#acute urticaria
Text
#urticaria#urticaria treatment#urticaria allergy#urticaria symptoms#urticaria treatment in hindi#acute urticaria#urticaria cause#urticaria means#urticaria causes#urticaria images#havis#chronic urticaria#urticaria medicine#how to cure urticaria#urticaria medicines#causes for urticaria#urticaria home remedies#urticaria home treatment#best treatment for urticaria#treatment of urticaria in hindi#best skin specialist for urticaria in delhi
0 notes
Text
Why am I only now registering that I am in fact disabled??? That I have a chronic illness??? That I am in chronic pain???
Like yeah this is a birth defect that will never go away and will always cause me pain and will always need special pillows and shit to cope with and yeah sometimes I cry because I don't want to deal with this for the rest of my life, but I'm not disabled???!!!
And like yeah this is happens in flare ups and yeah that causes me a lot of discomfort and pain and needs me to always have shorts and a tshirt on hand and yeah it might go away in 7,5-10 years (if I'm lucky), but I don't have a chronic illness?!???!
Why is my brain like this
#somehow I didn't want to claim that vocabulary????#I hate myself sometimes#acutally autistic#chronic illness#chronic pain#disability#disabled#0_0#scoliosis#heat hives#urticaria
1 note
·
View note
Text
Confess and be hanged
Kathy Griffin's elbow (Other congenital malformations of hair)
Dave Navarro's forehead (Subluxation of lens, unspecified eye)
Jessica Biel's eye (Other hammer toe(s) (acquired), left foot)
James Franco's fist (Solitary bone cyst, left ulna and radius)
Simon Doonan's thigh (Malignant neoplasm of left orbit)
Carson Palmer's head (School (private) (public) (state) as the place of occurrence of the external cause)
Pitbull's eye (Chondrolysis, hip)
Kevin Federline's eye (Osseous and subluxation stenosis of intervertebral foramina of abdomen and other regions)
Tate Donovan's thigh (Chronic myeloid leukemia, BCR/ABL-positive, in remission)
Ryan Gosling's arm (Pedal cycle passenger injured in collision with fixed or stationary object in traffic accident)
Sean Combs's neck (Mixed pediculosis and phthiriasis)
Katharine McPhee's chin (Calcific tendinitis, right lower leg)
Katrina Bowden's back (Kernicterus, unspecified)
Balthazar Getty's hair (Toxic effect of contact with other venomous marine animals, assault)
Elizabeth Taylor's ear (Displaced trimalleolar fracture of left lower leg)
Kelsey Grammer's eye (Major laceration of left kidney)
Kerry Diamond's neck (Scrotal transposition)
Jason Lee's wrist (Papyraceous fetus, first trimester)
Josh Holloway's upper arm (Activity, swimming)
Desiree Hartsock's ear (Swimmer's ear, left ear)
Jared Leto's eyebrow (Pathological fracture, right hand)
Rumer Willis's eye (Lesion of plantar nerve)
Ramona Singer's arm (Other specified injury of intrinsic muscle and tendon at ankle and foot level, left foot)
Emily VanCamp's calf (Nicotine dependence, cigarettes, with withdrawal)
Jane Krakowski's fist (Other unilateral secondary osteoarthritis of hip)
Vince Vaughn's lower leg (Unspecified complication following infusion and therapeutic injection)
Olivia Palermo's shoulder (Laceration without foreign body of right back wall of thorax with penetration into thoracic cavity)
Russell Brand's wrist (Malignant neoplasm of left orbit)
Jackson Rathbone's belly (Primary cyst of pars plana, unspecified eye)
Garth Brooks's eyebrow (Nondisplaced fracture of anterior process of left calcaneus)
Adrian Grenier's nose (Military operations involving flamethrower, civilian)
Jesse Tyler Ferguson's hair (Retinal hemorrhage, left eye)
Martin Lawrence's ankle (Hemorrhagic disease of newborn)
Spencer Pratt's neck (Perforated corneal ulcer, unspecified eye)
Ashley Hebert's bottom (Major laceration of left kidney)
Hugh Jackman's bottom (Laceration of radial artery at wrist and hand level of left arm)
Paris Hilton's chin (Preterm labor without delivery, unspecified trimester)
Simon Cowell's arm (Contusion of small intestine)
Tila Tequila's cheek (Other superficial bite of hand of unspecified hand)
Jennifer Grey's toe (Injury of quadriceps muscle, fascia and tendon)
Brody Jenner's hip (Laceration without foreign body of back wall of thorax without penetration into thoracic cavity)
Ciara's hair (Diffuse cystic mastopathy of unspecified breast)
Molly Sims's chin (Urticaria due to cold and heat)
Luke Bryan's buttocks (Urticaria due to cold and heat)
Richard Gere's breast (Endometriosis of pelvic peritoneum)
Jensen Ackles's calf (Other ulcerative colitis with intestinal obstruction)
Teresa Giudice's head (Laceration of extensor muscle, fascia and tendon of left middle finger at forearm level)
Stavros Niarchos III's ear (Striatonigral degeneration)
Winona Ryder's thumb (Acute embolism and thrombosis of right femoral vein)
Scott Disick's forearm (Extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type)
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Acquired Angioedema | Causes, Symptoms & Treatments
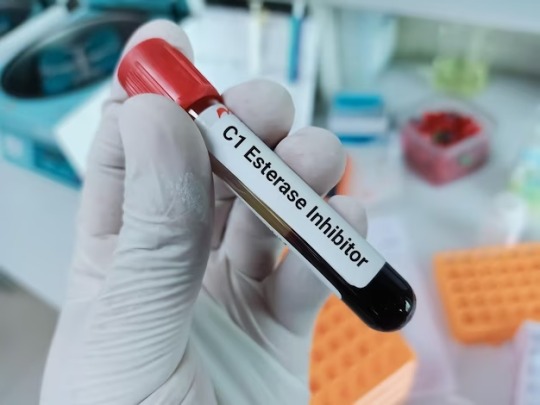
Acquired angioedema (AAE) is defined as a deficiency in the C1 esterase inhibitor.
It is a rare disorder characterized by recurring angioedema without urticaria that may be linked to lymphoproliferative disorders (LPD).
Acquired angioedema is classified into two types: AAE-I and AAE-II.
AAE results from an acquired deficiency of (C1-INH), which can be caused by consumption (type 1) or inactivation (type 2).
This increased catabolism can be caused by an autoimmune disorder (such as systemic lupus erythematosus) or a malignant tumor (such as lymphoma).
The primary symptom is swelling usually affects the face, mouth, and upper airways which can be severe. Itching and urticaria don’t occur.
Clinicians should suspect acquired C1 inhibitor deficiency or hereditary angioedema if angioedema is not accompanied by urticaria, recurs without apparent cause, or is triggered by local trauma.
Hereditary angioedema (types 1 and 2) or acquired C1 inhibitor deficiency is confirmed by: –
Low C4 levels, even between episodes.
Decreased C1 inhibitor level or function.
