#config server spring cloud
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Essential Components of a Production Microservice Application
DevOps Automation Tools and modern practices have revolutionized how applications are designed, developed, and deployed. Microservice architecture is a preferred approach for enterprises, IT sectors, and manufacturing industries aiming to create scalable, maintainable, and resilient applications. This blog will explore the essential components of a production microservice application, ensuring it meets enterprise-grade standards.
1. API Gateway
An API Gateway acts as a single entry point for client requests. It handles routing, composition, and protocol translation, ensuring seamless communication between clients and microservices. Key features include:
Authentication and Authorization: Protect sensitive data by implementing OAuth2, OpenID Connect, or other security protocols.
Rate Limiting: Prevent overloading by throttling excessive requests.
Caching: Reduce response time by storing frequently accessed data.
Monitoring: Provide insights into traffic patterns and potential issues.
API Gateways like Kong, AWS API Gateway, or NGINX are widely used.
Mobile App Development Agency professionals often integrate API Gateways when developing scalable mobile solutions.
2. Service Registry and Discovery
Microservices need to discover each other dynamically, as their instances may scale up or down or move across servers. A service registry, like Consul, Eureka, or etcd, maintains a directory of all services and their locations. Benefits include:
Dynamic Service Discovery: Automatically update the service location.
Load Balancing: Distribute requests efficiently.
Resilience: Ensure high availability by managing service health checks.
3. Configuration Management
Centralized configuration management is vital for managing environment-specific settings, such as database credentials or API keys. Tools like Spring Cloud Config, Consul, or AWS Systems Manager Parameter Store provide features like:
Version Control: Track configuration changes.
Secure Storage: Encrypt sensitive data.
Dynamic Refresh: Update configurations without redeploying services.
4. Service Mesh
A service mesh abstracts the complexity of inter-service communication, providing advanced traffic management and security features. Popular service mesh solutions like Istio, Linkerd, or Kuma offer:
Traffic Management: Control traffic flow with features like retries, timeouts, and load balancing.
Observability: Monitor microservice interactions using distributed tracing and metrics.
Security: Encrypt communication using mTLS (Mutual TLS).
5. Containerization and Orchestration
Microservices are typically deployed in containers, which provide consistency and portability across environments. Container orchestration platforms like Kubernetes or Docker Swarm are essential for managing containerized applications. Key benefits include:
Scalability: Automatically scale services based on demand.
Self-Healing: Restart failed containers to maintain availability.
Resource Optimization: Efficiently utilize computing resources.
6. Monitoring and Observability
Ensuring the health of a production microservice application requires robust monitoring and observability. Enterprises use tools like Prometheus, Grafana, or Datadog to:
Track Metrics: Monitor CPU, memory, and other performance metrics.
Set Alerts: Notify teams of anomalies or failures.
Analyze Logs: Centralize logs for troubleshooting using ELK Stack (Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana) or Fluentd.
Distributed Tracing: Trace request flows across services using Jaeger or Zipkin.
Hire Android App Developers to ensure seamless integration of monitoring tools for mobile-specific services.
7. Security and Compliance
Securing a production microservice application is paramount. Enterprises should implement a multi-layered security approach, including:
Authentication and Authorization: Use protocols like OAuth2 and JWT for secure access.
Data Encryption: Encrypt data in transit (using TLS) and at rest.
Compliance Standards: Adhere to industry standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI-DSS.
Runtime Security: Employ tools like Falco or Aqua Security to detect runtime threats.
8. Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD)
A robust CI/CD pipeline ensures rapid and reliable deployment of microservices. Using tools like Jenkins, GitLab CI/CD, or CircleCI enables:
Automated Testing: Run unit, integration, and end-to-end tests to catch bugs early.
Blue-Green Deployments: Minimize downtime by deploying new versions alongside old ones.
Canary Releases: Test new features on a small subset of users before full rollout.
Rollback Mechanisms: Quickly revert to a previous version in case of issues.
9. Database Management
Microservices often follow a database-per-service model to ensure loose coupling. Choosing the right database solution is critical. Considerations include:
Relational Databases: Use PostgreSQL or MySQL for structured data.
NoSQL Databases: Opt for MongoDB or Cassandra for unstructured data.
Event Sourcing: Leverage Kafka or RabbitMQ for managing event-driven architectures.
10. Resilience and Fault Tolerance
A production microservice application must handle failures gracefully to ensure seamless user experiences. Techniques include:
Circuit Breakers: Prevent cascading failures using tools like Hystrix or Resilience4j.
Retries and Timeouts: Ensure graceful recovery from temporary issues.
Bulkheads: Isolate failures to prevent them from impacting the entire system.
11. Event-Driven Architecture
Event-driven architecture improves responsiveness and scalability. Key components include:
Message Brokers: Use RabbitMQ, Kafka, or AWS SQS for asynchronous communication.
Event Streaming: Employ tools like Kafka Streams for real-time data processing.
Event Sourcing: Maintain a complete record of changes for auditing and debugging.
12. Testing and Quality Assurance
Testing in microservices is complex due to the distributed nature of the architecture. A comprehensive testing strategy should include:
Unit Tests: Verify individual service functionality.
Integration Tests: Validate inter-service communication.
Contract Testing: Ensure compatibility between service APIs.
Chaos Engineering: Test system resilience by simulating failures using tools like Gremlin or Chaos Monkey.
13. Cost Management
Optimizing costs in a microservice environment is crucial for enterprises. Considerations include:
Autoscaling: Scale services based on demand to avoid overprovisioning.
Resource Monitoring: Use tools like AWS Cost Explorer or Kubernetes Cost Management.
Right-Sizing: Adjust resources to match service needs.
Conclusion
Building a production-ready microservice application involves integrating numerous components, each playing a critical role in ensuring scalability, reliability, and maintainability. By adopting best practices and leveraging the right tools, enterprises, IT sectors, and manufacturing industries can achieve operational excellence and deliver high-quality services to their customers.
Understanding and implementing these essential components, such as DevOps Automation Tools and robust testing practices, will enable organizations to fully harness the potential of microservice architecture. Whether you are part of a Mobile App Development Agency or looking to Hire Android App Developers, staying ahead in today’s competitive digital landscape is essential.
