#geoffrey/constance
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

Your night cast light upon my day As if it were a great black stone And it was then that I was born
#twelfth century#ar men du beloved <3#i had to knock off geoff's dumb little hat for this one...i hope you can find it in your heart to forgive me 😔#i keep drawing them as too sweet bc they scratch my itch in the right way and also bc they get dogshit takes all the time#but i wanted to make them more.morally dubious-looking. unwell-adjusted people from my medieval chronicle <3#anyways sorry for posting cringe again (╥﹏╥)#geoffrey/constance#shakespeareomnibus
13 notes
·
View notes
Text

a family man
#geoffrey duke of brittany#12th century#constance of brittany#constance duchess of brittany#eleanor the fair maid of brittany#look at them having a Good Time for Once
14 notes
·
View notes
Note
Geoffrey’s lack of rizz makes him eventually having one of the more stable relationships 10x funnier to me
As Bertran called him, Geoffrey “who doesn’t know how to please the ladies” … In BKverse i think that his situation is basically that all the girlies swarm around and has parasocial crushes/relationships with Junior since he’s like a local celeb, but then they find out he’s taken so they try hitting up Richard who gives everyone the rude cold shoulder and then they give up and forget Geoffrey exists. And when he does try to put himself out there Rich and Henry make fun of him. So he tries to act like he’s Cool and smart and Above it all to avoid their being mean
#Gets with Constance bc they get stuck together at a summer job or group project awkwardly and are forced to get along#but then…can love blossom in even unexpected places#geoffrey
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
reading sharon kay penman’s plantagenet novels and i’m obsessed with the way she devotes pov sections to “minor” characters like constance of brittany and isabella of jerusalem and the more i read the more devastated i am she didn’t write more books about the plantagenets because i haven’t encountered any other historical fiction author so far who sheds light on lesser known historical figures ://
#random thoughts.#i would have trusted her w philippa of hainault ://#her portrayal of geoffrey and constance has me in shambles
0 notes
Note
I am so thankful that fire emblem introduced me to Chrom, Robin, Lissa, Miriel, Stahl, Henry, Olivia, Cherche, Sumia, Donnel, Lon'qu, Maribelle, Panne, Gaius, Cordelia, Tharja, Anna, Say'ri, Tiki, Lucina, Owain, Inigo, Cynthia, Severa, Morgan, Yarne, Laurent, Noir, Nah, Corrin, Azura, Felicia, Jakob, Kaze, Mozu, Ryoma, Hinoka, Takumi, Sakura, Saizo, Kagero, Setsuna, Hinata, Oboro, Subaki, Hayato, Orochi, Kaden, Xander, Camilla, Leo, Elise, Laslow, Peri, Selena, Odin, Niles, Effie, Nyx, Charlotte, Kaden, Flora, Kana, Shigure, Dwyer, Sophie, Midori, Shiro, Kiragi, Asugi, Mitama, Hisame, Caeldori, Rahjat, Selkie, Seigbert, Forrest, Soliel, Ophelia, Nina, Velouria, Lilith, Alm, Gray, Tobin, Kliff, Faye, Lukas, Silque, Clair, Clive, Forsyth, Python, Luthier, Delthea, Tatiana, Zeke, Celica, Mae, Boey, Genny, Saber, Leon, Palla, Catria, Est, Jesse, Atlas, Sonya, Deen