#Jurassic fossil shell
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Photo

Leptosphinctes leptus Fossil Ammonite – Middle Bajocian, Jurassic – Caen, France – Alice Purnell Collection – 100% Genuine with Certificate
This listing features a genuine Leptosphinctes leptus fossil ammonite from the Middle Bajocian Stage of the Jurassic Period, dating back approximately 170 to 168 million years ago. This beautiful specimen was discovered in Caen, France, and is part of the highly regarded Alice Purnell Collection, known for high-quality, curated fossil specimens.
Leptosphinctes leptus is a member of the family Perisphinctidae and is recognised by its relatively involute shell, fine and dense ribbing, and compressed whorl section. These marine cephalopods were free-swimming organisms that thrived in shallow seas, playing an important role in the Jurassic marine ecosystem as agile predators.
This specimen shows clear ribbing and whorl definition, with natural preservation in matrix, making it an ideal display piece for collectors or educational institutions.
Geological Context: The Middle Bajocian is part of the Dogger epoch of the Jurassic Period and is renowned for its rich marine fossil record, especially ammonites. The area surrounding Caen in northern France is well known for its Jurassic limestone and marl deposits, which frequently yield well-preserved ammonite specimens that are essential to biostratigraphic studies.
Key Details:
Species: Leptosphinctes leptus (Fossil Ammonite)
Fossil Type: Extinct marine cephalopod
Age: Middle Bajocian, Jurassic (~170–168 million years ago)
Location Found: Caen, France
Provenance: From the Alice Purnell Collection
Size: See photo with scale cube (1cm squares) for full sizing
Condition: Excellent preservation, natural matrix, visible shell morphology
Authenticity: Supplied with a Certificate of Authenticity
Photo: The actual specimen shown in the listing is what you will receive
Scientific & Collector Value: Leptosphinctes leptus is an excellent index fossil for the Bajocian and is used by paleontologists to correlate Jurassic rock layers. Its distinct morphology and provenance from a known locality such as Caen enhance its value. The inclusion in the Alice Purnell Collection further guarantees the fossil’s significance and authenticity.
All of our Fossils are 100% Genuine Specimens & come with a Certificate of Authenticity.
Fast & Secure Shipping – All items are carefully packed and dispatched quickly for safe delivery.
Add a beautifully preserved example of Jurassic marine life to your collection with this Leptosphinctes leptus ammonite fossil from Caen, France.
#Leptosphinctes leptus ammonite#Bajocian fossil ammonite#Jurassic ammonite France#Caen ammonite fossil#Middle Jurassic cephalopod#ammonite with certificate#certified fossil ammonite#Alice Purnell Collection#real ammonite France#Jurassic fossil shell
0 notes
Text
Round 3 - Reptilia - Gruiformes




(Sources - 1, 2, 3, 4)
Our next order of birds are the Gruiformes, a diverse order with a widespread geographical diversity. “Gruiform” means “crane-like”, even though the majority of gruiformes are rails. Gruiformes contains the families Psophiidae (“trumpeters”), Aramidae (“Limpkin”), Gruidae (“cranes”), Rallidae (“rails”, “coots”, and “crakes”), Heliornithidae (“finfoots”), and Sarothruridae (“flufftails”).
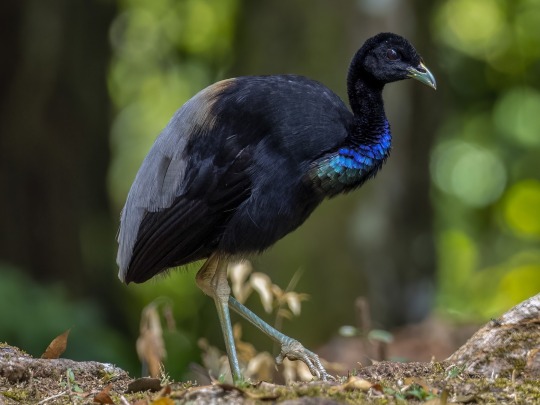
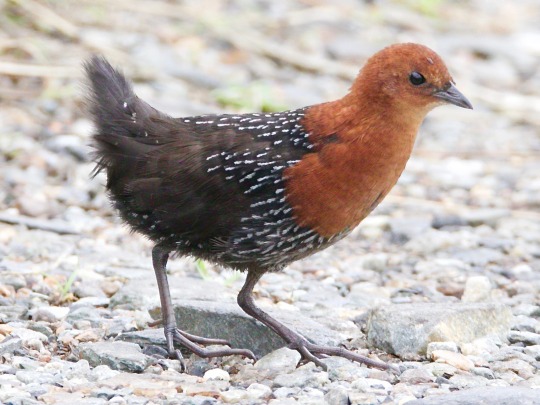
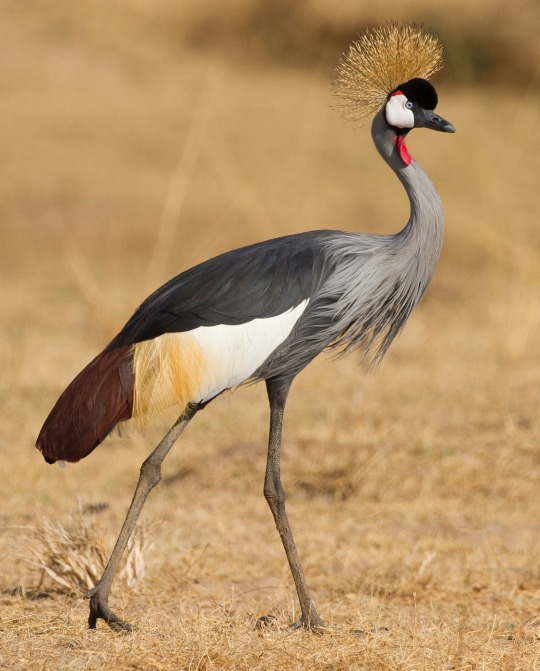
Gruiformes are terrestrial or wading birds with a considerable amount of diversity. The Trumpeters (genus Psophia) (image 1) are rotund birds with long, flexible necks and legs, downward-curving bills, soft plumage, large eyes, and a “hunched” appearance. They are weak fliers but fast runners, and can also swim across rivers. The cranes (Gruidae) (image 3 and gif below) and the Limpkin (Aramus guarauna) are long-necked, long-legged, long-beaked waders, some of which are the world’s tallest flying birds. Their plumage varies by habitat. The Rallidae (image 4) are the most diverse family of Gruiformes. Many are associated with wetland habitats, some being semi-aquatic like waterfowl (such as the coot), and some being more like wading birds or shorebirds. The finfoots (Heliornithidae) resemble rails; they have long necks, slender bodies, broad tails, and sharp, pointed bills. Their legs and feet are brightly coloured and they are capable of walking well and even moving quickly on land. The flufftails (Sarothruridae) (image 2) are small- to medium-sized ground-living birds. Due to the diversity of this order, it is difficult to summarize them further!
Gruiformes evolved in the Paleocene, around 60 million years ago.