0 notes
Text
Why Java Spring Boot is Ideal for Building Microservices

In modern software development, microservices have become the go-to architecture for creating scalable, flexible, and maintainable applications. Java full-stack development is one of the most popular frameworks used for building microservices, thanks to its simplicity, powerful features, and seamless integration with other technologies. In this blog, we will explore why Java Spring Boot is an ideal choice for building microservices.
What are Microservices?
Microservices architecture is a design pattern where an application is broken down into smaller, independent services that can be developed, deployed, and scaled individually. Each microservice typically focuses on a specific business functionality, and communicates with other services via APIs (often RESTful). Microservices offer several advantages over traditional monolithic applications, including improved scalability, flexibility, and maintainability.
Why Spring Boot for Microservices?
Spring Boot, a lightweight, open-source Java framework, simplifies the development of stand-alone, production-grade applications. It comes with several features that make it an excellent choice for building microservices. Here are some key reasons why:
1. Rapid Development with Minimal Configuration
Spring Boot is known for its "convention over configuration" approach, which makes it incredibly developer-friendly. It removes the need for complex XML configurations, allowing developers to focus on the business logic rather than boilerplate code. For microservices, this means you can quickly spin up new services with minimal setup, saving time and increasing productivity.
Spring Boot comes with embedded servers (like Tomcat, Jetty, and Undertow), so you don’t need to worry about setting up and managing separate application servers. This makes deployment and scaling easier in microservices environments.
2. Microservice-Friendly Components
Spring Boot is tightly integrated with the Spring Cloud ecosystem, which provides tools specifically designed for building microservices. Some of these key components include:
Spring Cloud Config: Centralizes configuration management for multiple services in a microservices architecture, allowing you to manage configuration properties in a version-controlled repository.
Spring Cloud Netflix: Includes several tools like Eureka (for service discovery), Hystrix (for fault tolerance), and Ribbon (for client-side load balancing), which are essential for building resilient and scalable microservices.
Spring Cloud Gateway: Provides a simple, effective way to route requests to different microservices, offering features like load balancing, security, and more.
Spring Cloud Stream: A framework for building event-driven microservices, making it easier to work with messaging middleware (e.g., RabbitMQ, Kafka).
These tools help you quickly build and manage your microservices in a distributed architecture.
3. Scalability and Flexibility
One of the main reasons organizations adopt microservices is the ability to scale individual components independently. Spring Boot’s lightweight nature makes it an ideal choice for microservices because it enables easy scaling both vertically (scaling up resources for a single service) and horizontally (scaling across multiple instances of a service).
With Spring Boot, you can run multiple instances of microservices in containers (e.g., Docker) and orchestrate them using platforms like Kubernetes. This makes it easier to handle high traffic, optimize resource usage, and maintain high availability.
4. Fault Tolerance and Resilience
In a microservices architecture, failures in one service can affect others. Spring Boot provides built-in mechanisms for handling fault tolerance and resilience, which are critical for maintaining the integrity and uptime of your application. With Spring Cloud Netflix Hystrix, you can implement circuit breakers that prevent cascading failures, providing a more robust and fault-tolerant system.
By using tools like Resilience4j, Spring Boot makes it easier to implement strategies like retries, timeouts, and fallbacks to ensure your services remain resilient even when some of them fail.
5. Easy Integration with Databases and Messaging Systems
Microservices often require interaction with various data stores and messaging systems. Spring Boot makes this integration straightforward by providing support for relational databases (like MySQL, PostgreSQL), NoSQL databases (like MongoDB, Cassandra), and message brokers (like RabbitMQ, Kafka).
With Spring Data, you can easily interact with databases using a simplified repository model, without having to write much boilerplate code. This enables microservices to manage their own data stores, promoting the independence of each service.
6. Security Features
Security is critical in microservices, as services often need to communicate with each other over the network. Spring Security provides a comprehensive security framework that integrates well with Spring Boot. With Spring Security, you can secure your microservices with features like:
Authentication and Authorization: Implementing OAuth2, JWT tokens, or traditional session-based authentication to ensure that only authorized users or services can access certain endpoints.
Secure Communication: Enabling HTTPS, encrypting data in transit, and ensuring that communications between services are secure.
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Ensuring that each microservice has the appropriate permissions to access certain resources.
These security features help ensure that your microservices are protected from unauthorized access and malicious attacks.
7. Monitoring and Logging
Monitoring and logging are essential for maintaining microservices in a production environment. With Spring Boot, you can easily implement tools like Spring Boot Actuator to expose useful operational information about your microservices, such as metrics, health checks, and system properties.
In addition, Spring Cloud Sleuth provides distributed tracing capabilities, allowing you to trace requests as they flow through multiple services. This helps you track and diagnose issues more efficiently in a microservices architecture.
Conclusion
Java full-stack development provides a solid foundation for building microservices, making it an excellent choice for developers looking to implement a modern, scalable, and resilient application architecture. The framework’s ease of use, integration with Spring Cloud components, scalability, and security features are just a few of the reasons why Spring Boot is an ideal platform for microservices.
As a Java full-stack development, understanding how to build microservices with Spring Boot will not only enhance your skill set but also open doors to working on more complex and modern systems. If you’re looking to develop scalable, flexible, and fault-tolerant applications, Java Spring Boot is the right tool for the job.
This concludes the blog on "Why Java full-stack development is Ideal for Building Microservices". Let me know if you'd like to continue to the next topic!
0 notes
Text
hi
. how to implement expection handling using Spring boot/rest 2. how to configure/implement Spring cloud config server. 3. How to setup two way SSL using Java/Spring boot 4. difference between Bean factory vs Application context in spring application 5. what happens when u send a request to spring boot ? 6. How does Spring Marshall/unmarshall? 7. How to implement Transactions using Spring boot. 8. How to do load balancing using Spring boot both client side and server side. 9. How to add css/javascript/images to spring boot application UI 10. Any spring /spring boot performance issues you encountered. 11. how to implement spring boot security using OAuth 12. How to setup multiple datasources using spring boot
0 notes
Text
Mastering Java Scope in Emerging Technologies
Your Gateway to the Future Java, the ubiquitous programming language, has stood the test of time, remaining relevant and evolving alongside technological advancements. While its core principles stay strong, mastering Java scope in emerging technologies unlocks a new level of development prowess. This article delves into the exciting intersection of Java scope and cutting-edge fields, equipping you with the knowledge and skills to navigate the software landscape of tomorrow.
