#Extinct
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Deinosuchus: Giant Alligator or something older?
I know the title sucks, I couldn't think of anything poetic or clever ok? Anyways, still catching up on croc papers to summarize and this one did make a few waves when it was published about a week ago.
"Expanded phylogeny elucidates Deinosuchus relationships, crocodylian osmoregulation and body-size evolution" is a new paper by Walter, Massonne, Paiva, Martin, Delfino and Rabi, with quite a few of these authors having considerable experience with crocodile research. The thesis of the study is both simple and unusual. They suggest that several crocodilians traditionally held as stem-alligators, namely Deinosuchus, Leidyosuchus and Diplocynodon, weren't alligatoroids at all. In fact, if the study holds up they might not have been true crocodilians.
Ok, lets take a step back and briefly look at our main three subjects. Deinosuchus of course needs no introduction, a titan of the Cretaceous also known as the terror crocodile in some more casual sources, its easily one of the most iconic fossil crocodiles. It lived on either side of the Western Interior Seaway during the Campanian, fed on giant turtles and dinosaurs and with size estimates of up to 12 meters its easily among the largest crocodylomorphs who have ever lived.
Artwork by Brian Engh

Leidyosuchus also lived during the Campanian in North America and I would argue is iconic in its own right, albeit in a different way. It's historic to say the least and once housed a whole plethora of species, but has recently fallen on hard times in the sense that most of said species have since then been transferred to the genus Borealosuchus.
Artwork by Joschua Knüppe

Finally there's Diplocynodon, the quintessential croc of Cenozoic Europe. With around a dozen species found from the Paleocene to the Miocene all across Europe, it might be one of the most well studied fossil crocs there is, even if its less well known by the public due to its relatively unimpressive size range.
Artwork by Paleocreations

