#geocode
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Webマーケティングとクラウドセールステックを展開する株式会社ジオコード(本社:東京都新宿区、代表取締役:原口大輔、証券コード:7357)は、SEO(検索エンジン最適化)に関する日々の調査と研究をまとめた「SEO最新動向レポート2024年11月号」を発表しました。このレポートは、SEOに関する重要なトピックや最新ニュース、さらには実践的なアドバイスを提供することで、企業やマーケティング担当者のSEO対策を強力にサポートします。
0 notes
Text
Revolutionize Mapping with Cutting-Edge AI API Solutions
Explore the future of geospatial technology with AI API innovations on AllThingsDev. Our in-depth resources and expert insights dive into how AI-powered APIs are transforming mapping solutions—making them faster, smarter, and more intuitive. From real-time location analysis to intelligent route optimization, discover how developers and businesses can leverage AI API tools to build next-gen mapping applications. Stay ahead of the curve with the latest trends, tutorials, and practical guides designed to boost your development workflow
0 notes
Text
Forward Geocoding Explained: How Addresses Are Transformed Into Geographic Coordinates

In today's digital landscape, where location-based services are integral to various applications, understanding how textual addresses are converted into precise geographic coordinates is essential. This process, known as forward geocoding, enables applications to map addresses to specific locations on the Earth's surface, facilitating services like navigation, delivery routing, and spatial analysis.
What is Forward Geocoding?
Forward geocoding is the process of converting human-readable addresses, such as "1600 Amphitheatre Parkway, Mountain View, CA," into geographic coordinates—latitude and longitude—that can be used to place markers on a map or for other spatial computations.
This process is fundamental in various applications, including:
Mapping services
Location-based search
Delivery and logistics optimization
Geospatial data analysis
How Forward Geocoding Works
The forward geocoding process involves several steps:
Input Parsing: The address is parsed to identify components like street number, street name, city, state, and postal code.
Standardization: The parsed address is standardized to match the format used in the geocoding reference database.
Matching: The standardized address is matched against a geographic database that contains address ranges and their corresponding coordinates.
Interpolation: If an exact match isn't found, interpolation is used to estimate the location based on nearby address ranges.
Output Generation: The final output is the geographic coordinates corresponding to the input address.
Applications of Forward Geocoding
Forward geocoding is utilized in various domains:
Navigation Systems: Converting user-entered addresses into coordinates for route planning.
E-commerce: Determining delivery locations for online orders.
Emergency Services: Locating incidents based on reported addresses.
Urban Planning: Analyzing spatial distribution of infrastructure and services.
Challenges in Forward Geocoding
While forward geocoding is powerful, it faces several challenges:
Ambiguous Addresses: Multiple locations may share similar addresses, leading to confusion.
Incomplete or Inaccurate Data: Missing components in an address can hinder accurate geocoding.
Dynamic Environments: Changes in address data due to new developments or renaming can affect accuracy.
Best Practices for Effective Forward Geocoding
To enhance the accuracy and efficiency of forward geocoding:
Use Standardized Address Formats: Ensure addresses follow a consistent format.
Validate Input Data: Check for completeness and correctness before processing.
Leverage Reliable Geocoding Services: Utilize reputable APIs and databases that are regularly updated.
Handle Ambiguities Gracefully: Implement logic to manage multiple matches or uncertain results.
Conclusion
Forward geocoding plays a crucial role in bridging the gap between human-readable addresses and machine-understandable geographic coordinates. By understanding its mechanisms, applications, and challenges, businesses and developers can better harness its capabilities to enhance location-based services and decision-making processes.
youtube
SITES WE SUPPORT
Verify Location GeoCodes – Wix
0 notes
Video
youtube
A nice tool was developed for UK address cleansing and geocoding in Bing. Very smart in use.
1 note
·
View note
Text
How to Geocode Excel Data into a Map?
Introduction
Turning raw Excel data into a visual map can be a game-changer for businesses, researchers, and urban planners. Whether you need to analyze sales territories, track deliveries, or study demographic trends, mapping your data helps unlock insights that spreadsheets alone can't offer. This article will walk you through the process of geocoding Excel data and transforming it into an interactive map.

What is Geocoding?
Geocoding is the process of converting addresses or place names into geographic coordinates (latitude and longitude). Once geocoded, this data can be visualized on a map for better spatial analysis.