(source)
Propaganda under the cut:
Grey-winged Trumpeters (Psophia crepitans) are polyandrous and cooperative breeders. Up to three males mate with the dominant female of the flock, and all members of the flock contribute to raising the young.
One of the handful of non-avian dinosaurs we know the colors of is the Late Jurassic Caihong juji. Thanks to some exquisitely fossilized melanosomes (pigment cells) within the animals feathers, paleontologists were able to determine Caihong’s coloration by comparing it to those of living birds. The sheets of platelet-like melanosomes were solid and lacked air bubbles, and were thus most similar to the iridescent feathers that exist in modern Trumpeters (genus Psophia). It is thanks to trumpeters for preserving this type of melanosome, that we know the appearance of a dinosaur from the Late Jurassic!
The Limpkin (Aramus guarauna) has a beak that is slightly open near the end, giving it a tweezer-like action to remove their main prey, Apple Snails (family Ampullariidae), from their shells. In many individuals the tip of their beak curves slightly to the right, matching the Apple Snails’ shells.
Most species of cranes have been affected by human activities and are at the least classified as threatened, if not critically endangered. The plight of the Whooping Crane (Grus americana) of North America inspired some of the first US legislation to protect endangered species. After being pushed to the brink of extinction due to unregulated hunting and loss of habitat, just 21 wild (and two captive) Whooping Cranes remained by 1941. Thanks to conservation efforts, the total number of cranes in the surviving migratory population, including those in captivity, only slightly exceeds 911 birds as of 2020.
The Sanskrit epic poet Valmiki was inspired to write the first śloka couplet by the pathos of seeing a male Sarus Crane (Antigone antigone) shot while dancing with its mate.
The endangered South Island Takahē (Porphyrio hochstetteri) is a flightless swamphen indigenous to New Zealand. Takahē were hunted extensively by both early European settlers and Māori, and takahē's bones, as well as fossil remains, have been found in middens in the South Island. They were not named and described by Europeans until 1847, and then only from fossil bones. In 1850 a living bird was captured, and three more collected in the 19th century. After another bird was captured in 1898, and no more were to be found, the species was presumed extinct. Fifty years later, however, after a carefully planned search, South Island Takahē were dramatically rediscovered in November 1948 by Geoffrey Orbell in an isolated valley in the South Island's Murchison Mountains. Since then, takahē have been reintroduced to numerous locations across the country. As of 2023, the population is around 500 and is growing by 8% per year.
The Guam Rail (Hypotaenidia owstoni) came perilously close to extinction when Brown Tree Snakes (Boiga irregularis) were introduced to Guam, but some of the last remaining individuals were taken into captivity and have been breeding well. They have since been successfully introduced to the nearby Rota and Cocos islands, as the Brown Tree Snakes have yet to be eradicated in Guam. In 2019, the Guam Rail became the second bird species to be reclassified by the International Union for the Conservation of Nature from Extinct in the Wild, to Critically Endangered.
#sorry if there are any mistakes here and if it’s a bit short#it’s midnight and I’m fighting sleep to finish this#animal polls#round 3#reptilia#Gruiformes
83 notes
·
View notes
Text
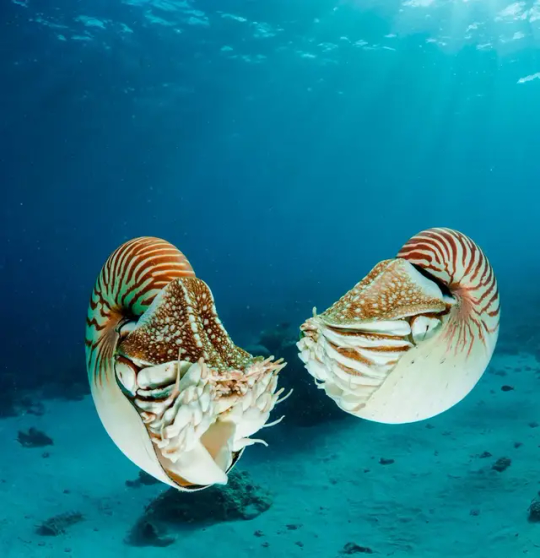
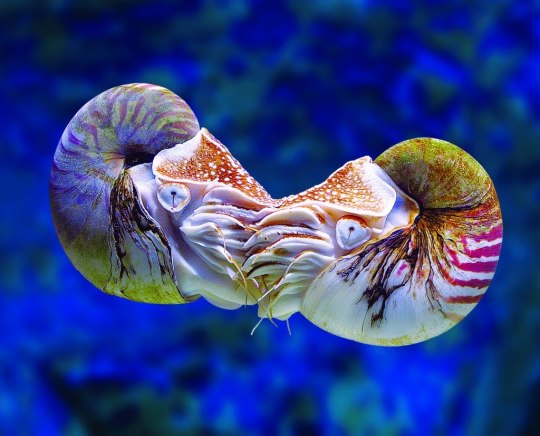
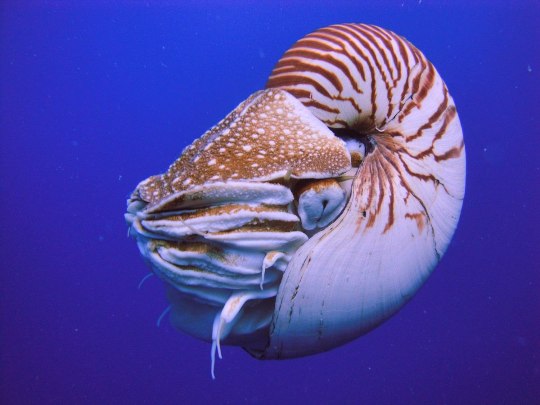
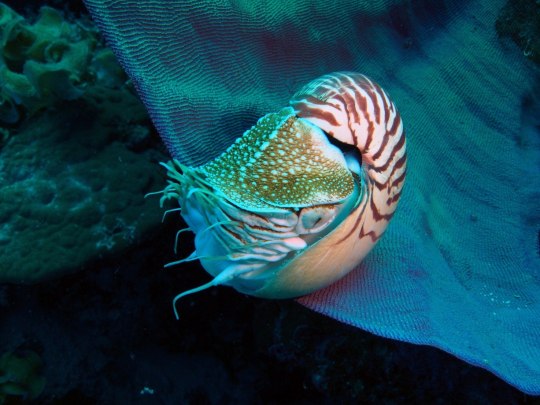
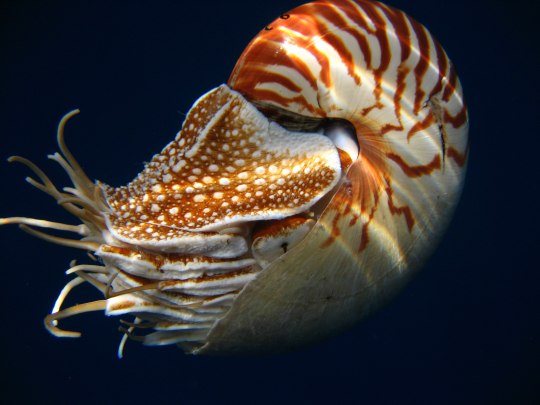
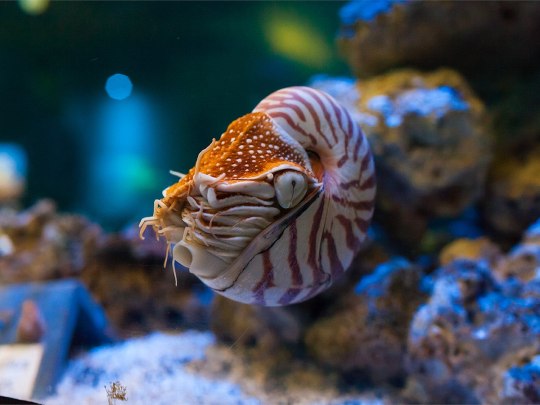
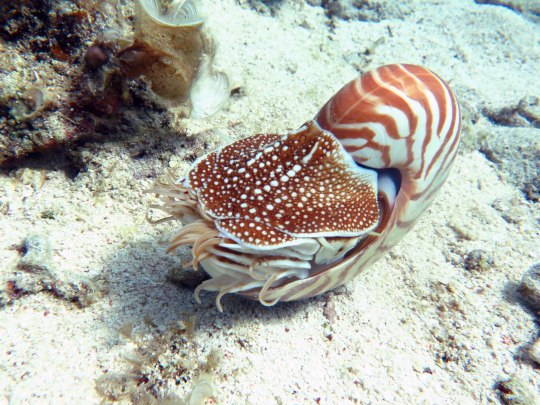
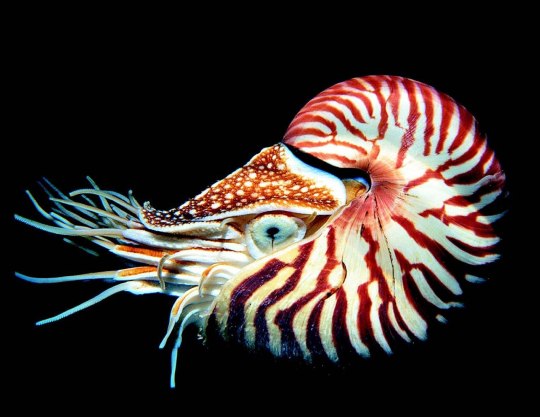
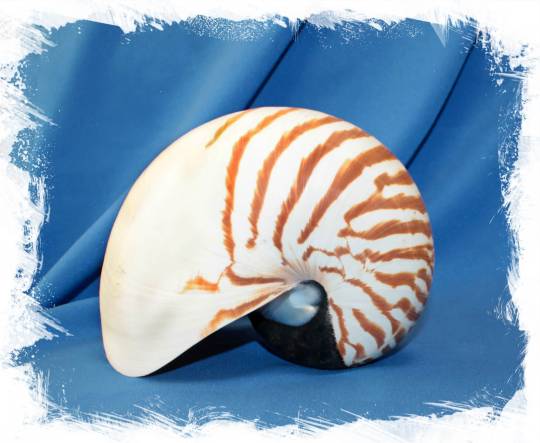





















