#National Electrical Manufacturers Association
Text
Seven major US labor unions representing about 6 million workers sent a letter to Joe Biden on Tuesday calling on his administration to "immediately halt all military aid to Israel" ahead of a visit to the US from Benjamin Netanyahu, Israel's prime minister, this week.
The unions that signed on to the letter include the Association of Flight Attendants (AFA), American Postal Workers Union (APWU), International Union of Painters (IUPAT), National Education Association (NEA), Service Employees International Union (SEIU), United Auto Workers (UAW) and United Electrical Workers (UE).
"Our unions are hearing the cries of humanity as this vicious war continues," said Mark Dimondstein, the APWU president, in a press release. "Working people and our unions are horrified that our tax dollars are financing this ongoing tragedy. We need a ceasefire now, and the best way to secure that is to shut off US military aid to Israel."
In the letter, the unions expressed concerns that the US president's three-part ceasefire plan announced in May 2024 has not been fully accepted as violence in Gaza has persisted.
"Large numbers of Palestinian civilians, many of them children, continue to be killed, reportedly often with US-manufactured bombs. Rising tensions in the region threaten to ensnare even more innocent civilians in a wider war. And the humanitarian crisis deepens by the day, with famine, mass displacement, and destruction of basic infrastructure including schools and hospitals. We have spoken directly to leaders of Palestinian trade unions who told us heart-wrenching stories of the conditions faced by working people in Gaza," wrote the unions in the letter.
"The time to act decisively to end this war is now. Stopping US military aid to Israel is the quickest and most sure way to do so, it is what US law demands, and it will show your commitment to securing a lasting peace in the region."
Earlier this year, US labor unions launched the National Labor Network for Ceasefire, which has been signed by dozens of local unions around the US, including the letter signatories and National Nurses United.
The letter comes as activists are planning protest demonstrations in Washington DC this week over Netanyahu's visit, his first to the US since 7 October. Thousands of protesters are expected to descend on Washington DC to call for an end to the US aid to Israel that has been fueling the war in Gaza.
120 notes
·
View notes
Text
"In cities across the country, people of color, many of them low income, live in neighborhoods criss-crossed by major thoroughfares and highways.
The housing there is often cheaper — it’s not considered particularly desirable to wake up amid traffic fumes and fall asleep to the rumble of vehicles over asphalt.
But the price of living there is steep: Exhaust from all those cars and trucks leads to higher rates of childhood asthma, cancer, cardiovascular disease, and pulmonary ailments. Many people die younger than they otherwise would have, and the medical costs and time lost to illness contributes to their poverty.
Imagine if none of those cars and trucks emitted any fumes at all, running instead on an electric charge. That would make a staggering difference in the trajectory, quality, and length of millions of lives, particularly those of young people growing up near freeways and other sources of air pollution, according to a study from the American Lung Association.
The study, released [February 28, 2024], found that a widespread transition to EVs could avoid nearly 3 million asthma attacks and hundreds of infant deaths, in addition to millions of lower and upper respiratory ailments...
Prior research by the American Lung Association found that 120 million people in the U.S. breathe unhealthy air daily, and 72 million live near a major trucking route — though, Barret added, there’s no safe threshold for air pollution. It affects everyone.
Bipartisan efforts to strengthen clean air standards have already made a difference across the country. In California, which, under the Clean Air Act, can set state rules stronger than national standards, 100 percent of new cars sold there must be zero emission by 2035.
[Note: The article doesn't explain this, but that is actually a much bigger deal than just California. Basically, due to historically extra terrible pollution, California is the only state that's allowed to allowed to set stronger emissions rules than the US government sets. However, one of the rules in the Clean Air Act is that any other state can choose to follow California's standards instead of the US government's. And California by itself is the world's fifth largest economy - ahead of all but four countries. California has a lot of buying power. So, between those two things, when California sets stricter standards for cars, the effects ripple outward massively, far beyond the state's borders.]
Truck manufacturers are, according to the state’s Air Resources Board, already exceeding anticipated zero-emissions truck sales, putting them two years ahead of schedule...
Other states have begun to take action, too, often reaching across partisan lines to do so. Maryland, Colorado, New Mexico, and Rhode Island adopted zero-emissions standards as of the end of 2023.
The Biden administration is taking similar steps, though it has slowed its progress after automakers and United Auto Workers pressured the administration to relax some of its more stringent EV transition requirements.
While Barret finds efforts to support the electrification of passenger vehicles exciting, he said the greatest culprits are diesel trucks. “These are 5 to 10 percent of the vehicles on the road, but they’re generating the majority of smog-forming emissions of ozone and nitrogen,” Barret said...
Lately, there’s been significant progress on truck decarbonization. The Biden administration has made promises to ensure that 30 percent of all big rigs sold are electric by 2030...
Such measures, combined with an increase in public EV charging stations, vehicle tax credits, and other incentives, could change American highways, not to mention health, for good."
-via GoodGoodGood, February 28, 2024
#asthma#asthma attack#medical news#pollution#air pollution#ev#evs#environmental racism#good news#hope#auto industry#auto news#public health#medicine
220 notes
·
View notes
Text
June 6, 2024.
Israel targetted and bombed a school in central Gaza with Palestinian refugees, with the excuse that "Hamas" must be at the school.
Quote: "Witnesses and hospital officials said the predawn strike hit the al-Sardi School, run by the United Nations agency for Palestinian refugees known by the acronym UNRWA. The school was filled with Palestinians who had fled Israeli operations and bombardment in northern Gaza, they said.
Ayman Rashed, a man displaced from Gaza City who was sheltering at the school, said the missiles hit classrooms on the second and third floor where families were sheltering. He said he helped carry out five dead, including an old man and two children, one with his head shattered open. "It was dark, with no electricity, and we struggled to get out the victims," Rashed said." [...]
Hospital records and an Associated Press reporter at the hospital recorded at least 33 dead from the strike, including 14 children and nine women. Another strike on a house overnight killed six people, according to the records. Both strikes occurred in Nuseirat, one of several built-up refugee camps in Gaza dating to the 1948 war surrounding Israel's creation, when hundreds of thousands of Palestinians fled or were driven from their homes in what became the new state.
Excuse with no evidence by Israeli Occupation Forces:
Rear Adm. Daniel Hagari, the spokesman for the Israeli military, said it carried out a "precise strike" based on concrete intelligence that militants were planning and conducting attacks from inside three classrooms. He said only those rooms were attacked.
"We conducted the strike once our intelligence and surveillance indicated that there were no women or children inside the Hamas compound, inside those classrooms," he said.
Hagari said there were around 30 suspected militants in the three rooms. He said the military had confirmed killing nine of them, and displayed a slide showing their names and photos. He provided no other evidence to substantiate the military's claims.
Note: Excusing slaughter of Palestinians by insisting they must be ""hamas"" is a form of propaganda to manufacture consent of mass death and genocide. To target schools and refugee camps.
57 notes
·
View notes
Text
In late May, 19 Republican attorneys general filed a complaint with the Supreme Court asking it to block climate change lawsuits seeking to recoup damages from fossil fuel companies.
All of the state attorneys general who participated in the legal action are members of the Republican Attorneys General Association (RAGA), which runs a cash-for-influence operation that coordinates the official actions of these GOP state AGs and sells its corporate funders access to them and their staff. The majority of all state attorneys general are listed as members of RAGA.
Where does RAGA get most of its funding? From the very same fossil fuel industry interests that its suit seeks to defend. In fact, the industry has pumped nearly $5.8 million into RAGA’s campaign coffers since Biden was elected in 2020.
The recent Supreme Court complaint has been deemed “highly unusual” by legal experts.
The attorneys general claim that Democratic states, which are bringing the climate-related suits at issue in state courts, are effectively trying to regulate interstate emissions or commerce, which are under the sole purview of the federal government. Fossil fuel companies have unsuccessfully made similar arguments in their own defense.
