#Solar Grid
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
"Evening is approaching at the confluence of two rivers in the Bay of Bengal — the Payra and Bishkhali. Still, the fishermen at the pier in Gazimahmud village are busy preparing for the next day’s work — every boat here is now illuminated by small solar-powered devices.
“Solar power is now not only in homes, it is also at our work. Now, there is no rush to return home when it is evening,” says fisherman Altaf Hossain, who is arranging fishing nets in his boat so that he’s ready for tomorrow.
Hossain is now able to work longer hours and boost his income, and he doesn’t have to worry about his wife and kids at home at night. The children sit under a solar-powered light to study, while Hossain’s wife, Roksana Begum, does various chores.
“The sun gives us light both during the day and at night,” Begum says. “It has made our lives much easier and has changed our livelihoods.”
Gazimahmud village is about 30 kilometres away from Barguna Sadar, the southernmost district of Bangladesh. A winding road leads to this village, where the sea and two rivers meet. The people of this remote community still remember the devastation caused by the powerful Cyclone Sidr in 2007, when 30 locals died. When the storm hit, it was difficult for many to reach safety as the entire area was dark. Now, thanks to most of the houses in the village having solar power, the community feels better prepared for future disasters.
“We have more faith in solar power, because, when a storm comes, the electricity connection may be disconnected or the power may be turned off, but solar power helps us to find a safe shelter by showing us the way,” says resident Monir Hossain.
Unprecedented success
Bangladesh has implemented the world’s largest off-grid solar power programme, with 20 million people across the country benefiting, according to the World Bank.
What began as a pilot project in 2003, involving 50,000 households, ultimately reached 14% of the population within 15 years, while some 200,000 rural businesses and religious facilities benefited from the Solar Home Systems (SHS) initiative as well.
The programme, which officially ran until 2018, was implemented in partnership with the private sector. Among other measures, the state provided generous incentives, such as tax breaks, for rooftop solar installers, and also focused on ensuring financing mechanisms were in place.
Together with 56 partner organisations, the government installed 4.1 million solar systems in remote areas by 2018.
According to the World Bank, the initiative has improved health and living conditions — including by reducing the use of kerosene lamps and thereby tackling indoor air pollution — and boosted school attendance. It also led to household solar becoming “a credible electricity source”.
“The Solar Home Systems programme has shown that millions of dollars raised internationally can be efficiently leveraged to provide loans of as little as $100 in remote corners of the country, enabling a rural household to purchase a solar home system,” according to Amit Jain, a senior energy specialist at the World Bank...
To clean up its power grid and contribute to the fight against climate change, Bangladesh plans to install 4.1GW of renewable energy capacity by 2030, up from around 1.2GW today."
-via The Progress Playbook, March 10, 2025
#bangladesh#asia#solar power#solar panels#solar grid#renewable energy#green energy#solar energy#solar pv#climate change#climate action#climate resilience#natural disasters#electricity#electrification#infrastructure#good news#hope
626 notes
·
View notes
Text
Dandelion News - March 22-28
Like these weekly compilations? Tip me at $kaybarr1735 or check out my Dandelion Doodles! This month’s doodles, like every third month, will be free to the public, so take a look!
1. Crucial and heartwarming: see world’s first-ever wild jaguar translocation in Argentina

“Miní[, an offspring of rewilded jaguars,] is the first-ever release of a wild-born jaguar that’s been translocated for conservation purposes. […] Miní has joined two previously captive female jaguars [in a park] where a small, all-male wild population had been dwindling.”
2. Illinois Gov. Pritzker stands up for LGBTQ+ community in fiery HRC speech

“The governor particularly spoke out for transgender youth, saying we must not sacrifice the most persecuted for the most popular. [… “]Bullies respond to one thing, and one thing only, a punch in the face.”
3. The UK’s First ‘Stork Village’ Takes Flight

“For the first time in more than six centuries, white storks are calling Britain home again thanks to a dedicated conservation initiative to save the species. […] At the end of 2024, breeding numbers saw egg-straordinary results with 27 nests and 53 baby storks, doubling the previous year’s numbers.”
4. A quiet shift: The grid is being redefined by household consumers who no longer need it full time