Наутилус (лат. Nautilus) — род головоногих моллюсков, которых относят к «живым ископаемым». Самый распространенный вид — Nautilus pompilius. Наутилусы относятся к единственному современному роду подкласса наутилоидей. Первые представители наутилоидей появились в кембрии, а его развитие пришлось на палеозой. Наутилиды почти вымерли на границе триаса и юры, но все же дожили до наших дней, в отличие от своих родственников аммонитов. Некоторые виды древних наутилусов достигали размера в 3,5 м. Представители самого крупного вида современных наутилусов достигают максимального размера в 25 см.
Спиральный «домик» моллюска состоит из 38 камер и «построен» по сложному математическому принципу (закон логарифмической прогрессии). Все камеры, кроме последней и самой большой, где размещается тело наутилуса с девятью десятками «ног», соединяются через отверстия между собой сифоном. Раковина наутилуса двухслойная: верхний (наружный) слой – фарфоровидный – действительно напоминает хрупкий фарфор, а внутренний, с перламутровым блеском – перламутровый. «Домик» наутилуса растет вместе с хозяином, который перемещается по мере роста раковины в камеру попросторней. Пустое жилище моллюска после его гибели можно встретить далеко от его места обита��ия – после гибели «хозяина» их раковины остаются на плаву и перемещаются по воле волн, ветров и течений.
Интересно, что двигается наутилус «в слепую», задом наперед, не видя и не представляя препятствий, которые могут оказаться на его пути.И еще одно удивительное качество этих древних обитателей Земли – у них потрясающая регенерация: буквально через несколько часов раны на их телах затягиваются, а в случае потери щупальца быстро отрастает новое.
Nautilus is a genus of cephalopods, which are classified as "living fossils". The most common species is Nautilus pompilius. Nautilus belong to the only modern genus of the Nautiloid subclass. The first representatives of the Nautiloids appeared in the Cambrian, and its development took place during the Paleozoic. The Nautilids almost died out on the border of the Triassic and Jurassic, but still survived to the present day, unlike their Ammonite relatives. Some species of ancient Nautilus reached a size of 3.5 m. Representatives of the largest species of modern nautilus reach a maximum size of 25 cm.
The spiral "house" of the mollusk consists of 38 chambers and is "built" according to a complex mathematical principle (the law of logarithmic progression). All chambers, except the last and largest, where the nautilus body with nine dozen "legs" is located, are connected through holes with a siphon. The nautilus shell is two–layered: the upper (outer) layer – porcelain–like - really resembles fragile porcelain, and the inner, with a mother-of-pearl luster - mother-of-pearl. The nautilus's "house" grows with its owner, who moves as the shell grows into a larger chamber. The empty dwelling of a mollusk after its death can be found far from its habitat – after the death of the "owner", their shells remain afloat and move at the will of waves, winds and currents.
Interestingly, the Nautilus moves "blindly", backwards, without seeing or imagining the obstacles that may be in its path.And another amazing quality of these ancient inhabitants of the Earth is that they have amazing regeneration: in just a few hours, the wounds on their bodies heal, and in case of loss of tentacles, a new one grows quickly.
Источник:://t.me/+t0G9OYaBjn9kNTBi, /sevaquarium.ru/nautilus/, /habr.com/ru/articles/369547/, //wallpapers.com/nautilus, poknok.art/6613-nautilus-molljusk.html, //wildfauna.ru/nautilus-pompilius, /www.artfile.ru/i.php?i=536090.
#fauna#video#animal video#marine life#marine biology#nature#aquatic animals#cephalopods#Nautilus#nautilus pompilius#living fossils#ocean#benthic#coral#plankton#beautiful#animal photography#nature aesthetic#видео#фауна#природнаякрасота#природа#океан#бентосные#головоногие моллюски#Наутилус#живое ископаемое#коралл#планктон
187 notes
·
View notes
Text
Throwback Thursday: Jurassic Park
You knew this was coming, admit it. When you hear the word T. rex you can easily picture:

Now, I could go on and on about inaccuracies but that's what everyone does. Let's talk about what they did right and why it made dinosaurs popular again.
First off, it wasn't a monster. It was an animal doing animal things.

It flipped the car because it recognized it had a hard "shell" like a certain dinosaur it lived longside.

To get to the soft, tasty parts of Ankylosaurus, Tyrannosaurus would have to flip it over.
And just like most animals, it was very intrigued by the flair.
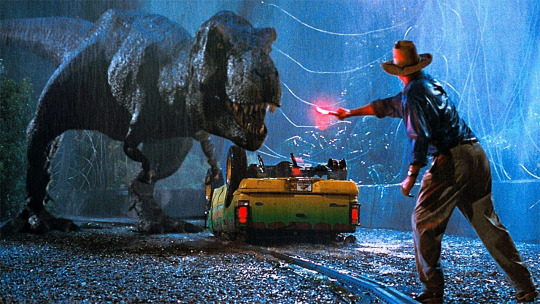
It hunted like a proper predator.

