#environmental companies in Texas
Text
something i saw once that has stuck with me ever since was a comment on a post about some scientific discovery made by the mars rover perseverance that said "why are we wasting time looking at rocks when we should be preparing for colonization?
another comment was on a post about the environmental issues surrounding the spacex launch site in southern texas, which said "human expansion to mars delayed to protect some turtles"
and comments like these perplexed me. space is a subject of science, and people interested in space are always talking about the wonders of the unknown, and how many fascinating and beautiful things are out there. so how could people interested in space be so fundamentally uncaring and incurious not only about the places they're supposedly interested in, but about nature in general?
it's not just random people in twitter replies who are like this. elon musk once posted this picture:

thing is, that's not mars, that's the moon during a lunar eclipse (when sunlight tinted red after passing through earth's atmosphere lights up the moon in earth's shadow). you'd think that someone known for wanting to bring people, himself included, to mars would care enough about mars to at least know what it looks like, but apparently not
he also rather infamously says he wants to nuke the ice caps of mars to warm the planet up. the ice caps of mars look like this, by the way (image credit: ESA/DLR/FU Berlin/Aster Cowart):
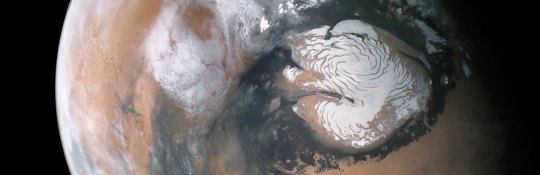
they are beautiful places, that hold an irreplaceable scientific record of the geologically recent martian climate, and are shaped by unique processes. there's no other place quite like them in our solar system. but elon musk thinks we should nuke them. again, no care, no curiosity
nothing has made me feel jaded and cynical about the entire enterprise of spaceflight quite like learning that the people ultimately in charge of it and funding it don't give a shit about space. it's not just elon musk. space nerds love quoting kennedy's "we choose to go the moon" speech as inspiration, but kennedy is also on record saying "I'm not that interested in space" in a conversation where he was arguing to the nasa administrator that they should prioritize beating the soviets to the moon over space science. no curiosity, only a desire for geopolitical showmanship and maintaining hegemony. it's the same thing when many modern politicians only seem to care about space exploration as a way of keeping a technological lead over china
this leaves the people who do genuinely love and care about space in an awkward position. they basically have two choices: A) become jaded and give up on space exploration, or at least parts of it (abandoning human spaceflight but maintaining interest in robotic science missions, for example) or B) give in. work with military contractors. spout the jingoistic rhetoric that the politicians writing the checks want to hear, even if you don't believe it. go along with the colonialist ideology, the hypercapitalism, and the extractivism. sell your soul for pictures of mars and let your passions be exploited for the ends of powerful people who don't care
the sad reality is that our society only values those things deemed useful or profitable. we hear it all the time. the idea that schools should only teach things useful for jobs, that people who try to make a living in fields like art, the humanities, or philosophy are all getting useless degrees and will inevitably end up stuck working retail, and of course, the idea that space exploration is a waste of time and money
space nerds are often deeply insecure about their greatest passion, because it's true, space exploration offers no immediate practical benefit. but they still love space and want to explore it
so they believe the lies. they repeat the colonialist ideology. they say there's money in mining asteroids, that we can terraform planets and let number go up forever. they let themselves be exploited by companies and governments that see everything in the universe and all the people in it as things to be used, and that will ultimately chew them up and spit them out if it's expedient to do so. and those who reject the ideology and keep their love for the cosmos pure often find themselves with no place in the project of space exploration
i don't know how to fix this, but i do hope that i will live to see the day when our curiosity and interest and love for the wider universe is valued for its own sake, and no longer shackled by colonialism, capitalism, and political ambitions
110 notes
·
View notes
Text
Anyone who has spent even 15 minutes on TikTok over the past two months will have stumbled across more than one creator talking about Project 2025, a nearly thousand-page policy blueprint from the Heritage Foundation that outlines a radical overhaul of the government under a second Trump administration. Some of the plan’s most alarming elements—including severely restricting abortion and rolling back the rights of LGBTQ+ people—have already become major talking points in the presidential race.
But according to a new analysis from the Technology Oversight Project, Project 2025 includes hefty handouts and deregulation for big business, and the tech industry is no exception. The plan would roll back environmental regulation to the benefit of the AI and crypto industries, quash labor rights, and scrap whole regulatory agencies, handing a massive win to big companies and billionaires—including many of Trump’s own supporters in tech and Silicon Valley.
“Their desire to eliminate whole agencies that are the enforcers of antitrust, of consumer protection is a huge, huge gift to the tech industry in general,” says Sacha Haworth, executive director at the Tech Oversight Project.
One of the most drastic proposals in Project 2025 suggests abolishing the Federal Reserve altogether, which would allow banks to back their money using cryptocurrencies, if they so choose. And though some conservatives have railed against the dominance of Big Tech, Project 2025 also suggests that a second Trump administration could abolish the Federal Trade Commission (FTC), which currently has the power to enforce antitrust laws.
Project 2025 would also drastically shrink the role of the National Labor Relations Board, the independent agency that protects employees’ ability to organize and enforces fair labor practices. This could have a major knock on effect for tech companies: In January, Musk’s SpaceX filed a lawsuit in a Texas federal court claiming that the National Labor Relations Board (NLRB) was unconstitutional after the agency said the company had illegally fired eight employees who sent a letter to the company’s board saying that Musk was a “distraction and embarrassment.” Last week, a Texas judge ruled that the structure of the NLRB—which includes a director that can’t be fired by the president—was unconstitutional, and experts believe the case may wind its way to the Supreme Court.