Treatment options include: –
Plasma-derived or recombinant C1-INH for acute attacks.
Icatibant which alleviate AAE symptoms and was well tolerated.
Ecallantide is used in the treatment of AAE and is also considered another treatment option for patients who have developed resistance to C1-INH replacement.
Fresh frozen plasma (FFP) may be used if neither of these treatments is available.
Read more at: https://medicaregate.com/acquired-angioedema-causes-symptoms-treatments/
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
*Dr. Smita Goel Homeopathy Clinic*
Urticaria – also known as hives, weals, welts or nettle rash – is a raised, itchy rash that appears on the skin. It may appear on one part of the body or be spread across large areas.
The rash is usually very itchy and ranges in size from a few millimetres to the size of a hand.
Although the affected area may change in appearance within 24 hours, the rash usually settles within a few days.
Doctors may refer to urticaria as either:
• acute urticaria– if the rash clears completely within 6 weeks
• chronic urticaria –in rarer cases, where the rash persists or comes and goes for more than 6 weeks, often over many years
A much rarer type of urticaria, known as urticaria vasculitis, can cause blood vessels inside the skin to become inflamed. In these cases, the weals last longer than 24 hours, are more painful, and can leave a bruise.
When to seek medical advice
Visit your doctor/ General Practitioner (GP) if your symptoms don't go away within 48 hours.
You should also contact your doctor / GP if your symptoms are:
• severe
• causing distress
• disrupting daily activities
• occurring alongside other symptoms
Who's affected by urticaria?
Acute urticaria (also known as short-term urticaria) is a common condition, estimated to affect around 1in 5 people at some point in their lives.
Children are often affected by the condition, as well as women aged 30 to 60, and people with a history of allergies.
What causes urticaria?
Urticaria occurs when a trigger causes high levels of histamine and other chemical messengers to be released in the skin.These substances cause the blood vessels in the affected area of skin to open up (often resulting in redness or pinkness) and become leaky. This extra fluid in the tissues causes swelling and itchiness.
Histamine is released for many reasons, including:
• an allergic reaction – such as a food allergy or a reaction to an insect bite or sting
• cold or heat exposure
• infection – such as a cold
• certain medications – such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)or antibiotics
However, in many cases of urticaria, no obvious cause can be found.
Some cases of long-term urticaria may be caused by the immune system mistakenly attacking healthy tissue. However, this is difficult to diagnose and the treatment options are the same.
Certain triggers may also make the symptoms worse. These include:
• drinking alcohol or caffeine
• emotional stress
• warm temperature
Read more about the causes of urticaria.
Diagnosing urticaria
Your GP will usually be able to diagnose urticaria by examining the rash. They may also ask you questions to find out what triggered your symptoms.
If your GP thinks that it's caused by an allergic reaction, you may be referred to an allergy clinic for an allergy test. However, if you've had urticaria most days for more than 6 weeks, it's unlikely to be the result of an allergy.
You may also be referred for a number of tests, including a full blood count (FBC), to find out whether there's an underlying cause of your symptoms.
Read more about diagnosing urticaria.
Treating urticaria
In many cases, treatment isn't needed for urticaria, because the rash often gets better within a few days.
If the itchiness is causing you discomfort, antihistamines can help. Antihistamines are available over the counter at pharmacies – speak to your pharmacist for advice.
A short course of steroid tablets (oral corticosteroids) may occasionally be needed for more severe cases of urticaria.
If you have persistent urticaria, you may be referred to a skin specialist (dermatologist). Treatment usually involves medication to relieve the symptoms, while identifying and avoiding potential triggers.
Read about treating urticaria.
Complications of urticaria
Around a quarter of people with acute urticaria and half of people with chronic urticaria also develop angioedema, which is a deeper swelling of tissues.
Chronic urticaria can also be upsetting and negatively impact a person's mood and quality of life.
Angioedema
Angioedema is swelling in the deeper layers of a person's skin. It's often severe and is caused by a build-up of fluid. The symptoms of angioedema can affect any part of the body, but usually affect the:
• eyes
• lips
• genitals
• hands
• feet
Medication such as antihistamines and short courses of oral corticosteroids (tablets) can be used to relieve the swelling.
Read more about treating angioedema.
Emotional impact
Living with any long-term condition can be difficult. Chronic urticaria can have a considerable negative impact on a person's mood and quality of life. Living with itchy skin can be particularly upsetting.
One study found that chronic urticaria can have the same negative impact as heart disease. It also found that 1 in 7 people with chronic urticaria had some sort of psychological or emotional problem, such as:
• stress
• anxiety
• depression
See your GP if your urticaria is getting you down. Effective treatments are available to improve your symptoms.
Talking to friends and family can also improve feelings of isolation and help you cope better with your condition.
Anaphylaxis
Urticaria can be one of the first symptoms of a severe allergic reaction known as anaphylaxis.
Other symptoms of anaphylaxis include:
• swollen eyes, lips, hands and feet
• feeling lightheaded or faint
• narrowing of the airways, which can cause wheezing and breathing difficulties
• abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting
• collapsing and becoming unconscious
#ghaziabad#homeopathy clinics#best homeo clinic in indirapuram#best skin doctor in ghaziabad#homeopathy#homeopathy doctor#greater noida#homeopathy for ibs#homeopathy cold treatment in indirapuram#homeopathy medicine#laser treatment in indirapuram#skin specialist in indirapuram#homeopathy skin allergies treatment in indirapuram#homeopathy specialist in indirapuram#best schools in indirapuram#laser hair removal in indirapuram#child specialist in noida#child doctor in noida#homeopathy skin allergies treatment in noida#noida news#dentist in noida#noida#east delhi#best astrologer in delhi#delhi news#deletefacebook#faridabad#gurgaon
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
*Dr. Smita Goel Homeopathy Clinic*
www.thehomeopathyclinic.co.in
Irritated skin can be caused by a variety of factors. These include immune system disorders, medications and infections. When an allergen is responsible for triggering an immune system response, then it is an allergic skin condition.
Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema)
Eczema is the most common skin condition, especially in children. It affects one in five infants but only around one in fifty adults. It is now thought to be due to “leakiness” of the skin barrier, which causes it to dry out and become prone to irritation and inflammation by many environmental factors. Also, some people with eczema have a food sensitivity which can make eczema symptoms worse. In about half of patients with severe atopic dermatitis, the disease is due to inheritance of a faulty gene in their skin called filaggrin. Unlike with urticaria (hives), the itch of eczema is not only caused by histamine so anti-histamines may not control the symptoms. Eczema is often linked with asthma, allergic rhinitis (hay fever) or food allergy. This order of progression is called the atopic march.
Allergic Contact Dermatitis
Allergic contact dermatitis occurs when your skin comes in direct contact with an allergen. For instance, if you have a nickel allergy and your skin comes in contact with jewelry made with even a very small amount of nickel, you may develop red, bumpy, scaly, itchy or swollen skin at the point of contact.