There was even a scene with smaller annoyances that she dealt with much the way that a modern day raptor would deal with pests.
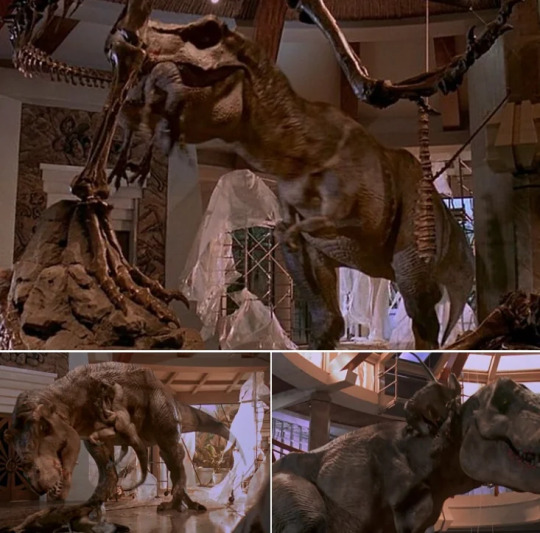

The puppeteering was beautiful and that roar (even though it probably wouldn't have roared in real life) is one of the most recognizable sounds in cinema.

This movie also created many paleontologists and dinosaur enthusiasts like me! Yes, according to my parents, when I saw this movie I wanted to be a paleontologist and it was all downhill from there. I still love watching this movie. One of my comfort films. What about you? What is your favorite part of the movie?
Tune in tomorrow for one last tyrannosaur Fossil Friday. Fossilize you later!
#paleontology#fossils#dinosaur#science#science education#science side of tumblr#science history#jurassic park
28 notes
·
View notes
Note
Ayo, I was pondering if humans were in Pac-World? I was thinking about if real people like us were in Pac-Man’s world? Try imagine how it would feels like your on Pac-World or the Netherworld 🤔 (Last night I had a dream that I was in Betrayus’ world, held as a damsel in distress)

I mean, what if humans were in Pac-World… *Thinks for a sec*
Lol we'd probably be shell-shocked at how smooth, round, and textureless everything in Pacworld would be!
I have two theories about humans; one, Earth is so far away from Pacworld in the universe that neither has discovered the other yet.
Or two, Pacworld IS Earth, but several trillion years in the future when humans have long gone extinct and the planet went through several new ice ages and jurassic periods to where it is now home to a simpler ecosystem inhabited by Pacworlders. Archaeologists discovered Pacosaurs and other Pac-sized dinosaurs and prehistoric creatures in fossils first, but then the deeper they dug, the more they came across the remains of a lost, ancient civilisation that once belonged to humans, or as Pacworlders called them, "the giants." An adult human fossil is three times the size of a Pacworlder, and human-made structures were several times bigger than the biggest Pacworlder-made structure, so when they were discovered, it was like discovering an alien race that Pacworlders couldn't fathom. They're still trying to figure out the lengths and depths of the human era and the impact it's had on the planet's ancient past.
That's all the thoughts I really have on humans in Pacworld! I might make a separate post going more in-depth with the fan-theory.
15 notes
·
View notes
Text

A landslide on a Dorset beach has attracted dozens of fossil hunters in search of relics.
Some 200 enthusiasts combed the beach in the village of Charmouth, on the Jurassic Coast, collecting scores of ammonite fossils.
The majority are said to have picked up ammonites, extinct sea molluscs prized for their intricate spiral shells, which measure from 2cm to 2ft and were washed out of the mud and shale by the sea.
Very cool, if you like such things. I know good examples sell to collectors for a tidy price.

13 notes
·
View notes
Text


Literally haven’t posted paleoart in the same span between now and the fucking Jurassic but here’s a dilophosaurus I did from memory at a Tyrrell internship/youth camp type thing lol (PLUS A FOSSILIZED TURTLE SHELL I FOUND WHILE PROSPECTING) uhhhh I’m still super autistic for ATLA rn tho so prob won’t post a lot more lmfao
Enjoy it while it lasts (probably gonna draw more dinosaurs again soon tho bc I have a school project I’m doing about like either translation of Saurischian hips into bird hips or uhh fossilized evidence of parental care in the Mesozoic I’m DEAD)
#art#paleoart#dinosaur#dilophosaurus#theropod#theropoda#Jurassic#sketch#royal tyrrell museum#Royal tyrrell
24 notes
·
View notes
Text

