#daily sculpts
Text
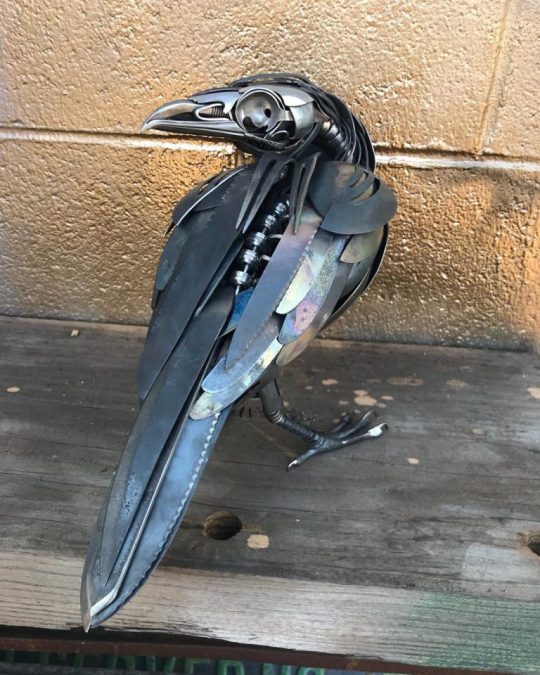

No Context Crow #169: Cutlery Crow
Sculpture by Matt Wilson.
Instagram, Website.
#crows#corvids#corvidae#birds#animals#art#sculpting#sculpture#art made from cutlery#cutlery sculpture#cutlery#metalwork#metal sculpture#metal scrap#has credit#daily crows#crow queue#No Context Crow No. 169
524 notes
·
View notes
Text
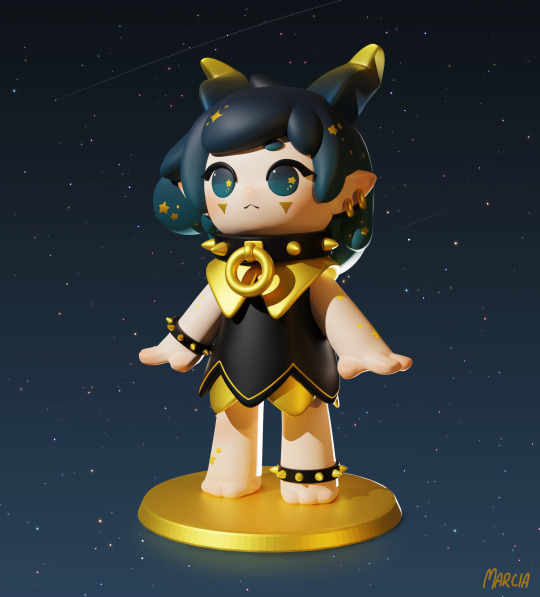
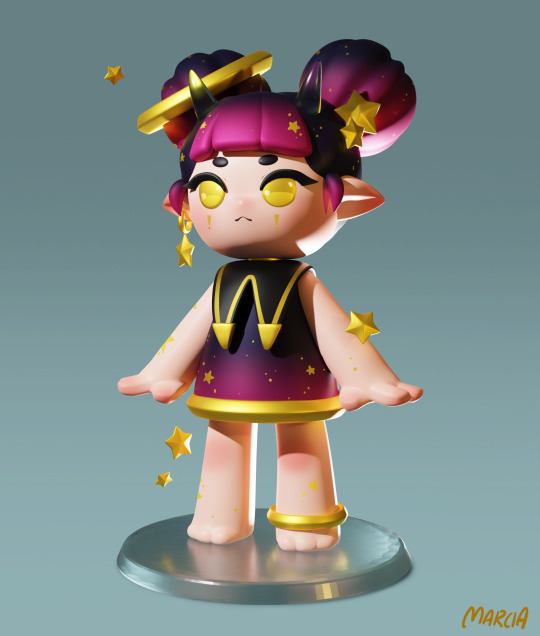
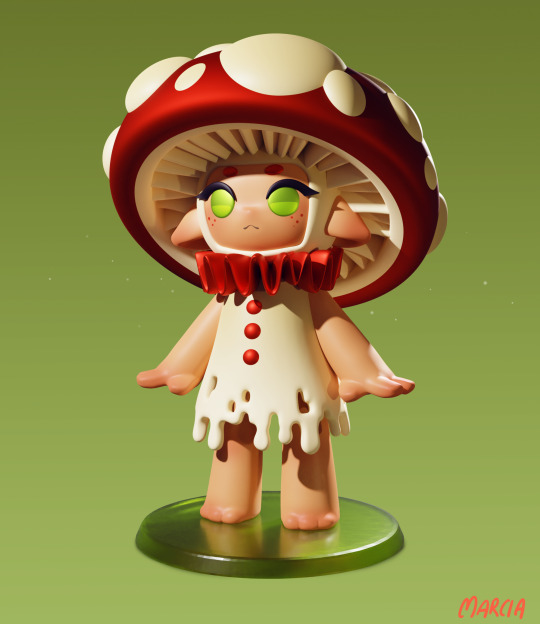



my little girlie collection is growing
#marcia in her little lady phase#just a little daily sculpt during my week off#original character#oc art#marcia#3d art
209 notes
·
View notes
Text
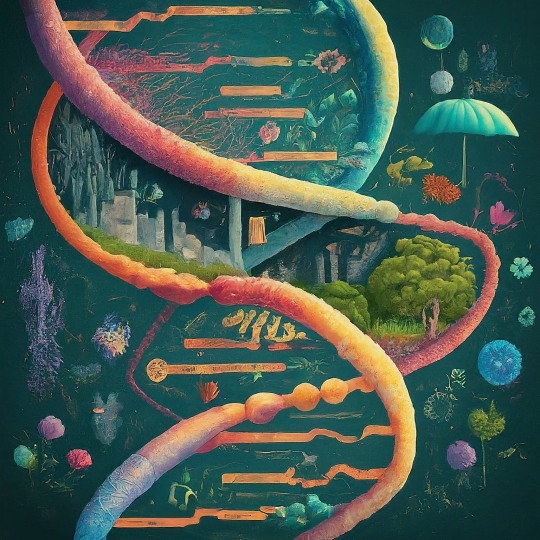

Epigenetics: A Journey Through Inheritance Beyond Genes
For centuries, scientists have been fascinated by the mysteries of heredity and how traits are passed down from generation to generation. DNA, the molecule that stores our genetic code, was once thought to be the sole determinant of our characteristics. However, a new frontier in biology, revealing a captivating layer of complexity beyond the DNA sequence itself: Epigenetics.
What is Epigenetics?
The term "epigenetics" was first coined in the 1940s by British biologist Conrad Waddington, but it wasn't until the late 20th century that its significance truly blossomed. Epigenetics, literally meaning "above genetics," refers to the study of heritable changes in gene expression that occur without alterations to the DNA sequence itself. Imagine DNA as the musical score, but epigenetics are the conductor and musicians who determine how the music is played. Through chemical modifications and adjustments to the proteins around DNA, epigenetics dictates which genes are turned on or off, influencing how cells function and ultimately shaping our health, development, and even behavior. Think of your DNA as the hardware: it contains the basic instructions for building and running your body. But epigenetics acts like the software, fine-tuning those instructions and determining which genes get turned on or off at specific times and in specific cells. These modifications, like chemical tags or changes in the packaging of DNA, don't alter the underlying code itself, but they can have a profound impact on how it's read and interpreted.
The Key Players:
DNA methylation: This process involves adding a methyl group to DNA, essentially silencing the gene it's attached to. Imagine it like putting a dimmer switch on a light bulb.
