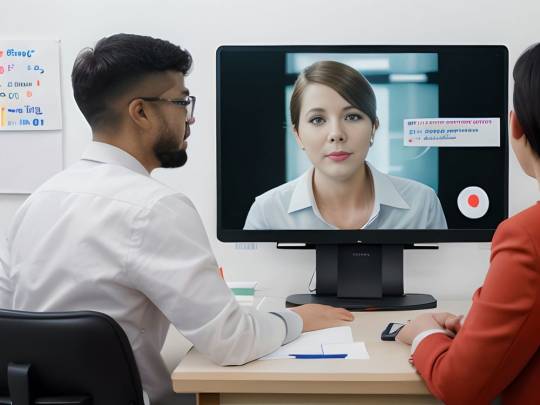

Engagement is another critical piece of the puzzle. In the digital age, this means more than just responsive customer service. It's about creating a community around your brand, engaging customers through social media, blogs, and other digital platforms. It's about telling a story that resonates, creating content that adds value, and fostering a sense of belonging among your customer base. This level of engagement not only drives loyalty but turns satisfied customers into vocal advocates for your brand.
In conclusion, cultivating consumer loyalty in the digital marketplace is both an art and a science. It requires a blend of strategic insight, technological savvy, and, fundamentally, a commitment to understanding and meeting the evolving needs of your customers. The brands that get this right, those that offer personalised, engaging experiences that resonate on a personal level, are the ones that will not just attract customers, but keep them. In the race for loyalty, there's no time for complacency. The digital marketplace waits for no one, and the time to act is now.
#digital customer loyalty#personalised marketing#customer engagement#data analytics in marketing#brand community building#consumer behaviour insights#loyalty program strategies
0 notes
Text
Anthony Deighton, CEO of Tamr – Interview Series
New Post has been published on https://thedigitalinsider.com/anthony-deighton-ceo-of-tamr-interview-series/
Anthony Deighton, CEO of Tamr – Interview Series
Anthony Deighton is CEO of Tamr. He has 20 years of experience building and scaling enterprise software companies. Most recently, he spent two years as Chief Marketing Officer at Celonis, establishing their leadership in the Process Mining software category and creating demand generation programs resulting in 130% ARR growth. Prior to that, he served for 10+ years at Qlik growing it from an unknown Swedish software company to a public company — in roles from product leadership, product marketing and finally as CTO. He began his career at Siebel Systems learning how to build enterprise software companies in a variety of product roles.
Can you share some key milestones from your journey in the enterprise software industry, particularly your time at Qlik and Celonis?
I began my career in enterprise software at Siebel Systems and learned a lot about building and scaling enterprise software companies from the leadership team there. I joined Qlik when it was a small, unknown, Swedish software company with 95% of the small 60-person team located in Lund, Sweden. I joke that since I wasn’t an engineer or a salesperson, I was put in charge of marketing. I built the marketing team there, but over time my interest and contributions gravitated towards product management, and eventually I became Chief Product Officer. We took Qlik public in 2010, and we continued as a successful public company. After that, we wanted to do some acquisitions, so I started an M&A team. After a long and reasonably successful run as a public company, we eventually sold Qlik to a private equity firm named Thoma Bravo. It was, as I like to say, the full life cycle of an enterprise software company. After leaving Qlik, I joined Celonis, a small German software company trying to gain success selling in the U.S. Again, I ran marketing as the CMO. We grew very quickly and built a very successful global marketing function.
Both Celonis and Qlik were focused on the front end of the data analytics challenge – how do I see and understand data? In Qlik’s case, that was dashboards; in Celonis’ case it was business processes. But a common challenge across both was the data behind these visualizations. Many customers complained that the data was wrong: duplicate records, incomplete records, missing silos of data. This is what attracted me to Tamr, where I felt that for the first time, we might be able to solve the challenge of messy enterprise data. The first 15 years of my enterprise software career was spent visualizing data, I hope that the next 15 can be spent cleaning that data up.
How did your early experiences shape your approach to building and scaling enterprise software companies?
