#NutritionGuide
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
youtube
Become Your Own Nutritionist | Master Your Metabolic Health
Learn how to become your own nutritionist and master your metabolic health with self-nutrition and wellness strategies.
In this video, Justin dives deep into the world of self-nutrition and wellness strategies, offering you the tools and knowledge you need to take control of your own health. Learn how to use blood glucose monitoring and biohacking to optimize your metabolic health.
Discover actionable steps and wellness strategies that will help you become confident in managing your own nutrition. This video is packed with valuable information on blood glucose testing, biochemistry, and self-improvement strategies that can transform your health.
#SelfNutrition#MetabolicHealth#Biohacking#WellnessStrategies#SelfImprovement#BloodGlucoseMonitoring#NutritionalIndependence#HealthyLiving#ClovisCulture#HealthHacks#HealthJourney#WellnessJourney#NutritionTips#HealthyLivingTips#FitnessGoals#NutritionGuide#Biohacker#HealthTips#WellnessCommunity#HealthyLifestyle#EatHealthy#BloodSugarControl#DietaryTips#NutritionAdvice#HealthOptimization#DietHack#NutritionScience#DietAndWellness#HealthyChoices#Youtube
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Enhancing Athletic Performance: A Comprehensive Guide to Sports Nutrition
Eating a healthy balanced diet is an essential component of any exercise program. The quality of the food people eat can break their progress toward their fitness objectives. Sports nutrition is the secret to peak performance and better health, whether they're a professional athlete or just trying to keep in shape. In this blog, let's know about the proper nutrition which fuels performance.
People's awareness of the value of exercise is growing, and the sports industry is developing swiftly. Thus, it is estimated to drive the market expansion. In addition, according to a research report by Astute Analytica, the Global Sports Nutrition Market is likely to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.8% over the projection period from 2022 to 2030.
Sports nutrition's significance:
Athletes can prepare for and recover from workouts and contests with the help of adequate nutrition, which increases their total performance. Furthermore, maintaining body weight and increasing the workout effect requires an adequate intake of calories.

The focus of sports nutrition is on the particular dietary requirements for performance. Let's start by talking about which nutrients are crucial for athletes and whether certain supplements are required.
Fats:
Fat serves as the main energy source for low to moderate-intensity activity and fuels the muscles during endurance training. Additionally, it contributes to the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins, offers important fatty acids, safeguards vital organs, and improves satiety.
The recommended daily allowance for fat is between 20 and 35 percent of total calories. It is estimated that poly-unsaturated and mono fats make up about 15-20% and 5–10% of this total.
Seeds, nuts, avocados, fatty fish, and extra-virgin olive oil are a few examples of nutrient-dense dietary fat sources.
Protein:
Protein intake has been linked favorably to metabolic, bone, and weight control. Athletes' performance, lean body mass, recuperation, and strength have all been reported to increase with it. Furthermore, research indicates that consuming protein after exercise may maximize muscle recovery and improve strength.
According to research, active adults and athletes need 1.4–2.0 g of protein per kilogram of body weight per day to grow and maintain muscle mass. Higher protein consumption (>3.0 g/kg/d) may benefit body composition.
Red meat, poultry, dairy, fish, eggs, legumes, tofu, and fortified foods are a few examples of dietary sources of protein.
Food categories to eat:
Particular food groups should be a part of a person's diet when it comes to sports nutrition. It is possible to provide their body the energy it requires to function at its peak by consuming a range of nutrient-dense foods. The following foods are among the best to put in a sports nutrition plan:
Whole grains
Healthy fats
Lean proteins
Vegetables and fruits
The vitamins and minerals included in fruits and vegetables can assist the functioning of a person's body. Lean proteins and healthy fats can help them feel full and provide their body the resources it needs to stay healthy, while whole grains give their body slow-burning energy.
#SportsNutrition#AthleticPerformance#NutritionGuide#HealthyEating#FitnessFuel#PerformanceNutrition#NutritionTips#AthleteFuel#SportsDiet#PeakPerformance#FitnessNutrition#TrainingFuel#NutritionAdvice#SportsScience#FuelYourBody#SportsDietitian#EatForPerformance#NutritionGoals#NutritionForAthletes#SportsTraining
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
🦠 Influenza: More Than Just a Flu
Influenza has a rich history and significant impact on global health. Learn about its symptoms, causes, and how to stay protected in 2025.
