#OCR Computer Science
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Apparently this is the first year OCR Computer Science hasn't made somebody kill themselves that must've been a really good paper
5 notes
·
View notes
Note
How did you distinguish between lowercase L and capital i? I see that they have slightly different images in your repo, but I'm not sure how you managed to tell them apart in the original image.
exactly that. i took both, classified one as I and the other as l, and checked the result. whichever of the two ways gave me most of the image back (the wrong way actually didn't even give me a valid JPEG header) was the correct one. i just checked both
Ah, I see, so ClearType actually ensures that even the color aliasing artifacts around each letter will be consistent, so that a lowercase L will always be "column of light yellow, column of near black, column of light blue" while uppercase i will always be "column of reddish orange, column of medium blue"?

Does this mean that ANYTHING using ClearType with this font & point size will have the same color patterns? Or is it only guaranteed to be consistent within one particular block of text, with the specific aliasing patterns determined on the fly based on some magic formula?
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ok but was anyone else mildly disappointed in CS paper 2 when there was no ocr-themed company/game etc?
#gcse computer science#gcses#gcse student#ocr zoo simulator my beloved you will always be famous to me
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
College started
I had to wake up at 6:30 for the first time in like 2 months and dug up my blazer jacket that I bought for prom and paired it with a white summer shirt, a yellow hoodie, light grey jeans and a tie I nicked from my dad and had to watch a youtube video just to figure out how to tie it. I don't know why the blazer looks grey and crumpled in the photo, in real life it's turquoise and has less noticeable creases in it. Mum now sees what I mean when I say that hoodies, ties and blazers go well together. God it got hot while walking though but it was worth it in the name of style.
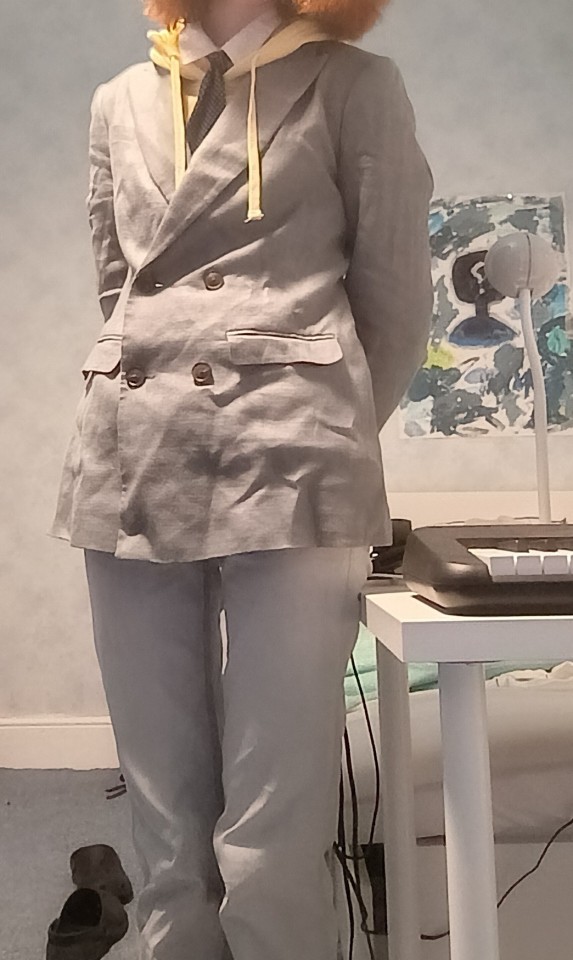

I also had a packed lunch for the first time as keyboard lessons were more expensive due to them being twice as long so buying hot lunches was chucked out of the budget. I made a cheese bagel sandwich with mozzarella slices and packed it in a bag with a little pancake, 4 crackers, a little brownie and a banana that I didn't eat because it had been waiting for so long that it was going brown. I didn't think about how all the food would sit so everything that wasn't in the sandwich bag (the sandwich) had a faint taste of banana. I also bought a packet of crisps at the college's cafe as I was still a bit hungry afterwards so maybe I should figure that out.
I walked 20 minutes and across a roundabout to reach my new bus stop and a new bus came every 15 minutes so I didn't bother mesmerising the timetable. Luckily I live quite close so the journey only took like 35 minutes and I was an hour early and didn't know what to do. Very few students were there and I was mostly looking for the library so I could vibe until I had A-Level Music. After a google search I found the building but turns out it's being moved to some other building (there's like 8 buildings across 2 sides of a road and it resembles a uni campus) so I just drew in the study centre by myself for about half an hour. Someone I knew (kinda) from my old school came up to me to say hello. I walked over to the building with music in but ended up a couple minutes late as I was washing my hands when the bell went off and I though "oh it's the warning bell" when no, no it wasn't. The teacher didn't seem to care considering it's the first day.
The lessons are so much longer here. So long that in the middle there was a 15 minute break. I didn't really have anywhere better to be so I remained in the classroom drawing. There seems to be a lot of emphasis on performance but I kinda suck at preforming. At least A-Level also has composition. I had to leave in the last half hour though to go to an orthodontist appointment and I left when they were talking about intervals and intervals are cool and now I have to do catch up work just because my teeth jewellery needed tightening.
I ate my lunch at a table all by myself in the student commons room and I don't know if all the groups already knew each other or if this was a case of extroverts having good social skills, but almost everyone was sitting in a group. One of the teachers talked to me when I was eating my bagel. Nothing deep just general new school small talk. He said I'll find new friends due to the way classes are structured around A-levels, which you choose yourself so there's a common interest, but tbh I'm probably just going to be known as that weird quiet kid that knows way too much on video game consoles. I don't mind not having any friends my entire time there, but when you've been stuck in an all girls private school since you were a toddler to now, it shelters you and I want to not be that as I'll have one hell of a shock once I enter the real world and/or act like a snob unintentionally. Eh, whatever. I bought the aforementioned crisps in beef flavoured and it was mostly air dammit. I then did my music homework in one of the practice rooms so I could test the musical dictation on the piano. I then just started playing whatever and some girl hovered around my door so I let her in and apparently she could hear me blasting my music because I have no dynamic control on a piano and she said that she really liked it. Then my music teacher appeared and I said I was doing my homework, and then they both left. Someone was playing some ballad piano song (I assume it's the girl as it sounds like it's coming from the other room) which would occasionally change to fur elise. Then I still had some time left but I was bored so after asking a history teacher for directions on where the mac lab is, I went into Music Technology like 10 minutes early and was just fiddling with the mac until everyone else came in. (Music tech is a BTEC which is a different exam board and is more DAW stuff while Music A-Level is performance and theory. I was supposed to be doing Computer Science but I fucked up my exam because OCR sucks the devil's ass while marking so I didn't have the qualifications so the careers people suggested music tech as the 3rd subject and oh god I'm so thankful as I'm certain my college uses OCR for it's A Levels and I would rip my wrists open and develop a caffeine addiction if I had to deal with OCR again).
The actual lesson was interesting but I was the only one putting my hand up most of the time and also I've already used a DAW before (LMMS) so I picked up on how to use Logic Pro quicker than the others (I think, idk I was sitting by myself on an empty row) but Logic Pro has cool sounds that I want in a soundfont, but is full of little things that makes it a bit annoying. And mac. Mac OS is annoying. I wasn't really following the instructions and was mostly doing my own thing in Logic Pro. Use this plugin to automatically augment a bassline? Nah I'm going to keep pressing keys with this acoustic bass sound until I get a cool bassline. I stayed for half an hour afterwards to finish the song as it was cool and this is what I did:
There was also theory stuff too. In groups we had to type out a list of places you find music and I just ignored the people in my group and wrote my own list. Also music kept randomly playing and the teacher couldn't figure out where it was coming from so I listed "the poltergeist from the mac lab" as one place music comes from. After that I took the bus home and now I'm going to watch the 2nd Deadpool film because I'm tired and don't feel like doing anything but sit in my chair and morph into it.
#college in britain is 16-18 btw#not to be confused with music colleges#those are unis#a levels#a level music#music#a level#music tech#music technology#btec#mum's making me do some online course for computer science and i got the textbook today and it's AQA!#fuck ocr#logic pro#couldn't find that cool synth sound#i know it's there#i spent my break trying to find it#my 3rd subject is film studies btw#in case you were wondering#britain#uk#united kingdom#great britain#england#school#british school#college#student
0 notes
Text
AI’s “human in the loop” isn’t