One important lesson I learned in the shift from Siebel to Qlik was the power of simplicity. Siebel was very powerful software, but it was killed in the market by Salesforce.com, which made a CRM with many fewer features (“a toy” Siebel used to call it), but customers could get it up and running quickly because it was delivered as a SaaS solution. It seems obvious today, but at the time the wisdom was that customers bought features, but what we learned is that customers invest in solutions to solve their business problems. So, if your software solves their problem faster, you win. Qlik was a simple solution to the data analytics problem, but it was radically simpler. As a result, we could beat more feature-rich competitors such as Business Objects and Cognos.
The second important lesson I learned was in my career transition from marketing to product. We think of these domains as distinct. In my career I have found that I move fluidly between product and marketing. There is an intimate link between what product you build and how you describe it to potential customers. And there is an equally important link between what prospects demand and what product we should build. The ability to move between these conversations is a critical success factor for any enterprise software company. A common reason for a startup’s failure is believing “if you build it, they will come.” This is the common belief that if you just build cool software, people will line up to buy it. This never works, and the solution is a robust marketing process connected with your software development process.
The last idea I will share links my academic work with my professional work. I had the opportunity at business school to take a class about Clay Christensen’s theory of disruptive innovation. In my professional work, I have had the opportunity to experience both being the disruptor and being disrupted. The key lesson I’ve learned is that any disruptive innovation is a result of an exogenous platform shift that makes the impossible finally possible. In Qlik’s case it was the platform availability of large memory servers that allowed Qlik to disrupt traditional cube-based reporting. At Tamr, the platform availability of machine learning at scale allows us to disrupt manual rules-based MDM in favor of an AI-based approach. It’s important to always figure out what platform shift is driving your disruption.
What inspired the development of AI-native Master Data Management (MDM), and how does it differ from traditional MDM solutions?
The development of Tamr came out of academic work at MIT (Massachusetts Institute of Technology) around entity resolution. Under the academic leadership of Turing Award winner Michael Stonebraker, the question the team were investigating was “can we link data records across hundreds of thousands of sources and millions of records.” On the face of it, this is an insurmountable challenge because the more records and sources the more records each possible match needs to be compared to. Computer scientists call this an “n-squared problem” because the problem increases geometrically with scale.
Traditional MDM systems try to solve this problem with rules and large amounts of manual data curation. Rules don’t scale because you can never write enough rules to cover every corner case and managing thousands of rules is a technical impossibility. Manual curation is extremely expensive because it relies on humans to try to work through millions of possible records and comparisons. Taken together, this explains the poor market adoption of traditional MDM (Master Data Management) solutions. Frankly put, no one likes traditional MDM.
Tamr’s simple idea was to train an AI to do the work of source ingestion, record matching, and value resolution. The great thing about AI is that it doesn’t eat, sleep, or take vacation; it is also highly parallelizable, so it can take on huge volumes of data and churn away at making it better. So, where MDM used to be impossible, it is finally possible to achieve clean, consolidated up-to-date data (see above).
What are the biggest challenges companies face with their data management, and how does Tamr address these issues?
The first, and arguably the most important challenge companies face in data management is that their business users don’t use the data they generate. Or said differently, if data teams don’t produce high-quality data that their organizations use to answer analytical questions or streamline business processes, then they’re wasting time and money. A primary output of Tamr is a 360 page for every entity record (think: customer, product, part, etc.) that combines all the underlying 1st and 3rd party data so business users can see and provide feedback on the data. Like a wiki for your entity data. This 360 page is also the input to a conversational interface that allows business users to ask and answer questions with the data. So, job one is to give the user the data.
Why is it so hard for companies to give users data they love? Because there are three primary hard problems underlying that goal: loading a new source, matching the new records into the existing data, and fixing the values/fields in data. Tamr makes it easy to load new sources of data because its AI automatically maps new fields into a defined entity schema. This means that regardless of what a new data source calls a particular field (example: cust_name) it gets mapped to the right central definition of that entity (example: “customer name”). The next challenge is to link records which are duplicates. Duplication in this context means that the records are, in fact, the same real-world entity. Tamr’s AI does this, and even uses external 3rd party sources as “ground truth” to resolve common entities such as companies and people. A good example of this would be linking all the records across many sources for an important customer such as “Dell Computer.” Lastly, for any given record there may be fields which are blank or incorrect. Tamr can impute the correct field values from internal and 3rd party sources.