Coming in contact with poison ivy, poison oak and poison sumac can also cause allergic contact dermatitis. The red, itchy rash is caused by an oily coating covering these plants. The allergic reaction can come from actually touching them, or by touching clothing, pets or even gardening tools that have come in contact with the oil.
Urticaria (Hives)
Hives are an inflammation of the skin triggered when the immune system releases histamine. This causes small blood vessels to leak, which leads to swelling in the skin. Swelling in deep layers of the skin is called angioedema. There are two kinds of urticaria, acute and chronic. Acute urticaria occurs at times after eating a particular food or coming in contact with a particular trigger. It can also be triggered by non-allergic causes such as heat or exercise, as well as medications, foods, insect bites or infections. Chronic urticaria is rarely caused by specific triggers and so allergy tests are usually not helpful. Chronic urticaria can last for many months or years. Although they are often uncomfortable and sometimes painful, hives are not contagious.
Angioedema
Angioedema is swelling in the deep layers of the skin. It is often seen together with urticaria (hives). Angioedema many times occurs in soft tissues such as the eyelids, mouth or genitals. Angioedema is called "acute" if the condition lasts only a short time such as minutes to hours. Acute angioedema is commonly caused by an allergic reaction to medications or foods. Chronic recurrent angioedema is when the condition returns over a long period of time. It typically does not have an identifiable cause.
Hereditary angiodema (HAE)
Hereditary angiodema (HAE) is a rare, but serious genetic condition involving swelling in various body parts including the hands, feet, face, intestinal wall and airways. It does not respond to treatment with antihistamines or adrenaline so it is important to go see a specialist.
Skin conditions are one of the most common forms of allergy treated and managed by an allergist / immunologist, a physician with specialized training and expertise to accurately diagnose your condition and provide relief for your symptoms.
Homeopathy has good medicines for skin allergy.

0 notes
Text
Managing Hives: Acute and Chronic Urticaria Treatments

Managing hives, whether acute or chronic, involves understanding triggers and employing effective treatments to alleviate symptoms and prevent recurrence.
Acute Urticaria: Typically lasts less than six weeks and is often triggered by allergies to food, medications, insect stings, or infections. Antihistamines are the mainstay of treatment, targeting histamine release and reducing itching and swelling. For severe cases, oral corticosteroids may be prescribed for a short duration to suppress inflammation. Identifying and avoiding triggers is crucial to preventing future episodes.
Chronic Urticaria: Lasts longer than six weeks and can significantly impact quality of life. Unlike acute urticaria, triggers are often more elusive and may include autoimmune disorders, infections, or hormonal imbalances. Treatment involves higher doses of non-sedating antihistamines, often in combination with other medications like leukotriene inhibitors or immunosuppressants for refractory cases. Lifestyle changes such as stress management, avoiding known triggers, and maintaining a healthy diet can also help manage symptoms.
1 note
·
View note
Text

A "contrast reaction" is to be distinguished from a "toxicity." Toxicities includes entities such as thyrotoxicosis, contrast-induced nephropathy, or nephrogenic systemic fibrosis.
Contrast reactions are acute to subacute reactions to contrast media administration. When contrast reactions occur they should be classified by type and severity. Allergic-type reactions include hives, pruritis, cutaneous edema, bronchospasm, laryngeal edema, and anaphylaxis. Physiologic reactions include nausea/vomiting, headache, vasovagal reaction, hypertensive urgency/emergency, arrhythmia and seizure.
Most severe reactions occur within 20 minutes of injection, although anaphylaxis can occur up to ~4 hours afterward. Mild reactions (esp. hives) can be delayed.
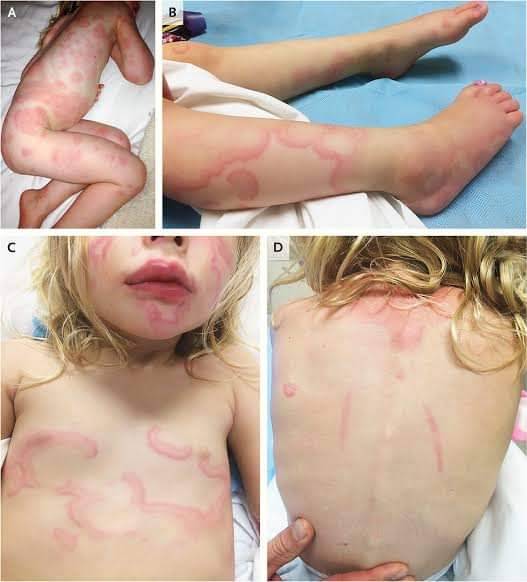
Image depicts a patient with diffuse drug-induced urticaria.
Source: Choo, et al. Drug-induced Urticaria. From "Drug Eruptions," Springer, 2022.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Urticaria, commonly known as hives or wheals, is a common skin condition characterized by raised, itchy, red welts on the skin. It often comes and goes rapidly, with individual welts lasting anywhere from a few hours to a maximum of 24 hours. Though ...
#Mirari #MirariDoctor #MirariColdPlasma #ColdPlasma
0 notes
Text
What are Hives? How to rid from Hives Naturally?

Hives also known as urticaria, in this condition skin rash triggered by a reaction to food, medicine or other irritants. The skin rash could be hives, and the itching from hives range from mild to severe. This condition also known as urticaria. Hives can go away quickly it is acute hives, or last a long time it is chronic hives. Allergic reaction occurs when your immune system comes in contact with an allergen. Allergens are proteins that are harmless to many people but cause an allergic reaction in sensitive people. There is a difference between hives and rash.
Rash is a skin condition that involves something out of the ordinary like spots, swelling, redness or itchiness and hives is an example of a rash but not all rashes are hives.
Types of hives
Acute urticaria refers to hives that don’t last very long. Chronic urticarial happens at least twice a week for more than six weeks. There is also a condition called physical urticaria or inducible urticarial. Physical hives usually appear within an hour after exposure, this type of hives can also be chronic.
What causes hives?
The welts that come with hives are caused by the release of immune system chemicals, such as histamine, into your bloodstream. The skin reaction may be triggered by –
Sunlight
Heat or cold
Pressure on the skin as from a tight waistband
Vibration such as caused by jogging
Medical conditions such as infection, thyroid disease, allergy and cancer
Causes of acute hives-
Acute hives are often an allergic reaction to something you put into your body, like drink or food, medication or something that you touch. The skin has immune cells called mast cells. When these cells go into action, they release chemicals including called histamine. Histamine is the reason that hives form. Some of reasons include having infection, stress or physical pressure on your skin.
Causes of Chronic hives
Chronic hives are not usually caused by allergies. They caused by infections from bacteria or viruses, or other medical conditions like lupus. Chronic hives last for long periods of time but usually are not permanent. They can be uncomfortable, but they are not life threatening.
