#OpenWrt as firewall
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
youtube
How to configure OpenWrt as Firewall for your home network and Guest Wifi and IPTables explained
Guest Wifi in your home network can easily be done with OpenWrt. How to configure OpenWrt as Firewall, how to build a firewall for your home network, How to make a Guest Wifi and a separate IOT Wifi and Firewall zone ? IPTables are explained in the middle part.
#openwrt#open source#free education#IPTables explained#router#education#educate yourselves#hacking#educate yourself#tips and tricks#OpenWrt as firewall#cyber security#computer security#data security#computer tips#tips and techniques#Youtube
1 note
·
View note
Text
Micro Appliance: Ratgeber für Hardware und Software 2023
Eine Micro Appliance ist eine kleine Hardwareplattform, die für bestimmte Aufgaben innerhalb der Netzwerkinfrastruktur entwickelt und eingesetzt wird. Die häufig nur handgroßen Systeme, erfreuen sich aufgrund ihrer hohen Energieeffizienz...[Weiterlesen]
0 notes
Text
GL.iNet Wireless Routers: Revolutionizing Home and Business Networks
1. Introduction to GL.iNet Wireless Routers
In today's world, where connectivity is more important than ever, a reliable wireless router is essential. GL.iNet routers have emerged as an innovative solution for both home and business networking needs. Known for their cutting-edge technology, these routers provide high-performance, security, and customizable features. GL.iNet has consistently aimed to meet the growing demand for seamless internet experiences across various devices. Whether you're streaming movies, working remotely, or running a business, a GL.iNet router ensures stable and secure connections. In a crowded market full of generic routers, GL.iNet stands out by offering powerful devices that are easy to use yet highly customizable. This brand is especially popular among tech enthusiasts and those looking for open-source options. By offering firmware compatibility with OpenWRT, GL.iNet opens the door to advanced configurations, making it an excellent choice for people who want more control over their network settings.

2. Features and Benefits of GL.iNet Routers
GL.iNet routers are packed with features that make them stand out from the competition. One of the key aspects is the support for OpenWRT firmware, which allows users to tailor the router’s functions to their specific needs. This opens up a world of possibilities for network administration, from installing custom applications to optimizing the network for specific tasks. Another major benefit is their emphasis on security. With built-in VPN support, users can easily protect their online activity and ensure their connection remains private. This is crucial in today’s digital age, where data breaches and cyber threats are more common than ever. Furthermore, GL.iNet routers offer exceptional ease of use, even for beginners. The user-friendly interface makes setting up the router and managing your network a hassle-free experience. With multiple connectivity options, including dual-band Wi-Fi, Ethernet ports, and USB support, GL.iNet routers offer the flexibility to handle a wide range of devices and network demands.
3. OpenWRT and Customization
One of the most significant advantages of GL.iNet wireless routers is their support for OpenWRT, an open-source firmware that allows users to customize their routers in ways that most standard consumer routers do not. OpenWRT opens up a range of advanced features and settings, from improving network performance to adding new capabilities. Users can tweak settings related to the router’s wireless performance, security protocols, and bandwidth management, enabling them to fine-tune the router to meet specific needs. For tech-savvy individuals and network professionals, this level of customization is a major draw. With OpenWRT, you can install third-party apps, create secure VPN tunnels, set up advanced firewalls, and optimize routing protocols, all of which can significantly enhance your network's efficiency and security. The ability to modify the firmware and settings gives users the power to turn their GL.iNet router into a tailored networking solution that works perfectly for them.
4. Security and Privacy Features
When it comes to protecting your data online, security is a top priority, and GL.iNet routers take this seriously. These routers come with integrated VPN support, which ensures that your online activities remain private and secure. Whether you're browsing, streaming, or working from home, a VPN encrypts your connection, protecting it from hackers and prying eyes. This is particularly beneficial for users who handle sensitive information or frequently use public Wi-Fi networks, which are notorious for being less secure. Additionally, GL.iNet routers come with pre-configured security settings, including WPA3 encryption, ensuring that your network is protected from unauthorized access. Advanced firewall features and content filtering also provide an extra layer of defense, allowing you to control what traffic enters or exits your network. For those who value their online privacy, these routers provide the tools needed to ensure that their personal information remains safe and that their browsing activity stays private.
5. Versatility for Home and Business Use
GL.iNet routers are designed to cater to both home users and businesses, offering features that appeal to both groups. For home users, these routers provide stable, high-speed connections for streaming, gaming, and browsing. They are also ideal for those who need to set up secure networks for IoT devices, such as smart home appliances. The ability to configure the router for specific needs, such as creating a guest network or limiting bandwidth for certain devices, makes GL.iNet an excellent choice for home users looking for flexibility and control. On the business side, these routers can handle larger workloads, supporting multiple devices and ensuring high uptime. Features like VPN support and the ability to set up multiple network segments allow businesses to create secure and isolated networks, which is essential for protecting company data. Whether for personal or business use, GL.iNet routers provide a versatile, powerful networking solution that delivers both performance and security.
6. Easy Setup and User-Friendly Interface
One of the reasons GL.iNet routers are so popular is their ease of use. Setting up a new router can be a daunting task for those unfamiliar with networking, but GL.iNet has simplified this process. The routers come with a quick start guide, and the setup interface is intuitive, making it easy for anyone to get their network up and running in no time. The user-friendly web interface allows for easy navigation, where users can adjust settings, monitor network activity, and configure VPN connections without having to dive into complicated technical jargon. The mobile app also offers a simple way to manage your router on the go, providing a convenient solution for those who prefer to control their network from their smartphones or tablets. With these user-centric features, GL.iNet ensures that even those without technical expertise can easily manage their network while enjoying advanced features.
7. Performance and Speed
When it comes to wireless routers, speed and performance are crucial factors. GL.iNet routers offer impressive speeds and reliable performance across multiple devices, making them ideal for households or offices with high-bandwidth needs. The dual-band support provides faster speeds by allowing devices to connect to either the 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz band, depending on their needs. The 5 GHz band offers higher speeds and less interference, making it perfect for high-demand activities like streaming HD videos or online gaming. Furthermore, GL.iNet routers come with high-quality antennas that help enhance signal range and stability. Whether you're in a large house or a small apartment, you can count on consistent and fast connectivity. For businesses, this means that the router can handle multiple devices and users simultaneously without sacrificing speed, ensuring that operations run smoothly without interruptions. In a world where reliable internet speed is a must, GL.iNet routers deliver impressive performance for various use cases.
youtube
8. Conclusion: Why Choose GL.iNet Routers?
GL.iNet wireless routers represent an excellent choice for those seeking high-performance, secure, and customizable networking solutions. Whether you are a home user who values easy setup and reliable connectivity or a business professional who needs advanced security features and flexibility, GL.iNet offers a range of routers that cater to your needs. The support for OpenWRT firmware opens up countless customization options, while the built-in VPN, firewall, and encryption features ensure that your network is protected. Their versatile designs allow for both personal and professional use, and the user-friendly interface makes setup and management a breeze. With fast speeds, strong signal range, and dependable performance, GL.iNet routers are an investment in your network's future. For anyone looking to elevate their internet experience, GL.iNet offers an affordable, efficient, and feature-packed option.