Fossil Friday: Ammonite
Ammonite is a preserved shell belonging to an Ammolite or other creature belonging to the subclass Ammonoidea. These fossils are the remains of an extinct marine cephalopod (mollusc) from the Jurassic period (about 200 million years ago) to the late Cretaceous period (about 66 million years ago). Ammonites died off at roughly the same time as flightless dinosaurs. Ammonites were a unique group of creatures, likely having eight separate arms, resembling a coleoid (squids, octopuses, and cuttlefish), while the shell and it's shape closer resembling a nautilus. An estimated 10-20 thousand species of ammonite have been discovered, so no two fossils will be the same. The largest ammonite specimen found was over 1.8 metres (approx. 5.9 feet) in length, while being an incomplete fossil. Ammonite can be found at any location where prehistoric oceans once were. Ammonite is often used as an index fossil, being used to date the approximate age of the rocks it is embedded in. Ammonite is considered to be one of the world's rarest gemstones when the shell appears iridescent.
It is crucial to be aware of laws and regulations governing fossil collection in your area. Many places require all fossils found to be sent to a palaeontologist, and have strict regulations on the selling of locally found specimens.
More information about ammonites can be found here.
Stay tuned for next week's Fossil Friday!
#crystals#geology#minerals#rocks#fossils#rock collection#gemstone#geoscience#rock hounding#rock of the day#paleo#palaeontology#paleontology#fossil friday by let's talk rocks#fossil friday#let's talk rocks#ammonite
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
Qianlong shouhu Han et al., 2023 (new genus and species)
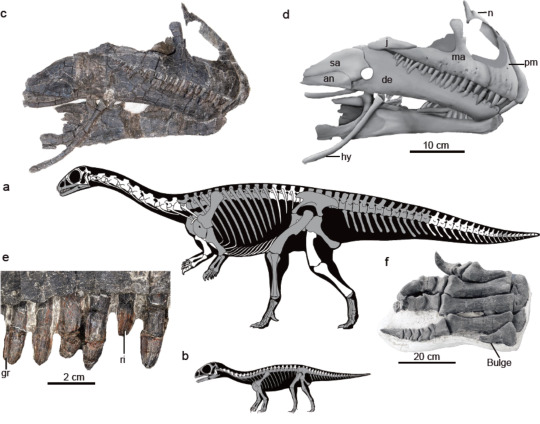
(Select bones and schematic skeletals of adult [a] and embryonic [b] individuals of Qianlong shouhu, with preserved bones in gray, from Han et al., 2023)
Meaning of name: Qianlong = Qian [alternative name for Guizhou] dragon [in Chinese]; shouhu = guarding [in Chinese]
Age: Early Jurassic (Sinemurian?)
Where found: Ziliujing Formation, Guizhou, China
How much is known: Three partial skeletons of adult individuals and five clutches of 3–16 eggs containing embryos.
Notes: Qianlong was an early sauropodomorph. It is notable not only for the exceptional preservation of its fossils, but also the fact that these specimens appear to be associated with nests, thus offering valuable information on their growth and reproductive behavior. As has also been found for some early sauropodomorphs, such as Massospondylus from the Early Jurassic of Southern Africa and Mussaurus from the Early Jurassic of Argentina, Qianlong appears to have laid its eggs in breeding colonies with adult individuals potentially watching over their nests. Qianlong was additionally similar to these other early sauropodomorph in being bipedal as an adult, but likely quadrupedal as a young juvenile.
Rigid, hard-shelled eggs have been found in multiple groups of dinosaurs, including tetanuran theropods (such as birds), hadrosaurids (duck-billed dinosaurs), and titanosaurian sauropods, as well as their closest living relatives, the crocodylians. As a result, it was long assumed that all dinosaurs probably laid hard-shelled eggs. However, recent evidence has suggested that the eggs of early dinosaurs may have instead had flexible, leathery shells, more similar to those of most lizards and some turtles, with rigid eggshells evolving several times in later dinosaur groups. The eggshells of Qianlong appear to have been leathery in structure, lending support to this hypothesis.
Reference: Han, F., Y. Yu, S. Zhang, R. Zeng, X. Wang, H. Cai, T. Wu, Y. Wen, S. Cai, C. Li, R. Wu, Q. Zhao, and X. Xu. 2023. Exceptional Early Jurassic fossils with leathery eggs shed light on dinosaur reproductive biology. National Science Review advance online publication. doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwad258
144 notes
·
View notes
Text
Thalattosuchus and Leedsichthys
Quickly stopping by to report on a new paper describing stomach contents of a thalattosuchian (Jurassic marine crocodile).
The paper in brief describes a specimen of Metriorhynchus superciliosus (aka Thalattosuchus) with preserved stomach contents, which is already rare enough as is. What's even more interesting is that the stomach contents preserve both the gill rakes of the large fish Leedsichthys as well as various mollusc shells. Strange prey for what's a rather small piscivore. Although it was previously suggested that Metriorhynchus/Thalattosuchus attacked living Leedsichthys, this appears to have been based on missinterpreted evidence and given the enormous size difference its way more likely that the fish was simply scavenged, sorta like a kind of Jurassic whalefall. This actually finds support in the mollusc shells, which might have been ingested on accident alongside the fish remains.
Top left: The skeleton of this Thalattosuchus specimen Top right: The stomach contents in detail (G are gill rakes, S are shells) Bottom left: Live reconstriction of Thalattosuchus by Gabriel Ugueto Bottom right: Live reconstruction of Leedsichthys by @knuppitalism-with-ue
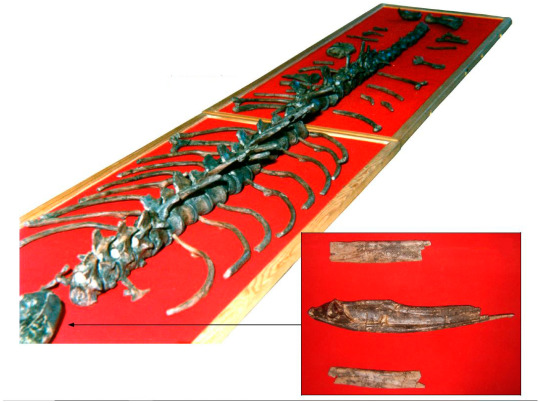
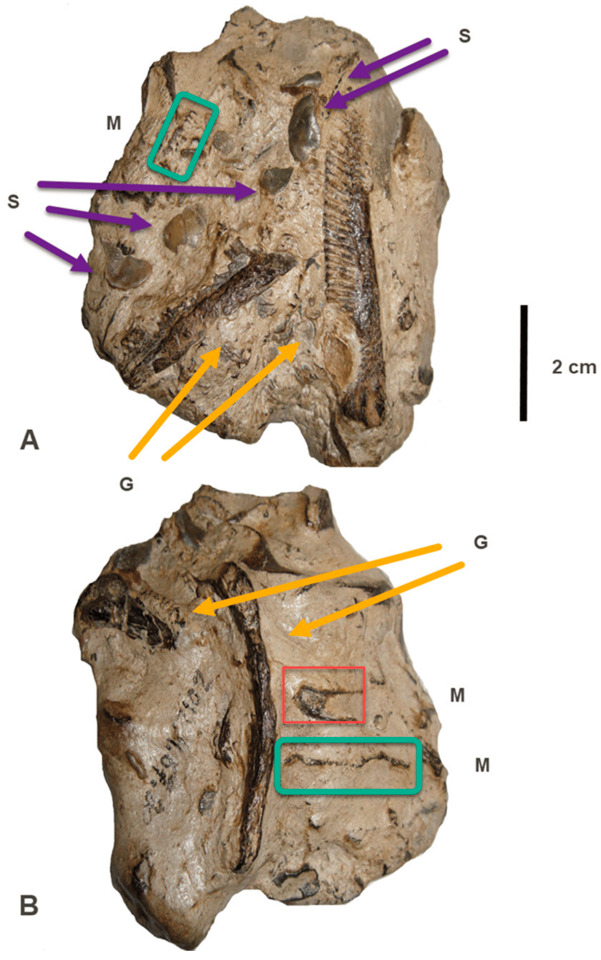


The paper itself: Fossil Studies | Free Full-Text | The Diet of Metriorhynchus (Thalattosuchia, Metriorhynchidae): Additional Discoveries and Paleoecological Implications (mdpi.com)
#thalattosuchus#thalattosuchia#metriorhynchus#metriorhynchidae#leedsichthys#palaeoblr#paleontology#prehistory#jurassic
38 notes
·
View notes
Text
Archaeology vs. Paleontology, how it feels to be elegantly told by Hawkman that you're dumb

From All-Star Comics #61 & 62 (1976) by Gerry Conway, Keith Giffen & Wally Wood
I'm currently reading a JSA comic in which an astronaut flies to the surface of the sun and, instead of dying, becomes a powerful being capable of manipulating high levels of energy. I'm having fun, so I don't care about the science of it. However few pages later I get the panel above... Mixing up archaeology and paleontology? Now this is too much, that's where I draw the line! (Although I was too quick to judge, and Hawkman had my back all along).
I have no idea what is the scientific field of Dr. Kliburn's studies, but when he says: "Mucking about the ruins of Egypt, exploring ancient Inca pyramids, digging up dinosaur bones in Arizona -- all of that makes sense for an archaeologist" to Carter Hall a.k.a. Hawkman, an archaeologist, he badly mixes things up making dinosaur bones part of an archaeologist job. So ok, studying the remains of life is the business of many branches of science, and both archaeology and paleontology study the remains of organisms, but there's a difference in the type of remains they study.
Archaeology is the scientific study of ancient and recent human remains and artifacts (bones and teeth, ancient cool pottery, statues, funeral urns, tools, vases). Think: Lara Croft; Indiana Jones (I'm not saying he's good at his job though!).
Paleontology is the scientific study of all past life on Earth (dinosaurs, extinct fungi, plants, saber-tooth tigers etc), primarily through the study of fossils - so way beyond the remains of humans and their artifacts. Think: all the smart people in Jurassic Park; Ross, from Friends? (Oh boy we need better representation).
A little about objects of study: fossils studied by paleontologists and archeologists include bones, shells, body imprints, wood etc; so these fields of study might overlap (i.e. similar tools and excavation techniques), though their goals are different. Fossils can be remains of anything, there are different kinds of it. Trace fossils for example are like footprints, nests, or handprints left behind by creatures.