This proposal from Project 2025 could help quash the nascent unionization efforts within the tech sector, says Darrell West, a senior fellow at the Brookings Institution’s Center for Technology Innovation. “Tech, of course, relies a lot on independent contractors,” says West. “They have a lot of jobs that don't offer benefits. It's really an important part of the tech sector. And this document seems to reward those types of business.”
For emerging technologies like AI and crypto, a rollback in environmental regulations proposed by Project 2025 would mean that companies would not be accountable for the massive energy and environmental costs associated with bitcoin mining and running and cooling the data centers that make AI possible. “The tech industry can then backtrack on emission pledges, especially given that they are all in on developing AI technology,” says Haworth.
The Republican Party’s official platform for the 2024 elections is even more explicit, promising to roll back the Biden administration’s early efforts to ensure AI safety and “defend the right to mine Bitcoin.”
All of these changes would conveniently benefit some of Trump’s most vocal and important backers in Silicon Valley. Trump’s running mate, Republican senator J.D. Vance of Ohio, has long had connections to the tech industry, particularly through his former employer, billionaire founder of Palantir and longtime Trump backer Peter Thiel. (Thiel’s venture capital firm, Founder’s Fund, invested $200 million in crypto earlier this year.)
Thiel is one of several other Silicon Valley heavyweights who have recently thrown their support behind Trump. In the past month, Elon Musk and David Sacks have both been vocal about backing the former president. Venture capitalists Marc Andreessen and Ben Horowitz, whose firm a16z has invested in several crypto and AI startups, have also said they will be donating to the Trump campaign.
“They see this as their chance to prevent future regulation,” says Haworth. “They are buying the ability to avoid oversight.”
Reporting from Bloomberg found that sections of Project 2025 were written by people who have worked or lobbied for companies like Meta, Amazon, and undisclosed bitcoin companies. Both Trump and independent candidate Robert F. Kennedy Jr. have courted donors in the crypto space, and in May, the Trump campaign announced it would accept donations in cryptocurrency.
But Project 2025 wouldn’t necessarily favor all tech companies. In the document, the authors accuse Big Tech companies of attempting “to drive diverse political viewpoints from the digital town square.” The plan supports legislation that would eliminate the immunities granted to social media platforms by Section 230, which protects companies from being legally held responsible for user-generated content on their sites, and pushes for “anti-discrimination” policies that “prohibit discrimination against core political viewpoints.”
It would also seek to impose transparency rules on social platforms, saying that the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) “could require these platforms to provide greater specificity regarding their terms of service, and it could hold them accountable by prohibiting actions that are inconsistent with those plain and particular terms.”
And despite Trump’s own promise to bring back TikTok, Project 2025 suggests the administration “ban all Chinese social media apps such as TikTok and WeChat, which pose significant national security risks and expose American consumers to data and identity theft.”
West says the plan is full of contradictions when it comes to its approach to regulation. It’s also, he says, notably soft on industries where tech billionaires and venture capitalists have put a significant amount of money, namely AI and cryptocurrency. “Project 2025 is not just to be a policy statement, but to be a fundraising vehicle,” he says. “So, I think the money angle is important in terms of helping to resolve some of the seemingly inconsistencies in the regulatory approach.”
It remains to be seen how impactful Project 2025 could be on a future Republican administration. On Tuesday, Paul Dans, the director of the Heritage Foundation’s Project 2025, stepped down. Though Trump himself has sought to distance himself from the plan, reporting from the Wall Street Journal indicates that while the project may be lower profile, it’s not going away. Instead, the Heritage Foundation is shifting its focus to making a list of conservative personnel who could be hired into a Republican administration to execute the party’s vision.
63 notes
·
View notes
Text
Hey, yanno how Climate Change is a real thing that is tangibly, at this moment, affecting our world?
Well it turns out, the wealthy and their investment firms have been seeing the mounting evidence that oil companies have had for decades and are slowly starting to think more long-term about their portfolios in the face of rising sea levels, more extreme weather, and the myriad of ways climate crises are affecting...well. Everything. Maybe this means they invest more into sustainability, green energy, building more resilient infrastructure, or carbon offsets. Some of it, of course, is simple corporate greenwashing, but there are those that are taking this trend and packaging it into something called ESG (Environmental, Social, and corporate Governance).
Now some people would say this is predictable, even sensible. Just the good ol’ Free Market(tm) rationally responding to market forces and a changing world.
But those people would be fools! Insidious fools! For conservative sorcerers have come out with a new cursed phrase to explain this new market trend: Woke Investing.
What makes this investing “woke?” Well, much like how conservatives normally flounder when trying to define a word they stole from black people, “Woke Investing” essentially just means any kind of capital investment that they, the fossil fuel billionaire class and their sycophants, don’t personally profit from.
One of these aforementioned sycophants is Andy Puzder, conservative commentator, fellow at The Heritage Foundation, and former fast-food CEO. He calls this kind of so-called woke investing “socialism in sheep’s clothing,” further explaining in leaked audio of a closed-door meeting:
“My father's generation's challenge was the Nazis, who, by the way, were, of course, very proud socialists[citation fucking needed]. The challenge of my generation was the communists, who were, of course, very committed socialists. The challenge of your generation is ESG investing, and it's more insidious than communism or the Nazis.”(source)
You heard it here first, folks. Not investing as much in fossil fuels is more insidious than the Third Fucking Reich.
As usual, the Heritage Foundation is putting their petro-chemical donor’s money where their mouth is. Bills are being proposed to blacklist banks that don’t invest in key state industries, such as West Virginia coal or Texas oil. Fourteen states have already passed bills to restrict ESG-type investing, with Florida Governor Ron “Bullies Kids for Wearing Masks” Desantis leading the charge.
In other words, Climate Denial has reached such a point that so-called Free Market Conservatives who claim to hate big government are trying to make it illegal for banks, investment firms, and financial institutions to make any financial decisions that acknowledges Climate Change is real.