Can you share a success story where Tamr significantly improved a company’s data management and business outcomes?
CHG Healthcare is a major player in the healthcare staffing industry, connecting skilled healthcare professionals with facilities in need. Whether it’s temporary doctors through Locums, nurses with RNnetwork, or broader solutions through CHG itself, they provide customized staffing solutions to help healthcare facilities run smoothly and deliver quality care to patients.
Their fundamental value proposition is connecting the right healthcare providers with the right facility at the right time. Their challenge was that they didn’t have an accurate, unified view of all the providers in their network. Given their scale (7.5M+ providers), it was impossible to keep their data accurate with legacy, rules-driven approaches without breaking the bank on human curators. They also couldn’t ignore the problem since their staffing decisions depended on it. Bad data for them could mean a provider gets more shifts than they can handle, leading to burnout.
Using Tamr’s advanced AI/ML capabilities, CHG Healthcare reduced duplicate physician records by 45% and almost completely eliminated the manual data preparation that was being done by scarce data & analytics resources. And most importantly, by having a trusted and accurate view of providers, CHG is able to optimize staffing, enabling them to deliver a better customer experience.
What are some common misconceptions about AI in data management, and how does Tamr help dispel these myths?
A common misconception is that AI has to be “perfect”, or that rules and human curation are perfect in contrast to AI. The reality is that rules fail all the time. And, more importantly, when rules fail, the only solution is more rules. So, you have an unmanageable mess of rules. And human curation is fallible as well. Humans might have good intentions (although not always), but they’re not always right. What’s worse, some human curators are better than others, or simply might make different decisions than others. AI, in contrast, is probabilistic by nature. We can validate through statistics how accurate any of these techniques are, and when we do we find that AI is less expensive and more accurate than any competing alternative.
Tamr combines AI with human refinement for data accuracy. Can you elaborate on how this combination works in practice?
Humans provide something exceptionally important to AI – they provide the training. AI is really about scaling human efforts. What Tamr looks to humans for is the small number of examples (“training labels”) that the machine can use to set the model parameters. In practice what this looks like is humans spend a small amount of time with the data, giving Tamr examples of errors and mistakes in the data, and the AI runs those lessons across the full data set(s). In addition, as new data is added, or data changes, the AI can surface instances where it is struggling to confidently make decisions (“low confidence matches”) and ask the human for input. This input, of course, goes to refine and update the models.
What role do large language models (LLMs) play in Tamr’s data quality and enrichment processes?
First, it’s important to be clear about what LLMs are good at. Fundamentally, LLMs are about language. They produce strings of text which mean something, and they can “understand” the meaning of text that’s handed to them. So, you could say that they are language machines. So for Tamr, where language is important, we use LLMs. One obvious example is in our conversational interface which sits on top of our entity data which we affectionately call our virtual CDO. When you speak to your real-life CDO they understand you and they respond using language you understand. This is exactly what we’d expect from an LLM, and that is exactly how we use it in that part of our software. What’s valuable about Tamr in this context is that we use the entity data as context for the conversation with our vCDO. It’s like your real-life CDO has ALL your BEST enterprise data at their fingertips when they respond to your questions – wouldn’t that be great!
In addition, there are instances where in cleaning data values or imputing missing values, where we want to use a language-based interpretation of input values to find or fix a missing value. For example, you might ask from the text “5mm ball bearing” what is the size of the part, and an LLM (or a person) would correctly answer “5mm.”
Lastly, underlying LLMs are embedding models which encode language meaning to tokens (think words). These can be very useful for calculating linguistic comparison. So, while “5” and “five” share no characters in common, they are very close in linguistic meaning. So, we can use this information to link records together.
How do you see the future of data management evolving, especially with advancements in AI and machine learning?