Steps to Geocode Excel Data
1. Prepare Your Data
Before uploading your Excel file, ensure it contains:
Address fields (Street, City, State, ZIP Code, Country) OR latitude & longitude columns.
A clear and consistent format without duplicate entries.
2. Use an Online Geocoding Tool
Several platforms offer geocoding services where you can upload Excel files and generate maps. Pick one such tool allows users to geocode their data seamlessly like MAPOG, making mapping a hassle-free experience.
3. Upload and Process Your File
Import your Excel file (.csv or .xls format).
Map the appropriate columns to ensure accuracy.
Run the geocoding process, which assigns latitude and longitude to each entry.
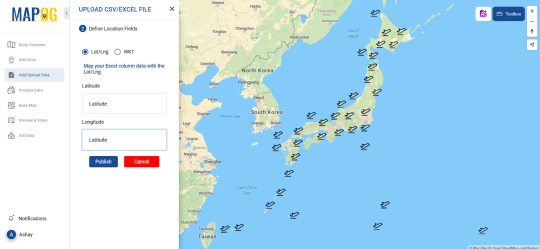
4. Visualize Your Data on a Map
Once geocoded, your data points will appear on an interactive map. You can customize it by:
Changing basemaps (road, satellite, hybrid views).
Applying color-coded categories for better analysis.
Adding additional attributes like time zones, demographics, or custom fields.
Real-World Applications of Geocoded Maps
Business & Sales Tracking
Companies can map customer locations to optimize delivery routes.
Sales teams can analyze which regions have the highest conversions.
Urban & Environmental Planning
City planners can study population density and infrastructure needs.
Environmentalists can track pollution sources and their impact zones.
Healthcare & Public Services
Hospitals can map patient distributions to allocate resources efficiently.
Emergency responders can analyze risk-prone areas for better preparedness.
Tools to Explore
Platforms like MAPOG provide useful tools for geocoding and mapping. The Upload CSV-Excel tool is specifically designed to help users transform spreadsheet data into actionable maps while supporting formats like CSV, XLSX, XLS, ODS . If you're looking for a user-friendly, powerful way to visualize data where you can upload both latitude, longitude and WKT data, it's worth exploring.
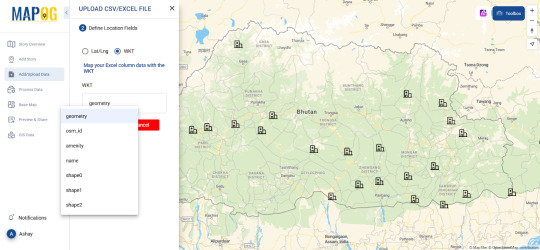
Conclusion
Geocoding Excel data into a map can simplify complex datasets, reveal patterns, and enhance decision-making. Whether you're in business, urban planning, or research, mapping your data brings it to life.
Ready to get started? Try out mapping tools and see how geocoding can elevate your workflow!
0 notes
Text
How Do Credit Repair Companies Work? What Marketing Strategies Do They Implement?
In today's economy, many people face challenges related to their credit scores, which can affect everything from obtaining a loan to securing a job. Credit repair companies offer a solution to individuals looking to improve their credit. This article will explore how these companies work and the marketing strategies they employ to attract clients.

What Do Credit Repair Companies Do?
Credit repair companies specialize in helping individuals improve their credit scores by addressing errors or inaccuracies on their credit reports. They act as intermediaries between clients and credit bureaus, often disputing incorrect information that could negatively impact credit scores. Here’s a breakdown of how they typically operate:
1. Credit Report Analysis
The first step credit repair companies take is to request copies of their clients' credit reports from major credit bureaus like Experian, TransUnion, and Equifax. They review the reports for potential inaccuracies, such as wrong account details, outdated information, or fraudulent activity.
2. Disputing Errors
Once errors are identified, credit repair companies file disputes with credit bureaus on behalf of their clients. This involves submitting formal requests for investigation, along with supporting documentation to prove that the disputed items are incorrect.
3. Negotiating with Creditors
In some cases, credit repair companies may negotiate directly with creditors to remove negative information or settle outstanding debts. They may also help clients develop payment plans to pay off outstanding debt over time.