Symptoms
Welts that might be purple, red or skin colored, depending on your skin color
Itchiness which can be intense
Batches of welts that can rise anywhere on the body
Welts that vary in size, change shape and appear and fade repeatedly
Painful swelling around the cheeks, eyes or lips
Symptoms that persist for more than six weeks and recur often and anytime, sometimes for months or years
Flares triggered by exercise, heat or stress
Complications of Hives
Severe acute allergic reaction could have life threatening swelling of the airways- your throat and lungs, this condition is known as anaphylaxis.
Anaphylaxis is triggered by a severe allergic reaction to a certain food like peanuts or to a bee sting.
Symptoms of anaphylaxis include trouble in breathing, dizziness, swelling of the lips, tongue, mouth or throat.
Prevention of Hives
Avoid known triggers- if you know what has triggered your hives try to avoid that substance.
Cut certain food products out of your diet
Switch to detergents and soaps without scents or dyes
Reduce exposure to airborne allergens
Avoid extreme changes in temperature
Relax and take a break when you are stressed or overworked.
Wear loose fitting, lightweight clothing
If pollen or animal contact has triggered your hives in the past, take a bath or shower and change your clothes if you are exposed to pollen or animals.
Management of Urticaria according to Ayurveda-
In ayurveda urticaria is classified as a Sheetapitta. Sheetapitta is comprised of two words – sheeta and pitta. This condition occurs due to the dominance of cold over pitta dosha.
In ayurveda sheetpitta is caused due to the following reasons such as-
Overconsumption of sour gruels
Sleeping during the day
Contact with cold substances
Exposure to cold wind
Improper emesis
Insect bite
Coming in contact with poisonous bugs and insects
Excess intake of pungent and salty food
Effect of seasonal changes on the body
Due to these factors Kapha and Vata doshas become aggravated and inevitably combine with pitta dosha, these spread all over the body and produce rashes on the surface of your skin.
Ayurvedic treatment for sheetapitta / urticarial involves body purification therapy like samshodhana . Abhyanga, svedana, vaman and virechen are very effective in treating Urticaria.
Pathya –
Consume old grains
Mudga green gram
Aamalaki
Karela
Drink warm water
Apathya-
Excess spicy, sour food
Avoid heavy to digest food
Cold water
Wrong food combinations ( virudha aahar)
Lifestyle Improvement in Urticaria as per Ayurveda-
Avoid exposure to cold breeze
Don’t suppress natural urges
Daily exercise, meditation and yoga
Avoid day time sleep after lunch
Sleep on time after dinner
Follow ritucharya and deencharya as per ayurveda
Hot water bath daily
Use chemical free products
Yoga and Asanas – with the help of yoga asanas reduces stress that promotes relaxation by deep breathing. Yoga and asanas are helpful in urticarial are as following-
Halasana
Surya namaskar
Brashtrika pranayama
Matsyasana
Bhujangasana
External therapies for Urticaria-
Lepa with durva and nishi
Abhyanga with kshara, lavana , taila
Parisheka with ushnambu
Purificatory thearpies for urticaria-
Vamana
Virechana
Herbs used in Ayurveda for urticaria-
Nimba
Haridra
Amrita
Nishotah
Triphala
Katuki
Chronic Urticaria Kit
1) Aloe Vera Gulab Gel –
Aloe Vera Gulab Gel is formed with the pure extract of herb Aloe Vera and the mixture of rose petals. Thus this wonderful composition provides a cooling effect on the skin that relieves from burning sensation, itchiness, etc. The gel helps in maintaining healthy skin and repairing skin damage.
Recommended Dosage – Gently apply over the affected area of the skin.
2) Panchatikta Ghrita Guggulu –
The tablets are very beneficial in curing skin diseases as it contains the Pitta pacifying ingredients such as Shuddh guggulu (Commiphora mukul), Neem (Azadirachta indica), Amrita (Tinospora cordifolia), Gajapippali (Piper chaba), Shunthi (Zingiber officinalis), etc. The tablet is Tridoshahara, thus is very effective in maintaining the hormonal level in the body.
Recommended Dosage – Take 2 tablets twice daily with normal water.
3) Skin care tablet –
Skin care tablet is a pure ayurvedic formulation. It helps to maintain the texture of your skin depending on the type of skin you have. It contains various herbs like Haridra khand, Panchnimb churna, Khadir chahal, Chirayta, Mulethi, Chopchini, Gandhak, Ajmoda that work very effectively on all skin types. Skin care is a blood purifying tablet. It cools and detoxifies the blood, increase blood circulation of the skin. It minimizes the blemishes, lighten sun tan, delay ageing of skin and heal skin problems. These tablets also act as a skin moisturizer, Improves blood circulatio, reduce itching and burning sensation of skin, Prevent acne and pimples.
Recommended Dosage: Take 1 tablet twice daily with normal water.
4) Neem Capsules –
NEEM capsules 100% Safe and purely Ayurvedic preparation. CAC NEEM CAPSULES is natural and herbal product prepared from the standard extract of herb Neem (Azadirachta indica). Neem herb is widely used to cure acute to chronic Skin problems such as Pimples, Itching, Dryness, Blemishes, Dark spots, Pigmentation, Scars etc. Neem leaves are rich in Vitamin-E, Fatty acids & emollients.
Recommended Dosage: Take 1 capsules twice daily with normal water.
5) Detox Premium Powder:
This is a herbo-mineral preparation that contains ingredients like Parwal Pishti, Giloy satv, Shukta Pishti, Kamdudha Ras, Gandhak Rasayan, etc.
Parwal Pishti: This Pishti reduces inflammation, flaking, itching of the skin. The Pishti is composed of natural coral calcium processed with rose water.
Shukta Pishti: It helps to balance the Pitta dosha in the body. All signs and symptoms related to Psoriasis patients are managed with this article.
Giloy Satv: This satv is prepared from the herb Giloy (Tinospora cordifolia). The anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and analgesic properties of this herb deal with psoriasis easily.
Kamdudha Ras: This herbal-mineral classical preparation balances Pitta dosha in the body.
Gandhak Rasayana: This herbal preparation is used since ancient times for all types of skin disorders.
Tal Sindoor: It contains ingredients like Shuddh parad, Aloe vera, Gandhak, etc that relieve redness in psoriasis patients.
Akik Pishti: This Pishti reduces all types of Pitta related disorder hence it gives good results in psoriasis.
Recommended Dosage: Take 1 sachet twice daily with plain water.
6) Itch Care Tablet
It is pure herbal combination which is purely natural. Skin primarily protect our body from toxins present in environment. Itching is related to various skin problems like dermatitis or irritates such as nickel in jewelry, infected cut. Chronic skin condition like psoriasis, Acne and due to internal conditions like blood, lungs, and liver. Mainly toxins in skin arises due to excess rakta dhatu and rasa or plasma nourishes the skin.
Recommended Dosage: Take 1 tablet twice daily with plain water.
0 notes
Text
Hives: How Long Do They Last & What Helps?