#of course ESG has also been used to describe any kind of internal corporate action#to increase diversity in the work place or implementing new anti-discrimination policies#(which are usually more performative than actually meaningful but that's a separate issue)#a Republican Presidential candidate#Vivek Ramaswamy#has even made ESG investing his personal bugbear#writing such books as 'Woke Inc' and warning of socially conscious investors ''forcing'' companies they invest in#to devote resources to environmental and social policies that are anathema to the right#which is just...a brand new invented crisis by a political movement#in constant need of a crisis to rally their base and justify for draconian legal controls#to favor certain industries and undercut their competition#all under the guise of red scare-type moral and economic panic#ESG#Woke Politics#Climate Change#Capitalism#Republicans#Investment
121 notes
·
View notes
Text
Business Group Sues Texas Officials Over Law That Shields Oil Industry. (New York Times)
Excerpt from this New York Times story:
A liberal business group sued Texas officials this week in a major challenge to a 2021 law that bars state entities from doing business with investment firms that the state comptroller says are boycotting energy companies.
The suit, filed by the American Sustainable Business Council in United States District Court in Austin, argues that the law violates the First Amendment because it prohibits doing business with firms on the basis of their “actual or perceived” political views on fossil fuels.
The law prohibits state entities like retirement funds from placing investments with firms it says have enacted boycotts by including environmental principles in their investment strategies. Twenty states have passed such laws in recent years, according to a tally by Pleiades Strategy, a policy research group.
The laws were part of a backlash in some states against a surge of interest over the past decade in what’s known as E.S.G. investing, or making investment decisions that take into account environmental, social and governance issues like pollution and climate change, among others. A similar anti-E.S.G. law in Oklahoma was successfully challenged in court this year and has been temporarily blocked by a judge.
The Texas suit names the state attorney general, Ken Paxton, and the state comptroller, Glenn Hegar, as the defendants. In a statement, Mr. Hegar assailed the suit, calling it an attempt “to force companies to follow a radical environmental agenda that is often contrary to the interests of their shareholders.”
He added that the group had “ignored the critical role” that the oil and gas industry plays in Texas as projections about future demand continue to rise. A June report by Goldman Sachs concluded that worldwide demand for oil would grow for the next decade, an assessment it attributed to slow sales of electric vehicles and rising consumption.
22 notes
·
View notes
Text
If you walk into a Whole Foods in Oakland and pick up a container of non-dairy yoghurt marked “local”, you might be surprised to learn that though the company is headquartered nearby in San Francisco, the cashews the yoghurt is made of come from Vietnam, more than 7,500 miles (12,000km) away, or Ivory Coast, about 7,300 miles in the opposite direction.
This yoghurt made with ingredients from the other side of the globe points to the contradictory nature of so-called local food today: though the term holds appeal for customers, nearly two-thirds of whom perceive local food to be more environmentally friendly, experts suggest it may not always mean what you think.
“Most of it is bullshit,” says Austin, Texas-based Errol Schweizer, who led grocery merchandising for Whole Foods from 2009 to 2016. “Every retailer has a different definition [of “local”]. Even the retailers themselves will have different definitions, depending on where they are, and the original purpose of localization has totally gotten lost.”
[...]
These days, Kennedy adds, local food has “worn out its welcome as a monolithic concept”. That doesn’t mean she’s uninterested in where her food comes from – just that she thinks we’re going to need to ask questions that go beyond how far away our kale was grown to fix the food system. And for Tamm, that means prioritizing local in terms of her produce, but intentionally buying some imports with the intention of supporting “peasant farmers globally”.
Kennedy says it’s more useful to think about the bigger picture of where food comes from, including the ecological impacts of how it was grown and other effects on its place of origin. When thinking about how to redesign food systems, there are many other factors to consider: everything from affordability and availability to race, class, government subsidies and international trade agreements – in addition to, yes, how far away it was packaged or grown.
In other words, the “local” label at your nearest grocery store may not mean all that much. But maybe rather than seeing that as a reason to throw up your hands, you can take it as an invitation to dive deeper into what it might take to actually build a food system that works for everyone.
78 notes
·
View notes
Text
A few days after the release was discovered in June 2017, Stan met with Southcreek and the Oklahoma Corporation Commission, the state’s oil and gas regulatory agency. At the meeting, the company characterized the incident as a “small spill,” the Ledgerwoods later alleged in court. It was unclear how long the leak lasted, but the saltwater plume had already saturated the soil and killed 2 acres of vegetation by the time it broke the surface, according to state oil regulators.
Samples analyzed a month later by Oklahoma State University found that the soil’s concentration of chloride, which occurs in the type of salt water injected into the well, had risen to more than 12 times the state’s acceptable level and was “sufficiently high to reduce yield of even salt tolerant crops.”
Other tests showed that chloride levels in the family’s water well had spiked to more than five times what the Environmental Protection Agency deems safe. The tests didn’t look for other contaminants like heavy metals that are often left behind by the oil production process.
-
-
Don began traveling 30 miles round-trip to Walmart to buy bottled water. Stan and Tina’s steel pots rusted after being washed, and their 2-year-old great-niece’s skin became irritated and inflamed after repeatedly washing her hands while they potty-trained her. In a text message, the girl’s mother described her hands as looking like they had “a burn.”
-
-
As is common in American oil fields, property rights in this part of Oklahoma often create split estates, where one person owns the land while another owns the underlying minerals, such as oil and gas. The owner of the minerals has a right to drill, even if the landowner would prefer they didn’t.
-
-
But Oklahoma has more than 260,000 unplugged wells — behind only Texas — according to data from energy industry software firm Enverus. To plug and clean up the state’s wells could cost approximately $7.3 billion, according to an analysis of state records. Oklahoma has just $45 million in bonds.