👉 https://revisiontown.com/influenza-explained-symptoms-causes-treatments-and-prevention-in-2025/

0 notes
Text
Create Your Personalized Diet Plan in Seconds – Absolutely Free! 🥗✨
Want to eat healthier but don’t know where to start?
Try My Healthy Meal Planner – a smart, free online tool that generates personalized diet plans based on your age, weight, gender, and working hours.
🍎 Why You'll Love It:
✅ Tailored diet plans based on your lifestyle
✅ Supports weight loss, maintenance, or healthy eating goals
✅ Simple, no sign-up required
✅ Perfect for busy professionals, students, and fitness lovers
✅ All for FREE — just a few clicks away!
Whether you're starting a health journey or just need better meal structure, this tool helps you make smarter food choices effortlessly.
👉 Get your free meal plan now: https://myhealthymealplanner.blogspot.com
Healthy eating made easy — for every body, every goal 🥗💪

#HealthyMealPlanner#FreeDietPlan#MealPlanning#HealthyLifestyle#WeightLossTips#NutritionGuide#WellnessTools#SmartEating#DietGenerator#EatBetterLiveBetter#FreeMealPlans#PersonalizedDiet
0 notes
Text
Nine Essential Vitamins Not Stored in the Body: You Must Take Them Daily

Nine Essential Vitamins Not Stored in the Body: You Must Take Them Daily The human body is a finely tuned machine requiring a constant supply of vitamins and minerals to function optimally. While some nutrients are stored for future use, others must be replenished daily as the body does not retain them. These vitamins are vital for processes such as energy production, immune defense, and maintaining bone health. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore nine crucial vitamins you need every day, their importance, and how to ensure you’re getting enough.
Table of Contents
- Introduction: Why Daily Vitamin Intake Matters - Nine Vitamins You Must Take Every Day - Vitamin C - Vitamin B1 (Thiamine) - Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin) - Vitamin B3 (Niacin) - Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic Acid) - Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine) - Vitamin B7 (Biotin) - Vitamin B9 (Folate) - Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin) - Health Risks of Vitamin Deficiency - How to Incorporate These Vitamins into Your Diet - Supplements: When and How to Use Them - Recommended Daily Intake for Adults - Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) - Conclusion
Introduction: Why Daily Vitamin Intake Matters
Vitamins are micronutrients essential for various biochemical and physiological processes. Unlike macronutrients (carbohydrates, proteins, and fats), vitamins are needed in smaller quantities but are no less critical. Certain vitamins, like the B-complex group and vitamin C, are water-soluble, meaning they are not stored in the body and must be consumed daily. Without them, deficiencies can develop, leading to serious health problems.
Nine Vitamins You Must Take Every Day
1. Vitamin C Vitamin C is a potent antioxidant that protects cells from damage, boosts immunity, and aids in collagen production for healthy skin and tissues. Sources: Oranges, strawberries, bell peppers, broccoli, and kiwi. Recommended Intake: 75 mg for women, 90 mg for men. 2. Vitamin B1 (Thiamine) Thiamine helps convert food into energy and supports nerve function. It is especially vital for the brain and cardiovascular system. Sources: Whole grains, pork, sunflower seeds, and legumes. Recommended Intake: 1.1 mg for women, 1.2 mg for men. 3. Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin) Riboflavin supports energy production and the breakdown of fats, drugs, and steroids. It also promotes healthy skin and eyes. Sources: Dairy products, eggs, almonds, and green leafy vegetables. Recommended Intake: 1.1 mg for women, 1.3 mg for men. 4. Vitamin B3 (Niacin) Niacin is critical for DNA repair, energy production, and maintaining healthy skin and nerves. Sources: Chicken, fish, peanuts, and whole grains. Recommended Intake: 14 mg for women, 16 mg for men. 5. Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic Acid) This vitamin helps synthesize and metabolize proteins, carbohydrates, and fats. It also supports the production of coenzyme A. Sources: Avocados, mushrooms, sweet potatoes, and chicken. Recommended Intake: 5 mg for adults. 6. Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine) B6 is essential for neurotransmitter synthesis, red blood cell production, and immune system health. Sources: Bananas, potatoes, fortified cereals, and poultry. Recommended Intake: 1.3 mg for adults up to 50, 1.5–1.7 mg for older adults. 7. Vitamin B7 (Biotin) Biotin supports healthy hair, skin, and nails, and plays a role in carbohydrate and fat metabolism. Sources: Eggs, nuts, seeds, and salmon. Recommended Intake: 30 mcg for adults. 8. Vitamin B9 (Folate) Folate is vital for cell growth and DNA synthesis, making it especially important during pregnancy. Sources: Leafy greens, citrus fruits, beans, and fortified cereals. Recommended Intake: 400 mcg for adults, 600 mcg during pregnancy. 9. Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin) B12 supports nerve function, red blood cell formation, and DNA production. Deficiency can lead to anemia and neurological issues. Sources: Meat, fish, eggs, dairy, and fortified plant-based foods. Recommended Intake: 2.4 mcg for adults.