“With rising adoption of rooftop solar, batteries, and electric vehicles, households are gradually altering their relationship with the grid. […] This redefined relationship doesn’t signal rejection — it reflects the growing capacity of households to meet part of their own needs.”
5. Europe’s Wolf Population On The Rise

““The recovery of wolves across human-dominated landscapes of Europe has been continuing during the past decade, with their population growing to over 21,500 individuals by 2022—a 58% increase in a decade,” the authors wrote. [… O]n average wolves killed 0.02% of livestock each year.”
6. Hospitals awarded funding for solar power work

“The investment of £8.5m by state-owned Great British Energy will enable rooftop panels and solar car ports to be installed at [several hospitals]. […] "Together, these panels will generate estimated savings of more than £635,000 a year."”
7. Nebraska Boards Sponsor Grain Bin Rescue Equipment, Training for Fire Departments

“[Nebraska Corn and Soybean boards are] donating two grain rescue tubes and two training sessions to fire and rescue departments in Nebraska. [… T]he initiative aims to equip rural fire and rescue teams with the knowledge and tools to respond to grain bin entrapments effectively.“
8. Sugar beet pulp fibers show potential for nutritional supplements and sustainable plastic alternatives

“New technology can separate the fibers in the sugar beet pulp left over after sugar production. Part of the fiber can be used as a nutritional supplement due to its anti-inflammatory properties[… and a]nother part of the fiber, the cellulose, can be made into components to replace, for example, plastic.”
9. Osmotic Power: The Next Wave of Renewable Energy

“Sweetch Energy’s technology could [produce] around 20 or 25 W/m2, a significant leap compared to the 1 W/m2 achieved by previous membrane devices. Moreover, by utilizing a biosourced material readily available within the industry for their membranes, the company anticipates the cost of materials would be reduced to one-tenth of the current price[….]”
10. Renegade Colorado Farmer Pushes Deeper into Unconventional Agriculture

“The grasshoppers stayed in the [pollinator] strips, and that triggered praying mantis to come in and eat. […] An agrivoltaic system […] has reduced moisture consumption by significant levels[….] “Local food nationwide is how to counter the industrial scale food industry.””
March 15-21 news here | (all credit for images and written material can be found at the source linked; I don’t claim credit for anything but curating.)
#hopepunk#good news#conservation#jaguar#big cats#illinois#us politics#lgbt+#lgbtq#trans rights#stork#britain#birds#electricity#electric grid#solar panels#wolves#wolf#animals#solar energy#agriculture#grain#fire department#sustainability#plastic#renewableenergy#osmosis#clean energy#farming#research
137 notes
·
View notes
Text


Atlantica Solana Generating Station - Arizona - USA 🌎 4K links : 1 & 2
#4k#wallpaper#google earth#satellite view#aerial photography#solar panels#power station#arizona#solana#usa#lines#geometry#abstract#texture#pattern#grid#atlas#landscape#desert#industrial#electricity#dji
523 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
Thirty years ago, a group of permaculture experts purchased 329 acres of degraded land in Western North Carolina with a vision: to restore the landscape while creating a new model of communal living.
What began as an experiment in living well off the land has grown into one of the nation’s oldest cohousing communities, where residents live collaboratively and in close connection with their environment.
The community now spans 13 distinct neighborhoods with over 100 residents, each offering a different approach to shared living. Some neighborhoods function as housing co-ops (North Carolina law requires at least five members for this designation), while others feature apartments, duplexes, or single-family homes.
Earthaven’s infrastructure reflects decades of experimentation and ingenuity. From hydroelectric power generated by mountain streams to solar systems energizing both communal and private spaces, the village is a model of thoughtful design.
Residents live in hand-built homes that range from timber-framed duplexes to snug cob cottages, sharing resources like kitchens, workshops, and gardens. Guided by principles of self-governance, consensus decision-making, and cooperative ownership, Earthaven fosters deep connections—not only with the natural world but also among its members, creating a way of life rooted in resilience and shared purpose.
Recently, Earthaven suffered significant damage from Hurricane Idalia, which tore through the region, leaving many homes and shared facilities in need of repair. The community is currently rebuilding and has launched a fundraising campaign to restore its infrastructure and continue its mission of regenerative living.
—Donate to Earthaven's Hurricane Helene recovery fund: https://www.gofundme.c...
—Take a Virtual Tour: https://www.schoolofin...
—Become a Friend: https://www.schoolofin...
—Take a class with the School of Integrated Living: https://www.schoolofin...
—More videos: / @earthavenecovillage
—Earthaven on Wikipedia: https://en.wikipedia.o...
On *faircompanies: https://faircompanies....
#Kirsten Dirksen#solarpunk#eco village#Earthaven#north carolina#USA#co op#co op housing#sustainable architecture#sustainability#off grid#off grid living#solar power#hydroelectric power#green energy#clean energy#renewable energy#Youtube
40 notes
·
View notes
Text



