#NiSu
Text
Eliittilaakson tarinoita:
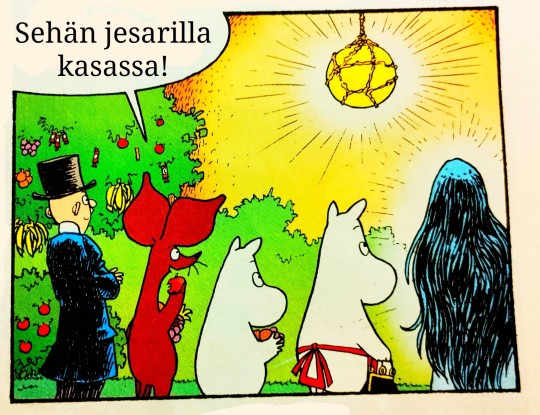
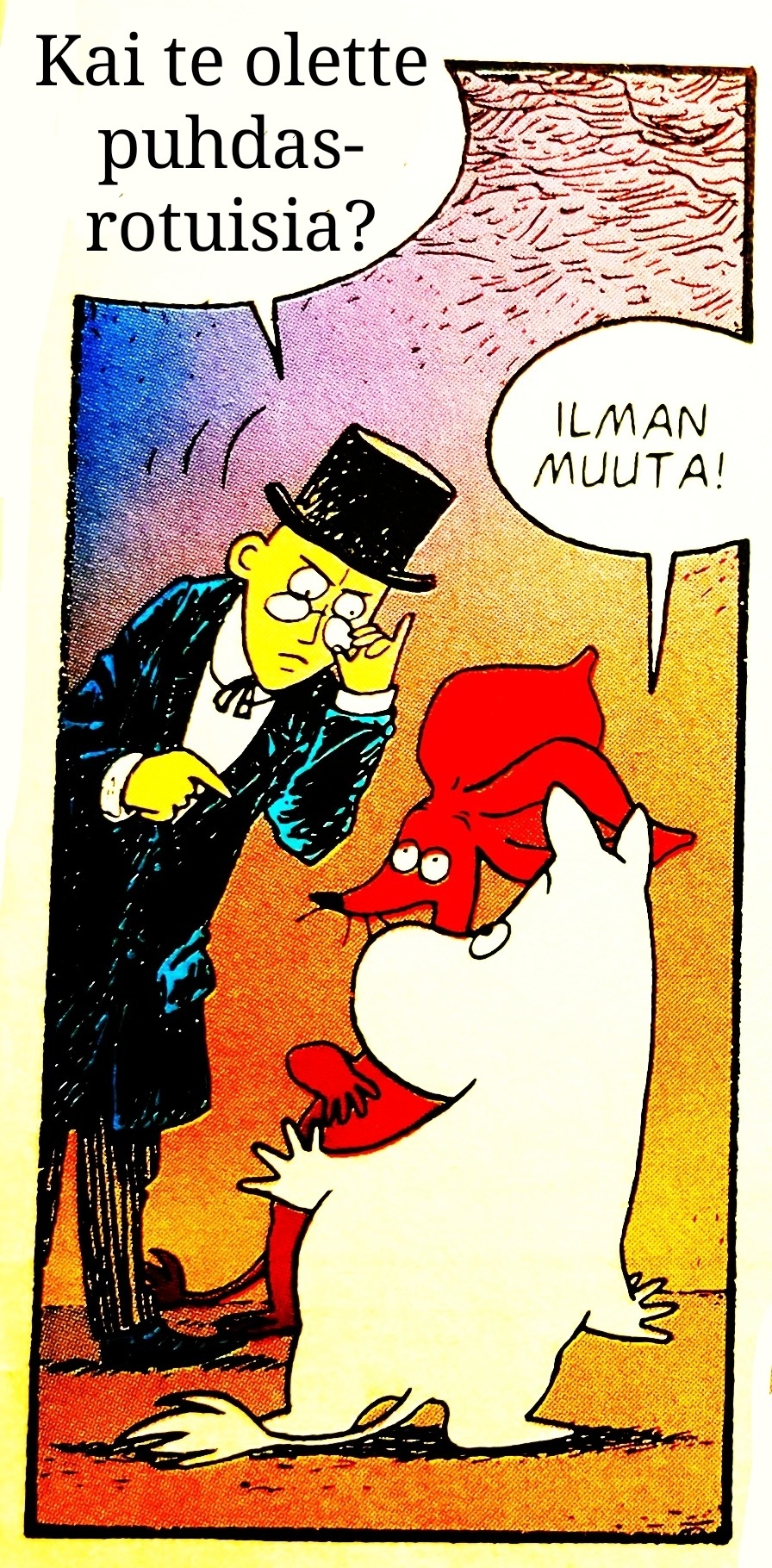