The oil industry’s bonds are “shockingly inadequate,” said Peter Morgan, a Sierra Club senior attorney. “It’s clear that abandoning wells and leaving communities and taxpayers to foot the bill to clean them up is baked into the oil and gas industry business model.”
At the Capitol in Oklahoma City, which features repurposed oil derricks outside its main entrance, Republican state Rep. Brad Boles has tried for several years to address the shortfall. This year, he introduced a bill to create a tiered bonding system based on the number of wells a company operates, increasing the highest required bond to $150,000. [passed House, did not gt a vote in Senate]
-
-
A stream of trucks rumbled down the Ledgerwoods’ once-quiet gravel road as workers removed enough dirt to fill 750 dump trucks and pumped more than 71,000 gallons from the Ledgerwoods’ water well.
But the dangerous concentrations of chloride didn’t change, according to Fox Hollow’s report.
-
-
Progress in the lawsuit was short-lived. In November 2019, shortly after the Ledgerwoods’ attorney sent discovery requests to Wise Oil & Gas, the company filed in a Texas court for voluntary Chapter 7 bankruptcy — a full liquidation of its assets.
Company executives acknowledged they declared bankruptcy to avoid legal fees associated with the Ledgerwoods’ suit, according to court records.
-
-
But two months later, Mullin ruled against the Ledgerwoods. He disagreed that Wise Oil & Gas had entered bankruptcy to shed bad investments and dodge cleanup obligations. He blasted the Ledgerwoods for requesting sanctions against the Cocanoughers.
“Merely because the Ledgerwood Creditors have been damaged by the saltwater contamination, this does not provide them with an unfettered right to retaliate or lash out against unrelated and far-removed targets, such as the Cocanougher Sanction Targets,” Mullin wrote.
If the Ledgerwoods wanted to continue seeking damages against the Cocanoughers and their businesses, they would have to pay the oil company’s attorneys’ fees, about $107,000, Mullin ruled.
It's worth reading the whole article for a breakdown of exactly HOW a company that poisoned a family's well and farm got out of fixing it or paying compensation.
Not as relevant in this particular case, but uncapped out of service wells like this are a major source of methane, an even more potent greenhouse gas than CO2
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
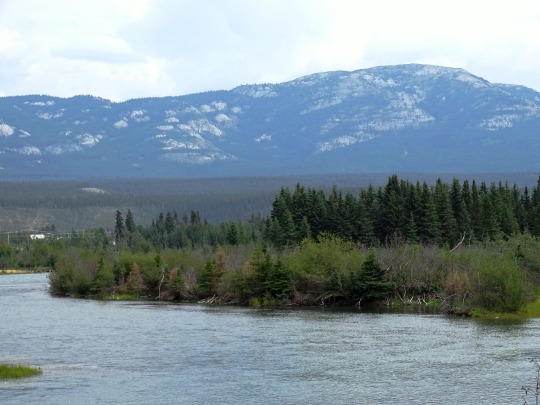
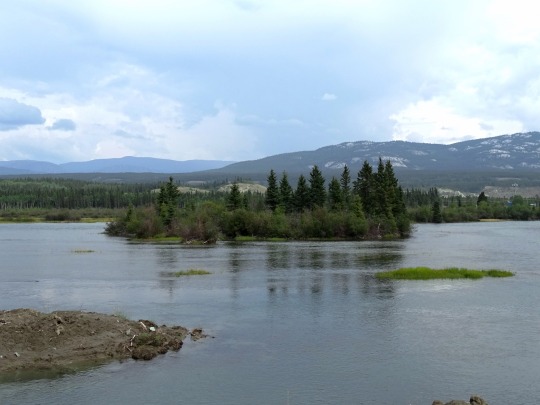
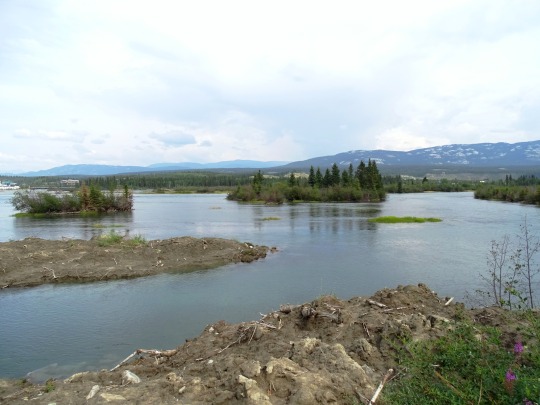
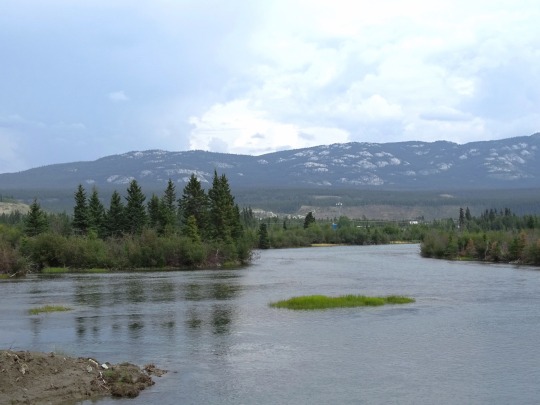
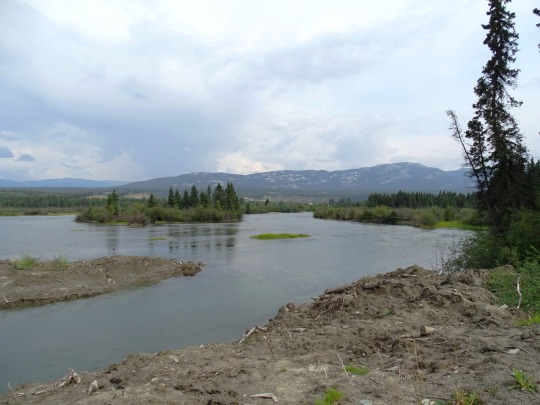
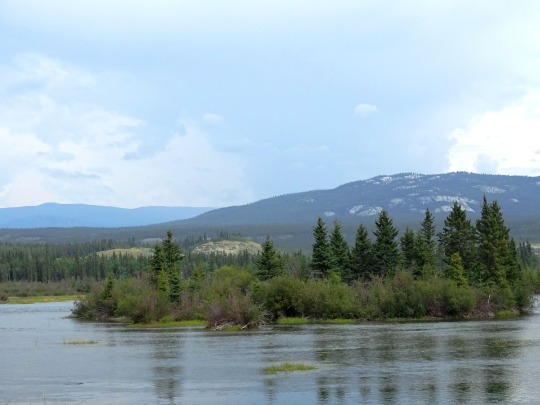










Yukon River, Whitehorse (No. 1)
The Yukon River is a major watercourse of northwestern North America. From its source in British Columbia, Canada, it flows through Canada's territory of Yukon (itself named after the river). The lower half of the river continues westward through the U.S. state of Alaska. The river is 3,190 kilometres (1,980 mi) long and empties into the Bering Sea at the Yukon–Kuskokwim Delta. The average flow is 6,400–7,000 m3/s (230,000–250,000 cu ft/s). The total drainage area is 833,000 km2 (321,500 sq mi), of which 323,800 km2 (125,000 sq mi) lies in Canada. The total area is more than 25% larger than Texas or Alberta.