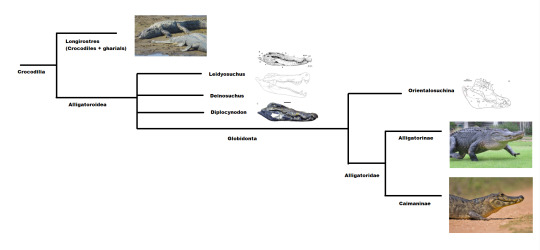
All three of these have traditionally been regarded as early members of the Alligatoroidea, one of the three main branches that form Crocodilia. In these older studies, Alligatoroidea can be broken up into three groups nested within one another. Obviously the crown is formed by the two living subfamilies, Alligatorinae and Caimaninae, both of which fall into the family Alligatoridae. If you take a step further out you get to the clade Globidonta, which in addition to proper Alligatorids also includes some basal forms with blunt cheek teeth as well as Orientalosuchina, tho jury's still out on whether or not they are truly alligator-relatives. And if you take a final step back and view Alligatoroidea as a whole, then you got our three main subjects neatly lined up outside of Globidonta in varying positions.
Below a highly simplified depiction of previous phylogenies. Deinosuchus, Leidyosuchus and Diplocynodon are often regarded as non-globidontan alligatoroids.
This new study however changes that long standing concensus. The team argues that several features we once thought defined alligatoroids are actually way more common across Crocodilia and even outside of it while also leverging some of the features of Deinosuchus and co. that have always been out of the ordinary. For instance, early alligatoroids are generally characterized as being comparably small, having had short, rounded heads, the afforementioned globular cheek teeth and of course the feature that still allows us to differentiate them from true crocodiles, the fact that they have a clear overbite. Now Leidyosuchus, Deinosuchus and Diplocynodon all have proportionally longer snouts than alligatoroids, their teeth interfinger like in crocodiles and most prominently (and namegiving for Diplocynodon) there is a large notch behind the snout tip that serves to receive two enlarged teeth of the lower jaw. These are of course just superficial examples, but if you wanna get into the nitty gritty check out the paper.
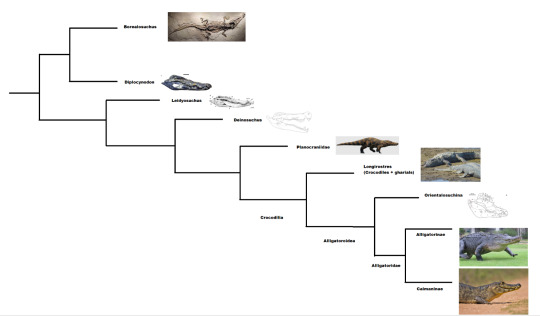
Below a simplified version of the papers phylogeny. Borealosuchus clades with Diplocynodon and Leidyosuchus and Deinosuchus are successive taxa. Planocraniidae are the sister to Crocodilia, which consists of Crocodyloids, Gavialoids (together Longirostres) and Alligatoroids.
Something also worth addressing in light of these results is salt tolerance in crocodilians and paleogeography. Basically, if you ignore Deinosuchus and co. (or well, just follow this new paper), then it is most likely that alligatoroids originated on the continent of Laramidia, i.e. the western half of America back when it was bisected by an enormous inland sea. Today, alligatoroids are famously intolerant of saltwater, yes, there are instances where alligators have been known to enter coastal waters, but its a far cry from what true crocodiles can achieve (just an example here's my recent post on Caribbean crocodiles). Given that alligatoroids don't appear on Appalachia, the other half of North America, until after the inland sea closes, this very much suggest that this intolerance goes way back. This has however always been at odds with Deinosuchus, which famously showed up along both the eastern and the western coast of the inland sea and at least lived close enough to the coast to leave its mark on the shells of sea turtles. We know it inhabited various near-shore environments and even stable isotope analysis of its teeth points towards it consuming either saltwater or prey that lives in the ocean. To a lesser degree its worth mentioning Diplocynodon, which though usually a freshwater animal has at least one species from coastal deposits. Now I do think its worth highlighting that just being salt tolerant doesn't necessarily mean they can't have been alligatoroids, given that salt glands could have easily been lost after Deinosuchus split off from other alligatoroids. Nevertheless, a position as a stem-crocodilian does add up with it being salt tolerant, with the assumption being that being tolerant to saltwater is basal to crocodilians as a whole and was simply lost in a select few lineages such as alligatoroids.
Given that its range spanned both coastlines of the Western Interior Seaway as well as direct evidence for interactions with marine life, Deinosuchus likely ventured out into the sea from time to time like some modern crocodiles.


There's also the matter of timing. When alligatoroids first appeared 82 million years ago, we already see the classic blunt-snouted morphotype with Brachychampsa and our dear giant Deinosuchus. Now if both were alligatoroids, this would suggest that they've been separate quite some time before that to bring forth these drastically different forms, yet attempts to estimate the divergence date suggest that they split no earlier than 90 million years ago. So if Deinosuchus is not an alligatoroid, then the timeline adds up a bit better. However I think the best example of this new topology really explaining an evolutionary mystery doesn't come from Deinosuchus, but from Diplocynodon. Those that know me might remember that I started working on researching Diplocynodon for Wikipedia, a process that's been slow and painfull both due to the 200 years of research history and the good dozen or so species placed in this genus. Tangent aside, one big mystery around Diplocynodon is its origin. They first appear in the Paleocene and survive till the Miocene, tend to stick to freshwater and oh yeah, species of this genus are endemic to Europe. Given that previous studies recovered them as alligatoroids, nobody was quite sure where Diplocynodon came from. Did they originate in North America and cross the Atlantic? Where they salt tolerant before and simply stuck to freshwater once in Europe? Or are they a much older alligatoroid lineage that entered Europe via Asia after having crossed Beringia. You know, the kind of headbreaking stuff we get when the fossil record is incomplete. But this new study recovers Diplocynodon as being closely related to the non-crocodilian Borealosuchus from the Cretaceous to Paleogene of North America. And that makes some sense, historically the two have been noted to be similar, hell there were even cases when Borealosuchus remains were thought to be North American examples of Diplocynodon. And Borealosuchus has the same double caniniforms as the other crocs we discussed so far. So when our three former alligatoroids got pushed outside of Crocodilia, Diplocynodon ended up forming a clade with Borealosuchus. And since Borealosuchus was wide spread in America by the late Cretaceous, and possibly salt tolerant, then it could have easily spread across Greenland and Scandinavia after the impact, giving rise to Diplocynodon.
The results of this study seem to suggest that Borealosuchus and Diplocynodon are more closely related that previously thought.


