#ReactJS website development
Text
Power of React JS in Modern Website Development - Check expert Recommendations Now
In the ever-evolving landscape of web development, staying ahead of the curve is essential for creating dynamic and responsive websites. It has emerged as a game-changer, revolutionizing the way developers build user interfaces. In this article, we will delve into the world of React JS, by exploring its key features, advantages, and the impact it has had on modern web development.
What is React JS?
React JS Website Development, developed by Facebook, is an open-source JavaScript library designed for building user interfaces or UI components. It allows developers to create interactive and dynamic web applications with a seamless user experience. By making the code more modular and maintainable, architectural components summarize the structure and behavior of different parts of the website.
One of the key features of React JS website development is its use of a Virtual DOM. It allows React to update only the parts of the webpage that have changed, leading to faster rendering and improved performance. This optimization technique is beneficial for large-scale web applications with frequent data updates.
React JS is well-suited for building various types of websites, including single-page applications, progressive web apps, and e-commerce platforms.
By ensuring that your project is developed with best practices and optimized for performance, React JS web development companies bring in-depth knowledge and experience. They also provide expertise in customization, scalability, and cross-platform compatibility, helping you create a website that meets your specific requirements and objectives. By leveraging the expertise of a specialized React JS web development company, businesses can unlock the full potential of React JS and deliver exceptional results.
As per Statista data in 2022, 42.62% of global websites are using the React JS framework for front-end development. React JS is the second most used framework for UI development. It has proved itself time and again as one of the best JavaScript libraries for creating multi-faceted websites.
Build Your Website with React JS Effortlessly
With simplicity and power, building your website has never been easier. That’s the magic of React JS. You can build your website attractively with React JS Website Development flawlessly. Let's explore how React JS can empower you to create stunning websites effortlessly.
Getting Started: Getting started with React JS is simple. You can set up your development environment quickly and start building your website right away. With a plethora of resources and tutorials available online, learning React JS has never been more accessible.
Creating Components: In React JS, everything is a component. Whether it's a header, footer, or a complex form, you can break it down into reusable components. This modular approach makes it easy to manage and update different parts of your website.
Leveraging React JS Libraries: React JS has a vibrant ecosystem of libraries and tools that can enhance your website development process. From state management to UI components, there is a library for almost every need. These libraries can help you streamline your workflow and add advanced functionalities to your website effortlessly.
The Advantages of React JS
React JS has emerged as a powerhouse, by bringing a host of advantages. Let's take a closer look at the key benefits of leveraging React JS, especially when partnering with a React JS Web Development Company.
Reusability and Component-Based Architecture: The component-based architecture of React promotes reusability in React JS Web Development Company, by enabling developers to build a library of components that can be utilized across various parts of a website or even in different projects. This not only saves time but also enhances consistency and maintainability.
Declarative Syntax: React uses declarative syntax, allowing developers to describe the desired outcome rather than focusing on the step-by-step process of achieving it. This makes the code more readable and easier to understand, promoting collaboration among team members.
Virtual DOM for Enhanced Performance: As mentioned earlier, React's Virtual DOM is a powerful optimization technique. By updating only the components that have changed, React minimizes the number of updates to the actual DOM, resulting in faster rendering and a smoother user experience.
Strong Community Support: React has a vast and active community of developers, which means a wealth of resources, tutorials, and third-party libraries are available. This support network not only facilitates learning but also provides solutions to common challenges, making React JS a reliable choice for developers.
Scalability and Flexibility: Whether you're launching a startup or expanding an established business, the scalability of React JS ensures that your web application can evolve with your needs in React JS Web Development Company. It can leverage the flexibility to customize solutions that align with your unique business requirements.
SEO-Friendly Application: React JS by offering a seamless, app-like experience to users excels in the development of single page applications. It can be SEO-friendly through server-side rendering or pre-rendering.
Hiring a React JS Web Development Company
By entrusting your web development endeavors to a reputable React JS Website Development Company, you unlock the potential for innovative and high-performing digital experiences. The specialized React development companies bring expertise and experience, by ensuring flawless execution of React JS projects.
The Importance of Expertise: While React JS is accessible to developers at various skill levels, harnessing its full potential often requires expertise. A React JS Web Development Company can bring in-depth knowledge and experience to the table, ensuring that your project is developed with best practices and optimized for performance.
Customization and Scalability: React's flexibility allows for highly customized solutions tailored to specific project requirements. A specialized React JS web development company can leverage this flexibility to create scalable and maintainable web applications that can grow alongside your business needs.
Cross-Platform Compatibility: With the increasing diversity of devices and platforms, cross-platform compatibility is crucial. React Native, an extension of React JS enables the development of mobile applications for both iOS and Android platforms. A skilled React JS web development company can seamlessly integrate React Native into your project, ensuring a consistent user experience across different devices.
Conclusion
React JS has become a cornerstone in modern web development, by offering a strong framework for creating interactive and dynamic user interfaces. Its component-based architecture and virtual DOM contribute to enhanced performance and maintainability. When considering a web development project, the choice of a React JS Web Development Company can play a pivotal role in ensuring the success of your endeavor. Embrace the power of React JS, and unlock a world of possibilities in crafting innovative and user-centric web applications.
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Link
Here in this blog, we are sharing the "Reasons You Must Consider for ReactJS Website Development"
0 notes
Text
JavaScript Fundamentals
I have recently completed a course that extensively covered the foundational principles of JavaScript, and I'm here to provide you with a concise overview. This post will enable you to grasp the fundamental concepts without the need to enroll in the course.
Prerequisites: Fundamental HTML Comprehension
Before delving into JavaScript, it is imperative to possess a basic understanding of HTML. Knowledge of CSS, while beneficial, is not mandatory, as it primarily pertains to the visual aspects of web pages.
Manipulating HTML Text with JavaScript
When it comes to modifying text using JavaScript, the innerHTML function is the go-to tool. Let's break down the process step by step:
Initiate the process by selecting the HTML element whose text you intend to modify. This selection can be accomplished by employing various DOM (Document Object Model) element selection methods offered by JavaScript ( I'll talk about them in a second )
Optionally, you can store the selected element in a variable (we'll get into variables shortly).