, Conrad, Fernand, Emma, Randal, Yuzu, Shade, Byleth, Edelgard, Hubert, Ferdinand, Linhardt, Caspar, Bernadetta, Dorothea, Petra, Dimitri, Felix, Sylvain, Mercedes, Annette, Ingrid, Claude, Lysithea, Marianne, Seteth, Flayn, Manuela, Shamir, Jertiza, Yuri, Balthus, Constance, Hapi, Sothis, Rhea, Shez, Randolph, Rodrigue, Nader, Sothis, Arval, Alear, Vander, Framme, Clanne, Alfred, Celine, Boucheron, Etie, Louis, Chloe, Jean, Diamant, Alcryst, Amber, Jade, Citrinne, Lapis, Yunaka, Saphir, Ivy, Hortensia, Zelkov, Kagetsu, Rosado, Goldmary, Timerra, Fogado, Merrin, Panette, Bunet, Pandreo, Seadall, Veyle, Mauvier, Nel, Rafal, Zelestia, Gregory, Madeline, Zephia, Griss, Marni, Sommie, Lumera, Eve, Morion, Sephoria, Hyacinth, Itsuki, Tsubasa, Touma, Kiria, Eleonora, Mamori, Yashiro, Maiko, Alfonse, Sharena, Askr, Ash, Veronica, Embla, Elm, Feh, Fehnix, Nifil, Fijorm, Gunnthra, Hrid, Muspell, Laegjarn, Eir, Ymir, Peony, Mirabilis, Freyr, Triandra, Plumeria, Freyja, Eitr, Ginnungagap, Nioavellir, Otr, Nott, Seior, Gullveig, Kvasir, Heior, Nerpuz, Ratatoskr, Hraesvelgr, Heiorun, Eikpyrnir, Loki, Thorr, Baldr, Hoor, Rowan, Lianna, Eirika, Ephiram, Gilliam, Vanessa, Ross, Neimi, Colm, Artur, Lute, Natasha, Joshua, Forde, Kyle, Tana, Innes, Gerik, Tethys, Marisa, L'Arachel, Saleh, Ewan, Cormag, Rennac, Knoll, Dussel, Myrrh, Syrene, Ismaire, Glen, Lyon, Lyn, Sain, Kent, Florina, Wil, Serra, Erk, Rath, Mathew, Nils, Lucius, Eliwood, Rebecca, Hector, Guy, Priscilla, Raven, Canas, Fiora, Ninian, Heath, Geitz, Farina, Pent, Louise, Karel, Harken, Nino, Jaffar, Karla, Llyod, Roy, Alen, Lance, Wolt, Elen, Dieck, Rutger, Dorothy, Sue, Noah, Lilina, Gwendolyn, Ogier, Geese, Klein, Thea, Larum, Elffin, Melady, Perceval, Cecilia, Sophia, Fae, Hugh, Zeiss, Juno, Narcian, Galle, Brunnya, Sigurd, Naoise, Azelle, Lex, Quan, Ethlyn, Finn, Midir, Dew, Edain, Ayra, Deirdre, Chulainn, Lachesis, Lewyn, Silvia, Tailtiu, Brigid, Eldigan, Seliph, Lana, Larcie, Scathach, Lester, Julia, Fee, Arthur, Shannan, Daisy, Leif, Nanna, Ares, Lene, Tine, Linda, Febail, Ced, Marth, Ceada, Cain, Xane, Camus, Linde, Mineva, Michalis, Julian, Lena, Merric, Wolf, Jeorge, Elice, Ronan, Safy, Lifis, Lara, Asbel, Shiva, Cain, Mareeta, Salem, Perne, Tina, Homer, Linoan, Sara, Shannam, Alva, Robert, Fred, Diarmuid, Micaiah, Edward, Leonardo, Laura, Sothe, Ilyana, Volug, Zihark, Tormod, Vika, Rafiel, Black Knight, Elincia, Marcia, Leanne, Haar, Nephenee, Lucia, Lethe, Geoffrey, Kieran, Astrid, Ike, Titania, Oscar, Boyd, Shinon, Soren, Mist, Gatrie, Rhys, Ranulf, Kyza, Lyre, Reyson, Sigrun, Naesala, Skrimir, Sanaki, Tibarn, Pelleas, Stefan, Volke, Ena, Kurthnaga, Nasir.
I adore them all so much, they all live in my head rent free, I cannot stop thinking and I absolutely love drawing them when I get the chance to do so. I've been a fan of this series for 9 years now and it's still going strong!!!
I really really do love fire emblem... I also suspect that I may not be neurotypical...
!
44 notes
·
View notes
Text
Golden Age of Hollywood Actors Born Before (And Including) 1937 Still Alive
This only includes actors that had at least one credited role in a Hollywood feature film or short up to 1959.