RAGA’s official actions — and those of its member attorneys general — closely align with the goals of its biggest donors.
The group, a registered political nonprofit that can raise unlimited amounts of cash from individuals and corporations, solicits annual membership fees from corporate donors in exchange for allowing those donors to shape legal policy via briefings and other interactions with member attorneys general.
A Center for Media and Democracy (CMD) analysis of IRS filings since November 24, 2020 shows that Koch Industries (which recently rebranded) leads as the largest fossil fuel industry donor to RAGA, having donated $1.3 million between 2021 and June 2024.
Other large donors include:
• American Petroleum Institute (API), the oil and gas industry’s largest trade association
• Southern Company Services, a gas and electric utility holding company
• Valero Services, a petroleum refiner
• NextEra Energy Resources, which runs both renewable and natural gas operations
• Anschutz Corporation, a Denver-based oil and gas company
• American Fuel & Petrochemical Manufacturers, a major trade organization
• Exxon Mobil, one of the largest fossil fuel multinationals in the world
• National Mining Association, the leading coal and mineral industry trade organization
• American Chemical Council, which represents major petrochemical producers and refiners
Many of these donors are being sued for deceiving the public about the role fossil fuels play in worsening climate change: many states — including California, Connecticut, Minnesota, New Jersey, and Rhode Island — as well as local governments — such as the city of Chicago and counties in Oregon and Pennsylvania — have all filed suits against a mix of fossil fuel companies and their industry groups. In the cases brought by New York and Massachusetts, ExxonMobil found support from Texas Attorney General Ken Paxton, who filed a friend-of-the-court brief in defense of the corporation.
Paxton has accepted $5.2 million in campaign contributions from the oil and gas industry over the past 10 years, according to data compiled by OpenSecrets and reviewed by CMD.
Fossil Fuel Contributions to the Republican Attorneys General Association
Includes aggregate contributions of $10K or more from the period November 2020 to March 2024.



Note: This funding compilation does not include law firms, front groups, or public relations outfits that work on behalf of fossil fuel clients, many of which use legal shells to shield themselves from outright scrutiny. For example, Koch Industries, through its astroturf operation Americans for Prosperity, has deployed a shell legal firm in a major Supreme Court case designed to dismantle the federal government’s regulatory authority.
CARRYING BIG OIL’S WATER
This is far from the first time RAGA members have banded together to try to defeat clean energy and environmental regulations. In 2014, the New York Times initially reported on how RAGA circulates fossil fuel industry propaganda opposing federal regulations.
The Times investigation revealed thousands of documents exposing how oil and gas companies cozied up to Republican attorneys general to push back against President Obama’s regulatory agenda. “Attorneys general in at least a dozen states are working with energy companies and other corporate interests, which in turn are providing them with record amounts of money for their political campaigns,” the investigation found. That effort, which RAGA dubbed the Rule of Law campaign, has since morphed into RAGA’s political action arm, the nonprofit Rule of Law Defense Fund (RLDF).
Since then, RAGA’s appetite to go to bat for the industry has only grown.
In 2015, less than two weeks after representatives from fossil fuel companies and related trade groups attended a RAGA conference, Republican AGs petitioned federal courts to block the Obama administration’s signature climate proposal, as CMD has previously reported. Additional reporting revealed collusion between Republican AGs and industry lobbyists to defend ExxonMobil and obstruct climate change legislation.
There was also the 2016 secret energy summit that RAGA held in West Virginia with industry leaders, along with private meetings with fossil fuel companies to coordinate how to shield ExxonMobil from legal scrutiny. Later that year, West Virginia Attorney General Patrick Morrisey — aided by 19 other Republican AGs — successfully brought a case before the court that hobbled Obama’s signature climate plan.
Morrisey is currently leading the Republican effort to take down an Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulation that targets coal-fired power plants.
Often, the attorneys general bringing these cases share many of the same donors who backed the confirmation of Republican-appointed Supreme Court justices, as pointed out by the New York Times.
And in 2021, Republican attorneys general from 19 states sent a letter to the U.S. Senate committees on Environment and Public Works and on Energy and Natural Resources hoping to persuade senators to vote against additional regulations on highly polluting methane emissions, a leading contributor to global warming.
Since 2022, RLDF’s “ESG Working Group” has been coordinating actions taken by Republican AGs against sustainable investing. Communications from that group obtained by CMD show that it was investigating Morningstar/Sustainalytics and the Net-Zero Banking Alliance. Republican AGs announced investigations into the six largest banks for information on their involvement in the Net-Zero Banking Alliance later that year.
LEGACY OF RIGHT-WING ACTIONS
It’s not only about fossil fuels. Attorneys general who are members of — and financially backed by — RAGA have a long track record of pursuing right-wing agendas. In Mississippi, Attorney General Lynn Fitch helped bring the legal case that ultimately overturned Roe v. Wade. In Texas, Paxton has attempted to overturn the Affordable Care Act and sued the federal government over Title IX civil rights protections, and safeguards for seasonal workers, among other policy irritants to the far Right. With support from fellow Republican AGs, he also led one of many efforts to overturn the results of the 2020 election.
In recent years, other pro-corporate major donors have included The Concord Fund, which is controlled by Trump’s “court whisperer” Leonard Leo, Big Tobacco, and the U.S. Chamber of Commerce’s Institute for Legal Reform.
#us politics#news#EXPOSEDbyCMD#truthout#2024#republicans#conservatives#attorneys general#us supreme court#climate change lawsuits#climate change#global warming#Republican Attorneys General Association#Center for Media and Democracy#Koch Industries#Americans for Prosperity#American Petroleum Institute#Southern Company Services#Valero Services#NextEra Energy Resources#Anschutz Corporation#American Fuel & Petrochemical Manufacturers#Exxon Mobil#National Mining Association#American Chemical Council#ken paxton#Rule of Law Defense Fund#Patrick Morrisey#environmental protection agency#Net-Zero Banking Alliance
21 notes
·
View notes
Text
August 06, 2024
Unless you’ve been living under a rock, you are probably aware of the massive push to transition to green energy. The goal is to have wind and solar replace coal and natural gas; the electric vehicle (EV) will supposedly replace internal combustion engines. Directives are coming from the highest office in the land; the current administration has made green energy a large part of its agenda.
We are being told that these technologies are clean and will save the planet from climate change. However, these alternative forms of energy being espoused are riddled with their own problems.
Hidden behind the solar panels, wind turbines, and EV batteries are some dirty secrets that get swept under the rug and ignored by climate enthusiasts. Fossil fuels are constantly put under a microscope and condemned as an evil destructive polluter; green energy is typically put on a pedestal. Green energy, however, is not as perfect and wonderful as we are made to believe. Yet, we are putting a lot of trust into these energy sources, without considering their ramifications.
The American Consumer Institute just released a report detailing many of the environmental impacts associated with the so-called green energy forms being heavily promoted. The life cycle of all three—the wind turbine, solar panel, and EV battery—involve significant environmental consequences that should not be overlooked and need to be part of the discussion when implementing energy policies.
One of the biggest issues involved with these forms is the extraction and manufacturing processes of various critical minerals that are required for wind turbines, solar panels, and EV batteries. Many underdeveloped nations, where there’s an abundance of minerals, are at risk. The operations and procedures not only overtake land but contaminate surrounding soil and water sources. In the worst cases, this work is accomplished through slave labor.
Various toxins and other greenhouse gases are released into the atmosphere, where workers and even nearby communities are potentially affected. Landscape is tarnished and various animal habitats are shrinking and/or experiencing stress. The massive amount of land occupied by both wind and solar may never be recoverable.
China dominates the green energy supply chains, but their environmental standards are subpar. CO2 emissions associated with refineries in China are 1.5 times greater than those in the EU or U.S.