I'll be in TUCSON, AZ from November 8-10: I'm the GUEST OF HONOR at the TUSCON SCIENCE FICTION CONVENTION.

AI's ability to make – or assist with – important decisions is fraught: on the one hand, AI can often classify things very well, at a speed and scale that outstrips the ability of any reasonably resourced group of humans. On the other hand, AI is sometimes very wrong, in ways that can be terribly harmful.
Bureaucracies and the AI pitchmen who hope to sell them algorithms are very excited about the cost-savings they could realize if algorithms could be turned loose on thorny, labor-intensive processes. Some of these are relatively low-stakes and make for an easy call: Brewster Kahle recently told me about the Internet Archive's project to scan a ton of journals on microfiche they bought as a library discard. It's pretty easy to have a high-res scanner auto-detect the positions of each page on the fiche and to run the text through OCR, but a human would still need to go through all those pages, marking the first and last page of each journal and identifying the table of contents and indexing it to the scanned pages. This is something AI apparently does very well, and instead of scrolling through endless pages, the Archive's human operator now just checks whether the first/last/index pages the AI identified are the right ones. A project that could have taken years is being tackled with never-seen swiftness.
The operator checking those fiche indices is something AI people like to call a "human in the loop" – a human operator who assesses each judgment made by the AI and overrides it should the AI have made a mistake. "Humans in the loop" present a tantalizing solution to algorithmic misfires, bias, and unexpected errors, and so "we'll put a human in the loop" is the cure-all response to any objection to putting an imperfect AI in charge of a high-stakes application.
But it's not just AIs that are imperfect. Humans are wildly imperfect, and one thing they turn out to be very bad at is supervising AIs. In a 2022 paper for Computer Law & Security Review, the mathematician and public policy expert Ben Green investigates the empirical limits on human oversight of algorithms:
https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=3921216
Green situates public sector algorithms as the latest salvo in an age-old battle in public enforcement. Bureaucracies have two conflicting, irreconcilable imperatives: on the one hand, they want to be fair, and treat everyone the same. On the other hand, they want to exercise discretion, and take account of individual circumstances when administering justice. There's no way to do both of these things at the same time, obviously.
But algorithmic decision tools, overseen by humans, seem to hold out the possibility of doing the impossible and having both objective fairness and subjective discretion. Because it is grounded in computable mathematics, an algorithm is said to be "objective": given two equivalent reports of a parent who may be neglectful, the algorithm will make the same recommendation as to whether to take their children away. But because those recommendations are then reviewed by a human in the loop, there's a chance to take account of special circumstances that the algorithm missed. Finally, a cake that can be both had, and eaten!
For the paper, Green reviewed a long list of policies – local, national, and supra-national – for putting humans in the loop and found several common ways of mandating human oversight of AI.
First, policies specify that algorithms must have human oversight. Many jurisdictions set out long lists of decisions that must be reviewed by human beings, banning "fire and forget" systems that chug along in the background, blithely making consequential decisions without anyone ever reviewing them.
Second, policies specify that humans can exercise discretion when they override the AI. They aren't just there to catch instances in which the AI misinterprets a rule, but rather to apply human judgment to the rules' applications.
Next, policies require human oversight to be "meaningful" – to be more than a rubber stamp. For high-stakes decisions, a human has to do a thorough review of the AI's inputs and output before greenlighting it.
Finally, policies specify that humans can override the AI. This is key: we've all encountered instances in which "computer says no" and the hapless person operating the computer just shrugs their shoulders apologetically. Nothing I can do, sorry!
All of this sounds good, but unfortunately, it doesn't work. The question of how humans in the loop actually behave has been thoroughly studied, published in peer-reviewed, reputable journals, and replicated by other researchers. The measures for using humans to prevent algorithmic harms represent theories, and those theories are testable, and they have been tested, and they are wrong.
For example, people (including experts) are highly susceptible to "automation bias." They defer to automated systems, even when those systems produce outputs that conflict with their own expert experience and knowledge. A study of London cops found that they "overwhelmingly overestimated the credibility" of facial recognition and assessed its accuracy at 300% better than its actual performance.
Experts who are put in charge of overseeing an automated system get out of practice, because they no longer engage in the routine steps that lead up to the conclusion. Presented with conclusions, rather than problems to solve, experts lose the facility and familiarity with how all the factors that need to be weighed to produce a conclusion fit together. Far from being the easiest step of coming to a decision, reviewing the final step of that decision without doing the underlying work can be much harder to do reliably.
Worse: when algorithms are made "transparent" by presenting their chain of reasoning to expert reviewers, those reviewers become more deferential to the algorithm's conclusion, not less – after all, now the expert has to review not just one final conclusion, but several sub-conclusions.
Even worse: when humans do exercise discretion to override an algorithm, it's often to inject the very bias that the algorithm is there to prevent. Sure, the algorithm might give the same recommendation about two similar parents who are facing having their children taken away, but the judge who reviews the recommendations is more likely to override it for a white parent than for a Black one.
Humans in the loop experience "a diminished sense of control, responsibility, and moral agency." That means that they feel less able to override an algorithm – and they feel less morally culpable when they sit by and let the algorithm do its thing.
All of these effects are persistent even when people know about them, are trained to avoid them, and are given explicit instructions to do so. Remember, the whole reason to introduce AI is because of human imperfection. Designing an AI to correct human imperfection that only works when its human overseer is perfect produces predictably bad outcomes.
As Green writes, putting an AI in charge of a high-stakes decision, and using humans in the loop to prevent its harms, produces a "perverse effect": "alleviating scrutiny of government algorithms without actually addressing the underlying concerns." The human in the loop creates "a false sense of security" that sees algorithms deployed for high-stakes domains, and it shifts the responsibility for algorithmic failures to the human, creating what Dan Davies calls an "accountability sink":
https://profilebooks.com/work/the-unaccountability-machine/
The human in the loop is a false promise, a "salve that enables governments to obtain the benefits of algorithms without incurring the associated harms."
So why are we still talking about how AI is going to replace government and corporate bureaucracies, making decisions at machine speed, overseen by humans in the loop?
Well, what if the accountability sink is a feature and not a bug. What if governments, under enormous pressure to cut costs, figure out how to also cut corners, at the expense of people with very little social capital, and blame it all on human operators? The operators become, in the phrase of Madeleine Clare Elish, "moral crumple zones":
https://estsjournal.org/index.php/ests/article/view/260
As Green writes:
The emphasis on human oversight as a protective mechanism allows governments and vendors to have it both ways: they can promote an algorithm by proclaiming how its capabilities exceed those of humans, while simultaneously defending the algorithm and those responsible for it from scrutiny by pointing to the security (supposedly) provided by human oversight.

