#United States Colored Troops
Text
Tucked away in an amendment to the FY2023 U.S. defense authorization bill is a rare instance of congressional bipartisanship and a tribute to U.S. President Ulysses S. Grant.
If approved, the measure would posthumously promote Grant to the rank of General of the Armies of the U.S., making him only the third person – along with John J. Pershing and George Washington – to be awarded the nation’s highest military honor.
As Executive Director of the Ulysses S. Grant Presidential Library, I believe that the promotion would be much more than a symbolic nod to a great military general. Rather, it would highlight the overlooked legacy of a man who fought to end the last vestiges of slavery.
OUTBREAK OF CIVIL WAR
During the Civil War, Grant rose to fame as a decisive leader who was willing to doggedly pursue Confederate armies and avoid retreat at all costs. He first gained his reputation for tenacity with Union victories at Shiloh, the Battles for Chattanooga and the Siege of Vicksburg.
Like most white Northerners, Grant signed up to fight for the Union – not for emancipation.
But by 1862, the freedom of enslaved African Americans had become vital to the Union war strategy, if not yet its cause.
A year before President Abraham Lincoln signed in 1863 the Emancipation Proclamation that freed enslaved people in the Confederate states, Grant oversaw the establishment of refugee, or contraband camps, throughout the Mississippi Valley. Those camps provided basic housing, food and work for Black men and women who had fled from slavery.
Grant also administered the enlistment of African American men into United States Colored Troops units during the Vicksburg campaign.
In March 1864, Lincoln appointed Grant to the rank of lieutenant general and ordered him to take on the Confederate Army in Virginia, a task at which numerous other Union leaders had failed.
At this point during the war, Grant assumed the role of chief strategist for the entire Union war effort. It took the next 13 months of fighting during the Overland campaign before Confederate General Robert E. Lee surrendered to Grant at Appomattox on April 9, 1865.

In this illustration, Gen. Ulysses S, Grant, left, accepts the surrender of Gen. Robert E. Lee. (Getty Images)
After the Federal victory, many Americans hailed Grant as the man who saved the Union.
But Grant was magnanimous in victory.
Multiple times during the war he honored the dignity of his defeated adversaries, most famously at Appomattox, where he did not require Lee to hand over his sword, as usually required. Grant also allowed Confederate officers to keep their sidearms and horses.
Lee appreciated Grant’s actions, remarking: “This will have the best possible effect upon the men … it will be very gratifying, and will do much toward conciliating our people.”
IMPACT OF THE ‘LOST CAUSE’
But after the war, the conciliatory feelings vanished.
Southern partisans constructed the narrative of the “Lost Cause.” It held that the root of the Civil War was not slavery, but the rights of states to control their own destinies. It further held that the Union victory had nothing to do with Confederate character or leadership, but rather the Union’s sheer numbers and superior resources.
In this Lost Cause narrative, Grant was seen as a bumbling butcher devoid of any meaningful strategic vision, who succeeded only by mercilessly throwing more soldiers at his enemy. It also revived the old rumors of his excessive drinking.
In this storyline, Grant’s foil was always the courtly gentleman, Robert E. Lee. The hagiography of Lee demanded Grant’s inferiority.
By the early 20th century, the Lost Cause was no longer isolated in the South and had spread across America. Crowds flocked to see the racist anti-Reconstruction “Birth of a Nation” in movie theaters, and during the World War I rush to build military bases, the Army named 10 of them after Confederate generals.
PRESIDENT GRANT’S FIGHT FOR EQUALITY
Grant served as President from 1869 to 1877 during a time when white Southerners proved hostile toward federal Reconstruction measures that sought equal rights for recently freed enslaved people.
Grant saw his role of enforcing these policies as an extension of his wartime duty and necessary to protect the gains of the Union victory, especially the newly established rights for African Americans.
He used the resources of the federal government to crush the Ku Klux Klan, established the Department of Justice to investigate civil rights abuses and signed the Civil Rights Act of 1875.
GRANT’S LATEST CAUSE
In recent years, the American public has questioned the Lost Cause and taken steps to mitigate its pervasiveness throughout the U.S.
Southerners themselves have chosen to remove Confederate leaders from town squares and state flags. The U.S. Army has established a Naming Commission to rebrand Confederate-named bases.
It is telling, too, that Grant’s Presidential Library is now located in Mississippi, a Deep South state he once conquered.
It remains to be seen whether the request made to elevate Grant’s rank by U.S. Senators Sherrod Brown of Ohio, a Democrat, and Roy Blunt of Missouri, a Republican – along with GOP U.S Rep. Ann Wagner – will be finally approved by Congress as part of the FY2023 National Defense Authorization Act.
Either way, in my view, a thoughtful reconsideration of Grant’s wartime and post-war contributions is long overdue.
#us politics#us history#Anne Marshall#news#Ulysses S. Grant Presidential Library#national defense authorization act#General of the Armies of the U.S.#John J. Pershing#George Washington#american civil war#american slavery#president ulysses s. grant#Emancipation Proclamation#president abraham lincoln#United States Colored Troops#confederate surrender#Lost Cause myth#reconstruction#birth of a nation#ku klux klan#Civil Rights Act of 1875#department of justice#Grant’s Presidential Library#Sen. sherrod brown#sen. roy blunt#Rep. Ann Wagner#2022#the conversation
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
The War of the Rebellion really does deserve the title of the Second American Revolution....because of these men:
The most revolutionary aspect of the War of the Rebellion was the raising of United States Colored Troops, most of whom were freedmen who'd escaped slavery and were given uniforms and guns to secure their freedom from their former masters at the point of the bayonet. These troops were vital, essential parts of the war from 1863-5. Without them the US Army would have been worn down by attrition and unable to best the Confederacy between the cost of offensives and the need to garrison occupied territories.
The postwar generations, by the time of the McKinley era, achieved a kind of unity in the wake of the savagery of the 1861-5 war by denying these people existed and denying them their just due. This is just one of many betrayals of the truth surrounding the era, and what it actually was versus what it was pretended to be.
#lightdancer comments on history#war of the rebellion#black history month#slavery and resistance#united states colored troops
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Frev Friendships — Saint-Just and Robespierre