4. Providing Credit Counseling
Many credit repair companies offer additional services, such as credit counseling, which helps clients understand better financial habits. This includes budgeting tips, debt management, and education on how to maintain a healthy credit score moving forward.
What Marketing Strategies Do Credit Repair Companies Use?
Given the competitive nature of the credit repair industry, companies must implement effective marketing strategies to attract and retain clients. Below are some of the most common marketing tactics used:
1. Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
Credit repair companies use SEO to improve their online visibility on search engines like Google. They optimize their websites with relevant keywords such as "credit repair," "improve credit score," or "fix credit." By ranking high in search results, companies increase their chances of attracting organic traffic from individuals seeking credit repair services.
2. Content Marketing
Educational content is a valuable marketing tool in the credit repair industry. Companies create blogs, eBooks, videos, and infographics to inform potential clients about credit scores, how to repair credit, and common pitfalls to avoid. This content not only helps build trust but also drives organic traffic and leads.
3. Pay-Per-Click (PPC) Advertising
Many credit repair companies invest in PPC advertising to appear at the top of search engine results for high-converting keywords. Platforms like Google Ads allow companies to bid on specific keywords, such as “fix bad credit,” ensuring that their ads are seen by individuals actively searching for credit repair services.
4. Social Media Marketing
Credit repair companies often leverage social media platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and LinkedIn to reach their target audience. Social media allows companies to engage with potential clients through posts, videos, and ads. Many also use paid social media ads to target specific demographics.
5. Email Marketing
Email marketing is another effective strategy for credit repair companies. They build email lists by offering free consultations or downloadable content in exchange for contact information. Once they have a list, they send regular emails offering tips, success stories, and special promotions, keeping their services top of mind for potential clients.
6. Affiliate Marketing
Some credit repair companies partner with affiliates, such as financial advisors, mortgage brokers, and real estate agents, to refer clients. In exchange, affiliates earn commissions for every customer they send to the credit repair company. This type of partnership can be a significant source of leads.
Conclusion
Credit repair companies provide an essential service for individuals looking to improve their financial standing. Through services like credit report analysis, disputing errors, and offering credit counseling, they help clients rebuild their credit scores. The marketing strategies they implement, including SEO, PPC, content marketing, and social media engagement, allow them to attract clients in a competitive market.
youtube
SITES WE SUPPORT
Credit Geocodes Mail – Wix
0 notes
Text
Geolocation in Boosting Retail Industry

Geolocation Technology plays a pivotal role in boosting the growth of the retail industry. Enhanced customer experiences, Targeted marketing, and operational efficiency are key benefits.
1. Personalized Marketing Geolocation allows retailers to send targeted promotions and discounts to customers based on their location. Tailored offers increase customer engagement and drive foot traffic to stores.
2. Location-Based Services Retailers leverage geolocation for services like in-store navigation, helping customers easily find products. This enhances the overall shopping experience and encourages repeat visits.
3. Inventory Management Geolocation assists in tracking inventory across multiple locations. Retailers can optimize stock levels, reduce overstock situations, and enhance supply chain efficiency.
4. Competitive Advantage Retailers gain a competitive edge by analyzing foot traffic patterns. Insights into customer behavior help in optimizing store layouts and making informed decisions on product placement.
5. E-commerce Enhancements Geolocation enables personalized online shopping experiences by recommending products based on the user's location, weather, or local trends.
Conclusion
Geolocation technology is a game-changer for the retail industry, offering a multitude of opportunities to enhance customer engagement, streamline operations, and stay ahead in a competitive market.
0 notes
Text
Invoice and Statement Mailing Service
Invoice and statement mailing service allows your business to save money while allowing your staff to focus on the tasks they are best at. Trying to do this work in-house can require a lot of floor space and equipment, while also taking up valuable time from employees who could be better used elsewhere in the organization. Outsourcing your invoice and statement processing to a professional company removes the burden from your staff, enabling you to collect payments faster.

A good invoice printing and mailing service will take care of all of the design and formatting of your document. They will use your existing templates, and can customize them to include your logo and branding for consistency. This will give your customers the impression that they are receiving a professionally designed document from you each month.
The printing and distribution of statements is a critical part of your customer relationship, but it’s not something you want to attempt to do yourself. A good transactional print and mail partner will ensure that your bills and statements are delivered in a timely manner and with the quality your customers deserve.
