#amazon aurora postgresql
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Amazon Aurora Database Explained for AWS Cloud Developers
Full Video Link - https://youtube.com/shorts/4UD9t7-BzVM Hi, a new #video #tutorial on #amazonrds #aws #aurora #database #rds is published on #codeonedigest #youtube channel. @java @awscloud @AWSCloudIndia @YouTube #youtube @codeonedigest #cod
Amazon Aurora is a relational database management system (RDBMS) built for the cloud & gives you the performance, availability of commercial-grade databases at one-tenth the cost. Aurora database comes with MySQL & PostgreSQL compatibility. Amazon Aurora provides built-in security, continuous backups, serverless compute, up to 15 read replicas, automated multi-Region replication, and…

View On WordPress
#amazon aurora#amazon aurora mysql#amazon aurora postgresql#amazon aurora serverless#amazon aurora tutorial#amazon web services#amazon web services tutorial#aurora database aws#aurora database tutorial#aurora database vs rds#aurora db#aurora db aws#aurora db aws tutorial#aurora db cluster#aurora db with spring boot#aws#aws aurora#aws aurora mysql#aws aurora postgresql#aws aurora tutorial#aws aurora vs rds#aws cloud#what is amazon web services
0 notes
Text
Amazon RDS Extended Support for MySQL 5.7 & PostgreSQL 11

Your MySQL 5.7 and PostgreSQL 11 database instances on Amazon Aurora and Amazon RDS will automatically enroll in Amazon RDS Extended Support commencing February 29, 2024.
This will prevent unanticipated downtime and compatibility concerns from automated major version upgrades. You have more control over when to upgrade your major database.
RDS Extended Support may cost more due to automated enrollment. Upgrade your database before RDS Extended Support to prevent these expenses.
Describe Amazon RDS Extended Support
Amazon RDS Extended Support, announced in September 2023, lets you run your database on a major engine version on Amazon Aurora or Amazon RDS after its end of standard support date for a fee.
The MySQL and PostgreSQL open source communities identify CVEs, generate patches, and resolve bugs until community end of life (EoL). Until the database major version is retired, the communities release a quarterly minor version with security and bug updates. CVE patches and bug fixes are no longer available after the community end of life date, making such engines unsupported. As of October and November 2023, the communities no longer support MySQL 5.7 and PostgreSQL 11. AWS appreciate community support of these major versions and a transparent transition process and schedule to the latest major version.
Amazon Aurora and RDS engineer crucial CVE patches and bug fixes for up to three years after a major version’s community EoL with RDS Extended Support. Amazon Aurora and RDS will find engine CVEs and problems, develop patches, and deploy them swiftly for three years. Under RDS Extended Support, AWS will continue to support an engine’s major version after the open source community ends support, protecting your applications from severe security risks and unresolved problems.
You may ask why we charge for RDS Extended Support instead of including it in RDS. AWS must invest developer resources in crucial CVE patches and bug fixes to preserve community EoL engine security and functionality. Because of this, RDS Extended Support only charges clients that need the flexibility to stay on a version past its EoL.
If your applications depend on a specific MySQL or PostgreSQL major version for plug-in compatibility or bespoke functionality, RDS Extended Support may help you satisfy your business objectives. If you’re running on-premises database servers or self-managed Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) instances, you can migrate to Amazon Aurora MySQL-Compatible Edition, Amazon Aurora PostgreSQL-Compatible Edition, Amazon RDS for MySQL, and Amazon RDS for PostgreSQL beyond the community EoL date and use them with RDS Extended Support in a managed service. RDS Extended Support lets you phase a large database transfer to ensure a smooth transition without straining IT resources.
RDS Extended Support will be provided in 2024 for RDS for MySQL 5.7, PostgreSQL 11, Aurora MySQL-compatible 2, and Aurora PostgreSQL 11. A supported MySQL major version on Amazon RDS and Amazon Aurora major versions in the AWS documentation lists all future supported versions.
Why are all databases automatically enrolled in Amazon RDS Extended Support?
AWS were told you RDS Extended Support would deliver opt-in APIs and console functionality in December 2023. AWS announced that if you did not opt your database into RDS Extended Support, it would automatically update to a newer engine version on March 1, 2024. You would be upgraded from Aurora MySQL 2 or RDS for MySQL 5.7 to Aurora MySQL 3 or RDS for MySQL 8.0, and from Aurora PostgreSQL 11 to 15 and RDS for 15.
However, several users complained that these automated upgrades may damage their applications and cause other unpredictable behavior between major community DB engine releases. If applications are not ready for MySQL 8.0 or PostgreSQL 15, an unplanned major version upgrade could cause compatibility issues or downtime.
Automatic enrollment in RDS Extended Support allows you more time and control to organize, schedule, and test database upgrades on your own timeline while receiving essential security and bug fixes from AWS.
Upgrade before RDS standard support ends to prevent automatic enrollment in RDS Extended Support and associated fees.
Upgrade your database to avoid RDS Extended Support fees
RDS Extended Support helps you schedule your upgrade, but staying with previous versions means missing out on the greatest price-performance for your database workload and paying more for support.
Global Database, Amazon RDS Proxy, Performance Insights, Parallel Query, and Serverless v2 deployments are supported in Aurora MySQL 8.0, also known as Aurora MySQL 3. RDS for MySQL 8.0 supports AWS Graviton2 and Graviton3-based instances, Multi-AZ cluster deployments, and Optimized Reads and Writes for up to three times better performance than MySQL 5.7.
Aurora PostgreSQL 15 Aurora I/O Optimized, Aurora Serverless v2, Babelfish for Aurora PostgreSQL, pgvector extension, TLE, AWS Graviton3-based instances, and community additions are supported by PostgreSQL. RDS for PostgreSQL 15 adds Multi-AZ DB cluster deployments, RDS Optimized Reads, HypoPG extension, pgvector extension, TLEs, and AWS Graviton3-based instances.