You who supports the tottering fatherland against the torrent of despotism and intrigue, you whom I only know, like God, through his miracles; I speak to you, monsieur, to ask you to unite with me in order to save my sad fatherland. The city of Gouci has relocated (this rumour goes around here) the free markets from the town of Blérancourt. Why do the cities devour the privileges of the countryside? Will there remain no more of them to the latter than size and taxes? Support, please, with all your talent, an address that I make for the same letter, in which I request the reunion of my heritage with the national areas of the canton, so that one lets to my country a privilege without which it has to die of hunger. I do not know you, but you are a great man. You are not only the deputy of a province, you are one of humanity and of the Republic. Please, make it that my request be not despised. I have the honour to be, monsieur, your most humble, most obedient servant.
Saint-Just, constituent of the department of Aisne.
To Monsieur de Robespierre in the National Assembly in Paris.
Blérancourt, near Noyon, August 19, 1790.
Saint-Just’s first letter ever written to Robespierre, dated August 19 1790
Citizens, you are aware that, to dispel the errors with which Roland has covered the entire Republic, the Society has decided that it will have Robespierre's speech printed and distributed. We viewed it as an eternal lesson for the French people, as a sure way of unmasking the Brissotin faction and of opening the eyes of the French to the virtues too long unknown of the minority that sits with the Mountain. I remind you that a subscription office is open at the secretariat. It is enough for me to point it out to you to excite your patriotic zeal, and, by imitating the patriots who each deposited fifty écus to have Robespierre's excellent speech printed, you will have done well for the fatherland.
Saint-Just at the Jacobins, January 1 1793
Patriots with more or less talent […] Jacquier, Saint-Just’s brother-in-law.
Robespierre in a private list, written sometime during his time on the Committee of Public Safety
Saint-Just doesn’t have time to write to you. He gives you his compliments.
Lebas in a letter to Robespierre October 25 1793
Trust no longer has a price when we share it with corrupt men, then we do our duty out of love for our fatherland alone, and this feeling is purer. I embrace you, my friend.
Saint-Just.
To Robespierre the older.
Saint-Just in a post-scriptum note added to a letter written by Lebas to Robespierre, November 5 1793. Saint-Just uses tutoiement with Robespierre here, while Lebas used vouvoiement.
We have made too many laws and too few examples: you punish but the salient crimes, the hypocritical crimes go unpunished. Punish a slight abuse in each part, it is the way to frighten the wicked, and to make them see that the government has its eye on everything. No sooner do we turn our backs than the aristocracy rises in the tone of the day, and commits evils under the colors of liberty.
Engage the committee to give much pomp to the punishment of all faults in government. Before a month has passed you will have illuminated this maze in which counter-revolution and revolution march haphazardly. Call, my friend, the attention of the Jacobin Club to the strong maxims of the public good; let it concern itself with the great means of governing a free state. I invite you to take measures to find out if all the manufactures and factories of France are in activity, and to favor them, because our troops would within a year find themselves without clothes; manufacturers are not patriots, they do not want to work, they must be forced to do so, and not let down any useful establishment. We will do our best here. I embrace you and our mutual friends.
Saint-Just
To Robespierre the older.
Saint-Just in a letter to Robespierre, December 14 1793
Paris, 9 nivôse, year 2 of the Republic.
Friends.
I feared, in the midst of our successes, and on the eve of a decisive victory, the disastrous consequences of a misunderstanding or of a ridiculous intrigue. Your principles and your virtues reassured me. I have supported them as much as I could. The letter that the Committee of Public Safety sent you at the same time as mine will tell you the rest. I embrace you with all my soul.
Robespierre.
Robespierre in a letter to Saint-Just and Lebas, December 29 1793
Why should I not say that this (the dantonist purge) was a meditated assassination, prepared for a long time, when two days after this session where the crime was taking place, the representative Vadier told me that Saint-Just, through his stubbornness, had almost caused the downfall of the members of the two committees, because he had wanted that the accused to be present when he read the report at the National Convention; and such was his obstinacy that, seeing our formal opposition, he threw his hat into the fire in rage, and left us there. Robespierre was also of this opinion; he believed that by having these deputies arrested beforehand, this approach would sooner or later be reprehensible; but, as fear was an irresistible argument with him, I used this weapon to fight him: You can take the chance of being guillotined, if that is what you want; For my part, I want to avoid this danger by having them arrested immediately, because we must not have any illusions about the course we must take; everything is reduced to these bits: If we do not have them guillotined, we will be that ourselves.
À Maximilien Robespierre aux enfers (1794) by Taschereau de Fargues and Paul-Auguste-Jacques. Robespierre and Saint-Just had also worked out the dantonists’ indictment together.
…As far from the insensibility of your Saint-Just as from his base jealousies, [Camille] recoiled in front if the idea of accusing a college comrade, a companion in arms. […] Robespierre, can you really complete the fatal projects which the vile souls that surround you no doubt have inspired you to? […] Had I been Saint-Just’s wife I would tell him this: the sake of Camille is yours, it’s the sake of all the friends of Robespierre!
Lucile Desmoulins in an unsent letter to Robespierre, written somewhere between March 31 and April 4 1794. Lucile seems to have believed it was Saint-Just’s ”bad influence” in particular that got Robespierre to abandon Camille.
In the beginning of floréal (somewhere between April 20 and 30) during an evening session (at the Committee of Public Safety), a brusque fight erupted between Saint-Just and Carnot, on the subject of the administration of portable weapons, of which it wasn’t Carnot, but Prieur de la Côte-d’Or, who was in charge. Saint-Just put big interest in the brother-in-law of Sijas, Luxembourg workshop accounting officer, that one thought had been oppressed and threatened with arbitrary arrest, because he had experienced some difficulties for the purpose of his service with the weapon administration. In this quarrel caused unexpectedly by Saint-Just, one saw clearly his goal, which was to attack the members of the committee who occupied themselves with arms, and to lose their cooperateurs. He also tried to include our collegue Prieur in the inculpation, by accusing him of wanting to lose and imprison this agent. But Prieur denied these malicious claims so well, that Saint-Just didn’t dare to insist on it more. Instead, he turned again towards Carnot, whom he attacked with cruelty; several members of the Committee of General Security assisted. Niou was present for this scandalous scene: dismayed, he retired and feared to accept a pouder mission, a mission that could become, he said, a subject of accusation, since the patriots were busy destroying themselves in this way. We undoubtedly complained about this indecent attack, but was it necessary, at a time when there was not a grain of powder manufactured in Paris, to proclaim a division within the Committee of Public Safety, rather than to make known this fatal secret? In the midst of the most vague indictments and the most atrocious expressions uttered by Saint-Just, Carnot was obliged to repel them by treating him and his friends as aspiring to dictatorship and successively attacking all patriots to remain alone and gain supreme power with his supporters. It was then that Saint-Just showed an excessive fury; he cried out that the Republic was lost if the men in charge of defending it were treated like dictators; that yesterday he saw the project to attack him but that he defended himself. ”It’s you,” he added, ”who is allied with the enemies of the patriots. And understand that I only need a few lines to write for an act of accusation and have you guillotined in two days.”
”I invite you, said Carnot with the firmness that only appartient to virtue: I provoke all your severity against me, I do not fear you, you are ridiculous dictators.” The other members of the Committee insisted in vain several times to extinguish this ferment of disorder in the committee, to remind Saint-Just of the fairer ideas of his colleague and of more decency in the committee; they wanted to call people back to public affairs, but everything was useless: Saint-Just went out as if enraged, flying into a rage and threatening his colleagues. Saint-Just probably had nothing more urgent than to go and warn Robespierre the next day of the scene that had just happened, because we saw them return together the next day to the committee, around one o'clock: barely had they entered when Saint-Just, taking Robespierre by the hand, addressed Carnot saying: ”Well, here you have my friends, here are the ones you attacked yesterday!” Robespierre tried to speak of the respective wrongs with a very hypocritical tone: Saint-Just wanted to speak again and excite his colleagues to take his side. The coldness which reigned in this session, disheartened them, and they left the committee very early and in a good mood.
Réponse des membres des deux anciens Comités de salut public et de sûreté générale (Barère, Collot, Billaud, Vadier), aux imputations renouvellées contre eux, par Laurent Lecointre et declarées calomnieuses par décret du 13 fructidor dernier; à la Convention Nationale (1795), page 103-105
My friends, the committee has taken all the measures within its control at this time to support your zeal. It has asked me to write to you to explain the reasons for some of its provisions. It believed that the main cause of the last failure was the shortage of skilled generals, it will send you all the patriotic and educated soldiers that can be found. It thought it necessary at this time to re-use Stetenhofen, whom it is sending to you, because he has military merit, and because the objections made against him seem at least to be balanced by proofs of loyalty. He also relies on your wisdom and your energy. Salut et amitié.
Paris, 15 floréal, year 2 of the Republic.
Robespierre.
Robespierre to Saint-Just and Lebas, May 4 1793
Dear collegue,
Liberty is exposed to new dangers; the factions arise with a character more alarming than ever. The lines to get butter are more numerous and more turbulent than ever when they have the least pretexts, an insurrection in the prisons which was to break out yesterday and the intrigues which manifested themselves in the time of Hébert are combined with assassination attemps on several occasions against members of the Committee of Public Safety; the remnants of the factions, or rather the factions still alive, are redoubled in audacity and perfidy. There is fear of an aristocratic uprising, fatal to liberty. The greatest peril that threatens it is in Paris. The Committee needs to bring together the lights and energy of all its members. Calculate whether the army of the North, which you have powerfully contributed to putting on the path to victory, can do without your presence for a few days. We will replace you, until you return, with a patriotic representative.
The members composing the Committee of Public Safety.
Robespierre, Prieur, Carnot, Billaud-Varennes, Barère.
Letter to Saint-Just from the CPS, May 25 1794, written by Robespierre. It was penned down just two days after the alleged attempt on Robespierre’s life by Cécile Renault.
Robespierre returned to the Committee a few days later to denounce new conspiracies in the Convention, saying that, within a short time, these conspirators who had lined up and frequently dined together would succeed in destroying public liberty, if their maneuvers were allowed to continue unpunished. The committee refused to take any further measures, citing the necessity of not weakening and attacking the Convention, which was the target of all the enemies of the Republic. Robespierre did not lose sight of his project: he only saw conspiracies and plots: he asked that Saint-Just returned from the Army of the North and that one write to him so that he may come and strengthen the committee. Having arrived, Saint-Just asked Robespierre one day the purpose of his return in the presence of the other members of the Committee; Robespierre told him that he was to make a report on the new factions which threatened to destroy the National Convention; Robespierre was the only speaker during this session. He was met by the deepest silence from the Committee, and he leaves with horrible anger. Soon after, Saint-Just returned to the Army of the North, since called Sambre-et-Mouse. Some time passes; Robespierre calls for Saint-Just to return in vain: finally, he returns, no doubt after his instigations; he returned at the moment when he was most needed by the army and when he was least expected: he returned the day after the battle of Fleurus. From that moment, it was no longer possible to get him to leave, although Gillet, representative of the people to the army, continued to ask for him.
Réponse de Barère, Billaud-Varennes, Collot d’Herbois et Vadier aux imputations de Laurent Lecointre (1795)
On 10 messidor (June 28) I was at the Committee of Public Safety. There, I witnessed those who one accuses today (Billaud-Varenne, Barère, Collot-d'Herbois, Vadier, Vouland, Amar and David) treat Robespierre like a dictator. Robespierre flew into an incredible fury. The other members of the Committee looked on with contempt. Saint-Just went out with him.
Levasseur at the Convention, August 30 1794. If this scene actually took place, it must have done so one day later, 11 messidor (June 29), considering Saint-Just was still away on a mission on the tenth.
Isn’t it around the same time (a few days before thermidor) that Saint-Just and Lebas would dine at your father’s house with Robespierre?
Lebas often dined there, having married one of my sisters. Saint-Just rarely there, but he frequently went to Robespierre’s and climbed the stairs to his office without speaking to anyone.
During the dinner which I’m talking about, did you hear Saint-Just propose to Robespierre to reconcile with some members of the Convention and Committees who appeared to be opposed to him?
No. I only know that they appeared to be very devided.
Do you have any ideas what these divisions were about?
I only learned about it through the discussions which took place on this subject at the Jacobins and through the altercation which was said to have taken place at the Committee of Public Safety between Robespierre older and Carnot.
Robespierre’s host’s son Jacques-Maurice Duplay in an interrogation held January 1 1795
Saint-Just then fell back on his report, and said that he would join the committee the next day (9 thermidor) and that if it did not approve it, he would not read it. Collot continued to unmask Saint-Just; but as he focused more on depicting the dangers praying on the fatherland than on attacking the perfesy of Saint-Just and his accomplices, he gradually reassured himself of his confusion; he listened with composure, returning to his honeyed and hypocritical tone. Some time later, he told Collot d'Herbois that he could be reproached for having made some remarks against Robespierre in a café, and establishing this assertion as a positive fact, he admitted that he had made it the basis of an indictment against Collot, in the speech he had prepared.
Réponse des membres des deux anciens Comités de salut public et de sûrété générale… (1795) page 107.
I attest that Robespierre declared himself a firm supporter of the Convention and never spoke but gently in the Committee so as not to undermine any of its members. […] Billaud-Varenne said to Robespierre, “We are your friends, we have always walked together.” This dishonesty made my heart shudder. The next day, he called him Peisistratos and had written his act of accusation. […] If you reflect carefully on what happened during your last session, you will find the application of everything I said: a man alienated from the Committee due to the bitterest treatments, when this Committee was, in fact, no longer made up of more than the two or three members present, justified himself before you; he did not explain himself clearly enough, to tell the truth, but his alienation and the bitterness in his soul can excuse him somewhat: he does not know why he is being persecuted, he knows nothing except his misfortune. He has been called a tyrant of opinion: here I must explain myself and shine light on a sophism that tends to proscribe merit. And what exclusive right do you have to opinion, you who find that it is a crime to touch souls? Do you find it wrong that a man should be tenderhearted? Are you thus from the court of Philip, you who make war on eloquence? A tyrant of opinion? Who is stopping you from competing for the esteem of the fatherland, you who find it so wrong that someone should captivate it? There is no despot in the world, save Richelieu, who would be insulted by the fame of a writer. Is it a more disinterested triumph? Cato is said to have chased from Rome the bad citizen who had called eloquence at the tribune of harangues, the tyrant of opinion. No one has the right to claim that; it gives itself to reason and its empire is not the in the power of governments. […] The member who spoke for a long time yesterday at this tribune did not seem to have distinguished clearly enough who he was accusing. He had no complaints and has not complained either about the Committees; because the Committees still seem to me to be dignified of your estime, and the misfortunes that I have spoken to you of were born of isolation and the extreme authority of several members left alone.
Saint-Just defending Robespierre in his last, undelivered speech, July 27 1794
One brings St. Just, Dumas and Payan, all of them shackled, they are escorted by policemen. They stay a good quarter of an hour standing in front of the door of the Committee’s room; one makes them sit down onto a windowsill; they have still not uttered a single word, pleasant people make the persons who surround these three men step aside, and say move back, let these gentlemen see their King sleep on a table, just like a man. Saint-Just moves his head in order to see Robespierre. Saint-Just’s figure appeared dejected and humiliated, his swollen eyes expressed chagrin.
Faits recueillis aux derniers instants de Robespierre et de sa saction, du 9 au 10 thermidor (1794) by anonymous.
The Committee of General Security was being spied on by Héron, D…, Lebas: Robespierre knew, through them, word for word, everything that was happening at said committee. This espionage gave rise to more intimate connections between Couthon, Saint-Just and Robespierre. The fierce and ambitious character of the latter gave him the idea of establishing the general police bureau, which, barely conceived, was immediately decreed.
Révélations puisées dans les cartons des comités de Salut public et de Sûreté générale ou mémoires (inédits) (1824) by Gabriel Jérôme Sénart.
Intimately linked with Robespierre, [Saint-Just] had become necessary to him, and he had made himself feared perhaps even more than he had desired to be loved. One never saw them divided in opinion, and if the personal ideas of one had to bow to those of the other, it is certain that Saint-Just never gave in. Robespierre had a bit of that vanity which comes from selfishness; Saint-Just was full of the pride that springs from well-established beliefs; without physical courage, and weak in body, to the point of fearing the whistling of bullets, he had the courage of reflection which makes one wait for certain death, so as not to sacrifice an idea.
Memoirs of René Levasseur (1829) volume 2, page 324-325.
Often [Robespierre] said to me that Camille was perhaps the one among all the key revolutionaries whom he liked best, after our younger brother and Saint-Just.
Mémoires de Charlotte Robespierre sur ses deux frères (1834) page 139.
After the month of March, 1794, Robespierre's conduct appeared to me to change. Saint-Just was to a great degree the cause of this, and this leader was too youthful ; he urged him into the vain and dangerous path of dictatorship which he haughtily proclaimed. From that time all confidences in the two committees were at an end, and the misfortunes that followed the division in the government became inevitable. […] We did not hide from [Robespierre] that Saint-Just, who was formed of more dictatorial stuff, would have ended by overturning him and occupying his place ; we knew too that he would have us guillotined because of our opposition to his plans; so we overthrew him.
Memoirs of Bertrand Barère (1896), volume 1, page 103-104.
About this time Robespierre felt his ambition growing, and he thought that the moment had come to employ his influence and take part in the government. He took steps with certain members of the committee and the Convention, asking them to show a desire that he, Robespierre, should become a member of the Committee of Public Safety. He told the Jacobins it would be useful to observe the work and conduct of the members of the committee, and he told the members of the Convention that there would be more harmony between the Convention and the committee if he entered it. Several deputies spoke to me about it, and the proposal was made to the committee by Couthon and Saint-Just. To ask was to obtain, for a refusal would have been a sort of accusation, and it was necessary to avoid any split during that winter which was inaugurated in such a sinister manner. The committee agreed to his admission, and Robespierre was proposed.
Ibid, volume 2, page 96-97
The continued victories of our fourteen armies were as a cloud of glory over our frontiers, hiding from allied Europe our internecine struggles, and that unhappy side of our national character which acts and reacts so deplorably as much on the whole population as on our nghts and our manners. The enthusiasm with which I announced these victories from the tnbune was so easily seen that Saint- Just and Robespierre, being in the committee at three in the morning, and learning of the taking of Namur and some other Belgian towns, insisted for the future that the letters alone of the generals should be read, without any comments which might exaggerate their contents. I saw at once at whom this reproach was directed, and I took up the gauntlet with the deasion of a man willing to once more merit the hatred of the enemies of our national glory, and the bravery of our armies. Then Samt-Just cried, “ I beg to move that Barère be no longer allowed to add froth to our victories.” […] While Saint-Just was reproving me, Robespierre supported the longsightedness of his friend… […] The next day my report on the taking of Namur was somewhat more carefully drawn up, and I alluded to the observation of my critics, who were envious of the power of public opinion in favour of our troops, then busied in saving the country. This phrase in my report was much commented on, although its meaning was only clear to those who had heard the debate in the committee on the previous evening “Sad are the tunes, sad is the period, when the recital of the triumphs and glories of the armies of the Repubhc is coldly hastened to in this place! Henceforth liberty will be no longer defended by the country, it will be handed over to its enemies!”This pronouncement was not of a nature to be forgiven by Saint-Just and Robespierre, so they determined to supplant me with regard to these reports. They forced that idiot Couthon to attend the Committee of Public Safety at eleven in the morning, before I got there Couthon asked for the letters of the generals that had come in during the night, and took his usual seat at the back of the hall, waiting until the assembly was sufficiently full for him to announce the victones. About one, Couthon, being paralysed and unable to stand up in the tribune, coldly read the news from the armies from his place. This time, no effect was produced in the Assembly, or upon the public. This attempt, authorised by Robespierre and Saint-Just, having missed fire completely, the committee signified its dissatisfaction at the innovation.
Ibid, volume 2, page 123-125
After his return from Fleurus, Saint-Just remained some time in Paris, although his mission as representative to the armies of the Sambre and Meuse and the Rhine and Moselle was unfinished. The campaign was only beginning, but he had several projects in hand, and he stayed in committee, or rather his office, where he was always absorbed and thoughtful. Robespierre, in speaking of him at the committee, said familiarly, as if speaking of an intimate friend: ”Saint-Just is silent and observant, but I have noticed, in his personality, he has a great likeness to Charles IX.” This did not flatter Saint-Just, who was a deeper and cleverer revolutionist than Robespierre. One day, when the former was angry about several legislative propositions or decrees that did not please him, Saint-Just said to him, “Be calm, it is the phlegmatic who govern.”
Ibid, volume 2, page 139
This tyrannical law was the work of Saint-Just Consult the Momteuv of the 22nd of Germinal, where it is reported with the explanation of his motives, and you will see that, if there had been no committee, SamtJust would have used his power with as much dictatorial fanaticism as did Manus, that great enemy of the Roman anstocracy. Robespierre’s fnend never forgave me for having dimmished the force of this blow. Whilst I was at the tnbune of the Convention, he came, with someone unknown, and perused my register of requisitions. He took down certain names, and some days after, towards midnight, Robespierre and Saint-Just entered the committee, where they did not usually come (for they worked in a private office, under pretext that their duties were completely private) A few moments after their entry Saint-Just complained of the abuse I had made of the requisitions, which had been granted, said he, in such profusion that the law of the 21st of Germinal had become null and void.
Ibid, volume 2, page 146
Robespierre, Saint-Just and Couthon were inseparable. The first two had a dark and duplicitous character; they pushed away with a kind of disdainful pride any familiarity or affectionate relationship with their colleagues. The third, a legless man with a pale appearance, affected good-nature, but was no less perfidious than the other two. All three of them had a cold heart, without pity, they interacted only with each other, holding mysterious meetings outside, having a large number of protégés and agents, impenetrable in their designs.
Révélations sur le Comité de salut public by Prieur-Duvernois
Robespierre, who had great confidence in Le Bas because he knew his wise and prudent character well, had chosen him to accompany Saint-Just, whose burning love of the fatherland sometimes led to too much severity, and who had a tendency to get carried away. […] [Saint-Just] also had friendship for me and came often enough to our house. […] Finally our providence, our good friend Robespierre, spoke to Saint-Just to engage him to let me depart with them, along with my sister-in-law Henriette. He consented, but with some conditions.
Memoirs of Élisabeth Lebas (1901)
Volume 8 — page 153. ”Saint-Just, his (Robespierre’s) only confident.” His only confident?
Élisabeth Lebas corrects a passage in Alphonse de Lamartine’s Histoire des Girondins (1847)
The Lamenths and Péthion in the early days, quite rarely Legendre, Merlin de Thionville and Fouché, often Taschereau, Desmoulins and Teault, always Lebas, Saint-Just, David, Couthon and Buonarotti.
Élisabeth Lebas regarding visitors to the Duplay’s during the revolution
—
When arriving in Paris in September 1792, Saint-Just first lived on No. 7 rue de Gaillon up until March 1794, and then on No. 3 rue de Caumartin (today’s No. 5) up until his death. Both those places were within a ten minute walking distance from Robespierre’s home on 398 Rue Saint-Honoré.
Saint-Just was away from Paris (and therefore Robespierre) on missions between March 9 to March 31, October 17 to December 4, December 10 to December 30 (1793), January 22 to February 13, April 30 to May 31 and June 10 to June 29 (1794).
#sj and max holding hands 🤗💓#robespierre#saint-just#maximilien robespierre#louis antoine de saint just#barère#élisabeth lebas#philippe lebas#frev#frev friendships#long post#saintspierre
203 notes
·
View notes
Text