Tor Books as just published two new, free LITTLE BROTHER stories: VIGILANT, about creepy surveillance in distance education; and SPILL, about oil pipelines and indigenous landback.


If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/10/30/a-neck-in-a-noose/#is-also-a-human-in-the-loop

Image: Cryteria (modified) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:HAL9000.svg
CC BY 3.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/deed.en ==
290 notes
·
View notes
Text
Dr. Watts' impact on Remnant is so fascinating




James' and Yang's prosthetics look alike in style while Pietro's chair has green/yellow accents, so the chair and Penny are fully Pietro's work, but it's mainly Watts' previous innovations that heavily influences biomechanical engineering and computer science across Remnant. Otherwise we'd see green/yellow on the other prosthetics, I think. We do see circular shapes in Pietro's designs while Arthur's are rectangular/polygons just like the Hardlight Dust.

The teal color significance is cool too, Watts is represented with yellow/ocre, opposites. He's a self-serving guy who isolated himself but his inventions left a major impact on mobility and communication. (Except Tyrian's purple but Arthur's closet is made out of very transparent Hardlight.) Makes the yellow on Pietro even more interesting as long as we don't know how involved he was.
Yang and Maria are interesting because they aren't rich or in the atlasian military, but earned theirs by being badass women!! 🩷🩷
And then there is Mercury!!!! (And by the gods we don't talk about him enough)


His legs are a darker metal than every other prosthetic, visible screws and cables, a lot clunkier too. As far as I know Merc and Em weren't aware of Salem and the others until Vol4? He built his own prosthetics by utilizing unnamed Arthur's basis?
It proves Watts' things are accessible to every social class and guaranteed that's why (likely a former) Atlas council (maybe Jacques too) wanted Watts gone. Taiyang even says it's rare Atlas-Tech gets sent out of Atlas, because the tech wasn't meant to make it out. Watts humbled the entire capitalist pro-profit system and escaped by staging his death, iconic.
#˖˚ joi talks rwby ⊹₊#arthur watts#oh look at me talking about that middle aged man again#rwby#mercury black#pietro polendina#james ironwood
31 notes
·
View notes
Text
i'll not lie i'm still traumatised from the 2023 Computer Science Paper 2 GCSE. thank you OCR very cool
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Herculaneum papyri, ancient scrolls housed in the library of a private villa near Pompeii, were buried and carbonized by the eruption of Vesuvius in 79 AD. For almost 2,000 years, this lone surviving library from antiquity was buried underground under 20 meters of volcanic mud. In the 1700s, they were excavated, and while they were in some ways preserved by the eruption, they were so fragile that they would turn to dust if mishandled. How do you read a scroll you can’t open? For hundreds of years, this question went unanswered.
CT scanners are used to image the scrolls, then software "unrolls" them virtually so that the individual layers may be seen. Finally specialized OCR software identifies individual letters. All without physically manipulating the fragile scrolls.
Neat!
26 notes
·
View notes
Text
the original captcha's (Completely Automated Public Turing test to tell Computers and Humans Apart) were not used for this, it is a generic term, you are thinking of reCaptcha, which is a specific company that google purchased.
And the thing is, it was a good idea! OCR is such a great tool! it was sort of a science at home thing that paired up a known word and an unknown word, if you got the known word correct, the unknown word was then accepted (after a bunch of people gave the same answer for the unknown word).
And then "Formerly: Don't Be Evil" google purchased it and now use it to train all sorts of stuff as well as collect data on what users are doing.
There is an alternative! if you are a web dev look into Friendly Captcha! its more accessible and works off a proof of work thing, basically the idea is "look, computers can solve capatchas easily these days, so instead of trying to stop them and just resulting in humans doing work, we make it so it takes about 10 seconds before you can continue. to a human this doesn't matter because you spend that time filling out a form, but to a bot farm it does matter because it VASTLY slows down how many accounts they can make" its more complicated then that and there are other things that make it work better but the main important thing to me is that it is accessible and doesn't require data collection.