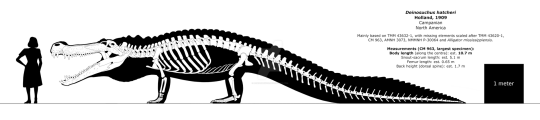
And since this is a Deinosuchus paper...of course theres discussion about its size. A point raised by the authors is that previous estimates typically employ the length of the skull or lower jaw to estimate body length, which might not be ideal and is something I definitely agree with. The problem is that skull length can vary DRASTICALLY. Some animals like early alligatoroids have very short skulls, but then you have animals in gharials in which the snout is highly elongated in connection to their ecology. Given that Deinosuchus has a relatively long snout compared to early alligatoroids, size estimates based on this might very well overestimate its length, while the team argues that head width would yield a more reasonable results. Previous size estimates have ranged from as low as 8 meters to as large as 12, which generally made it the largest croc to have ever existed. Now in addition to using head width, the team furthermote made use of whats known as the phylgenetic approach, which essentially bypasses the problem of a single modern analogue with peculariar proportions influencing the result. Now there is a bunch more that went into the conclusion, but ultimately the authors conclude that in their opinion, the most likely length for the studied Deinosuchus riograndensis specimen was a mere 7.66 meters in total length. And before you jump to any conclusions, DEINOSUCHUS WOULD HAVE GOTTEN BIGGER TRUST ME. I know having read "12 meter upper estimate" earlier is quite a contrast with the resulting 7.66 meters, but keep in mind this latter estimate is just one specimen. A specimen that in previous studies was estimated to have grown to a length of somewhere between 8.4 - 9.8 meters. Now yes, this is still a downsize overall, but also given that this specimen is far from the largest Deinosuchus we have, this means that other individuals would have certainly grown larger. Maybe not those mythical 12 meters, but still very large. So please keep that in mind.
Two different interpretations of the same specimen of Deinosuchus. Top a proportionally larger-headed reconstruction by randomdinos, bottom a smaller-headed reconstruction by Fadeno. I do not care to weigh in on the debate other than to say that size tends to fluctuate a lot between studies and that I'm sure this won't be the last up or downsize we see.

Regardless of the details, this would put Deinosuchus in the "giant" size category of 7+ meters, while early alligatoroids generally fall into the small (<1.5 meters) or medium (1.5-4 meters) size categories. The authors make an interesting observation relating to gigantism in crocs at this point in the paper. Prevously, temperature and lifestyle were considered important factors in crocs obtaining such large sizes, but the team adds to that the overall nature of the available ecosystem. In the case of Deinosuchus, it inhabited enormous coastal wetlands under favorable temperature conditions and with abundant large sized prey, a perfect combination for an animal to grow to an enormous size. And this appears to be a repeated pattern that is so common its pretty much regarded as a constant. To quote the authors, "a world with enormous crocodyliforms may have been rather the norm than the exception in the last ~ 130 million years." For other examples look no further than the Miocene of South America, the extensive wetlands of Cretaceous North Africa or even Pleistocene Kenya.
One striking example for repeated gigantism in crocodilians can be found in Miocene South America, when the caimans Purussaurus and Mourasuchus both independently reached large sizes alongside the gharial Gryposcuhus. The illustration below by Joschua Knüppe features some of the smaller earlier members of these species in the Pebas Megawetlands.