Histone modifications: Histones are proteins that package DNA, and changes in their structure can make genes more or less accessible to the cellular machinery needed for expression. Think of it like adjusting the curtains around a window - open wide for full light, slightly closed for filtered light.
Non-coding RNAs: These are molecules that don't code for proteins but can regulate gene expression in various ways. They're like the backstage crew in a play, ensuring everything runs smoothly.
The Power of Epigenetic Regulation
Epigenetic regulation plays a crucial role in various biological processes, including:
Development: During embryonic development, different cell types emerge from the same DNA blueprint by activating or silencing specific gene sets through epigenetic modifications.
Cellular differentiation: Specialized cells like muscle or nerve cells have unique functions due to differences in their active genes, controlled by epigenetic mechanisms.
Learning and memory: Epigenetic changes in brain cells are thought to be essential for learning and forming memories.
Aging: As we age, our epigenome accumulates changes that can contribute to age-related decline and disease.
Environmental influences: Diet, exercise, stress, and exposure to toxins can leave epigenetic marks on our genes, potentially impacting our health and even the health of future generations.
Epigenetics reminds us that we are not simply products of our genes. Our environment, choices, and experiences leave their mark, shaping who we are and potentially influencing our children's health. This deeper understanding of ourselves opens doors for self-awareness, empowerment, and potentially reshaping our narratives – not just as individuals, but as a species with the potential to leave a healthier legacy for generations to come.
#life science#biology#science sculpt#molecular biology#biotechnology#epigenetics#daily dose of science#dna#genetic inheritance#genetics#decoding dna#genetic code#science#double helix
106 notes
·
View notes
Text

fighting the urge to start a gameplay with this sim omg..
#1st outfit for sculpting in the studio... 2nd outfit for visiting art galleries or just like. daily errands...#the vision... the vision!#ts4 cas#simblr#i watched oshinsims' recent vid about elders and hauled my ass into cas
91 notes
·
View notes
Text
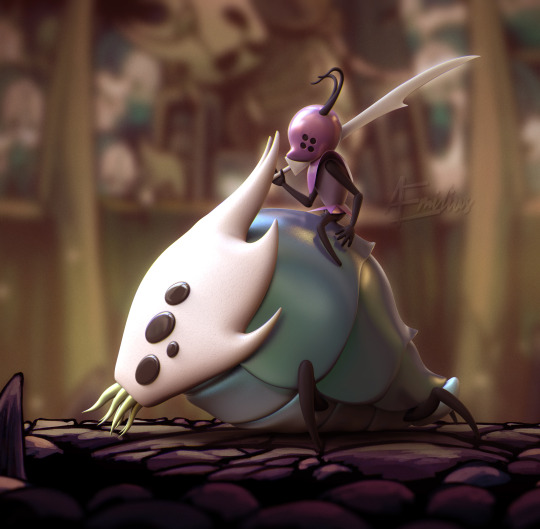

Daily Challenge 2024, Day 3. This is my 3D sculpture of the God Tamer boss from "Hollow Knight".