41K notes
·
View notes
Text
Beyond the Books: Real-World Coding Projects for Aspiring Developers
One of the best colleges in Jaipur, which is Arya College of Engineering & I.T. They transitioning from theoretical learning to hands-on coding is a crucial step in a computer science education. Real-world projects bridge this gap, enabling students to apply classroom concepts, build portfolios, and develop industry-ready skills. Here are impactful project ideas across various domains that every computer science student should consider:
Web Development
Personal Portfolio Website: Design and deploy a website to showcase your skills, projects, and resume. This project teaches HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and optionally frameworks like React or Bootstrap, and helps you understand web hosting and deployment.
E-Commerce Platform: Build a basic online store with product listings, shopping carts, and payment integration. This project introduces backend development, database management, and user authentication.
Mobile App Development
Recipe Finder App: Develop a mobile app that lets users search for recipes based on ingredients they have. This project covers UI/UX design, API integration, and mobile programming languages like Java (Android) or Swift (iOS).
Personal Finance Tracker: Create an app to help users manage expenses, budgets, and savings, integrating features like OCR for receipt scanning.
Data Science and Analytics
Social Media Trends Analysis Tool: Analyze data from platforms like Twitter or Instagram to identify trends and visualize user behavior. This project involves data scraping, natural language processing, and data visualization.
Stock Market Prediction Tool: Use historical stock data and machine learning algorithms to predict future trends, applying regression, classification, and data visualization techniques.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Face Detection System: Implement a system that recognizes faces in images or video streams using OpenCV and Python. This project explores computer vision and deep learning.
Spam Filtering: Build a model to classify messages as spam or not using natural language processing and machine learning.
Cybersecurity
Virtual Private Network (VPN): Develop a simple VPN to understand network protocols and encryption. This project enhances your knowledge of cybersecurity fundamentals and system administration.
Intrusion Detection System (IDS): Create a tool to monitor network traffic and detect suspicious activities, requiring network programming and data analysis skills.
Collaborative and Cloud-Based Applications
Real-Time Collaborative Code Editor: Build a web-based editor where multiple users can code together in real time, using technologies like WebSocket, React, Node.js, and MongoDB. This project demonstrates real-time synchronization and operational transformation.
IoT and Automation
Smart Home Automation System: Design a system to control home devices (lights, thermostats, cameras) remotely, integrating hardware, software, and cloud services.
Attendance System with Facial Recognition: Automate attendance tracking using facial recognition and deploy it with hardware like Raspberry Pi.
Other Noteworthy Projects
Chatbots: Develop conversational agents for customer support or entertainment, leveraging natural language processing and AI.
Weather Forecasting App: Create a user-friendly app displaying real-time weather data and forecasts, using APIs and data visualization.
Game Development: Build a simple 2D or 3D game using Unity or Unreal Engine to combine programming with creativity.
Tips for Maximizing Project Impact
Align With Interests: Choose projects that resonate with your career goals or personal passions for sustained motivation.
Emphasize Teamwork: Collaborate with peers to enhance communication and project management skills.
Focus on Real-World Problems: Address genuine challenges to make your projects more relevant and impressive to employers.
Document and Present: Maintain clear documentation and present your work effectively to demonstrate professionalism and technical depth.
Conclusion
Engaging in real-world projects is the cornerstone of a robust computer science education. These experiences not only reinforce theoretical knowledge but also cultivate practical abilities, creativity, and confidence, preparing students for the demands of the tech industry.
0 notes
Text
AI in Action: Use Cases Transforming Medical Billing