So that's it then, case closed. Deinosuchus and co aren't salt-tolerant alligators, they are stem-crocodilians. Deinosuchus was smaller than previously thought and Diplocynodon diverged from Borealosuchus. Leidyosuchus is also there. It all adds up, right? Well not quite. This all is a massive upheaval from what has previously been accepted and while there were outliers before, the alligatoroid affinities of these animals were the concensus for a long time. Future studies will need to repeat the process, analyse the data and the anatomical features and replicate the results before we can be sure that this isn't just a surprisingly logical outlier. Already I heard some doubts from croc researchers, so time will tell if Deinosuchus truly was some ancient crocodilian-cousin or if previous researchers were correct in considering it a stem-alligator. I for one will keep my eyes peeled.
#pseudosuchia#crocodylomorph#eusuchia#crocodilia#crocodile#alligator#deinosuchus#leidyosuchus#diplocynodon#palaeoblr#cretaceous#fossils#prehistory#extinct#long post#science news#croc#gator#borealosuchus#evolution
125 notes
·
View notes
Text
In a monumental discovery for paleontology and the first of its kind "Mummy of a juvenile sabre-toothed cat Homotherium latidens from the Upper Pleistocene of Siberia"

Abstract The frozen mummy of the large felid cub was found in the Upper Pleistocene permafrost on the Badyarikha River (Indigirka River basin) in the northeast of Yakutia, Russia. The study of the specimen appearance showed its significant differences from a modern lion cub of similar age (three weeks) in the unusual shape of the muzzle with a large mouth opening and small ears, the very massive neck region, the elongated forelimbs, and the dark coat color. Tomographic analysis of the mummy skull revealed the features characteristic of Machairodontinae and of the genus Homotherium. For the first time in the history of paleontology, the appearance of an extinct mammal that has no analogues in the modern fauna has been studied. For more read here: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-024-79546-1
#sabertooth#homotherium#homotheriummummy#mummy#fossilmummy#extinct#paleontology#iceage#pleistocene#syberia#kitten#oneofakind
26K notes
·
View notes
Text

My old piece with quaggas.
watercolour on wallpaper back
5K notes
·
View notes
Text

#environment#animals#snakes#frogs#newts#amphibians#endangered#love#extinct#conservation#nature#stolen#true#reptiles#spiders#arachnids
33K notes
·
View notes
Note
If you're willing to share, what are your thoughts and opinions on the whole "dire wolf" situation?

They are not "Dire Wolves"
You can't do some gene editing to a gray wolf, and call it a dire wolf.
My feelings are summed up well in this article:
Scientists: No, those are definitely not 'resurrected' dire wolves
Scientists: No, those are definitely not "resurrected" dire wolves - Earth.com
661 notes
·
View notes
Text