Understanding the Power of Scope
Java scope defines the accessibility and visibility of variables, methods, and classes within your code. Traditionally, mastering scope involved understanding local and global variables, access modifiers, and class hierarchies. However, emerging technologies introduce novel contexts where scope takes on new dimensions.
Cloud-Native Development:
The cloud has revolutionized software deployment, and Java thrives in this distributed environment. Microservices architectures, built with loosely coupled, independently deployable services, demand a nuanced understanding of scope. Each service has its own scope, but inter-service communication necessitates controlled data sharing. Frameworks like Spring Cloud Config Server enable centralized configuration management, while techniques like API gateways manage service boundaries. Mastering scope in this context involves balancing autonomy and collaboration, ensuring secure and efficient communication between microservices.
Web Development Training In Jodhpur, Full Stack Web Development Training In Jodhpur, Python Training In Jodhpur, Flutter Training In Jodhpur, Android App Development Training In Jodhpur, Java Training In Jodhpur, Google Ads Training In Jodhpur, Coding Class In Jodhpur, oilab, Digital marketing Training In Jodhpur , Seo Training In Jodhpur, Digital Marketing Course In Jodhpur, SEO Training In Udaipur, Digital Marketing Course In Udaipur, Digital Marketing Training In Udaipur, Full stack web Development Training In Udaipur, Web Development Course In Udaipur
Big Data and Analytics:
The ever-growing data deluge demands robust tools for processing and analysis. Java plays a crucial role in big data ecosystems, with frameworks like Hadoop and Spark leveraging its concurrency and scalability. When dealing with massive datasets, understanding scope becomes vital for optimizing performance and memory usage. Partitioning data into separate scopes based on processing needs or geographical distribution allows for efficient parallel processing and targeted analysis.

Opens in a new window
Big Data and Analytics with Java
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning:
AI and ML are transforming various industries, and Java is making its mark in this domain as well. Libraries like TensorFlow and PyTorch utilize Java for building and deploying complex machine learning models. Scope plays a crucial role in managing training data, ensuring efficient access to relevant subsets while preventing unauthorized modifications. Additionally, understanding scope within AI algorithms helps developers control the visibility and influence of different variables on the model's output.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning with Java
Internet of Things (IoT):
The interconnected world of the IoT presents unique challenges for Java developers. Embedded devices often have limited resources, necessitating careful memory management. Scoping techniques like local variable caching and resource pooling become crucial for optimizing code footprint and ensuring efficient operation. Additionally, secure communication protocols in the IoT ecosystem rely on controlled data access, where proper scope management plays a vital role in protecting sensitive information.
Internet of Things (IoT) with Java
Mastering the Art of Scope in Emerging Technologies:
As you delve into these frontiers, remember these key takeaways:
Think in terms of context: Understand the specific needs and constraints of each emerging technology when applying scope principles.
Leverage appropriate frameworks and libraries: Utilize tools designed for specific domains to manage scope effectively.
Prioritize security and data privacy: Implement proper access control mechanisms within your code to protect sensitive information.
Stay informed and adaptable: Emerging technologies evolve rapidly, so continuous learning and upskilling are essential.
By mastering Java scope in the context of these emerging technologies, you unlock a world of possibilities. You become a builder of the future, crafting innovative solutions that leverage the power of Java in groundbreaking ways. So, embrace the challenge, expand your horizons, and let Java scope be your gateway to a thriving future in software development.
Remember, the journey to mastering Java scope in emerging technologies is an ongoing process. Embrace the learning curve, experiment with different approaches, and actively seek out new challenges. The rewards are plentiful, not just in terms of career opportunities but also in the satisfaction of shaping the software landscape of tomorrow.
0 notes
Text
Create Spring Cloud Configuration Server | Setup Eureka Service Discovery Registry Server
Full Video Link https://youtu.be/Exoy4ZNAO9Y Hello friends, new #video on #springcloud #configserver #eureka #servicediscovery setup is published on #codeonedigest #youtube channel. @java #java #aws #awscloud @awscloud @AWSCloudIndia #sal
In this video we will learn how to create spring cloud configuration server and eureka service registry server step by step in spring boot framework. Service registry will be use for service discovery. Configuration server is used to store application configuration in central storage. Application, microservices connect configuration server to fetch respective configuration from central…

View On WordPress
#config server#config server firewall#config server in microservices#config server in spring boot example#config server in spring boot microservices#config server spring#config server spring boot#config server spring boot github#config server spring cloud#configuration server#configuration server dns#configuration server in microservices#configuration server spring boot#configuration server step by step#eureka service#eureka service discovery#eureka service discovery example#eureka service discovery example spring boot#eureka service discovery spring boot#eureka service in microservices#eureka service registry#eureka service registry example#eureka service registry spring boot#eureka service spring boot
0 notes
Text
Kubernetes alternatives to Spring Java framework
Spring Cloud and Kubernetes both complement each other to build a cloud-native platform and run microservices on the Kubernetes containers. Kubernetes provides many features which are similar to Spring Cloud and Spring Config Server features. Spring framework has been around for many years. Even today, many organizations prefer to go with Spring because it provides many advanced features with…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Link
0 notes
Text
Microservices Architecture with Spring Cloud
What are microservices?
Microservices is an architecture(service-oriented architecture) (SOA). In this architecture, applications are broken down into various services. The motivation behind this is separation and modularity.
Monolithic architecture and microservices are more beneficial.
We don’t need to specify all business logic into a single software module. It leads to complexity and time-consuming debugging.