Medical billing is often described as the financial backbone of healthcare, yet for years, it’s been bogged down by manual processes, outdated systems, and endless codebooks. The result? Billing errors, claim denials, delayed reimbursements, and frustrated staff who’d rather focus on patient care than paperwork.
Enter artificial intelligence.
From reading complex clinical notes to predicting claim denials before they happen, AI is rapidly rewriting the rules of revenue cycle management. And this isn’t science fiction; it’s happening now. Hospitals and clinics across the globe are leveraging intelligent automation to boost accuracy, speed up reimbursements, and cut operational costs.
In this blog, we’ll explore how AI is being applied to real-world medical billing workflows. Whether you’re a provider, billing professional, or healthcare tech leader, here’s how AI is solving long-standing challenges and transforming medical billing from a costly pain point into a strategic advantage.
Why Medical Billing Needed a Makeover?
Medical billing has long been one of the most complex and error-prone parts of healthcare administration. With over 73,000 diagnosis codes in the ICD-10-CM system and new ones added every year, keeping up is a full-time job in itself. Add in thousands of payer-specific rules, documentation standards, and ever-changing compliance regulations, and you’ve got a recipe for chaos.
Even a small oversight, a missing modifier, an outdated code, or an eligibility mismatch can result in a denied claim. And denial rates are climbing. According to industry data, nearly 1 in 5 claims gets denied on the first pass, forcing billing teams into costly and time-consuming rework cycles. Meanwhile, payment cycles can stretch anywhere from 30 to 90 days, leaving providers waiting weeks (or even months) for reimbursement. For clinics operating on thin margins, this delay directly impacts cash flow and financial stability.
Simply put, the traditional, manual way of doing things isn’t sustainable. As healthcare grows more complex, medical billing systems must evolve too, and that’s exactly where AI is stepping in to revolutionize the process.
AI Building Blocks in Revenue Cycle Management (RCM)
Before diving into specific use cases, it’s important to understand the core technologies powering AI’s transformation of medical billing. These aren’t buzzwords—they’re practical tools reshaping how healthcare providers manage revenue cycles from end to end.
1. Natural Language Processing (NLP) & Large Language Models (LLMs): NLP and LLMs (like GPT-style models) can read and interpret free-text clinical notes, discharge summaries, and physician documentation. They help automate medical code generation, suggest CPT/ICD codes, and ensure claims are built on complete and accurate data, significantly reducing human error and coder fatigue.
2. Machine Learning Predictive Models: These models learn from historical billing and claims data to predict which claims are likely to be denied, and why. They can also flag unusual billing patterns that might indicate fraud, upcoding, or unintentional errors, offering early warnings before issues spiral into costly audits or lost revenue.
3. Robotic Process Automation (RPA): RPA uses bots to handle repetitive, rule-based tasks like checking patient eligibility, updating insurance details, or posting payments. These bots work around the clock, never get tired, and integrate seamlessly with existing EHR and billing systems, freeing up staff for higher-value work.
4. Computer Vision & Optical Character Recognition (OCR): Yes, many healthcare providers still rely on paper forms, faxed referrals, and scanned documents. OCR and computer vision convert these into structured digital data that can be processed by AI tools, enabling faster workflows and fewer transcription errors.
Together, these technologies form the foundation of intelligent, automated RCM, reducing delays, improving accuracy, and helping healthcare organizations get paid faster.
Six High-Impact AI Use Cases in Medical Billing
The complexity of medical billing leaves plenty of room for inefficiencies, errors, and delays. AI doesn’t just improve these processes, it transforms them. Here are six impactful ways AI is redefining how revenue cycle teams operate across hospitals, clinics, and healthcare systems.
1. Automated Medical Coding with NLP & LLMs: Medical coders often navigate thousands of ICD-10, CPT, and HCPCS codes, interpreting physician notes and clinical documentation to assign the correct ones. AI models—powered by Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Large Language Models (LLMs) can now read and understand unstructured text like discharge summaries, operative reports, and physician notes. These tools automatically extract relevant details and suggest the most accurate codes in real-time.
Why It Matters: Manual coding is slow and error-prone. Automating this step leads to fewer mistakes, faster billing cycles, and ensures coders spend less time on routine work and more time on complex cases.
2. Real-Time Claim Scrubbing and Payer Rule Validation: Submitting a clean claim is critical to getting paid on the first try. AI systems can automatically scan claims before submission, checking for issues like missing modifiers, mismatched diagnosis/procedure combinations, outdated codes, or violations of payer-specific rules. These intelligent tools integrate with billing systems to validate documentation in real-time.
Why It Matters: Reducing human oversight in early claim preparation prevents denials and delays. The result? Higher first-pass acceptance rates and fewer appeals or rework cycles.
3. Predictive Denial Management & Root-Cause Analysis: AI-powered predictive analytics engines can analyze years of historical claim data to identify patterns that commonly lead to denials, such as inconsistent documentation, incorrect coding, or insurance eligibility mismatches. These tools flag high-risk claims before submission and offer actionable insights to correct them. Post-denial, AI can also uncover trends by grouping denial reasons, helping RCM teams tackle the root causes.
Why It Matters: By catching issues before claims are rejected, healthcare providers can reduce denial rates, shorten A/R cycles, and increase overall reimbursement.
4. Prior Authorization Automation: Prior authorizations are notorious for slowing down care and overwhelming administrative staff. AI streamlines this process by automatically gathering the required clinical documentation, verifying medical necessity, matching payer-specific criteria, and auto-submitting requests through integrated platforms or clearinghouses. Some advanced systems even track authorization status and trigger alerts for follow-up.
Why It Matters: Speeding up authorizations means fewer scheduling delays, better patient experiences, and less revenue leakage from denied or delayed services.
5. AI-Driven Patient Cost Estimation and Counseling Support: Patients are increasingly responsible for a larger portion of their healthcare bills. AI tools use real-time benefit data, historical pricing, procedure complexity, and insurance contracts to generate highly accurate out-of-pocket estimates. When integrated with front-desk systems, they empower staff to communicate costs, offer payment plans, and initiate financial counseling earlier in the patient journey.
Why It Matters: Improved cost transparency builds trust, encourages timely payments, and enhances patient satisfaction, especially in high-deductible plans or elective procedures.
6. Fraud Detection and Revenue Integrity Monitoring: AI systems trained on large billing datasets can detect patterns that deviate from the norm, like repetitive billing for the same service, inconsistent charge amounts, or unbundled procedures. These systems continuously monitor billing activity and alert compliance teams to potential fraud, abuse, or unintentional coding errors.
Why It Matters: Proactive fraud detection reduces audit risks, protects revenue, and ensures regulatory compliance, while also safeguarding an organization’s reputation.
These six use cases illustrate how AI is not just enhancing existing workflows, but reshaping the very foundation of how revenue cycle management operates. When applied strategically, AI tools can cut costs, improve accuracy, accelerate reimbursement, and ultimately support better healthcare delivery.
Implementation Roadmap
Bringing AI into medical billing isn’t just about plugging in a new tool. It requires a structured, strategic rollout. Here's a high-level roadmap to get started:
1. Data Readiness: AI systems are only as good as the data they’re trained on. Ensure access to clean, structured historical claim and remit data for model training and validation. Remove duplicates, standardize formats, and address missing values to avoid biased outcomes.
2. Integration Layer: Seamless interoperability is key. Build secure connections to your EHR, practice management system, and clearinghouse using APIs, HL7, or FHIR standards. This enables real-time data flow and automates key touchpoints in the billing cycle.
3. Compliance & Governance: Maintain HIPAA compliance, robust audit trails, and AI model explainability. Stakeholders must understand how decisions are made, especially when AI flags claims or suggests code changes.
4. Pilot with Human-in-the-Loop: Start small. Deploy AI in one facility or specialty. Keep human oversight in place and track key KPIs like denial rates, days in A/R, and claim turnaround time to measure impact.
5. Change Management: AI adoption requires buy-in. Provide up-skilling for coders, train physicians on documentation best practices, and clearly communicate how AI supports, not replaces, human expertise.
What’s Next (2025–2027)
The next wave of innovation is set to make medical billing even more intelligent and intuitive. By 2025, Generative AI copilots will be embedded directly into EHR systems, assisting physicians in real time with documentation, coding, and compliance checks. Ambient scribe technology will capture doctor-patient conversations, auto-generate structured notes, and trigger automated coding all at the point of care, drastically reducing administrative burden.
Looking ahead, we’ll see the rise of end-to-end “touchless” claims processing for routine visits, where AI handles everything from eligibility checks to claim submission without human intervention. These advancements promise a future where healthcare professionals can spend less time on paperwork and more time on patient care.
AI is no longer a futuristic concept in healthcare, it’s already transforming the medical billing landscape from the ground up. By automating repetitive tasks, predicting denials, enhancing compliance, and accelerating reimbursement cycles, AI is helping healthcare organizations reclaim lost time, reduce costly errors, and strengthen financial performance.
But successful implementation isn’t just about technology. It requires clean data, thoughtful integration, human oversight, and a culture that embraces innovation. Now is the time for providers to act. Whether you're just starting or scaling AI across facilities, the right strategy today can position your organization for sustainable, tech-driven success tomorrow.
0 notes
Text
My GCSE Predictions
I will come back to this post on results day, and let everyone know how favoured I am by Apollo or not.
English Language, AQA: 7
English Literature, AQA: 6
Maths, Edexcel higher: 8
Physics AQA triple higher: 9
Chemistry AQA triple higher: 7
Biology, AQA triple higher: 6
Computer Science, OCR: 9
Really hope this doesn't jinx anything 😬
History, Edexcel: 8
French, AQA higher: 7
18 notes
·
View notes
Text
What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
Artificial intelligence (AI) is a set of technologies that enable computers to perform a variety of advanced functions, including the ability to see, understand and translate spoken and written language, analyze data, make recommendations, and more.
AI is the backbone of innovation in modern computing, unlocking value for individuals and businesses. For example, optical character recognition (OCR) uses AI to extract text and data from images and documents, turns unstructured content into business-ready structured data, and unlocks valuable insights.
Ready to get started? New customers get $300 in free credits to spend on Google Cloud.
Get started for free
Stay informed
22:54