Employ the innerHTML function to substitute the existing text with your desired content.
Element Selection: IDs or Classes
You have the opportunity to enhance your element selection by assigning either an ID or a class:
Assigning an ID:
To uniquely identify an element, the .getElementById() function is your go-to choice. Here's an example in HTML and JavaScript:
HTML:
<button id="btnSearch">Search</button>
JavaScript:
document.getElementById("btnSearch").innerHTML = "Not working";
This code snippet will alter the text within the button from "Search" to "Not working."
Assigning a Class:
For broader selections of elements, you can assign a class and use the .querySelector() function. Keep in mind that this method can select multiple elements, in contrast to .getElementById(), which typically focuses on a single element and is more commonly used.
Variables
Let's keep it simple: What's a variable? Well, think of it as a container where you can put different things—these things could be numbers, words, characters, or even true/false values. These various types of stuff that you can store in a variable are called DATA TYPES.
Now, some programming languages are pretty strict about mentioning these data types. Take C and C++, for instance; they're what we call "Typed" languages, and they really care about knowing the data type.
But here's where JavaScript stands out: When you create a variable in JavaScript, you don't have to specify its data type or anything like that. JavaScript is pretty laid-back when it comes to data types.
So, how do you make a variable in JavaScript?
There are three main keywords you need to know: var, let, and const.
But if you're just starting out, here's what you need to know :
const: Use this when you want your variable to stay the same, not change. It's like a constant, as the name suggests.
var and let: These are the ones you use when you're planning to change the value stored in the variable as your program runs.
Note that var is rarely used nowadays
Check this out:
let Variable1 = 3;
var Variable2 = "This is a string";
const Variable3 = true;
Notice how we can store all sorts of stuff without worrying about declaring their types in JavaScript. It's one of the reasons JavaScript is a popular choice for beginners.
Arrays
Arrays are a basically just a group of variables stored in one container ( A container is what ? a variable , So an array is also just a variable ) , now again since JavaScript is easy with datatypes it is not considered an error to store variables of different datatypeslet
for example :
myArray = [1 , 2, 4 , "Name"];
Objects in JavaScript
Objects play a significant role, especially in the world of OOP : object-oriented programming (which we'll talk about in another post). For now, let's focus on understanding what objects are and how they mirror real-world objects.
In our everyday world, objects possess characteristics or properties. Take a car, for instance; it boasts attributes like its color, speed rate, and make.
So, how do we represent a car in JavaScript? A regular variable won't quite cut it, and neither will an array. The answer lies in using an object.
const Car = {
color: "red",
speedRate: "200km",
make: "Range Rover"
};
In this example, we've encapsulated the car's properties within an object called Car. This structure is not only intuitive but also aligns with how real-world objects are conceptualized and represented in JavaScript.
Variable Scope
There are three variable scopes : global scope, local scope, and function scope. Let's break it down in plain terms.
Global Scope: Think of global scope as the wild west of variables. When you declare a variable here, it's like planting a flag that says, "I'm available everywhere in the code!" No need for any special enclosures or curly braces.
Local Scope: Picture local scope as a cozy room with its own rules. When you create a variable inside a pair of curly braces, like this:
//Not here
{ const Variable1 = true;
//Variable1 can only be used here
}
//Neither here
Variable1 becomes a room-bound secret. You can't use it anywhere else in the code
Function Scope: When you declare a variable inside a function (don't worry, we'll cover functions soon), it's a member of an exclusive group. This means you can only name-drop it within that function. .
So, variable scope is all about where you place your variables and where they're allowed to be used.
Adding in user input
To capture user input in JavaScript, you can use various methods and techniques depending on the context, such as web forms, text fields, or command-line interfaces.We’ll only talk for now about HTML forms
HTML Forms:
You can create HTML forms using the <;form> element and capture user input using various input elements like text fields, radio buttons, checkboxes, and more.
JavaScript can then be used to access and process the user's input.
Functions in JavaScript
Think of a function as a helpful individual with a specific task. Whenever you need that task performed in your code, you simply call upon this capable "person" to get the job done.
Declaring a Function: Declaring a function is straightforward. You define it like this:
function functionName()
{
// The code that defines what the function does goes here
}
Then, when you need the function to carry out its task, you call it by name:
functionName();
Using Functions in HTML: Functions are often used in HTML to handle events. But what exactly is an event? It's when a user interacts with something on a web page, like clicking a button, following a link, or interacting with an image.
Event Handling: JavaScript helps us determine what should happen when a user interacts with elements on a webpage. Here's how you might use it:
HTML:
<button onclick="FunctionName()" id="btnEvent">Click me</button>
JavaScript:
function FunctionName() {
var toHandle = document.getElementById("btnEvent");
// Once I've identified my button, I can specify how to handle the click event here
}
In this example, when the user clicks the "Click me" button, the JavaScript function FunctionName() is called, and you can specify how to handle that event within the function.
Arrow functions : is a type of functions that was introduced in ES6, you can read more about it in the link below
If Statements
These simple constructs come into play in your code, no matter how advanced your projects become.
If Statements Demystified: Let's break it down. "If" is precisely what it sounds like: if something holds true, then do something. You define a condition within parentheses, and if that condition evaluates to true, the code enclosed in curly braces executes.
If statements are your go-to tool for handling various scenarios, including error management, addressing specific cases, and more.
Writing an If Statement:
if (Variable === "help") {
console.log("Send help"); // The console.log() function outputs information to the console
}
In this example, if the condition inside the parentheses (in this case, checking if the Variable is equal to "help") is true, the code within the curly braces gets executed.
Else and Else If Statements
Else: When the "if" condition is not met, the "else" part kicks in. It serves as a safety net, ensuring your program doesn't break and allowing you to specify what should happen in such cases.
Else If: Now, what if you need to check for a particular condition within a series of possibilities? That's where "else if" steps in. It allows you to examine and handle specific cases that require unique treatment.