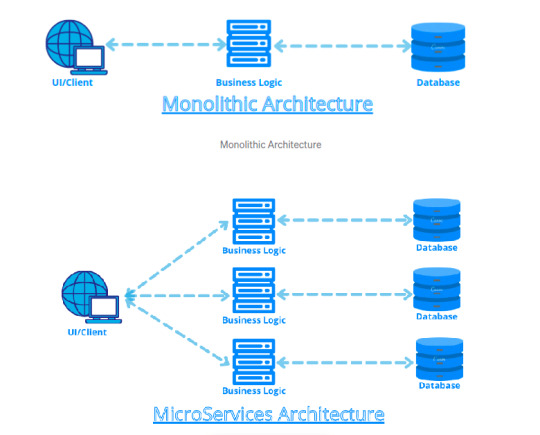
In the above diagram, as we can see, we have only one unit of application in a monolithic architecture. In a microservices architecture, we can see three different services.
Advantages
Increases scalability
More flexibility
Modular architecture
Ease of introducing new features
More reliable and robust structure
Challenges
Cost management
Network latency and load balancing
Complexity at the end-to-end testing
Health Care Example
Let’s take an example
Spring Cloud
It helps us build microservices architecture with various components it provides. Spring cloud helps us manage communication, security threats, maintenance and fault tolerance with different components. Let’s see them one by one.
Spring Cloud Components
Spring Cloud Config Server
Feign Client
Service Discovery and Registry with Eureka
Spring Cloud Gateway
Resillience4j
Spring Cloud Bus
Spring Cloud -> Config Server
Config server uses the git repo to store configurations.
Ease of managing configuration of multiple microservices in a single place
Configurations can be managed with the application.yaml / properties files within a git repo
Each microservice can connect to the config server and get the required configurations
Spring Cloud -> Feign Client
Microservices need to communicate with each other to exchange information. Feign client can be used for that learn more
#microservices#cloud blogs#spring#Healthcare#healthcare software development company#Healthcare interoperability#healthcare solutions
0 notes
Text
Spring Boot Start Tomcat

Unable to start embedded tomcat spring-boot 2
Spring Boot Doesn't Start Tomcat
Spring Boot Don't Start Tomcat
Spring Boot Not Start Tomcat
Spring boot: Unable to start embedded Tomcat servlet container , Try to change the port number in application.yaml (or application.properties ) to something else. In my condition when I got an exception ' Unable to start embedded Tomcat servlet container', I opened the debug mode of spring boot by adding debug=true in the application.properties,
Chase online lets you manage your Chase accounts, view statements, monitor activity, pay bills or transfer funds securely from one central place. To learn more, visit the Banking Education Center. For questions or concerns, please contact Chase customer service or let us know about Chase. Make purchases with your debit card, and bank from almost anywhere with your phone, tablet or computer and at our 16,000 ATMs and more than 4,700 branches nationwide. For questions or concerns, please contact Chase customer service or let us know about Chase complaints and feedback. Sports & Entertainment. Phone number for chase debit card.
SpringBoot - Unable to Start embedded TomCat, Probably you can avoid this by changing your project sdk. In my project I initially used java-11-openjdk-amd64 as my JDK and had the same issue. Unable to start spring boot 2 embedded tomcat with trust store #21014. ajitdas91 opened this issue Apr 19, 2020 · 2 comments Labels. for: stackoverflow. Comments.
Your system need to have the following minimum requirements to create a Spring Boot application −. Java 7; Maven 3.2; Gradle 2.5; Spring Boot CLI. The Spring Boot CLI is a command line tool and it allows us to run the Groovy scripts. This is the easiest way to create a Spring Boot application by using the Spring Boot Command Line Interface. In this tutorial, we learned how to configure and use a Tomcat connection pool in Spring Boot. In addition, we developed a basic command line application to show how easy is to work with Spring Boot, a Tomcat connection pool, and the H2 database. As usual, all the code samples shown in this tutorial are available over on GitHub.
Unable to start embedded Tomcat · Issue #10 · spring-guides/gs , Stack trace of thread: [email protected]/jdk.internal.misc. WebServerException: Unable to start embedded Tomcat 2018-10-22 09:55:16.880 INFO 8552 --- ( main) RELEASE) at org.springframework.boot.web.embedded.tomcat. @philwebb Thanks!. Here is the background: I have spring boot 2.0 + jsp. Therefore, I need extend from SpringBootServletInitializer. Last weekend, I noticed its package has been changed from import org.springframework.boot.web.support.SpringBootServletInitializer to import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.support.SpringBootServletInitializer, which gave me the impression there might be
Unable to start embedded tomcat gradle
Unable to start embedded tomcat Spring boot, I'm working on Spring Boot Gradle application. So If you are using embedded tomcat you dont need the Tomcat dependency and 9001 for management, but when I tried to run it on Tomcat, it failed with the same exception you posted. Application run failed org.springframework.boot.web.server.WebServerException: Unable to start embedded Tomcat server my build.Gradle dependencies config as follows.
Spring 5, Embedded Tomcat 8, and Gradle, As such, when starting a new Java project, Spring is an option that must be considered. Spring vs. Spring Boot. In the past, Spring was known for Unable to start embedded container Spring Boot Application org.apache.catalina.LifecycleException: A child container failed during start 0 Not able run Spring boot application as runnable jar from command prompt
Unable to start embedded Tomcat · Issue #10 · spring-guides/gs , I simply cloned the repo and ran 'mvn spring-boot:run' on the 'eureka-service'. > (ERROR) Failed to execute goal So with the Angel.SR4 (or SR6) for cloud and running a gradle dependencies you will notice that spring-boot 1.2.x is pulled in. As described in the migration guide you have to change your build.gradle :
Caused by: org.springframework.boot.web.server.webserverexception: unable to start embedded tomcat
Spring boot: Unable to start embedded Tomcat servlet container , springframework.boot.web.server.WebServerException: Unable to start embedded Tomcat. I have gone through all of the stackoverflow and articles related to unable to start web server; nested exception is org.springframework.boot.web.server.WebServerException: Unable to start embedded Tomcat. I have gone through all of the stackoverflow and articles related to Unable to start embedded tomcat.