0 notes
Text
Guide to building Software routers and IP Proxies: Improving the efficiency of network operations
With the growing demand for Internet, the concept of Software router is becoming familiar to the public. For individuals, businesses or technology enthusiasts, Software router not only provides highly flexible network management, but also allows users to realize more complex network operations by configuring Proxies IP. It transforms into a powerful router through a software-defined router system, typically used on low-power computing devices such as a Raspberry Pi or a mini-PC running Linux, with the addition of specific router software (e.g. OpenWRT, LEDE, etc.).
In this article, I'll provide a comprehensive introduction to Software routers, discuss how to improve network efficiency through Soft Routing with Proxies IP, and provide concrete steps to follow.
What is a Software router?
Software routers and hard routes are two common routing methods used in current network architectures. First of all, before we figure out Software router, we need to understand what is hard routing?
What is hard routing?

Introduction to Software router?
From the official definition, Software router is actually a router solution through desktop or server with corresponding software. Users can choose the operating system and hardware devices according to their needs, and can even set up and optimize them to achieve some advanced functions.
Compared to hard routing, Software router is a more flexible and powerful routing solution. The concept of Software router is to use desktops, servers or virtual machines as hardware carriers and utilize a specific software system to realize the routing function. The most important feature of Software router is that its software and hardware are completely independent and separate.

The core components of a Software router include: a system, a network card, and a proxy service or firewall. At least two of these network cards are required, one for connecting to the external network (WAN) and the other for managing the internal network (LAN). Advanced users can also use multiple network ports for features such as broadband aggregation.
What are the advantages of Software router?
Software routers have several significant advantages over hard routes:
Flexibility: Software router does not depend on a specific device and users can choose to run it on any supported device, including desktops, servers, and even virtual machines. By choosing different operating systems and software packages, users can adapt the router's functionality to their needs.
Feature-rich: Software router is not only limited to basic Internet access functions, it can also realize traffic management, QoS (quality of service control), VLAN (virtual LAN) and other advanced functions. Users can customize various routing policies to achieve more complex network management needs.
High scalability: Since Software router relies on software to realize its functions, users can constantly expand its functions by upgrading software or adding plug-ins. For example, adding services such as ad blocking, firewall, Proxies, etc. can be realized by simply installing the corresponding software packages on the Software router.
Hardware selection for Software router
While Software routers are highly flexible, it is also important to choose the right hardware device in order to run stably for a long period of time:
Low Power Consumption: Software router needs to run for a long time, the host with power consumption under 20W is more energy efficient and suitable for long-term use.
Multi-port support: If bandwidth aggregation is required, choose a device with multiple ports to enhance network speed.
Compact size: The device should be small enough to be easily placed in the home or office without taking up space.
USB interface: convenient for external large-capacity hard disk, suitable for home server.
Gigabit/2.5G ports: Prepare for future network upgrades and adapt to higher bandwidth demands.
Construction diagram of a Software router
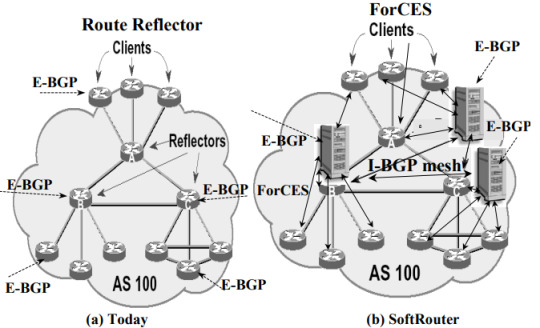
What can I do with a Software router?
With Software router, users can achieve a variety of network functions, it can optimize network performance and traffic management, multiple broadband aggregation, firewall and network security management, advertisement blocking and web filtering, self-built home cloud servers, remote control and monitoring network, Proxies IP setup and management, virtual local area network (VLAN) segmentation, customized routing policies, and so on and so forth.
Especially when used in combination with Proxies IP, it can significantly enhance network flexibility and security. First, Software router enables users to flexibly configure complex network policies, such as traffic management and access control, to ensure rational allocation of network resources. Users can set traffic limits for different devices and optimize bandwidth utilization to ensure smooth operation of critical applications.
With Software routers, users can easily use Proxy IPs to hide their real IP addresses, reducing the risk of being traced, ensuring secure access to websites and avoiding information leakage. In addition, Proxy IPs can also improve access speeds, as Proxy Services can provide faster response times in some cases.
Combined with Proxy IPs, Software router users are able to flexibly configure multiple proxy connections and choose different Proxies to fulfill different usage scenarios, such as Web Crawling, Web Scraping or Market Research. This flexibility enables users to achieve higher efficiency and success rates when dealing with diverse network tasks.
Software routers are also quite scalable, allowing users to enhance the security of their network through plug-ins or additional configurations, such as adding firewalls and intrusion detection systems. Even when using Proxy IP for network activities, users are still able to maintain a high level of security protection and effectively avoid potential Secure Proxy threats. Overall, the combination of Software router and Proxy IP provides users with a more Secure Proxy and efficient Porfiles. Here I focus on how to use Software router to configure Proxies IP.
Proxies IP Introduction
Proxies IPs are intermediate servers that allow users to perform network operations through another IP address. Using Proxies IPs can hide real IP addresses, break through certain geographic restrictions, enhance privacy, and prevent IP blocking by certain websites. There are many types of Proxies, including Static Residential Proxies, Rotating Residential Proxies, and more.
Static Residential IP: unchanged for a long period of time, suitable for operations that require a stable connection.
Rotating Residential IP: The IP address changes periodically, suitable for scenarios that require random IP switching.
Advantages of Software routers with Proxies
When Software router is used in combination with Proxies IP, the flexibility and controllability of network operation will be greatly improved. This combination is suitable for a variety of application scenarios, especially when frequent IP switching or batch network operations are required, and has significant advantages.
1. Fine-grained control of network traffic
Software router allows users to precisely manage and control traffic. By pairing Proxy IPs, users can assign different network requests to different Proxy Services. For example, certain requests can be sent through a residential IP while other sensitive operations are performed through a Rotating IP. This enhances privacy while ensuring the stability of the network connection.
2. Automated Proxies switching
The power of Software router lies in its programmability, which allows users to write scripts or use existing plug-ins to switch Proxies IPs automatically.This is especially important for those who need to operate in bulk or visit multiple websites. For example, by automatically rotating IPs with Software router, you can effectively avoid the same IP being blocked or flagged as abnormal behavior by multiple websites.
3. Enhancing privacy and security
Software router itself can provide additional Secure Proxies through its firewall function, while Proxy IP further enhances network privacy. When combining the two, users can not only hide their real IPs, but also realize multiple levels of Secure Proxies through Proxies Chaining (chained proxies) to prevent traffic from being traced or monitored.
