#continental drift
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Fossil Friday: Cynognathus

Cynognathus crateronotus has been a pretty big deal in paleontology since the late 1880's but was brought to the public's attention by this gem:

(If you are somehow not aware, this is BBC's 1999 Walking with Dinosaurs. If you haven't seen it, go watch it now. It's fantastic).
While the show depicted Cynognathus living alongside Postosuchus and Coelophysis, it actually hasn't been found in North America where the pseudosuchian and dinosaur have been found. Those two are also Late Triassic animals while Cynognathus is a middle Triassic animal.

Cynognathus was first discovered by Harry Seeley in southern Africa in 1889. He also named the genus and type species. The name Cynognathus means "dog jaw" in reference to the very mammalian -looking jaw.

Cynognathus was part of the cynodont family of early therapsids, the clade which mammals belong to. It had many characteristics in common with mammals including differentiated teeth,
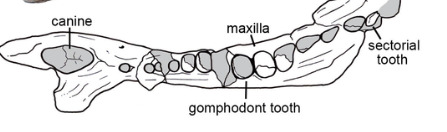
a secondary palate which indicates it could breathe and swallow simultaneously, a lack of belly ribs which might indicate the presence of a diaphragm and concentrations of pits and canals on the snout which could support whiskers.

However, it still retained some primitive features like multiple lower jaw bones, and semi-sprawled legs (however, recent studies of living mammals indicate that only certain groups of mammals have the upright posture we've come to associate with mammals).

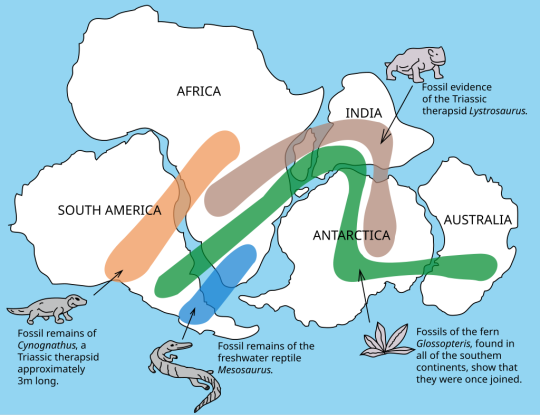
Cynognathus was one of the fossils used as a piece of evidence for continental drift by Alfred Wegener as it has been found in southern Africa, Argentina, and Antarctica.

Tune in Sunday at 6pm for live stream discussion with colleagues as we talk about a large sauropodomorph from China. We will also answer a handful of questions at the end, some come prepared and we may choose you! Fossilize you later!
#paleontology#fossils#fun facts#geology#science education#mammals#cynodonts#cynognathus#continental drift#pangaea
36 notes
·
View notes
Text
The discovery of continental drift, colorized:

#yeah callumerica and raylafrica change positions between scenes#but it was that or have them change identities#the dragon prince#the dragon prince memes#alfred wegener#geology memes#continental drift#more people were involved and I could probably give Bait a name as well but I didn't want to clutter the gif
328 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
Had a little breakthrough with my Blender mapmaking process, and got so excited I made a video about it. I hope some of you will find this useful as a resource but ultimately I'm just overjoyed at how easy I've just made things for myself.
Enjoy!
#mapmaking#imaginary maps#plate tectonics#continental drift#Blender#Blender panoramic camera#digital sculpture#video#demonstration of process#artistic resource#Youtube link#Christopher Maida Artwork#Youtube
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
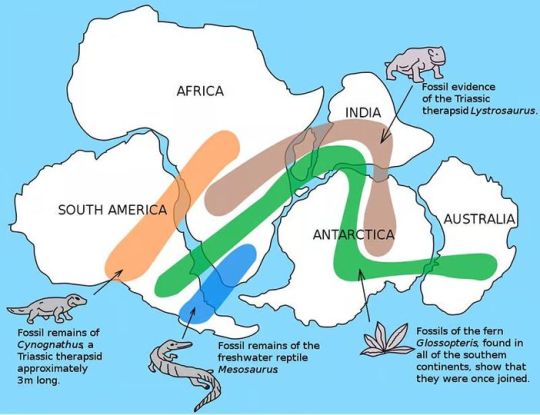
Continental drift fossil evidence.
As noted by Snider-Pellegrini and Alfred Wegener, the locations of certain fossil plants and animals on present-day, widely separated continents would form definite patterns (shown by the bands of colors), if the continents are rejoined.
via: United States Geological Survey (USGS)
#synapsid#cynognathus#lystrosaurus#mesosaurus#maps#fossils#prehistoric#earth science#science#paleontology#animals#nature#evolution#geology#continental drift#pangea
120 notes
·
View notes
Text