The longest river in Alaska and Yukon, it was one of the principal means of transportation during the 1896–1903 Klondike Gold Rush. A portion of the river in Yukon—"The Thirty Mile" section, from Lake Laberge to the Teslin River—is a national heritage river and a unit of Klondike Gold Rush International Historical Park. Paddle-wheel riverboats continued to ply the river until the 1950s, when the Klondike Highway was completed. After the purchase of Alaska by the United States in 1867, the Alaska Commercial Company acquired the assets of the Russian-American Company and constructed several posts at various locations on the Yukon River.
The Yukon River has a recent history of pollution from military installations, dumps, wastewater, and other sources. However, the Environmental Protection Agency does not list the Yukon River among its impaired watersheds, and water-quality data from the U.S. Geological Survey shows relatively good levels of turbidity, metals, and dissolved oxygen. The Yukon and Mackenzie rivers have much higher suspended sediment concentrations than the great Siberian Arctic rivers.
The Yukon River Inter-Tribal Watershed Council, a cooperative effort of 70 First Nations and tribes in Alaska and Canada, has the goal of making the river and its tributaries safe to drink from again by supplementing and scrutinizing government data.
Source: Wikipedia
#Whitehorse#Yukon#travel#original photography#vacation#tourist attraction#landmark#cityscape#landscape#Yukon River#summer 2023#woods#forest#flora#nature#mountains#the North#fireweed#widlflower#river bank#Canada#architecture#SS Klondike#clouds
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
By Brett Wilkins
Common Dreams
Nov. 17, 2023
Seven of 12 proposed science textbooks for Texas 8th graders were rejected Friday by the Republican-controlled state Board of Education because they propose solutions to the climate emergency or were published by a company with an environmental, social, and governance policy.
The Texas Tribunereported that the 15-member board, which for the first time was required to include climate education for 8th graders, approved five of 12 proposed science textbooks, but called on their publishers to remove content deemed false or presenting a negative portrayal of oil and gas in the nation's biggest fossil fuel producer.
"America's future generations don't need a leftist agenda brainwashing them in the classroom to hate oil and natural gas," said Republican state energy regulator Wayne Christian, who had urged the board to choose books that promote planet-heating fossil fuels.
Some board members also objected to textbooks that did not include alternatives to the theory of evolution. One textbook was approved only after the removal of images highlighting that human beings—taxonomically classified as great apes—share ancestry with monkeys.
"Teaching creationism or any of its offshoots, such as intelligent design, in Texas' public schools is unlawful, because creationism is not based in fact," Chris Line, an attorney with the Freedom from Religion Foundation, said Friday. "Courts have routinely found that such teachings are religious, despite many new and imaginative labels given to the alternatives."
"Federal courts consistently reject creationism and its ilk, as well as attempts to suppress the teaching of evolution, in the public schools," Line added.
State standards approved by the board's conservative majority in 2021 do not include creationism as an alternative to evolution. The standards also acknowledge that human activities contribute to climate change.
Despite an overwhelming scientific consensus that human activity—primarily, the burning of fossil fuels—drives global heating, Republican board Secretary Patricia Hardy argued before the vote that such a stance amounts to "taking a position that all of that is settled science, and that our extreme weather is caused by climate change."
One textbook was rejected because its publisher has an environmental, social, and governance (ESG) policy. ESG frameworks account for workplace diversity, the treatment of employees, and preparedness for the climate crisis.
Democratic board member Marisa Perez-Diaz said during debate on the textbooks that "my fear is that we will render ourselves irrelevant moving forward when it comes to what publishers want to work with us and will help us get proper materials in front of our young people, and for me that's heartbreaking."
The National Science Teaching Association—a group of 35,000 U.S. science educators—on Thursday implored the board to reject "misguided objections to evolution and climate change [that] impede the adoption of science textbooks in Texas."
As in other GOP-run states, Texas officials have pushed book bans and other restrictions in schools and libraries, even as they portray themselves as champions of freedom. According to freedom of expression defenders PEN America, only Florida banned more books in schools than Texas during the 2022-23 academic year.