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
Most batteries used in technology like smart watches and electric cars are made with lithium that travels across the world before even getting to manufacturers. But what if nearly half of the lithium used in the U.S. could come from Pennsylvania wastewater?
A new analysis using compliance data from the Pennsylvania Department of Environmental Protection suggests that if it could be extracted with complete efficiency, lithium from the wastewater of Marcellus shale gas wells could supply up to 40% of the country's demand.
Already, researchers in the lab can extract lithium from water with more than 90% efficiency according to Justin Mackey, a researcher at the National Energy Technology Laboratory and PhD student in the lab of Daniel Bain, associate professor of geology and environmental sciences in the Kenneth P. Dietrich School of Arts and Sciences.
Read more.
12 notes
·
View notes
Text




On August 21st 1754 William Murdock, the Scottish engineer, was born.
Murdock invented coal-gas lighting, the first new form of lighting in the Industrial Age, and which remained the principal form of illumination until Edison’s invention of electric lighting 100-years later.
He was a close friend and associate of James Watt, who he met when he moved south to join Boulton & Watt, a partnership that was selling James Watt ’s new steam engines. During the job interview, Matthew Boulton noticed that Murdock was nervously handling a fine piece of woodwork that he had brought with him. Boulton recognized Murdock’s talent and hired him on the spot.
Soon Murdock began the experiments in gas lighting for which he is famous today. Murdock was the first to realize that gas was a more convenient energy source than coal, primarily because it could be piped and controlled more easily. Despite ridicule from his peers and the danger of gas explosions, Murdock Installed gaslighting in his house, using gas made from coal in his backyard and piped in through a hole in a window frame. Murdock went on to develop methods for manufacturing, storing, and purifying coal-g
Murdock’s employers were unenthusiastic about this sideline until they heard that a similar gaslighting system, made by Philippe Lebon, was being used in France. Boulton and Watt then asked Murdock to install gaslighting at their main factory in Birmingham in 1802, as part of England’s celebration of a temporary peace treaty with France. Soon the firm received its first commercial order to install gaslights at a cotton spinning factory. By 1806, Murdock had improved the odour of the coal-gas.
Meanwhile, Murdock had continued to apply his ingenuity to steam engine improvements, many of which were patented in 1799. He invented a new machine for boring cylinders and a better method for casting jacketed cylinders. Today, he is still known for inventing the slide valve, which injects and removes steam alternately from each end of the cylinder. Murdock also built the first model of an oscillating engine and the first free-standing steam engine.
Although Murdock eventually became a limited partner in Boulton & Watt, he remained essentially a hired hand throughout his career, rather than an independent businessman. Nevertheless, he earned great respect from many rivals who were wealthier and better educated.
In September 1830, in declining health at age 76, Murdoch's partnership with Boulton & Watt which began in 1810 came to an end, at which point he was receiving £1,000 per year. The reasons for this appear to be both the increasing unprofitability of Boulton and Watt and Murdoch's increasing ill health. Murdoch died on November 15th 1839, aged 85.
Murdock might be a lesser well known name than his boss and contemporary James Watt, but he is just as important figure, and should be recognised as such . In 1892 he celebrated more, a bust was unveiled in The National Wallace Monument of the engineer, there is also a bust in at St. Mary's Church, Handsworth. The town of Redruth has an Annual Murdoch Day in June. The 2007 event included a parade of schoolchildren with banners on the theme "Earth, Wind, Fire and Water" and the first public journey of a full-size, working reproduction of Murdoch's Steam Carriage.
The house he lived at in Redruth has been restored and preserved and is a listed building, there is also a primary school in Birmingham named after him. In 2019, he was inducted into the Scottish Engineering Hall of Fame.
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
Excerpt from this story from the Associated Press (AP):
A tiny, low-priced electric car called the Seagull has American automakers and politicians trembling.
The car, launched last year by Chinese automaker BYD, sells for around $12,000 in China, but drives well and is put together with craftsmanship that rivals U.S.-made electric vehicles that cost three times as much. A shorter-range version costs under $10,000.
Tariffs on imported Chinese vehicles probably will keep the Seagull away from America’s shores for now, and it likely would sell for more than 12 grand if imported.
But the rapid emergence of low-priced EVs from China could shake up the global auto industry in ways not seen since Japanese makers exploded on the scene during the oil crises of the 1970s. BYD, which stands for “Build Your Dreams,” could be a nightmare for the U.S. auto industry.
“Any car company that’s not paying attention to them as a competitor is going to be lost when they hit their market,” said Sam Fiorani, a vice president at AutoForecast Solutions near Philadelphia. “BYD’s entry into the U.S. market isn’t an if. It’s a when.”
U.S. politicians and manufacturers already see Chinese EVs as a serious threat. The Biden administration on Tuesday is expected to announce 100% tariffs on electric vehicles imported from China, saying they pose a threat to U.S. jobs and national security.
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
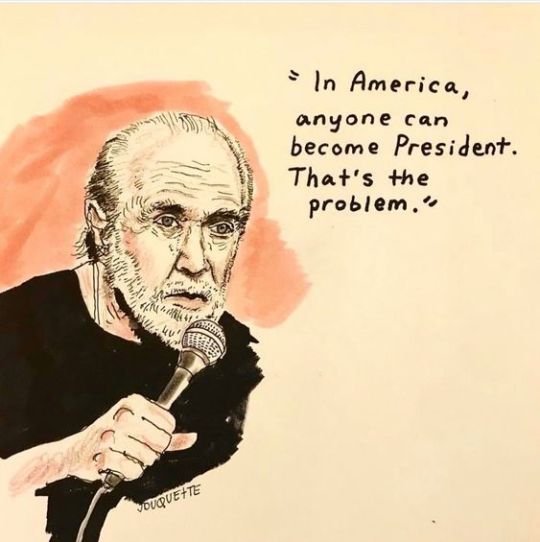
Jesse Duquette
* * * *
LETTERS FROM AN AMERICAN
May 13, 2024
HEATHER COX RICHARDSON
MAY 14, 2024
Today illustrated that the Democrats have become America’s cheerleaders, emphasizing how investment in the nation’s infrastructure has created jobs and rebuilt the country. This week, the Biden-Harris administration is touting its investments in rebuilding roads and bridges, making sure Americans have clean water, getting rid of pollution, expanding access to high-speed internet, and building a clean energy economy, contrasting that success with Trump’s eternal announcements of an “Infrastructure Week” that never came.
The White House today announced that it has awarded nearly $454 billion in funding from the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law, including more than 56,000 projects across more than 4,500 communities across the nation. Those include fixing more than 165,000 miles of roads and more than 9,400 bridges and improving more than 450 ports and 300 airport terminals. It has funded more than 1,400 drinking water and wastewater projects and projects to replace up to 1.7 million toxic lead pipes, as well as more than 8,000 low- and zero-emission buses. It has funded 95 previously unfunded Superfund projects to clean up contaminated sites. It has improved the electrical grid and funded 12,000 miles of high-speed internet infrastructure, and exposed internet junk fees.
The White House explained that this investment is making it cheaper to install clean energy technology and lowering families’ monthly energy bills, and highlighted today the available rebates to enable people to take advantage of the new technologies.
On Wednesday, May 8, a report from the Semiconductor Industry Association and the Boston Consulting Group explored the “breathtaking speed,” as the president of the semiconductor organization put it, at which the industry is growing. In the Financial Times on May 9, John Thornhill reported that the CHIPS and Science Act, which provided a $39 billion investment in the semiconductor industry, has “primed a torrent of private sector investment.” With the influx of both federal money and an additional $447 billion of private investment in 83 projects in 25 states, the report forecasts that the U.S. will increase its share of global manufacturing capacity for leading-edge chips from today’s rate of 0% to 28% by 2032. Thornhill compared this investment to that spurred by Russia’s 1957 launch of the Sputnik satellite.