throwback to that time me and my roomies watched all of the ice age movies, the fourth one was undeniably the worst but at least we got another boringly designed female character with softer less interesting features. gif i made unrelated
#redesign#ice age#ice age shira#sabertooth#gif#ice age 4#continental drift#pirate#character design#big cat
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
I like my random thoughts.
Especially ones to do with characters!!! Recently, I’ve gotten into hollow knight and a random thought about Hornet appeared in my head. For some reason, I want to blame Hornet for Continental drift. It just kinda fits.
#continental drift#hollow knight hornet#hornet#hk hornet#hollow knight headcanon#random thoughts#3 am thoughts
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
50 Million Years of Climate Change with Christina!
Have you ever thought about how dinosaurs lived on a warm, swampy Earth and how we live on one that’s cold enough to keep pretty much the entirety of Greenland and Antarctica buried under kilometers-thick sheets of solid ice and wondered, hmm, how did we get from there to here? The short answer is that it took 50 million years of declining atmospheric carbon dioxide concentrations and dropping temperatures, not to mention building an ice sheet or two. For the longer story of the last 50 million years of climate change, including some of the reasons why, catch this episode of our podcast with Dr De La Rocha! You’ll hear about plate tectonics and continental drift, silicate weathering, carbonate sedimentation, and the spectacular effects the growth of Earth’s ice sheets have had on Earth’s climate. There are also lessons here for where anthropogenic global warming is going and whether or not its effects have permanently disrupted the climate system. Fun fact: the total amount of climate change between 50 million years ago and now dwarfs what we’re driving by burning fossil fuels, and yet, what we’re doing is more terrifying, in that it’s unfolding millions of times faster.
Bonus content: If you want to see sketches and plots of the data discussed in this episode, you can do so here!
!!Nerd alert!!
If you're interested in the primary scientific literature on the subject, these four papers are a great place to start.
Dutkiewicz et al (2019) Sequestration and subduction of deep-sea carbonate in the global ocean since the Early Cretaceous. Geology 47:91-94.
Müller et al (2022) Evolution of Earth’s plate tectonic conveyor belt. Nature 605:629–639.
Rae et al (2021) Atmospheric CO2 over the last 66 million years from marine archives. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences 49:609-641.
Westerfeld et al (2020) An astronomically dated record of Earth’s climate and its predictability over the last 66 million years. Science 369: 1383–1387.
Connect with Christina at her blog, on Twitter, and on Mastodon
Support the show on Patreon or make a one-time donation via PayPal.
#climate change#solarpunk presents podcast#ice sheets#climate#plate tectonics#continental drift#silicate weathering#carbonate sedimentation#anthropogenic global warming#global warming#climate system#science
11 notes
·
View notes
Text


I am not immune to goofy animated movie
58 notes
·
View notes
Text
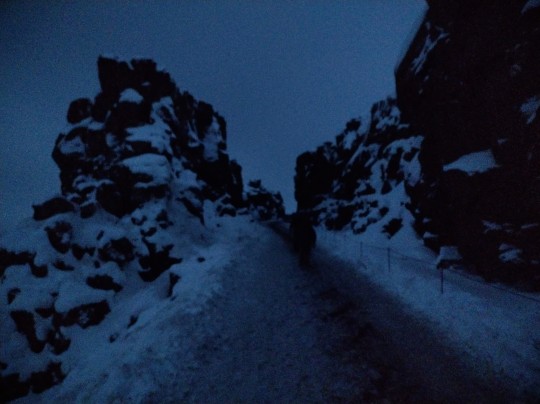



Standing between two continents.
This gap is where the North American and European tectonic plates are slowly pulling away from each other.
It's where the Vikings would meet to settle disputes.
These pictures were taken around 9/10am but it was still pitch black.
#iceland#icelandic#vikings#viking#plate tectonics#continental drift#history#geography#volcanic#nature#landscape aesthetic#icy#snowy landscape#goblincore
6 notes
·
View notes
Text