5. Improving marketing and data collection efficiency
In e-commerce, advertising, market research and other scenarios, batch operation is a common demand. With Software router combined with Proxies IP, users can automate data crawling through different IP addresses to avoid being blocked due to excessive access from a single IP address. This approach not only improves operational efficiency, but also significantly reduces the risk of account blocking.
Software router configuration Proxies IP implementations
Step 1: Install the Software router operating system
First, choose a device that can run stably as a Software router server, such as an old computer with strong performance, a mini-server, or a dedicated Software router device (e.g., a host with x86 architecture). Make sure the device has at least two network cards, one connecting to the external network (WAN) and the other for the internal network (LAN).
Download and install the Software router system:
OpenWRT: Lightweight and suitable for a wide range of hardware devices.
pfSense: full-featured and suitable for users who need more advanced features.
MikroTik: Powerful and flexible, but requires a bit of a learning curve.
Take OpenWRTas an example, the download and installation steps are as follows:
Visit the official OpenWRT website to download the image file for your device architecture.
Use a USB utility (e.g. Rufus) to write the image to a USB flash drive, then plug it into the Software router device, go into the BIOS to set up booting from the USB flash drive and install the system.
Basic network configuration:
Enter the Web management interface of the Software router (usually accessed through the intranet IP address, initially set to 192.168.1.1).
Configure the WAN port to connect to the Internet and ensure that the LAN port can assign IP addresses to internal devices.
Verify that the network connection is working properly: use intranet devices to access the Internet and ensure that basic network functions are working well.
Step 2: Configure Proxies IPs
Configuring Proxy IP is the core step to realize the combination of Software router and Proxy service. The following is the detailed Proxies IP configuration process, specifically OpenWRT as an example for illustration, other Software router operating systems such as pfSense and MikroTik operation is similar.
Get Proxy IP service information: Get Proxies information through Proxy IP service provider (e.g. Proxy4Free.com).
Install Proxies Plug-ins (e.g. Shadowsocks, Privoxy, etc.): On the Software router, install the relevant Proxies plug-ins via the package manager (opkg). For example, Shadowsocks can handle multiple Proxies.
Install the Shadowsocks client on OpenWRT:
In the web management interface, go to "System" -> "Software" and click on "Update lists ".
Search for "shadowsocks", select and install the shadowsocks-libev package.
Once the installation is complete, go to "Services" -> "Shadowsocks" and start configuring Proxies.
Configure Proxies IP:
Go to the Shadowsocks configuration page and click "Add new instance".
Basic settings:
Server: Enter the IP address of the Proxies you obtained from your proxy service provider.
Port: Enter the port number provided by the Proxies service provider.
Password: Enter the Proxies account password (if any).
Encryption Method: Select the encryption protocol recommended by the Proxies service provider (usually aes-256-gcm, etc.).
Advanced Settings(optional):
Setting Multi-Proxies Policy: If there are multiple Proxies IPs to choose from, you can assign different Proxies IPs to different devices and applications.
Save and apply the settings.
Configure routing rules:
In the web management interface of Software router, go to "Network" -> "Firewall" -> "Traffic Rules". Rules".
Create a new rule to forward specific traffic (e.g. HTTP, HTTPS traffic) through Proxies IP. Traffic rules can be customized for different device or application types.
If you need to use Proxies for specific external websites or destination IPs, you can set up IP-based routing policies in the Routing section to forward these specific traffic through the Proxy IP.
Verify the Proxies configuration:
After the configuration is complete, open a device connected to the Software router and visit the IP address lookup website to see if the IP currently in use is a Proxies IP.
Check that the Proxy Service is working properly to ensure that traffic is passing through the proxy server correctly.
Step 3: Implement automated switching of Proxies IPs
Sometimes, users may need to switch Proxies IPs automatically, especially for batch operations or to avoid website blocking. Software router supports automated switching of Proxies IP through scripts or plug-ins. Here is how to realize this function in OpenWRT.
Install the cron timed task plugin:
Go to "System" -> "Software" and search for and install the cron plugin.
cron allows you to create timed tasks that can switch Proxies IPs periodically.
Write switching scripts:
Connect to the Software router using SSH and edit the script file (e.g. /etc/proxy-switch.sh) which will operate by modifying the Proxies settings or switching between different Proxies IPs.#!/bin/sh # Switch Proxies IP ifconfig eth0 down # Modify Proxies settings uci set shadowsocks.server='New Proxies IP' uci commit shadowsocks etc/init.d/shadowsocks restart ifconfig eth0 up
Set up timed tasks:
Ensure that Proxies IPs are switched on a regular basis by running scripts on a regular basis via a cron task.
Go to "System" -> "Scheduled Tasks" and add the following timed task
0 * * * * * /etc/proxy-switch.sh
The task will be automatically executed every hour, switching Proxies.
Test automated switching functions:
Wait for the timed task to execute and verify that the Proxies IPs are automatically switched as expected. You can check the current IP address by visiting the IP Lookup website or other extranet services.
Suppose you want to perform batch operations or data capture on an e-commerce platform, by using a combination of Software routers and Proxies IP, you can easily automate the following tasks:
1. Create and manage multiple accounts in bulk:

Conclusion
To summarize, the combination of Software router and Proxies IP provides users with great flexibility and privacy protection. Whether you are conducting e-commerce operations, social media management, or data crawling and market analysis, this solution can significantly improve your operational efficiency and reduce risks.
Overall, by utilizing a combination of Software routers and Proxies IP, you can do all kinds of network operations more easily, protect your privacy, and improve your work efficiency at the same time.
0 notes
Text
how to block vpn on router
🔒🌍✨ Ganhe 3 Meses de VPN GRÁTIS - Acesso à Internet Seguro e Privado em Todo o Mundo! Clique Aqui ✨🌍🔒
how to block vpn on router
Configurações de VPN no roteador
Uma VPN (Rede Virtual Privada) é uma ferramenta essencial para garantir a segurança e privacidade dos dados transmitidos pela internet. Configurar uma VPN no roteador é uma maneira eficaz de proteger todos os dispositivos conectados à rede local.
Para configurar uma VPN no roteador, é necessário primeiro escolher um serviço de VPN confiável e compatível com roteadores. Em seguida, acessando as configurações do roteador através do navegador web digitando o endereço IP do roteador, é possível configurar a VPN seguindo as instruções fornecidas pelo provedor de serviços VPN.
É importante ressaltar que nem todos os roteadores suportam nativamente a configuração de VPN. Nesses casos, pode ser necessário utilizar um firmware alternativo, como o DD-WRT ou OpenWRT, que permitem uma maior customização das configurações do roteador, incluindo a configuração de VPN.
Ao configurar uma VPN no roteador, todos os dados transmitidos pela rede local serão criptografados, garantindo a privacidade das comunicações. Além disso, uma VPN no roteador permite acessar conteúdos geograficamente restritos, proteger dispositivos IoT (Internet das Coisas) e manter-se anônimo enquanto navega na internet.
Em resumo, configurar uma VPN no roteador é uma medida importante para proteger a segurança e privacidade das informações pessoais e profissionais transmitidas pela rede local. Certifique-se de escolher um serviço de VPN confiável e seguir corretamente as instruções de configuração para desfrutar de uma navegação segura e privada.