The Economist yesterday announced that the U.S. “is in the midst of an extraordinary startup boom,” and explored “[h]ow the country revived its “go-getting spirit.”
In contrast to the Democrats’ confidence in America, the Republicans are all-in on the idea that the country is an apocalyptic wasteland. At a rally in New Jersey Saturday, Trump announced: “On day one we will throw out Bidenomics and reinstate MAGAnomics.” He promised to extend his 2017 tax cuts for the wealthy and corporations.
But the gist of his speech was an angry, vitriolic picture of a failing nation full of “enemies” that are “more dangerous” than China and Russia and who are “going to destroy our country.” In his telling, the criminal case against him in Manhattan is “bullsh*t,” and President Biden has done more damage than the “ten worst presidents in the history of our country” combined: “[h]e’s a fool; he’s not a smart man…[h]e’s a bad guy…the worst president ever, of any country. The whole world is laughing at him.”
Trump lied that other countries are “emptying out their mental institutions into the United States, our beautiful country. And now the prison populations all over the world are down. They don’t want to report that the mental-institution population is down because they’re taking people from insane asylums and from mental institutions.” Then he riffed into “the late great Hannibal Lecter,” the fictional murderer and cannibal in the film The Silence of the Lambs, apparently to suggest that similar individuals are migrating to the U.S.
House Republicans this week are working to pass a nonbinding resolution to condemn Biden’s immigration policies, although it was Republicans, under orders from Trump, who killed a strong bipartisan immigration bill earlier this year.
The only way to turn back this apocalypse, Trump and his supporters insist, is to put Trump and his team back into the White House. From there, Republicans will return those they consider “real” Americans to power.
The last few days have added new information about what that means. On Thursday, May 9, Senators Katie Britt (R-AL), Marco Rubio (R-FL), and Kevin Cramer (R-ND) introduced the More Opportunities for Moms to Succeed (MOMS) act. Britt—who is best known for her disastrous response to Biden’s State of the Union speech from her kitchen—said the measure would provide a federal database of resources for pregnant women and women parenting young children, but that information excludes anything that touches on abortion.
The measure is clear that it enlists the government in opposition to abortion, but more than that, it establishes that the government will create a database of the names and contact information of pregnant women, which the government can then use “to follow up with users on additional resources that would be helpful for the users to review.”
A government database of pregnant women would give the federal government unprecedented control over individuals, and it is especially chilling after the story Caroline Kitchener broke in the Washington Post on May 3, that a Texas man, Collin Davis, filed a petition to stop his ex-partner from traveling to Colorado, where abortion is legal, to obtain an abortion. Should she do so, his lawyer wrote, he would “pursue wrongful-death claims against anyone involved in the killing of his unborn child.” Now Davis wants to be able to depose his former partner along with others he says are “complicit” in the abortion.
Antiabortion activists are also seeking to make mifepristone and misoprostol, drugs used in many abortions, hard to obtain. In Louisiana, state lawmakers are considering classifying the drugs as “controlled dangerous substances,” which would make possessing them carry penalties of up to ten years in prison and fines of up to $75,000.
More than 240 Louisiana doctors wrote to lawmakers saying that the drugs have none of the addictive characteristics associated with dangerous controlled substances and warning that the drugs are crucial for inducing routine labor and preventing catastrophic hemorrhage after delivery, in addition to their use in abortions. “Given its historically poor maternal health outcomes, Louisiana should prioritize safe and evidence-based care for pregnant women,” the doctors wrote.
Louisiana lawmakers also rejected a bill that would have allowed anyone under age 17, the age of consent in Louisiana, to have an abortion if they became pregnant after rape or incest. Passionate testimony from those who suffered such attacks or who treated pregnant girls as young as 8 failed to convince the Republican lawmakers to support the measure. “That baby [in the womb] is innocent.… We have to hang on to that,” said Republican state representative Dodie Horton.
Today, at the Asian Pacific American Institute for Congressional Studies, a nonpartisan, nonprofit organization promoting Asian American and Native Hawaiian/Pacific Islander participation and representation at all levels of the political process, Vice President Kamala Harris encouraged young people to innovate and to move into spaces from which they have been traditionally excluded.
“So here’s the thing about breaking barriers,” she said. “Breaking barriers does not mean you start on one side of the barrier and you end up on the other side. There’s breaking involved. And when you break things you get cut. And you may bleed. And it is worth it every time…. We have to know that sometimes people will open the door for you and leave it open. Sometimes they won’t. And then you need to kick that f*cking door down.”
Harris’s advice reflects the history that happened on this date in 1862, when the enslaved mariners on board the shallow-draft C.S.S. Planter gathered up their families, fired up the ship’s boilers, and sailed out of the Charleston, South Carolina, harbor. The three white officers of the ship had gone ashore, leaving enslaved 23-year-old pilot Robert Smalls to take control. Smalls knew how to steer the ship and give the proper signals to the Confederates at Fort Sumter, Fort Moultrie, and three other checkpoints.
Smalls piloted the Planter, the sixteen formerly enslaved people on it, and a head full of intelligence about the Confederate fortifications at Charleston to the U.S. Navy. In Confederate hands, the Planter had surveyed waterways and laid mines; now that information was in U.S. hands. Smalls went on to pilot naval vessels during the war, and in 1864 he bought the house formerly owned by the man who had enslaved him.
A natural leader, Smalls went on to become a businessman, politician, and strong advocate for education. After serving in the 1868 South Carolina Constitutional Convention that made school attendance compulsory and provided for universal male suffrage, he went on to serve in the South Carolina legislature from 1868 to 1874, when he was elected to the U.S. House of Representatives, where he served until 1887. When President Barack Obama signed an executive order establishing the nation’s first national monument concerning Reconstruction, he cited the life of Robert Smalls.
LETTERS FROM AN AMERICAN
HEATHER COX RICHARDSON
#history#Heather Cox Richardson#Jesse Duquette#election 2024#Biden Administration accomplishment#TFG hate speech#reconstruction#women#women's health concerns#reproductive rights#national database on pregnant women
4 notes
·
View notes
Text

Nearly half of American electric vehicle (EV) owners want to buy an internal combustion engine model the next time they buy a car, according to a new study from McKinsey and Company, a leading consulting firm.
Approximately 46% of Americans who own an EV want to go back to a standard vehicle for their next purchase, citing issues like inadequate charging infrastructure and affordability, according to McKinsey’s study, which was obtained and reviewed by the Daily Caller News Foundation. The study’s findings further suggest that the Biden administration’s EV push is struggling to land with American consumers, after 46% of respondents indicated that they are unlikely or very unlikely to purchase an EV in a June poll conducted by The Associated Press and the University of Chicago’s Energy Policy Institute.
Moreover, 58% of Americans are very likely to keep their current cars for longer, and 44% are likely to postpone a possible switch to EVs, McKinsey’s study found. Consumers’ concerns about EV charging infrastructure are notable given the slow rollout of the Biden administration’s $7.5 billion public EV charger program, which has so far led to the construction of only a handful of chargers in nearly three years.
The Biden administration has a stated goal of having EVs make up 50% of all new car sales by 2030, and the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) finalized stringent regulations in March that will force manufacturers to ensure that up to 56% of their light-duty vehicles are EVs by 2032. The EPA has also finalized strict emissions standards for medium- and light-duty vehicles, while the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) has also locked in fuel economy standards that will further push manufacturers to produce more EVs.
The administration is also spending billions of dollars to subsidize the production and purchase of EVs, but manufacturers are still losing considerable amounts of cash on their EV product lines. EVs remained below a 10% share of all auto sales in the U.S. in 2023, according to Cox Automotive.
The White House did not respond immediately to a request for comment.

Green madness. Electric cars belonging to the city of Paris. No one will buy them because of the cost of the replacement battery. Who will dispose of this junk, especially the batteries?