youtube
31 notes
·
View notes
Text

Loppu 💀
#käärijä#fanart#my art#cha cha cha#esc#daily käärijä sketchbook#i wanted to sculpt this like in clay and put him on my shelf like this#because mood
50 notes
·
View notes
Text
Day 35: iHop

#ihop is such a them date#they both get chocolate milk#they went to do dumb shit after#a clay sculpting class maybe#or a dance class#you gotta trust me#daily kimi ga shine#daily your turn to die#joe tazuna#joe yttd#joemaru#jou tazuna#jou yttd#kimi ga shine#ranmaru yttd#your turn to die#yttd ranmaru#yttd jou#yttd joe#ranmaru kageyama
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
Day 43
Hiatus project (part 2)
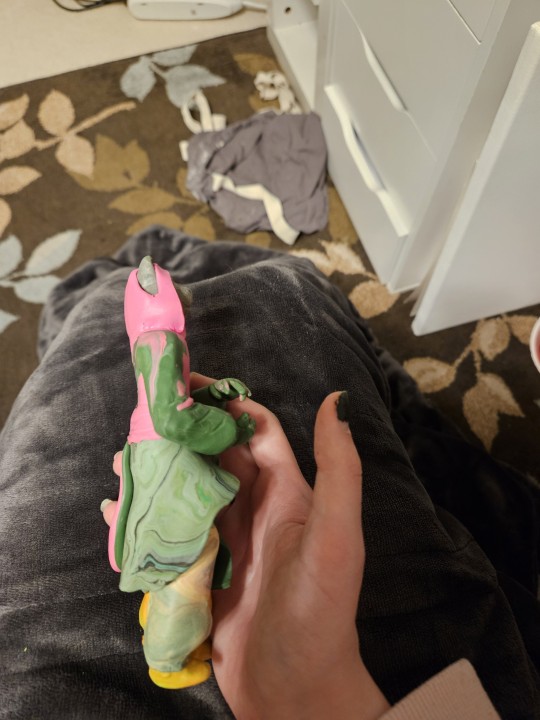
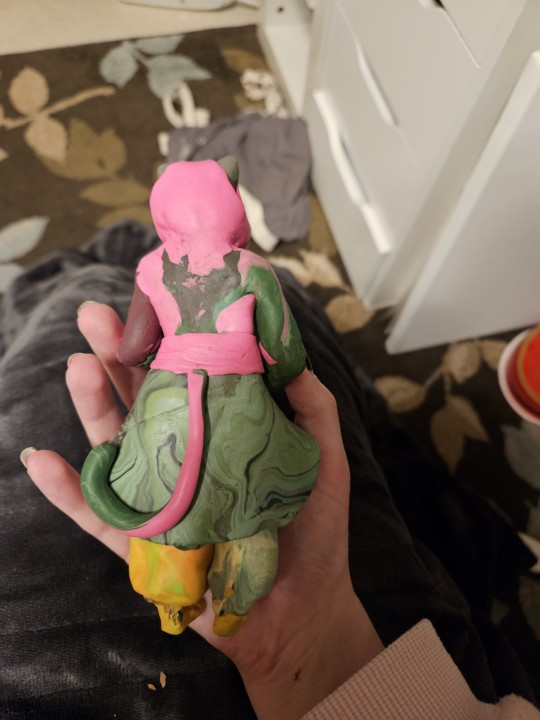



#final sculpt#legends of avantris#legends of avantris fanart#morning frost#morning frost daily#once upon a witchlight#polymer clay#polymer sculpture#heheheheh return to my roots#day 43
17 notes
·
View notes
Text
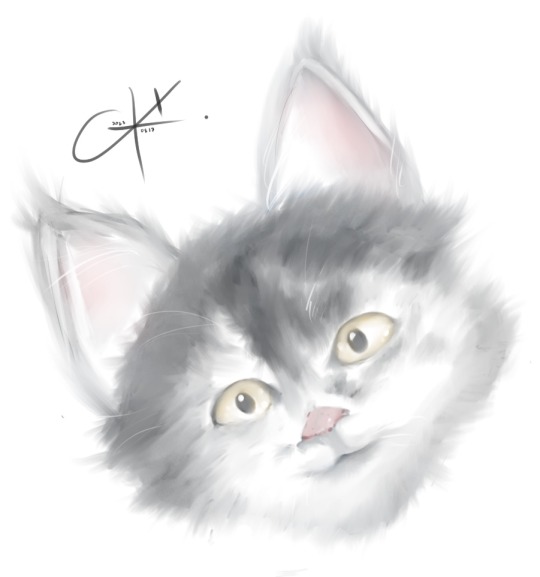

today’s doodle! lunchtime edition
something cute
i’m not good at drawing animals so i’m glad this didn’t turn out creepy lol
meow
digital art is so cool btw
i mean, i’m not new to the medium,
but now that i kind of found what style (or process?) i wanna do,
i guess it just feels more “for me” than anything hahaha
i love pencil and paper as my medium for traditional art,
but now i see that i indeed ruin the paper with my constant erasing and adding on,
erasing and adding on,
erasing and adding on.