An invoice is a commercial document that includes the details of products or services purchased, the purchase date, product or service descriptions and the final total. It may also feature payment terms and bank details. This document can be sent after a sale is made or at specific intervals, like quarterly, monthly, or bimonthly.
youtube
SITES WE SUPPORT
Print & Mail Geocodes– Wix
0 notes
Text
Here be treasure!
Geocoding provides competitive edge #DataQuality
Geocoding has historically been confined to the geographical information systems (GIS) arena and had limited use within mainstream business. This is changing as the importance of knowing one’s customer’s location is becoming increasingly obvious for marketing, planning and operational purposes. Location information can bring a vast amount of insight to any business – supporting an enhanced…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
How to Find a Geocoding API Free
A geocoding api free is a useful tool for companies looking to save time and money. These APIs are designed to help developers quickly get their application up and running without having to build all the necessary features from scratch. Many of these APIs also offer other helpful features that can make a developer's life much easier. These include the ability to track an IP address, find phone number and more.

There are several options for a geocoding api free, but you will want to make sure you choose the best one for your needs. Some of the most popular choices are Positionstack, TrueWay Matrix and Bing Maps Geocoder API. These APIs can be used to convert street addresses into latitude and longitude coordinates. They are ideal for applications that require high accuracy and worldwide coverage.
These APIs also provide a real-time usage graph. The rate element of the API response body and X-Ratelimit HTTP headers provide a snapshot of current usage. These APIs can be scaled to meet your application's specific needs. For example, you can increase the number of requests per minute or adjust the rate limit on a per account basis.
If you need to geocode in bulk, you can use the MMQGIS plugin. This geocoding plugin lets you input a list of addresses and will automatically mark them on the map. The plugin uses open source data from the OpenStreetMap database. The plugin supports multiple formats including XML and JSON.
youtube
SITES WE SUPPORT
Statement Mail Api – Blogger
0 notes
Text
Unlock Location Intelligence with Geocoding API | All Things Dev
Enhance your mapping applications with the power of Geocoding API, a crucial tool for converting addresses into geographic coordinates and vice versa. At All Things Dev, we explore how Geocoding APIs streamline location-based services, enabling developers to build smarter applications for navigation, logistics, and local search. Geocoding APIs provide accurate latitude and longitude data, helping businesses optimize routing, enhance delivery tracking, and improve location-based experiences. Reverse geocoding allows users to retrieve human-readable addresses from coordinates, making it essential for applications like ride-sharing, food delivery, and real estate mapping.
0 notes
Text
What Is Forward Geocoding? A Beginner’s Guide to Address-to-Coordinate Conversion
Forward geocoding is the process of converting human-readable addresses into geographic coordinates. This technique is fundamental in various applications, including mapping, navigation, and location-based services.
Understanding Forward Geocoding
Forward geocoding translates a physical address into latitude and longitude coordinates. For example, "1600 Amphitheatre Parkway, Mountain View, CA" becomes (37.4220, -122.0841).
Applications of Forward Geocoding
Mapping and Navigation
Geocoding enables the placement of addresses on digital maps, facilitating navigation and route planning for users and businesses.
Delivery and Logistics
Businesses use geocoded addresses to optimize delivery routes, ensuring timely and efficient distribution of goods and services.
Emergency Services
Emergency responders utilize geocoding to locate incidents quickly, improving response times and potentially saving lives.
Implementing Forward Geocoding
Several APIs and services offer forward geocoding capabilities, including Google Maps Geocoding API, Mapbox, and LocationIQ. These tools provide developers with the means to integrate geocoding into applications and systems.
Challenges and Considerations
While forward geocoding is powerful, it can face challenges such as ambiguous addresses or incomplete data. Ensuring data quality and using reliable geocoding services can mitigate these issues.
Conclusion
Forward geocoding is a vital process in translating addresses into geographic coordinates, enabling a wide range of applications from navigation to logistics. Understanding and implementing forward geocoding can significantly enhance the functionality of location-based services.
youtube
SITES WE SUPPORT
Verify Location GeoCodes – Wix
0 notes
Text
#web#design#code#codeblr#developer#developers#free#tool#tools#api#service#ai#app#cache#db#email#sms#image#geocoding#users
0 notes
Text
youtube
0 notes
Text
Geocoding 101: What Are Geocodes and How Are They Used?