Major version upgrades may change databases incompatible with existing apps. To upgrade to the major version, manually edit your database. Any major version upgrade should be tested on non-production instances before being applied to production to verify application compatibility. The AWS documentation describes an in-place upgrade from MySQL 5.7 to 8.0, including incompatibilities, Aurora MySQL in-place major version upgrade, and RDS for MySQL upgrades. Use pgupgrade to upgrade PostgreSQL 11 to 15 in-places.
AWS advocate Fully Managed Blue/Green Deployments in Amazon Aurora and Amazon RDS to reduce upgrade downtime. Amazon RDS Blue/Green Deployments can establish a synchronized, fully controlled staging environment that mimics production in a few clicks. A parallel green environment with upper-version clones of your production databases lower-version is needed. Traffic might transition to the green environment after validation. Blue environment can be discontinued. Blue/Green Deployments reduce downtime best in most cases, except with Amazon Aurora and Amazon RDS.
Currently accessible
Amazon RDS Extended Support is now available for clients utilizing MySQL 5.7, PostgreSQL 11, and higher versions in AWS Regions, including AWS GovCloud (US), beyond the 2024 standard support expiration. You can upgrade your databases and obtain 3 years of RDS Extended Support without opting in.
Read more on Govindhtech.com
0 notes
Text
모듈 5
AWS 스토리지 및 데이터베이스 서비스 요약
AWS는 다양한 유형의 스토리지 및 데이터베이스 서비스를 제공하여 애플리케이션의 특정 요구 사항을 충족하도록 돕습니다.
1. 블록 스토리지
인스턴스 스토어 (Instance Store)
Amazon EC2 인스턴스에 임시 블록 수준 스토리지를 제공합니다.
EC2 인스턴스의 호스트 컴퓨터에 물리적으로 연결되어 인스턴스와 수명이 동일합니다.
인스턴스가 종료되면 데이터가 손실됩니다.
Amazon Elastic Block Store (Amazon EBS)
Amazon EC2 인스턴스에서 사용할 수 있는 영구적인 블록 수준 스토리지 볼륨을 제공합니다.
EC2 인스턴스가 중지 또는 종료되더라도 데이터를 보존합니다.
EBS 스냅샷을 생성하여 볼륨의 증분 백업을 수행할 수 있습니다. 증분 백업은 최초 백업 시 모든 데이터를 복사하고, 이후에는 변경된 데이터 블록만 저장합니다.
EBS 볼륨은 단일 가용 영역에 데이터를 저장하며, EC2 인스턴스와 동일한 가용 영역에 있어야 연결할 수 있습니다.
2. 객체 스토리지
객체 스토리지 개념
각 객체는 **데이터(파일), 메타데이터(정보), 키(고유 식별자)**로 구성됩니다.
Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3)
객체 수준 스토리지를 제공하는 서비스입니다.
데이터를 **버킷(Bucket)**에 객체로 저장합니다.
무제한의 저장 공간을 제공하며, 최대 객체 크기는 5TB입니다.
파일 업로드 시 권한을 설정하여 가시성 및 액세스를 제어할 수 있습니다.
버전 관리 기능을 통해 객체 변경 사항을 추적할 수 있습니다.
다양한 스토리지 클래스를 제공하며, 데이터 검색 빈도 및 가용성 요구 사항에 따라 선택합니다.
S3 Standard: 자주 액세스하는 데이터용. 최소 3개의 가용 영역에 저장되며 고가용성을 제공.
S3 Standard-Infrequent Access (S3 Standard-IA): 자주 액세스하지 않지만 고가용성이 필요한 데이터용. S3 Standard와 유사하지만 스토리지 비용이 저렴하고 검색 비용이 높음.
S3 One Zone-Infrequent Access (S3 One Zone-IA): 단일 가용 영역에 데이터를 저장. 스토리지 비용이 가장 저렴하지만, 가용 영역 장애 시 데이터가 손실될 수 있으므로 쉽게 재현 가능한 데이터에 적합.
S3 Intelligent-Tiering: 액세스 패턴을 알 수 없거나 자주 변하는 데이터용. 액세스 패턴을 모니터링하여 자주 액세스하지 않으면 자동으로 S3 Standard-IA로 이동시키고, 다시 액세스하면 S3 Standard로 이동.
S3 Glacier Instant Retrieval: 즉각적인 액세스가 필요한 아카이브 데이터용. 몇 밀리초 만에 객체 검색 가능.
S3 Glacier Flexible Retrieval: 데이터 보관용 저비용 스토리지. 몇 분에서 몇 시간 이내에 객체 검색.
S3 Glacier Deep Archive: 가장 저렴한 객체 스토리지 클래스로 장기 보관에 적합. 12시간 이내에 객체 검색. 3개 이상의 지리적으로 분산된 가용 영역에 복제.
S3 Outposts: 온프레미스 AWS Outposts 환경에 객체 스토리지를 제공. 데이터 근접성 및 로컬 데이터 레지던시 요구 사항이 있는 워크로드에 적합.
3. 파일 스토리지
파일 스토리지 개념
여러 클라이언트(사용자, 애플리케이션, 서버 등)가 공유 파일 폴더에 저장된 데이터에 액세스할 수 있습니다.
블록 스토리지를 로컬 파일 시스템과 함께 사용하여 파일을 구성하며, 클라이언트는 파일 경로를 통해 데이터에 액세스합니다.
많은 수의 서비스 및 리소스가 동시에 동일한 데이터에 액세스해야 하는 사용 사례에 이상적입니다.
Amazon Elastic File System (Amazon EFS)
AWS 클라우드 서비스 및 온프레미스 리소스와 함께 사용되는 확장 가능한 파일 시스템입니다.
파일 추가/제거 시 자동으로 확장 또는 축소됩니다.
리전별 서비스로, 여러 가용 영역에 걸쳐 데이터를 저장하여 고가용성을 제공합니다.
온프레미스 서버에서도 AWS Direct Connect를 통해 액세스할 수 있습니다.
4. 관계형 데이터베이스
관계형 데이터베이스 개념
데이터가 서로 관련된 방식으로 저장됩니다.
정형 쿼리 언어(SQL)를 사용하여 데이터를 저장하고 쿼리합니다.