Above are the pictures of two cases of trace fossils, but while the study of the human footprints fossils on the left is a job for an archaeologist, the study of the non-human footprints, on the right, is a job for an paleontologist.
Now, what about poop? You might be asking yourself... and yes fossilized poop is also a fascinating object of study, they are scientifically called coprolites and by analyzing the fossilized poop of the Neolithic workers who built the the Stonehenge monument archaeologists found them littered with parasitic worm eggs. I mean... disgusting, but how cool is that we are able to learn that? They made these amazing structures which some people atribute to aliens and super advanced technology, but they had no idea they were eating infected meat, and that's such a human thing to do!
On the other hand when paleontologists study and collect animal fossil coprolites they find out more about that animal's way of life, their ecology, their environment, which is super important considering we can only study their remains. One of such early paleontologists, and true icon in the field of collecting ancient dinosaur feces and bones, was Mary Anning, a pioneer of paleontology in the early 1800s (she's cool as heck)!
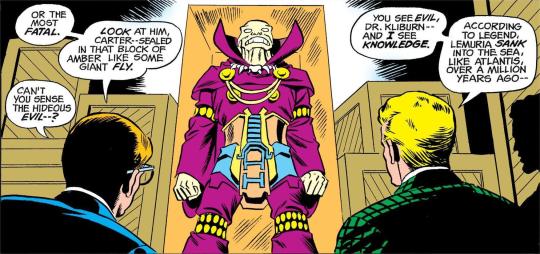
Now that we establish that: I'm sorry Dr. Kliburn, but that is obviously a human remain, therefore a job for Hall Carter, an archaeologist! He also mentions a fly trapped in amber (and I know it is a sort of metaphor, but), that would be a job for an paleontologist... Kliburn is a really confused man. And Hawkman is just too polite to bluntly correct his colleague, instead he chooses a more subtle approach:

By emphasizing that the "proper study of mankind is man" Carter very elegantly corrects Dr. Kliburn's wrong assertions, indirectly pointing that his field is the study of mankind and their artifacts, not other aspects of nature, he won't be looking into flies preserved in amber or excavating dinosaur bones in Arizona (although... to Kliburn's merit, Arizona is indeed a state with a rich fossil record with many different dinosaurs and other animal bones and trees preserved). A very polite way call someone a fool.
I'm guessing that the writer, Gerry Conway, was probably aware of the difference between the two occupations and interested in making a tongue in cheek comment on it. Not that comics need to be scientifically correct, far from it, I love it when they're not. But I also love it when we can use them to learn something.

Further indication of that point is that if we take a look at Hall Carter's home in the above panel, we don't see any signs of animal remains, we do see what look like human artifacts, tools, weapons and masks. It is clear Keith Giffen and Wally Wood, the artists of the issue, are aware of an archaeologist's objects of study. And if you're asking yourself who the uninvited guest is: yes it is Dr. Kliburn himself attempting to rob Hawkman's house...
Dr. Kliburn dies that same issue by the very human fossil he was trying to steal. So that's what you get for mixing up two serious and interesting scientific fields... Thank you for reading this!
#hawkman#justice society of america#comic book science#paleontology#archaeology#jsa#carter hall#all star comics#reading log#science#keith giffen#wally wood#gerry conway#dc comics#dc#comics#coprolites#fossils#text#comic panels#cw ross from friends#little essay
8 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Liparoceras cheltiense Ammonite Fossil - Lower Pliensbachian, Jurassic, Blockley, Gloucestershire, UK | 100% Genuine Specimen + COA
A stunning and rare Liparoceras cheltiense Ammonite Fossil from the Lower Pliensbachian Stage, Jurassic, Blockley, Gloucestershire, UK. This beautifully preserved ammonite showcases the intricate ribbing and robust shell structure characteristic of this species, making it a valuable piece for collectors, educators, and fossil enthusiasts alike.
✅ 100% Genuine Specimen – Every fossil we sell is authentic and comes with a Certificate of Authenticity.
✅ From the Alice Purnell Collection – A carefully curated specimen with historical significance.
✅ What you see is what you get – The listing photos show the exact specimen you will receive.
✅ Includes size reference – Scale cube in photos = 1cm. Please refer to the images for full dimensions.
✅ Ideal for collectors, display, or scientific study – A visually stunning and scientifically significant ammonite specimen.
About Liparoceras cheltiense Fossil Ammonites:
Liparoceras cheltiense is a species of ammonite from the Lower Pliensbachian Stage of the Early Jurassic period, approximately 190-195 million years ago. These ammonites belonged to an extinct group of marine cephalopods related to modern-day squids, octopuses, and nautiluses.
This species is known for its thick, evolute shell with strong ribbing and pronounced keels, making it a distinctive and highly recognizable ammonite. Fossils of Liparoceras are found in marine sedimentary deposits, particularly in Blockley, Gloucestershire, UK, a site well-known for its exceptional fossil preservation.
Ammonites like Liparoceras cheltiense played a crucial role in prehistoric marine ecosystems and are important index fossils used by paleontologists to date rock layers. Their intricate shell patterns and evolutionary significance make them highly sought-after by collectors and researchers.
Perfect for display, educational purposes, or as a unique gift for fossil lovers and paleontology enthusiasts, this ammonite is a one-of-a-kind addition to any fossil collection.
Shipping & Packaging:
🔹 Securely packed for safe transit 🔹 Worldwide shipping available 🔹 Tracked & insured delivery options
Why Buy from Us?
🔹 Trusted Seller – Specializing in fossils, minerals, and natural history specimens. 🔹 Certified Authenticity – Every purchase includes a signed Certificate of Authenticity. 🔹 Ethically Sourced – All our fossils are legally and responsibly collected.
Own a scientifically valuable piece of Jurassic history today!
#Liparoceras cheltiense#fossil ammonite#Jurassic ammonite#Blockley ammonite#Gloucestershire fossil#UK fossil#Lower Pliensbachian fossil#ammonite collector#ammonite specimen#ammonite shell#ammonite fossil for sale#rare ammonite#prehistoric fossil#fossilized ammonite#geological specimen#fossil display#ammonite identification#ammonite paleontology#fossil hunting#ammonite evolution#Alice Purnell Collection#cephalopod fossil#fossil enthusiast#ammonite shop#ammonite decor#ammonite history#fossil gift#ammonite energy
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Round 3 - Chondrichthyes - Heterodontiformes




(Sources - 1, 2, 3, 4)
While several extinct genera of Heterodontiformes are known from the Jurassic, today only one genus, Heterodontus, the “Bullhead Sharks” remains. Ten living species of bullhead shark have been described.
Bullhead sharks are relatively small, with the largest species reaching just 1.65 metres (5.5 ft) in maximum length. They have tapered bodies, with blunt, proportionally large heads, relatively small mouths, pig-like snouts, and pronounced ridges above their eyes. They have two large dorsal fins, the first larger than the second, and an anal fin. Both dorsal fins have a rigid spine at the front of each fin which is used for defense. Bullhead Sharks are bottom feeders in tropical and subtropical waters. They have cusped grasping teeth at the front of the mouth, and flattened teeth at the back of the mouth. They use the flattened teeth at the back of their mouth to crush hard-shelled prey like bivalves, crustaceans, and sea urchins, and the grasping teeth on soft-bodied prey like worms, anemones, and octopuses. They hunt at night by "walking" along the sea floor with alternating motions of their pectoral and pelvic fins.
Bullhead shark egg cases are shaped like an auger, with two spiral flanges. This allows the egg cases to become wedged in the crevices of rocky sea floors, where the eggs are protected from predators; however, some bullhead sharks deposit their eggs on sponges or seaweed. Due to their spiral shape, each egg case requires several hours to rotate out of the mother shark's cloaca (Oof). She usually lays two at a time. The eggs typically hatch after 7 to 12 months, depending on the species. The pups will usually reach over 14 cm in length by the time they leave the egg case.
The Heterodontiforms appear in the fossil record in the Early Jurassic, with modern forms appearing in the Late Jurassic. Despite the very ancient origins of the genus, phylogenetic evidence indicates that all living species in the genus arose from a single common ancestor that survived the K-Pg extinction.