Unable to start embedded Tomcat org.springframework.context , jar confliction between 'starter-web' and embedded tomcat ,use the following instead. <groupId>org.springframework.boot< > (ERROR) Failed to execute goal org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-maven-plugin:2.0.5.RELEASE:run (default-cli) on project eureka-service: An exception occurred while running. null: InvocationTargetException: Unable to start web server; nested exception is org.springframework.boot.web.server.WebServerException: Unable to start embedded
SpringBoot - Unable to Start embedded TomCat, Thread.run (Thread.java:844) Caused by: org.springframework.boot.web.server.WebServerException: Unable to start embedded Tomcat at @philwebb Thanks!. Here is the background: I have spring boot 2.0 + jsp. Therefore, I need extend from SpringBootServletInitializer. Last weekend, I noticed its package has been changed from import org.springframework.boot.web.support.SpringBootServletInitializer to import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.support.SpringBootServletInitializer, which gave me the impression there might be
Unable to start embedded tomcat eureka
unable to start embedded Tomcat when running Eureka Server , unable to start embedded Tomcat when running Eureka Server. For now I just want to run the server on localhost and later I want to add a sample Microservice that registers to it. The Problem is that I get an error when trying to start Eureka Server. I develop in Eclipse with Spring and Maven in an ubuntu vm. Stack Overflow Public Unable to start embedded Tomcat | Spring Boot Eureka Server WebServerException: Unable to start embedded Tomcat at org.springframework
Can't start embedded Tomcat Server when running an Eureka , Can't start embedded Tomcat Server when running an Eureka Then added @EnableEurekaServer. I'm unable to reproduce this error. Stack Overflow for Teams is a private, secure spot for you and your coworkers to find and share information. unable to start embedded Tomcat when running Eureka Chase chargeback phone number.
Unable to start embedded Tomcat · Issue #10 · spring-guides/gs , Working on a song book pdf. I simply cloned the repo and ran 'mvn spring-boot:run' on the 'eureka-service'. > (ERROR) Failed to execute goal > (ERROR) Failed to execute goal org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-maven-plugin:2.0.5.RELEASE:run (default-cli) on project eureka-service: An exception occurred while running. null: InvocationTargetException: Unable to start web server; nested exception is org.springframework.boot.web.server.WebServerException: Unable to start embedded
Spring boot tomcat admin console
Can I enable the tomcat manager app for Spring Boot's embedded , Does the embedded tomcat 7 used by Spring Boot contain a tomcat manager app. No, it doesn't and I'm not really sure that it makes sense to Does the embedded tomcat 7 used by Spring Boot contain a tomcat manager app No, it doesn't and I'm not really sure that it makes sense to try to add it. A primary function of the manager app is to allow you to start and stop individual applications without stopping the container and to deploy and undeploy individual applications.
Deploy a Spring Boot Application into Tomcat, Create a Spring Boot 2.1 app with Java 11 and deploy into Tomcat 9. Often you need console access to the server from which you pull the latest When you click on the Manager App button the user details you entered In this chapter, you are going to learn how to create a WAR file and deploy the Spring Boot application in Tomcat web server. Spring Boot Servlet Initializer. The traditional way of deployment is making the Spring Boot Application @SpringBootApplication class extend the SpringBootServletInitializer class. Spring Boot Servlet Initializer class file allows you to configure the application when it is launched by using Servlet Container.

How to Configure Spring Boot Tomcat, Learn how to reconfigure the embedded Tomcat server in Spring Boot for some common use cases. Spring Boot Configure Tomcat SSL over HTTPS. by MemoryNotFound · October 31, 2017
Standardengine(tomcat).standardhost(localhost).tomcatembeddedcontext() failed to start
Failed to start component (StandardEngine(Tomcat).StandardHost , Failed to start component (StandardEngine(Tomcat).StandardHost(localhost). TomcatEmbeddedContext()) at java.util.concurrent. void main(String() args) ( SpringApplication.run(SpringBootApplication.class, args); ) ) //ServletInitializer.java Stack Overflow for Teams is a private, secure spot for you and your coworkers to find and share information. Learn more Failed to start component (StandardEngine(Tomcat).StandardHost(localhost).TomcatEmbeddedContext())
Unable to start embedded Tomcat · Issue #10 · spring-guides/gs , StandardHost(localhost).TomcatEmbeddedContext() failed to start -> (Help 1). I tried changing the StandardEngine : Starting Servlet Engine: Apache Tomcat/8.5.34 2018-10-22 09:55:15.309 INFO 8552 --- (ost-startStop-1) o.a.catalina.core. Spring boot built Failed, Failed to start component (StandardEngine(Tomcat).StandardHost(localhost).StandardContext()) Ask Question Asked 3 years, 5 months ago
Spring boot test fails to start tomcat due to some sleuth and spring , LifecycleException: Failed to start component (StandardEngine(Tomcat). TomcatEmbeddedContext()) at org.apache.catalina.util. StandardHost(localhost)) at java.util.concurrent. #param args args */ public static void main(String() args) ( // BasicConfigurator.configure(); Set up a simple configuration that logs on the all i found solution for whatever you all get the exception like. org.apache.catalina.LifecycleException: Failed to start component (StandardEngine(Catalina).StandardHost(localhost).StandardContext()). the problem with bulid path of the jars. To over come this problem. place all jars in 'WebContent/lib' whatever you need to in your project.
Unable to start embedded tomcat java 11
SpringBoot - Unable to Start embedded TomCat, Go to project structure -> Project -> Project SDK and change the java version. I hope it helps. A 'good' pom would have 'spring-boot-starter-web' (for convenience) or else all the dependencies included in the starter listed individually. Just check that you have them. Build artifacts, debug, and deploy to major application servers in the cloud. Apache Tomcat, WildFly, Payara Server, Docker and others.
Spring boot: Unable to start embedded Tomcat servlet container , You need to add the tomcat dependency in your pom <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId> </dependency> and then rerun the code ,and it told me that java.lang. Chids 2,066○1111 silver badges○2020 bronze badges. unable to start web server; nested exception is org.springframework.boot.web.server.WebServerException: Unable to start embedded Tomcat. I have gone through all of the stackoverflow and articles related to Unable to start embedded tomcat.