The “Big Data” era of the early 2000s should be remembered as the “Small Data” era. While a lot of data has been created over the past 20+ years, enabled by the commoditization of storage and compute, the majority of data that has had an impact in the enterprise is relatively small scale — basic sales & customer reports, marketing analytics, and other datasets that could easily be depicted in a dashboard. The result is that many of the tools and processes used in data management are optimized for ‘small data’, which is why rules-based logic, supplemented with human curation, is still so prominent in data management.
The way people want to use data is fundamentally changing with advancements in AI and machine learning. The idea of “AI agents” that can autonomously perform a significant portion of a person’s job only works if the agents have the data they need. If you’re expecting an AI agent to serve on the frontlines of customer support, but you have five representations of “Dell Computer” in your CRM and it’s not connected with product information in your ERP, how can you expect them to deliver high-quality service when someone from Dell reaches out?
The implication of this is that our data management tooling and processes will need to evolve to handle scale, which means embracing AI and machine learning to automate more data cleaning activities. Humans will still play a big role in overseeing the process, but fundamentally we need to ask the machines to do more so that it’s not just the data in a single dashboard that is accurate and complete, but it’s the majority of data in the enterprise.
What are the biggest opportunities for businesses today when it comes to leveraging their data more effectively?
Increasing the number of ways that people can consume data. There’s no question that improvements in data visualization tools have made data much more accessible throughout the enterprise. Now, data and analytics leaders need to look beyond the dashboard for ways to deliver value with data. Interfaces like internal 360 pages, knowledge graphs, and conversational assistants are being enabled by new technologies, and give potential data consumers more ways to use data in their day-to-day workflow. It’s particularly powerful when these are embedded in the systems that people already use, such as CRMs and ERPs. The fastest way to create more value from data is by bringing the data to the people who can use it.
Thank you for the great interview, readers who wish to learn more should visit Tamr.
#acquisitions#agent#agents#ai#ai agent#AI AGENTS#AI/ML#amp#Analytics#approach#bank#bearing#Big Data#Building#burnout#Business#career#CDO#CEO#challenge#Companies#comparison#computer#consolidated#consumers#course#crm#CTO#customer experience#dashboard
0 notes
Text
Essential Geospatial Data Analysis Tools
Geospatial data analysis is a crucial aspect of numerous fields such as environmental science, urban planning, and geography. Various tools facilitate the collection, processing, analysis, and visualization of geospatial data. Here are some essential geospatial data analysis tools:

Geographic Information Systems (GIS) Software
ArcGIS: Developed by Esri, ArcGIS is a comprehensive and widely-used GIS software. It offers robust tools for mapping, spatial analysis, and data management. ArcGIS includes desktop applications (ArcMap, ArcGIS Pro), web-based solutions, and mobile apps.
QGIS: An open-source GIS software, QGIS provides a wide range of features for spatial data visualization, editing, and analysis. It’s highly extensible with plugins and supports various data formats.
GRASS GIS: Another powerful open-source GIS, GRASS (Geographic Resources Analysis Support System) GIS is known for its advanced geospatial data management and analysis capabilities, especially in raster data processing.
Remote Sensing Tools
ENVI: A software platform for processing and analyzing geospatial imagery. ENVI is particularly useful for remote sensing applications and supports a wide array of data formats from various sensors.
Google Earth Engine: A cloud-based platform for planetary-scale environmental data analysis. Google Earth Engine provides access to a vast archive of satellite imagery and geospatial datasets and is widely used for environmental monitoring and research.
Data Analysis and Visualization Tools
GDAL (Geospatial Data Abstraction Library): An open-source library for reading and writing raster and vector geospatial data formats. GDAL is a fundamental tool for data translation and processing.
R (with spatial packages like rgdal, sp, raster): R is a programming language and environment commonly used for statistical computing and graphics. With packages like rgdal, sp, and raster, R becomes a powerful tool for geospatial data analysis and visualization.
Python (with libraries like GeoPandas, Shapely, Rasterio): Python is widely used in geospatial analysis due to its readability and extensive libraries. GeoPandas simplifies working with geospatial data, Shapely provides tools for geometric operations, and Rasterio is used for raster data manipulation.
Also Read: Understanding Consumer Behavior Trends in 2024
Web Mapping Tools
Leaflet: An open-source JavaScript library for interactive maps. Leaflet is lightweight and mobile-friendly, making it a popular choice for web mapping applications.