Hives, also known as urticaria, are raised, itchy welts that appear on the skin. They're a common skin reaction that can affect people of all ages. While hives often go away on their own within a few hours to a day or two, sometimes they stick around longer, becoming a frustrating, even alarming, chronic issue. Let's take a closer look at hives how long does it last, the typical causes behind these pesky welts, and some simple ways to get relief.
So, how long do hives usually last? In many cases, a hives outbreak may last anywhere from a few hours to a couple days before fading away. This short-lived reaction is known as acute hives. It's often triggered by things like certain foods, medications, insect stings or bites, pollen, pet dander, or infections.
However, for some folks, hives can persist or keep coming back for six weeks or more. If you're breaking out in hives almost daily for over six weeks, you may have chronic hives.
What Causes Hives?
Hives pop up when your immune system releases a substance called histamine. This can happen for several reasons:
- Acute Hives: These are often caused by a specific trigger:
- Allergies: Common culprits include foods (like peanuts or shellfish), medications (like penicillin), or insect bites.
- Infections: Viral infections (like the common cold), bacterial infections, and even parasites can sometimes cause hives.
- Physical Irritation: Scratching, tight clothes, or exposure to harsh chemicals can lead to hives.
- Chronic Hives: Lasting more than six weeks, these hives often have less obvious causes:
- Underlying Conditions: Autoimmune disorders (like thyroid issues or lupus) can trigger chronic hives.
- Unexplained Reactions: Sometimes, your immune system just gets a little overzealous, leading to hives with no known trigger.
- Inducible Hives: Less common, these are triggered by specific physical stimuli:
- Cold temperatures
- Sunlight
- Pressure on the skin
- Exercise
How Long Do Hives Last?
- One Hive at a Time: Each hive tends to fade away within a few hours, usually less than 24 hours.
- Acute Cases: Hive outbreaks usually clear up completely within 2-6 weeks, especially if you can identify and avoid the trigger (like a food you're allergic to).
- Chronic Hives: If you're stuck with hives for over 6 weeks, they're considered chronic. Some unlucky folks can have chronic hives for months or even years.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0P2bFVGReRE&pp=ygUbaGl2ZXMgaG93IGxvbmcgZG9lcyBpdCBsYXN0
Diagnosing Hives
Medical History and Exam: To figure out what's causing your hives, your doc will ask about your symptoms, when they started, how long they last, and what seems to trigger them. They'll also check your skin closely and ask about your overall health.
Possible Tests: If needed, your doctor may order some tests to rule out specific causes:
- Allergy Testing: Skin prick or blood tests to identify potential triggers.
- Blood Work: To check for infections or signs of underlying thyroid problems.
Treating Hives & Finding Relief
The best way to treat hives depends on what's causing them and how severe they are.
- Identifying Triggers: Especially for acute hives, figuring out what sets them off is key. Keep a "hive diary" to track when they appear – it might surprise you!
- Antihistamines: These are the go-to for reducing itch and swelling:
- Over-the-counter options: Loratadine (Claritin), Cetirizine (Zyrtec)
- Stronger ones by prescription: Ask your doctor!
- Severe Cases: Sometimes, short-term oral steroids (like prednisone) are needed. Just remember, these have potential side effects.
- Chronic Hives: If over-the-counter medications aren't enough, your doctor may recommend specialized medications or refer you to an allergist or dermatologist.
Treatment TypeProsConsOver-the-Counter AntihistaminesEasy to access, generally safe, provide quick reliefMay not be effective for severe or chronic hives, some cause drowsinessPrescription MedicationsStronger options available, can target specific causes of chronic hivesMay have potential side effects, require doctor's supervisionNatural RemediesCool compresses, loose clothing can sootheLimited effectiveness, don't address the root cause of hives
Living with Hives
While you work towards a longer-term solution, here's what helps ease the itch:
- Cool Relief: Cool compresses, baths (not too hot!), or calamine lotion.
- Loose Clothing: Breathable fabrics can help prevent irritation.
- Stress Less: Stress can worsen hives. Try relaxation techniques like deep breathing or yoga.
- Emergency Care: If you have trouble breathing, throat swelling, or feel faint alongside your hives, get medical help immediately – this could be a sign of anaphylaxis.
"Hives are incredibly common, but if they last for more than a few weeks, it's best to see a doctor. There are many effective treatment options available."
Dr. Anne Davis, Board-Certified Dermatologist
FAQs for Easy Answers
- Are hives contagious? No! Hives themselves are not spread from person to person. However, if the hives are caused by a viral infection, that infection itself could be contagious.
- Can I prevent hives? If you identify your triggers, you may be able to prevent acute hives by avoiding them. For chronic hives where the cause is unknown, prevention can be more difficult.
- Will my hives go away on their own? Most of the time, yes. Individual hives fade quickly, and acute hives usually clear up in a few weeks. Chronic hives often need medical intervention to manage symptoms.
- What's the difference between hives and eczema? While both can be itchy, hives are raised, red bumps that come and go quickly. Eczema usually causes dry, scaly patches that last longer.
- Can stress cause hives? While stress doesn't directly cause hives, it can make existing hives worse or make you more prone to outbreaks.
- I'm pregnant and have hives. What should I do? Talk to your doctor before taking any medication for hives. Some over-the-counter options may not be safe during pregnancy. Your doctor can guide you to safe choices for managing your symptoms.
Key Takeaways
- Hives are itchy, red bumps on the skin that usually go away on their own.
- They can be caused by allergies, infections, physical triggers, or sometimes, unknown reasons.
- Chronic hives last longer than six weeks and might need specialized treatment.
Conclusion
Hives might be annoying, but they're rarely a serious issue. If you're dealing with persistent or severe hives, don't hesitate to talk to your doctor. Together, you can find a treatment plan that works for you, so you can finally say goodbye to those itchy bumps!
Disclaimer: The information provided on this website is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional before making any decisions about your health.
Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Fist drop (ETHEREAL)
Mel Gibson's arm (Adverse effect of antifungal antibiotics, systemically used)
Vampire Weekend's head (Edema of left upper eyelid)
Janice Dickinson's thumb (Laceration of flexor muscle, fascia and tendon of right index finger at forearm level)
Chrissy Teigen's eye (Subluxation of lens, unspecified eye)
Prince William's leg (Papyraceous fetus, first trimester)
Christina Hendricks's finger (Chondromalacia, left wrist)
Chris Pratt's chin (Urticaria due to cold and heat)
Minnie Driver's leg (Disorder of central nervous system, unspecified)
Frankie Delgado's tooth (Acute tonsillitis, unspecified)
Guy Ritchie's thigh (Rheumatoid arthritis without rheumatoid factor, wrist)
Scott Disick's chin (Other specified injury of other blood vessels at lower leg level, unspecified leg)
Eddie Murphy's neck (Legal intervention involving injury by tear gas, suspect injured)
Kevin Jonas's cheek (Other congenital malformations of hair)
Rosario Dawson's chin (Vesical fistula, not elsewhere classified)
Kat Graham's chin (Toxic effect of other seafood, assault)
Carson Daly's cheek (Basal cell carcinoma of skin of other parts of face)
Joshua Jackson's chin (Calcific tendinitis, right lower leg)
Will Arnett's bottom (Laceration of dorsal artery of right foot)
0 notes
Text
*Dr. Smita Goel Homeopathy Clinic*
www.thehomeopathyclinic.co.in
Urticaria – also known as hives, weals, welts or nettle rash – is a raised, itchy rash that appears on the skin. It may appear on one part of the body or be spread across large areas.