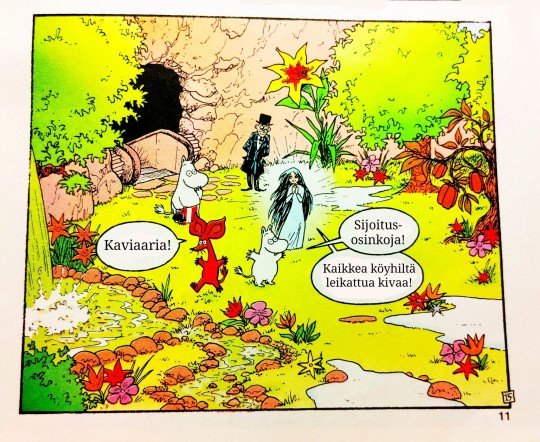


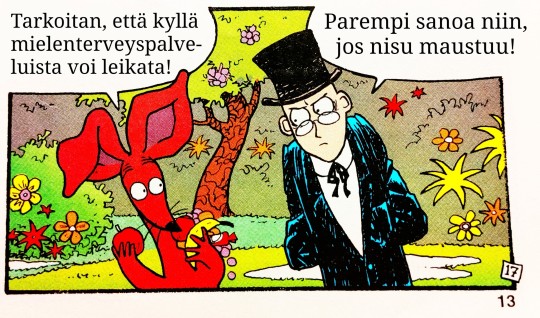


#sarjakuva#suomi#suomitumblr#muumipeikko#nipsu#muumimamma#vanha herra#muumit ja suuri tuhotulva#muumitjasuurituhotulva#tuhotulva#muumit#tulppaana#runous#nisu#hyvinvointi#hyvinvointivaltio#valtio#persut#kokoomus#sinimustahallitus#hallitus#politiikka#skumppa#kaviaari#aurinko#jussi halla aho#alexander stubb#presidentti#eliitti#leikkaukset
64 notes
·
View notes
Text
Transformative Works and Cultures Releases Issue No. 41

Transformative Works and Cultures’ special issue on Chinese Fandoms, guest edited by Zhen Troy Chen and Celia Lam, is out now! Explore the issue to learn about Dangai, Nisu, iWoman and more: https://otw.news/rlv
104 notes
·
View notes
Text
TWC 41: Chinese Fandoms [Special Issue]
Editorial
Zhen Troy Chen and Celia Lam, Special issue on Chinese fandoms: Prosumers, communities, and identities
Article
Yidong Wang and Yilan Wang, Dangai fandoms under crossfire: The making of queer love in a permeable and convergent media ecology
Kexin Sun, The politicization of Chinese celebrity fandoms: A case study of discursive practices in the 227 Movement
Agata Ewa Wrochna, Best TV show you have never seen: Maintaining collective identity among the Twitter fandom of Chinese dangai drama Immortality
Dania Shaikh, Reimagining queer Asias: Performativity, censorship and queer kinship in the fandoms of Grandmaster of Demonic Cultivation and The Untamed
Tingting Hu, Chenchen Zou, Erika Ningxin Wang, A male idol becoming a girl? Nisu fans' sexual fantasy about male stars
Yijia Du, Doing feminism through Chinese online fiction fandom
Meihua Lu, From Cinderella to i-woman: Web novels, fandom, and feminist politics in China
Yuhang Sheng and Qing Xiao, "Play with me!" Zhan jie as productive fans in the Chinese idol industry
Leiyuan Tian and Fan Liang, Cultural porters and banyun in Chinese fandoms on Bilibili
Symposium
Qing Xiao, Yuhang Zheng, “Are we friends or opponents?” Chinese idol fans’ relationship changes from online to off-line
Zhuwen Zhang, Crossing swords and cutting sleeves: The cross-cultural impact of Chinese fandom fan fiction on Asian American youths
Roland Wang and Peilin Li, Warhammer fandom in China: A brief introduction
Dongni Huang, "Treat male idols as toys": A case study of Chinese self-centered shipper communities
Book review
Kelsey Morgan Entrikin, "Dubcon: Fanfiction, power, and sexual consent," by Milena Popova
#twc#otw#fandom#fan studies#academia#fandom studies#dangai#bilibili#warhammer#i-woman#nisu#the untamed#immortality danmai
8 notes
·
View notes
Photo