Propaganda under the cut:
Female Japanese Bullhead Sharks (Heterodontus japonicus) are known to deposit their eggs in communal nests, with as many as 15 eggs left in the same nest.
Horn Sharks (Heterodontus francisci) (image 2) have relatively small territories they hunt in at night, returning to the same “house” during the day. They may remain faithful to the same territory for over a decade. Now that’s a homebody.
Horn Sharks are queued by light rather than by an internal clock. In laboratory settings, they will become active as soon as lights are turned off. If they are in the middle of something when the lights are turned on, they may stop swimming and sink to the bottom. In one experiment where the sharks were kept in darkness, they remained continuously active for 11 days before slowing from fatigue. (☹️)
The Horn Shark generates the highest known bite force relative to its size of any shark, which it uses to crack into mollusks, echinoderms, and crustaceans. One study found the average bite force for this species in the wild to be 95 N with a maximum of 135 N, while under experimental conditions sharks could be induced to bite with over 200 N of force.
Female Horn Sharks in the wild pick up their egg cases in their mouths and wedge them into crevices to keep them safe.
In July 2018, three people were arrested after stealing a juvenile Horn Shark from the San Antonio Aquarium. The shark was scooped out of its tank and smuggled out of the aquarium in a stroller, wrapped in a wet blanket. It was thankfully returned unharmed two days later.
The Crested Bullhead Shark (Heterodontus galeatus) (image 4) produces spiral-shaped egg capsules that are secured to seaweed or sponges with long tendrils.
The Crested Bullhead Shark is a major predator of the eggs of the Port Jackson Shark! Individual sharks have been observed taking the egg capsules in their mouths and chewing on the tough casing, rupturing it and allowing the yolk to be sucked out, or simply swallowing the capsules whole.
The Port Jackson Shark (Heterodontus portusjacksoni) (image 1) is a migratory species, traveling south in the summer and returning north to breed in the winter. Males tend to arrive to the breeding grounds first with the females arriving later and staying later, perhaps as a means to reduce egg predation upon their newly laid eggs.
While juvenile Port Jackson Sharks are not particularly social, adults are often seen resting in caves in groups, and prefer to associate with specific sharks based on sex and size. In lab settings, these sharks were shown to have unique personality traits and preferences, can be trained, can count, and can learn by watching other sharks.
66 notes
·
View notes
Text
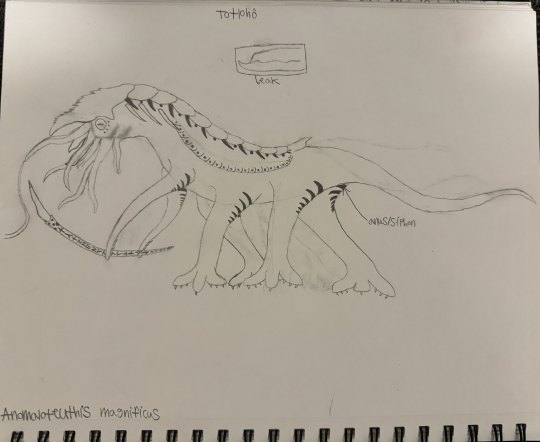

Totlohô
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Mollusca
Class: Cephalopoda
Subclass: Nautiloidea
Superorder: Alysidaceratoidea
Order: Paratetrapoda
Superfamily: Cotylopodoidea
Family: Cotylopodidae
Subfamily: Anomaloteuthiinae
Genus: Anomaloteuthis
Species: A. magnificus (”magnificent unusual squid”)
Ancestral species: possibly Plectronoceras cambria
Temporal range: Early Jurassic (Toarcian) to Early Cretaceous (Hauterivian) (180 - 130 mya)
Information:
While humans have long seen themselves as the first and only sapient species to inhabit their planet, in all truth, there existed another in Xenogaea several hundreds of millions of years ago, one whose legacy can still be felt throughout the region untold eons later in their bizarre ruins and artifacts: the Totlohô-tu-Tẋusko/Tẋusko-tu-Totlohô (IPA: /to̞t͡ɬo̞hɔ tu t͡ʃusko̞/ OR /t͡ʃusko̞ tu to̞t͡ɬo̞hɔ/, meaning "ancestor of (the) architect"), better known as simply the Totlohô (/to̞t͡ɬo̞hɔ/, simply meaning "architect").
As soft tissues of this species have only rarely been preserved, and hard tissues consist only of armor plating and beaks, their size and general appearance alone must be inferred purely based on known proportions from living relatives, other members of the aberrant nautiloid clade Alysidaceratoidea, known more colloquially as the shrikehounds. The most reliable size estimate places them at around 12 feet long, 6-7 feet tall, and weighing close to 600 lbs. The appearance of these creatures, based on ancient stone murals, would seem to suggest that they were centaur-like in build, sporting six main limbs along with a menagerie of smaller tentacles around the face, which housed a long, narrow beak with a noticeable underbite. The exact coloration of this species isn’t known, though as murals exist which depict them, it can be inferred that they might have had a similar coloration pattern to living nautili, with a creamy-colored body and eyes with an earthy red shell and head piece.
Living shrikehound species are not particularly vocal, with only the paratetrapods having an analogue to proper vocal cords. This species was presumably vocal in some capacity, though the exact vocalizations cannot be deduced. It has been suggested that like their living relatives, they might have been able to produce clicks, grunts, warbles, rumbles, belches, screeches, and shrieks. It has been suggested, however, that they may have convergently evolved chromatophores like some of their living relatives and may have had a primarily visual language instead, one which has not, as of yet, been decoded.
Much of these organism's general biology is not known conclusively. Most evidence points to a carnivorous diet, consisting mainly of small dinosaurs/paravians, but also other terrestrial nautiloids, small mammals, and a bizarre group of terrestrial acanthodians known as coelospondyls. Though the exact place where they first evolved has yet to be conclusively found, fossilized beaks first appear in the Matansitra Formation in the southwest of the Isle of Perils, though later formations across the entire archipelago show that almost every habitable landmass sported a population of these creatures at one point. Dubious material from areas outside the archipelago, including what is now China and Australia, suggests they may have eventually left the archipelago at some point as well. At their peak during the Kimmeridgian age of the Late Jurassic epoch roughly 150 millions years ago, their population size was likely upwards of 40 million. Very little (if anything) can be inferred about their reproductive biology, though murals would seem to suggest that courtship and copulation was a very long, drawn-out process, treated almost as an art form unto itself. From their closest relatives, it can be inferred that the males, using a modified tentacle, deposited sperm into a small groove on the female’s underside, where it could be absorbed and used to fertilize the eggs. Their clutch size is believed to have been anomalously small compared to other species in their clade, possibly no more than 10 eggs at a time. The young appear to have matured at a similar rate to human young, if not slightly faster. Sexual dimorphism does not appear to be a prominent trait within their species.
Not much can be inferred about the behavior of this species from what remnants have been found, though it can be inferred that they were likely highly social creatures with complex social structures. They appear to have engaged in agrarianism and the farming of other animals in their later stages of societal development, as evidenced by a high correlation in dump beak remains found near dump sites for animal bones and shell, and even built cities. Murals would seem to suggest Totlohô society was ruled by a class of elders, the oldest respective members of their society, while the youngest members formed the work force. Song and dance appear to have been ways to bond with one another, and spirituality played a large part in their society’s function. Warfare appears to have been an isolated phenomenon in their society and frequently on a much smaller scale than as seen in humanity, though there exists some evidence of widespread warfare in the later years of existence. Even in their later stages, when they evidently had significantly advanced technology (or, as the more conspiracy-minded would suggest, magic of some kind), the Totlohô still preferred to build their homes out of stone.
During the later stages of their existence, the Totlohô appear to have dabbled in what appears to be highly-advanced technology or potentially even magic of some kind, as evidenced by massive, seemingly Totlhômade, carved, levitating stones covered in glyphs. In a place known as the Square Chasm (picture below, artwork by Dipfruit), a reportedly supernatural space some weary jungle travelers have stumbled upon near a triple-forked river, one of these stones appears to have formed a perfectly square-shaped pocket dimension around itself, where gravity itself appears to bend to the stone’s whim.