The rash is usually very itchy and ranges in size from a few millimetres to the size of a hand.
Although the affected area may change in appearance within 24 hours, the rash usually settles within a few days.
Doctors may refer to urticaria as either:
• acute urticaria– if the rash clears completely within 6 weeks
• chronic urticaria –in rarer cases, where the rash persists or comes and goes for more than 6 weeks, often over many years
A much rarer type of urticaria, known as urticaria vasculitis, can cause blood vessels inside the skin to become inflamed. In these cases, the weals last longer than 24 hours, are more painful, and can leave a bruise.
When to seek medical advice
Visit your doctor/ General Practitioner (GP) if your symptoms don't go away within 48 hours.
You should also contact your doctor / GP if your symptoms are:
• severe
• causing distress
• disrupting daily activities
• occurring alongside other symptoms
Who's affected by urticaria?
Acute urticaria (also known as short-term urticaria) is a common condition, estimated to affect around 1in 5 people at some point in their lives.
Children are often affected by the condition, as well as women aged 30 to 60, and people with a history of allergies.
What causes urticaria?
Urticaria occurs when a trigger causes high levels of histamine and other chemical messengers to be released in the skin.These substances cause the blood vessels in the affected area of skin to open up (often resulting in redness or pinkness) and become leaky. This extra fluid in the tissues causes swelling and itchiness.
Histamine is released for many reasons, including:
• an allergic reaction – such as a food allergy or a reaction to an insect bite or sting
• cold or heat exposure
• infection – such as a cold
• certain medications – such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)or antibiotics
However, in many cases of urticaria, no obvious cause can be found.
Some cases of long-term urticaria may be caused by the immune system mistakenly attacking healthy tissue. However, this is difficult to diagnose and the treatment options are the same.
Certain triggers may also make the symptoms worse. These include:
• drinking alcohol or caffeine
• emotional stress
• warm temperature
Read more about the causes of urticaria.
Diagnosing urticaria
Your GP will usually be able to diagnose urticaria by examining the rash. They may also ask you questions to find out what triggered your symptoms.
If your GP thinks that it's caused by an allergic reaction, you may be referred to an allergy clinic for an allergy test. However, if you've had urticaria most days for more than 6 weeks, it's unlikely to be the result of an allergy.
You may also be referred for a number of tests, including a full blood count (FBC), to find out whether there's an underlying cause of your symptoms.
Read more about diagnosing urticaria.
Treating urticaria
In many cases, treatment isn't needed for urticaria, because the rash often gets better within a few days.
If the itchiness is causing you discomfort, antihistamines can help. Antihistamines are available over the counter at pharmacies – speak to your pharmacist for advice.
A short course of steroid tablets (oral corticosteroids) may occasionally be needed for more severe cases of urticaria.
If you have persistent urticaria, you may be referred to a skin specialist (dermatologist). Treatment usually involves medication to relieve the symptoms, while identifying and avoiding potential triggers.
Read about treating urticaria.
Complications of urticaria
Around a quarter of people with acute urticaria and half of people with chronic urticaria also develop angioedema, which is a deeper swelling of tissues.
Chronic urticaria can also be upsetting and negatively impact a person's mood and quality of life.
Angioedema
Angioedema is swelling in the deeper layers of a person's skin. It's often severe and is caused by a build-up of fluid. The symptoms of angioedema can affect any part of the body, but usually affect the:
• eyes
• lips
• genitals
• hands
• feet
Medication such as antihistamines and short courses of oral corticosteroids (tablets) can be used to relieve the swelling.
Read more about treating angioedema.
Emotional impact
Living with any long-term condition can be difficult. Chronic urticaria can have a considerable negative impact on a person's mood and quality of life. Living with itchy skin can be particularly upsetting.
One study found that chronic urticaria can have the same negative impact as heart disease. It also found that 1 in 7 people with chronic urticaria had some sort of psychological or emotional problem, such as:
• stress
• anxiety
• depression
See your GP if your urticaria is getting you down. Effective treatments are available to improve your symptoms.
Talking to friends and family can also improve feelings of isolation and help you cope better with your condition.
Anaphylaxis
Urticaria can be one of the first symptoms of a severe allergic reaction known as anaphylaxis.
Other symptoms of anaphylaxis include:
• swollen eyes, lips, hands and feet
• feeling lightheaded or faint
• narrowing of the airways, which can cause wheezing and breathing difficulties
• abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting
• collapsing and becoming unconscious

0 notes
Text
Shortness of Breath: What your body might be telling you?
Did you experience any sudden shortness of breath? Well, it's time to be alert. An episode of shortness of breath should not be taken lightly. On a serious note, any episode of shortness of breath must be addressed in the right way.

If you have ever experienced any shortness of breath, it is important to be aware of the causes, symptoms, treatment, solution, and prevention of shortness of breath. In this context, GS Hospital Hapur, the top heart care hospital in Ghaziabad, is well-known for its expertise in addressing serious symptoms related to shortness of breath. The hospital aims to spread awareness about shortness of breath among people which can cause many complications if left untreated.
Let us kick start this blog with a deep breath and learn more about shortness of breath in the next part of the article.
All you need to know about shortness of breath
Shortness of breath is considered as difficulty in breathing where enough oxygen does not reach into the lungs. This may result in gasping for breath. The breathing mechanism becomes very difficult and uncomfortable. Shortness of breath is medically termed as Dyspnea.
Shortness of breath occurs when the body is not getting enough oxygen requiring it harder to breathe more quickly and deeper. Not getting enough oxygen can cause many complications to other systems of the body affecting the overall health and well-being.
Types of breathlessness
There are two types of shortness of breath which include the following:
Acute breathlessness
An episode of breathlessness that has a sudden onset is considered acute breathlessness. This may be due to sudden changes in weather, extreme exertion, cardiac issues related to heart failure, or heart rhythm problems and respiratory problems making it difficult to breathe.
Chronic Persistent breathless
Persistent breathlessness is also known as chronic breathlessness. This is mainly prevalent in cases when the cardiac or respiratory condition is extreme and cannot be managed well leading to severe and recurrent episodes of breathlessness.
Causes of shortness of breath
The causes of shortness of breath may be medical or non-medical.
The causes of shortness of breath are as follows:
Medical causes of shortness of breath
Heart conditions such as angina, heart attacks, heart failure, abnormal heart rhythm, and atrial fibrillation.