Off-grid hideout.
Shower thoughts hits different when your water pressure depends on a nearby stream. 🚿🌲
#natureapproved #offgrid #offgridliving
#off grid#off grid living#off grid solar system#hideout#cottagecore#bedroom#bathroom#gardening#home#home decor#cabin#log cabin#cabin in the woods#cabin interior
23 notes
·
View notes
Text
The current U.S. power grid is not fully prepared to handle the rising demand from AI, EVs, and crypto without significant upgrades. While the grid is evolving, challenges include aging infrastructure, transmission bottlenecks, and the need for more renewable energy integration. Here’s a breakdown of key factors:
1. Capacity vs. Demand Growth
• The grid has enough total generation capacity today, but localized demand spikes (like AI data centers or EV clusters) can strain certain regions.
• By 2035, electricity demand could rise by 15-25%, requiring hundreds of gigawatts (GW) of new capacity.
• Many utilities are already struggling to build out transmission lines fast enough to keep up with demand.
2. Grid Reliability & Stress Points
• AI & Data Centers: Large data centers are being built in regions where power supply is already constrained (e.g., Northern Virginia, Texas).
• EV Charging Peaks: If too many EVs charge at the same time, local grids could experience voltage drops or blackouts.
• Extreme Weather: The grid is already vulnerable to extreme heat, storms, and wildfires, which could worsen with climate change.
3. Solutions & Grid Upgrades
• Transmission Expansion: The U.S. needs to build more high-voltage transmission lines to move power from wind/solar farms to urban areas.
• Battery Storage & AI for Grid Management: Advanced battery storage can smooth out supply-demand mismatches, and AI can optimize grid operations.
• Decentralized Energy: Microgrids, rooftop solar, and community battery projects can reduce strain on the centralized grid.
• Smart Charging for EVs: Managed charging (incentivizing off-peak charging) can help distribute demand more evenly.
Can the Grid Handle It?
• Short-term (2025-2030): The grid will face localized stress, especially in high-demand regions. Rolling blackouts or infrastructure failures could occur if upgrades don’t keep pace.
• Mid- to Long-term (2030+): If investments in transmission, renewables, and smart grid technology accelerate, the grid can handle these changes, but delays in modernization could lead to reliability issues.
#politics#us politics#political#donald trump#news#president trump#elon musk#american politics#jd vance#law#power grid#power#gas#oil#solar#wind power#crypto#cryptocurrency#crypto mining#infrastructure#us infrastructure
22 notes
·
View notes
Text




Solar Flare 2.0, Oasis Springs - Lounge
#The Sims 4#TS4#Sims 4#Solar Flare#Oasis Springs#Yes I take my shots from build mode#Maybe I need to turn the grid lines off haha#BAW: Oasis Springs
75 notes
·
View notes
Text
What’s the true cost of going off grid?
We’ve been inspired by so many off grid stories over the years like belovedcabin. What inspires you to make your own off grid getaway or make it a fully time lifestyle? No bills? No neighbours? Land to roam? Freedom to do whatever you want? Let’s find out…
https://theoffgridcabin.com/off-grid-living
#offgridcabin#off grid land#life off grid#diy cabin#homesteading#how to homestead#solar energy#solar
35 notes
·
View notes
Text
i don't want to sound like a doomer but even though the milestone of 40% renewable/"clean" energy generation was reached last year, emissions also reached an all-time high, 4% higher than ever before. this is allegedly due to the increased demand for air conditioning as the temperature of the planet rises. the new clean energy production mostly covered the cost of demand for new technology demand like LLM AI's use of power. i'm not saying AC is bad. the point is that new power is being generated for new demand while extant demand (and then some) is still being provided by the same source of power: fossil fuels. the goal can't just be adding newer greener power, it has to be about removing the sources of power causing emissions and fundamentally removing the option to continue increasing emissions as well.
it is projected that the production of "cleaner" electricity will outpace this increased demand -- for air conditioning, at least. cooling/ac also only accounts for 3% of total co2 emissions; heating actually causes far more emissions.