Styling Elements with JavaScript
This is the beginner-friendly approach to changing the style of elements in JavaScript. It involves selecting an element using its ID or class, then making use of the .style.property method to set the desired styling property.
Example:
Let's say you have an HTML button with the ID "myButton," and you want to change its background color to red using JavaScript. Here's how you can do it:
HTML: <button id="myButton">Click me</button>
JavaScript:
// Select the button element by its ID
const buttonElement = document.getElementById("myButton");
// Change the background color property buttonElement.style.backgroundColor = "red";
In this example, we first select the button element by its ID using document.getElementById("myButton"). Then, we use .style.backgroundColor to set the background color property of the button to "red." This straightforward approach allows you to dynamically change the style of HTML elements using JavaScript.
#studyblr#code#codeblr#css#html#javascript#java development company#python#study#progblr#programming#studying#comp sci#web design#web developers#web development#website design#ui ux design#reactjs#webdev#website#tech
374 notes
·
View notes
Text
Okay so for the past like. 5 weeks i think i've been on and off working on remaking my neocities site in react and adding some new features and just generally making it better !!
Ive got draggable windows, gifs for things im into, some songs i really like, some of my neocities moots, an 88x31 button for my site, and more planned!! i would really like it if u checked it out and followed me if u have a neocities! (ill follow u back)
edit: yeah the windows dont drag on mobile for some reason + i designed it for a pc screen sooo
18 notes
·
View notes
Text
Websites to practice Front-End
(22/02/2023)
Today I wanted to share websites to practice your frontend skills.
Front-end is complicated for my head (ask me to solve an algorithm with structure while but not to center a div HUEHHUE).
BUT at the same time I love a well done and coded design/ui. That's why today I want to share resources to help you train
1- Front-End Practice
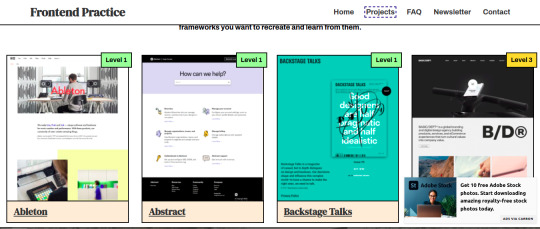
They have 3 levels, beginner, intermediate and advanced. There's no "answer" so you can't copy the code, it's just you trial and error until you get to the template (which really is a website that exists)

One thing I thought was really cool here was that it tells you what you're going to practice the most in the exercise, color palette and search features.
It's very interesting for a front-end not to be dependent on a tutorial, because from what I've seen in interviews, they ask you to make a layout and you won't be able to make one yourself if you don't learn to break down a single layout from the beginning and try and making mistakes until it's perfect.
2- DevChallenges
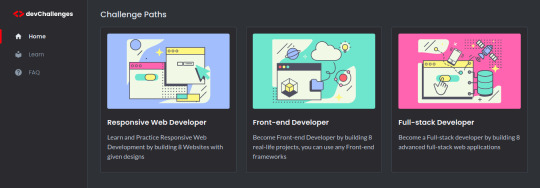
I find the projects not only beautiful visually but also interesting to practice. Here you already have the solutions that other people recommend, but again I think it's best for us to try and make mistakes until we get similar.And it also sorts the levels.
Here an example:
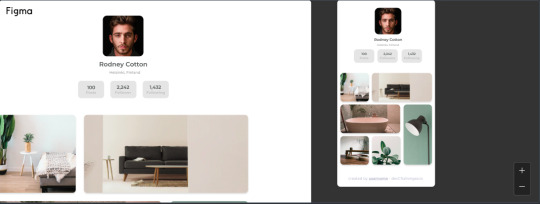
Cool huh? Well, I hope this helps someone who is looking for projects to practice with. We can invest a lot of time trying to make a layout, so having something ready I know helps a lot.
I wish you good studies and a great Wednesday, drink water.
#front end#frontenddevelopment#html css#html5#full stack developer#static website design tools#css3#javascript#reactjs#software engineer#practice#studyblr#studyblog#codeblr#resour#study tips
281 notes
·
View notes
Text
I'm a Web developer
Hello, my name is Bettina and i'm 27 years old. I live in Sweden 🇸🇪 but i'm born in Hungary 🇭🇺.
I'm currently studying web development focusing e-commerce. I've done it for a year now and i have one year left in school. I have not had my internship yet.
The languages i'm learning:
HTML
CSS
JavaScript, React.js, Node.js, expess.js,
MySQL, PHP.
I've even experience UX-design, web design, digital marketing, SEO and entrepreneurship. And i love talking about problem solving and accessibility 🪄🪲
Currently i'm developing wordpress with PHP, HTML and hierarchical CSS.
So, if you are into this stuff, especially wordpress and php, talk nerdy stuff with me! I would be so happy if i had more connections with people who are into this stuff, especially women. 🌸
My github:
My portfolio:
It is not done yet, i will update it soon 🫣🐢
🌦️ A weather app made in our Javascript course:
#web developer#webdeveloer#web developers#website#web design#web development#tiikiboo#frontenddevelopment#frontend#backend#php#phpdevelopment#php developers#php programming#php training#html css#javascript#reactjs#wordpress ecommerce#wordpress#wordpress php#wordpress development#portfolio#developer#juinor#women in tech#tech#codeblr#code#programming
33 notes
·
View notes
Text
Software Development using C# (Bootcamp)
Week 4 done ✨


So this week we learned about OOP & Dependency injection, DI is really hard and I plan to watch some YT videos to understand it better.