#texas#texas board of education#freedom from religion foundation#education#climate denial#fossil fuels#evolution#creationism#textbook banning
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
🔥Elon's SpaceX Company repeatedly polluted waters in Texas this year, regulators found
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
"As soon as a single Palestinian activist showed up at an anti-Dakota Access Pipeline camp on the edge of the Standing Rock reservation in 2016, intelligence analysts for the mercenary security firm TigerSwan were on alert. The analysts, who worked for the pipeline parent company Energy Transfer, confirmed via aerial surveillance that a Palestinian flag was flying above the camp, according to internal records obtained via a public records request and reviewed with support from the Center for Media and Democracy.
The Standing Rock movement was fast becoming one of the most important environmental and Indigenous uprisings of the past 50 years. For TigerSwan, keeping its contract meant convincing Energy Transfer that danger was everywhere. The security firm told its client that Palestinians meant an “Islamic” presence and the possibility of “terrorist type tactics.”
“It’s part of the dehumanization of my people and it directly enables the genocide that we’re witnessing now right now. It’s totally built on racism,” said Haithem El-Zabri, the Palestinian activist that TigerSwan first noticed at Standing Rock. “It’s not limited to a security company — it’s common across the board of government agencies.
By being at Standing Rock, El-Zabri and other Palestinian activists took on the risk of being subjected to fossil fuel industry surveillance. Now, as historic antiwar protests arise across the U.S., the roles have been reversed, with environmental and Indigenous activists standing in defense of Palestinians. In this case, land defenders of all stripes will absorb the sweeping criminalization of the Palestinian cause being pushed by advocates for Israel."
...
The recent history of environmental activism in the U.S. shows that the repressive policies being advanced now will have repercussions far beyond a single social movement — and that they’re likely to hit climate and land defenders particularly hard. A whole generation of young environmental activists, who are increasingly organizing in solidarity with the Palestinian liberation movement, and against what the International Court of Justice has called a plausible genocide in Gaza — is poised to be recast by proponents of Israel as supporters of terrorism and hate. At the same time, the university-sanctioned arrests and evictions of students are bound to be radicalizing experiences that will indelibly shape future social movements of all stripes.
...
As organizations work intersectionally, equating support for Palestinians with antisemitism and terrorism does not just impact Arab, Muslim, and Palestinian groups — it provides a pathway to spy on and disrupt a whole range of protest movements, including environmental and Indigenous movements.
El-Zabri, the Palestinian activist surveilled at Standing Rock, was among 79 people arrested this week while protesting at the University of Texas at Austin. “It really felt like the same as Standing Rock, when we were facing the police,” he said. “There was a whole army that looked like it was at war in riot gear. They eventually used tear gas and pepper spray.”
#indigenous issues#indigineous people#indigenous#standing rock#palestine#free palestine#colonization#settler colonialism#settler police#settler violence#land defenders#water defenders#enviromental activism#solidarity#solidarity encampments
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Today was less a PIH day, though I still had the pleasure of their company, and more a down day before a busy week after a long day of travel. It was also a ‘find some underwear’ day and a ‘watch people haggle’ day.
This morning we went to mass with Denis, who works in PIH’s finance office and was kind enough to bring us to where he worships locally. The thing about a Catholic church is that there will always be some of it that’s exactly the same no matter where in the world you go. Even if it’s not in English, though this was. As someone who spent a number of years in gospel choir (in a US high school) it was also familiar in ways that made me feel very at home. The priest began his homily with a call to the choir to sing the beginning of a hymn that illustrated the word as well as a lot of call and response in his message. It was a great way to start our week.
After mass we went to find the afore mentioned undergarments (which were easy to get if awkward to haggle over) . If you’re plugged into environmental concerns and the problems of fast fashion, you’ll know that much of the global north’s clothes end up in the global south. Much of what we saw was second hand, pristinely presented. My kid now has a Texas t-shirt and a red white and blue buttoned polo shirt. I had a harder time for various reasons but ended up with a few things thanks to Ashely’s haggling help and connections.
The rest of the day was visiting Tacugama Chimpanzee Sanctuary where we had lunch and had a tour of sanctuary. We did this mainly for my son but it is always good to see people doing the important work of conservation and protection.
Tomorrow we go to two PIH facilities in Freetown.



7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Excerpt from this story from Inside Climate News:
For the second time, a federal court struck down a regulatory agency’s authorization of two controversial, multi-billion-dollar gas export projects in far South Texas, one of which is already under construction.
In an Aug. 6 opinion, the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Washington, D.C. Circuit cited “the nature and severity of the flaws” in reviews by the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission of the two proposed gas liquefaction and export complexes, Rio Grande LNG and Texas LNG, along with the associated Rio Bravo Pipeline.
“Although we do not take this step lightly, the circumstances here require it,” the ruling said. “We appreciate the significant disruption vacatur may cause the projects. But that does not outweigh the seriousness of the Commission’s procedural defects.”
The court wrote that FERC failed in its analyses of environmental justice and climate impacts, air pollution modeling and procedural obligations. FERC and the developers now have 45 days to seek a re-hearing.
The two complexes in question plan to pipe in Texas shale gas, condense it and load millions of tons per year onto tanker ships for sale overseas as liquified natural gas, or LNG. Each complex costs billions of dollars, spans hundreds of acres and makes up part of an ongoing boom in gas export projects along the Gulf Coast of Texas and Louisiana.
Rio Grande LNG parent company NextDecade said in a statement it was “disappointed in the Court’s decision and disagrees with its conclusions.”
The company added that construction continues on the first three liquefaction trains and related infrastructure at Rio Grande LNG near Brownsville and it will examine what impact the court’s order will have on future plans for added infrastructure.
The company announced last July it had secured investor funding to begin construction on its 750-acre, $18 billion facility.