Introduction to generative AI
Artificial intelligence defined is a field of science concerned with building computers and machines that can reason, learn, and act in such a way that would normally require human intelligence or that involves data whose scale exceeds what humans can analyze.
AI is a broad field that encompasses many different disciplines, including computer science, data analytics and statistics, hardware and software engineering, linguistics, neuroscience, and even philosophy and psychology.
On an operational level for business use, AI is a set of technologies that are based primarily on machine learning and deep learning, used for data analytics, predictions and forecasting, object categorization, natural language processing, recommendations, intelligent data retrieval, and more.
How does AI work?
While the specifics vary across different AI techniques, the core principle revolves around data. AI systems learn and improve through exposure to vast amounts of data, identifying patterns and relationships that humans may miss.
This learning process often involves algorithms, which are sets of rules or instructions that guide the AI's analysis and decision-making. In machine learning, a popular subset of AI, algorithms are trained on labeled or unlabeled data to make predictions or categorize information.
Deep learning, a further specialization, utilizes artificial neural networks with multiple layers to process information, mimicking the structure and function of the human brain. Through continuous learning and adaptation, AI systems become increasingly adept at performing specific tasks, from recognizing images to translating languages and beyond.
Want to learn how to get started with AI? Take the free beginner's introduction to generative AI.
Types of artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence can be organized in several ways, depending on stages of development or actions being performed.
For instance, four stages of AI development are commonly recognized.
Reactive machines: Limited AI that only reacts to different kinds of stimuli based on preprogrammed rules. Does not use memory and thus cannot learn with new data. IBM’s Deep Blue that beat chess champion Garry Kasparov in 1997 was an example of a reactive machine.
Limited memory: Most modern AI is considered to be limited memory. It can use memory to improve over time by being trained with new data, typically through an artificial neural network or other training model. Deep learning, a subset of machine learning, is considered limited memory artificial intelligence.
Theory of mind: Theory of mind AI does not currently exist, but research is ongoing into its possibilities. It describes AI that can emulate the human mind and has decision-making capabilities equal to that of a human, including recognizing and remembering emotions and reacting in social situations as a human would.
Self aware: A step above theory of mind AI, self-aware AI describes a mythical machine that is aware of its own existence and has the intellectual and emotional capab
1 note
·
View note
Text
What Are the Most Popular Azure AI Services?
Azure AI services offer a collection of internet-hosted cognitive intelligence offerings that support programmers and enterprises in building smart, innovative, production-ready, and ethical systems using ready-made and built-in utilities, interfaces, and algorithms.
These offerings aim to assist in upgrading enterprise functions swiftly and develop accountable AI platforms to launch at business pace. Azure AI solutions can be accessed via REST interfaces and programming library SDKs across major coding languages.