Health Risks of Vitamin Deficiency
Deficiencies in these vitamins can lead to: - Fatigue and weakness - Weakened immune function - Cognitive decline and neurological issues - Poor skin and hair health - Increased risk of chronic diseases
How to Incorporate These Vitamins into Your Diet
- Balanced Meals: Include a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. - Fortified Foods: Opt for cereals and plant-based milks fortified with essential vitamins. - Snacks: Choose nutrient-dense options like nuts, seeds, and fruit. - Meal Prep: Plan meals to ensure you’re hitting daily vitamin targets.
Supplements: When and How to Use Them
Supplements can help fill gaps in your diet but should not replace whole foods. Consult a healthcare provider before starting any supplement regimen, especially if you have health conditions or take medications.
Recommended Daily Intake for Adults
Vitamin Daily Intake Vitamin C 75–90 mg Vitamin B1 1.1–1.2 mg Vitamin B2 1.1–1.3 mg Vitamin B3 14–16 mg Vitamin B5 5 mg Vitamin B6 1.3–1.7 mg Vitamin B7 30 mcg Vitamin B9 400 mcg Vitamin B12 2.4 mcg
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Can I get enough vitamins from food alone? Yes, a balanced diet can provide all necessary vitamins, but supplementation may be needed in specific cases like pregnancy or dietary restrictions. 2. Are multivitamins a good substitute? Multivitamins can help but should not replace nutrient-dense foods. 3. What happens if I exceed the recommended intake? Excessive intake, especially of supplements, can lead to toxicity and adverse effects. Stick to recommended levels.
Conclusion
Ensuring you get these nine essential vitamins daily is vital for overall health and well-being. By consuming a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, you can meet your nutritional needs. In cases where diet alone isn’t enough, supplements can be a useful addition, but they should be used wisely. Read the full article
#B-complexvitamins#balanceddiet#dailyvitamins#essentialvitamins#folate#healthbenefits#naturalvitamins#nutritionguide#riboflavin#thiamine#vitaminB12#vitaminB6#vitaminC#vitamindeficiency#vitaminsources#water-solublevitamins
1 note
·
View note
Text