데이터를 쉽게 이해할 수 있고 일관되며 확장 가능한 방식으로 저장합니다.
Amazon Relational Database Service (Amazon RDS)
AWS 클라우드에서 관계형 데이터베이스를 실행할 수 있는 관리형 서비스입니다.
하드웨어 프로비저닝, 데이터베이스 설정, 패치 적용, 백업 등 관리 작업을 자동화합니다.
대부분의 데이터베이스 엔진이 저장 시 암호화 및 전송 중 암호화를 제공합니다.
지원 데이터베이스 엔진: Amazon Aurora, PostgreSQL, MySQL, MariaDB, Oracle Database, Microsoft SQL Server.
Amazon Aurora: 엔터프라이즈급 관계형 데이터베이스로, MySQL 및 PostgreSQL과 호환되며 표준 데이터베이스보다 최대 5배/3배 빠릅니다. 6개의 데이터 복사본을 3개의 가용 영역에 복제하고 Amazon S3에 지속적으로 백업하여 고가용성을 제공합니다.
5. 비관계형 (NoSQL) 데이터베이스
비관계형 데이터베이스 개념
행과 열이 아닌 다른 구조를 사용하여 데이터를 구성합니다. (예: 키-값 페어)
테이블의 항목에서 속성을 자유롭게 추가/제거할 수 있으며, 모든 항목에 동일한 속성이 있어야 하는 것은 아닙니다.
Amazon DynamoDB
키-값 데이터베이스 서비스입니다.
모든 규모에서 한 자릿수 밀리초의 성능을 제공합니다.
서버리스이므로 서버 프로비저닝, 패치 적용, 관리 등이 필요 없습니다.
자동 크기 조정 기능을 통해 용량 변화에 맞춰 자동으로 크기를 조정하며 일관된 성능을 유지합니다.
6. 데이터 웨어하우징 및 마이그레이션
Amazon Redshift
빅 데이터 분석에 사용되는 데이터 웨어하우징 서비스입니다.
여러 원본에서 데이터를 수집하여 관계 및 추세 파악을 돕는 기능을 제공합니다.
AWS Database Migration Service (AWS DMS)
관계형 데이터베이스, 비관계형 데이터베이스 및 기타 데이터 저장소를 마이그레이션할 수 있는 서비스입니다.
원본과 대상 데이터베이스 유형이 달라도 마이그레이션이 가능하며, 마이그레이션 중 원본 데이터베이스의 가동 중지 시간을 줄일 수 있습니다.
주요 사용 사례: 개발/테스트 데이터베이스 마이그레이션, 데이터베이스 통합, 연속 복제.
7. 추가 데이터베이스 서비스
Amazon DocumentDB: MongoDB 워크로드를 지원하는 문서 데이터베이스 서비스.
Amazon Neptune: 그래프 데이터베이스 서비스. 추천 엔진, 사기 탐지, 지식 그래프 등 고도로 연결된 데이터 세트로 작동하는 애플리케이션에 적합.
Amazon Quantum Ledger Database (Amazon QLDB): 원장 데이터베이스 서비스. 애플리케이션 데이터의 모든 변경 사항에 대한 전체 기록을 검토 가능.
Amazon Managed Blockchain: 오픈 소스 프레임워크를 사용하여 블록체인 네트워크를 생성하고 관리.
Amazon ElastiCache: 데이터베이스 위에 캐싱 계층을 추가하여 자주 사용되는 요청의 읽기 시간을 향상. Redis 및 Memcached 지원.
Amazon DynamoDB Accelerator (DAX): DynamoDB용 인 메모리 캐시. 응답 시간을 밀리초에서 마이크로초까지 향상.
0 notes
Text
AWS adds observability support to Aurora PostgreSQL Limitless
Amazon Web Services (AWS) has added observability support to its managed Aurora PostgreSQL Limitless service to help enterprises monitor the health of their database fleet and troubleshoot issues around it. Observability of databases is crucial for enterprise stakeholders, including DevOps engineers, application developers, and database administrators (DBAs), as it allows them to understand the…
0 notes
Video
youtube
Amazon Aurora | High-Performance Managed Relational Database
Amazon Aurora
Amazon Aurora is a fully managed relational database engine compatible with both MySQL and PostgreSQL. It’s engineered for high performance, offering up to five times the throughput of standard MySQL and twice that of PostgreSQL. Aurora is ideal for high-demand applications requiring superior speed, availability, and scalability.
- Key Features:
- Automatic, continuous backups and point-in-time recovery.
- Multi-AZ deployment with automatic failover.
- Storage that automatically grows as needed up to 128 TB.
- Global database support for cross-region replication.
- Use Cases:
- High-traffic web and mobile applications.
- Enterprise applications requiring high availability and fault tolerance.
- Real-time analytics and e-commerce platforms.
Key Benefits of Choosing the Right Amazon RDS Database:
1. Optimized Performance: Select an engine that matches your performance needs, ensuring efficient data processing and application responsiveness.
2. Scalability: Choose a database that scales seamlessly with your growing data and traffic demands, avoiding performance bottlenecks.
3. Cost Efficiency: Find a solution that fits your budget while providing the necessary features and performance.
4. Enhanced Features: Leverage advanced capabilities specific to each engine to meet your application's unique requirements.
5. Simplified Management: Benefit from managed services that reduce administrative tasks and streamline database operations.
Conclusion:
Choosing the right Amazon RDS database engine is critical for achieving the best performance, scalability, and functionality for your application. Each engine offers unique features and advantages tailored to specific use cases, whether you need the speed of Aurora, the extensibility of PostgreSQL, the enterprise features of SQL Server, or the robustness of Oracle. Understanding these options helps ensure that your database infrastructure meets your application’s needs, both now and in the future.
#youtube#Amazon RDS RDS Monitoring AWS Performance Insights Optimize RDS Amazon CloudWatch Enhanced Monitoring AWS AWS DevOps Tutorial AWS Hands-On C
0 notes
Text
Top 5 Qualities to Look for in a Database Expert Witness

When legal cases hinge on complex data issues, a Database Expert Witness can be an invaluable asset. From intellectual property disputes to cybersecurity breaches and data integrity concerns, the technical insights of a Database Expert Witness can help courts understand highly complicated information. But choosing the right expert isn’t just about finding someone who knows databases—it’s about finding someone who can also thrive in the legal environment. Here are the top five qualities you should look for when hiring a Database Expert Witness.