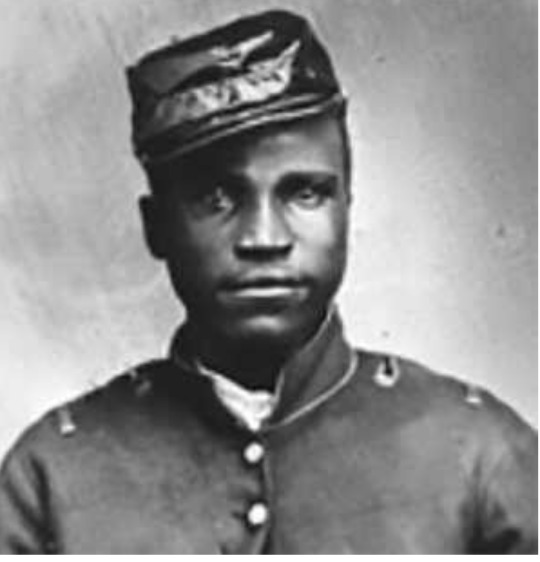
What happened to colored troops taken POW by Confederates in the Civil War?
Three-fifths of all African troops in the Union army were former slaves and those that fought in combat units did so at great risk to their lives (beyond the expected risks associated with combat). The Confederate government’s official position was that black POWs would be executed, reclaimed by their former masters or sold into slavery. Lincoln’s threats of reprisals helped minimize the impact of Confederate actions.
Details of the brutality African soldiers suffered are known, but with less specificity. We know of the multiple slaughters of surrendering or captured blacks that occurred. And, we know that armed Africans were the South’s worst nightmare as southerners were terrified that the example of these soldiers would “infect” the rest of the slave population and inspire them to take-up arms against their enslavers. In southern eyes, that alone warranted the harshest treatment for captured Africans.
What is clear is that these soldiers faced harsher and more cruel treatment at the hands of their captors than did their white counterparts. We know with clarity the physical violence that slaves suffered pre-war as well as after the war. Further, while 14% of Union prisoners died while being held as POWs and 11.8% of Confederate POWs died in northern captivity, historian Caroline Newhall notes that almost 35% of African POWs died in southern captivity. These data points converge with official Confederate statements and southern attitudes on slaves as property and provide strong evidence of the cruelty African Union soldiers faced.