Other than that, I am taking a React course from Shecodes (almost 60% done with it) + C# course from codecademy (almost 35% done with it) 💻✨
Next week, we will start backend development lessons and we will start to work on our first project in this bootcamp (in this project we will work in teams)
I love all the squares so far, I feel like I am really becoming a developer 🥹 I know I am nowhere close to a real developer but i am on my way ✨

My bootcamp score currently is 380 out of 400 (and no I am still bad at C# and 80% of my assignments are copycode but I am getting the hang of it. And sometimes I feel my commits are more like a diary, I like to express my feelings)

Some comments from my instructor that really made me happy ✨


And not to mention my other instructor (I call her teacher) also offered to give me an extra class on Friday 😭🤍🤍 I love her so much who would have thought my feelings with this boocamp would change that much 😭🤍
I can’t wait for our next week lessons already 🤍
#codeblr#coding#learn to code#programming#webdevelopment#womanintech#software development#c sharp#backenddevelopment#reactjs#full stack web development#web developers#website development#front end development#developer#bootcamp#study blog#computer science studyblr#studyspo#study motivation#studyblr
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
personal portfolio site v1 /ᐠ。ꞈ。ᐟ\
been working on my personal portfolio for a bit and while it's still got a long ways to go I wanted to share my progress ╰( ^o^)╮
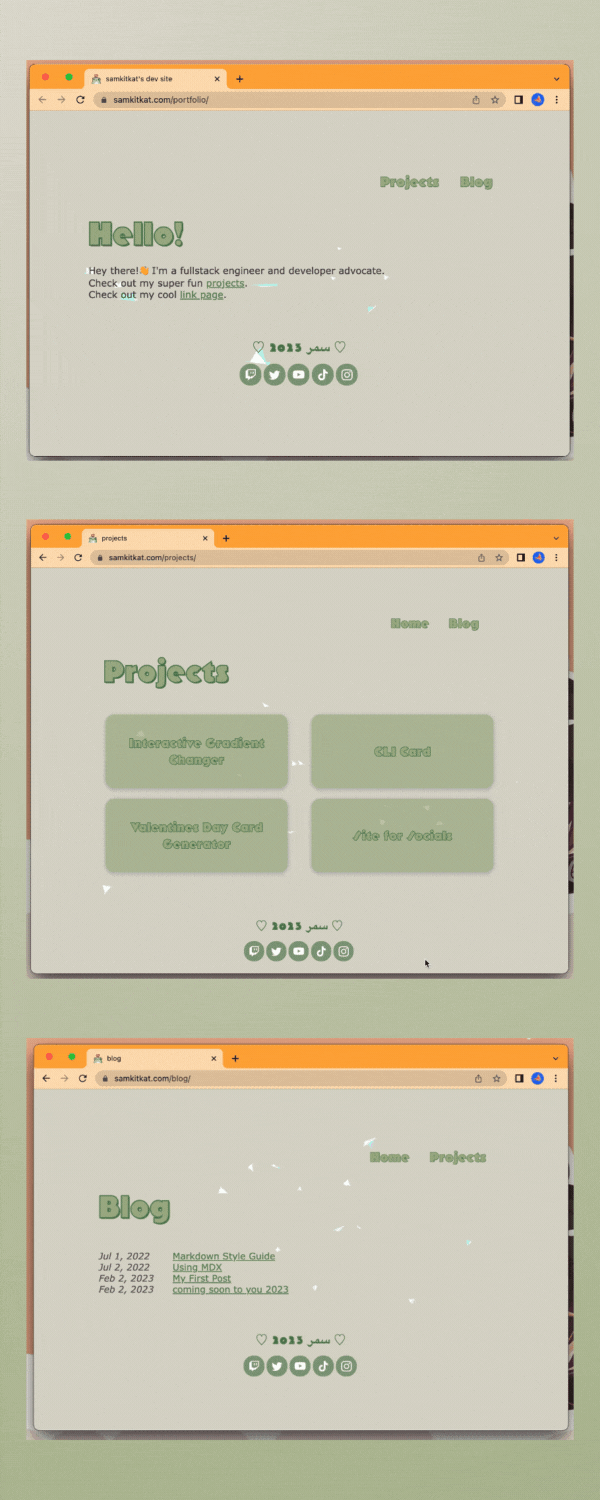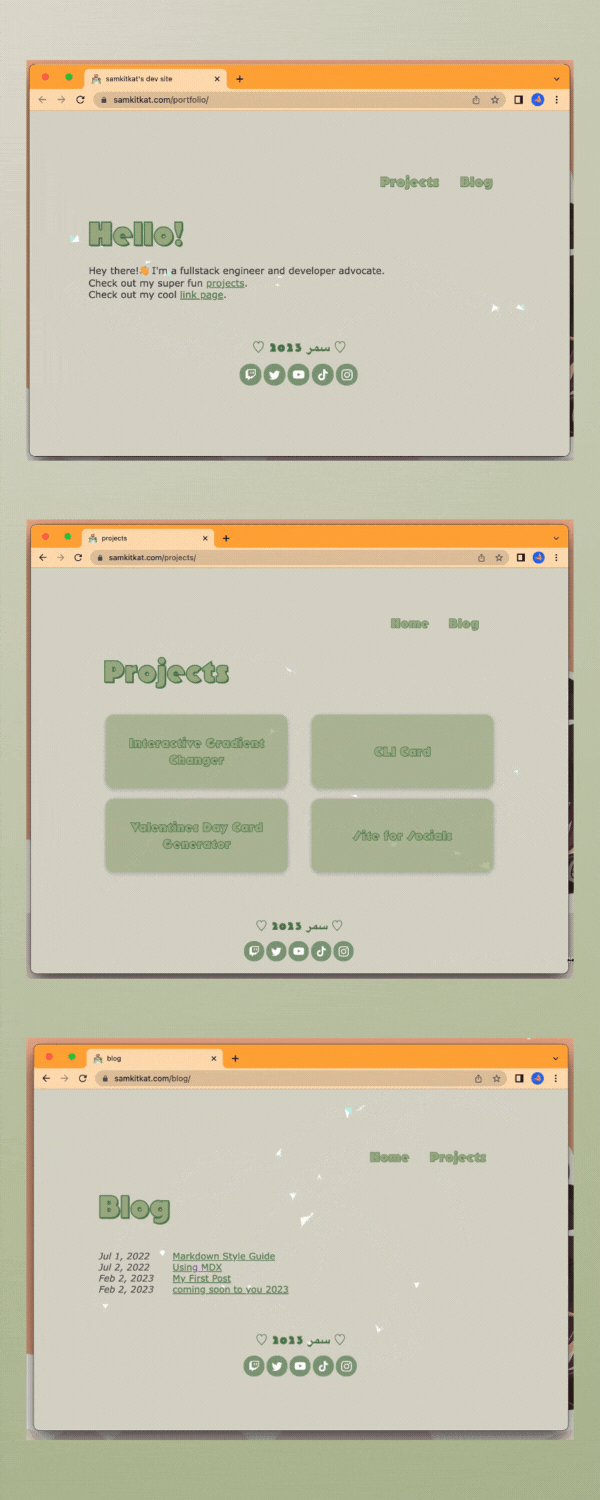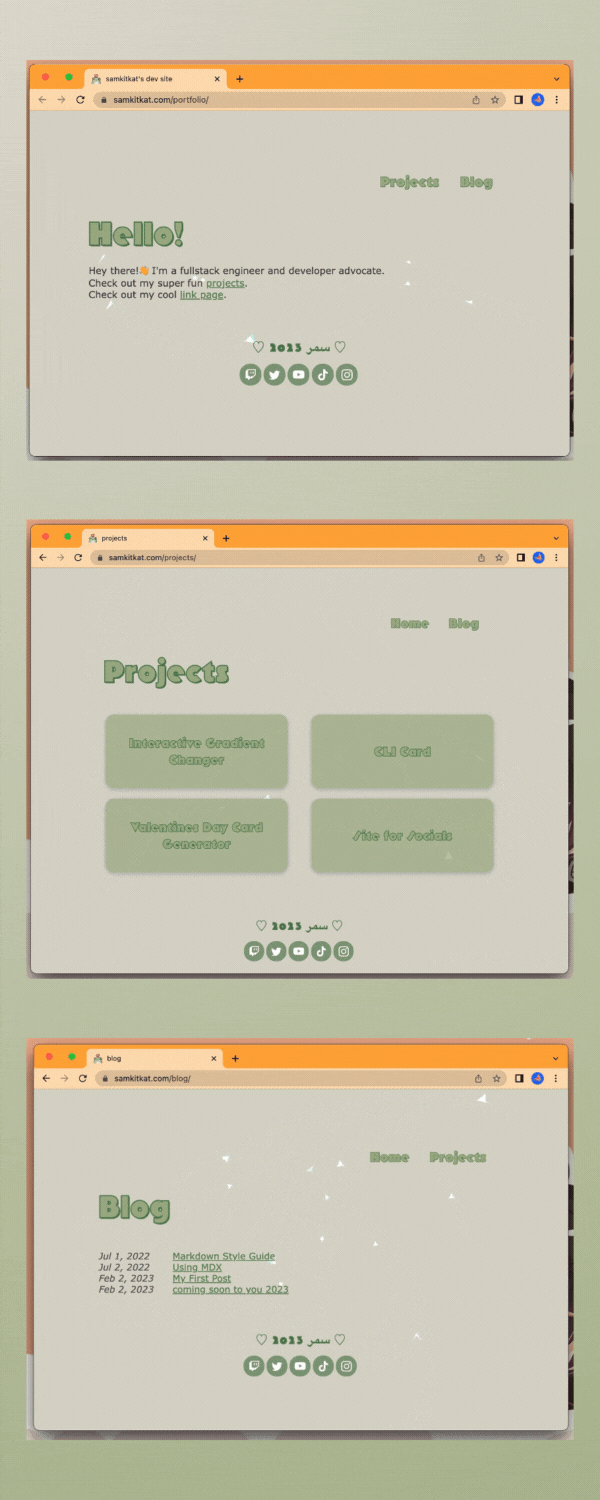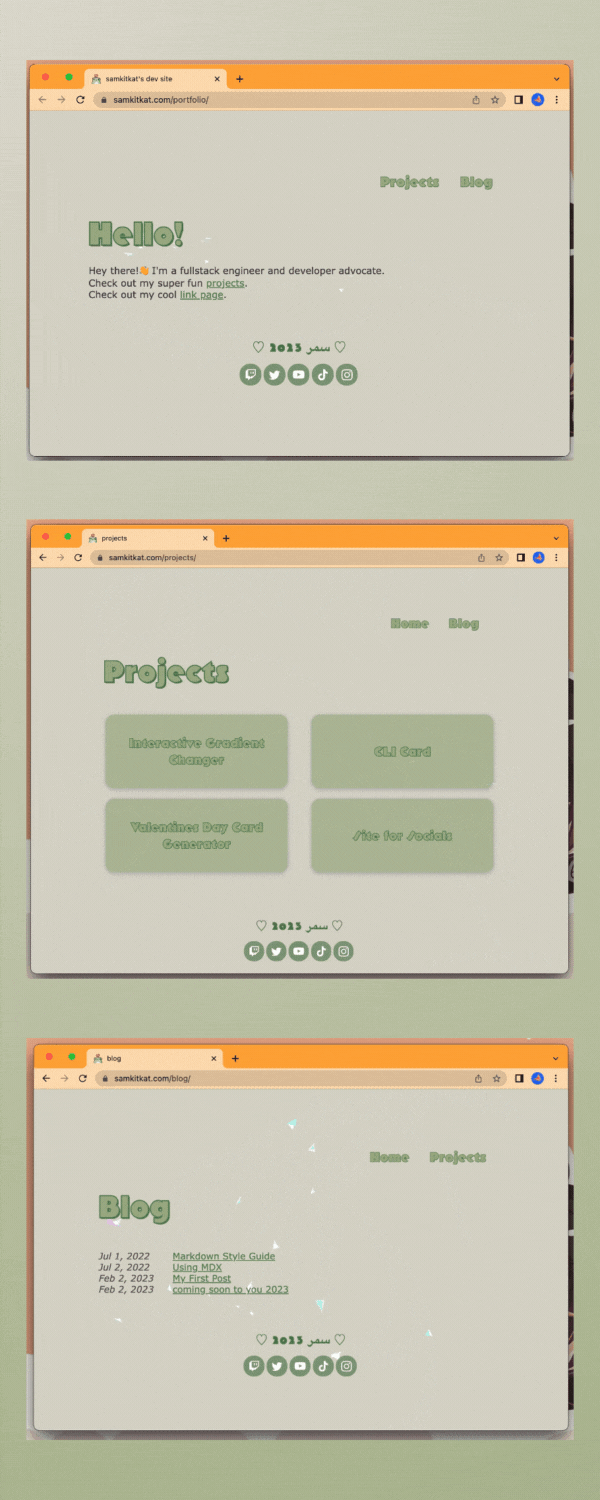
decided to build this site using the astro.build web framework. so far I really enjoy the framework! I absolutely love the idea of reusable components which is why I was drawn towards reactjs, this allows you to do the same even with just plain vanilla js ₍ᐢ•ﻌ•ᐢ₎*:・゚
#codeblr#progblr#astro.build#reactjs#website development#javascript#portfolio#software#webdev#programming#tech#front end dev
94 notes
·
View notes
Text
Check Out my Youtube Clone
# Youtube 2.0 Nexjs Supabase
# Live Site - https://youtube-nextjs.netlify.app/
# Time TO Finish This Project : 2 Months (working time :2 Hours/day)
# Live Working
# Features
- Upload/Edit/Delete Video
- Comment/Reply/ShoutOut
- Search/ Tag Filter, Voice Search
- Emoticon supported 🙂
- Like/Dislike Comment, Replies, Videos
- Subscribe/Unsubscribe
- Subscriptions Feed Recommendation
- Save to Watch Later
- Liked Video Playlist
- Studio Features ✨
- Edit Video Thumbnail
- Customization - Change Channel Image, Banner Image, ChannelName, Location
- Add Social Links
- Dark Mode Feature