Fossilized beaks and hard shells are really the only physical parts of these creatures to have been preserved, and they are the only indication of their existence outside of aforementioned ruins and murals. Their written languages have yet to be decoded, and there are believed to have been several thousand at a given time. What exactly led to their extinction has yet to be conclusively revealed, though murals seem to suggest that, from their perspective, supernatural forces may have been at play, with recurrent imagery of what appears to be demonic figures showing up across several murals. Another recurrent image in these murals is a white bird-like creature with horns, which some have suggested may be related to the mythical white bird seen in Xenogaean mythology, which was said to herald the apocalypse. While some have suggested that these murals may have been painted by one of the last Totlohô, who had simply gone insane from isolation and began painting their hallucinations, others suggest that there might be a grain of truth in these murals, perhaps a war of apocalyptic scale which engulfed the entire species, the demagogues fueling it being portrayed as demonic figures. What this doesn’t explain, however, are the high number of artifacts which appear to be made from an unknown metallic substance, one which is highly durable and in near-pristine condition hundreds of millions of years later. This substance, referred to colloquially as “anomalous tungsten”, is paradoxically lightweight yet durable with a high melting point, seemingly higher than almost any other known metal or metalloid. As this metal has not been found anywhere on Earth or even in any known compounds on Earth or another planet, this begs the question of how and where the Totlohô obtained this substance, leading to a wide menagerie of conspiracy theories, with everything from extraterrestrials to divine beings being suggested as the source from which they obtained this material. Whatever the case, those who have studied the artifacts have claimed to have had vivid dreams where they spoke to the Totlohô shortly after contact. Perhaps this is just a form of confabulation or merely even group hysteria, but nonetheless, it would appear that even long after the Totlohô have left this world, their legacy still manages to touch the human spirit. Finally, they appear to have domesticated a species of coelospondyl, Platycephale aridus, the so-called “flat-faced coelospondyl” (1st picture below, artwork by me), and another species of shrikehound, which is currently unnamed (2nd picture below, artwork by me). These appear to have been utilized as livestock animals.
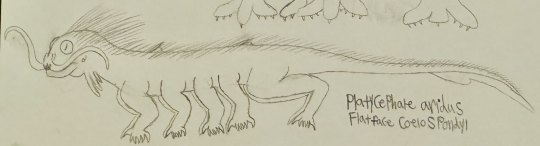

#novella#speculative evolution#fantasy#scifi#scififantasy#speculative biology#speculative fiction#speculative zoology#worldbuilding#creature art#sophont#sci fi creature#creature design#fantasy creature#creative writing#creature#scifi worldbuilding#fantasy worldbuilding#nautiloid#nautilus#cephalopod#mollusk#cephalopods
18 notes
·
View notes
Text
Throwback Thursday: Agnathans
Agnatha, meaning "without jaws", is a paraphyletic (descended from a common evolutionary ancestor but does not include all descendant groups) group consisting of jawless fishes. There are 9 clades within the group. The earliest and most basal fishes is the family Myllokunmingiidae. Currently, there are only 3 known genera and they all come from the Maotianshan Shale.

Anaspids were a group alive from the Early Silurian to the Late Devonian. They were small and lacked the armor of the other fishes of the time.

Conodonts are a re group that weren't recognized as fish for a very long time because all that was found were mineralized tooth-structures that had been in their mouths. They lived from the Cambrian until the Jurassic Period and are so common that tey are used as index fossils.

What few soft tissues we have preserved show is had a long, eel-like body.

The sister group to conodonta is Cyclostomi. These are the only living jawless fishes: lampreys and hagfishes.


Pteraspidomorphi is a clade that includes Astraspida and Arandaspida, small fishes with a mobile tail covered in protruding pointed plates and a massive bony head shield. They also possess the lateral line system present in all modern fish (minus hagfish).

Heterostracans are cousins of these two clades but they have only a single exhalent opening on each side into which the gills open.
All three groups share the synapomorphy of aspidin on their dermal armor plates.
Thelodonts (meaning "nipple tooth") are a group primarily known from scales and therefore difficult to place.

Osteostraci (meaning "bony shells") were the first vertebrates with paired fins.
They are the sister group to gnathostomes or jawed fishes.

Several synapomorphies support this including sclerotic ossicles

paired pectoral fins

a dermal skeleton with three layers,

and perichondral bone (dense layer of connective tissue that covers cartilage in developing bones).
Fossilize you later!

20 notes
·
View notes
Note
alright, connecting ronald reagan, bottled water and lilies to snailshell!!
1. ronald reagan is mentioned in the musical falsettos, a very popular musical ("half my patients: yucky pagans/modelled on the ronald reagans" - a day in falsettoland). another popular musical is ride the cyclone, which is one of the inspirations for hypothetical object show. whos in hypothetical object show? snailshell.
2. bottled water is encased in plastic, plastic is made of petroleum, which comes from fossiles. a specific type of fossils is ammonite shells from the jurassic period, these shells were from an extinct group of cephalopods molluscs who lived under the sea. what other creatures live under the sea? cone snails (conus marmoreus), which is the species of snail that inspired snailshell.
3. the lily flowers inspired the creation of white lily cookie from the game cookie run kingdom. white lily cookie was a scholar in the past, she studied alot to know the truth about cookies, but that truth corrupted her into dark enchantress cookie, who then formed the cookies of darkness. one of the members of that group is butter roll cookie, who studies and practices the creation of cookies. the practice of studying living creatures is called biology, which is one of many fields in science. who likes science? snailshell.
i overcomplicated this for myself btw
this is so funny good job
2 notes
·
View notes