Cruelty and atrocities against African Union soldiers were not random acts of war, but were legislated and directed by the Confederate Congress and Jefferson Davis himself.
In late 1862, Davis stated: “All negro slaves captured in arms be at once delivered over to the executive authorities of the respective States to which they belong.” A resolution later adopted by the Confederate Congress provided that all “negroes or mulattoes,” slave or free, taken in arms should be tried for inciting servile insurrection and be subject to the death penalty.
In a letter to General Beauregard on this issue, The Confederate Secretary of War pointed out that "Slaves in flagrant rebellion are subject to death by the laws of every slave-holding State" but that "to guard, however, against possible abuse...the order of execution should be reposed in the general commanding the special locality of the capture."
Lincoln responded to this by threatening to retaliate against Confederate prisoners whenever African soldiers were killed or enslaved.
Davis publicly denounced Lincoln’s order; but, it did have — for the most part — the desired effect, as most African prisoners were not treated with the harsh justice mandated by Confederate policy, even though the Confederacy never officially acknowledged African-Americans as P.O.W.’s. Instead, what emerged were inconsistent practices in dealing with captured African American troops, depending on the time, place and the commander into whose hands they fell. Indeed, some Confederate officers encouraged the killing of African-American soldiers rather than taking them prisoner, and the atrocities committed against surrendering African soldiers at Poison Spring, Fort Pillow and Petersburg are now well known.
If not executed, captured African soldiers often found themselves treated very differently from white prisoners. Instead of being confined to camps, many African-American prisoners were put to forced labor.
As Robert Jones, a African soldier captured at Milliken’s Bend, La., recalled, “They took me to … Rust, Tex., where they … had me at work doing every kind of work, loading steamboats, rebuilding breastworks, while I was in captivity.”
Near Fort Gilmer, Va., captured African troops were forced to work under enemy fire in the trenches. In retaliation, the Union general Benjamin F. Butler placed an equal number of Confederate P.O.W.’s on forward trenches. Within a week, the African prisoners were removed from the front lines.
The sentiment that Africans under arms aroused -- along with the ingrained hostility of many Confederate soldiers -- set the stage for wartime atrocities. The most notorious incident occurred at a small Federal outpost north of Memphis, Tennessee, where Confederate cavalrymen under Nathan Bedford Forrest attacked Fort Pillow, which was garrisoned by about 500 troops.
More than half of the soldiers were African. The superior Confederate force overwhelmed the fort's defenders; Union casualties were high. But after the Federals surrendered, Forrest's men shot and killed a number of unarmed soldiers and officers, both black and white.
In October 1864 Saltville, Virginia, Confederate soldiers executed unarmed African prisoners, even raiding a hospital on two separate occasions and murdering wounded Africans in their sickbeds.
High casualty rates in combat were also common for African American units — usually for two reasons. First, since Africans had not previously served in the military, they were inexperienced fighters. Second, feeling social pressure to prove themselves as men, they often took risks on the battlefield that their white counterparts would not.
But, despite facing intense racism and humiliating treatment from their own white colleagues in arms, Africans excelled in combat, providing an additional, critical edge in manpower to what the Union already possessed.
One Union captain explained the significance of African military participation on the attitudes of many white soldiers. "A great many [white people]," he wrote, "have the idea that the entire Negro race are vastly their inferiors. A few weeks of calm unprejudiced life here would disabuse them, I think. I have a more elevated opinion of their abilities than I ever had before. I know that many of them are vastly the superiors of those...who would condemn them to a life of brutal degradation."
Of the 180,000 African Americans who fought for the Union, 37,300 died. More than 20 African Americans were awarded the Congressional Medal of Honor, the nation's most prestigious military decoration. Fourteen of those men earned their medals at Chaffin's Farm.
#african american#african#afrakan#kemetic dreams#brownskin#afrakans#brown skin#africans#african history#african american history#medal of honor#chaffin farm#military#military history
380 notes
·
View notes
Text
Hey check this out
I was making a zine (solarpunk ofc) and decided to use a bunch of old National Geographic magazines to cut up and use in a scrappy diy scrapbook fashion and of course I started reading them. This one in particular:

It caught my eye because it’s from September 1980 & talks about the Middle East. My brain wonders if they mention Palestine and they do! I copied the text for accessibility, but I put pictures at the end of the original pages.
“Jerusalem: reunited or occupied? The question has divided the city's 400,000 Jews and 100,000 Arabs since Israel annexed East Jerusalem in 1967.
BEIRUT, JANUARY 1975. Armed soldiers lead me through labyrinthine back streets, up a dark stairway to a midnight rendez-vous. Only a bare bulb lights the temporary command post; Yasir Arafat, chairman of the Palestine Liberation Organization, seldom dares spend two days in the same place. “Our argument is not with the Jews” He tells me. "We are both Semites. They have lived with us for centuries. Our enemies are the Zionist colonizers and their backers who insist Palestine belongs to them exclusively.
We Arabs claim deep roots there too."
Two decades ago Palestinians were to be found in United Nations Relief Agency camps at places like Gaza and Jericho, in a forlorn and pitiable state. While Palestinian spokesmen pressed their case in world cap-itals, the loudest voice the world heard was that of terrorists, with whom the word Palestinian came to be associated. Jordan fought a war to curb them. The disintegration of Lebanon was due in part to the thousands of refugees within its borders.
Prospects for peace brightened, however, when President Anwar Sadat of Egypt, most powerful of the Arab countries, made his historic trip to Israel in November 1977. A year later Sadat and Israeli Prime Minister Menachem Begin signed the Camp David accords, a framework for the return of the occupied Sinai Peninsula to Egypt.
The former enemies established diplomatic relations and opened mail, telephone, and airline communications.
The Camp David accords also addressed the all-important Palestinian question but left it vague. Sadat insists that any lasting peace depends on an eventual Palestinian homeland in the Israeli-occupied West Bank and Gaza. Israel agrees to limited autonomy for those regions, but, fearful of a new and hostile Palestinian state suddenly planted on its borders, insists that Israeli troops must maintain security there.
Crowded Rashidiyah refugee camp, set among orange groves south of the ancient Phoenician port of Tyre in Lebanon, lies on the front lines. Frequent pounding by Israeli military jets and warships seeking PLO targets has war-hardened its population, some 13,700 Palestinians.
At the schoolyard I watched a solemn flag raising. Uniformed ashbal, or lion cubs, stood rigid as color guards briskly ran up the green-white-and-black Palestinian flag.
Ranging in age from 8 to 12, they might have been Cub Scouts— except for the loaded rifles they held at present arms. Behind them stood two rows of girls, zaharat, or little flowers. Same age, same weapons.
Over lunch of flat bread, hummus, yo-gurt, and chicken I commented to my hosts, a group of combat-ready fedayeen, that 30 years of bitter war had settled nothing nor gained the Palestinians one inch of their homeland. Was there no peaceful way to press their cause?
"Yes, and we are doing it. Finally, after 30 years, most countries in the United Nations recognize that we too have rights in Palestine. But we feel that until your country stops its unconditional aid to Israel, we have two choices: to fight, or to face an unmarked grave in exile."
AFTER CROSSING the Allenby Bridge from Amman, I drove across the fertile Jordan Valley through Arab Jericho and past some of the controversial new Jewish settlements: Mitzpe Jericho, Tomer, Maale Adumim, Shilat. Then as I climbed through the steep stony hills to Jerusalem, I saw that it too had changed. A ring of high-rise apartments and offices was growing inexorably around the occupied Arab side of the walled town. Within the wall, too, scores of Arab houses had been leveled during extensive reconstruction.
"Already 64 settlements have been built on the West Bank," said a Christian Palestinian agriculturist working for an American church group in Jerusalem. "And another 10 are planned," he said. Unfolding a copy of the master plan prepared in 1978 by the World Zionist Organization, he read: "Real-izing our right to Eretz-Israel... with or without peace, we will have to learn to live with the minorities...
The Israeli Government has reaffirmed the policy. In Prime Minister Menachem Begin's words: "Settlement is an inherent and inalienable right. It is an integral part of our national security."
"Security" is a word deeply etched into the Israeli psyche. The country has lived for 30 years as an armed camp, always on guard against PLO raids and terrorist bombings.
Whenever such incidents occur, the response is quick: even greater retaliation.
In Jerusalem I met with David Eppel, an English-language broadcaster for the Voice of Israel. "We must continue to build this country. Israel is our lawful home, our des-tiny. We have the determination, and an immense pool of talent, to see it through." His cosmopolitan friends a city plan-ner, a psychology professor, an author gathered for coffee and conversation at David's modern apartment on Jerusalem's Leib Yaffe Road.
Amia Lieblich's book, Tin Soldiers on Jerusalem Beach, studies the debilitating effects almost constant war has had on life in the Jewish state, a nation still surrounded by enemies. As she and her husband kindly drove me to my hotel in Arab Jerusalem afterward, some of that national apprehension surfaced in the writer herself.
"We don't often come over to this part of town," she said. "Especially at night."
I DROVE OUT of the Old City in the dark of morning and arrived a few hours later at the nearly finished Israeli frontier post, whence a shuttle bus bounced me through no-man's-land to the Egyptian ter-minal. As a result of the Egyptian-Israeli treaty, it was possible for the first time since 1948 to travel overland from Jerusalem to Cairo. An Egyptian customs man opened my bags on a card table set up in the sand. I took a battered taxi into nearby El Arish, to a sleepy bank that took 45 minutes to convert dollars into Egyptian pounds, Then 1 hired a Mercedes for the
200-mile run across the northern Sinai des-ert, the Suez Canal, and the Nile Delta. By sundown Cairo was mine.
Despite official government optimism, I found many in Cairo worried that President Sadat's bold diplomatic gestures might fail.
The city was noticeably tense as Israel officially opened its new embassy on Mohi el-Din Abu el-Ez Street in Cairo's Dukki quarter. Black-uniformed Egyptian troops guarded the chancery and nearby intersections as the Star of David flew for the first time in an Arab capital. Across town, police with fixed bayonets were posted every ten feet around the American Embassy. Others were posted at the TV station and the larger hotels. Protests were scattered, mostly peaceful. None disturbed the cadence of the city.
Welcoming ever larger delegations of tourists and businessmen from Europe and the U.S., Cairo was busier than ever-and more crowded. Despite a building boom, many Egyptians migrating from the countryside, perhaps 10,000 a month, still find housing only by squatting among tombs at the City of the Dead, the huge old cemetery on the southeast side of the capital.
Even with the new elevated highway and wider bridge across the Nile, half-hour traffic standstills are common. Commuters arrive at Ramses Station riding even the roofs of trains, then cram buses until axles break.
Cairo smog, a corrosive blend of diesel fumes and hot dust from surrounding des-erts, rivals tear gas.
Despite the rampant blessings of prog-ress, Cairo can still charm. In the medieval Khan el-Khalili bazaar near Cairo's thousand-year-old Al-Azhar University, I sought out Ahmad Saadullah's sidewalk café. I found that 30 piasters (45 cents) still brings hot tea, a tall water pipe primed with tobacco and glowing charcoal, and the latest gossip. The turbaned gentleman on the carpeted bench opposite was unusually talk-ative; we dispensed with weather and the high cost of living and got right to politics:
"Of course I am behind President Sadat, but he is taking a great risk. The Israelis have not fully responded. If Sadat fails, no other Arab leader will dare try for peace again for a generation."
Across town at the weekly Akhbar El-Yom newspaper, one of the largest and most widely read in the Middle East, chief editor Abdel-Hamid Abdel-Ghani drove home that same point.
"What worries me most is that President Sadat's agreement with Israel has isolated Egypt from our brother nations," he told me. "When Saudi Arabia broke with us, it was a heavy loss. The Saudis are our close neighbors. Now they have canceled pledges for hundreds of millions in development aid to Egypt. Some 200,000 Egyptians-teach-ers, doctors, engineers live and work in the kingdom.
"And Saudi Arabia, guardian of the holy cities of Mecca and Medina, remains for Muslim Egypt a spiritual homeland."