Unable to start embedded Tomcat · Issue #10 · spring-guides/gs , ApplicationContextException: Unable to start embedded container; nested exception is onRefresh(EmbeddedWebApplicationContext.java:140) have included spring-boot-starter-web and spring-boot-starter-tomcat dependencies in your pom.xml 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. <?xml version='1.0' encoding='UTF-8'?>. (ERROR) Failed to execute goal org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-maven-plugin:2.0.5.RELEASE:run (default-cli) on project eureka-service: An exception occurred while running. null: InvocationTargetException: Unable to start web server; nested exception is org.springframework.boot.web.server.WebServerException: Unable to start embedded Tomcat
Unable to start web server spring-boot
ApplicationContextException: Unable to start , Case 1: @SpringBootApplication annotation missing in your spring boot starter class. Case 2: For non web application, disable web application Spring Boot jar Unable to start web server due to missing ServletWebServerFactory bean Hot Network Questions Did Trump order tear gas to be used on protesters to clear a pathway to a church for a photoshot?
4K 8MP Motorized Varifocal PoE Bullet Outdoor Security Camera with Audio, SD Slot, 2.8-12mm 4X. Poe camera viewer windows 10. What's Power over Ethernet (PoE)? PoE stands for Power over Ethernet, it's a technology that. Blue Iris (Security and Webcam Software) Blue Iris is a CCTV video security program that gives you. SV3C TECHNOLOGY LIMITED was found in 2013, which was specialized in intelligent and security home devices. It is a Hi-tech company which united with R&D, manufacture and marketing. The main products are professional POE IP Camera, Wireless IP Camera, household DIY Camera, accessories etc.
Spring Boot Doesn't Start Tomcat
Ip cam viewer lite for pc. Exception starting up SpringBootApplication, Below is the stack trace in starting up a SpringBoot application. ApplicationContextException: Unable to start web server; nested exception is I have the following Main code in my SpringBoot application ```java package com.oc.springsample; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; public
Spring Boot Don't Start Tomcat
Fixing Spring Boot error 'Unable to start , I was building a new Spring WebFlux application with Spring Boot. ApplicationContextException: Unable to start web server; nested The solution is easy once the root cause is identified. We can either: Update Maven dependencies to exclude spring-webmvc, or; Set the web application type to WebApplicationType.REACTIVE explicitly, as shown below.
Spring Boot Not Start Tomcat
More Articles

0 notes
Text
Spring Cloud Eureka and Hystrix Circuit Breaker using Microservices
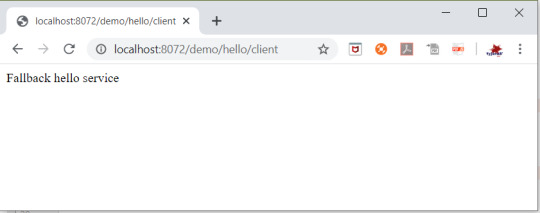
In this tutorial, we will use a microservice application created in previous post ( Microservices Example using Spring Cloud Eureka ) and add circuit breaker pattern using Hystrix Spring library in java. Using Hystrix in your application helps to add defensive mechanism and makes applications more resilient and fault tolerant. Tools Required – - Java 8 - IntelliJ IDE We have created three different applications as below – - Eureka Service– This Service will register every microservice and then the client microservice will look up the Eureka server to get a dependent microservice to get the job done.This Eureka Server is owned by Netflix and in this, Spring Cloud offers a declarative way to register and invoke services by using Java annotation. - demo-server – This service will return a simple hello message. - demo-client – It is similar to the standalone client service created in Bootiful Development with Spring Boot. It will consume the APIs provided by demo-server through Eureka Service . Hystrix Documentation - https://github.com/Netflix/Hystrix/wiki Microservices are deployed on Cloud . As cloud provides a distributed environment , there are more chances that some of your services may be down at some point of time. You can have several micro-services in your application which are dependent on each other. So one service can call to other service. If destination service is down then source will get an exception in normal scenario. But with the help of Hystrix annotations , you can add fallback mechanism and handle the exception in services. Thus it makes your service more fault tolerant, resilient . You need to add below dependency in your demo-client service application to enable Hystrix circuit breaker pattern - org.springframework.cloud spring-cloud-starter-hystrix 1.2.5.RELEASE We just have to add few annotations to handle fallback or break the service call in case your destination service(demo-server) is down. We need to change main class to enable Hystrix circuit breaker - package com.myjavablog.democlient; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.cloud.client.circuitbreaker.EnableCircuitBreaker; import org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.EnableDiscoveryClient; import org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer.LoadBalanced; import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.hystrix.EnableHystrix; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate; @EnableCircuitBreaker @EnableDiscoveryClient @SpringBootApplication public class DemoClientApplication { public static void main(String args) { SpringApplication.run(DemoClientApplication.class, args); } } @Configuration class Config{ @Bean @LoadBalanced public RestTemplate restTemplate(){ return new RestTemplate(); } } Also we need to change controller class to add fallback mehod as below - package com.myjavablog.democlient; import com.netflix.hystrix.contrib.javanica.annotation.HystrixCommand; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate; @RestController @RequestMapping("/demo/hello/client") public class TestController { @Autowired public RestTemplate restTemplate; @GetMapping @HystrixCommand(fallbackMethod = "handleFallback") public String test(){ String url = "http://demo-server/demo/hello/server"; return restTemplate.getForObject(url, String.class); } public String handleFallback(){ return "Fallback hello service"; } } By default hystrix has timeout of 1 second for every request. So we need to disable timeout by setting below property in application.properties file - hystrix.command.default.execution.timeout.enabled=false So now i am intentionally stopping demo-server microservice and then we will make call to api to see fallback is working properly .You can see demo-server is not registered with Eureka below -
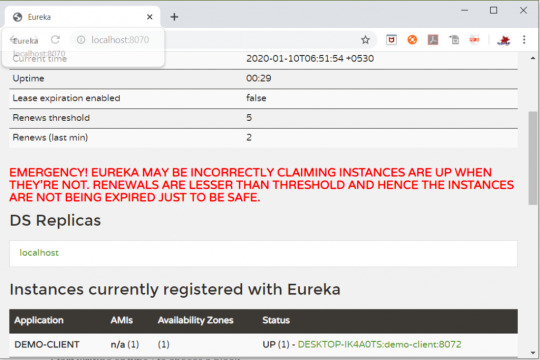
So now when you call the service ,it should show you a fallback message as below -
Github Downlod Link: Download Read the full article
0 notes
Text
interview
two way ssl spring - Google Search
www.google.com
multiple constructors chaining - Google Search
www.google.com
create singleton class in java when - Google Search
www.google.com
java memory leak - Google Search
www.google.com
PM
microservices refer application properties - Google Search
www.google.com
4:19 PM
spring boot - Common application property file for multiple microservice - Stack Overflow
stackoverflow.com
4:18 PM
Microservices: Access Properties From Spring Cloud Config Server - DZone Microservices
microservices eureka client discovery - Google Search
microservices callable - Google Search
www.google.com
4:15 PM
Building Microservices with Spring Boot
server side load balancing microservices - Google Search4:15 PM
Getting Started | Service Registration and Discovery
server side load balancing microservices - Google Search
www.google.com
4:14 PM
Server-side service discovery pattern
microservices.io
4:13 PM
server load balancing - Google Search
Hystrix Circuit Breaker Pattern - Spring Cloud - HowToDoInJava
howtodoinjava.com
4:12 PM
circuit breaker microservices spring - Google Search
www.google.com
4:11 PM
0 notes
Video
youtube
Create Spring Cloud Configuration Server for Microservices | Setup Eurek...