a digital canvas is way more forgiving,
i feel more like a sculptor than whatever it is i am hahaha
(i want to try sculpting someday, yknow, even just with clay)
blablabla random rambling
#artists on tumblr#digital art#digital painting#drawing#painting#artwork#daily doodle#digital illustration#practice#journal#sculpting#idk#cat#meow#kitty#meowmeow#meeeoooowwww#i want a cat#pls#someday
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
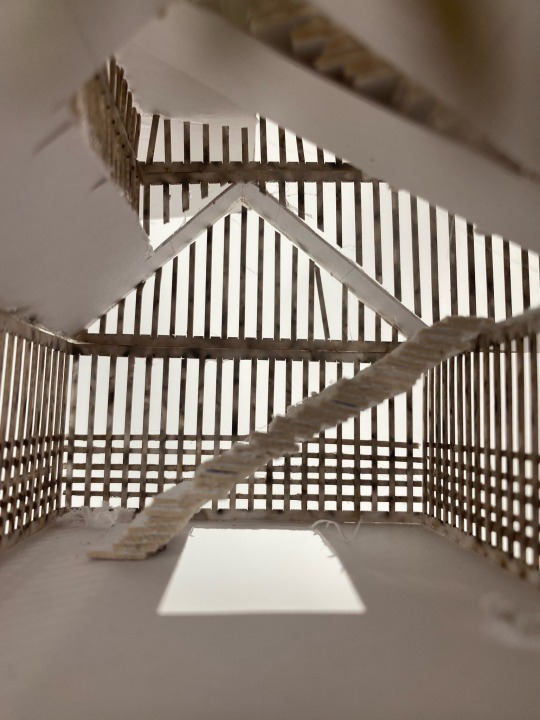
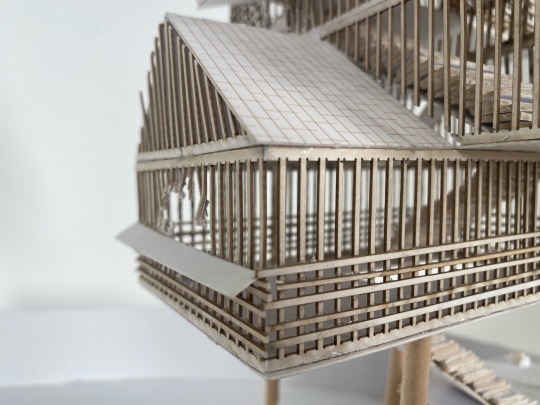
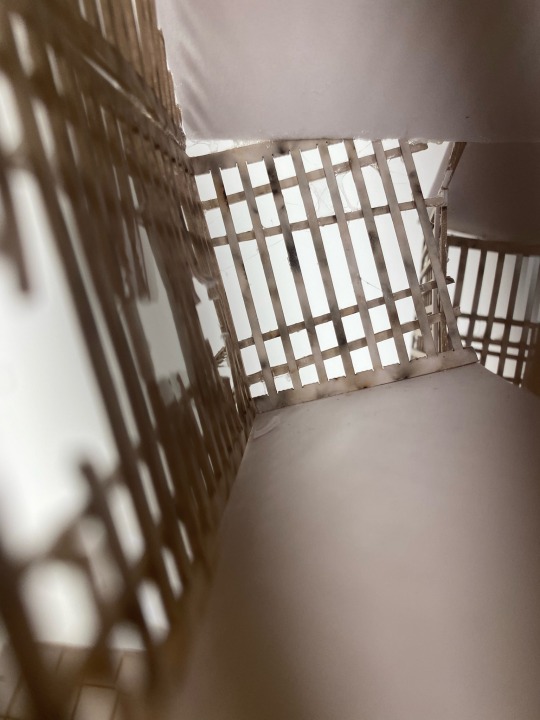
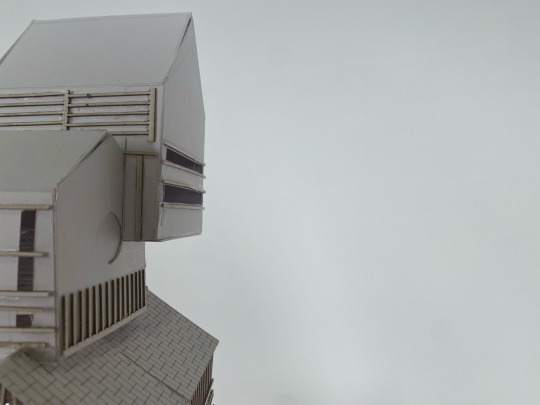
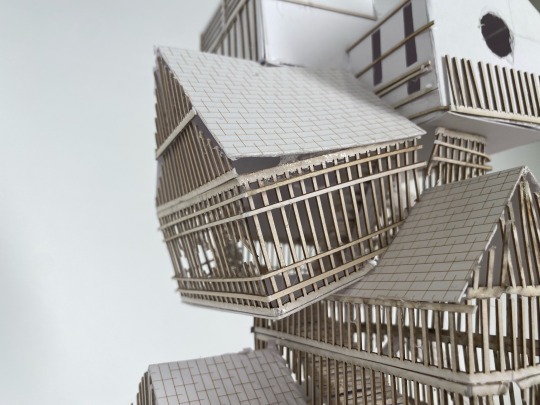






1:50 architecture model: the Wisbech hide