2 notes
·
View notes
Note
You know AIPAC isn’t even in the top 50 special interest lobbies in Washington DC right? You act like it’s some all powerful nefarious group of Zionist puppet masters controlling the US government. When in fact it’s just one of literally thousands of lobbying groups each trying to get their own interests acknowledged. There’s a big ANTI-Israel lobby in Washington too. And huge lobbies for many other countries (some of the biggest spenders include China, the UAE, Qatar, Liberia, Japan, Saudi Arabia, the frickin Marshall Islands for some reason.) Weird how you’re so obsessed with AIPAC when they are out-numbered and out-spent by dozens of other organizations and countries in DC. For reference? The lobby representing the interests of Native American casinos generally outspends AIPAC. Who are the top lobbying spenders of recent years you ask? The National Association of Realtors, the American Hospital Association, Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America, the American Medical Association, Blue Cross/Blue Shield, Business Roundtable, General Electric, Boeing, Lockheed Martin, AT&T, Verizon, AARP, Exxon Mobil, the National Association of Broadcasters, Edison Electric Institute, Comcast, Amazon, Meta, Pfizer, Unilever, Dow Chemical, FedEx, Open Society Foundation (that’s Israel-critical George Soros. I’m sure you’ve heard of him.) All have spent vastly more than AIPAC. You can look all this up on Open Secrets dot org or the Office of Public Records, btw. 182 different countries (since 2016) spend millions on lobbying activities in DC. Look up FARA on Wikipedia if you’re bored/interested.
(Can’t WAIT for you to find out about Liberia, personally. The origins, the history, the current reality, oof. It’s a LOT.)

#am yisrael chai#gaza genocide#israel#palestine#palestine genocide#free gaza#from the river to the sea palestine will be free#fuck israel#gaza strip#international court of justice#international criminal court#gaza#anti zionisim#tel aviv#all eyes on rafah#rafah#zionsim is terrorism#zionistterror#zionist#free palestine#idf terrorists#i stand with israel
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
May 13, 2024:
Key Quotes:
"The White House today announced that it has awarded nearly $454 billion in funding from the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law, including more than 56,000 projects across more than 4,500 communities across the nation."
"On Thursday, May 9, Senators Katie Britt (R-AL), Marco Rubio (R-FL), and Kevin Cramer (R-ND) introduced the More Opportunities for Moms to Succeed (MOMS) act...The measure is clear that it enlists the government in opposition to abortion, but more than that, it establishes that the government will create a database of the names and contact information of pregnant women"
Today illustrated that the Democrats have become America’s cheerleaders, emphasizing how investment in the nation’s infrastructure has created jobs and rebuilt the country. This week, the Biden-Harris administration is touting its investments in rebuilding roads and bridges, making sure Americans have clean water, getting rid of pollution, expanding access to high-speed internet, and building a clean energy economy, contrasting that success with Trump’s eternal announcements of an “Infrastructure Week” that never came.
The White House today announced that it has awarded nearly $454 billion in funding from the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law, including more than 56,000 projects across more than 4,500 communities across the nation. Those include fixing more than 165,000 miles of roads and more than 9,400 bridges and improving more than 450 ports and 300 airport terminals. It has funded more than 1,400 drinking water and wastewater projects and projects to replace up to 1.7 million toxic lead pipes, as well as more than 8,000 low- and zero-emission buses. It has funded 95 previously unfunded Superfund projects to clean up contaminated sites. It has improved the electrical grid and funded 12,000 miles of high-speed internet infrastructure, and exposed internet junk fees.
The White House explained that this investment is making it cheaper to install clean energy technology and lowering families’ monthly energy bills, and highlighted today the available rebates to enable people to take advantage of the new technologies.
On Wednesday, May 8, a report from the Semiconductor Industry Association and the Boston Consulting Group explored the “breathtaking speed,” as the president of the semiconductor organization put it, at which the industry is growing. In the Financial Times on May 9, John Thornhill reported that the CHIPS and Science Act, which provided a $39 billion investment in the semiconductor industry, has “primed a torrent of private sector investment.” With the influx of both federal money and an additional $447 billion of private investment in 83 projects in 25 states, the report forecasts that the U.S. will increase its share of global manufacturing capacity for leading-edge chips from today’s rate of 0% to 28% by 2032. Thornhill compared this investment to that spurred by Russia’s 1957 launch of the Sputnik satellite.
The Economist yesterday announced that the U.S. “is in the midst of an extraordinary startup boom,” and explored “[h]ow the country revived its “go-getting spirit.”
In contrast to the Democrats’ confidence in America, the Republicans are all-in on the idea that the country is an apocalyptic wasteland. At a rally in New Jersey Saturday, Trump announced: “On day one we will throw out Bidenomics and reinstate MAGAnomics.” He promised to extend his 2017 tax cuts for the wealthy and corporations.
But the gist of his speech was an angry, vitriolic picture of a failing nation full of “enemies” that are “more dangerous” than China and Russia and who are “going to destroy our country.” In his telling, the criminal case against him in Manhattan is “bullsh*t,” and President Biden has done more damage than the “ten worst presidents in the history of our country” combined: “[h]e’s a fool; he’s not a smart man…[h]e’s a bad guy…the worst president ever, of any country. The whole world is laughing at him.”
Trump lied that other countries are “emptying out their mental institutions into the United States, our beautiful country. And now the prison populations all over the world are down. They don’t want to report that the mental-institution population is down because they’re taking people from insane asylums and from mental institutions.” Then he riffed into “the late great Hannibal Lecter,” the fictional murderer and cannibal in the film The Silence of the Lambs, apparently to suggest that similar individuals are migrating to the U.S.
House Republicans this week are working to pass a nonbinding resolution to condemn Biden’s immigration policies, although it was Republicans, under orders from Trump, who killed a strong bipartisan immigration bill earlier this year.
The only way to turn back this apocalypse, Trump and his supporters insist, is to put Trump and his team back into the White House. From there, Republicans will return those they consider “real” Americans to power.
The last few days have added new information about what that means. On Thursday, May 9, Senators Katie Britt (R-AL), Marco Rubio (R-FL), and Kevin Cramer (R-ND) introduced the More Opportunities for Moms to Succeed (MOMS) act. Britt—who is best known for her disastrous response to Biden’s State of the Union speech from her kitchen—said the measure would provide a federal database of resources for pregnant women and women parenting young children, but that information excludes anything that touches on abortion.
The measure is clear that it enlists the government in opposition to abortion, but more than that, it establishes that the government will create a database of the names and contact information of pregnant women, which the government can then use “to follow up with users on additional resources that would be helpful for the users to review.”
A government database of pregnant women would give the federal government unprecedented control over individuals, and it is especially chilling after the story Caroline Kitchener broke in the Washington Post on May 3, that a Texas man, Collin Davis, filed a petition to stop his ex-partner from traveling to Colorado, where abortion is legal, to obtain an abortion. Should she do so, his lawyer wrote, he would “pursue wrongful-death claims against anyone involved in the killing of his unborn child.” Now Davis wants to be able to depose his former partner along with others he says are “complicit” in the abortion.
Antiabortion activists are also seeking to make mifepristone and misoprostol, drugs used in many abortions, hard to obtain. In Louisiana, state lawmakers are considering classifying the drugs as “controlled dangerous substances,” which would make possessing them carry penalties of up to ten years in prison and fines of up to $75,000.
More than 240 Louisiana doctors wrote to lawmakers saying that the drugs have none of the addictive characteristics associated with dangerous controlled substances and warning that the drugs are crucial for inducing routine labor and preventing catastrophic hemorrhage after delivery, in addition to their use in abortions. “Given its historically poor maternal health outcomes, Louisiana should prioritize safe and evidence-based care for pregnant women,” the doctors wrote.