- Tarmo Selter
#Elu#viljapõllud#nisu#rukis#oder#kaer#lill#mina#sina#tema#ta#ilu#elu#valu#võlu#salm#luuletus#mõttetera#omalooming#avastus#eestiloodus#Eestimaa#luuletused#luule
0 notes
Text


Another guest in my backyard this week. A fledgling Eurasian sparrowhawk. He wasn't very good at flying and spent quite some time on the ground so that I could take pictures from the balcony. Soon the mother flew by with a dead blackbird that she caught and that was the incentive for the young one to give flying another try.
While I find those birds really interesting, I at least partly blame the fact that they nest in my neighborhood also for the lack of fledgling crows this year, The sparrowhawk pair plus the buzzard I see every now have surly been responsible. Nature in the city becomes more diverse and so the predators come as well.
54 notes
·
View notes
Text
Yes, there are gay characters in Tolkien’s books
There seems to be an entrenched view among Tolkien fans that Tolkien did not write any gay characters, and that by interpreting any of his characters as gay you are going against what he would have wanted. Homophobes obviously believe this very strongly, and have always been hostile towards queer fans and queer interpretations of Tolkien’s works. Many members of the LGBTQ community also believe that they’re contradicting canon when they interpret Tolkien’s characters as gay—the only difference is they don’t mind doing so.
But is it so against canon to interpret any of Tolkien’s characters as gay? The assumption that Tolkien did not write gay characters hinges on his Catholicism, but I’m going to explain why this is flimsy reasoning.
First, it should be noted that Tolkien didn’t leave any writings expressing his views on homosexuality, so there is no evidence one way or another. But it seems relevant that Tolkien was good friends with W.H. Auden and corresponded with him over multiple decades. They first met when Auden listened to one of Tolkien’s lectures at Oxford and was inspired to learn Anglo-Saxon. Auden loved Tolkien’s poetry and prose and defended LOTR from critics at a time when it was seen as an unserious work in an unserious genre. Did Tolkien know Auden was gay? We don’t know for sure. But there’s at least a chance that he did: the secret of Auden’s homosexuality is one he “loosely kept”, according to an article in the Guardian.
So, Tolkien was friends with a gay man whom he may or may not have known was gay. But are there gay characters in Tolkien’s books? Unfortunately for the homophobes, even if you believe that Tolkien opposed homosexuality on principle, that still doesn’t mean no one in Middle-earth is gay. Actually, no one in Middle-earth is Catholic. I mean that literally, in the sense that Catholicism does not exist in the time period Tolkien wrote about, but I also mean it in the sense that Tolkien’s characters need not adhere to the tenets of his religion, even if it’s not named. Why would they?
It shouldn’t be controversial or surprising to point out that writers can, and often do, write characters that live very different lives from their own. Needless to say, Tolkien didn’t condone the actions of the antagonists of his work, but what about the protagonists? Are we to believe that all of them act in an unfailingly Catholic way at all times? In Laws and Customs of the Eldar, it is strongly implied that (especially in their younger years) Elves do have sex for pleasure and not just to beget children, something that is discouraged by Catholicism. That’s just one example.
(Please note that I’m not arguing that Tolkien’s Catholicism had no influence on his writings, because he explicitly said that it did. I’m saying that Tolkien’s characters themselves are not Catholic and do not necessarily behave like Catholics. So even if you think that all Catholics believe homosexuality is wrong, it has no bearing on Tolkien’s stories.)
Another line of reasoning goes that homosexuality is too taboo for Tolkien—but I have to wonder if people who believe this have read his books at all. The Silmarillion is full of taboo subjects. Túrin and Niënor marry, not knowing they are brother and sister; they find out the truth, and that she is pregnant, and they both commit suicide. Eöl’s relationship with Aredhel is one that, even if it didn’t start out as controlling and abusive—although I suspect it did—it clearly ended up that way, and depending on your interpretation of the text, he may have raped her. Celegorm attempts to force Lúthien to marry him, which would also involve rape, and there is a passage that implies that Morgoth also intends to rape Lúthien. Neither incest, rape or abuse are too taboo for Tolkien—neither are suicide, torture or mass murder, as the rest of the Silmarillion shows.
I don’t want anyone to take this in bad faith: I’m not saying that being gay is comparable to incest, rape or abuse, and I’m part of the LGBTQ community myself. What I am saying is that Tolkien clearly did not shy away from certain subjects, including sexual taboos, simply because they’re taboo. If you’re going to argue that none of Tolkien’s characters are queer because it wasn’t accepted at the time, that’s very unconvincing given the other subject matter in his books.