#art#uni student#daily art#architecture student#artists on tumblr#architecture#architecture drawing#uni#daily sketch#arty#artwork#sculpture#3d sculpting#model#architecture model#photography#aesthetic#light acadamia aesthetic
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
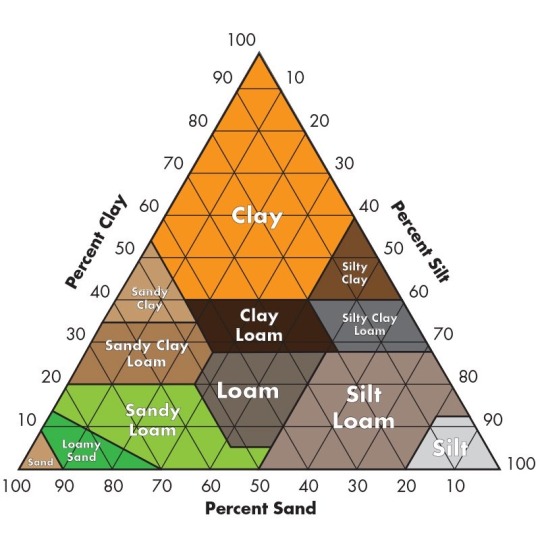
tag urself im silty clay loam 🤪🤪🤪🤪🤪
#help#help help help#help helpppp#egg magazine#loveyourself#this is what makes us girls#birds captures#kpop aesthetic#daily dino#eggpreg#meghan thee stallion#pumpkin soup#unintelligible goblin noises#clay puppington#clay sculpting#janus sanders
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
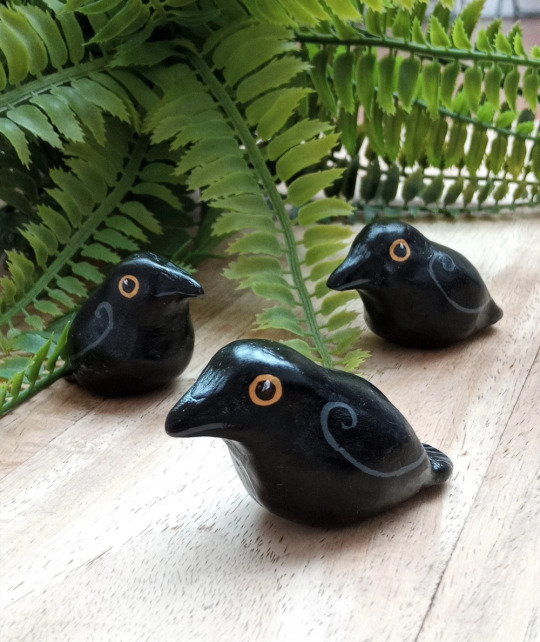

No Context Crow #337: Pocket Crow
Buy it on etsy, here!