Great Auk for a $15 Ko-fi supporter
The Great Auk (Pinguinus impennis) is also known as the Penguin. Though the name is contemporarily associated with an unrelated group of flightless birds from the southern hermisphere, these were named penguins by european explorers due to their superficial similarity to the Great Auks they were already familiar with. The Great Auk became extinct in the mid 19th century, and its extinction is believed to have been primarily caused by human exploitation. (x, x, x)
#i honestly could write a lot more for this species when it comes to facts but i dont want to overdo it#i do suggest reading about them though#art#my art#digital#digital art#clip studio#clip studio paint#csp#kofi#ko-fi#kofi doodle#kofi doodles#kofi request#doodle#request#illustration#stylized#linear#geometric#auk#great auk#Pinguinus impennis#garefowl#bird#birdblr#extinct#extinct animals#lazert#lazer-t
570 notes
·
View notes
Text
"Despite being arguably the most famous island chain in the world in terms of biodiversity, the Galápagos Islands are still surprising scientists today.
A bird seen and recorded by Charles Darwin on his visit to Floreana island in 1835 has been observed in the wild there for the first time in 190 years.
Darwin’s observations from the small, south-central island in the volcanic chain included the presence of a small, secretive bird called the Galápagos rail (Laterallus spilonota).
Just two years ago, several organizations began work on the large-scale Floreana Island Restoration Project. By removing invasive species that devastated native wildlife for generations, the local environment once again became a haven for species to recover and thrive.
The Galápagos rail, a land-bird endemic to the archipelago, has been severely impacted by these invasive species. It dwells on the ground, is extremely vulnerable to predators, and relies on dense, lush vegetation to hide in. But despite these dangers, the rail has proved to be a resilient and resourceful little bird.
The rails, locally known as Pachays, have been quick to return to restored islands. In 2018, six years after the conservation nonprofit Island Conservation successfully removed invasive species from nearby Pinzón Island, the Rails were among the first locally-extinct animals to reappear—along with other species such as the cactus finch.
It hasn’t been long since the Floreana Island Restoration Project began, but the rails have already repopulated it.
During their most recent annual landbird monitoring expedition on the island, teams from the Charles Darwin Foundation and Ecuador’s state agency for managing the archipelago recorded the bird’s presence at three distinct sites.
The birds were present and away from human habitation and agriculture, in a grassland shaded by guava trees. Confirmed findings include six acoustic records, two visual sightings, and one photograph. And it isn’t a coincidence that they’re back now—the site has been monitored for the Galápagos rail consistently since 2015, and this is the first year they’re back.
“The rediscovery of the Galápagos rail confirms what we’ve seen on islands worldwide—remove the invasive threats, and native species can recover in remarkable ways,” said Island Conservation’s Conservation Impact Program Manager Paula Castaño in a statement.
“This is an incredible win for Floreana, and fuels our excitement about what other native species might resurface as the island continues its journey toward ecological recovery.”
Next, scientists must use genetic sampling to determine whether these newly recorded birds are from a self-reintroduced lineage or whether there was a tiny population of rails that survived, undetected, for 190 years.
Island Conservation details how that’s not unheard of: on nearby Rábida, the organization’s restoration efforts led to the rediscovery of a species of gecko that was only known to science through subfossil records dated more than 5000 years old. They’d been living on the island in very low numbers for hundreds of years, but it was only once holistic restoration had taken place that they were able to increase their numbers to detectable levels.
MORE NEWS FROM THIS FAMOUS PLACE: 500 Giant Tortoises Reintroduced to Four Galapagos Islands in 2023
With a local population already establishing itself, chances are good for a successful reintroduction. Soon, it’s hoped, Floreana’s grasslands will be home to a large, thriving colony of rails.
“It gives us hope that there might be even more ‘extinct’ Galápagos species to find,” the statement read.""
-via Good News Network, March 3, 2025
#galapagos#galapagos islands#birds#birdblr#endangered species#extinction#conservation#extinct#ecosystem#wildlife conservation#good news#hope
702 notes
·
View notes
Text
I’d like to remind everyone that a photo of a nestling Kaua’i ō’ō exist and should give a BIG thank you to John Sincock who also has an unpublished paper about the ō’ō and his trips to Alaka’i swamp. This is the only known photograph of a nestling ō’ō. You can find this photo on the birds of the world website (linked in citation)

Sykes Jr., P. W., A. K. Kepler, C. B. Kepler, and J. M. Scott (2020). Kauai Oo (Moho braccatus), version 1.0. In Birds of the World (A. F. Poole, Editor). Cornell Lab of Ornithology, Ithaca, NY, USA. https://doi.org/10.2173/bow.kauoo.01
I hope the rest of his photos are out there somewhere. I was super lucky to be able to find his unpublished paper as well as some memos (shout out to Daniel Lewis who was able to send me the memos AND wrote about sincock and the ō’ō in his book Belonging on an Island : Birds, Extinction and Evolution in Hawai’i)
#kaua’i ‘o’o#kauai o'o#extinct birds#extinct#birds#Hawaiian honeyeater#recently extinct#moho#mohoidae
814 notes
·
View notes
Text

Fly in amber By: F. M. Carpenter From: Life Nature Library: The Earth 1962
278 notes
·
View notes
Text

The Mists of Lourinhã Eousdryosaurus encounters Lusotitan.
#my art#paleoart#sciart#dinosaur#lusotitan#eousdryosaurus#sauropod#ornithopod#herbivore#lourinha formation#portugal#jurassic#mesozoic#extinct#animal#nature#prehistoric
387 notes
·
View notes
Text