## Tech Stacks Used
- Next.js
- Supabase (For Auth And Backend)
- React Emoji Picker
- React Context Api
### I have added most of the features If You want to contribute you are Welcome :), you can add some more features which I have missed. Or You can Remove some bugs
GITHUB LINK:
#programming#webdev#web developers#codeblr#code#html#reactjs#coder#website#webdesign#frontend#coding#open source
56 notes
·
View notes
Text
How can I control render blocking in an HTML and React.js application?
Render blocking can significantly impact the performance of your HTML and React.js application, slowing down the initial load time and user experience.
It occurs when the browser is prevented from rendering the page until certain resources, like scripts or stylesheets, are loaded and executed. To control render blocking, you can employ various techniques and optimizations. Let's explore some of them with code examples.
#libraries#web design#website#reactjs#web development#web developers#html css#ui ux design#tumblr ui#figma#blue archive#responsivedesign#responsive website#javascript#coding#developer#code#software#php script#php programming#phpdevelopment#software development#developers#php#php framework#jquery
17 notes
·
View notes
Text
ERP Trends 2024: Unveiling the Future of ERP Systems.
Visit Website, Glasier Inc.
Our Blogs
Other Services,
erp software development company
hospital management system
Hire Angular Developers
Hire SaaS developer
Hire Flutter Developers
Hire ReactJs Developers
#Custom ERP software development#ERP development services#ERP development#ERP software development services#ERP development Company#app development cost#app development#website#ios application development services#offshore developers#hire dedicated reactjs developers
1 note
·
View note
Text
0 notes
Link
Picking the right ReactJS development company is not a simple task. You need to put extra effort into researching and properly analyzing and evaluating the skills and expertise of the company. But, at present, we are reducing your effort If you are looking for top quality ReactJS development Services then OrangeMantra is the best place for you. we are offering quality services from last 2 Decades.
0 notes
Photo

hanks for the support 🥇 . . . . . . . .📌 How to become a self-taught developer? ⚡ Useful links and roadmaps in my bio! ———————————————————————— 📌 Follow: @rehman_coding 💼 Portfolio: www.a-rehman.com ⚙️ GitHub: https://github.com/MuhRehman 💎 LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/in/abdul-rehman-%E2%9C%94-8611505b/. ... .. . . .Follow the Front End guide for more html, css, JavaScript and ReactJs lessons, tips and tricks 📈🚀 #frontend #html #css #javascript #reactjs #developer #programming #webdevelopment #softwaredevelopment #coder #fullstack #programminglife #fullstackdev #html5 #website #htmlcss #coding #programmer #frontendguide #redux https://www.instagram.com/p/CkX5RObj7bU/?igshid=NGJjMDIxMWI=