Are you ready to embark on your fitness journey? The Daily Fitness is your one-stop destination for fitness tips, workout routines, nutrition advice, and wellness hacks. Whether you're a beginner or a pro, this platform offers everything you need to stay motivated and healthy.
From expert blogs to practical guides, The Daily Fitness keeps you informed and inspired. Explore now and take the first step toward a healthier, happier you!
#FitnessJourney#DailyFitness#HealthAndWellness#WorkoutTips#NutritionGuide#StayHealthy#FitnessMotivation#HealthyLifestyle#WellnessGoals#FitnessCommunity#ExerciseDaily#MindAndBody#HealthyLiving#FitnessTips#StayActive
0 notes
Text
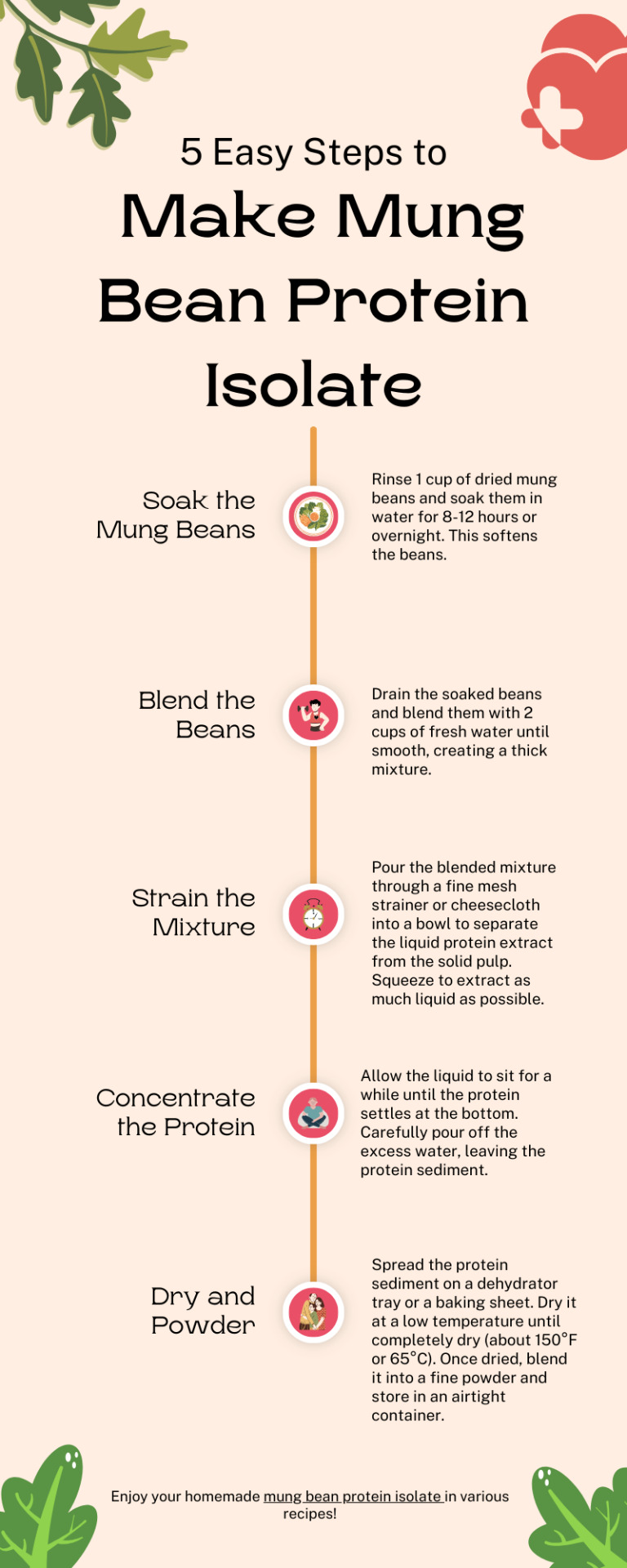
Learn how to make mung bean protein isolate at home with this simple step-by-step guide. Discover the benefits, nutritional value, and versatile uses of this plant-based protein source. Perfect for smoothies, baking, and more!
#MungBeanProtein#PlantBasedProtein#ProteinIsolate#HealthyEating#VeganProtein#Nutritious#SmoothieBoost#BakingWithProtein#DIYProtein#MungBeans#HealthyRecipes#CleanEating#NutritionGuide#PlantPower#FoodScience#ProteinSource#HomeCooking
0 notes
Text

Top Foods for Weight Loss: A Complete Guide to Delicious, Healthy Meals That Keep You Satisfied and Support Your Weight Loss Journey Looking for the best foods to help with weight loss? Discover a complete guide featuring nutritious, delicious meals that keep you full and help you meet your health goals. Learn more at finesshealthfood.com!
#WeightLoss#HealthyEating#NutritionGuide#DeliciousMeals#HealthyRecipes#FitnessJourney#FinessHealthFood
0 notes
Text
Unlock the Health Benefits of Salad!
Discover the numerous health benefits of salads in our comprehensive guide. Eating well has never been this easy! 🥗🌟
Read the full guide: Unlocking the Health Benefits of Salad: A Comprehensive Guide to Nutritional Well-Being

#SaladBenefits#HealthyLiving#NutritionGuide#EatHealthy#GreenSaladIn#healthbenefits#healthylifestyle#healthyfood#healthysalad
0 notes
Text
The Ultimate Guide to Protein Powder: Benefits, Misconceptions, and Choosing the Right One

Unlock the power of protein powder with our comprehensive guide on Men of Letters! Whether you're looking to build muscle, manage your weight, or simply enhance your nutrition, our guide has you covered. Discover the benefits, types, and how to choose the right one for you.