Restrição de VPN no roteador
Uma restrição de VPN no roteador é uma configuração que limita ou bloqueia o uso de serviços de redes privadas virtuais (VPNs) em dispositivos conectados à rede doméstica. Isso pode ser feito por diversos motivos, como preocupações com segurança, políticas de uso da rede ou restrições geográficas.
Ao restringir o uso de VPNs no roteador, os administradores da rede podem controlar quais dispositivos têm permissão para se conectar a servidores VPN externos. Isso pode ser útil em ambientes corporativos, onde a segurança da rede é uma prioridade, ou em residências, para impedir o acesso a conteúdos restritos por região.
Existem diferentes maneiras de implementar a restrição de VPN no roteador, como bloquear portas específicas usadas pelas conexões VPN ou utilizar listas de permissão para autorizar apenas determinados dispositivos a utilizarem VPNs.
É importante notar que a restrição de VPN no roteador pode afetar a privacidade e a liberdade dos usuários, especialmente em países onde o acesso à internet é restrito. Por outro lado, em ambientes corporativos, essa medida pode ser necessária para proteger informações confidenciais e garantir a integridade da rede.
Em resumo, a restrição de VPN no roteador é uma medida que pode ser útil em determinadas situações, mas é importante avaliar os prós e contras antes de implementá-la em sua rede doméstica ou corporativa.
Bloquear acesso VPN no roteador
Bloquear o acesso VPN no roteador é uma medida importante para manter a segurança da rede e impedir o acesso não autorizado. Uma rede privada virtual (VPN) é comumente usada para garantir a privacidade e a segurança dos dados ao navegar na internet. No entanto, em certos casos, pode ser necessário bloquear o acesso VPN no roteador, seja para restringir o uso da VPN a determinados dispositivos ou para evitar atividades suspeitas.
Para bloquear o acesso VPN no roteador, é possível utilizar diferentes métodos, dependendo da marca e do modelo do dispositivo. Uma opção é acessar as configurações do roteador por meio do navegador da web digitando o endereço IP na barra de endereços. Dentro das configurações, é possível procurar por opções de controle de acesso, firewall ou VPN, onde será possível bloquear o acesso à VPN.
Além disso, algumas opções avançadas de roteadores permitem criar regras específicas para bloquear o tráfego de VPN com base em endereços IP, protocolos ou portas. Essas configurações avançadas podem exigir conhecimentos técnicos mais especializados, sendo recomendável consultar o manual do roteador ou buscar ajuda de um profissional de TI.
Ao bloquear o acesso VPN no roteador, é importante lembrar de atualizar regularmente as configurações de segurança e monitorar o tráfego da rede para identificar possíveis irregularidades. Dessa forma, é possível garantir a integridade da rede e proteger os dados dos usuários contra possíveis ameaças cibernéticas.
Segurança de roteador contra VPN
A segurança dos roteadores contra VPN é uma preocupação crescente no mundo digital de hoje. Com o aumento do uso de redes privadas virtuais (VPNs) para proteger a privacidade e a segurança online, é crucial garantir que os roteadores estejam adequadamente protegidos contra possíveis ameaças.
Existem várias medidas que podem ser tomadas para garantir a segurança dos roteadores contra VPN. Uma delas é manter o firmware do roteador sempre atualizado. As atualizações de firmware frequentes são essenciais para corrigir vulnerabilidades de segurança e garantir que o roteador esteja protegido contra as últimas ameaças.
Além disso, é importante definir senhas fortes e exclusivas para o roteador e a conexão VPN. Senhas fracas são um convite para hackers e cibercriminosos acessarem a rede e comprometerem a segurança dos dados. Usar uma combinação de letras, números e caracteres especiais pode ajudar a fortalecer a segurança da conexão.
Outra medida importante é desativar o acesso remoto ao roteador, a menos que seja absolutamente necessário. O acesso remoto pode ser uma porta de entrada para invasores mal-intencionados, portanto, desativá-lo pode ajudar a proteger a rede contra ataques.
Em resumo, garantir a segurança dos roteadores contra VPN é essencial para proteger a privacidade e a segurança online. Ao tomar medidas proativas, como manter o firmware atualizado, usar senhas fortes e desativar o acesso remoto, os usuários podem desfrutar de uma conexão VPN segura e protegida.
Limitar uso de VPN no roteador
Limitar o uso de VPN no roteador é uma prática importante para garantir a segurança e a integridade da rede doméstica ou corporativa. As VPNs são frequentemente utilizadas para proteger a privacidade e a comunicação online, criptografando os dados e mascarando o endereço IP do usuário. No entanto, em certos contextos, o uso excessivo ou inadequado de VPNs pode representar um risco à segurança da rede.
Limitar o uso de VPN no roteador pode ser feito de várias maneiras. Uma opção é configurar regras no firewall do roteador para bloquear ou permitir o tráfego de VPN com base em endereços IP específicos. Além disso, é possível implementar políticas de segurança de rede que restrinjam o acesso a serviços de VPN não autorizados.
Ao restringir o uso de VPN no roteador, os administradores de rede podem ter um maior controle sobre quem está acessando a rede e como estão utilizando os recursos disponíveis. Isso é especialmente importante em ambientes corporativos, onde a segurança da informação e a conformidade com regulamentos são fundamentais.
Em resumo, limitar o uso de VPN no roteador pode contribuir significativamente para a proteção da rede contra potenciais vulnerabilidades e ataques cibernéticos. É essencial adotar uma abordagem proativa em relação à segurança cibernética e implementar medidas adequadas para garantir a integridade e a confiabilidade da rede.
0 notes
Text
does bridge mode vpn
🔒🌍✨ Get 3 Months FREE VPN - Secure & Private Internet Access Worldwide! Click Here ✨🌍🔒
does bridge mode vpn
Bridge mode VPN setup
Bridge mode VPN setup is a powerful solution for those seeking to enhance their network security and privacy. By configuring your VPN in bridge mode, you can create a seamless and secure connection between two or more networks, allowing for the transfer of data without the need for complicated routing or subnet configurations.
To set up a bridge mode VPN, you'll need compatible hardware and software. First, ensure that your VPN provider supports bridge mode connections and offers the necessary setup instructions. Then, acquire a router or firewall device capable of bridging VPN connections. Popular options include pfSense, OpenWRT, and DD-WRT.
Once you have the required hardware, follow these general steps to configure your bridge mode VPN:
Access your router or firewall's administration interface and navigate to the VPN settings.
Configure the VPN connection with the desired protocol (e.g., OpenVPN, IPSec) and authentication method.
Enable bridge mode or bridge mode support, depending on your device's terminology.
Specify the network interfaces that will participate in the bridge, typically the LAN and WAN interfaces.
Enter the necessary VPN server information provided by your VPN provider, such as server IP address, authentication credentials, and encryption settings.
Save your settings and establish the VPN connection.
Once your bridge mode VPN is set up, all network traffic between the bridged interfaces will be encrypted and routed through the VPN tunnel. This ensures that data transmitted between networks remains secure and private, protecting sensitive information from interception or monitoring by unauthorized parties.