Redwillow! First listed in the eclipse allegiances with Whitewater as his mentor. He has some appearances in the first few omen of the stars books, but mostly is a generic background character. By Night Whispers however he is in my opinion characterized as a seasoned warrior, even though he is very new to the books. He is put in charge of leading a boarder patrol, and is seen after the battle of the border covered in wounds. Later in the book however he is part of the group that plays on the frozen lake, skidding across the surface on his belly. I love this segment because he is mentioned alongside senior warriors Crowfrost and Ratscar who yowl in amusement at his antics.
There is some of what I'm going to call fan interpretation of Redwillow that he is a loner in Shadowclan, but in the books his moderate regard by his own leader and senior warriors suggests to me instead that he was well liked, and integrated into the clan, even though it's never established who his kin is. That's why to me he becomes an example later on of a cat who's ambition is used to radicalize him to the Dark Forest. He doesn't start out a traitor to Shadowclan, on the contrary Redwillow spends his time in the dark forest close to his living clanmates. It isn't until the Forgotten Warrior that Ivypool points out Redwillow specifically multiple times when she's looking for cats that may have loyalties outside their clans. He never says anything to that point, rather his body language and exchanged glances are what makes her think so. Within the Last hope he makes several remarks in the Dark Forest about becoming the best warrior he can be, and that training in the Dark Forest makes training with Shadowclan feel like working with kittypets. Ivypool confronts him in a conversation with Hollowflight asking if he would let his weaker Clanmates die and he says "O-of course not" just that they had a lot to learn from the Dark Forest Warriors. Even with that I remember finding his final moments in the Last Hope a departure from his character, where he declares the Dark Forest his new clan, and that Blackstar's time is over.
Idk I just wanted more out of the radicalization of the clan cats while it was happening. I guess as someone who grew up with the internet I'm not a stranger to what anarchy and rebellion look like behind closed doors and personally felt that the concept of being isolated in a toxic in group extremely interesting, I found the the non-committal conversations of the dark forest trainees to be much more innocent than the showy posturing of competitive vitriol I've known such spaces to inspire. The fact that Redwillow and Breezepelt at the end of the battle were the only two warriors we know by name that sided with the Dark Forest to the end seems like such an underestimate to me. All I'm saying is that while I do love Redwillow for being an example of this, Clan cat rebellion to the Dark Forest could have been much more catastrophic than it was, and especially for the amount of plot and hype that it was given in universe. Add to all that the possible reading of Redwillow as a transmasc character that is radicalized into toxic masculinity and I want it to be known that i do love this character, but that most of that love comes from meta analysis and not from the text itself. He shouldn't have died twice in the Broken Code because truthfully he just didn't deserve it.
#Redwillow#shadowclan#Dark forest#warriors#warriors designs#warriorcats#warrior cats#warrior#Extinct
207 notes
·
View notes
Text

HYAENODONS
Adopt a puppy here www.palaeoplushies.com
153 notes
·
View notes
Text

Greater Jaws
(All assets are done in Blender & made by me.)
#prehistoric#extinct#3dart#blender#paleontology#palaeontology#palaeoart#paleoart#mosasaurus#mosasaur#ocean#fish
442 notes
·
View notes
Text

Anomalocaris plushie 🦐
#request#anomalocaris#anomalocaris plush#plush#sorry i love the shrimp emoji any excuse to use it#it is sold under many sellers#like gage beasley and various amazon sellers but there is no outright brand#mystery anomalocaris plush…#prehistoric#extinct#shrimp#cambrian plush#cambrian#plushie#plushies#plushblr#bugs#<-for CW purposes#transparent
3K notes
·
View notes
Text

Lost Americans wheel. Watercolor and ink.
#extinct#extinct bird#great auk#carolina parakeet#passenger pigeon#eskimo curlew#labrador duck#ivory billed woodpecker#bachman's warbler#heath hen#dusky seaside sparrow#spectacled cormorant
950 notes
·
View notes