This magazine was published before my mom was born, and yet the sentiments have basically unchanged. An interesting look at the past, and more proof this didn’t start October 7th. (But imagine my followers already knew that)
#Palestine#free palestine#from the river to the sea palestine will be free#national geographic#September 1980
52 notes
·
View notes
Text

✦ It Had to be You: One ✦
John "Bucky" Egan x OC
Gale "Buck Cleven x OC
Disclaimer: This is a work of fiction and not associated with the real people mentioned from the show. This is simply based on the portrayals of the actors playing these characters.
Warning for this chapter: Cursing, mentions of sex, depression, rage anger.
● If you would like to be tagged, just comment below ●
⍆⍆⍆⍆⍆⍆⍆⍆⍆⍆⍆⍆⍆⍆⍆⍆⍆⍆⍆⍆⍆⍆⍆⍆⍆⍆⍆⍆⍆⍆⍆⍆⍆⍆⍆⍆
Black had become a staple in my wardrobe.
I used to despise the dark color – opting for more cheerful tones or floral patterns. I didn’t want to walk around looking like a depressive cloud – someone in constant mourning. I didn’t even own a black dress until I got the news – my mother making the journey to the store to buy one. I couldn’t bear to leave the house – not wanting the sympathetic glances of those in town that had learned the news. I can’t even begin to tell you how many letters I had received, those that knew Gale and even from those that didn’t. Each letter praised his heroic actions – thanking him in black ink for his level of service and dedication to the United States. Even received one from President Truman and the men of Washington D.C.
I used to look at women who had received the devastating news with such sorrow and sadness. Wonder how they would survive without their men - their source of comfort and love. I was certain that it would be very difficult to do so – have to learn to fend for yourself and go on without the man you loved. I didn’t realize that I would be in the same boat years later. I was a simple housewife – barely of age when we married. Gale and I were just two kids – two kids that were madly and deeply in love with each other. I had grown up more privileged than Gale or those that we knew. I didn’t know how to clean a house properly or cook a hearty meal that would fill the bellies of my husband and future children. I’ve always had someone do those things for me – my mother more focused on raising a proper lady. If you needed to know which fork went where, I was the girl to ask, but I couldn’t tell you anything domestic. I wanted to be able to learn all those things while he was away – making sure that when he returned home for good, I would be able to care for him like a wife should.
I had met Gale at a dance the local hall was putting on – a sendoff to some of the troops that lived in the area. He had just enlisted– saying that he was a week away from going to boot camp. He was cool as a cucumber – no evidence of fear etched on his beautiful face. He spoke of wanting to fight the good fight – getting up in the air and showing Germany the trouble they were in for. He was a born fighter – a genius when it came to life. We spent most of the night as close as two people could be while sitting upright- both speaking of our life and our dreams. Not to sound cliché but I was smitten as soon as I saw him. His blonde hair was slightly disheveled – his wool trousers fitting his frame nicely. His smile could light up a room – that deep voice causing my insides to quiver with a need that only he could give me.
I longed for him during those weeks he was away – smiling as I read his letters that would come bi-weekly. I could hear his voice as I read the words on paper – the excitement of finally flying and the annoyance he felt towards his roommate. The one true constant that popped up on each letter was the mention of his co-captain. His name was John Egan – Bucky – the nickname he had been given. Gale spoke highly of the man – praising him and saying that he couldn’t wait for us to meet. Gale was soft spoken – a bit reserved – he wasn’t into sports or gambling. He liked to sit outside the house and just listen to the sounds of nature. John Egan was the opposite that Gale needed in his life. He helped Gale open up and Gale helped John stay out of trouble...
Gale finally returned to me after weeks away – our reunion being one spent giving ourselves to one another. We were both virgins but the time away from one another ignited a feeling in both of us that we couldn’t suppress. He asked me to marry him a month after his return – wanting to get married sooner rather than later seeing as the war was ramping up. John Egan stood by Gale’s side as we exchanged vowels – his blue eyes shining bright as he watched us become husband and wife. He was the life of the party at our reception – singing along with the band as those around us danced to the music. I could see why Gale adored him so, but I was still weary.
That feeling came to a head when John convinced Gale that it was time for him to head over to England and join the ranks. He wrote to him about the fun he was having and all the missions they were accomplishing. He made it sound like a thrill ride – something that didn’t involve the chance of dying at any moment. Gale and I spent our last night together – wrapped up in each other – exploring and branding kisses into skin – almost as if we were creating a permanent road map to remember one another. It was the most sensual night we’ve had – that we would ever have.
The movie reel played on repeat in my head as I could still feel his lips on mine as he kissed me goodbye. Tears in both of our eyes as the sound of the car’s engine faded into the distance.
“I’m coming back to you – hell or high water – I will be back.”
He kept waving until his car was out of sight – my knees buckling – my body falling into grass below. A part of my heart left that Spring Day…
I received his first official letter a couple weeks later – screaming out in joy as I read his chicken scratch penmanship. He spoke of the area they were located – how it felt flying in – the fresh air that surrounded the base. He gushed about the new friends he had made –describing them as if he had known them for years. The most important was how much he missed and loved me – repeating the same words as above – hell or high water.
No letter from Gale would be complete without a mention of John Egan. Gale wrote of how John had taken him under his wing, but also being John’s protector. He wrote of how he’s stopped him from getting into several scuffles with the British soldiers or the townspeople. His writings detailing how much they truly cared for one another – they were like brothers.
As time progressed, his writings became darker – tragic even. He detailed his first mission in graphic detail – expressing his feelings and the slight betrayal that he felt towards Egan. He watched men he had befriended either die in the air in a fiery explosion or pass as they laid on the stretcher in the makeshift hospital on the base. He never wrote of his fear that I’m sure he had – choosing to stay strong and do everything he could for his squadron. He was the main pilot – he had the lives of nine other men to think about – he wanted them to be able to return home safely even if that meant he was the sacrificial lamb...
The last letter that would arrive on time came through the mail on October 10th, 1943. It was shorter than normal, Gale explaining that he was moments away from an important mission. He must’ve written “I love you” about a dozen times before signing off – xo following his name. I had learned about a week later that his plane had went down somewhere outside of Germany. The news articles praised their efforts – telling of how they put a damper into the German’s artillery. That was all well and good, but my husband was missing – the base having no record of his whereabouts or if he was still alive.
Months passed before a battered letter was placed inside the mail slot. The enveloped looked as if it had gone through hell, but Gale’s handwriting could be seen through the grime. He had been placed in a camp for captured soldiers. Many of the men that he had met at the base were there as well. He hadn’t been injured – keeping quiet and under the radar of the German soldiers. I fell to the floor after reading that letter – my heart shattering at the thoughts of what might happen. Tears fell on the paper as I replied – simply begging him to come back to me…
“Sweetheart?” I looked up from the mattress as my mother entered the room. “It’s nearing one in the afternoon, darling.” She threw open the curtains – the bright sunlight beaming into the once darkened room. “You need to get yourself together and get dressed.”
My mother had never seen me in such a state – not even recognizing the person I had become. Long gone was the smile and laughter – replaced by tears and screams of anger. I was angry at everyone – my parents, my friends, God.
Oh, I was especially mad at God.
Countless times I would ask why Gale – why was it his turn to be taken? Was he needed for greater things? Why wasn’t I granted more time with him? Just why?
Growing up in the church, it was frowned upon to ask why for anything, more so for why God chose those that he did. You never asked why – you just learned to accept the outcome. I was long past that – I wanted an answer – I demanded a Goddamn answer.
Sighing, I slowly moved to a sitting position as she laid the black dress and heels next to me. My eyes boring holes into the clothing – hoping that with another energy they would magically combust into flames, burning me alive with them. “I’ll do your hair when you get out of the bath.”
Our eyes connected, “I’m not taking a bath.”
Mother let out an exhausted sigh as her heels clicked on the hardwood floor. I watched as she walked to the window, her upper body jerking slightly as she wiped away the tears that started to fall. She never liked anyone to see her cry.
I started to speak, stopping before the first syllable could come out. I wanted to tell her not to cry but I didn’t have that right. She loved Gale too – she had been smitten by him from the get-go. We all held out hope that he would return to us – just not in a flag draped pine box.
A soft knock on the bedroom door caught both of our attention as my dad entered the room. His once bright face was downcast as he took in my appearance. “The car will be here soon, darling.” His voice soft as he exchanged glances with my mother.
The reality that I was an hour away from burying my only love hadn’t set in yet – just fog – fog that felt like it would never lift to clear skies. I fisted the black material, stepping over the kitten heels as I trudged towards the bathroom. The figure in the mirror was a stranger – someone who’s been through more things than a human is supposed to. Dark circles and pale skin stared back at me – my hair in a tangled mess – not even a comb could get through at this point. Gaunt would be the best word to describe this version of Carolina. I hadn’t bathed in several days – to numb to even remove myself from the bed at times. I barely made it to the bathroom to relieve myself, almost just wanting to go on myself so I wouldn’t have to get up.
Looking around, I noticed everything laid out by my mother. Toothbrush, toothpaste, the expensive makeup that I had collected over the years sitting on the vanity. I was supposed to look put together – still grieving – but have the attributes of a Hollywood starlet.
A guttural scream roared through my body as the vanity contents crashed to the floor – the glass bottles of perfume shattering as the liquid splashed in the air. I could feel the glass stabbing into my bare feet, the blood mixing with the perfume on the floor. I didn’t even register that my father had burst into the room until his arm wrapped around my waist, my back hitting his tailored chest. I thrashed against his hold like a wild animal trapped in a cage.
“Carolina, please!” My mother bawled as she took in my state. “Please, darling calm down before you hurt yourself!”
Another voice was added to the chaos – a deeper voice than that of my father. He was dressed in a black suit – his tall figure looming over my parents. His hands replaced my father’s – his grip on my waist tight and firm. “Calm down, Lina.” His hot breath hitting my ear as the world started to spin around me. My body was running on fumes – the last of those turning into smoke as my brain finally had enough, shutting down before any more damage could be done.
#callum turner#callum turner major john bucky egan#callum turner smut#callum turner imagine#callum turner x reader#callum turner x oc#callum turner x fanfiction#austin butler major gale buck cleven#austin butler fanfiction#austin butler smut#austin butler imagine#austin butler#masters of the air#mota#john egan#john egan x oc#john egan x reader#john egan fanfiction#gale cleven#gale cleven x oc#bucky egan x oc#bucky egan#buck cleven#masters of the air imagine#mota fanfic
48 notes
·
View notes
Text
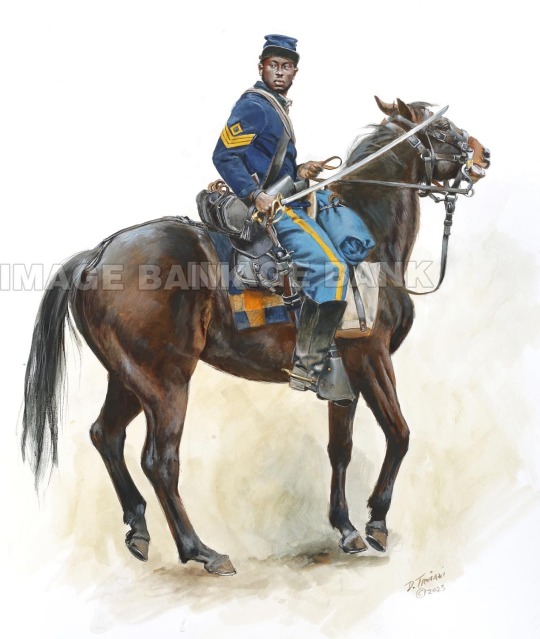

Absolutely loving this Don Troiani artwork of a First Sergeant of the 6th United States Colored Troops Cavalry, 1864.
208 notes
·
View notes
Text





Reseda green 1911 uniform
Sauce: RosalieLebel75.franceserv.com; lesfrancaisaverdun-1916.fr
First row : Modified reseda uniform c.1913
Second row : Reseda uniform concepts c.1910-11
Third Row : Reseda troop helmet and officer jacket made c.1911
Much like her adoption of a modern service rifle, the modification of France’s colorful uniform was started barely a few years before the start of World War 1, at a time when no change could have effectively been made before the start of the conflict. It's a time-honored tradition, where hindsight is 20/20 and rifles are 7/92.
Several modernisation projects ran concurrently between the years 1910 and 1914, but not all of them were quite as modern as they were claimed. For every Boer-inspired practical field dress, the state would bring in famed illustrators and painters like Edouard Detaille, whose practical considerations were vastly outweighed by the necessity to preserve bright red pants because "otherwise how the f*ck do you know who you be shooting at" [sic]. The most promising upgrade though was probably the so-called Tenue Reseda.