In conclusion, configuring a bridge mode VPN is an effective way to enhance network security and privacy by creating a secure connection between multiple networks. With the right hardware and configuration, you can enjoy the benefits of encrypted communication without the hassle of complex routing setups.
VPN in bridge mode
VPN in bridge mode is a configuration that allows a Virtual Private Network (VPN) to operate seamlessly with a network bridge. This setup is particularly useful for extending a VPN network to include devices that are connected to the bridge.
In bridge mode, the VPN functions as a secure and encrypted tunnel that connects two separate networks together, while the bridge acts as a connector that joins different network segments. By combining these two elements, users can enjoy the benefits of a VPN while maintaining the flexibility and scalability of a bridge network.
One of the key advantages of using a VPN in bridge mode is the ability to secure communication between devices on different network segments. This is especially important in scenarios where sensitive data needs to be transmitted securely between devices located in separate physical locations.
Additionally, VPN in bridge mode allows for more efficient use of network resources by reducing the need for complex routing configurations. It simplifies network management and can improve overall network performance.
It's worth noting that implementing VPN in bridge mode requires careful configuration to ensure compatibility and security. Users should follow best practices and consult with networking professionals to set up the VPN and bridge components correctly.
In conclusion, VPN in bridge mode offers a powerful solution for extending VPN networks across multiple network segments. By combining the security benefits of a VPN with the connectivity of a bridge network, users can enjoy seamless and protected communication between devices in different locations.
Benefits of bridge mode VPN
Bridge mode VPNs offer several advantages for users seeking enhanced privacy, security, and flexibility in their online activities. By understanding the benefits of utilizing bridge mode VPNs, individuals can make informed decisions about their digital security measures.
Firstly, bridge mode VPNs provide heightened privacy by effectively masking users' IP addresses and encrypting their internet traffic. This encryption ensures that sensitive information remains protected from potential cyber threats, including hackers, identity thieves, and government surveillance. With bridge mode VPNs, users can browse the web, access online services, and communicate with others without compromising their privacy.
Secondly, bridge mode VPNs enable users to bypass geographic restrictions and access region-locked content. Whether streaming movies and TV shows, accessing restricted websites, or playing region-specific online games, bridge mode VPNs allow individuals to enjoy unrestricted access to online content from anywhere in the world. This feature is particularly beneficial for travelers, expatriates, and individuals living in countries with strict internet censorship laws.
Moreover, bridge mode VPNs offer enhanced security for devices connected to public Wi-Fi networks. These networks are notorious for their vulnerability to cyber attacks, making them prime targets for hackers seeking to intercept sensitive data. By using a bridge mode VPN, users can create a secure, encrypted connection to the internet, safeguarding their personal information and preventing unauthorized access to their devices.
Additionally, bridge mode VPNs support a wide range of devices and operating systems, including computers, smartphones, tablets, routers, and smart TVs. This compatibility ensures that users can protect all their internet-connected devices with a single VPN solution, simplifying the management of their digital security measures.
In conclusion, bridge mode VPNs offer numerous benefits, including enhanced privacy, access to region-locked content, improved security on public Wi-Fi networks, and compatibility with various devices. By harnessing the power of bridge mode VPNs, individuals can safeguard their online activities and enjoy greater freedom and security in the digital world.
Bridge mode VPN configuration
When it comes to setting up a VPN connection in bridge mode, there are several key steps to consider to ensure a secure and efficient configuration.
First and foremost, understanding what bridge mode entails is crucial. Essentially, bridge mode allows a device to act as a transparent bridge or switch, connecting two different networks seamlessly. When configuring a VPN in bridge mode, it means that the VPN will operate at the network layer, allowing multiple devices to connect to the VPN without the need for individual client configurations.
To set up a bridge mode VPN, you will need to access the network settings of the device you are configuring. Typically, this involves accessing the device's web interface or command line interface to make the necessary changes. You will need to enable bridge mode and configure the VPN settings as per your network requirements.
It is important to ensure that the VPN server you are connecting to supports bridge mode configurations. Additionally, you may need to configure firewall rules and routing settings to allow traffic to flow through the VPN connection properly.
Testing the bridge mode VPN connection is essential to confirm that it is working correctly. You can do this by attempting to connect different devices to the VPN and testing network connectivity.
In conclusion, configuring a VPN in bridge mode can provide a seamless and secure way to connect multiple devices to a VPN network. By following the appropriate steps and testing the connection thoroughly, you can establish a reliable bridge mode VPN configuration for your network needs.
Bridge mode vs
Bridge Mode vs. Router Mode: Understanding the Difference
In the realm of networking, the choice between bridge mode and router mode can significantly impact the performance and functionality of your network setup. Both modes serve distinct purposes and are employed in different scenarios, so understanding their differences is crucial for optimizing your network infrastructure.
Firstly, let's delve into bridge mode. When a device, such as a modem or router, is set to bridge mode, it essentially functions as a bridge or pass-through device, allowing another device, typically a router, to handle the network routing tasks. In this mode, the bridging device doesn't perform any routing functions and simply forwards data packets between the connected devices without modification. Bridge mode is often used in scenarios where a separate router is desired to manage the network traffic and provide advanced features such as firewall protection, QoS (Quality of Service), and VPN (Virtual Private Network) capabilities.
On the other hand, router mode involves the device performing both bridging and routing functions. In router mode, the device not only forwards data packets between devices on the same network but also manages the routing of data packets between different networks, such as the local network and the internet. Routers in this mode typically offer features like NAT (Network Address Translation), DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) server functionality, port forwarding, and more, making them suitable for standalone network setups where all-in-one functionality is desired.
In summary, the choice between bridge mode and router mode depends on your specific networking requirements. Bridge mode is ideal when you need a separate router to manage network traffic and provide advanced features, while router mode is suitable for standalone setups where a single device handles both bridging and routing functions. Understanding the differences between these modes empowers you to make informed decisions when configuring your network infrastructure.
0 notes
Text
can you make your own vpn server with openwrt
🔒🌍✨ Get 3 Months FREE VPN - Secure & Private Internet Access Worldwide! Click Here ✨🌍🔒
can you make your own vpn server with openwrt
Setting up OpenWRT VPN server
Setting up an OpenWRT VPN server can give you secure and private access to the internet from your own home network. OpenWRT is an open-source firmware that can be installed on many router models, allowing you to customize and enhance your router's capabilities, including setting up a VPN server.
To begin setting up your OpenWRT VPN server, you will first need to flash your router with the OpenWRT firmware. Make sure to choose a router model that is compatible with OpenWRT and follow the installation instructions carefully. Once you have OpenWRT installed on your router, you can proceed to set up the VPN server.
There are different VPN protocols you can choose from, such as OpenVPN, WireGuard, or others, depending on your preferences and needs. OpenVPN is a popular choice for its security and flexibility, while WireGuard is known for its speed and simplicity.
After selecting a VPN protocol, you will need to configure the VPN server settings on your router, including encryption, authentication, and IP addressing. You can create user profiles with unique login credentials for added security.