Louisiana lawmakers also rejected a bill that would have allowed anyone under age 17, the age of consent in Louisiana, to have an abortion if they became pregnant after rape or incest. Passionate testimony from those who suffered such attacks or who treated pregnant girls as young as 8 failed to convince the Republican lawmakers to support the measure. “That baby [in the womb] is innocent.… We have to hang on to that,” said Republican state representative Dodie Horton.
Today, at the Asian Pacific American Institute for Congressional Studies, a nonpartisan, nonprofit organization promoting Asian American and Native Hawaiian/Pacific Islander participation and representation at all levels of the political process, Vice President Kamala Harris encouraged young people to innovate and to move into spaces from which they have been traditionally excluded.
“So here’s the thing about breaking barriers,” she said. “Breaking barriers does not mean you start on one side of the barrier and you end up on the other side. There’s breaking involved. And when you break things you get cut. And you may bleed. And it is worth it every time…. We have to know that sometimes people will open the door for you and leave it open. Sometimes they won’t. And then you need to kick that f*cking door down.”
Harris’s advice reflects the history that happened on this date in 1862, when the enslaved mariners on board the shallow-draft C.S.S. Planter gathered up their families, fired up the ship’s boilers, and sailed out of the Charleston, South Carolina, harbor. The three white officers of the ship had gone ashore, leaving enslaved 23-year-old pilot Robert Smalls to take control. Smalls knew how to steer the ship and give the proper signals to the Confederates at Fort Sumter, Fort Moultrie, and three other checkpoints.
Smalls piloted the Planter, the sixteen formerly enslaved people on it, and a head full of intelligence about the Confederate fortifications at Charleston to the U.S. Navy. In Confederate hands, the Planter had surveyed waterways and laid mines; now that information was in U.S. hands. Smalls went on to pilot naval vessels during the war, and in 1864 he bought the house formerly owned by the man who had enslaved him.
A natural leader, Smalls went on to become a businessman, politician, and strong advocate for education. After serving in the 1868 South Carolina Constitutional Convention that made school attendance compulsory and provided for universal male suffrage, he went on to serve in the South Carolina legislature from 1868 to 1874, when he was elected to the U.S. House of Representatives, where he served until 1887. When President Barack Obama signed an executive order establishing the nation’s first national monument concerning Reconstruction, he cited the life of Robert Smalls.
—
Notes and Citations available by subscribing to Letters from an American: https://heathercoxrichardson.substack.com/
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
"In cities across the country, people of color, many of them low income, live in neighborhoods criss-crossed by major thoroughfares and highways.
The housing there is often cheaper — it’s not considered particularly desirable to wake up amid traffic fumes and fall asleep to the rumble of vehicles over asphalt.
But the price of living there is steep: Exhaust from all those cars and trucks leads to higher rates of childhood asthma, cancer, cardiovascular disease, and pulmonary ailments. Many people die younger than they otherwise would have, and the medical costs and time lost to illness contributes to their poverty.
Imagine if none of those cars and trucks emitted any fumes at all, running instead on an electric charge. That would make a staggering difference in the trajectory, quality, and length of millions of lives, particularly those of young people growing up near freeways and other sources of air pollution, according to a study from the American Lung Association.
The study, released [February 28, 2024], found that a widespread transition to EVs could avoid nearly 3 million asthma attacks and hundreds of infant deaths, in addition to millions of lower and upper respiratory ailments...
Prior research by the American Lung Association found that 120 million people in the U.S. breathe unhealthy air daily, and 72 million live near a major trucking route — though, Barret added, there’s no safe threshold for air pollution. It affects everyone.
Bipartisan efforts to strengthen clean air standards have already made a difference across the country. In California, which, under the Clean Air Act, can set state rules stronger than national standards, 100 percent of new cars sold there must be zero emission by 2035.
[Note: The article doesn't explain this, but that is actually a much bigger deal than just California. Basically, due to historically extra terrible pollution, California is the only state that's allowed to allowed to set stronger emissions rules than the US government sets. However, one of the rules in the Clean Air Act is that any other state can choose to follow California's standards instead of the US government's. And California by itself is the world's fifth largest economy - ahead of all but four countries. So, between those two things, when California sets stricter standards for cars, they effects ripple outward massively, far beyond the state's borders.]
Truck manufacturers are, according to the state’s Air Resources Board, already exceeding anticipated zero-emissions truck sales, putting them two years ahead of schedule...
Other states have begun to take action, too, often reaching across partisan lines to do so. Maryland, Colorado, New Mexico, and Rhode Island adopted zero-emissions standards as of the end of 2023.
The Biden administration is taking similar steps, though it has slowed its progress after automakers and United Auto Workers pressured the administration to relax some of its more stringent EV transition requirements.
While Barret finds efforts to support the electrification of passenger vehicles exciting, he said the greatest culprits are diesel trucks. “These are 5 to 10 percent of the vehicles on the road, but they’re generating the majority of smog-forming emissions of ozone and nitrogen,” Barret said...
Lately, there’s been significant progress on truck decarbonization. The Biden administration has made promises to ensure that 30 percent of all big rigs sold are electric by 2030...
Such measures, combined with an increase in public EV charging stations, vehicle tax credits, and other incentives, could change American highways, not to mention health, for good."
-via GoodGoodGood, February 28, 2024
#cw cancer#cw infant death#asthma#respiratory infection#disability#air pollution#air quality#evs#electric vehicles#united states#us politics#biden administration#big rigs#trucks#public health#environmental racism#good news#hope#fossil fuels#carbon emissions
117 notes
·
View notes
Text
ESSEN, Germany (AP) — For most of this century, Germany racked up one economic success after another, dominating global markets for high-end products like luxury cars and industrial machinery, selling so much to the rest of the world that half the economy ran on exports.
Jobs were plentiful, the government's financial coffers grew as other European countries drowned in debt, and books were written about what other countries could learn from Germany.
No longer. Now, Germany is the world’s worst-performing major developed economy, with both the International Monetary Fund and European Union expecting it to shrink this year.
It follows Russia's invasion of Ukraine and the loss of Moscow's cheap natural gas — an unprecedented shock to Germany’s energy-intensive industries, long the manufacturing powerhouse of Europe.
The sudden underperformance by Europe's largest economy has set off a wave of criticism, handwringing and debate about the way forward.
Germany risks “deindustrialization” as high energy costs and government inaction on other chronic problems threaten to send new factories and high-paying jobs elsewhere, said Christian Kullmann, CEO of major German chemical company Evonik Industries AG.
From his 21st-floor office in the west German town of Essen, Kullmann points out the symbols of earlier success across the historic Ruhr Valley industrial region: smokestacks from metal plants, giant heaps of waste from now-shuttered coal mines, a massive BP oil refinery and Evonik's sprawling chemical production facility.
These days, the former mining region, where coal dust once blackened hanging laundry, is a symbol of the energy transition, dotted with wind turbines and green space.
The loss of cheap Russian natural gas needed to power factories “painfully damaged the business model of the German economy,” Kullmann told The Associated Press. “We’re in a situation where we’re being strongly affected — damaged — by external factors.”
After Russia cut off most of its gas to the European Union, spurring an energy crisis in the 27-nation bloc that had sourced 40% of the fuel from Moscow, the German government asked Evonik to keep its 1960s coal-fired power plant running a few months longer.
The company is shifting away from the plant — whose 40-story smokestack fuels production of plastics and other goods — to two gas-fired generators that can later run on hydrogen amid plans to become carbon neutral by 2030.
One hotly debated solution: a government-funded cap on industrial electricity prices to get the economy through the renewable energy transition.
The proposal from Vice Chancellor Robert Habeck of the Greens Party has faced resistance from Chancellor Olaf Scholz, a Social Democrat, and pro-business coalition partner the Free Democrats. Environmentalists say it would only prolong reliance on fossil fuels.
Kullmann is for it: “It was mistaken political decisions that primarily developed and influenced these high energy costs. And it can’t now be that German industry, German workers should be stuck with the bill.”