A spokesperson for Texas LNG, a smaller, adjacent project on the Brownsville Ship Channel that is yet to secure sufficient funding, said the ruling was a procedural decision to correct a technical deficiency, which they were still studying.
“We have full confidence FERC will address this matter judiciously and efficiently and look forward to working with them on this important issue,” the spokesperson said in a statement.
Three small surrounding cities and the local water district have passed resolutions opposing the projects, situated between national wildlife refuges and atop wetlands.
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
GUN NUTS Don’t Want Anyone Knowing How Many Guns and Bullets They Hoard

Legislation being pursued by Republicans in several U.S. states aims to limit use of a planned merchant code for credit card transactions at gun retailers meant to detect suspicious firearms and ammunition sales, undermining a tool welcomed by gun control advocates.
The bills were introduced in states including Texas, Florida, Mississippi, Oklahoma, West Virginia and Wyoming.
They would prohibit or limit banks or payment processors from using the "merchant category code," or MCC, approved for gun sellers in September by the Geneva-based non-governmental International Organization for Standardization (ISO), which develops standards on various aspects of technology and manufacturing.
The major credit and debit card companies have committed to using the code. Discover Financial Services (DFS.N) has said it will introduce it in April and that it is following other companies in doing so. Discover is the first company to publicly state a timetable.
The code was requested from the ISO by Amalgamated Bank (AMAL.O) of New York, which calls itself a socially responsible lender and investor.
The state proposals mark the latest flashpoint for U.S. Republicans in their attack on the growing corporate consideration of environmental, social and governance (ESG) factors - what some conservatives deride as "woke capitalism."
The Republican state lawmakers sponsoring the bills have said they want to prevent the code from being used to infringe upon gun rights enshrined in the U.S. Constitution's Second Amendment.
Jansen Owen, a state representative who is the author of legislation in Mississippi, said that as a conservative he worries that the code among other things could be used to track lawful ammunition purchases.
(continue reading)
#politics#republicans#republicans are evil#guns#gun nuts#gun violence#2a#gun culture#second amendment#hoarders#public safety
21 notes
·
View notes
Text
Climate action groups are vehemently rejecting the Biden administration's claim that the approval of a new offshore oil terminal—planned to be the largest in the U.S.—is in the "national interest," after the U.S. Department of Transportation announced the project had met several federal requirements and could begin operations by 2027.
The agency's Maritime Administration said last week that Enterprise Product Partners, a Houston-based pipeline company, had been granted a deepwater port license to build the Sea Port Oil Terminal (SPOT) near Freeport, Texas following a five-year federal review process.
The federal government determined the $1.8 billion terminal project had undergone sufficient environmental impact reviews and would overall benefit the country—even as it was projected by the Sierra Club, which has fought SPOT for several years, to emit greenhouse gases equivalent to those of nearly 90 coal-fired power plants.
"The evidence is clear that SPOT would be catastrophic to the climate, wildlife, and frontline communities of the Gulf," said Devorah Ancel, senior attorney with the Sierra Club. "It threatens the future existence of the endangered Rice's whale with a population of less than fifty, and its ozone pollution would compromise the health of thousands of Gulf residents who have endured decades of fossil fuel industry pollution. Make no mistake, SPOT is not in the national interest."
The project is expected to include two pipelines that would carry crude oil to the deepwater port each day, enabling the export of 2 million barrels of crude oil, loaded onto two supertankers at once, daily.
"Nothing about this project is in alignment with Biden's climate and environmental justice goals," said Kelsey Crane, senior policy advocate at Earthworks. "The communities that will be impacted by SPOT have once again been ignored and will be forced to live with the threat of more oil spills, explosions, and pollution. The best way to protect the public and the climate from the harms of oil is to keep it in the ground."
#enviromentalism#ecology#us politics#biden administration#oil industry#offshore drilling#Sea Port Oil Terminal#freeport#texas#oil pipeline
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Associated Press: 22 attorneys general oppose 3M settlement over water systems contamination with 'forever chemicals'
TRAVERSE CITY, Mich. (AP) — Twenty-two attorneys general urged a federal court Wednesday to reject a proposed $10.3 billion settlement over contamination of U.S. public drinking water systems with potentially dangerous chemicals, saying it lets manufacturer 3M Co. off too easily.
The deal announced in June doesn’t give individual water suppliers enough time to determine how much money they would get and whether it would cover their costs of removing the compounds known collectively as PFAS, said the officials with 19 states, Washington, D.C., and two territories. In some cases the agreement could shift liability from the company to providers, they said.
“While I appreciate the effort that went into it, the proposed settlement in its current form does not adequately account for the pernicious damage that 3M has done in so many of our communities,” said California Attorney General Rob Bonta, leader of the multistate coalition.
3M spokesman Sean Lynch said the agreement “will benefit U.S.-based public water systems nationwide that provide drinking water to a vast majority of Americans” without further litigation.
“It is not unusual for there to be objections regarding significant settlement agreements,” Lynch said. “We will continue to work cooperatively to address questions about the terms of the resolution.”
The company, based in St. Paul, Minnesota, manufactures per- and polyfluorinated substances — a broad class of chemicals used in nonstick, water- and grease-resistant products such as clothing and cookware, as well as some firefighting foams.
Described as “forever chemicals” because they don’t degrade naturally in the environment, PFAS have been linked to a variety of health problems, including liver and immune-system damage and some cancers.
3M has said it plans to stop making them by the end of 2025.
Some 300 communities have sued 3M and other companies over water pollution from the compounds. A number of states, airports, firefighter training facilities and private well owners also have pending cases.
They have been consolidated in U.S. District Court in Charleston, South Carolina, where the proposed settlement was filed last month.
Although the company put its value at $10.3 billion, an attorney for the water providers said it could reach as high as $12.5 billion, depending on how many detect PFAS during testing the Environmental Protection Agency has ordered over the next three years.