#frontend#html#css#javascript#reactjs#developer#programming#webdevelopment#softwaredevelopment#coder#fullstack#programminglife#fullstackdev#html5#website#htmlcss#coding#programmer#frontendguide#redux
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
Harnessing the Power of Node.js for Scalable and Fast Web Development

Introduction:
In today’s fast-paced digital world, building web applications that can handle massive traffic while maintaining quick response times is crucial. Node.js, an open-source, cross-platform JavaScript runtime environment, has emerged as a powerful tool for developers looking to create scalable and high-performance web applications. This blog explores how Node.js empowers developers to achieve these goals, with practical examples illustrating its benefits.
What is Node.js?
Node.js is a server-side platform built on Google Chrome’s V8 JavaScript engine. It enables developers to use JavaScript for server-side scripting, which means you can create the entire front and backend application using just one language. This unification simplifies development and allows for a more consistent and streamlined process.
Why Choose Node.js for Web Development?
1. Asynchronous and Event-Driven Architecture in Node.js
One of the most significant features distinguishing Node.js from other server-side platforms is its asynchronous, non-blocking architecture. This architectural choice allows Node.js to handle multiple tasks simultaneously, making it exceptionally well-suited for building high-performance, scalable web applications.
Understanding Asynchronous, Non-Blocking I/O
In traditional server environments, operations like reading a file from disk, querying a database, or making an API call are usually synchronous, meaning they block the execution of other tasks until the operation completes. This is known as blocking I/O. In such systems, if a request to read a file takes a few seconds, the server would be idle during that time, unable to handle other requests.
Node.js, however, adopts a different approach through its asynchronous, non-blocking I/O model. When a time-consuming operation is initiated, such as reading a file or querying a database, Node.js does not wait for the operation to complete. Instead, it continues processing other tasks. Once the operation is finished, a callback function is triggered to handle the result. This model allows Node.js to easily handle thousands of concurrent operations, making it highly efficient for I/O-bound tasks.