refrigerant emissions do not come anywhere near where they'd need to be to reach the level of emissions heating produces, also..
heat is direct energy demand because heat is literally energy. cooling is the use of energy to push air through a refrigerant system, causing a chemical interaction that reduces the total energy (heat) of the air as it's expelled back out of the unit -- meaning that it is using heat (and energy) indirectly to moderate temperature. heating can also frequently come from direct burning of fuel, which produces co2 by its very nature. you would literally do more on a personal level by never taking a hot shower again than turning off your ac, but personal lifestyle changes have limited effect anyway.
there are a lot of factors going into every statistic that makes even attempting to understand climate change confusing and depressing to read. they are all important, though. the most important one is emissions. we are making cleaner energy to reduce emissions. if we have failed to reduce emissions then it has not accomplished that goal.
#i'm also skeptical of the fact that most of it's solar#i also don't like the framing of ac as the cause of excess but it may be accounting for actual production and not projected totals#for example a server farm that has built its own solar grid for power will not produce many emissions#despite demanding a lot of power#whereas a person who lives in the south and has no option but to receive electricity from a coal plant to cool their home#if obviously going to produce more emissions even though the demand for energy is far less than the server farm#which is what i mean by producing more clean energy for new demand instead of replacing coal sources#and those new technologies also demand cooling...#but as far as i could tell the source of demand for cooling was people using their ac's more during heat waves
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
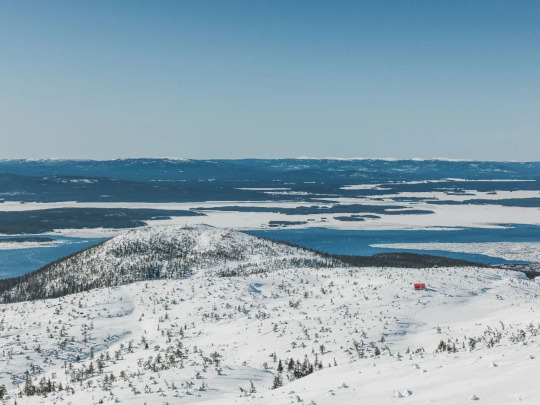
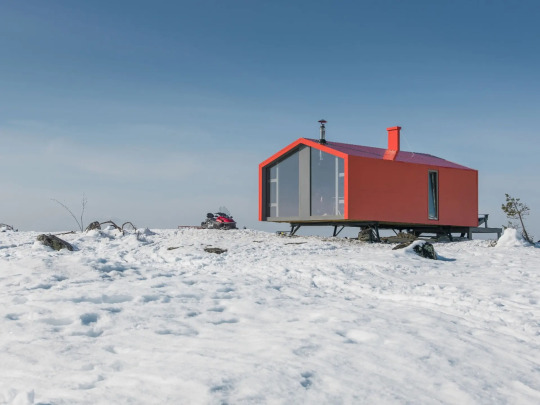
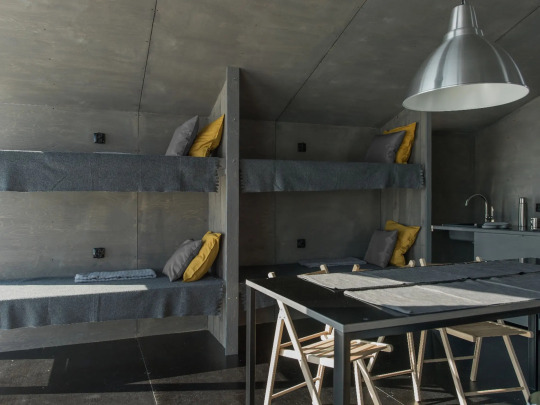
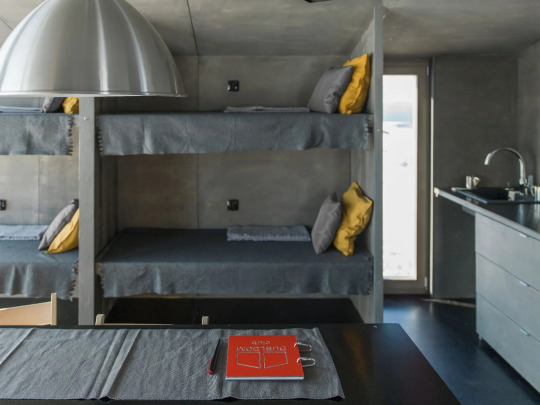
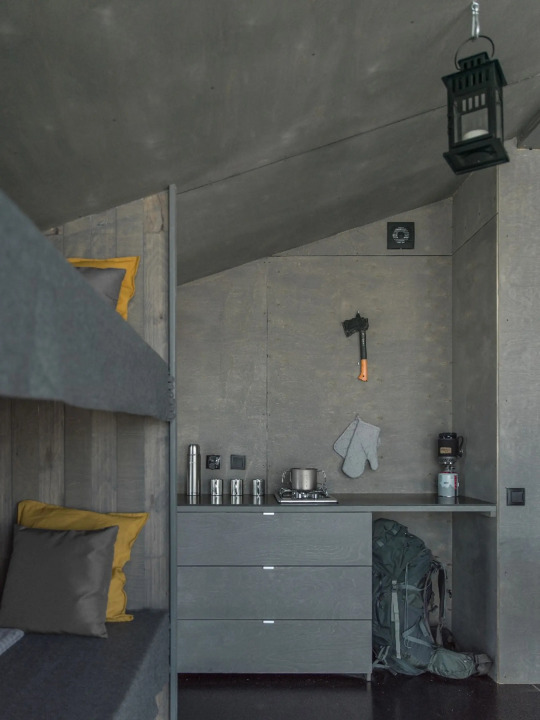
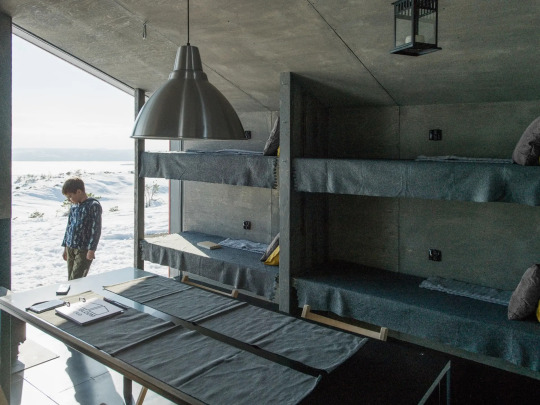