Understanding Azure AI Services
Azure AI platforms cover a wide range of resources, environments, and pre-trained networks crafted to support the creation, rollout, and oversight of AI-driven solutions.
These Azure AI services platforms use data science (DS), language comprehension processing, visual computing, and various AI strategies to address intricate company issues and propel digital evolution.
Some Lesser Known Facts About Azure AI
Azure provides 99.9% availability for its services.
Microsoft invests aggressively in cybersecurity; spent $20 billion for more than 5 years and exceeded 8,500 security experts.
Compared to companies that rely on on-premises solutions, Azure cloud users are more than twice as likely to find it easier to innovate with AI and ML: 77% versus only 34%.
Some of the Available Azure AI services
Azure AI provides a range of function-specific services that are designed to meet your business needs and requirements. These services aim to assist businesses in accelerating innovation, boosting user experience and resolving complex challenges with the help of AI. Given below are the popular AI Azure Services. Check them out:
Anomaly Detector
Anomaly Detector works as an Azure cognitive platform which allows programmers to recognize and evaluate and recognize deviations in their sequential data without extensive data science expertise.
This Azure AI services platform delivers a range of endpoints that support both multiple analysis and instantaneous evaluation. The core intelligence networks are configured and adapted utilizing the client’s dataset, allowing the feature to adapt to the specific requirements of their organization.
Azure OpenAI Service
The Azure OpenAI offering represents a revolutionary framework that enables enterprises to utilize the vast capabilities of powerful machine intelligence frameworks for their tailored use cases.
This platform works as an access point to state-of-the-art technologies including Codex, DALL*E, and GPT-3.5, which are leaders in AI breakthroughs.
Through the incorporation of these Azure AI and ML services into organizational processes, enterprises can explore innovative directions for creativity and effective solutions.
Azure AI Vision
Azure AI Vision is one of the Azure AI services that delivers a consolidated platform that supplies cutting-edge functions for interpreting pictures and video files and generating output using the graphical attributes that interest the individual user.
This utility supports reviewing visuals that adhere to certain criteria, such as being formatted in BMP, GIF, JPEG, or PNG, maintaining a size below 4 MB, and featuring dimensions above 50 x 50 pixels.
Azure AI Vision is applicable in areas like spatial insight, optical character recognition (OCR), and image diagnostics.
Azure AI Speech
Azure AI Speech delivers a supervised platform that supplies top-tier audio capabilities including voice-to-text, text-to-audio, audio conversion, and speaker identification.
This Azure AI services platform enables programmers to swiftly craft premium voice-integrated application functions and design personalized digital assistants.
Azure AI Speech includes adaptable models and voice options, and engineers can incorporate chosen terminology into the base lexicon or develop tailored algorithms.
The platform is adaptable and deployable in various environments, including the cloud or on-premises via containers.
Azure AI Speech supports converting recordings in over 100 dialects and styles, extract client feedback with support center transcription, elevate user interaction using speech-powered interfaces, and document vital conversations during sessions.
Azure AI Machine Learning
Azure Machine Learning offers a robust web-based framework for designing, refining, and distributing data science models at scale.
It creates an integrated workspace where analysts and engineers can unite on AI initiatives, streamlining essential phases in the model development journey.
Azure AI Content Moderator
Azure AI Content Moderator delivers an intelligence-powered feature that helps organizations manage input that could be inappropriate, harmful, or unsuitable.
This feature uses automated moderation powered by AI to evaluate language, pictures, and video clips and triggers moderation indicators instantly. It supports embedding moderation logic into software to align with compliance or preserve the right experience for users.
It acts as a broad-ranging tool made to identify unsafe user-submitted and algorithm-generated data within services and digital platforms.
Azure AI Document Intelligence
Azure AI Document Intelligence represents an intelligent information handling platform that utilizes cognitive tools and OCR for fast extraction of content and formatting from files.
This system from the Azure AI services leverages sophisticated learning models to retrieve data, paired fields, structured grids, and layouts from records precisely and efficiently.
Azure AI Document Intelligence transforms static records into actionable inputs and allows teams to prioritize decision-making over information gathering.
The solution enables the creation of smart document workflows, offering flexibility to begin with existing templates or construct personalized models, deployed either locally or using cloud support through the AI Document Intelligence SDK or studio.
Azure AI QnA Maker
QnA Maker is one of the most useful Azure AI services which provides an online-based NLP-driven utility that empowers teams to generate interactive dialogue layers on top of their datasets.
The system is designed to deliver the best-matched response for each prompt from a personalized information base. QnA Maker is frequently applied to develop engaging communication systems like chatbot frameworks, voice-assisted programs, and community platform tools.
It organizes knowledge into question-response datasets and recognizes connections within structured or semi-structured material to establish links among the Q&A records.
Azure AI Personalizer
Azure AI Personalizer is one of the most interesting Azure AI services that offers a smart automation feature that allows systems to make improved choices at scale using reinforcement techniques.
The platform evaluates input regarding the status of the system, use-case, and/or individuals (environments), and a collection of potential selections and linked properties (options) to pick the most suitable action.
User response from the system (rewards) is transmitted to Personalizer to enhance and evolve its choice-making efficiency almost instantly.
It serves as a robust solution for engineers and teams striving to deliver adaptive, tailored interactions per individual. The platform can be engaged using a development kit SDK, RESTful endpoint, or via the Personalizer online dashboard.
Azure AI Metrics Advisor
Azure AI Metrics Advisor functions as a series data inspection tool that delivers a group of endpoints for information input, outlier discovery, and root cause exploration.
This tool automates the method of applying analysis models to data and offers an online-based workspace for feeding, recognizing outliers, and diagnostics without needing expertise in data science.
Metrics Advisor supports the integration and intake of multivariate metric datasets from various storage services, like Azure Blob Storage, MongoDB, SQL Server, and others.
The tool belongs to Azure’s intelligent services and leverages AI capabilities to track information and identify irregular patterns within sequential datasets.
Azure AI Immersive Reader
Azure AI Immersive Reader provides a cognitive capability that assists people in understanding and engaging with content.
The tool boosts interpretation and performance through intelligent algorithms and integrates comprehension and text-reading abilities into digital experiences.
Azure AI Immersive Reader is built upon Azure’s AI layer to streamline the deployment of a smart solution that aids individuals of any demographic or literacy level with reader utilities and components such as voice narration, multilingual translation, and attention aids via visual cues and formatting tools.
What are the benefits of Azure AI Services?
Azure AI services allow businesses and developers to create secure and scalable apps. With the help of pre-built models and flexible deployment options, AI integrates with real-life scenarios seamlessly. Given below are the benefits of AI services by Azure.
Comprehensive Ecosystem
Microsoft Azure AI services deliver a flourishing AI ecosystem so that it meets your diverse business needs.
No matter what features it is; NLP, computer vision, machine learning, speech recognition and so on, Azure offers APIs and pre-built models to integrate with your apps.
Flexibility and Scalability
Scalability is one of its features that makes it the best one in the market. As your company grows, Azure AI services can scale accordingly.
Irrespective of your business size. Azure cloud AI ensures that your resources are allocated as needed.
Boosted Customer Experience
Today, meeting customer demands efficiently has become even more important than before. Azure AI allows businesses to create personalized experiences with the help of sentiment analysis.
By using the insights that AI provides, businesses can create customized offers, deals, and interactions to provide maximum customer satisfaction.
Data-oriented Decision Making
You can get robust data analytics in Azure AI services that assist businesses in making better, more informed choices. Businesses can identify patterns and trends in their data that might otherwise go overlooked by utilizing machine learning.
Greater predicting, more intelligent planning, and better comprehension of the future result from this.
Azure AI helps transform raw data into insightful knowledge that produces tangible outcomes, whether it be forecasting customer demands, optimizing supply chains, or identifying market changes.
Streamlined Business Processes
It also helps streamline a business by automating routine tasks to carry out complicated workflows.
It reduces errors, minimizes human intervention, and frees up human resources so that it can focus on more valuable tasks.
Pricing Benefits of Using Azure AI Services
The pricing policies of Azure are one of the best things about it. Let’s find out how you can save with its pricing models.
Monthly or yearly plans: Some services offer fixed pricing plans. These include a set number of uses each month, and you can pay monthly or yearly. This helps if you want to plan your budget ahead of time.
You are charged for what you use: A lot of Azure's AI services are pay-as-you-go. This implies that you only pay for the services you use, such as the volume of data your app processes or the frequency with which it accesses the service. For apps that don't have a monthly usage cap, this is fantastic.
Free use and free Trials: Microsoft frequently offers a free trial or a restricted period of free use. This enables you to test the services out before you buy them.
Additional fees for personalized AI models: The cost of training your AI model (for instance, with Azure Machine Learning or Custom Vision) is determined by the amount of data you utilize and the amount of processing power required.
Costs of management and storage: Paying for things like data storage and AI system management, particularly if it operates in real-time, may be necessary in addition to the basic service.
Savings and exclusive deals: Azure gives you a discount if you pay in advance, use the service frequently, or are a nonprofit or student. They occasionally provide exclusive discounts as well.
Exchange rates and currency: Microsoft adjusts the prices using the London market currency rate if you aren't paying in US dollars.
Conclusion
Azure AI services embody a dynamic collection of utilities and capabilities that equip engineers and enterprises to utilize the disruptive promise of machine intelligence.
Through a wide selection of ready-to-use frameworks, endpoints, and development kits, Azure AI offerings support the design of smart, scalable products that accelerate digital progress and technological creativity.
From pattern spotting to vision analysis, and voice interaction to language interpretation, Azure AI services span a wide array of functions, establishing it as a full-spectrum ecosystem for intelligence-powered developments.
These features not only speed up building timelines but also reinforce ethical AI usage, helping firms launch tools rapidly while adhering to compliance and responsible guidelines.
Additionally, the provision of Azure AI tools via REST-based services and native SDKs in widely used programming environments ensures straightforward use and seamless connectivity with current pipelines and systems.
To sum up, Azure AI resources go beyond basic technology, they serve as a foundation for crafting smart, visionary systems that reshape our digital interactions.
By adopting these intelligent Azure AI services, professionals and businesses can not only remain pioneers in tech advancement but also help shape a smarter, more equitable digital tomorrow.
If you are looking for these services, you must find the best Azure AI consultant for the premium results.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What are AI services in Azure?
These are a set of Azure products which are used to use AI services easily. Some of the common products may include AI search, Content Safety, Azure OpenAI service, and AI speech.
Q2. Which one is easier to use, Azure AI or AWS?
Azure AI is considered better than AWS when it comes to ease of usability.
Q3. What are Microsoft AI tools?
They are typically a set of apps and services that provide task automation, boosted productivity, and deep insights with the help of AI.
Q4. How is Azure AI Beneficial?
It allows continuous adjustments, updates, application deployments and model programming.
0 notes
Text
Image Processing with Programming