The law firm representing the water providers did not immediately respond Wednesday to messages seeking comment.
EPA in March proposed strict limits on two common types, PFOA and PFOS, and said it wanted to regulate four others.
In addition to California, states urging Judge Richard Gergel to reject the deal included Arizona, Colorado, Connecticut, Hawaii, Maine, Maryland, Massachusetts, Minnesota, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New Mexico, New York, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Tennessee, Texas, Vermont and Wisconsin. Also opposed were Washington, D.C., Puerto Rico and the Northern Mariana Islands.
In a court filing, the attorneys general said it would force nearly all public water providers nationwide to participate unless they withdraw individually — even those that haven’t filed suits or tested for PFAS.
“Troublingly, they would have to make their opt-out decisions without knowing how much they would actually receive and, in many cases, before knowing the extent of contamination in their water supplies and the cost of remediating it,” the officials said in a statement.
A provision in the proposed deal would shift liability from 3M to water suppliers that don’t opt out, the statement said. That could enable the company to seek compensation from providers if sued over cancer or other illnesses in PFAS-affected communities, it said.
“As such, the proposed settlement is worth far less than the advertised $10.5 billion to $12.5 billion,” the attorneys general said.
The attorneys general did not take a position on a separate $1.18 billion deal to resolve PFAS complaints against DuPont de Nemours Inc. and spinoffs Chemours Co. and Corteva Inc.
#pfas#pfas settlement#Michigan#Water#Poison water#water#forever chemicals#22 attorneys general oppose 3M settlement over water systems contamination with 'forever chemicals'
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Texas entrepreneur working to bring back the woolly mammoth has added a new species to his revival list: the dodo.
Recreating this flightless bird, a symbol of human-caused extinction, is a chance for redemption. It might also motivate humans to remove invasive species from Mauritius, the bird's native habitat, said Ben Lamm, CEO and co-founder of Colossal Biosciences.
"Humanity can undo the sins of the past with these advancing genetic rescue technologies," Lamm said. "There is always a benefit for carefully planned rewilding of a species back into its native environment."
The dodo is the third animal that Colossal Biosciences — which announced Tuesday it has raised $225 million since September 2021 — is working to recreate.
And no, the company isn't cloning extinct animals — that's impossible, said Lamm, who lives in Dallas. Instead, it's focusing on genes that produce the physical attributes of the extinct animals. The animals it's creating will have core genes from those ancestors, engineered for the same niche the extinct species inhabited.
The woolly mammoth, for instance, is being called an Arctic elephant. It will look like a woolly mammoth and contribute to the Arctic ecosystem in a way that’s similar to the woolly mammoth. But it will technically be an Asian elephant with genes altered to survive in the cold. Asian elephants and woolly mammoths share 99.6 percent of their DNA.
The mammoth was the company's first project because it had long been a passion for Harvard University geneticist and Colossal co-founder George Church. He believes that Arctic elephants are the key to creating an Ice Age-like ecosystem with grasslands and grazing mammals, and this could help fight climate change by sequestering carbon under permanently frozen grounds that span areas including Siberia, Canada, Greenland and Alaska.
The altered genes could also give elephants a new habitat that’s far away from the destructive forces of (most) humans, and the company's gene editing technologies could help eradicate elephant diseases.
The company's de-extinction projects seek to fill ecological voids and restore ecosystems, Lamm said. The Tasmanian tiger, which Colossal announced as its second de-extinction animal in August of 2022, is a good example. This tiger was the only apex predator in the Tasmanian ecosystem. No other animal filled its place when it went extinct.
Apex predators eat sick and weak animals, which helps control the spread of disease and improves an ecosystem's genetic health. So the tiger's extinction could have contributed to the near-extinction of Tasmanian devils that lived in the same ecosystem, Lamm said.
For the dodo, Colossal is partnering with evolutionary biologist Beth Shapiro, a scientific advisory board member for Colossal who led the team that first fully sequenced the dodo's genome.
The dodo went extinct in 1662 as a direct result of human settlement and ecosystem competition. They were killed off by hunting and the introduction of invasive species. Creating an environment where the dodos can thrive will require humans to remove the invaders (the non-human invaders, anyway), and this environmental restoration could have cascading benefits on other plants and animals.
"Everybody has heard of the dodo, and everybody understands that the dodo is gone because people changed its habitat in such a way that it could not survive," Shapiro said. "By taking on this audacious project, Colossal will remind people not only of the tremendous consequences that our actions can have on other species and ecosystems, but also that it is in our control to do something about it."
The company has secured $150 million in funding to revive this bird and build an Avian Genomics Group, bringing the company's total fundraising to $225 million.
Colossal has more than 40 scientists and three laboratories working to recreate the woolly mammoth, and they hope to have mammoth calves in 2028. There are 30 scientists working on the Tasmanian tiger.
Reviving extinct animals is not a quick process, especially when considering the development of new technologies and the natural processes of Mother Nature (elephant gestation takes 22 months!). Some of Colossal's projects will take nearly a decade to complete, which is why the company is working to reintroduce multiple animals at the same time.
"Given the rapidly changing planet and various ecosystems heavily influenced by humankind, we need more tools in our tool belt to also help species adapt faster than they are currently evolving," Lamm said.
And the tools aren't limited to extinct animals. Colossal is developing technology that can benefit other industries, and it's spinning these out into new companies. Last year, it spun out a software platform called Form Bio that's designed to help scientists collaborate and work with their data, visualizing it in meaningful ways rather than looking at raw numbers in a spreadsheet.
"Synthetic biology will allow the world to solve various human-induced, world-wide problems," Lamm said, "like making drought-resistant livestock, curing certain disease states in humans, creating corals that are tolerant to various salinities and higher temperatures ... and much more."
18 notes
·
View notes