Lastly, you will need to forward the VPN server port on your router and configure the firewall to allow VPN traffic. Once everything is set up correctly, you can connect to your OpenWRT VPN server from any device with VPN client software installed.
Setting up an OpenWRT VPN server may require technical knowledge, but the added security and privacy benefits make it worthwhile for those looking to protect their online activities and data.
Self-hosted VPN with OpenWRT
Title: Setting Up a Self-Hosted VPN with OpenWRT: A Comprehensive Guide
In an age of increasing online surveillance and privacy concerns, having a secure and private internet connection has become paramount. One effective solution gaining popularity is setting up a self-hosted VPN (Virtual Private Network) using OpenWRT, a Linux-based open-source firmware for routers. This allows users to create their own VPN server, giving them full control over their data and online activities.
To begin, you'll need compatible hardware and a router supported by OpenWRT. Once you've installed OpenWRT on your router, the next step is to configure it to act as a VPN server. This involves installing the necessary packages and configuring the VPN protocols, such as OpenVPN or WireGuard.
OpenVPN is a widely used protocol known for its robust security features and compatibility with various devices. Setting up OpenVPN on OpenWRT involves installing the OpenVPN package and generating configuration files. You'll also need to set up encryption keys and certificates for secure communication.
Alternatively, WireGuard is gaining popularity for its simplicity and performance. Configuring WireGuard on OpenWRT requires installing the WireGuard package and generating public and private keys. You'll then configure the interface and peers to establish secure connections.
Once your VPN server is set up, you can connect to it from any device with VPN support, whether it's your laptop, smartphone, or tablet. This allows you to encrypt your internet traffic and mask your IP address, enhancing your online privacy and security.
In conclusion, setting up a self-hosted VPN with OpenWRT offers a cost-effective and customizable solution for protecting your online privacy. By taking control of your VPN server, you can ensure that your data remains secure and inaccessible to unauthorized parties. With the right hardware and configuration, you can enjoy a secure and private internet experience from the comfort of your home.
Configuring VPN on OpenWRT
To configure a Virtual Private Network (VPN) on OpenWRT, you can enhance the security and privacy of your internet connection. OpenWRT is a Linux-based open-source firmware for routers and other networking devices, allowing users to customize their network settings and functionality beyond what is typically offered by stock firmware.
Firstly, ensure your OpenWRT device is up to date with the latest firmware version to guarantee compatibility with VPN configurations. Then, access the OpenWRT web interface by entering the router's IP address in a web browser and log in with your credentials.
Next, install the VPN package on your OpenWRT device. Depending on your VPN provider, you can choose from various protocols such as OpenVPN, WireGuard, or others. Install the necessary packages for your chosen protocol by accessing the System > Software tab on the web interface.
Once the VPN packages are installed, configure the VPN settings by going to the Network > Interfaces tab. Create a new interface for the VPN and input the required settings provided by your VPN provider, such as server addresses, authentication details, and encryption settings.
After configuring the VPN interface, enable and start the VPN connection. Verify the connection status to ensure that your OpenWRT device is securely connected to the VPN server.
In conclusion, by following these steps, you can successfully configure a VPN on your OpenWRT device, adding an extra layer of security and privacy to your internet browsing experience. Remember to test the VPN connection to confirm that all settings are correctly configured and that your online activities are protected.
OpenWRT VPN server tutorial
Title: Setting Up a VPN Server on OpenWRT: A Comprehensive Tutorial
In today's interconnected world, safeguarding your online privacy and security is paramount. One effective way to achieve this is by setting up your own Virtual Private Network (VPN) server. OpenWRT, a popular open-source firmware for routers, provides an excellent platform for creating a VPN server within your network. In this tutorial, we'll guide you through the process step by step.
Choose a Compatible Router: Not all routers support OpenWRT, so ensure yours is compatible. Refer to the OpenWRT website for a list of supported devices.
Install OpenWRT: Follow the installation instructions provided on the OpenWRT website to flash your router with the firmware.
Access the Router Interface: Once OpenWRT is installed, access the router's web interface using a browser. You can usually do this by entering the router's IP address in the address bar.
Install VPN Software: OpenWRT supports various VPN protocols such as OpenVPN and WireGuard. Choose the one that suits your needs and install the necessary packages through the router's interface.
Configure VPN Server: After installation, configure the VPN server settings according to your preferences. This includes setting up encryption, authentication, and defining IP address pools.
Port Forwarding: To allow external connections to your VPN server, configure port forwarding on your router. This involves forwarding the VPN protocol's port (e.g., 1194 for OpenVPN) to the internal IP address of your VPN server.
Testing and Troubleshooting: Once configured, test your VPN server to ensure it's functioning correctly. Troubleshoot any issues that arise by checking configuration settings and consulting online resources or forums for assistance.
Connect Clients: Finally, connect your devices to the VPN server using compatible VPN client software. Configure the client with the necessary server details and credentials provided during setup.
By following this tutorial, you can establish a secure VPN server on your OpenWRT-powered router, enhancing your online privacy and security. Enjoy the benefits of encrypted internet traffic and unrestricted access to your home network from anywhere in the world.
DIY VPN using OpenWRT
A DIY VPN using OpenWRT enables users to establish a secure and private network connection from the comfort of their own home. OpenWRT is an open-source firmware that can be installed on various routers, providing users with advanced customization options not typically found in standard router firmware.
To create a DIY VPN using OpenWRT, users can start by selecting a compatible router model and installing the OpenWRT firmware. Once the firmware is installed, users can configure the router to act as a VPN server, allowing them to connect to their home network securely from remote locations.
Setting up a VPN on OpenWRT involves configuring VPN protocols such as OpenVPN or WireGuard, creating user accounts, and setting up encryption to secure the VPN connection. Users can also customize their VPN settings to suit their specific privacy and security needs.
Using a DIY VPN with OpenWRT offers several benefits, including enhanced privacy protection, secure access to home network resources while on the go, and the ability to bypass geo-restrictions on certain websites or services.
It is important to note that creating a DIY VPN using OpenWRT requires a moderate level of technical expertise. Users should carefully follow tutorials and guides provided by the OpenWRT community to ensure a successful setup.
Overall, setting up a DIY VPN using OpenWRT is a cost-effective and versatile solution for those looking to enhance their online privacy and security. By taking the time to configure and maintain a VPN server, users can enjoy the benefits of a secure and private network connection wherever they go.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Due to its low cost and ease of customization, Linux is often used in embedded systems. In the non-mobile telecommunications equipment sector, the majority of customer-premises equipment (CPE) hardware runs some Linux-based operating system. OpenWrt is a community-driven example upon which many of the OEM firmware releases are based.
For example, the popular TiVo digital video recorder also uses a customized Linux, as do several network firewalls and routers from such makers as Cisco/Linksys. The Korg OASYS, the Korg KRONOS, the Yamaha Motif XS/Motif XF music workstations, Yamaha S90XS/S70XS, Yamaha MOX6/MOX8 synthesizers, Yamaha Motif-Rack XS tone generator module, and Roland RD-700GX digital piano also run Linux. Linux is also used in stage lighting control systems, such as the WholeHogIII console.