Read the article
#ProteinPower#FitnessGoals#HealthSupplements#WheyProtein#CaseinProtein#PlantBasedProtein#MuscleGrowth#WeightManagement#HealthyLiving#NutritionTips#FitnessJourney#ProteinShake#WorkoutSupplement#ProteinMyths#DietarySupplements#NutritionGuide#ProteinBenefits#ProteinPowderGuide#FitnessBlog#MenOfLetters
0 notes
Text
Fuel Your Workout: The Ultimate Guide to Pre and Post-Gym Nutrition
#FitnessFuel#WorkoutNutrition#GymFuel#NutritionGuide#PostWorkoutNutrition#PreWorkoutFuel#FuelYourFitness#FitnessNutritionTips#FitnessFood#HealthyFuel
0 notes
Text
#SemiVegetarian#Flexitarian#PlantBasedLife#BalancedDiet#MeatlessMondays#VegetarianLifestyle#HealthyEating#NutritionGuide#MealPlanning#MeatAlternatives#DietaryChoices#HealthAndWellness#GreenEating#FlexiDiet#SustainableFood#VeggieLove#NutritionTips#VeggieMeals#EatingWell#PlantPower
0 notes
Text
Nutrition for Women: A Practical Guide to Eating Well


A Comprehensive Guide to Women's Nutrition for Optimal Health Why Women Have Special Nutritional Requirements Key Nutrients Women Should Emphasize How Nutrition Needs Change Throughout A Woman's Life Healthy Eating Guidelines for Teen Girls Nutrition Priorities During Pregnancy Menopause Nutrition Strategies Healthy Aging Dietary Guidelines Benefits of a Largely Plant-Based Diet Two Lifelong Healthy Habits: Physical Activity and Adequate Hydration The Bottom Line on Women's Health Meal Planning Tips for Healthy Eating Key Nutrients for Strong Bones Across a Woman's Lifespan The Anti-Inflammatory Diet: Ideal for Women's Health Nutrient-Dense Foods to Help Women Meet Iron Needs Tips for Healthy Eating on a Budget Simple Snack Ideas to Curb Hunger Takeaway Message on Women's Lifelong Health References
A Comprehensive Guide to Women's Nutrition for Optimal Health
Eating well is essential for women's health and wellbeing at all stages of life. What we put into our bodies has a tremendous impact on our energy, mood, disease risk and quality of life as we age. This in-depth guide explores women's unique nutritional needs and provides science-backed advice for healthy eating during every phase from puberty through menopause and beyond.
Why Women Have Special Nutritional Requirements
Women's nutritional needs differ from men's in significant ways due to hormonal differences, the demands of pregnancy and breastfeeding, and changes through key life stages. Here's an overview of the key factors driving women's specialized needs: Hormonal Effects Women experience major hormonal fluctuations during puberty, menstruation, pregnancy and menopause. These hormonal shifts affect everything from mood to metabolism. Consuming adequate nutrients can help balance hormones for optimal wellbeing. Higher Iron Needs Due to blood loss during menstruation, women require up to twice as much iron daily compared to men. Insufficient iron causes anemia and fatigue. Importance of Calcium Estrogen helps women absorb and retain calcium more efficiently before menopause. Calcium supports bone health, which declines rapidly after estrogen drops during menopause. Folate for Fetal Development Folate requirements surge prior to and during pregnancy to lower the risk of neural tube birth defects. Adequate folate intake remains important during the childbearing years. Pregnancy and Breastfeeding Carrying and nursing a baby significantly increases nutritional needs for nutrients like protein, omega-3s, choline, iodine, magnesium and B vitamins. Nutrient Absorption Changes Gastrointestinal changes as women age can result in decreased absorption of key nutrients like calcium, vitamin D, B12 and iron over time. Given these varied needs, it's clear women must take special care to tailor their dietary choices to their current life stage for optimal wellbeing.
Key Nutrients Women Should Emphasize
While all essential vitamins and minerals are necessary, research shows women commonly fall short on the following key micronutrients: Iron Iron enables red blood cells to carry oxygen efficiently. Inadequate iron causes fatigue, weakness and impaired cognition. Women aged 19-50 need 18 mg daily. Meat, seafood, spinach, lentils, fortified cereal and tofu are good sources. Calcium Calcium maintains bone strength. Low bone density raises fracture risk as we age. Women aged 19-50 need 1000 mg daily from yogurt, milk, kale, broccoli, cheese, calcium-set tofu, sardines with bones and fortified plant milks. Folate Folate forms new cells and prevents neural tube defects. Childbearing aged women need 400 mcg daily from leafy greens, asparagus, legumes, avocado, beets, oranges and nutritional yeast. Folic acid from fortified foods and supplements is more bioavailable than food folate. Vitamin D Vitamin D aids calcium absorption for bone health. Low levels are linked to diabetes, cancer and autoimmune diseases. Get your daily 600 IU from sunlight, fortified milk/juice, mushrooms and fatty fish or consider a supplement. Magnesium Magnesium regulates hundreds of bodily functions including blood pressure, blood sugar and PMS symptoms. Women need 320 mg per day from spinach, pumpkin seeds, yogurt, kefir, almonds, black beans, avocado, dark chocolate and bananas. Omega-3s These healthy fats lower inflammation and heart disease risk while aiding fetal brain development. Aim for 500 mg EPA/DHA daily from fatty fish, walnuts, ground flax/chia seeds and algae supplements. Antioxidants Antioxidants like vitamin C, vitamin E, carotenoids and polyphenols fight free radicals that cause cell damage. Eat a rainbow of vegetables and fruits to meet needs. Berries, citrus fruits, broccoli, leafy greens, tomatoes and nuts are top sources. Getting enough of these nutrients from whole food sources should form the foundation of every woman's daily diet. Supplements can fill in gaps when needed.