Edouard Detaille's new uniform proposal, featuring an early shade of the lighter blue used from 1915 to 1935.
Commissioned by French war minister Maurice Berteaux and designed by a team led by général Dubail, the reseda green uniform was one of the aforementioned several proposed reforms meant to provide better camouflage to soldiers. It was made up almost in its entirety of a verdigris cloth, using a pigment from the reseda plant. Rank and file soldiers were also equipped with a cork/pith helmet fitted with a removable brass comb/crest piece, meant not to protect about shell fragments but rather saber blows. This last and very ostentatious part was replaced in the field with a simple cockade. Cavalry units would retain their old armor pieces save a few light cavalry helmet models, and artillery crews were equipped with Edouard Detaille’s Mle1902 helmet.
This was an overall satisfying design to a modern eye, but decidedly less so to Berteaux’s colleagues at the time. The design was bashed for being unsightly, unpatriotic and looking too much like the German feldgrau uniform, with many arguing that all the modernization French soldiers needed was putties and a cap cover. The project received its biggest blow when Berteaux got ran over by a biplane, as one does, and his successor Messimy did not back it to the same extent. The new minister otherwise noted the “experience [to be] conclusive on a tactical level, and I considered it beyond reproach”, and even later about the madder red pants that remained in service: “this blind and imbecile attachment to the most conspicuous of colors would have cruel consequences.”
The reseda uniform would see one last review in a slightly modified version developed between 1912 and 1913, now retaining the very French red pants and epaulettes for maximum patriotic efficiency. The helmet was also modified to resemble the future Adrian Mle1915 even more closely, with a fixed brass comb. Neither it nor the two Detaille uniforms it competed with managed to get adopted. Messimy, in final attempt at modesty, pushed for an odd allegedly blueish-bruised color competitor made up of a combination of red, white and blue wools. As the war erupted a month after this final decision, the design was never put into large production and French soldiers marched into Alsace wearing the same uniforms as when they first lost it.

1912 review of prototype uniforms, featuring from left to right Detaille’s horizon blue type, Dubail’s modified reseda green type and Detaille’s steel blue type.
250 notes
·
View notes
Text
Information on what Israel has (and is) doing.
Israel has dropped almost 30,000 bombs and shells in 100 days at Gaza. That is eight times more than what the United States aimed at Iraq (during six years of war.) Not only are bombs being dropped, but the Israeli troops in Palestine are terrorizing Palestinians. They chase them, beat them, humiliate them, strip them, and shoot at schools.
https://x.com/eyeonpalestine/status/1759999235435704618?s=46
This did not happen because of the Hamas. Israel is now bombing Lebanon and Syria where Hamas is NOT. This was never about Hamas and yet people believed it.
https://x.com/shaykhsulaiman/status/1759601987341926502?s=46
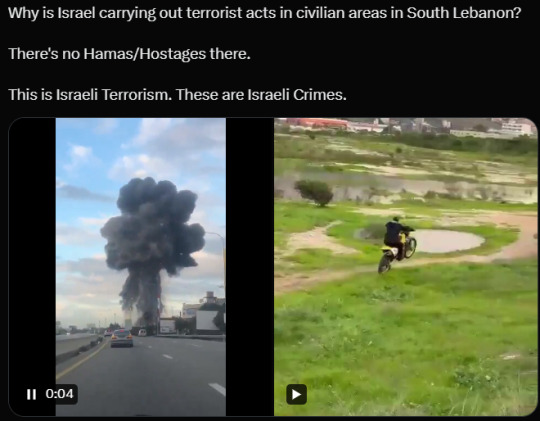
They don’t care about the hostages they claim to want back home safely. They don’t care about their troops. In fact 17% of their troops that died their died at the hands their own army. They don’t care.

How can you help?
1. You should educate yourself! It is always beneficial to read up on the information so you can understand what is happening fully.
https://decolonizepalestine.com/
https://docs.google.com/document/d/16hSogPulZskEYNeDQ06VsRxT6XJAwEYsGQCqfrM5hGs/mobilebasic
https://docs.google.com/document/d/1RsRT57ucvNmrpwHCvK0fGyR1SaM3lxt0USmaZ15GXjU/mobilebasic
2. Donate to resources or if you are not in a place to donate, just click! Every bit helps.
https://gofund.me/11dab5e6
https://gazaesims.com/
http://piousprojects.org/campaign/2712
https://www.gofundme.com/f/rebuild-hope-in-gaza-support-bisan-and-families
https://arab.org/click-to-help/palestine/
3. Boycott, Boycott, Boycott!
Follow the BDS list, but also avoid companies that are pro-Israel. While Starbucks is not on the official BDS list, the owner is a zionist and is suing their union for a pro-Palestine post. They are actively profiting from the money given to them and continually in power to be able to sure their union.
Are you not sure if an item at the store is from a company you should boycott? Use this app to see! https://apps.apple.com/us/app/no-thanks-app/id6476206516

Make companies like this sweat. Denounce your favorite actor/artist/celebrity that is pro-Israel. If they are silent they are complacent. There is not room for silence now. Children, women, men, are dying every day. Having their lives altered completely.
4. Join strikes!
There is a current strike from the 18th to the 25th. Strikes aim to debilitate the globe so people in power are forced to help Palestine.
- During a strike if you are able to refrain from going to work or school.
- Don’t buy anything (outside of necessities and follow BDS if you have to buy something)
- Be loud, be visible, use your voice because our voices are our power
- Be absent from the economy
- Don’t post anything outside of information for Palestine and how to help them
- Do what you can to support Palestine
5. Sign petitions!
https://t.co/v5crIr9Q5x
https://t.co/alyekM4EWU
https://t.co/36yvajNeej
https://t.co/l2vKH7y3ZT
https://irusa.quorum.us/campaign/52005/
https://t.co/qaHQnIYZTq
More here: https://x.com/v4mpirui/status/1750060158422487177?s=46 (avoid change.org posts because they take a percentage of your donation.)
6. Educate yourself on other genocides and humanitarian issues
https://x.com/sapphiredazai/status/1759247407550775801?s=46
https://x.com/rosethearsonist/status/1756693126478008672?s=46
https://x.com/silverspookguy/status/1691152517001011202?s=46
https://x.com/devilnaives/status/1760086034748944678?s=46




Note: adding colors is not for an “aesthetic” i used it to draw attention
#call of duty#cod modern warfare#rdr2#red dead redemption 2#red dead redemption#outer banks#the last of us#free gaza#gazaunderattack#john price#rafe cameron#marvel#palestine
34 notes
·
View notes
Text
Thomas Fountain Blue

Thomas Fountain Blue, the first African American to head a public library in the United States, was also a civic, educational, and religious leader. Blue was born in Farmville, Virginia, on March 6, 1866, to Noah Blue, a carpenter, and Henry Ann Crawley Blue. They were parents of two other children, Alice Blue and Charles Blue.
Blue enrolled in Hampton Institute in Hampton, Virginia, in 1885 and graduated in 1888. In 1894, he enrolled in Richmond Theological Seminary (now Virginia Union University) in Richmond, Virginia, finishing in 1898 with a Bachelor of Divinity degree. One week later, when the United States declared war on Spain after the sinking of the USS Maine off the coast of Cuba, touching off the Spanish-American War, Blue joined the Sixth Virginia Volunteers battalion comprising African American soldiers and was stationed first in Camp Poland in Tennessee and later at Camp Haskell in Georgia.
In 1905, Blue was selected to lead the Western Branch Library of the Louisville Free Public Library on South 10th and Chestnut Street, the first Carnegie Library in the nation to serve African American patrons with an exclusively African American staff. The facility cost $31,024.31 to build and when completed had over 4,000 books and 53 periodicals.
In 1914, Blue opened Louisville’s second Carnegie Library for African Americans, the Eastern Branch Library. During World War I, Blue was drafted, left the branch, and was appointed the Education Secretary at Camp Zachary Taylor in Louisville, one of sixteen national Army training camps created across the nation. Blue worked with Black troops who mostly had supporting and laboring roles in the United States.
After the war ended in 1918, Blue returned to Louisville, and a year later, in 1919, he was named head of the “Colored Department” for the city’s public library system and supervised eight African American assistants. The Colored Department was the first in the United States to have a staff which served multiple Black library branches.
In 1922, Blue was a presenter at the American Library Association Conference in Detroit, Michigan, where he gave a paper titled, “Training Class at the Western Colored Branch,” and led the subsequent discussion with the Negro Roundtable composed of other African American Library staffers from across the nation.
On June 18, 1925, Blue married Cornelia Phillips Johnson from Columbia, Tennessee, and they parented two children, Thomas Fountain Blue, Jr., and Charles Blue (named after his younger brother). Two years later, in 1927, Blue founded the Negro Library Conference and conducted its first meeting at Hampton Institute.
Later becoming a minister, Reverend Thomas Fountain Blue—who held membership in the American Library Association, the Special Committee of Colored Ministers of Louisville on Matters Interracial, and was a charter member of the Louisville Chapter of the Association for the Study of Negro Life and History—died on November 10, 1935, in Louisville, Kentucky. He was 69.
At the 2003 joint conference of the American Library Association with the Canadian Library Association Annual Conference at the Metro Toronto Convention Centre in Toronto, Ontario, Blue was posthumously honored when the organization passed a resolution recognizing his leadership in promoting professionalism among the staff of African American libraries across the United States. In 2022, a headstone honoring Blue and his wife, Cornelia Phillips Johnson, was placed at Eastern Cemetery in Louisville by the Frazier History Museum.
https://www.blackpast.org/african-american-history/people-african-american-history/thomas-fountain-blue-1866-1935/
23 notes
·
View notes
Text