OK, tumblr I am back lol
It's been a while since I last opened this account and I posted something here.
This is the most recent poem I have written. If anyone happen to come across my account or this post, I hope you'll give it a like or a comment.
I wish to be active again in this account.
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Throwback Thursday: Continental Drift
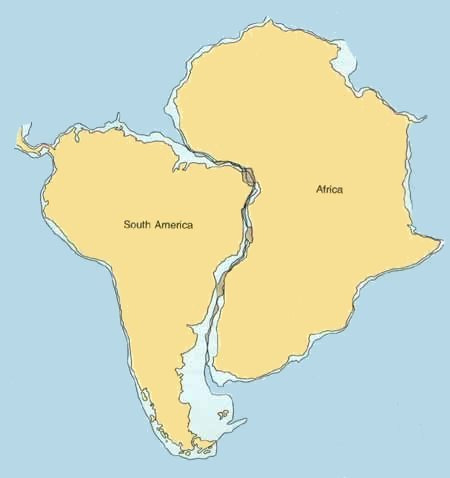
Before there was the Theory of Plate Tectonics, there was the theory of continental drift. Almost as soon as maps were invented , people noticed how certain continents looked like they could be pieced together. In 1800, Alexander von Humboldt noticed that the west coast of Africa and the east coast of South America seemed to fit together.
Antonio Snider-Pellegrini, a French geographer and geologist in the 1800s noticed that North American and European coal deposits had identical plant fossils. e said ha could be explained if the two continents had been joined. He even drew his own map:
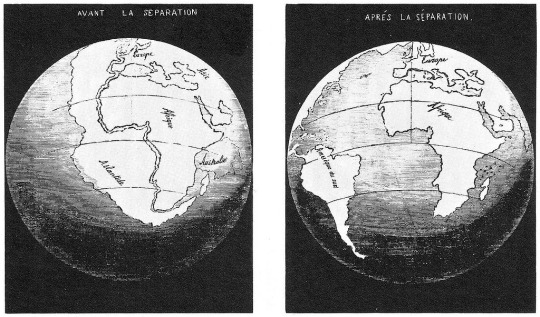
Perhaps the most well known of the geologists to bring up continental drift was Alfred Wegener. Born in 1880 in Berlin, he would become a very important figure in 20th century science.

He was primarily a climatologist but his feld work led him to some very big ideas. He too noticed how the landmasses seemed to fit together. He drew this to demonstrate the drifting pattern.
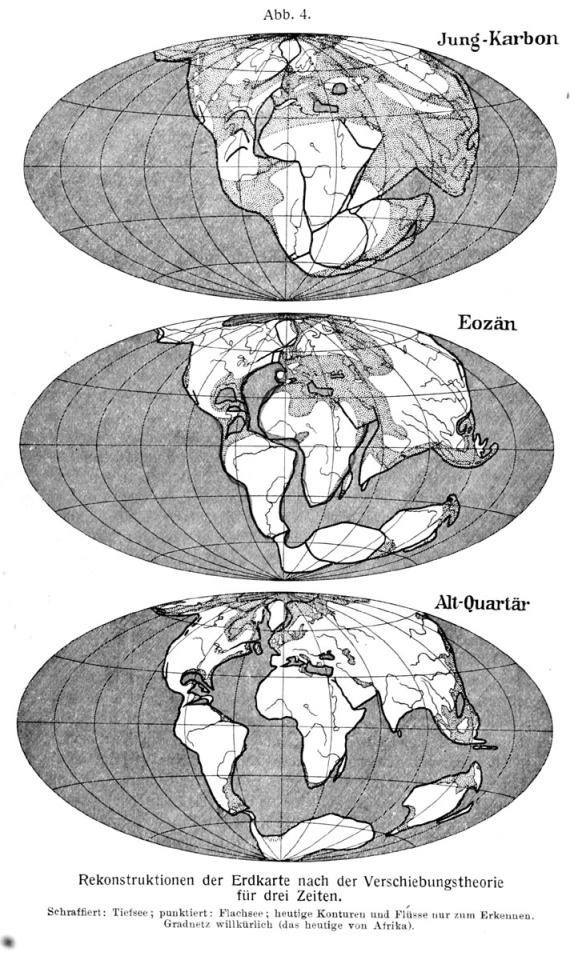
He did more than look at maps though. He analysed both sides of the Atlantic Ocean and found matching rock types, matching geologic structures and matching fossils.
The biggest issue he had in publicly advocating for this was that he had no method for how continental drift worked. Unfortunately, he would never know the mechanism as it was discovered in the 1960's long after his death.
Want to know more about Alfred Wegener and his Theory of Continental Drift? Check out my mini Geology 101 lessons on Patreon!
#fun facts#geology#science#science education#plate tectonics#fossils#rocks#rock formations#continental drift
25 notes
·
View notes
Text
Duckbill Dinosaurs evolved in North America but somehow came to North Africa with Africa being surrounded by water like Australia.
Paleontologists are trying to find out how Duckbill Dinosaurs were able to make that trip long after the continent of Pangea split up.
Thie Minqaria bata dinosaur was 250kg and 3-4 meters long small for Duckbills.
#paleontology#fossil#dinosaur#morroco#evolution#continental drift#hypothesis#science article#biology
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Keep this in mind when the establishment tells you something is impossible.
God could you imagine how mad geologists must have been to slowly watch the "hey all the continents kinda fit like puzzle pieces :)" guy get proven right
102K notes
·
View notes