How Nutrition Needs Change Throughout A Woman's Life
A woman's nutrient requirements fluctuate based on growth, pregnancy, breastfeeding and hormonal changes. Understanding these shifts enables proper nutrition during each life stage. Childhood Adequate protein, calcium, vitamin D and iron support growth and development. Establish healthy eating patterns like eating breakfast, getting 5 servings of fruits/vegetables daily and limiting junk foods. Puberty & Adolescence Rapid growth demands more protein, vitamins D and C, B vitamins, magnesium and zinc. Extra calcium and iron are critical. Set the foundation for lifelong nutrition habits like preparing nutritious meals and snacks. Early Adulthood Eating nutritiously, exercising regularly and maintaining a healthy weight in the 20s/30s boosts lifelong health. Consume a balanced diet with adequate iron, calcium and folate. Limit alcohol and salty, sugary processed foods. Pregnancy Prenatal vitamins with iron, folate and DHA safeguard mom and baby. Increase protein, vitamins A/C/B6/B12, magnesium, omega-3s and choline. Stay hydrated. Avoid alcohol, unpasteurized dairy/juice and raw meat/eggs. Breastfeeding Nursing moms need extra calories, protein, B vitamins, vitamin C, iron, magnesium, zinc, selenium and iodine. Drink to thirst and munch on nutrient-packed snacks for energy. Calcium and vitamins D/A are still important after pregnancy. Perimenopause Hormone shifts may increase PMS and menstrual changes. Balance hormones and mood with whole grains, healthy fats, phytoestrogen-rich foods like flaxseeds and soy, plus B vitamins, magnesium and vitamin D. Menopause Estrogen drop increases heart disease and osteoporosis risk. Emphasize bone-protecting calcium and vitamin D. Eat heart healthy fats, manage stress and body weight. Be vigilant about getting enough iron, vitamins B12 and D. Postmenopause Nutrition vigilance is vital as appetite and absorption decline. Cook with bone broth for calcium. Consume magnesium and zinc-rich foods. Keep bowels regular with fiber. Supplements may be warranted if needs aren't met through diet. No matter what stage a woman is traversing, paying attention to evolving nutritional needs is the foundation of lifelong health and wellness.
Healthy Eating Guidelines for Teen Girls
Establishing healthy eating patterns during adolescence sets the stage for proper nutrition during adulthood. Here are diet tips for thriving teens: Make Nutritious Foods the Mainstay Construct balanced meals and snacks from whole foods like fruits, veggies, whole grains, lean protein, legumes, nuts, seeds and dairy. Limit sweets, salty snacks and sugary drinks. Power Up with Iron Menstruation increases iron needs. Young girls should regularly eat iron-rich meat, poultry, oysters, pumpkin seeds, white beans, lentils, spinach and iron-enriched cereal. Vitamin C boosts iron absorption. Pile on Phytochemical-Rich Produce Phytochemicals in fruits and vegetables act as antioxidants, support hormone health and protect growing bodies. Strive for 2-3 servings of fruit and 2-3 servings of veggies daily. Maximize Bone-Building Nutrients Consistently eating calcium and vitamin D rich foods like yogurt, cheese, milk, leafy greens, nuts, fortified juice and salmon facilitates maximum bone mass accrual. Hydrate Healthfully Water is best. Limit excess calories from sugary bottled teas, sports drinks, juices and sodas. Caffeine shouldn't exceed 100mg daily from sodas, coffee, tea or energy drinks. Portion Perfectly Moderate portions of nutritious foods ensure adequate calories for growth without excess weight gain. Practice mindful eating by paying attention to hunger/fullness cues. Develop a Nutrition Game Plan Collaborate as a family to meal plan, grocery shop, batch prep breakfasts & snacks, limit eating out and have wholesome dinners together. Modeling healthy habits at home is powerful. Equipping teen girls with fundamental nutrition knowledge positions them for a lifetime of wellness. Establishing healthy habits now pays dividends across their lifespan.