DublDom Kandalaksha, Kandalaksha, Russia,
DublDom in Association with Bio Architects
#art#design#architecture#minimal#interior design#retreat#off-grid#solar system#sustainability#russia#dubldom#kandalaksha#bio architects#prefab#nature#wilderness#wildlife#shelter
135 notes
·
View notes
Text
Scientists have developed a new solar-powered system to convert saltwater into fresh drinking water which they say could help reduce dangerous the risk of waterborne diseases like cholera.
Via tests in rural communities, they showed that the process is more than 20% cheaper than traditional methods and can be deployed in rural locations around the globe.
Building on existing processes that convert saline groundwater to freshwater, the researchers from King’s College London, in collaboration with MIT and the Helmholtz Institute for Renewable Energy Systems, created a new system that produced consistent levels of water using solar power, and reported it in a paper published recently in Nature Water.
It works through a process called electrodialysis which separates the salt using a set of specialized membranes that channel salt ions into a stream of brine, leaving the water fresh and drinkable. By flexibly adjusting the voltage and the rate at which salt water flowed through the system, the researchers developed a system that adjusts to variable sunshine while not compromising on the amount of fresh drinking water produced.
Using data first gathered in the village of Chelleru near Hyderabad in India, and then recreating these conditions of the village in New Mexico, the team successfully converted up to 10 cubic meters, or several bathtubs worth of fresh drinking water. This was enough for 3,000 people a day with the process continuing to run regardless of variable solar power caused by cloud coverage and rain.
[Note: Not sure what metric they're using to calculate daily water needs here. Presumably this is drinking water only.]
Dr. Wei He from the Department of Engineering at King’s College London believes the new technology could bring massive benefits to rural communities, not only increasing the supply of drinking water but also bringing health benefits.
“By offering a cheap, eco-friendly alternative that can be operated off the grid, our technology enables communities to tap into alternative water sources (such as deep aquifers or saline water) to address water scarcity and contamination in traditional water supplies,” said He.
“This technology can expand water sources available to communities beyond traditional ones and by providing water from uncontaminated saline sources, may help combat water scarcity or unexpected emergencies when conventional water supplies are disrupted, for example like the recent cholera outbreaks in Zambia.”
In the global rural population, 1.6 billion people face water scarcity, many of whom are reliant on stressed reserves of groundwater lying beneath the Earth’s surface.
However, worldwide 56% of groundwater is saline and unsuitable for consumption. This issue is particularly prevalent in India, where 60% of the land harbors undrinkable saline water. Consequently, there is a pressing need for efficient desalination methods to create fresh drinking water cheaply, and at scale.
Traditional desalination technology has relied either on costly batteries in off-grid systems or a grid system to supply the energy necessary to remove salt from the water. In developing countries’ rural areas, however, grid infrastructure can be unreliable and is largely reliant on fossil fuels...
“By removing the need for a grid system entirely and cutting reliance on battery tech by 92%, our system can provide reliable access to safe drinking water, entirely emission-free, onsite, and at a discount of roughly 22% to the people who need it compared to traditional methods,” He said.
The system also has the potential to be used outside of developing areas, particularly in agriculture where climate change is leading to unstable reserves of fresh water for irrigation.
The team plans to scale up the availability of the technology across India through collaboration with local partners. Beyond this, a team from MIT also plans to create a start-up to commercialize and fund the technology.
“While the US and UK have more stable, diversified grids than most countries, they still rely on fossil fuels. By removing fossil fuels from the equation for energy-hungry sectors like agriculture, we can help accelerate the transition to Net Zero,” He said.
-via Good News Network, April 2, 2024
#water#water scarcity#clean water#saline#desalination#off grid#battery technology#solar power#solar energy#fossil fuels#water shortage#india#hyderabad#new mexico#united states#uk#united kingdom#good news#hope#aquifers
1K notes
·
View notes
Text