#crows#corvids#corvidae#birds#animals#art#clay#clay art#figurine#figurines#animal figurine#clay animal#sculpture#sculpting#daily crows#crow queue#No Context Crow No. 337
148 notes
·
View notes
Text

#61
#koga oogami#oogami koga#vape#daily#edit#meme#enstars#november#tuesday#2022#koga#iwould like to sculpt him
3 notes
·
View notes
Text

A snip, a splice : Power of rDNA Technology
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), the blueprint of life, holds the secrets to the intricate workings of every living organism. But what if we could manipulate this blueprint, adding, removing, or tweaking its code? This revolutionary concept forms the core of recombinant DNA (rDNA) technology, a powerful tool that has transformed biology and medicine.
The story starts in the early 1970s with two brilliant scientists; Stanley Cohen at Stanford University and Herbert Boyer at the University of California, San Francisco. Cohen, a microbiologist, had been studying plasmids – small circular DNA molecules found in bacteria. Boyer, a biochemist, was an expert on restriction enzymes – molecular scissors that could cut DNA at specific sequences. Their collaboration proved groundbreaking. They envisioned combining these tools to create the first ever recombinant DNA molecule. Cohen provided the plasmids, which would act as vectors to carry foreign DNA into host cells. Boyer, on the other hand, used restriction enzymes to cut both the plasmid and the desired foreign DNA, allowing them to be pieced together. Through meticulous experimentation, they successfully created the first recombinant DNA molecule, forever altering the course of biology.
Cohen and Boyer's work wouldn't have been possible without the earlier discoveries of restriction enzymes. These "molecular scissors" were independently identified by three separate research groups in the 1960s. Werner Arber in Switzerland, along with Hamilton Smith and Daniel Nathans in the US, unraveled the role of restriction enzymes in bacterial defense mechanisms. These enzymes helped bacteria defend against invading viruses by cutting up their foreign DNA. Recognizing the potential of these "genetic scalpels," the groundwork was laid for their application in rDNA technology.
Here's a simplified breakdown of the rDNA process:
Isolation of DNA: The journey starts with isolating DNA from a donor organism.
Cleavage with Restriction Enzymes: Specific enzymes cut the DNA at defined sequences.
Selection of Vector: A carrier molecule (often a plasmid) is chosen to transport the recombinant DNA.
Ligation: The DNA fragments and vector are stitched together using DNA ligase, an enzyme.
Transformation: The recombinant DNA enters a host cell (usually bacteria or yeast).
Selection and Expression: The transformed cells are selected, and the gene of interest is expressed, leading to the desired protein production.
Since its inception, rDNA technology has played a pivotal role in several groundbreaking advancements. Let's take a whirlwind tour through some of the most significant moments in R-DNA history:
1978: Birth of Insulin on the Factory Floor: Scientists achieved a feat of genetic engineering by using R-DNA to produce human insulin in bacteria. This marked a turning point for diabetics, offering a readily available and more consistent source of this life-saving hormone.
1980s: Gene Wars and the Rise of GMOs: The 1980s saw the development of genetically modified organisms (GMOs). Plants were engineered with genes for insect resistance or herbicide tolerance, sparking debates about the safety and ethics of this technology. R-DNA research continues to be at the forefront of discussions regarding genetically modified foods.