Mapbox: A platform for designing and publishing custom maps. Mapbox offers robust APIs and SDKs for integrating maps into web and mobile applications.
Database Management Systems
PostGIS: An extension of the PostgreSQL database, PostGIS adds support for geographic objects. It allows spatial queries to be run in SQL and is highly efficient for managing large spatial datasets.
Spatialite: An extension of the SQLite database, Spatialite provides support for spatial data. It’s lightweight and useful for applications where a full-scale spatial database like PostGIS isn’t necessary.
Workflow and Automation Tools
FME (Feature Manipulation Engine): A tool for data integration and automation, FME supports a vast range of data formats and helps automate the transformation and movement of geospatial data.
Kepler.gl: An open-source tool developed by Uber for large-scale geospatial data visualization. Kepler.gl is user-friendly and excels in handling and visualizing large datasets interactively.
These tools cover a broad spectrum of needs in geospatial data analysis, from data management and processing to advanced spatial analysis and interactive visualization. The choice of tools often depends on the specific requirements of the task, the scale of the data, and user expertise.
0 notes
Text
The Future of Marketing AI-Driven Predictive Analytics
Diving straight into the heart of the future, let's chat about AI-driven predictive analytics and its revolutionary impact on marketing. Picture this: marketing not as a guessing game but as a precise, data-driven science where every move is calculated and every outcome, nearly foreseen. It's not just futuristic talk; it's the now – and if you're not in on it, you're seriously missing out.
AI-driven predictive analytics is like having a crystal ball but one backed by data, algorithms, and real-world application. It's about understanding your customer's next move before they even make it, tailoring experiences so personalised they feel magical. It's marketing but turned up to eleven. By harnessing the power of AI to predict trends, consumer behaviours, and potential market shifts, businesses are not just reacting; they're proactively shaping the future of their customer's journey.
But, here's the rub – with such a powerful tool comes the need for savvy minds who can wield it. It's not enough to have the technology; you need the know-how to translate complex data into actionable strategies. If you're not building a team capable of navigating the intricate world of AI and data analytics, you're setting yourself up for a fall. In the ultra-competitive UK market, being prepared and ahead of the curve isn't just advantageous; it's essential.
Then there's the aspect of real-time decision-making. Imagine tweaking your marketing strategy on the fly, optimising campaigns in real-time based on incoming data, and predicting consumer responses with uncanny accuracy. This level of agility and precision isn't just nice to have; it's becoming the new standard. If your marketing efforts lack this dynamic adaptability, you're playing a game of catch-up with those who've already embraced the AI-driven approach.
In conclusion, AI-driven predictive analytics isn't just shaping the future of marketing; it's defining it. The fear of missing out (FOMO) is real here. If you're not leveraging AI to anticipate market trends and consumer needs, you're not just behind; you're becoming obsolete. In a world where personalisation, precision, and agility are king, stepping up your AI game isn't just a good idea – it's imperative. Don't just watch the future happen; be a part of creating it.
#AI predictive analytics#real-time marketing#data-driven decision-making#marketing technology#consumer behavior analysis#marketing automation
0 notes
Text
Growth Strategies for FMCG Companies
Discover tailored growth strategies for FMCG companies! From digital transformation to sustainability, explore expert insights at Strategii At Work. Elevate your FMCG success now!
#Strategii At Work#Growth Strategies for FMCG Companies#Growth Strategies#FMCG Companies#Fast-Moving Consumer Goods#FMCG#FMCG firms#AI#data analytics#IoT#robotics#business#FMCG growth#FMCG giants#product life cycle of FMCG#product life cycle#FMCG brands#Data-Driven Decision-Making#Globalization Strategies#Agile Marketing#Direct-to-Consumer#Artificial Intelligence#FMCG business strategy#Go-To-Market (GTM) strategy#consumer packaged goods consulting.#FMCG consultants#FMCG Business Strategy Consulting#Go-To-Market (GTM) Strategy Consulting#Consumer Packaged Goods (CPG) Consulting#CPG consultant
0 notes