Circular Entitled Colored Soldiers! Equal State Rights! And Monthly Pay with White Men!
Record Group 94: Records of the Adjutant General's OfficeSeries: Letters ReceivedFile Unit: Consolidated File for Major Martin Delaney, 104th USCT Infantry Regiment
BLACK NATIONAL DEFENDERS! The State or Connecticut is authorized to raise Colored Troops; and any number of her quota of 5,000 may be colored men. 29th Regiment Connecticut Volunteers, is now being formed at Camp Buckingham, composed entirely of Colored Men, located at the beautiful City of New Haven, the seat of Yale University. STATE BOUNTY, $200.00 CASH! On being sworn in. By an old law of the State, 30 dollars a year are allowed to each soldier for clothing, 10dol- lars of which is paid down at the time of entering the service, the other 20 dollars being paid in four month payments each, making 210 dollars Bounty--cash, on joining the Regiment--and 20 dollars more during the year. An important fact connected with this recruiting is, that the contract for raising the troops has been given to a Colored Man; and Connecticut is the first State, since the war commenced, which has been thus liberal and considerate. This fact alone should be an inducement for COLORED MEN to rally to her standard; all the Recruiting Agents in the West being Colored; and this principle should prevail everywhere. Colored Men should recruit Colored Men, as best adapted to it. The most liberal compensation will be given to Good Agents, about 50 such being now wanted, and to whom will be paid Cash so soon as service is rendered. APPLY WITHOUT DELAY TO DR. M.R. DELANY, State Contractor, Head-quarters of the West and South-Western States and Territories, 172 Clark Street, Top Story, Chicago, Ill. JOHN JONES, Assistant. LIEUT [crossed out] W.F. STAINES, Evansville, Ind. [image of hand, pointing] For further information, address Dr. M.R. Delany, Box 764, Chicago, Ill. NOTE--I may add here that I am much indebted for obtaining this contract to Major Sanford, of Heavy Artillery Service, and other gentlemen in the Rhode Island Heavy Artillery, who reom- mended me to the authorities of Cleveland. [crossed out] Connecticut. [hand-written] M.R. Delany, State Contractor. Chicago, Ill., Dec. 1st, 1863. P.S.--All recruiting in the States in which it is prohibited is hereby forbidden. M.R.D. Chicago Evening Journal Print, 50 Dearborn Street. D 135 A.G.O. C.T. 1863 [hand-written in red ink along bottom right side]COLORED SOLDIERS! EQUAL STATE RIGHTS! AND MONTHLY PAY WITH WHITE MEN! On the 1st day of January, 1863, the President of the United States proclaimed FREEDOM TO OVER THREE MILLIONS OF SLAVES! The decree is to be enforced by all the power of the Nation. On the 21st of July last he issued the following order:-- PROTECTION OF COLORED TROOPS. "WAR DEPARTMENT, ADJUTANT GENERAL'S OFFICE,"} WASHINGTON, JULY 21. General Order, No. 233. "The following order of the President is published for the information and government of all concerned:-- EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, July 30. '"It is the duty of every Government to give protection to its citizens, of whatever class, color, or condition, and especially to those who are duly organized as soldiers in the public service. The law of nations, and the usages and customs of war, as carried on by civilized powers, permit no distinction s to color in the treatment of prisoners of war as public enemies. To sell or enslave any captured person on account of his color, is a relapse into barbarism, and a crime against the civilization of the age. '"The Government of the United States will give the same protection to all its soldiers, and if the enemy shall sell or enslave any one because of his color, the offence shall be punished by retaliation upon the enemy's prisoners in our possession. It is, therefore ordered, for every soldier of the United States, killed in violation of the laws of war, a rebel soldier shall be executed; and for every one enslaved by the enemy, or sold into slavery, a revel soldier shall be placed at hard labor on the public works, and continued at such labor until the other shall be released and receive the treatment due to prisoners of war. '"ABRAHAM LINCOLN."' '"By order of the Secretary of War. '"E.D. TOWNSEND, Assistant Adjutant General."' That the [full transcription at link]
43 notes
·
View notes
Text

(House Of Ashes) Jason Kolchek & Salim Othman's Outfit
Note:This Is Basically Remastered Version of My Old Works Back in 2022. I Decide to Improve Some Outfit And Of Course Include The Weapons that Used in the Game. Honestly I Never Played this Game At All. I Only Know this Game From Tumblr's Forum About Shipping Between this two Character with Codename "JaLim". But I Found the Other Reason To Loving This Game: It was Brought The Iraqi Conflict Of 2003 Mixed it with Horror Elements which I Found it Interesting. But Without Futher A do Let's Let This Show On The Road.
thanks to @hornydotsblog For Borrowing Her Sims for My Promotions. Such Magnificent Work, Sister and Keep up a good Work
🇺🇸Jason Kolchek

First Lieutenant Jason Kolchek (cir. 1973) is one of the five main protagonists and a playable character in The Dark Pictures Anthology's third installment, House of Ashes. He is a United States Marine Corps Force Reconnaissance First Lieutenant and the squad leader of Mailman 2-1. Jason is a white American man. He has a white complexion with smooth skin, brown eyes and short brown hair.
For personal items, Jason wears a Blue T-shirt, a gray-green shemagh, black watch on left wrist, and a gray baseball cap with "Remember 9/11" marking. He has two tattoos on his arms: one on left forearm, other - on right upper arm
For his Marine uniform, Jason wears interceptor PASGT vest in woodland camouflage with small bags and tan backpack. He also dons 3-color desert camouflage fatigue pants with two kneepads and combat boots. During the operation, Jason wears an earpiece with a small light and radio on his left ear and is armed with a modified M4A1 carbine.
Set Include:
- Jason's Uniform:

1 Color Swatch
Male Only
Custom Thumbnail
Full Body
Age Range:Teen-Elder
Jason's Baseball Cap:

1 Color Swatch
Male Only
Custom Thumbnail
Baseball Cap Category
Age Range:Teen-Elder
🇮🇶 Salim Othman

This outfit set is created from Lt. Salim Ohman's character from the "House of Ashes" game series, which is a young Iraqi officer. But this outfit set quite resemble on what Iraqi troops wore during the Gulf War and Operation Iraqi Freedom campaign.
Actually since 1980s, Iraqi forces haven't clear pattern of uniform, in other words, Iraqi forces utilised anything they could wear to their troops, even some source show the usage of DPM camo set within the Army mixed by the SSh-68 helmet or what we show here. The outfit itself might be an influence from the old British army's field dress, as well as in other Arab states at that time.
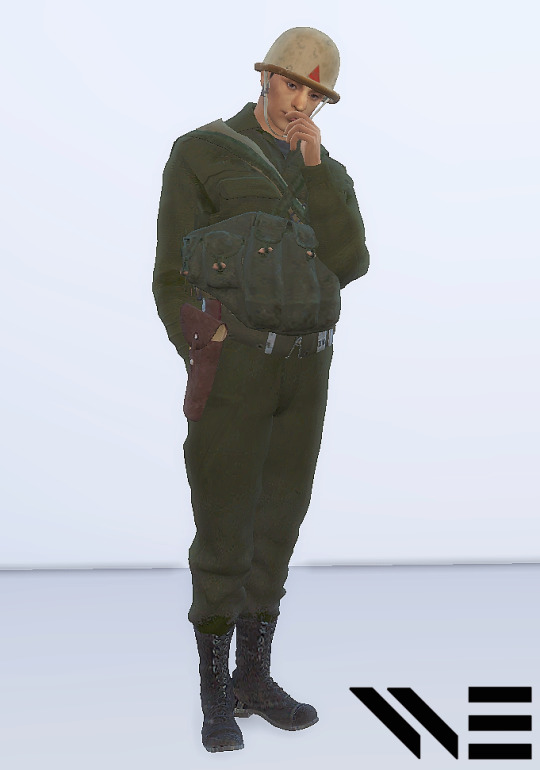

- Salim's Uniform:
1 Color Swatch
Male Only
Custom Thumbnail
Full Body
Age Range:Teen-Elder
-Iraqi M80 Helmet:

-1 Color Swatch
-Unisex
-Custom Thumbnail
-Brimmed-Age Range:Teen-Elder
Weapons (Exclusive to This Set)
-M4A1

I personally fond of the weapons design in this game. but sadly I disapprove of the anachronism featured in the accessories selection. Starting with the Magpul products, Magpul Industries was established in 1999, resulting in its existence by the time of the Iraq War. The products depicted in the game were not accurate. Firstly, the MOE (Magpul Original Equipment) product lines were not officially released until 2008, which makes the stock on the M4A1 anachronistic. The pistol grip is not an original A2 type pistol grip since it does not have a finger hump, and there is an extension to the receiver. The handgrip could be a MOE handgrip, but it could also be the Magpul MIAD (Mission Adaptable) handgrip with adjustable back and front straps. The MIAD was released earlier than the MOE, but it was released in 2004, a year after the game's setting. The Marines used Magpul EMAGS (export mags) that had flat sides and a witness window for ammunition. These magazines were not released until 2009. The old steel or aluminum STANAGS would be accurate. While the M4A1 was correctly portrayed with a quad-railed handguard, the type of handguard used for military-issued carbines was incorrect. The rail that should be used is the Knight's Armament Company M4 RAS Forend. The rail system in the game seemed to be heavily influenced by the UTG two-piece handguard and the Surefire M82 handguard. While according to three veterans I talked to about military issued small arms (two Army and one Navy) it is possible to set up your rifle with what you want so having the UTG handguard is not impossible, but it begs the question of why these Marines would go out of their way to pay for the lesser quality of the UTG instead of using the standard issued Knight’s system. UTG was most likely what developers had access to for a reference.
[Custom]Colt M4 (Custom #65)

But Fear Me Not I Eventually Decide to Fix All Those Fiasco With more Era Appropriate and Authentic M4 With Genuine Colt M16A2 Pistol Grip, Real M4A1 Stock, Steel STANAG 30-Rounds Magazine, Authentic Military-Issue Quad Rail Made By Knights Armaments Company (KAC). With Trijicon The Advanced Combat Optical Gunsight (ACOG)
-Glock 17

While Glocks did exist by 2003, but the Glock shown in the game would be 15 years too early because the game used the Generation 5 model of Glocks and Glock’s Gen 5 came out in 2018. The Gen 5 is characterized with the beveled front of the slide and frame, hole in the middle of the guide rod, front slide serrations (although the real Gen 5s’ serrations are straight, not slanted), no finger grooves on the the bottom of the frame (where the flashlight is attached in the game), an ambidextrous slide release, and only one trigger pin.
Glock 17 (#Custom 21)

I made another fix to make it Fit into Game Settings and replaced it with Gen 3 Glocks. as This Particular Generation was Introduced in 1998. The Gen 3 has finger grooves, no front slide serrations, no ambidextrous slide release, no beveled front slide nor beveled frame, a rail on the bottom of the frame and two trigger pins. Attaching an aftermarket flashlight is possible with a rail on the bottom.
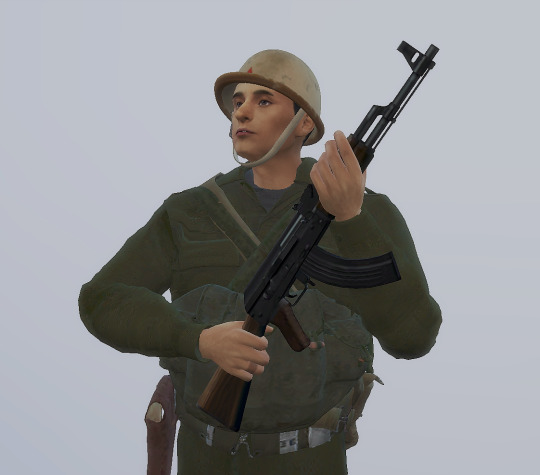