In the world of data-driven decision-making, geocoding has become a pivotal tool. It plays a crucial role in mapping technologies, logistics, urban planning, and even marketing. But what exactly is geocoding, and how are geocodes used in practical applications? This comprehensive guide will help you understand geocoding, its types, the role of geocodes, and the vast range of applications it supports.

What Is Geocoding?
Geocoding is the process of converting an address or a location description (such as a city name, ZIP code, or landmark) into geographic coordinates, such as latitude and longitude. These coordinates can then be used to place the location on a digital map, which enables further analysis and utilization of the data for various purposes.
Geocoding is essential for mapping, as it translates human-readable locations into machine-readable data that can be used in digital systems, navigation apps, and various location-based services.
Types of Geocoding
There are two main types of geocoding processes:
Forward Geocoding: This is the most commonly used geocoding method. It converts a physical address or location description into geographic coordinates (latitude and longitude). For example, if you input "1600 Pennsylvania Avenue, Washington D.C.," forward geocoding will return the corresponding coordinates.
Reverse Geocoding: This process is the opposite of forward geocoding. It converts geographic coordinates into a human-readable address. For instance, when you drop a pin on Google Maps, reverse geocoding will tell you the corresponding street address of that location.
What Are Geocodes?
Geocodes are unique numeric representations (latitude and longitude) that represent specific geographic locations. They are the output of the geocoding process and serve as a precise identifier for a physical location on the Earth's surface.
For example, the geocode for the Eiffel Tower in Paris is approximately 48.8584° N latitude and 2.2945° E longitude. These coordinates help applications pinpoint the exact location on maps.
How Are Geocodes Used?
Geocodes have numerous applications, spanning a wide range of industries. Here are some of the most common uses of geocoding:
1. Navigation and GPS Systems
Geocodes are the foundation of navigation apps and GPS systems. By converting addresses into geographic coordinates, GPS devices can guide users to their desired destinations. Apps like Google Maps and Waze rely on geocoding to provide turn-by-turn directions.
2. Location-Based Marketing
Businesses use geocoding to target potential customers based on their location. By analyzing geocoded data, companies can create hyper-localized marketing campaigns, such as offering discounts to customers near a specific store location or targeting ads to users in a particular city.
3. Urban Planning and Infrastructure Development
Urban planners and government agencies use geocoding to analyze population distribution, infrastructure needs, and traffic patterns. This data is essential for making informed decisions about where to build roads, hospitals, schools, and other public facilities.
4. Logistics and Supply Chain Management
Geocoding is vital for optimizing delivery routes and improving the efficiency of supply chains. By converting delivery addresses into geographic coordinates, companies can calculate the shortest and fastest delivery routes, saving time and resources.
5. Disaster Management
In times of natural disasters, geocoding helps authorities identify affected areas and coordinate rescue efforts. By geocoding disaster reports and distress calls, response teams can quickly reach the impacted locations and allocate resources effectively.
6. Real Estate
Real estate professionals use geocoding to locate properties, analyze market trends, and provide potential buyers with relevant information about property locations. For example, they can use geocoded data to show homes in a specific neighborhood or proximity to schools, parks, and public transport.
7. Environmental Monitoring
Geocoding is used in environmental science to track pollution, monitor wildlife migration patterns, and study climate change. Geographic coordinates are essential for collecting and analyzing location-based data in various environmental research efforts.
Geocoding Challenges
While geocoding is a powerful tool, it does come with certain challenges:
Accuracy: The quality of the geocoding result depends on the precision of the input data. Poorly formatted addresses or incomplete information can lead to inaccurate geocodes.
Data Privacy: Handling location data raises privacy concerns, as geocoded information can reveal sensitive details about individuals' movements and habits.
Cost: Some geocoding services, such as Google Maps API, charge fees for high-volume requests, which can be a consideration for businesses that require large-scale geocoding.
Conclusion
Geocoding plays a critical role in various industries, enabling better decision-making and more efficient processes. From navigation apps to marketing campaigns, geocodes help bridge the gap between physical locations and digital applications. Understanding the importance of geocoding and how it is used can open up new opportunities for businesses and developers alike.
youtube
SITES WE SUPPORT
Credit Geocodes Mail – Wix
0 notes