Example: Asynchronous File Reading in Node.js
To illustrate how this works, let’s consider a simple example: a Node.js server reads a file from the filesystem and sends its contents to the client.const http = require('http'); const fs = require('fs'); http.createServer((req, res) => { fs.readFile('file.txt', (err, data) => { if (err) { res.writeHead(500); return res.end('Error loading file'); } res.writeHead(200); res.end(data); }); }).listen(8080);
In this example:
Server Setup: We set up an HTTP server using Node.js. When a request is received, the server attempts to read the contents of a file named file.txt.
Asynchronous File Read: The fs.readFile function is called to read the file. This function is asynchronous, meaning it does not block the server while the file is being read. Instead, Node.js continues to listen for and handle other incoming requests.
Callback Function: Once the file has been read, the callback function provided to fs.readFile is executed. If an error occurs during the file reading, the server responds with an error message. Otherwise, it sends the file’s contents to the client.
Non-Blocking Behavior: While the file is being read from the disk, the server is free to handle other requests. This non-blocking behavior is what makes Node.js highly efficient, as it allows the server to maximize resource utilization and serve multiple clients simultaneously.
Deep Dive: How the Event Loop Works
The magic behind Node.js’s non-blocking I/O lies in its event-driven architecture, powered by the event loop. The event loop is a fundamental part of Node.js that manages asynchronous operations.
Event Loop Basics:The event loop is a loop that continuously checks if there are tasks, like I/O operations, that need to be processed. When an asynchronous operation is initiated (e.g., a file read operation), it’s offloaded to the system’s I/O operations, and Node.js continues to run the event loop. Once the operation is complete, the result is pushed onto the event loop, which then executes the associated callback function.
Single-Threaded Nature:Despite being single-threaded, Node.js handles concurrency through the event loop. This single-threaded model eliminates the overhead associated with managing multiple threads, such as context switching, making Node.js lightweight and fast.
Scalability:
Because of its non-blocking I/O and event-driven nature, Node.js can handle a large number of concurrent connections with minimal resource consumption. This makes it ideal for applications that need to scale efficiently, like real-time applications (e.g., chat apps, gaming servers), APIs, and microservices.
Advantages of Asynchronous, Non-Blocking I/O
Improved Performance: By not waiting for I/O operations to complete, Node.js can process many requests simultaneously, reducing idle time and improving overall performance.
Scalability: Node.js’s ability to handle multiple operations concurrently allows it to scale easily, making it a preferred choice for applications that expect a high volume of traffic.
Resource Efficiency: Because Node.js operates on a single thread, it uses system resources more efficiently compared to multi-threaded systems that require more memory and CPU to manage multiple threads.
Real-Time Capabilities: Node.js’s asynchronous nature makes it particularly well-suited for real-time applications that require quick and continuous interaction, such as messaging apps, collaborative tools, and live dashboards.
2. Deep Dive into High Scalability in Node.js
Node.js has become a cornerstone for developers aiming to build applications that can handle a massive number of concurrent connections without compromising performance. At the heart of its scalability lies the single-threaded, event-driven architecture that allows Node.js to manage thousands of connections simultaneously with minimal overhead. This approach contrasts sharply with traditional server environments that often struggle with scalability due to the need to spawn a new thread for each connection.
Understanding the Single-Threaded Event Loop
The event loop is a core concept in Node.js. Unlike traditional multi-threaded servers, where each connection or request spawns a new thread, Node.js operates on a single thread. This single thread handles all incoming connections using an event loop, which is a continuous loop that listens for and processes events or messages in the system.
When a new connection is made, Node.js doesn’t create a new thread or process. Instead, it registers a callback function, which will be invoked when a particular event (like receiving data) occurs. This non-blocking, asynchronous approach allows Node.js to handle thousands of connections without the overhead of creating and managing thousands of threads.
Why is This Architecture So Scalable?
Reduced Overhead: Traditional server environments like those built with Java or PHP often create a new thread for each incoming connection. Each thread consumes system resources, including memory and CPU. As the number of concurrent connections grows, the system can quickly become overwhelmed by the sheer number of threads it needs to manage.
In contrast, Node.js uses a single thread to manage all connections. The event loop handles I/O operations asynchronously, which means the server can process multiple requests without waiting for any single operation to complete. This significantly reduces the system’s overhead, allowing Node.js applications to scale much more efficiently.
Efficient Resource Utilization: Because Node.js doesn’t create a new thread for each connection, it can efficiently utilize the system’s CPU and memory. The event-driven architecture ensures that CPU resources are not wasted on idle threads. Instead, the CPU is only engaged when there’s actual work to do (i.e. when an event occurs).
Handling High Throughput: Node.js excels in environments where high throughput is required, such as real-time applications or APIs that serve thousands of requests per second. Since the event loop can process multiple I/O-bound requests simultaneously, the server can handle a large volume of connections without being bogged down by the need to manage numerous threads.
Practical Example: A Scalable WebSocket Server
To illustrate how Node.js’s scalability works in practice, let’s consider the example of a simple WebSocket server. WebSockets are used for real-time communication between a client and server, such as in chat applications, online gaming, or live collaboration tools.const WebSocket = require('ws'); const wss = new WebSocket.Server({ port: 8080 }); wss.on('connection', (ws) => { ws.on('message', (message) => { console.log(`Received: ${message}`); ws.send(`Server: ${message}`); }); });
How It Works:
WebSocket Server Setup: The server is set up to listen on port 8080. When a client connects, the connection event is triggered.
Event-Driven Message Handling: For each connection, the server listens for messages from the client. When a message is received, the server logs it and sends a response back to the client.
No New Threads: Crucially, when a new connection is established, Node.js doesn’t create a new thread. Instead, it simply registers the event listeners (like connection and message) and continues running. This approach allows the server to handle a large number of connections concurrently.