The price of gas is roughly double what it was in 2021, hurting companies that need it to keep glass or metal red-hot and molten 24 hours a day to make glass, paper and metal coatings used in buildings and cars.
A second blow came as key trade partner China experiences a slowdown after several decades of strong economic growth.
These outside shocks have exposed cracks in Germany's foundation that were ignored during years of success, including lagging use of digital technology in government and business and a lengthy process to get badly needed renewable energy projects approved.
Other dawning realizations: The money that the government readily had on hand came in part because of delays in investing in roads, the rail network and high-speed internet in rural areas. A 2011 decision to shut down Germany's remaining nuclear power plants has been questioned amid worries about electricity prices and shortages. Companies face a severe shortage of skilled labor, with job openings hitting a record of just under 2 million.
And relying on Russia to reliably supply gas through the Nord Stream pipelines under the Baltic Sea — built under former Chancellor Angela Merkel and since shut off and damaged amid the war — was belatedly conceded by the government to have been a mistake.
Now, clean energy projects are slowed by extensive bureaucracy and not-in-my-backyard resistance. Spacing limits from homes keep annual construction of wind turbines in single digits in the southern Bavarian region.
A 10 billion-euro ($10.68 billion) electrical line bringing wind power from the breezier north to industry in the south has faced costly delays from political resistance to unsightly above-ground towers. Burying the line means completion in 2028 instead of 2022.
Massive clean energy subsidies that the Biden administration is offering to companies investing in the U.S. have evoked envy and alarm that Germany is being left behind.
“We’re seeing a worldwide competition by national governments for the most attractive future technologies — attractive meaning the most profitable, the ones that strengthen growth,” Kullmann said.
He cited Evonik’s decision to build a $220 million production facility for lipids — key ingredients in COVID-19 vaccines — in Lafayette, Indiana. Rapid approvals and up to $150 million in U.S. subsidies made a difference after German officials evinced little interest, he said.
“I'd like to see a little more of that pragmatism ... in Brussels and Berlin,” Kullmann said.
In the meantime, energy-intensive companies are looking to cope with the price shock.
Drewsen Spezialpapiere, which makes passport and stamp paper as well as paper straws that don't de-fizz soft drinks, bought three wind turbines near its mill in northern Germany to cover about a quarter of its external electricity demand as it moves away from natural gas.
Specialty glass company Schott AG, which makes products ranging from stovetops to vaccine bottles to the 39-meter (128-foot) mirror for the Extremely Large Telescope astronomical observatory in Chile, has experimented with substituting emissions-free hydrogen for gas at the plant where it produces glass in tanks as hot as 1,700 degrees Celsius.
It worked — but only on a small scale, with hydrogen supplied by truck. Mass quantities of hydrogen produced with renewable electricity and delivered by pipeline would be needed and don't exist yet.
Scholz has called for the energy transition to take on the “Germany tempo,” the same urgency used to set up four floating natural gas terminals in months to replace lost Russian gas. The liquefied natural gas that comes to the terminals by ship from the U.S., Qatar and elsewhere is much more expensive than Russian pipeline supplies, but the effort showed what Germany can do when it has to.
However, squabbling among the coalition government over the energy price cap and a law barring new gas furnaces has exasperated business leaders.
Evonik's Kullmann dismissed a recent package of government proposals, including tax breaks for investment and a law aimed at reducing bureaucracy, as “a Band-Aid.”
Germany grew complacent during a “golden decade” of economic growth in 2010-2020 based on reforms under Chancellor Gerhard Schroeder in 2003-2005 that lowered labor costs and increased competitiveness, says Holger Schmieding, chief economist at Berenberg bank.
“The perception of Germany's underlying strength may also have contributed to the misguided decisions to exit nuclear energy, ban fracking for natural gas and bet on ample natural gas supplies from Russia,” he said. “Germany is paying the price for its energy policies.”
Schmieding, who once dubbed Germany “the sick man of Europe” in an influential 1998 analysis, thinks that label would be overdone today, considering its low unemployment and strong government finances. That gives Germany room to act — but also lowers the pressure to make changes.
The most important immediate step, Schmieding said, would be to end uncertainty over energy prices, through a price cap to help not just large companies, but smaller ones as well.
Whatever policies are chosen, “it would already be a great help if the government could agree on them fast so that companies know what they are up to and can plan accordingly instead of delaying investment decisions," he said.
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Two MIT teams selected for NSF sustainable materials grants
New Post has been published on https://thedigitalinsider.com/two-mit-teams-selected-for-nsf-sustainable-materials-grants/
Two MIT teams selected for NSF sustainable materials grants

Two teams led by MIT researchers were selected in December 2023 by the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) Convergence Accelerator, a part of the TIP Directorate, to receive awards of $5 million each over three years, to pursue research aimed at helping to bring cutting-edge new sustainable materials and processes from the lab into practical, full-scale industrial production. The selection was made after 16 teams from around the country were chosen last year for one-year grants to develop detailed plans for further research aimed at solving problems of sustainability and scalability for advanced electronic products.
Of the two MIT-led teams chosen for this current round of funding, one team, Topological Electric, is led by Mingda Li, an associate professor in the Department of Nuclear Science and Engineering. This team will be finding pathways to scale up sustainable topological materials, which have the potential to revolutionize next-generation microelectronics by showing superior electronic performance, such as dissipationless states or high-frequency response. The other team, led by Anuradha Agarwal, a principal research scientist at MIT’s Materials Research Laboratory, will be focusing on developing new materials, devices, and manufacturing processes for microchips that minimize energy consumption using electronic-photonic integration, and that detect and avoid the toxic or scarce materials used in today’s production methods.
Scaling the use of topological materials
Li explains that some materials based on quantum effects have achieved successful transitions from lab curiosities to successful mass production, such as blue-light LEDs, and giant magnetorestance (GMR) devices used for magnetic data storage. But he says there are a variety of equally promising materials that have shown promise but have yet to make it into real-world applications.
“What we really wanted to achieve is to bring newer-generation quantum materials into technology and mass production, for the benefit of broader society,” he says. In particular, he says, “topological materials are really promising to do many different things.”
Topological materials are ones whose electronic properties are fundamentally protected against disturbance. For example, Li points to the fact that just in the last two years, it has been shown that some topological materials are even better electrical conductors than copper, which are typically used for the wires interconnecting electronic components. But unlike the blue-light LEDs or the GMR devices, which have been widely produced and deployed, when it comes to topological materials, “there’s no company, no startup, there’s really no business out there,” adds Tomas Palacios, the Clarence J. Lebel Professor in Electrical Engineering at MIT and co-principal investigator on Li’s team. Part of the reason is that many versions of such materials are studied “with a focus on fundamental exotic physical properties with little or no consideration on the sustainability aspects,” says Liang Fu, an MIT professor of physics and also a co-PI. Their team will be looking for alternative formulations that are more amenable to mass production.
One possible application of these topological materials is for detecting terahertz radiation, explains Keith Nelson, an MIT professor of chemistry and co-PI. This extremely high-frequency electronics can carry far more information than conventional radio or microwaves, but at present there are no mature electronic devices available that are scalable at this frequency range. “There’s a whole range of possibilities for topological materials” that could work at these frequencies, he says. In addition, he says, “we hope to demonstrate an entire prototype system like this in a single, very compact solid-state platform.”
Li says that among the many possible applications of topological devices for microelectronics devices of various kinds, “we don’t know which, exactly, will end up as a product, or will reach real industrial scaleup. That’s why this opportunity from NSF is like a bridge, which is precious, to allow us to dig deeper to unleash the true potential.”