1. Comprehensive Technical Knowledge
The first and most important quality in a Database Expert Witness is comprehensive technical expertise. Databases come in many forms—SQL, NoSQL, cloud databases, data warehouses, and more. A top Database Expert Witness should have a deep understanding of database design, management, optimization, security, and recovery processes.
They should also be familiar with the leading database platforms, such as Oracle, MySQL, PostgreSQL, Microsoft SQL Server, and emerging technologies like MongoDB and Amazon Aurora. Understanding how databases scale, how transactions are handled, and how failures occur are critical skills for any Database Expert Witness.
When evaluating candidates, prioritize those with certifications, advanced degrees, and years of hands-on experience managing complex database systems.
2. Clear Communication Skills
Even the most brilliant Database Expert Witness won't help your case if they can't explain technical concepts clearly. Judges, jurors, and attorneys are rarely database experts themselves, so it's essential that a Database Expert Witness can translate complex database terminology into language that is easy to understand.
Your Database Expert Witness should be able to write clear, well-organized expert reports, deliver persuasive courtroom testimony, and break down technical arguments into relatable narratives. Effective communication ensures that the core issues are understood, which can greatly influence how a judge or jury views the evidence.
Strong verbal and written communication skills are must-haves for any Database Expert Witness who hopes to be truly effective in court.
3. Unwavering Objectivity and Credibility
One of the key roles of a Database Expert Witness is to provide objective, fact-based analysis. No matter who hires them, a Database Expert Witness must present impartial opinions based on sound evidence and proven methodologies. Bias can quickly destroy an expert's credibility in the courtroom.
A credible Database Expert Witness will openly discuss the strengths and weaknesses of their findings, acknowledge the limits of their analysis, and resist the temptation to advocate for one side. Courts value neutrality and will view an expert more favorably if they consistently demonstrate it.
Before selecting a Database Expert Witness, review their previous testimonies and ensure they have a reputation for honesty and professionalism.
4. Litigation and Courtroom Experience
The best Database Expert Witness will not only be technically brilliant but also highly familiar with the legal process. Expert witnesses must know how to handle depositions, withstand cross-examinations, and navigate the challenges that come with testifying in front of a judge and jury.
A Database Expert Witness who has testified multiple times will be more comfortable under pressure and better prepared to defend their analysis. They understand how to stay composed, remain on point, and respond effectively to opposing counsel’s questions.
When considering a Database Expert Witness, ask about their litigation experience. Knowing they have successfully testified in similar cases gives you confidence that they can perform when it matters most.
5. Extreme Attention to Detail
Databases are intricate systems where small errors can have huge consequences. A Database Expert Witness must be meticulous in their review of evidence, whether they are analyzing data logs, evaluating database schemas, or tracing the origins of a data breach.
Overlooking a single inconsistency can open the door for opposing counsel to undermine the expert’s credibility. The best Database Expert Witness will carefully verify every fact, recheck their work, and ensure that their conclusions are backed by strong documentation.
A commitment to thoroughness not only strengthens the expert's analysis but also shields your case from unnecessary vulnerabilities.
Conclusion
Selecting the right Database Expert Witness can be the deciding factor in a data-centric legal dispute. You want someone who brings technical excellence, clear communication skills, unwavering objectivity, extensive litigation experience, and meticulous attention to detail to the table.
In today’s digital-first world, data is at the heart of many legal battles. Whether you are dealing with data breaches, database failures, intellectual property theft, or regulatory compliance issues, a seasoned Database Expert Witness can clarify complex topics, bolster your legal arguments, and help you achieve a favorable outcome.
Choose your Database Expert Witness carefully, and you'll have a powerful ally who not only understands the intricacies of data but also knows how to make a lasting impact in the courtroom.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Azure vs. AWS: A Detailed Comparison
Cloud computing has become the backbone of modern IT infrastructure, offering businesses scalability, security, and flexibility. Among the top cloud service providers, Microsoft Azure and Amazon Web Services (AWS) dominate the market, each bringing unique strengths. While AWS has held the position as a cloud pioneer, Azure has been gaining traction, especially among enterprises with existing Microsoft ecosystems. This article provides an in-depth comparison of Azure vs. AWS, covering aspects like database services, architecture, and data engineering capabilities to help businesses make an informed decision.
1. Market Presence and Adoption
AWS, launched in 2006, was the first major cloud provider and remains the market leader. It boasts a massive customer base, including startups, enterprises, and government organizations. Azure, introduced by Microsoft in 2010, has seen rapid growth, especially among enterprises leveraging Microsoft's ecosystem. Many companies using Microsoft products like Windows Server, SQL Server, and Office 365 find Azure a natural choice.
2. Cloud Architecture: Comparing Azure and AWS
Cloud architecture defines how cloud services integrate and support workloads. Both AWS and Azure provide robust cloud architectures but with different approaches.
AWS Cloud Architecture
AWS follows a modular approach, allowing users to pick and choose services based on their needs. It offers:
Amazon EC2 for scalable compute resources
Amazon VPC for network security and isolation
Amazon S3 for highly scalable object storage
AWS Lambda for serverless computing
Azure Cloud Architecture
Azure's architecture is designed to integrate seamlessly with Microsoft tools and services. It includes:
Azure Virtual Machines (VMs) for compute workloads
Azure Virtual Network (VNet) for networking and security
Azure Blob Storage for scalable object storage
Azure Functions for serverless computing
In terms of architecture, AWS provides more flexibility, while Azure ensures deep integration with enterprise IT environments.
3. Database Services: Azure SQL vs. AWS RDS
Database management is crucial for any cloud strategy. Both AWS and Azure offer extensive database solutions, but they cater to different needs.
AWS Database Services
AWS provides a wide range of managed database services, including:
Amazon RDS (Relational Database Service) – Supports MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQL Server, MariaDB, and Oracle.