Fluid buildup in the lungs like pleural effusion or pulmonary edema
Lung infections such as pneumonia, tuberculosis
Interstitial lung disease
Asthma or COPD
Lung cancer
Blood clots in the lungs
Low Hb count
Anxiety and panic attacks
Allergic reactions such as anaphylactic reaction or urticaria
Non-medical causes of shortness of breath
Physical exertion such as climbing stairs or shopping
Exercising such as gym, walking, or jogging
Being overweight or obese
Pollution or exposure to carbon monoxide
Living in a dusty environment
Inhalation of fumes and chemicals
It is important to remember that there are different reasons for breathlessness related to the heart. If your heart isn't pumping enough oxygen-enriched blood, then the body responds in a negative manner leading to breathing faster in order to get enough oxygen making you feel restless and short of breath. It is important to stay positive about your health while dealing with shortness of breath.
Signs and symptoms due to shortness of breath- What your body is telling you?
The signs and symptoms due to shortness of breath are as follows:
Difficulty in catching breath
Noisy breathing
Gasping for breath
Very fast and shallow breathing
Labored respirations
Feeling suffocated
Sudden increase in pulse rate
Wheezing
Chest congestion and chest pain
Breathless on exertion also known as exertional dyspnea
Anxiety and panicky feeling
Cold clammy and sweaty skin
Pale skin which looks slightly blue and cyanosed
Dizziness with tiredness and low energy levels
Air hunger and working harder to breathe
Reduced ability to work
Chest pain associated with leg swelling
Blurry vision with lightheadedness.
How breathlessness can affect daily lifestyle?
Your breathing mechanism is a natural process and should be completely unforceful. Steady breathing makes you feel good and is regular, making your lungs healthy. Breathing is an automatic process and is carried out without any effort. When breathing becomes a conscious effort, it is a matter of concern. The episode of breathlessness can be very frightening especially if you have never experienced it before.
Breathlessness can affect your daily lifestyle. It can make you feel edgy while dealing with your activities. Many people with breathlessness feel frustrated or frightened at times. But, on a positive note, it is important to know that you can cope with breathlessness in the right manner. Most patients with breathlessness may feel overwhelmed, depressed, stressed, and anxious. Do not feel lonely or edgy with breathlessness.
Diagnosis of breathless
Diagnosis and early detection of breathlessness is very important. This is possible under the guidance of your doctor. Here are the important steps for diagnosis which can be done by your doctor.
Complete physical examination
Checking oxygen saturation levels
Detailed case-taking to know about the episodic attacks of breathlessness
X-ray scans
Computerized tomography scan or CT scan of the chest
Electrocardiogram or ECG
Spirometry test
Pulmonary function tests or PFTs
Top tips to manage shortness of breath
Here are some of the top tips to deal with shortness of breath through lifestyle modifications. Let's begin!
It is important to know the cause of shortness of breath and get it treated in the right way under the guidance of your doctor.
It is essential to always sit in an airy room with a fan, AC, or open windows which allows good oxygen support
Ensure to take a regular walk or jog in an open environment early morning or evening which provides you with fresh air
In case of any episode of breathlessness, it is important to find a comfortable position that will ease out your breathlessness such as lying in bed, resting on a reclining chair, or lying down with support on cushions or bed rest.
Control your stress levels and stay calm all the time to avoid any kind of breathless attacks
You can also practice some breathing techniques such as taking slow and relaxed breaths right from your tummy with expansion and contraction of the chest wall.
Practice mindful breathing with meditation through yoga which helps in deep inhalation and exhalation to improve the functional capacity of the lungs.
Take a warm or cool shower whichever is relaxing for your morning and evening
Ensure to sip in water to keep yourself hydrated all the time
Avoid any kind of physical and mental overexertion
Deal with anxiety and worries in a positive manner by listening to music, and gentle stretching exercises.
Plan your day according to schedule and ensure to take regular breaks to reactivate yourself
Opt for smaller meals rather than big ones which can make you feel heavy and breathless.
If breathlessness is not associated with internal or external problems, your breath will recover after rest.
Be open about the breathlessness issue and reach out to your friends and family members.
A Note from GS Hospital
GS Hospital Hapur, a top private hospital in Delhi, NCR, is focused on providing quality care and support to patients with cardiac and respiratory-related shortness of breath. This makes it the best heart hospital in Uttar Pradesh. Living with breathlessness can be quite difficult at times. You need to find the right way to cope with it.
GS Hospital Hapur, the best hospital in Meerut, offers exceptional care and support to all its patients battling with shortness of breath. The hospital is located in the heart of Delhi, NCR, with a team of professional and dedicated doctors who help you to adapt to daily life positively as you battle out shortness of breath related to cardiac and respiratory issues. Shortness of breath can make life difficult to deal with. With the right kind of treatment and lifestyle modifications, you can overcome the problem of shortness of breath.
If shortness of breath continues to progress in spite of lifestyle modifications and treatment, it is important to reach out to your doctor who shall refer you to a pulmonologist or cardiologist for medical intervention.
#ShortnessOfBreath#HeartFailure#HeartDisease#Symptoms#Complications#GSHospital#GSGroup#DelhiNCR#UttarPradesh#India
0 notes
Text
Etoricoxib Tablet: A Comprehensive Guide
Etoricoxib Tablet: A Comprehensive Guide
Etoricoxib is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that is commonly used to relieve pain and inflammation in conditions such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, and gout. It is available in tablet form and is marketed under various brand names, including Arcoxia, Etorix, and Etoricoxib.
Mechanism of Action:
Etoricoxib works by inhibiting the enzyme cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), which is responsible for the production of prostaglandins. Prostaglandins are chemical messengers in the body that play a role in pain, inflammation, and fever. By blocking the COX-2 enzyme, etoricoxib reduces the production of prostaglandins, thereby reducing pain and inflammation.
Indications:
Etoricoxib is primarily indicated for the symptomatic relief of pain and inflammation associated with various musculoskeletal conditions. It is commonly prescribed for the following conditions:
Osteoarthritis: Etoricoxib helps to relieve the pain and stiffness associated with osteoarthritis, a degenerative joint disease that commonly affects the knees, hips, and hands.
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Etoricoxib is used to reduce pain, swelling, and joint stiffness in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, an autoimmune disease that causes chronic inflammation of the joints.
Ankylosing Spondylitis: Etoricoxib can provide relief from the pain and stiffness associated with ankylosing spondylitis, a chronic inflammatory disease that primarily affects the spine.
Acute Gout: Etoricoxib is sometimes prescribed to manage the pain and inflammation during acute gout attacks, a type of arthritis caused by the buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints.
Dosage and Administration:
The dosage of etoricoxib may vary depending on the specific condition being treated and the individual patient's response. It is important to follow the dosage instructions provided by the healthcare professional or as mentioned on the product label.
Typically, the recommended starting dose for most conditions is 60 mg once daily. However, in some cases, a higher dose of 90 mg may be prescribed. The maximum daily dose should not exceed 120 mg.
Etoricoxib tablets should be taken with a full glass of water, preferably with or after food, to minimize the risk of gastrointestinal side effects. It is important not to crush or chew the tablets, as they are designed to be swallowed whole.