1 note
·
View note
Text
My latest project is building a combined travel router-firewall and miniserver. It’s based on PC Engines APU2 (specifically apu2d4) embedded platform running either pfsense or OpenWRT. Turns out that there are fewer and fewer miniPCIe form-factor LTE/5G modems, so I’m experimenting with an m.2 to miniPCIe adapter to see if an m.2 cellular modem could be an option. Physically the adapter just fits!
Notes to self: M.2 and miniPCIe carry both PCIe and USB in the same physical connector. The APU2 mPCIe slots 1 and 2 support PCIe 2.0 and USB 2.0. An LTE modem using USB 3.0 data link must be able to fall back to USB 2.0 gracefully or it won’t work. Aside from improved frequency band support, anything beyond LTE Cat 6 card is wasted unless it uses a PCIe data link. It’s possible that PCIe-based LTE/5G modem can work at full speed; possibly worth experimenting if not too expensive.

#miniserver#personal projects#PC Engines#APU2#Internet-in-a-box#embedded computing#firewall#this thing is super low power consumption#but the processor is also pretty slow#albeit faster than most consumer router-firewalls#still it’s got at least a terabyte of storage#and wifi#and cellular#and 4GB of ECC memory#and a cryptoprocessor#and it can route at gigabit speed#it’s both making-do and extravaganza#depending on how you look at it#and I like to make things do more than they were meant to
1 note
·
View note
Text
Routers for Optimum
A router may have interfaces for different types of body connection components, such as copper wires, fiber optics, or wireless transmissions. It can also support different power lines communication. The links used make it possible to combine paper bags from one ad to another. Routers can also be used to connect two or more relevant computer components popular subnets, each with a different website.buy routers. com
Ways to find links within businesses, between businesses and the Internet, or between internet service providers' (ISPs') 'websites. Large networks (such as the Cisco CRS-1 or Juniper PTX) connect to different ISPs, or they may be used by large companies. [5] Smaller vehicles often provide connections for regular homes and office buildings.
Many types of vehicles can be found in the business. [6] The most powerful methods are commonly found in ISPs, training and research sites. Large businesses may also need more vehicles to meet and increase online trading needs. It is a great example of online communication for network traffic on the most commonly used networks. [7]
Opportunity, theme and distribution
A snapshot of the LuCI website used by OpenWrt. This page configures Dynamic DNS. Road access, including small office / office building (SOHO) models, is home to home and customer locations such as branch offices that do not need to be self-contained. Typically, they are ideal for low prices. Some SOHO routers can run other Linux based firmware such as Tomato, OpenWrt or DD-WRT. [8] [failure evidence]
Distributed routes unite travelers from multiple routes. Distributed routers are often responsible for enhancing the quality of service over a wide area (WAN), so they may have more memory, more WAN network connections, and more onboard normal operation information. They may also be able to provide links to batch files or other external links. [Citation needed]
In business, a core router may have a collumbb backbone connection distributing tier routers from large buildings of a campus, or large business locations. They try to ensure for high bandwidth, but there are no features of roadside. [9] [unconfirmed]
Safety External links should be carefully considered as part of the overall security plan of the internal network. A router may include a firewall, VPN handling, and other security functions, or these may be handled by different devices. Routers also often make network address translations that restrict starting connections from external connections but are not considered a security feature by all experts. [10] Some experts argue that open people on the road are safer and more reliable than closed railways, because of the open space available and corrected. [11]
Order different websites Routers are also often distinguished on the basis of the network on which they operate. A router in a local area network (LAN) is one organization called an internal router. A router running the back-end internet is defined as an external router. A router is connected to the LAN and the Internet or broadband network (WAN) is called a border router, or gateway router. [12]
Internet communication and internal use Plans for ISPs and many business networks typically exchange data streams using the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP). RFC 4098 describes the types of BGP pathways according to their function: [13]
Edge router (also called edge edge provider): Placed on the edge of the ISP network. The router uses the Exterior Border Gateway Protocol (EBGP) to routers to other ISPs or large private businesses. The top edge registry (also called the router edge): It is located at the end of the client network, which also uses EBGP in the company’s independent management. It is often used in an (enterprise) organization. High-speed Networks Connected: The BGP router for ISP networks maintains BGP routers and other BGP routers over ISP Autonomous Systems. Core router: The location in the Autonomous System is a backbone that carries traffic between the ends of the road. [14] Within the ISP: In an ISP stand-alone system, the router uses the internal BGP to communicate with other ISP employees, other intranet users, or border users of the ISP. ISP. Backbone: The Internet is no more
1 note
·
View note
Text
You can do basically anything with OpenWRT, including mesh networks, wifi extensions, fast roaming, Adblock, router level VPN, advanced firewalls, NAS, printer servers, and customs DNS!
People should talk to me about openWRT actually

21 notes
·
View notes
Text
6 Useful Ways to Reuse an Old Router: Don’t Throw It Away!

If your ISP has sent you a replacement router, otherwise you simply fancy an upgrade, you’ll run into a drag.
What do you have to do with the old router?
In the case of switching your ISP, you’ll often be asked to return the older device. But if you've got an old router kicking around the place, here are several ways you'll reuse it.
What you'll Do With an Old Router
It might be during a box; it might be cluttering up a drawer or lost at the rear of a wardrobe. regardless of the case, old routers and modem/router combo units are often reused.
We’ve identified nine ways you'll reuse an old Wi-Fi router: Guest Wi-Fi connection Wireless repeater Cheap internet radio Use the old router as a network switch Adapt it as a wireless bridge Build a sensible home hub Convert your router into a NAS Use an old router as an internet server A DIY VPN router Sell the router on eBay
Let’s take a glance at each of those uses for old routers in additional detail. 1. Build a Wireless Repeater
What if your Wi-Fi network doesn’t extend across the complete range of your home? Although you would possibly choose powerline Ethernet adapters, adding a second router into the combination may be a good alternative.
This means connecting the old router to your new wireless network, using the Wi-Fi signal. It can then share access to the Wi-Fi network, giving greater coverage. Although there could also be some latency issues, overall this is often a fast and straightforward thanks to extending your wireless network.
It has various uses, from giving better Wi-Fi access to a foreign a part of the house, to letting you stream video to your tablet while you’re within the garden. 2. Guest Wi-Fi Connection
If you've got people regularly dropping in and using your wireless internet, why not give them their network?
This is just like the wireless repeater project, but with a twist. The router connects to your existing, password-protected network, but gives password-free access to new devices. this may use the guest network feature of your old router. By default, this prevents guests from accessing other devices on your network.
If this level of security isn’t enough, check the firewall settings on the most router to regulate. 3. Cheap Internet Radio Streamer
Want to enjoy your favorite radio stations on the internet? Some routers are often configured to play internet radio if you’re prepared to put in OpenWrt or DD-WRT custom router firmware.
You’ll need another software, also as a USB soundcard to output audio.