GASHJDKSDHSJ I LOVE THEM😭
Art trade!!!! With the AWESOMEST @colinmkl !!!! Gave me the opportunity of drawing ✨the girls✨ again and I’m just OBSESSED!!! AFJFJJSJJDJDXKJS THANK YOU SO MUCH!! This was SO much fun!!!!
#Happy Pride Month to THEM AND THEM ONLY <3#ari#Remi#ellarien#power rangers#skylandart#my art#fanart#art#power rangers fanart#boom! comics power rangers#power rangers boom! comics#ari x Remi#solar rangers#beyond the grid#shattered grid#power rangers beyond the grid#pride month#:D
46 notes
·
View notes
Text

Copper Mountain Solar 3 - Nevada - USA 🌎 4k link
#4k#wallpaper#google earth#satellite view#aerial photography#nevada#solar plant#geometric#lines#diagonals#parallels#blue#grid#desert#usa#landscape#earth art#earth from space#earth from above#abstract#atlas#texture#dji#worldview
27 notes
·
View notes
Text
Earth ships don’t sink.
#earthship#ecology#off the grid#sustainableliving#sustainability#homes#unique homes#new mexico#solar power#recycled water#green
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
"everything you want is on the other side of fear" no it's on the other side of brutal burnout, fuck you
#hallie speaks#“home improvement” is an interesting process when you have no grid power and are running off diy solar you got secondhand#Figuring out how to get it from the panels to the outlets is a tripppp and I'm not even the one doing most of the work
7 notes
·
View notes
Text



This weekend had the most perfect run of weather I've ever had at the cabin. This is good, because I was installing solar panels on the roof of my studio. Now, it's all wired up and producing its own power, and I think the studio is done for now.
I mean, I still have to figure out the piping for the wood stove, but it's a long time before winter hits, right?
2 notes
·
View notes