Scalability in Action:
Multiple Connections: Whether the server is handling 10, 100, or 10,000 connections, the event loop processes each event in turn, ensuring that no connection is left waiting for long. This is particularly important in scenarios like chat applications, where low latency and high throughput are essential.
Real-Time Updates: In real-time applications like online games or live dashboards, the ability to send and receive messages almost instantaneously is crucial. Node.js’s non-blocking architecture ensures that messages are processed as soon as they are received, without delays caused by waiting for other operations to complete.
3. Unified Language Environment: JavaScript Everywhere
One of the standout features of Node.js is its ability to use JavaScript for both client-side and server-side development. This unification of languages is a game-changer in the development process, offering several key advantages that improve efficiency, consistency, and collaboration across the entire development cycle.
A. Streamlined Development Process
In traditional web development, different languages are often used for the front end and back end. For example, you might use JavaScript for frontend tasks like DOM manipulation and PHP or Python for backend operations like handling server requests or database interactions. This separation can create a disconnect between different parts of the development process, as developers need to switch contexts and sometimes even skill sets when moving between frontend and backend tasks.
In Node.js, JavaScript is used for both the client (frontend) and server (backend), creating a more seamless development process. This unification means that developers can focus on mastering a single language, reducing the cognitive load and increasing productivity.
B. Improved Team Communication and Collaboration
When the entire stack is written in JavaScript, team members across different roles—such as frontend developers, backend developers, and full-stack developers—can communicate more effectively. Everyone speaks the same language, which fosters better collaboration and understanding.
For example, if a frontend developer needs to implement a feature that requires backend support, they can easily discuss the requirements and potential solutions with a backend developer, since they’re both working within the same language framework. This reduces the chances of miscommunication and speeds up the development process.
C. Code Reusability Across the Application
One of the most significant advantages of using JavaScript across both the frontend and backend is the ability to reuse code throughout the application. Code reusability not only saves time but also ensures consistency and reduces the likelihood of bugs.
Example: Validation Function
Let’s take the example of a validation function. In many applications, you need to validate user input—such as checking if a username is at least a certain number of characters long. Traditionally, you might write this validation logic twice: once in the front end to provide instant feedback to the user and once in the back end to ensure that the input is still valid when it reaches the server.
In a Node.js environment, you can write this validation function once and use it in both places:// Validation function function validateInput(input) { return input && input.length > 3; } // Client-side usage if (validateInput(userInput)) { console.log('Valid input on client side'); } // Server-side usage app.post('/submit', (req, res) => { if (validateInput(req.body.input)) { res.send('Valid input on server side'); } else { res.send('Invalid input'); } });
In this example, the validateInput function is written once and then reused in both the client-side code (e.g., within the browser) and the server-side code (within the Node.js backend). This approach eliminates the need to duplicate code and ensures that the validation logic is consistent no matter where it’s applied.
D. Consistency and Reduced Redundancy
When you use the same language throughout your stack, you naturally reduce redundancy in your codebase. This reduction not only simplifies the maintenance of your application but also makes it easier to debug and extend in the future.
Consistency across the application is crucial for maintainability. If the same logic is applied consistently across different parts of the application, it’s easier to ensure that changes are implemented correctly and that all parts of the application behave as expected.
Example in Practice:Consider a scenario where you need to update the validation logic, such as changing the minimum length requirement for a username from 3 to 5 characters. In a non-unified environment, you would have to update this logic in both the frontend and backend codebases, potentially missing one of them and causing inconsistencies. With Node.js, you update the function in one place, and the change is automatically reflected everywhere it’s used.// Updated validation function function validateInput(input) { return input && input.length > 5; } // The same function is now applied across the app, maintaining consistency
This ability to maintain a single source of truth for critical business logic reduces the likelihood of errors and simplifies ongoing maintenance.
E. Easier Learning Curve for Full-Stack Development
Because JavaScript is used both on the client and server sides, developers who are familiar with frontend development can more easily transition to backend development (and vice versa). This unified environment lowers the barrier to becoming a full-stack developer, enabling more team members to contribute to different parts of the project.
Learning and adapting to full-stack roles becomes less daunting when developers only need to master one language. This versatility also increases the agility of development teams, as members can shift between tasks as needed without the friction of learning a new language or framework.
4. Rich Ecosystem with npm
Node.js comes with npm (Node Package Manager), which hosts a vast repository of packages and libraries. With npm, you can easily find and integrate third-party modules into your project, speeding up development and adding robust functionality without having to build everything from scratch.
Example:
Let’s say you need to set up a web server. Instead of writing server logic from scratch, you can use Express.js, a popular framework for Node.js:const express = require('express'); const app = express(); app.get('/', (req, res) => { res.send('Hello World!'); }); app.listen(3000, () => { console.log('Server is running on port 3000'); });
This example shows how easy it is to set up a web server using Express.js. With just a few lines of code, you have a functioning server, and you can focus on adding the features that make your application unique.
5. Real-Time Applications
Node.js excels in building real-time applications where data needs to be processed and displayed instantly, such as chat applications, live dashboards, or online gaming.
Example:
Consider a live chat application where users need to receive and send messages in real-time. Node.js, with its non-blocking I/O and WebSocket support, can handle such applications with ease.const io = require('socket.io')(server); io.on('connection', (socket) => { socket.on('chat message', (msg) => { io.emit('chat message', msg); }); });
This code snippet shows how to create a basic real-time chat application using Socket.IO, a library that enables real-time, bidirectional communication between clients and servers.
Conclusion
Node.js is a versatile and powerful platform for modern web development, offering scalability, speed, and a unified development environment. Its asynchronous architecture, rich ecosystem, and real-time capabilities make it an ideal choice for building applications that need to handle large numbers of concurrent users or require quick response times.
By leveraging the strengths of Node.js, developers can build high-performance, scalable web applications that meet the demands of today’s fast-paced digital landscape. Whether you’re working on a small project or a large enterprise application, Node.js provides the tools and flexibility to create robust and efficient solutions.
#web development#ui ux design#web design#e commerce#digita marketing#businessgrowth#nodejs#phpdevelopment#node.js#reactjs#software development#website development#web design company#web design services#web developers#software
0 notes