Amazon Aurora – High-performance relational database compatible with MySQL and PostgreSQL.
Amazon DynamoDB – NoSQL database for low-latency applications.
Amazon Redshift – Data warehousing for big data analytics.
Azure Database Services
Azure offers strong database services, especially for Microsoft-centric workloads:
Azure SQL Database – Fully managed SQL database optimized for Microsoft applications.
Cosmos DB – Globally distributed, multi-model NoSQL database.
Azure Synapse Analytics – Enterprise-scale data warehousing.
Azure Database for PostgreSQL/MySQL/MariaDB – Open-source relational databases with managed services.
AWS provides a more mature and diverse database portfolio, while Azure stands out in SQL-based workloads and seamless Microsoft integration.
4. Data Engineering and Analytics: Which Cloud is Better?
Data engineering is a critical function that ensures efficient data processing, transformation, and storage. Both AWS and Azure offer data engineering tools, but their capabilities differ.
AWS Data Engineering Tools
AWS Glue – Serverless data integration service for ETL workloads.
Amazon Kinesis – Real-time data streaming.
AWS Data Pipeline – Orchestration of data workflows.
Amazon EMR (Elastic MapReduce) – Managed Hadoop, Spark, and Presto.
Azure Data Engineering Tools
Azure Data Factory – Cloud-based ETL and data integration.
Azure Stream Analytics – Real-time event processing.
Azure Databricks – Managed Apache Spark for big data processing.
Azure HDInsight – Fully managed Hadoop and Spark services.
Azure has an edge in data engineering for enterprises leveraging AI and machine learning via Azure Machine Learning and Databricks. AWS, however, excels in scalable and mature big data tools.
5. Pricing Models and Cost Efficiency
Cloud pricing is a major factor when selecting a provider. Both AWS and Azure offer pay-as-you-go pricing, reserved instances, and cost optimization tools.
AWS Pricing: Charges are based on compute, storage, data transfer, and additional services. AWS also offers AWS Savings Plans for cost reductions.
Azure Pricing: Azure provides cost-effective solutions for Microsoft-centric businesses. Azure Hybrid Benefit allows companies to use existing Windows Server and SQL Server licenses to save costs.
AWS generally provides more pricing transparency, while Azure offers better pricing for Microsoft users.
6. Security and Compliance
Security is a top priority in cloud computing, and both AWS and Azure provide strong security measures.
AWS Security: Uses AWS IAM (Identity and Access Management), AWS Shield (DDoS protection), and AWS Key Management Service.
Azure Security: Provides Azure Active Directory (AAD), Azure Security Center, and built-in compliance features for enterprises.
Both platforms meet industry standards like GDPR, HIPAA, and ISO 27001, making them secure choices for businesses.
7. Hybrid Cloud Capabilities
Enterprises increasingly prefer hybrid cloud strategies. Here, Azure has a significant advantage due to its Azure Arc and Azure Stack technologies that extend cloud services to on-premises environments.
AWS offers AWS Outposts, but it is not as deeply integrated as Azure’s hybrid solutions.
8. Which Cloud Should You Choose?
Choose AWS if:
You need a diverse range of cloud services.
You require highly scalable and mature cloud solutions.
Your business prioritizes flexibility and a global cloud footprint.
Choose Azure if:
Your business relies heavily on Microsoft products.
You need strong hybrid cloud capabilities.
Your focus is on SQL-based workloads and enterprise data engineering.
Conclusion
Both AWS and Azure are powerful cloud providers with unique strengths. AWS remains the leader in cloud services, flexibility, and scalability, while Azure is the go-to choice for enterprises using Microsoft’s ecosystem.
Ultimately, the right choice depends on your organization’s needs in terms of database management, cloud architecture, data engineering, and overall IT strategy. Companies looking for a seamless Microsoft integration should opt for Azure, while businesses seeking a highly scalable and service-rich cloud should consider AWS.
Regardless of your choice, both platforms provide the foundation for a strong, scalable, and secure cloud infrastructure in today’s data-driven world.
0 notes
Text
Top 15 Database for Web Apps to Use in 2025
In 2025, the world of databases continues to evolve rapidly, offering a variety of powerful options to cater to different business needs. Among the top contenders are cloud-native databases like Amazon Aurora and Google BigQuery, which offer high scalability and low-latency performance. These cloud-based solutions are becoming the go-to for businesses that need to manage large-scale web applications and data warehousing. On the other hand, traditional relational databases like MySQL and PostgreSQL still hold strong, offering robust support for transactional systems and a wealth of developer tools. Additionally, NoSQL databases like MongoDB and Cassandra are increasingly popular for handling unstructured data, providing flexibility and speed in applications where scalability and fault tolerance are critical.
As companies continue to prioritize speed, reliability, and seamless integration, the database landscape of 2025 is filled with various solutions that cater to different use cases. Whether you are building a web app, a mobile application, or a data-intensive platform, choosing the right database is critical for ensuring optimal performance and scalability. The right choice ultimately depends on factors such as data structure, speed, and whether you require flexibility for handling big data. To explore more options for databases in 2025.
click here to know more: https://www.intelegain.com/top-15-database-for-web-apps-to-use-in-2025/
0 notes
Text
AWS Modernization: Ambitiously Rejuvenating the Cloud Journey with Innovation
Firms are all rushing towards the cloud-basted solution due to massive demand for agility, cost-effectiveness, and innovation within this fast-paced digital epoch. AWS offers innovation solutions to modernize legacy architecture, optimize workloads and achieve operational excellence. This blog analyzes the features of some top AWS modernization services, showing how they can change the course of your cloud journey.
1. AWS Lambda
AWS Lambda is a serverless computing service that runs code without having to provision or manage servers. It scales automatically according to demand, so you can build scalable applications and reduce the infrastructure complexity.
2. Amazon ECS and EKS
Modernization of application deployment is now easier with Amazon ECS and EKS. This allows organizations to move towards containerization, has simplified application management, and assures scalability across environments.