Full Video Link https://youtu.be/Exoy4ZNAO9Y
Hello friends, new #video on #springcloud #configserver #eureka #servicediscovery setup is published on #codeonedigest #youtube channel.
@java #java #aws #awscloud @awscloud @AWSCloudIndia #salesforce #Cloud #CloudComputing @YouTube #youtube #azure #msazure #configserver #configserverspringboot #configserverinmicroservices #configserverinspringbootmicroservices #configserverinspringbootexample #configserverspringbootgithub #configserverfirewall #configserverspringcloud #configserverspring #configurationserver #configurationserverspringboot #configurationserverdns #configurationserverinmicroservices #configurationserverstepbystep #eurekaservice #eurekaservicediscovery #eurekaserviceregistryspringboot #eurekaservicediscoveryexamplespringboot #eurekaserviceregistry #eurekaserviceinmicroservices #eurekaservicediscoveryexample #eurekaservicediscoveryspringboot #eurekaserviceregistryexample #eurekaservicespringboot
#youtube#spring cloud#spring cloud config#spring cloud config server#spring config server#configuration server#config service#config server#eureka service discovery#service discovery#service registry#netflix eureka#eureka service registry#service discovery pattern#microservices#microservice configuration server
1 note
·
View note
Link
2012年に Heroku によって提唱された「The Twelve-Factor App」は素晴らしく,アプリケーションをうまく開発し,うまく運用するための「ベストプラクティス」として知られている.2020年になった現在でもよく引用されていると思う.日本語訳もある. 12factor.net Beyond the Twelve-Factor App とは? クラウド化が進むなど,提唱された2012年と比較すると技術的な変化もあり,今までの「The Twelve-Factor App」で宣言されていた観点以外にも必要な観点やベストプラクティスがあるのでは?という意見もある.そこで,2016年に Pivotal は「Beyond the Twelve-Factor App」を提唱した.The Twelve-Factor App にあった「12項目をアップデート」し,新しく「3項目を追加」した.「計15項目」となる. 今回は Beyond the Twelve-Factor App を読んで,興味を持った箇所を中心にメモ程度に残しておく(正確に言うと,もっと前に読み終わっていたけど,記事を書いていなかった).オリジナルの The Twelve-Factor App よりは具体的に書かれてい���けど,それでもまだ抽象的なところもある.とは言え,議論の種になって良いと思う.以下のサイトにメールアドレスを登録すると,無料で PDF をダウンロードできる. content.pivotal.io The Twelve-Factor App と Beyond the Twelve-Factor App まず,The Twelve-Factor App と Beyond the Twelve-Factor App に宣言されている項目を一覧しておく.Beyond the Twelve-Factor App には正式な日本語訳がなく,個人的に載せているため,参考程度にしてもらればと!Beyond the Twelve-Factor App で新しく追加された項目は「2. API first」と「14. Telemetry」と「15. Authentication and authorization」となる. The Twelve-Factor App Codebase(コードベース) Dependencies(依存関係) Config(設定) Backing services(バックエンドサービス) Build, release, run(ビルド、リリース、実行) Processes(プロセス) Port binding(ポートバインディング) Concurrency(並行性) Disposability(廃棄容易性) Dev/prod parity(開発/本番一致) Logs(ログ) Admin processes(管理プロセス) Beyond the Twelve-Factor App One codebase, one application(1 コードベース、1 アプリケーション) API first(API ファースト) Dependency management(依存関係管理) Design, build, release, and run(デザイン、ビルド、リリース、実行) Configuration, credentials, and code(設定、機密情報、コード) Logs(ログ) Disposability(廃棄容易性) Backing services(バックエンドサービス) Environment parity(環境一致) Administrative processes(管理プロセス) Port binding(ポートバインディング) Stateless processes(ステートレスプロセス) Concurrency(並行性) Telemetry(テレメトリ) Authentication and authorization(認証/認可) 1. One codebase, one application The Twelve-Factor App では「Codebase」という項目だったけど,Beyond the Twelve-Factor App では「One codebase, one application」という項目になり,より具体的な名前に変わった.とは言え,内容は「コードベースとアプリケーションを 1対1 にすること」となり,大きく変わっていないと思う.なお,リポジトリ構成で議論になることもある「モノレポ」に関しては明確な言及はなかった. ただし「キューを使った非同期アプリケーション」を題材とし,「メインアプリケーション」と「密結合ワーカー」が同じリポジトリルートを共有する場合は項目に違反していると書いてあったり,1個の EAR ファイルを複数の起動スクリプトによって制御している場合も,複数のアプリケーションを管理していることになり項目に違反していると書いてある.さらに「コンウェイの法則」に対する言及もあり,より具体的に解説されている点は Beyond the Twelve-Factor App の素晴らしい点だと思う. 2. API first 次に Beyond the Twelve-Factor App で追加された項目「API first」は,今でこそ「言わずもがな」な印象を受けるけど,確かに The Twelve-Factor App には明確に言及されていなかった.具体的には,開発中にうまくサービス間を結合できなかったりすると悪夢だから,API を「ファーストクラス」と考えることにより,干渉せず「公開されたインタフェース」を中心に開発を進められるようになると書いてある. また,サービスの例としては API Blueprint と Apiary(前職で使ってた)を使ってモックサーバを立てるプラクティスも載っていた.最近だと Swagger や OpenAPI って書いておくと良さそう. swagger.io 4. Design, build, release, and run The Twelve-Factor App では「Build, release, run」という項目だったけど,Beyond the Twelve-Factor App では「Design, build, release, and run」という項目になり,「Design」が追加された. 意味としては「設計」だけど,本書を読むと「リリースする小さな機能の設計」と書いてあったり「アプリケーションの依存関係」と書いてあったり「うまく作られた CI/CD パイプラインを使えば Design から Run まで数分で終わる」と書いてあったりする.正直言って「要件を整理する話」なのか「Design Doc のように技術仕様を整理する話」なのか「ライブラリ依存を整理する話」なのか,ハッキリと理解できなかった.ライブラリ依存だとすると「Dependency management」と重複する.もう少し具体例を解説している情報などを探しておく必要がありそう. 