1990s: The Human Genome Project Sets Sail: This ambitious international project aimed to sequence the entire human genome. R-DNA techniques played a crucial role in deciphering the 3 billion letters of our genetic code, opening doors for personalized medicine and a deeper understanding of human health and disease.
2000s: Gene Therapy Takes Center Stage: The first successful gene therapy trials for inherited diseases like severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) took place. R-DNA technology offered a glimmer of hope for treating genetic disorders by introducing healthy genes to replace defective ones.
2010s and Beyond: CRISPR Takes Over: The emergence of CRISPR-Cas9, a revolutionary gene editing tool based on R-DNA principles, has ushered in a new era of genetic manipulation. With unprecedented precision, scientists can now edit genes in various organisms, holding immense potential for gene therapy, crop improvement, and even the eradication of diseases.
But with great power comes great responsibility, and R-DNA raises a host of ethical concerns.Tinkering with the building blocks of life carries the risk of unintended consequences. Engineered genes could escape and disrupt ecosystems, or modified organisms could have unforeseen health effects. The ability to edit human genes opens the door to designer babies, raising questions about social equity and the potential misuse of the technology for eugenics.
Who Controls the Tools? Access to R-DNA technology could be restricted to wealthy nations or corporations, exacerbating existing inequalities. Biosecurity is also a concern, as the technology could be misused for bioterrorism. Creating entirely new organisms forces us to confront what it means to be "natural." Should we modify plants and animals for human benefit, or preserve their original forms? R-DNA technology is a powerful tool, and we must have open discussions about its ethical implications. Scientists, policymakers, and the public all need to be involved in shaping the future of this technology. As we move forward, open dialogue and collaboration between scientists, policymakers, and the public are crucial to ensure the safe and ethical application of this powerful technology.
The journey of rDNA technology is a testament to human ingenuity and its potential to reshape our world. From decoding the secrets of life to creating solutions for healthcare, agriculture, and beyond, rDNA technology continues to evolve, promising a future filled with exciting possibilities.
#science sculpt#life science#science#molecular biology#biology#biotechnology#artists on tumblr#dna#double helix#genetics#recombinant#genetic engineering#insulin#research#education#learning#academics#scientific research#scientific illustration#medical science#scifi#daily dose of science#scientific advancements#scientific tools#medical school
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
I need to bingewatch the scream movies again or I will die right now.
#comfort franchise 💚#but i promised myself the next slasher franchise I’d binge-consume would be Halloween/Michael Myers.#but I also don’t want to consume any media that isn’t Doom right now.#I might just rewatch the first and second ones only. the others were kind of lame in comparison im not going to lie.#especially the 4th one I fucking hated the 4th one it doesn’t exist in my mind.#but I’d have to Not play Doom in order to consume any of that media#I don’t really have the time or will go indulge in all 3.#since I did have to make a schedule in order to ensure that i have workout time; research time & time for my hobbies on a daily basis.#& if I try to multi-task it will definitely fuck with the schedule.#speaking of hobbies. wasnt I supposed to sculpt on the holidays…. what happened to that.#gh. there’s so much to do. fuck.#OH I GOT IT.#I have a personal thing about not really wanting to bring my switch to bed so.#I can just watch the movies in those like 4 hours i spend decomposing there.#i usually just spend them online anyway; i can just. be online while indulging myself. no biggie.#i find multi-tasking while watching movies to be pretty easy.#the only time i Can’t multi-task/talk is when I’m playing doom? not really the type of person to talk inbetween.#it’s fine with other games too i have no idea why it’s the one exception but it is what it is.#will to indulge* (7th tag)
4 notes
·
View notes
Text

3D-Sculpting Daily Challenge 2024, Day 12. This is my 3D sculpture of "Daria".
youtube
#zbrush#3d sculpting#keyshot#render#fan art#daily challlenge#turntable#daria morgendorffer#daria#mtv#Youtube
23 notes
·
View notes