Contraindications and Precautions:
While etoricoxib is generally well-tolerated, it is important to be aware of certain contraindications and precautions before starting the medication.
Etoricoxib should not be used in patients who have a known hypersensitivity to the drug or any of its components. It is also contraindicated in patients with a history of allergic reactions, including asthma, urticaria, or other allergic-type reactions to aspirin or other NSAIDs.
Caution should be exercised when prescribing etoricoxib to patients with a history of gastrointestinal bleeding or peptic ulcers, as it may increase the risk of these conditions. It is also important to consider the cardiovascular risks associated with NSAIDs, particularly in patients with a history of heart disease, high blood pressure, or stroke.
Side Effects:
Like any medication, etoricoxib may cause side effects in some individuals. The most commonly reported side effects include:
Gastrointestinal Effects: These may include stomach pain, indigestion, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and constipation.
Cardiovascular Effects: Etoricoxib may increase the risk of heart attack, stroke, and other cardiovascular events, particularly when used at high doses or for long durations.
Skin Reactions: Some individuals may experience skin rashes, itching, or hives as a result of taking etoricoxib.
Other Side Effects: Other less common side effects may include dizziness, headache, fluid retention, and elevated liver enzymes.
It is important to promptly report any unusual or severe side effects to the healthcare professional.
Conclusion:
Etoricoxib is a widely used NSAID that provides effective relief from pain and inflammation associated with various musculoskeletal conditions. However, it is important to use the medication under the guidance of a healthcare professional and to be aware of the potential side effects and precautions. If you have any concerns or questions about etoricoxib tablets, it is best to consult with your healthcare provider for personalized advice.
0 notes
Text
The 9 Most Common Early symptoms of kidney problem

An Overview Of Kidney Disease
Several disorders can disrupt the normal functioning of the kidneys, collectively referred to as kidney disease or renal disease. The kidneys are essential because they cleanse the blood, eliminate waste, and maintain a healthy balance of electrolytes, hormones, and fluids. The most common type is chronic kidney disease (CKD), frequently brought on by illnesses such as diabetes and hypertension. It develops gradually and can result in renal failure, requiring dialysis or a transplant if left untreated. Acute kidney injury (AKI) refers to a sudden decrease in kidney function, which is typically brought on by infections or the use of certain drugs. The detection through early symptoms of kidney problems, changes in lifestyle, and medical therapy are all essential components in kidney disease management and the maintenance of kidney function.
Changes In Urination:-
Alterations in urine patterns are one of the early symptoms of kidney problems. This may manifest as an increased need to urinate, particularly during the night (a condition known as nocturia), frothy or bubbly pee, blood in the urine (a condition known as hematuria), or trouble urinating.
Swelling:-
Oedema, another name for swelling, is one of the most common early symptoms of kidney problems. It manifests most frequently in the hands, feet, ankles, or face, and its symptoms may become more severe at different times of the day or after extended bouts of sitting or standing.
Fatigue And Weakness:-
The accumulation of toxins and waste products in the body, which occurs when kidney function decreases, is the cause of exhaustion and weakness. The disease known as anaemia, characterized by a low red blood cell count, can also contribute to feelings of weariness.
Shortness Of Breath:-
The accumulation of fluid in the lungs, which can be a symptom of kidney illness, can make breathing harder or cause shortness of breath, particularly during strenuous physical exercise.
Persistent Itching:-
A buildup of waste products in the blood can be an early symptom of kidney problems, which can cause intense itching that most commonly affects the skin but can also spread to other parts of the body. This condition is known as urticaria.
High Blood Pressure:-
Kidney disease can cause high blood pressure (also known as hypertension) or worsen the condition of those who already have it. Healthy kidneys are essential for maintaining healthy blood pressure. High blood pressure can further damage the kidneys, causing a vicious cycle of increasing renal dysfunction.
Changes In Appetite And Weight Loss:-
A loss of appetite, nausea, and vomiting are among the symptoms that can accompany kidney illness. Consequently, some people may suffer a loss of weight that they did not intend.
Muscle Cramps And Twitches:-
Kidney disease can cause an imbalance of electrolytes, resulting in cramping and muscle twitching. A lack of calcium and potassium can cause this.
Trouble Concentrating And Mental Fog:-
The accumulation of waste materials in the blood can affect brain function, resulting in difficulty concentrating, memory issues, and mental fogginess. This effect can occur when kidney function declines.
How To Improve Your Kidney Health?
Hydration:-
Maintaining a healthy level of hydration is essential for proper kidney function. Consuming an appropriate amount of water assists in flushing out waste products and toxins from the body, reducing the strain placed on the kidneys. Aim to drink at least 8 to 10 glasses of water daily, but remember that your requirements may vary depending on factors such as the climate where you live, your degree of physical activity, and your overall health.
Balanced And Healthy Diet:-
Adopting a diet that is both well-balanced and nutritious can have a considerable impact on one’s kidney health. Your meals should contain various foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean meats, and healthy fats. Because overeating processed food, foods that are heavy in salt, and red meat can stress the kidneys and contribute to high blood pressure, it is important to limit how much of each you consume.
Manage Blood Pressure:-
The most common contributor to kidney disease is hypertension, also known as high blood pressure. To maintain healthy kidney function, it is essential to regularly check and control one’s blood pressure within a normal range. You should work closely with your healthcare practitioner to build a specific treatment plan if you have hypertension. This plan may involve changes to both your lifestyle and your drug regimen.
Control Blood Sugar Levels:-
Diabetes is another critical condition that significantly increases the likelihood of developing renal disease. If you have diabetes, you must effectively manage your blood sugar levels with a proper diet, regular physical activity, and the medicine your doctor prescribed for you. Keeping a close eye on and under control of your blood sugar levels can aid in preventing kidney injury.
Regular Exercise:-
Regular physical activity has several positive effects on one’s health, including improving one’s kidney health. Exercising contributes to managing one’s weight, cardiovascular health, blood pressure, and blood sugar levels and promoting overall health. Aim for at least 150 minutes of activity per week at a moderate level, such as brisk walking or swimming.
In conclusion, recognizing the early symptoms of kidney problems and seeking medical examination as soon as possible are essential for detecting and managing renal illness. Taking preventative measures to improve one’s kidney health can have a sizeable and positive effect on one’s overall health and quality of life.
Conclusion
Chronic kidney disease is a serious illness if you keep ignoring the symptoms it even worsens with time if left untreated, so it is important to talk to the general health practitioner The more you delayed the more it became difficult to treat chronic kidney disease stages. If you are facing severe Most Common Kidney Diseases, then you should consult Dr. Nisha Gaur. Dr. Nisha Gaur is the most reputed Nephrologist doctor in Jaipur and has years of work experience and is the Best Nephrologist in Jaipur for Chronic Kidney Disease Care and also for treating ailments such as Kidney Transplantation, Peritoneal Dialysis, Hemodialysis, and Kidney Biopsy.
0 notes