Nutrition Priorities During Pregnancy
Maintaining excellent nutrition during pregnancy benefits both mother and developing baby. Here are diet priorities for expectant mothers: Energy Balance Weight gain should follow recommended guidelines. Only increase calories by 300 per day in the 2nd and 3rd trimesters as needed to support baby's growth and Hungry for 2." Supercharge Micronutrient Intake Eat folate, iron, calcium and omega-3 rich foods. Take a prenatal vitamin with iron and 150 mcg iodine. Iodized salt, dairy, seafood and eggs also supply iodine for fetal brain development. Amp up Protein Choose protein sources like poultry, fish, eggs, Greek yogurt, cottage cheese, beans, lentils, nuts and seeds daily. Protein is vital for baby's cellular growth and placental development. Stay Hydrated Drink when thirsty to allow for increased blood volume and amniotic fluid. Water, fruit/veggie juices, milk, soups and decaf tea all contribute to fluid goals. Limit caffeine and avoid alcohol. Satisfy Cravings and Food Aversions Wisely Give in to cravings in moderation by choosing healthy versions like fruit instead of candy or yogurt instead of ice cream. Discuss severe aversions with your doctor. Practice Food Safety Avoid raw fish/meat, unpasteurized juices/dairy, raw sprouts, deli meats and smoked seafood to prevent foodborne illness. Handle, store and reheat foods properly. Wash all produce. Meeting increased nutritional needs through a balanced, whole food diet plus supplementation positions mothers-to-be for safe pregnancy and delivery.
Postpartum Nutrition for New Moms
Nourishing the body after giving birth is essential. Here are nutrition tips for recovering from delivery and adjusting to motherhood: Replenish Nutrient Stores Continue taking your prenatal vitamin and emphasize iron, folate, fiber and magnesium rich foods to recoup depleted nutrient reserves following delivery. Rehydrate Thoroughly Drink to satisfy thirst and enrich milk supply. Water, fruit juices, soups, herbal teas and low-sodium broths temporarily replace caffeinated/alcoholic beverages. Nourish Exhausted Bodies New moms need about 400 extra calories daily. Snack frequently on hummus and veggie dippers, smoothies, nuts and seeds, full-fat Greek yogurt and cheese for energy. Feed Hungry Babies Breastfeed on demand to stimulate ample milk production. Stay hydrated and keep quick, nourishing snacks like bananas, boiled eggs, oatmeal and applesauce on hand. Boost Nutrients Important for Lactation Eat plenty of vitamin C, A and B rich foods. Seafood, nuts, avocados and olive oil provide DHA for baby's brain. Consider an omega-3 supplement too. Heal Completely Before Rigorous Exercise Postpartum yoga, walking and low-impact cardio can begin once approved at 6 week follow-up. Build back intensity gradually. Rest to recover. Seek Personalized Supplement Recommendations Talk to your doctor about supplements like probiotics, vitamin D, calcium, magnesium or iron that may enhance your postpartum nutrition regimen. Optimal post-delivery nourishment coupled with ample rest, hydration and a gradual return to exercise promotes full recovery for mom and baby.
Menopause Nutrition Strategies
Fluctuating hormones during perimenopause and menopause affect energy, mood and health. Strategic dietary changes can ease common symptoms. Choose Complex Carbohydrates Whole grains, starchy vegetables and fruits provide steady energy. Limit refined grains, sugar and alcohol which cause blood sugar crashes and exacerbate symptoms. Increase Plant Protein Beans, lentils, tofu and tempeh support heart health and hormone balance. Limit red meat linked to heart disease and diabetes risk. Embrace Estrogen-Containing Foods Phytoestrogens in flaxseeds, soybeans, oats, apples, carrots and alfalfa help minimize hot flashes, night sweats and mood swings. Fortify Bones Boost calcium and vitamin D to compensate for bone loss from dropping estrogen levels. Weight-bearing and muscle strengthening exercise also helps. Stay Hydrated Drink at least 8 cups of fluids like water, herbal tea and diluted fruit juice daily. Dehydration worsens menopausal discomforts. Practice Mindful Eating Make time to sit down and savor nutritious meals. Control portions and avoid mindless snacking in front of screens which can lead to weight gain. Targeting menopausal symptoms with nutrition and lifestyle interventions promotes thriving through this transitional life phase.