In addition to Li, Palacios, Fu, and Nelson, the Topological Electric team includes Qiong Ma, assistant professor of physics in Boston College; Farnaz Niroui, assistant professor of electrical engineering and computer science at MIT; Susanne Stemmer, professor of materials at the University of California at Santa Barbara; Judy Cha, professor of materials science and engineering at Cornell University; industrial partners including IBM, Analog Devices, and Raytheon; and professional consultants. “We are taking this opportunity seriously,” Li says. “We really want to see if the topological materials are as good as we show in the lab when being scaled up, and how far we can push to broadly industrialize them.”
Toward sustainable microchip production and use
The microchips behind everything from smartphones to medical imaging are associated with a significant percentage of greenhouse gas emissions today, and every year the world produces more than 50 million metric tons of electronic waste, the equivalent of about 5,000 Eiffel Towers. Further, the data centers necessary for complex computations and huge amount of data transfer — think AI and on-demand video — are growing and will require 10 percent of the world’s electricity by 2030.
“The current microchip manufacturing supply chain, which includes production, distribution, and use, is neither scalable nor sustainable, and cannot continue. We must innovate our way out of this crisis,” says Agarwal.
The name of Agarwal’s team, FUTUR-IC, is a reference to the future of the integrated circuits, or chips, through a global alliance for sustainable microchip manufacturing. Says Agarwal, “We bring together stakeholders from industry, academia, and government to co-optimize across three dimensions: technology, ecology, and workforce. These were identified as key interrelated areas by some 140 stakeholders. With FUTUR-IC we aim to cut waste and CO2-equivalent emissions associated with electronics by 50 percent every 10 years.”
The market for microelectronics in the next decade is predicted to be on the order of a trillion dollars, but most of the manufacturing for the industry occurs only in limited geographical pockets around the world. FUTUR-IC aims to diversify and strengthen the supply chain for manufacturing and packaging of electronics. The alliance has 26 collaborators and is growing. Current external collaborators include the International Electronics Manufacturing Initiative (iNEMI), Tyndall National Institute, SEMI, Hewlett Packard Enterprise, Intel, and the Rochester Institute of Technology.
Agarwal leads FUTUR-IC in close collaboration with others, including, from MIT, Lionel Kimerling, the Thomas Lord Professor of Materials Science and Engineering; Elsa Olivetti, the Jerry McAfee Professor in Engineering; Randolph Kirchain, principal research scientist in the Materials Research Laboratory; and Greg Norris, director of MIT’s Sustainability and Health Initiative for NetPositive Enterprise (SHINE). All are affiliated with the Materials Research Laboratory. They are joined by Samuel Serna, an MIT visiting professor and assistant professor of physics at Bridgewater State University. Other key personnel include Sajan Saini, education director for the Initiative for Knowledge and Innovation in Manufacturing in MIT’s Department of Materials Science and Engineering; Peter O’Brien, a professor from Tyndall National Institute; and Shekhar Chandrashekhar, CEO of iNEMI.
“We expect the integration of electronics and photonics to revolutionize microchip manufacturing, enhancing efficiency, reducing energy consumption, and paving the way for unprecedented advancements in computing speed and data-processing capabilities,” says Serna, who is the co-lead on the project’s technology “vector.”
Common metrics for these efforts are needed, says Norris, co-lead for the ecology vector, adding, “The microchip industry must have transparent and open Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) models and data, which are being developed by FUTUR-IC.” This is especially important given that microelectronics production transcends industries. “Given the scale and scope of microelectronics, it is critical for the industry to lead in the transition to sustainable manufacture and use,” says Kirchain, another co-lead and the co-director of the Concrete Sustainability Hub at MIT. To bring about this cross-fertilization, co-lead Olivetti, also co-director of the MIT Climate and Sustainability Consortium (MCSC), will collaborate with FUTUR-IC to enhance the benefits from microchip recycling, leveraging the learning across industries.
Saini, the co-lead for the workforce vector, stresses the need for agility. “With a workforce that adapts to a practice of continuous upskilling, we can help increase the robustness of the chip-manufacturing supply chain, and validate a new design for a sustainability curriculum,” he says.
“We have become accustomed to the benefits forged by the exponential growth of microelectronic technology performance and market size,” says Kimerling, who is also director of MIT’s Materials Research Laboratory and co-director of the MIT Microphotonics Center. “The ecological impact of this growth in terms of materials use, energy consumption and end-of-life disposal has begun to push back against this progress. We believe that concurrently engineered solutions for these three dimensions will build a common learning curve to power the next 40 years of progress in the semiconductor industry.”
The MIT teams are two of six that received awards addressing sustainable materials for global challenges through phase two of the NSF Convergence Accelerator program. Launched in 2019, the program targets solutions to especially compelling challenges at an accelerated pace by incorporating a multidisciplinary research approach.
#000#2023#ai#analog#applications#approach#assessment#Blue#bridge#Business#CEO#chemistry#chips#Cleaner industry#climate#climate change#CO2#collaborate#Collaboration#college#computer#Computer Science#computing#concrete#Concrete Sustainability Hub#conductors#continuous#cutting#data#Data Centers
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Animals

Snow monkeys, also called Japanese macaques, are a terrestrial Old World monkey species native to Japan (http://animaldiversity.ummz.umich.edu/site/accounts/information/Macaca_fuscata.html.)
They communicate by vocalization. There are six types of vocalizations, including peaceful, defensive, aggressive, and warning vocalizations, which signal their mood (http://animaldiversity.ummz.umich.edu/site/accounts/information/Macaca_fuscata.html.)
Snow monkeys often take baths in natural hot springs to keep warm during the winter (https://www.japan.travel/en/itineraries/snow-monkeys-and-hot-springs-in-nagano/.)
They live in social groups and are known for their complex social hierarchies (https://wpsu.pbslearningmedia.org/resource/nat14.sci.lifsci.hierarchy/the-social-hierarchy-of-snow-monkeys/.)
Snow monkeys are omnivores and have a varied diet that includes fruits, leaves, insects, and small vertebrates (https://www.snowmonkeyresorts.com/smr/snowmonkeypark/snow-monkeys-food/.)
Now, let us talk about the technological and consumerist elements to this piece.
The Toshiba laptop. Founded in 1965 in Japan, Toshiba has grown its company worldwide yet employs just 6,600 people today (https://www.toshiba.com/tai/about_us.jsp.)
Electrical outlet and wires. Harvery Hubbell invented the first electrical plug, but it seems unclear as to when our modern-day outlets were normalized in households (https://illumin.usc.edu/a-powerful-history-the-modern-electrical-outlet/.)
Mercedes-Benz. This is the 2002 SL, paired with the slogan "Style. Unlike any other." A fun fact about MB is that the Weeknd paired up with the company to promote their first electric car, the EQC (https://www.carscoops.com/2019/12/mercedes-and-the-weeknd-team-up-for-what-may-be-the-no-1-car-ad-of-the-year/).
The computer. As of today, Lenovo is the largest computer manufacturing company, with ~24% market share of PC vendors (https://www.gartner.com/en/newsroom/press-releases/2023-01-11-gartner-says-worldwide-pc-shipments-declined-28-percent-in-fourth-quarter-of-2022-and-16-percent-for-the-year.)
Domo. He became an icon in American media around 2002. The writer in this TIME article likened him to Harrison Ford, "if Harrison Ford were a small, feral Teletubby" (https://content.time.com/time/subscriber/article/0,33009,1002529,00.html.)
Attendance Prompt:
The Secret Lives of Color - Rosso Corsa
“In honor of their victory their car's original hue became Italy's national racing color and later the one adopted by Enzo Ferrari for his cars: rosso corsa, racing red" (p. 149).
This passage taught me how Ferrari contributed to "racing red" becoming Italy's national racing color. I am fascinated with racing and cars, but I hadn't known the historical significance and cultural influence that went along with Ferrari. The iconic racing red color that many people associate with fast cars all stemmed from him. The influence of Ferrari and his red car is an interesting piece of automotive and art history.
4 notes
·
View notes