3. AWS Fargate
AWS Fargate is a serverless compute engine for containers that eliminated the need for server management; therefore, the developers can focus on just developing apps. This not only optimizes resource use due to pay-as-you-go pricing and automatic scaling.
4. Amazon Aurora
Amazon Aurora is an extremely high-performing, resilient cloud-native relational database service that is compatible with open-source engines MySQL and PostgreSQL, making the tool ideal for any organization looking to migrate databases.
5. AWS Application Migration Service
The AWS Application Migration Service (AWS MGN) makes it easier to move applications from on-premises to AWS. It automates significant parts of the migration process and minimizes downtime.
6. AWS DevOps Tools
AWS has matured in terms of using numerous development tools, from AWS CodePipeline, AWS CodeBuild, and AWS CodeDeploy, that allow for continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD), thus minimizing changes to development cycle times and effectiveness of deployment.
7. AWS Modernization Hub
The AWS Modernization Hub is a one-stop solution for the planning and execution of modernization projects. It provides insights, resources, and guidance toward fine-tuning modern architecture migration.
Utilization of AWS modernization solutions keeps organizations at the forefront, innovating ahead of time and optimizing business processes. With serverless computing, containerization, and automated migrations, AWS is the secret to your future-proof cloud. Using these very available solutions, organizations can create new avenues for growth and digital transform.
Conclusion
AWS modernization is a wholesale cleanup and not merely an upgrade in technologies for an enterprise to innovate, simplify, and expand at speed. The adoption of cloud-native architectures, serverless architectures, AI-driven automations, and DevOps practices envelop these capabilities with new levels of efficiency, security, and cost-competitiveness.
With this ambitious reimagination of the cloud experience, organizations are capable of taking the lead in the fast-paced competition of the digital world. Scaling modernization is assured with AWS tooling and frameworks, no matter if it is based on microservices, containerization, or machine learning integration.
Cloud innovation is endless. Organizations that respond nimbly and continuously update their AWS strategies will continue to prosper, taking advantage of the latest technologies in pursuing business growth and stability.
1 note
·
View note
Text
AWS RDS: Simplifying Database Management in the Cloud
AWS RDS: Simplifying Database Management in the Cloud Amazon Relational Database Service (AWS RDS) is a fully managed service that makes setting up, operating, and scaling relational databases in the cloud simple and efficient.
AWS RDS supports popular database engines such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, SQL Server, MariaDB, and Amazon Aurora, offering users flexibility in choosing the right database for their applications.
Key Features:
Automated Management: RDS handles routine database tasks like backups, patching, and scaling, reducing operational overhead.
High Availability: With Multi-AZ (Availability Zone) deployments, RDS ensures failover support and business continuity.
Scalability: It allows seamless scaling of database storage and compute resources to meet changing demands.
Security: Offers encryption at rest and in transit, along with integration with AWS IAM and VPC for access control.
Monitoring: Provides performance insights and integration with Amazon CloudWatch for tracking database health and metrics.
Benefits: Reduces the complexity of managing on-premises databases.
Saves time with automatic provisioning and maintenance.
Supports disaster recovery and high availability, crucial for modern applications.
Common Use Cases:
E-commerce platforms with MySQL or PostgreSQL databases.
Analytics applications using Amazon Aurora for faster query performance. Enterprise applications relying on SQL Server or Oracle databases.
AWS RDS is an ideal solution for developers and businesses looking to focus on building applications rather than managing databases.
WEBSITE: https://www.ficusoft.in/aws-training-in-chennai/
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Text
Aurora DSQL: Amazon’s Fastest Serverless SQL Solution

Amazon Aurora DSQL
Availability of Amazon Aurora DSQL is announced. As the quickest serverless distributed SQL database, it provides high availability, almost limitless scalability, and low infrastructure administration for always-accessible applications. Patching, updates, and maintenance downtime may no longer be an operational burden. Customers were excited to get a preview of this solution at AWS re:Invent 2024 since it promised to simplify relational database issues.
Aurora DSQL architecture controlled complexity upfront, according to Amazon.com CTO Dr. Werner Vogels. Its architecture includes a query processor, adjudicator, journal, and crossbar, unlike other databases. These pieces grow independently to your needs, are cohesive, and use well-defined APIs. This architecture supports multi-Region strong consistency, low latency, and global time synchronisation.
Your application can scale to meet any workload and use the fastest distributed SQL reads and writes without database sharding or instance upgrades. Aurora DSQL's active-active distributed architecture provides 99.999 percent availability across many locations and 99.99 percent in one. An application can read and write data consistently without a Region cluster endpoint.
Aurora DSQL commits write transactions to a distributed transaction log in a single Region and synchronously replicates them to user storage replicas in three Availability Zones. Cluster storage replicas are distributed throughout a storage fleet and scale automatically for best read performance. One endpoint per peer cluster region Multi-region clusters boost availability while retaining resilience and connection.
A peered cluster's two endpoints perform concurrent read/write operations with good data consistency and provide a single logical database. Third regions serve as log-only witnesses without cluster resources or endpoints. This lets you balance connections and apps by speed, resilience, or geography to ensure readers always see the same data.
Aurora DSQL benefits event-driven and microservice applications. It builds enormously scalable retail, e-commerce, financial, and travel systems. Data-driven social networking, gaming, and multi-tenant SaaS programs that need multi-region scalability and reliability can use it.
Starting Amazon Aurora DSQL
Aurora DSQL is easy to learn with console expertise. Programmable ways with a database endpoint and authentication token as a password or JetBrains DataGrip, DBeaver, or PostgreSQL interactive terminal are options.
Select “Create cluster” in the console to start an Aurora DSQL cluster. Single-Region and Multi-Region setups are offered.
Simply pick “Create cluster” for a single-Region cluster. Create it in minutes. Create an authentication token, copy the endpoint, and connect with SQL. CloudShell, Python, Java, JavaScript, C++, Ruby,.NET, Rust, and Golang can connect. You can also construct example apps using AWS Lambda or Django and Ruby on Rails.