Healthy Aging Dietary Guidelines
Advancing age brings changes in nutritional needs. Here are tips for mature women to eat well and age vibrantly: Know Key Nutrient Recommendations RDA guidelines provide daily targets for nutrients like calcium (1200mg), vitamin D (600 IU), vitamin B12 (2.4mcg over age 50), and vitamin B6 (1.7mg over age 50). Cook with Nutrient-Rich Ingredients Whip up dishes that incorporate fatty fish, leafy greens, mushrooms, beans, nuts, seeds, whole grains and fruits and vegetables of all colors. Address Chewing and Swallowing Issues Difficulty with eating due to dental problems or swallowing issues increases malnutrition risk. Choose soft, moist, pureed foods. Discuss significant issues with your doctor. Remain Physically Active Aerobic, muscle strengthening and balance exercises help maintain strength and mobility needed for daily living. Adequate protein intake preserves muscle. Discuss Supplements with Your Physician Absorption issues mean many older adults can benefit from supplements containing vitamin B12, vitamin D, calcium, magnesium and omega-3s. Ask your doctor for guidance based on your needs. Tweaking nutrition and lifestyles appropriately facilitates healthy aging, longevity and improved quality of life.
Benefits of a Largely Plant-Based Diet
Emphasizing wholesome plant foods offers myriad benefits for women throughout adulthood. Here's a closer look: Lower Risk for Numerous Chronic Diseases Plant-based diets are associated with decreased inflammation which underlies conditions like diabetes, heart disease, obesity, cancer and osteoporosis. Healthy Gut Environment Fiber nourishes gut microbiota which then produce beneficial compounds that reduce inflammation and improve gut barrier integrity. This promotes good digestion and immunity. Ideal Weight Management Higher fiber and lower calorie density aid sustainable weight management. Fiber improves satiety while fruits and vegetables have fewer calories than many processed snack foods. Increased Antioxidant Intake The wide array of antioxidants, polyphenols and phytochemicals in plant foods reduce free radical damage that can lead to premature aging and disease. Blood Sugar and Insulin Regulation Higher fiber content blunts blood sugar spikes. Polyphenols may also improve insulin response and sensitivity thereby reducing diabetes risk. Cardiovascular Protection Soluble fiber lowers LDL cholesterol. Nitrates in vegetables improve blood flow. Carotenoids reduce oxidation and inflammation which underlie heart disease. Lower Environmental Impact Choosing plant-based proteins over meat vastly reduces carbon emissions plus land and water usage making this a diet with sustainability benefits. A predominantly plant-focused diet centered around whole foods clearly offers today's woman superior nutrition for optimal health.
Two Lifelong Healthy Habits: Physical Activity and Adequate Hydration
Along with proper nutrition, two lifestyle factors—regular exercise and optimal hydration—are vital for a woman's health across her lifespan. Make Physical Activity Non-Negotiable Aim for at least 150 minutes per week of moderate intensity activity like brisk walking. This lowers risk for numerous chronic diseases and age-related declines in mobility and cognition. Any movement counts, so take the stairs, walk around while on the phone and limit sedentary time. Drink Up for Wellness Carry a water bottle as a reminder to sip frequently. Let thirst guide intake. Fluids are essential for energy, organ function, blood pressure, body temperature regulation and metabolism. Read the full article
#adolescence#diettips#dietarychoices#healthyaging#healthyeating#lifelongwellness#menopause#nutritionguide#plant-baseddiet#postpartum#pregnancy#sustainablewellness#women'snutrition#women'shealth
1 note
·
View note
Text
Spot reduction is not effective. When you lose weight, your body determines where it will burn fat, and it's generally not just from the targeted area. A combination of a balanced diet, cardio exercises, and strength training is the most effective way to reduce overall body fat.
Official Store, link below ⤵️ 🌐 http://bit.ly/3jOa9TC
For more information Call 📞 99 4258 4258 / 0172 500 2999 .
#Halt#nutritionstore#haltchd#haltchandigarh#haltnutrition#healthguide#nutritionguide#healthylife#myth&fact
0 notes
Text
Fat Loss Diet Plan for 7-Day: A Scientifically-Backed and Sustainable Approach
1 note
·
View note
Text
HealthyandWeightLoss: Your Path to Wellness
HealthyandWeightLoss is your go-to resource for expert tips on weight loss. Website: https://healthyandweightloss.com/
1 note
·
View note