5. Configuration, credentials, and code The Twelve-Factor App では「Config」という項目だったけど,Beyond the Twelve-Factor App では「Configuration, credentials, and code」という項目になり,より具体的な名前に変わった. 例えば「接続する API のエンドポイント情報」だったり「データベースの接続情報」だったり,環境依存な設定を環境変数に入れておくというプラクティスはもともと言及されていた.ただし,言い換えると今までは「環境変数に入れておく」以外に言及されていなかった. Beyond the Twelve-Factor App では,環境変数を外部化 (Externalizing Configuration) する必要性と,可能なら外部サービスに入れると書いてあった.サービスの例としては Spring Cloud Config Server が載ってて,Git と連携できる Config Server は良さそう.最近だと AWS Systems Manager Parameter Store だったり,HashiCorp Vault だったり,選択肢は多いと思う. cloud.spring.io 8. Backing services 「Backing services」は The Twelve-Factor App から変わってないけど,内容はとても充実していた.「バックエンドサービス」とは何か?を定義しつつ,例えば「クラウドだとファイルシステムを一時的なリソースとして考える」など,クラウド化により活発に議論されるようになった観点も言及されていた.さらに「サーキットブレーカー」に対する言及もあり,誤ったバックエンドサービスに対するアクセスを遮断する必要性も書かれていて良かった. martinfowler.com 14. Telemetry Beyond the Twelve-Factor App で追加された項目「Telemetry」は,意味としては「モニタリング全般」と言える.クラウド時代に必要なテレメトリとして「3種類」紹介されていた. APM (Application Performance Monitoring) ドメイン情報 稼働状況/ログ 「ドメイン情報」の具体的な例が載っていて,例えば「秒間 HTTP リクエスト平均数」よりも「直近 20min に iPad 経由で販売された件数」の方がビジネスインパクトがあるよね?という内容だった.稼働状況に関しては,例えば「外形監視」など,ユーザー目線でモニタリングをする重要性が書かれている.また,クラウド時代の「監視戦略」として,例えば「インスタンスが 100台 までスケールしたら,単純計算でログも 100倍 になる可能性がある」など,ログの���存量まで考えることもテレメトリを正しく行うために重要であると書かれていた. kakakakakku.hatenablog.com 15. Authentication and authorization 最後も Beyond the Twelve-Factor App で追加された項目で,認証と認可など,セキュリティ面にフォーカスした「Authentication and authorization」となる.内容としては,全てのエンドポイントを RBAC (Role-Based Access Control) のような仕組みで保護すると書いてある.ようするに,クライアント側が必要な認可を持っているか確認できるようにすることを意味している. 実現する技術の例としては OAuth2 や OpenID Connect や SSO (Single Sign-On) が載っていた.最近だと Amazon Cognito だったり,認証認可 SaaS の Auth0 だったり,選択肢は多いと思う. auth0.com まとめ 2012年に提唱された「The Twelve-Factor App」と,2016年に提唱された「Beyond the Twelve-Factor App」を読んで,興味を持った箇所を整理した.多分意図的に抽象的に書かれているところもあり,そのあたりは議論をして実践的な解釈を深めていければと思う.興味があったら読んでみると良いのではないでしょうか! content.pivotal.io
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Text
How do you setup TEST/DEV environments for big data batch jobs? (Control-M / Hadoop / Spark)
I'm working with a Hadoop cluster of about ~100 machines and manage a fairly complex pipeline of jobs that are scheduled in control-m. There are about 50-ish jobs that are co-linked to each other as dependencies in order to run. Some of the data sets we read in are 20 billion records. We don't have a proper test or dev environment for any of this stuff because we lack the resources to replicate all of our data. I'm looking for some advice on how we approach setting something like another environment up.
One idea I was looking into was integrating Spring Cloud Config Server with Spark and having the ability to simply swap what config file I wish to use when ordering up a job in control-m. The only problem I've run into with this is that it causes jobs that may be co-linked to trigger early. Ie I could run jobA using TEST configuration, but this causes jobB to run with PROD config because the condition was met. Unfortunately there is no way around this without using control-m jobs as code and their config transformer.
Another option was using the control-m api to export the jobs as code and apply a transform file that would transform all of the conditions so that they don't collide with the production ones. I could setup a Jenkins pipeline that would promote the code to control-m for each build and that would help keep things in sync. The only issue I have with this is that we create dependencies into control-m for our stuff to work, and future plans seem to point to us moving away from control-m and into AWS.
Third option was combining both the jobs as code in control-m with spring cloud config so isolate configuration files from the job code itself.
This still doesn't solve the issue of how we could possibly replicate our data - some of our jobs take third party data as inputs, and replicating another flow of jobs for TEST might cause a race condition where multiple jobs are trying to read from the same input files at the same time. I don't know how complex or bad the scheduling conflicts can get.
Anyone have any experience in this area and could provide some pointers? Maybe some other tech alternative?
submitted by /u/Igneous001 [link] [comments] from Software Development - methodologies, techniques, and tools. Covering Agile, RUP, Waterfall + more! https://ift.tt/2L3Cm4d via IFTTT
0 notes