Multi-region clusters need ARNs to peer. Open Multi-Region, select Witness Region, and click “Create cluster” for the first cluster. The ARN of the first cluster is used to construct a second cluster in another region. Finally, pick “Peer” on the first cluster page to peer the clusters. The “Peers” tab contains peer information. AWS SDKs, CLI, and Aurora DSQL APIs allow programmatic cluster creation and management.
In response to preview user comments, new features were added. These include easier AWS CloudShell connections and better console experiences for constructing and peering multi-region clusters. PostgreSQL also added views, Auto-Analyze, and unique secondary indexes for tables with existing data. Integration with AWS CloudTrail for logging, Backup, PrivateLink, and CloudFormation was also included.
Aurora DSQL now supports natural language communication between the database and generative AI models via a Model Context Protocol (MCP) server to boost developer productivity. Installation of Amazon Q Developer CLI and MCP server allows the CLI access to the cluster, allowing it to investigate schema, understand table structure, and conduct complex SQL queries without integration code.
Accessibility
As of writing, Amazon Aurora DSQL was available for single- and multi-region clusters (two peers and one witness region) in AWS US East (N. Virginia), US East (Ohio), and US West (Oregon) Regions. It was available for single-Region clusters in Ireland, London, Paris, Osaka, and Tokyo.
Aurora DSQL bills all request-based operations, such as read/write, monthly using a single normalised billing unit, the Distributed Processing Unit. Total database size, in gigabytes per month, determines storage costs. You pay for one logical copy of your data in a single- or multi-region peered cluster. Your first 100,000 DPUs and 1 GB of storage per month are free with AWS Free Tier. Find pricing here.
Console users can try Aurora DSQL for free. The Aurora DSQL User Guide has more information, and you may give comments via AWS re:Post or other means.
#AuroraDSQL#AmazonAuroraDSQL#AuroraDSQLcluster#DistributedProcessingUnit#AWSservices#ModelContextProtocol#technology#technews#technologynews#news#govindhtech
0 notes
Text
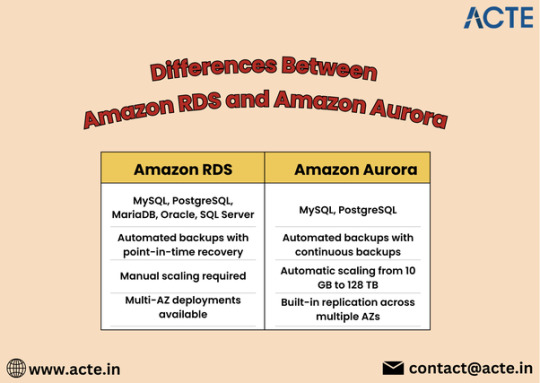
Comparing Amazon RDS and Aurora: Key Differences Explained
When it comes to choosing a database solution in the cloud, Amazon Web Services (AWS) offers a range of powerful options, with Amazon Relational Database Service (RDS) and Amazon Aurora being two of the most popular. Both services are designed to simplify database management, but they cater to different needs and use cases. In this blog, we’ll delve into the key differences between Amazon RDS and Aurora to help you make an informed decision for your applications.
If you want to advance your career at the AWS Course in Pune, you need to take a systematic approach and join up for a course that best suits your interests and will greatly expand your learning path.

What is Amazon RDS?
Amazon RDS is a fully managed relational database service that supports multiple database engines, including MySQL, PostgreSQL, MariaDB, Oracle, and Microsoft SQL Server. It automates routine database tasks such as backups, patching, and scaling, allowing developers to focus more on application development rather than database administration.
Key Features of RDS
Multi-Engine Support: Choose from various database engines to suit your specific application needs.
Automated Backups: RDS automatically backs up your data and provides point-in-time recovery.
Read Replicas: Scale read operations by creating read replicas to offload traffic from the primary instance.
Security: RDS offers encryption at rest and in transit, along with integration with AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM).
What is Amazon Aurora?
Amazon Aurora is a cloud-native relational database designed for high performance and availability. It is compatible with MySQL and PostgreSQL, offering enhanced features that improve speed and reliability. Aurora is built to handle demanding workloads, making it an excellent choice for large-scale applications.
Key Features of Aurora
High Performance: Aurora can deliver up to five times the performance of standard MySQL databases, thanks to its unique architecture.
Auto-Scaling Storage: Automatically scales storage from 10 GB to 128 TB without any downtime, adapting to your needs seamlessly.
High Availability: Data is automatically replicated across multiple Availability Zones for robust fault tolerance and uptime.
Serverless Option: Aurora Serverless automatically adjusts capacity based on application demand, ideal for unpredictable workloads.
To master the intricacies of AWS and unlock its full potential, individuals can benefit from enrolling in the AWS Online Training.
Key Differences Between Amazon RDS and Aurora
1. Performance and Scalability
One of the most significant differences lies in performance. Aurora is engineered for high throughput and low latency, making it a superior choice for applications that require fast data access. While RDS provides good performance, it may not match the efficiency of Aurora under heavy loads.
2. Cost Structure
Both services have different pricing models. RDS typically has a more straightforward pricing structure based on instance types and storage. Aurora, however, incurs costs based on the volume of data stored, I/O operations, and instance types. While Aurora may seem more expensive initially, its performance gains can result in cost savings for high-traffic applications.
3. High Availability and Fault Tolerance
Aurora inherently offers better high availability due to its design, which replicates data across multiple Availability Zones. While RDS does offer Multi-AZ deployments for high availability, Aurora’s replication and failover mechanisms provide additional resilience.
4. Feature Set
Aurora includes advanced features like cross-region replication and global databases, which are not available in standard RDS. These capabilities make Aurora an excellent option for global applications that require low-latency access across regions.
5. Management and Maintenance
Both services are managed by AWS, but Aurora requires less manual intervention for scaling and maintenance due to its automated features. This can lead to reduced operational overhead for businesses relying on Aurora.
When to Choose RDS or Aurora
Choose Amazon RDS if you need a straightforward, managed relational database solution with support for multiple engines and moderate performance needs.
Opt for Amazon Aurora if your application demands high performance, scalability, and advanced features, particularly for large-scale or global applications.