There is another reason why I think there are gay characters in Middle-earth, and it has to do with Tolkien’s inspirations. It’s well understood by Tolkien fans that you can see echoes of other mythologies in Tolkien’s works. But which ones? When Lúthien brings Beren back from the Halls of Mandos, there are obvious parallels with the myth of Orpheus and Eurydice—though the genders are reversed, and Lúthien succeeds where Orpheus did not. There are parallels between Túrin and Kullervo. There are numerous examples of this kind of thing throughout the Silmarillion and LOTR. Even the name Middle-earth clearly has its roots in the Norse name Midgard. There are some influences that Tolkien explicitly acknowledged, like the Kalevala and the Völuspá, and some that Tolkien scholars have only theorized about. While there are some scholarly articles on Tolkien and the Aeneid, one thing I have never seen anyone discuss is the parallel between Beleg’s death and the story of Nisus and Euryalus.
In the Aeneid, Nisus and Euryalus are a pair of friends and lovers who are fighting for Aeneas in Latium. Nisus, the older of the two men, is said to be a skilled javelin-thrower and archer. Nisus proposes a night raid on an enemy camp, and Euryalus insists on going with him. During the raid they kill many men in their sleep, collecting some of their armor as loot, as was customary. But when they leave the camp, the glint of light on a helmet taken by Euryalus is seen by a group of enemy horsemen, who capture and kill him before Nisus can stop them. Nisus is distraught and kills many of them in retaliation, ultimately dying beside his lover’s body. (In some versions, it’s a stolen belt, not a helm—but the constant motif is the glint of light that reveals Euryalus to the enemy.)
There are so many similarities with Beleg and Túrin that it cannot be a coincidence. Beleg and Túrin also fight side by side, first on the marches of Doriath and later when Túrin is an outlaw. They are very loyal to each other, and clearly love each other. Like Nisus, Beleg is known to be a great archer. Meanwhile, although it does not feature in Beleg’s death scene, Túrin is associated with a particularly significant helm. There are differences too: Túrin’s captivity is the reason for Beleg’s raid on the Orc-camp, whereas Euryalus is captured after the raid; both Nisus and Euryalus are slain one after the other, whereas only Beleg dies in the raid on the Orc-camp. But there is still the overarching parallel of the night raid, in which the enemy guards are killed silently in their sleep; the raid’s connection with an attempted rescue; the chance moment that leads to the tragic death; the imagery of the flash of light; and the distraught reaction of Nisus and Túrin when they see that Euryalus and Beleg are dead. Tolkien read the Aeneid as a student and so would have been familiar with its contents.
There is also the fact that in some versions of the story Túrin kisses Beleg on the mouth in this scene. Although kissing someone on the mouth has not always been a romantic gesture in all cultures and time periods, the clear parallels to the scene in the Aeneid lead me to think that it is in this case. Whether you see the relationship between Túrin and Beleg as romantic is up to you—all that I’m trying to do is show that it’s a legitimate interpretation.
Ultimately, like I wrote here, I don’t think you need permission from anyone in order to interpret Tolkien’s stories the way you want to. If you want to interpret one of his characters as gay, you don’t need to cite obscure plotlines from the Aeneid to justify it. But I do take issue with the idea—which is so pervasive in the fandom—that Tolkien’s stories must not have gay, or bisexual, or trans people in them, and that any interpretations to that effect are against canon. At the end of the day, Middle-earth is supposed to be our world, and guess what? Queer people exist.
#lotr#tolkien#lord of the rings#silmarillion#my writing#Most of the people I encounter in the Tolkien fandom are either members of the LGBTQ community themselves or supportive of it#but once in a while the homophobes rear their ugly heads#I’ve been wanting to write a post about the Beleg/Turin/Nisus/Euryalus parallel for a while now#Plus I’m a Latin nerd myself and also studied the Aeneid in school!#For the record I call that plot line obscure because it’s obscure nowadays but I don’t think it would have been obscure to Tolkien#like I said in the post#and the parallel really adds to the romantic subtext between Beleg and Turin#I do believe it was intentional
785 notes
·
View notes
Text
i am once again asking for advice on greek mythology and my dissertation
can anyone recommend what they think to be the best translations of virgil's aeneid, euripides' orestes, and aeschylus' oresteia? i'll be researching them with a particular focus on nisus and euryalus, and orestes and pylades
(essentially what i'm asking is which translator really brings out the homoeroticism between their characters)
#i've heard good things about anne carson in this regard? but no clue on the others#greek mythology#orestes and pylades#orestes#pylades#nisus and euryalus#nisus#euryalus#classical studies#classical literature#the aeneid#virgil#the oresteia#aeschylus#euripides#les mis#les miserables#enjoltaire#exr#enjolras#grantaire#question#grace's dissertation struggles
40 notes
·
View notes
Text
i need someone to tell me about Nisus and Euryalus, and not Wikipedia T-T all i heard is they are from roman mythology and were like achilleas and patroklos of roman myth so i am interested but i also heard it is greek myth too? I'm so confused but i would love to know more about them
#nisus and euryalus#achilles#patrochilles#achilles and patroclus#nisus#euryalus#greek myths#ancient greek mythology#roman mythology#the trojan war
18 notes
·
View notes
Text
#Sperber#Greifvogel#Eurasian sparrowhawk#Accipiter nisus#Bird of Prey#Wild Life#Nature#Wild Life Germany#4th October 2023
64 notes
·
View notes
Text