BULGARIAN AKK-47
Just some Creativity Liberty I Take, Despite I Know the Facts AK That Used in Game in Fact Soviet Type 3 AK, But I Found it Interesting if they using Bulgarian Ones
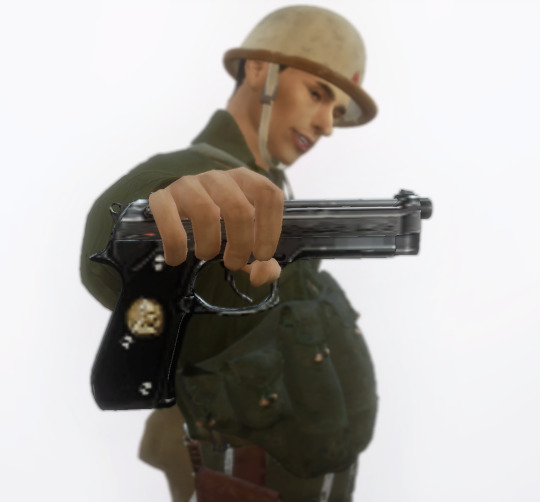


Iraqi Tariq Pistol
The pistol of the Republican Guard in the game was the Beretta 1951, or rather its Iraqi copy: the Tariq. The giveaway that it’d likely be the Tariq was the presence of a medallion on the pistol grip, something the original Beretta did not have. Besides the incorrect shape of the slide release and the three holes in the trigger.
DOWNLOAD
@cctreasuretrove @sssvitlanz @exzentra-reblog @ts4-poses
#the sims 4#the sims#the sims 4 custom content#ts4 cc#ts4military#the sims 4 military#ts4#the sim#the sims 4 cc#ts4cc#the sims 4 gun#ts4 gun#ts4 military#jalim#dark pictures house of ashes#jason x salim#salim othman#jason kolchek#house of ashes
56 notes
·
View notes
Text
The largest massacre of Black soldiers by Confederate soldiers was in the Battle of the Crater:
The biggest massacre of Black soldiers in the war was in the Battle of the Crater. Part of the Siege of Petersburg, the war's longest campaign and the one where it really did start to foreshadow the war of 1914 (and ironically the one campaign of which the least is written about in spite of being both the longest and the most modern for a variety of reasons), it was the most ill-starred battle of the campaign. It saw a plan that could have worked bungled by Burnside, Mead, and Grant.
The plan was to do a very medieval method of breaking a siege and a very unsubtle one. Blow a hole in the line, advance around the hole, roll the line up. The plan was assigned to Black soldiers, then Mead got cold feet, talked Grant and Burnside into changing this, and the plan that unfolded was a prime example of how to kill a lot of people in a short amount of time for no gain. The troops originally assigned were drawn into the killing field in the Crater because the white troops that replaced them forced the battle there.
General William Mahone, a future pro-civil rights 'Readjustor' orchestrated accordingly the largest massacre of Black soldiers in the entire war, one done by Lee's Army of Northern Virginia and one noted at the time. Leading to the grim irony that General Mead's racism brought about the very thing he claimed he didn't want.
#lightdancer comments on history#black history month#war of the rebellion#battle of the crater#siege of petersburg#army of the potomac#army of northern virginia#black resistance#united states colored troops
2 notes
·
View notes
Text

Monday, April 8, 2024
(Posted on Tuesday)
Monday had a lot going on, needless to say. We had our third Girl Scout meeting for our Citizen Scientist Journey, but it was because of the eclipse. We embarked on our citizen science project by recording the eclipse for NASA! It was the most amazing thing to watch too. We were in the path of totality, so it worked out really well. I don't know if I have ever seen something so beautiful when it went into totality and we were able to take our eclipse glasses off. Even watching it through the glasses go completely dark was incredible. And then when the sun came back out, that split second that told us to put our glasses back on, that too was stunning! We won't have another one until 2044, but I think we would have to travel for that one. I am so happy that we were able to experience it together as a troop. I love that we can make such breathtaking memories like this together.
Tasks Completed:
Geometry - Learned about two-way tables + practice + learned about probability with two-way tables + practice
Lit and Comp II - Copied Unit 23 vocabulary + read chapter 53 of Emma by Jane Austen
Spanish 2 - Presented questions and answers in Spanish to Dad (30/30) + reviewed vocabulary
Bible I - Read 1 Samuel 11-12
World History - Read about Holocaust notes + read different articles from the United States Holocaust Museum website
Biology with Lab - Read about bacterial growth + read about bacteria control and benefits
Foundations - Read more on thoroughness + took next quiz on Read Theory + read sample persuasive speech by Stephanie Cloward
Piano - Practiced for one hour
Khan Academy - None today
CLEP - None today
Streaming - Watched Greatest Events of World War II in Color episode 2
Duolingo - Studied for 15 minutes (Spanish, French, Chinese) + completed daily quests
Reading - Read pages 277- 322 of Accountable: The True Story of a Racist Social Media Account and the Teenagers Whose Lives It Changed by Dashka Slater
Chores - Took the trash and recycling out
Activities of the Day:
Personal Bible Study (2 Timothy 2)
Girl Scout Citizen Science Project
Volunteered 2 hours at the library
Ballet
Contemporary
Journal/Mindfulness
#study blog#study inspiration#study motivation#studyblr#studyblr community#study community#study-with-aura
12 notes
·
View notes
Photo
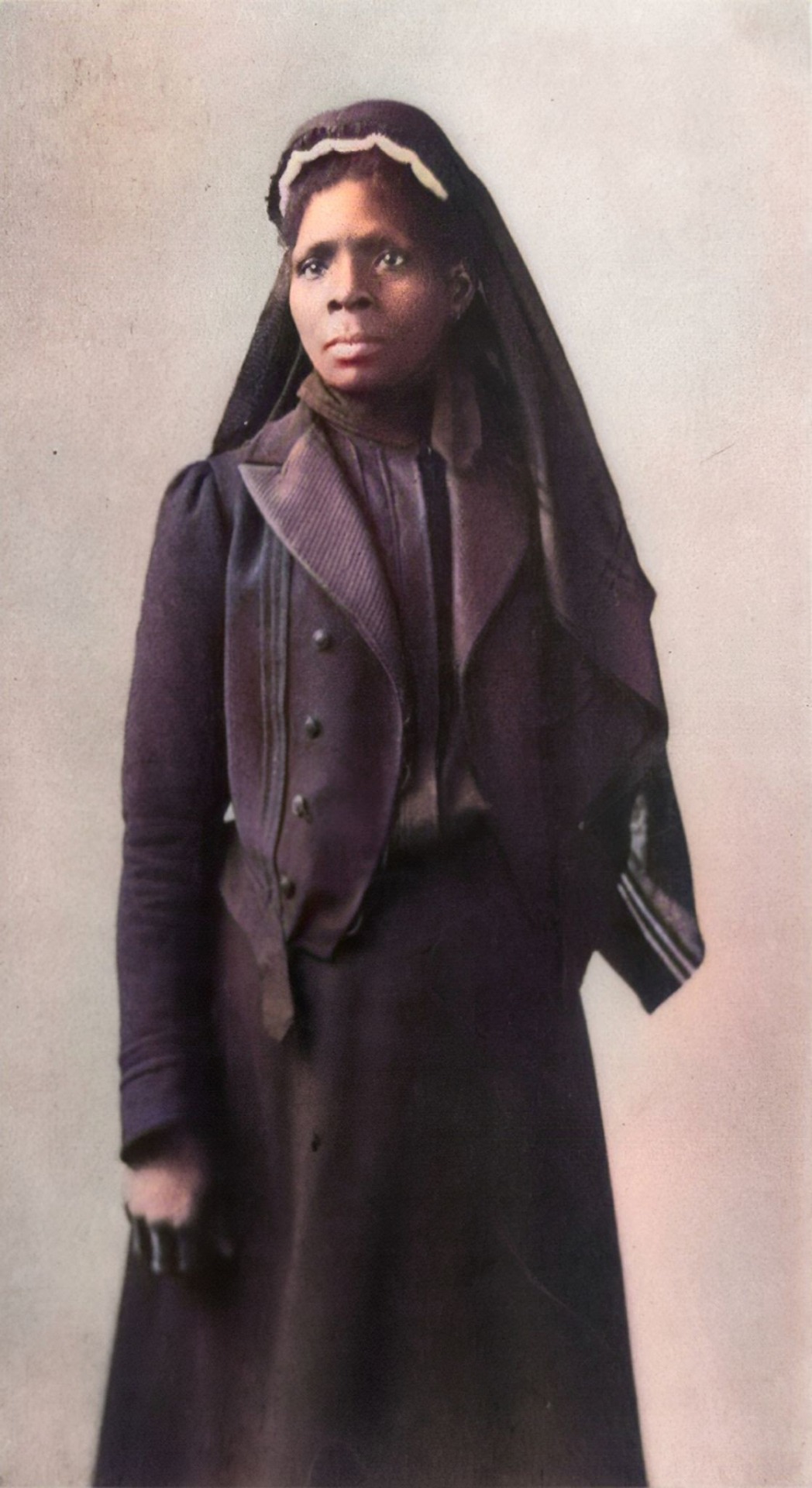

Susie King Taylor was an activist, educator, and volunteer nurse on the Union side in the Civil War. She documented her experiences in her memoir Reminiscences of My Life in Camp with the 33rd United States Colored Troops, Late 1st S.C. Volunteers. After the Civil War, she opened several schools in Georgia for formerly enslaved people. This daguerreotype had been lost to history until it was discovered by collector Stephen Restelli. We see Taylor in a military-inspired bodice and petticoated gingham gown, looking directly at the photographer with a confident gaze.
131 notes
·
View notes
Text
🇺🇸Army of the United States🇺🇲: a military lookbook

PART II
Spanish-American War (1898): The soldiers wore a khaki uniform with a high collar and brass buttons. This uniform included a campaign hat, and troops often wore canvas leggings and brown leather gaiters.
World War I (1917-1918): The iconic uniform of World War I was the M1917 uniform, commonly known as the "Doughboy" uniform. It featured a flat-brimmed helmet, a tunic, and trousers, all made of olive drab wool.
World War II (1941-1945): The U.S. Army transitioned to a more functional and comfortable olive drab uniform during World War II. The M1941 uniform included a field jacket, a garrison cap, and cargo pants.
Vietnam War (1955-1975): The U.S. Army adopted the M1965 uniform during the early years of the Vietnam War. It was made of ripstop cotton and came in an olive green color. The most recognizable feature was the slant pockets on the jacket.
CC @viktorviolettaenterprises
#sims 4#sims 4 cc#ts4 military#ts4 historical#ts4 lookbook#ww2#ww1#ts4 history challenge#ts4 history cc#viktorvolkenterprises#revolution-sims
16 notes
·
View notes