While not a simple build, and many of other internet radio options are available, this is often still an excellent project. It gives you an insight into installing custom firmware, also as an appreciation of the way to stream music. 4. Use the Router as an inexpensive Network Switch
Most routers don’t have quite six Ethernet ports. With the rise in wireless technology around the home, this figure might even be as low as four. But with a transparent need for devices to be connected over Ethernet, you would possibly run out of ports.
For example, household appliance monitoring devices, smart TVs and decoders, games consoles, and more may need no wireless networking. they have a physical connection to your network, which means Ethernet.
If you run out of Ethernet ports, you'll add more with a network switch. It’s the networking version of a mains power bar, with additional ports plugged into one port on the router.
Your old router typically has four or more ports, so connecting will instantly increase the number of ports available. you ought to disable wireless networking on the old router, to avoid conflicts. 5. Turn Your Old Router Into a Wireless Bridge
What if your new router is wireless only? Perhaps the ISP doesn’t offer a router with Ethernet ports, or even you employ a 4G internet provider. Either way, if you would like to attach Ethernet devices to your home network, a wireless bridge is that the answer.
This works a touch sort of a wireless repeater, but instead of sharing the Wi-Fi connection, the wireless bridge offers Ethernet. The old router connects to an existing Wi-Fi network—simply connect devices to the Ethernet ports. 6. Build a sensible Home Hub
Some routers ship with some useful additional ports. In some cases, this could be a USB port, which makes flashing OpenWRT or DD-WRT router firmware easy.
Other devices might accompany a serial port; these routers are often repurposed as a home automation server.
The router runs a server that you simply hook up with together with your browser. This could be on a PC, or for convenience, through your smartphone. This Instructables explains the way to create a basic smart home setup with an Arduino, the router, and a few RF-controlled switches.
While easier options are available, you would possibly use this to urge a far better understanding of home automation.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Ios shadowsocks

#Ios shadowsocks software
#Ios shadowsocks code
#Ios shadowsocks license
#Ios shadowsocks free
Shadowsocks, however, is based on a proxy protocol called SOCKS5 that secures the connection using an AEAD cipher-roughly along the same lines as an SSH tunnel. However, regular proxies are notoriously unsafe: there’s no good way to secure the connection, for one, and generally speaking, most sites can figure out quite easily that you’re using one. Using a proxy means you go from the ISP to an unblocked server and then to the site you want. If the authorities want to block a site, the internet service provider (ISP) is usually told to prevent access to its IP address. In a regular network connection, like the one you’re likely using now, you connect to your internet service provider’s server and then to the website you want to visit.
#Ios shadowsocks code
He also was forced to delete the code on GitHub and he had “no choice but to obey.” He added that “I hope one day I’ll live in a country where I have freedom to write any code I like without fearing.” In 2015, however, Clowwindy left a message on a GitHub thread stating that the police had found him and had asked him to stop working on Shadowsocks and, presumably, ShadowVPN.
#Ios shadowsocks free
The protocol was a huge success and clowwindy kept working on it for several years, as well as developing a free VPN called ShadowVPN. Shadowsocks was developed by a Chinese programmer only known as “clowwindy,” who put the initial commit (a version of a program or script) on GitHub in 2012. However, before we go into any more detail, let’s first go over where Shadowsocks comes from. Not only is using Shadowsocks free, it also hides traffic a little better than VPNs do. In fact, Shadowsocks is so good at getting past China’s blocks that there’s a good case to be made for it over another tool, virtual private networks (VPNs). RELATED: What to Expect from the Internet in China It’s used widely in China by people looking to tunnel under the Great Firewall-the digital barrier that keeps the Chinese internet “safe” from foreign influence-as it’s completely free, though you’ll need some tech know-how to set it up. Shadowsocks is a connection tool that lets you circumvent censorship. Let’s see what this protocol can and cannot do. Not only is its name intriguing, it also promises to get you past any blocks safely. If you’re looking to escape internet censorship, one interesting option is something called Shadowsocks.
#Ios shadowsocks license
You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License along with this program. See the GNU General Public License for more details. This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
#Ios shadowsocks software
This program is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or (at your option) any later version. To view the source codes or build your own apk, please refer to: To setup your own server, please refer to: Ģ. Visit our project site for more details: ġ. Open source implementions in python, node.js, golang, C#, and pure C. Avaliable on multiple platforms, including PC, MAC, Mobile (Android and iOS) and Routers (OpenWRT).Ĥ. Low resource comsumption, suitable for low end boxes and embedded devices.ģ. Bleeding edge techniques with Asynchronous I/O and Event-driven programming.Ģ. *NOTE: You may need to unisntall and reinstall the app, after upgrading to 3.x or above.*ġ. It will help you surf the internet privately and securely. Shadowsocks is a high-performance cross-platform secured socks5 proxy.

0 notes
Text
[Media] GL.
GL.iNetGL-XE300(Puli) A portable 4G smart router that is perfect for home, business, and IoT solutions. With its OpenWrt-supported feature and large storage compatibility, it is designed for you to develop a DIY IoT project. It also comes with a rechargeable battery, so you can bring it anywhere with you! Apart from its powerful built-in firewall, Puli (GL-XE300) also supports OpenVPN, WireGuard and customized DNS server in order to level up your online security. With our brand-new Web UI 3.0, you can set up VPN server easily and access your files securely and remotely as if you were at home. DNS over TLS is a security protocol for encrypting and wrapping Domain Name System (DNS) queries and answers via the Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocol. It serves to increase user privacy and security by preventing eavesdropping and manipulation of DNS data via man-in-the-middle attacks. OpenWRT SDK for GL.iNet devices: https://github.com/gl-inet/sdk Buy online: 🛒 https://ali.ski/IWwRz #router #portable

0 notes
Text
Xiaomi 4A Giga - OpenWRT - OpenVPN
I spent the last 3 days trying to do this. The guide looks pretty simple and straight forward, but like anything in IT there are always gotchas.
youtube
Gotchas
1 - If you are flashing from a VM, obtain the STOK code from the VM, because each client gets a different code as oppose to a single code for each onine instance of the Router
2 - The OpenWRTInvasion tool exploit code is very simple and I would recommend all to print the output for lines 69 & 78 to get a more verbose output of the payload execution, so you can tell if the exploit has been executed correctly or not, by default the script would always give a successful message, which can be misleading combined with issue #1
3 - If you need to debrick, the tool provided by Hoddy is fantastic and works every time, however make sure you use a standard network card and not some usb-to-ethernet adapter, because my usb-to-ethernet adapter couldn’t serve PXE boot at all.
4 - if you like Luci interface for OpenWRT, flash it with https://github.com/araujorm/openwrt/releases/ firmware instead of the one in in the guide.
5 - OpenVPN setup is pretty much straight forward like all guides you can find on the internet, the OpenWRT standard guide for OpenVPN client is good, you will also need to check with your VPN provider as the setup options can be different depend on the VPN providers. The step to add the firewall for VPN is important.
6 - I am a simple guy, so my network at home is on the 192.168.1.0 network, and this interfered with my VPN setup, so make sure change your OpenWRT LAN range to a different range compared to your existing home network LAN, for OpenVPN to work
0 notes