Sparrowhawk & European Starling | William Dickson
#blood#hunt#accipitridae#sturnidae#accipitrinae#accipiter#sturnus#accipiter nisus#sturnus vulgaris#eurasian sparrowhawk#european starling
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
We're studying the Aeneid in class and I'm gradually coming to discover that any time my teacher asks if we "noticed anything interesting going on here" 99% of the time the answer is homoeroticism
#literally hadn't even read book 10 because i was away at the weekend and i guessed it#aeneas and pallas#nisus and euryalus#classicists look at any two dudes virgil writes and immediately rush to open wattpad#virgil#aeneid#queueusque tandem abutere catilina patientia nostra
54 notes
·
View notes
Text
Yumeii silly

below the unedited version :3
:333
#art#digital art#digital artist#artist#artists on tumblr#ibis paint x#Yumeii Nisu#oc#my oc#my oc art#moe art#moecore#2000s anime#animecore#weebcore#otakucore#kawaii#cutecore#2000s#webcore
23 notes
·
View notes
Text

repost from x for fjweek 2024:
day 5: decade
#jean kirstein#floch forster#flojean#mineee#aot#art#jeanfloch#greek tumblr#peloponnesian war#inspired by nisus and euryalus#artists on tumblr
10 notes
·
View notes
Text


The swans I saw on a walk on saturday
#pokušali smo ih nahraniti nekim sjemenkama i čak grožđem jer kao zdravo je za njih#osim što su se ovi očigledno navukli na smoki i neće da jedu ništa na šta nisu navikli pa su htjeli samo moj smoki
7 notes
·
View notes
Photo
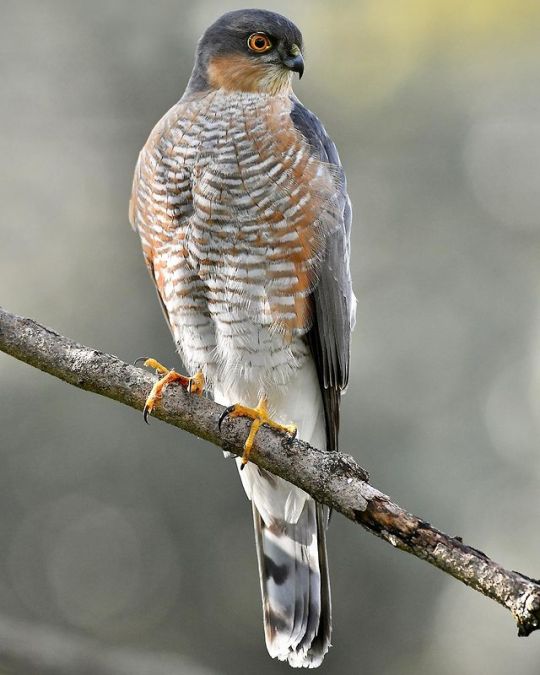

Eurasian Sparrowhawk
#eurasian sparrowhawk#sparrowhawk#northern sparrowhawk#Accipiter nisus#Accipitriformes#Accipitridae#Accipiter#bird#upl
122 notes
·
View notes