Conclusion
Amazon RDS and Amazon Aurora both offer robust solutions for managing relational databases in the cloud, but they serve different purposes. Understanding the key differences can help you select the right service based on your specific requirements. Whether you go with the simplicity of RDS or the advanced capabilities of Aurora, AWS provides the tools necessary to support your database needs effectively.
0 notes
Text
Google adds natural language query capabilities to AlloyDB
Google is enhancing AlloyDB, its fully managed database-as-a-service (DBaaS), to help developers build applications underpinned by generative AI. Announced at Google’s annual Cloud Next conference, the updates could give the PostreSQL-compatible AlloyDB an edge over PostgreSQL itself or other compatible offerings such as Amazon Aurora. Among the additions, a new AlloyDB AI query engine enables…
0 notes
Video
youtube
Amazon RDS DB Engines | Choose the Right Relational Database
Selecting the right Amazon RDS database engine is crucial for achieving optimal performance, scalability, and functionality for your applications. Amazon RDS offers a variety of relational database engines, each tailored to specific needs and use cases. Understanding these options helps you make an informed decision that aligns with your project requirements.
Types of Amazon RDS Databases:
- Amazon Aurora: A high-performance, fully managed database compatible with MySQL and PostgreSQL. Aurora is known for its speed, reliability, and scalability, making it suitable for high-demand applications. - MySQL: An open-source database that is widely used for its flexibility and ease of use. It is ideal for web applications, content management systems, and moderate traffic workloads. - MariaDB: A fork of MySQL with additional features and improved performance. MariaDB is well-suited for users seeking advanced capabilities and enhanced security. - PostgreSQL: Known for its advanced data types and extensibility, PostgreSQL is perfect for applications requiring complex queries, data integrity, and sophisticated analytics. - Microsoft SQL Server: An enterprise-grade database offering robust reporting and business intelligence features. It integrates seamlessly with other Microsoft products and is ideal for large-scale applications.
When and Where to Choose Each Engine:
- Amazon Aurora: Choose Aurora for applications that demand high availability, fault tolerance, and superior performance, such as high-traffic web platforms and enterprise systems. - MySQL: Opt for MySQL if you need a cost-effective, open-source solution with strong community support for web applications and simple data management. - MariaDB: Select MariaDB for its advanced features and enhanced performance, especially if you require a more capable alternative to MySQL for web applications and data-intensive systems. - PostgreSQL: Use PostgreSQL for applications needing complex data operations, such as data warehousing, analytical applications, and scenarios where advanced querying is essential. - Microsoft SQL Server: Ideal for enterprise environments needing extensive business intelligence, reporting, and integration with other Microsoft products. Choose SQL Server for complex enterprise applications and large-scale data management.
Use Cases:
- Amazon Aurora: High-traffic e-commerce sites, real-time analytics, and mission-critical applications requiring high performance and scalability. - MySQL: Content management systems, small to medium-sized web applications, and moderate data workloads. - MariaDB: Advanced web applications, high-performance data systems, and scenarios requiring enhanced security and features. - PostgreSQL: Complex business applications, financial systems, and applications requiring advanced data manipulation and integrity. - Microsoft SQL Server: Large-scale enterprise applications, business intelligence platforms, and complex reporting needs.
Key Benefits of Choosing the Right Amazon RDS Database:
1. Optimized Performance: Select an engine that matches your performance needs, ensuring efficient data processing and application responsiveness. 2. Scalability: Choose a database that scales seamlessly with your growing data and traffic demands, avoiding performance bottlenecks. 3. Cost Efficiency: Find a solution that fits your budget while providing the necessary features and performance. 4. Enhanced Features: Leverage advanced capabilities specific to each engine to meet your application's unique requirements. 5. Simplified Management: Benefit from managed services that reduce administrative tasks and streamline database operations.
Conclusion:
Choosing the right Amazon RDS database engine is essential for optimizing your application’s performance and scalability. By understanding the types of databases available and their respective benefits, you can make a well-informed decision that supports your project's needs and ensures a robust, efficient, and cost-effective database solution. Explore Amazon RDS to find the perfect database engine for your application.
Amazon RDS, RDS Monitoring, AWS Performance Insights, Optimize RDS, Amazon CloudWatch, Enhanced Monitoring AWS, AWS DevOps Tutorial, AWS Hands-On, Cloud Performance, RDS Optimization, AWS Database Monitoring, RDS best practices, AWS for Beginners, ClouDolus
#AmazonRDS #RDSMonitoring #PerformanceInsights #CloudWatch #AWSDevOps #DatabaseOptimization #ClouDolus #ClouDolusPro
📢 Subscribe to ClouDolus for More AWS & DevOps Tutorials! 🚀 🔹 ClouDolus YouTube Channel - https://www.youtube.com/@cloudolus 🔹 ClouDolus AWS DevOps - https://www.youtube.com/@ClouDolusPro
*THANKS FOR BEING A PART OF ClouDolus! 🙌✨*
***************************** *Follow Me* https://www.facebook.com/cloudolus/ | https://www.facebook.com/groups/cloudolus | https://www.linkedin.com/groups/14347089/ | https://www.instagram.com/cloudolus/ | https://twitter.com/cloudolus | https://www.pinterest.com/cloudolus/ | https://www.youtube.com/@cloudolus | https://www.youtube.com/@ClouDolusPro | https://discord.gg/GBMt4PDK | https://www.tumblr.com/cloudolus | https://cloudolus.blogspot.com/ | https://t.me/cloudolus | https://www.whatsapp.com/channel/0029VadSJdv9hXFAu3acAu0r | https://chat.whatsapp.com/BI03Rp0WFhqBrzLZrrPOYy *****************************
#youtube#Amazon RDS RDS Monitoring AWS Performance Insights Optimize RDS Amazon CloudWatch Enhanced Monitoring AWS AWS DevOps Tutorial AWS Hands-On C
0 notes
Link
In this post, we walk you through configuring and integrating Amazon Q for Business with Aurora PostgreSQL-Compatible to enable your database administrators, data analysts, application developers, leadership, and other teams to quickly get accurate #AI #ML #Automation
0 notes