Image processing is a field of computer science that involves manipulating digital images through programming. It’s widely used in applications like facial recognition, medical imaging, autonomous vehicles, and graphic design tools. With just a bit of code, developers can analyze, transform, and enhance images in powerful ways.
What is Image Processing?
Image processing is the technique of performing operations on images to extract information or produce a new version of the image. This can include adjusting brightness, applying filters, detecting edges, or even recognizing objects.
Common Applications of Image Processing
Photo editing software
Face and object detection
Medical image analysis (e.g., X-rays, MRI scans)
Traffic and surveillance systems
Autonomous vehicle navigation
Optical character recognition (OCR)
Popular Programming Languages for Image Processing
Python: Most popular due to libraries like OpenCV, Pillow, and scikit-image.
Java: Used in Android development and JavaCV.
C++: Offers speed and is widely used with OpenCV.
MATLAB: Preferred in academia and research for prototyping.
Key Libraries and Tools
OpenCV: Open-source computer vision library with support for real-time processing.
Pillow (PIL): Python Imaging Library, great for basic image manipulation.
scikit-image: Image processing module for SciPy in Python.
Tesseract: Optical character recognition engine.
Basic Image Processing Operations
Reading and displaying images
Resizing and cropping
Color adjustments (brightness, contrast, etc.)
Blurring and sharpening
Edge detection and filtering
Image transformation (rotate, flip, etc.)
Sample Code in Python Using OpenCV
import cv2 # Load an image image = cv2.imread('example.jpg') # Convert to grayscale gray = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) # Apply Gaussian blur blurred = cv2.GaussianBlur(gray, (5, 5), 0) # Edge detection edges = cv2.Canny(blurred, 50, 150) # Show the result cv2.imshow('Edges', edges) cv2.waitKey(0) cv2.destroyAllWindows()
Advanced Topics
Feature detection: Detecting faces, eyes, or corners in images.
Image segmentation: Dividing an image into parts or objects.
Machine learning with images: Classifying and recognizing objects using AI.
Augmented Reality (AR): Overlaying digital content on real-world images.
Best Practices
Use high-resolution images for better analysis.
Understand the color space (RGB, HSV, Grayscale) of your images.
Pre-process images to remove noise before applying complex algorithms.
Test algorithms on multiple image datasets for accuracy.
Conclusion
Image processing with programming opens up countless possibilities in software development, AI, and beyond. With tools like OpenCV and Python, even beginners can start building projects involving image analysis, transformation, and recognition. Dive in, experiment, and bring your visual ideas to life!
0 notes
Text
Custom AI Development Services - Grow Your Business Potential

AI Development Company
As a reputable Artificial Intelligence Development Company, Bizvertex provides creative AI Development Solutions for organizations using our experience in AI app development. Our expert AI developers provide customized solutions to meet the specific needs of various sectors, such as intelligent chatbots, predictive analytics, and machine learning algorithms. Our custom AI development services are intended to empower your organization and produce meaningful results as it embarks on its digital transformation path.
AI Development Services That We Offer
Our AI development services are known to unlock the potential of vast amounts of data for driving tangible business results. Being a well-established AI solution provider, we specialize in leveraging the power of AI to transform raw data into actionable insights, paving the way for operational efficiency and enhanced decision-making. Here are our reliably intelligent AI Services that we convert your vision into reality.
Generative AI
Smart AI Assistants and Chatbot
AI/ML Strategy Consulting
AI Chatbot Development
PoC and MVP Development
Recommendation Engines
AI Security
AI Design
AIOps
AI-as-a-Service
Automation Solutions
Predictive Modeling
Data Science Consulting
Unlock Strategic Growth for Your Business With Our AI Know-how
Machine Learning
We use machine learning methods to enable sophisticated data analysis and prediction capabilities. This enables us to create solutions such as recommendation engines and predictive maintenance tools.
Deep Learning
We use deep learning techniques to develop effective solutions for complex data analysis tasks like sentiment analysis and language translation.
Predictive Analytics
We use statistical algorithms and machine learning approaches to create solutions that predict future trends and behaviours, allowing organisations to make informed strategic decisions.
Natural Language Processing
Our NLP knowledge enables us to create sentiment analysis, language translation, and other systems that efficiently process and analyse human language data.
Data Science
Bizvertex's data science skills include data cleansing, analysis, and interpretation, resulting in significant insights that drive informed decision-making and corporate strategy.
Computer Vision
Our computer vision expertise enables the extraction, analysis, and comprehension of visual information from photos or videos, which powers a wide range of applications across industries.
Industries Where Our AI Development Services Excel
Healthcare
Banking and Finance
Restaurant
eCommerce
Supply Chain and Logistics
Insurance
Social Networking
Games and Sports
Travel
Aviation
Real Estate
Education
On-Demand
Entertainment
Government
Agriculture
Manufacturing
Automotive
AI Models We Have Expertise In
GPT-4o
Llama-3
PaLM-2
Claude
DALL.E 2
Whisper
Stable Diffusion
Phi-2
Google Gemini
Vicuna
Mistral
Bloom-560m
Custom Artificial Intelligence Solutions That We Offer
We specialise in designing innovative artificial intelligence (AI) solutions that are tailored to your specific business objectives. We provide the following solutions.
Personlization
Enhanced Security
Optimized Operations
Decision Support Systems
Product Development
Tech Stack That We Using For AI Development
Languages
Scala
Java
Golang
Python
C++
Mobility
Android
iOS
Cross Platform
Python
Windows
Frameworks
Node JS
Angular JS
Vue.JS
React JS
Cloud
AWS
Microsoft Azure
Google Cloud
Thing Worx
C++
SDK
Kotlin
Ionic
Xamarin
React Native
Hardware
Raspberry
Arduino
BeagleBone
OCR
Tesseract
TensorFlow
Copyfish
ABBYY Finereader
OCR.Space
Go
Data
Apache Hadoop
Apache Kafka
OpenTSDB
Elasticsearch
NLP
Wit.ai
Dialogflow
Amazon Lex
Luis
Watson Assistant
Why Choose Bizvertex for AI Development?
Bizvertex the leading AI Development Company that provides unique AI solutions to help businesses increase their performance and efficiency by automating business processes. We provide future-proof AI solutions and fine-tuned AI models that are tailored to your specific business objectives, allowing you to accelerate AI adoption while lowering ongoing tuning expenses.
As a leading AI solutions provider, our major objective is to fulfill our customers' business visions through cutting-edge AI services tailored to a variety of business specializations. Hire AI developers from Bizvertex, which provides turnkey AI solutions and better ideas for your business challenges.
#AI Development#AI Development Services#Custom AI Development Services#AI Development Company#AI Development Service Provider#AI Development Solutions
0 notes