Elisabeth Waldo (b. 1918)
Caren Marsh Doll (b. 1919)
Patricia Wright (b. 1921)
Jacqueline White (b. 1922)
Annette Warren (b. 1922)
Ray Anthony (b. 1922)
Jimmy Thompson (b. 1923)
Eva Marie Saint (b. 1924)
Anne Vernon (b. 1924)
Maria Riva (b. 1924)
June Lockhart (b. 1925)
Lee Grant (b. 1925)
Peggy Webber (b. 1925)
Lise Bourdin (b. 1925)
Brigitte Auber (b. 1925)
Kerima (b. 1925)
Bob Graham (b. 1925)
Terry Kilburn (b. 1926)
Marilyn Erskine (b. 1926)
Bambi Linn (b. 1926)
David Frankham (b. 1926)
Tommy Morton (b. 1926)
Marilyn Knowlden (b. 1926)
Stan Ross (b. 1926)
Robert Roark (b. 1926)
Genevieve Page (b. 1927)
Donna Martell (b. 1927)
William Smithers (b. 1927)
Peter Walker (b. 1927)
H.M. Wynant (b. 1927)
Betty Harford (b. 1927)
Marilyn Granas (b. 1927)
Ann Blyth (b. 1928)
Nancy Olson (b. 1928)
Peggy Dow (b. 1928)
Colleen Townsend (b. 1928)
Marion Ross (b. 1928)
Gaby Rodgers (b. 1928)
Walter Maslow (b. 1928)
Tom Troupe (b. 1928)
Sidney Kibrick (b. 1928)
Garry Watson (b. 1928)
Fay Chaldecott (b. 1928)
Ron Hartmann (b. 1928)
Mark Rydell (b. 1929)
Terry Moore (b. 1929)
Vera Miles (b. 1929)
Ann Robinson (b. 1929)
Liseotte Pulver (b. 1929)
James Hong (b. 1929)
Rachel Ames (b. 1929)
Michael Forest (b. 1929)
Vikki Dougan (b. 1929)
Steve Terrell (b. 1929)
Margaret Kerry (b. 1929)
Priscilla Montgomery (b. 1929)
James Congdon (b. 1929)
Betsy Gay (b. 1929)
Jack Betts (b. 1929)
Clint Eastwood (b. 1930)
Joanne Woodward (b. 1930)
Nita Talbot (b. 1930)
Robert Wagner (b. 1930)
John Astin (b. 1930)
Tommy Cook (b. 1930)
Mary Costa (b. 1930)
Lois Smith (b. 1930)
Peggy King (b. 1930)
Lynn Hamilton (b. 1930)
Don Burnett (b. 1930)
Clark Burroughs (b. 1930)
Robert Hinkle (b. 1930)
Sheila Connolly (b. 1930)
Rita Moreno (b. 1931)
Leslie Caron (b. 1931)
Carroll Baker (b. 1931)
William Shatner (b. 1931)
Mamie Van Doren (b. 1931)
Robert Colbert (b. 1931)
Barbara Eden (b. 1931)
Angie Dickinson (b. 1931)
Claire Bloom (b. 1931)
Marianne Koch (b. 1931)
Sylvia Lewis (b. 1931)
Carmen De Lavallade (b. 1931)
Zohra Lampert (b. 1931)
Michael Dante (b. 1931)
Ann McCrea (b. 1931)
Jack Grinnage (b. 1931)
Maralou Gray (b. 1931)
Billy Mindy (b. 1931)
Sugar Dawn (b. 1931)
Joanne Arnold (b. 1931)
Joel Grey (b. 1932)
George Chakiris (b. 1932)
Felicia Farr (b. 1932)
Abbe Lane (b. 1932)
Steve Rowland (b. 1932)
Ron Hagerthy (b. 1932)
Jacqueline Beer (b. 1932)
Colleen Miller (b. 1932)
Joanne Gilbert (b. 1932)
Neile Adams (b. 1932)
Jacqueline Duval (b. 1932)
Edna May Wonnacott (b. 1932)
Richard Tyler (b. 1932)
Mickey Roth (b. 1932)
Leon Tyler (b. 1932)
Peggy McIntyre (b. 1932)
Christiane Martel (b. 1932)
Elsa Cardenas (b. 1932)
Claude Bessy (b. 1932)
Carlos Fernández (b. 1932)
Kim Novak (b. 1933)
Julie Newmar (b. 1933)
Debra Paget (b. 1933)
Constance Towers (b. 1933)
Joan Collins (b. 1933)
Kathleen Nolan (b. 1933)
Brett Halsey (b. 1933)
Robert Fuller (b. 1933)
Pat Crowley (b. 1933)
Barrie Chase (b. 1933)
Jackie Joseph (b. 1933)
Geoffrey Horne (b. 1933)
Tsai Chin (b. 1933)
Lita Milan (b. 1933)
Vera Day (b. 1933)
Diana Darrin (b. 1933)
Ziva Rodann (b. 1933)
Jeanette Sterke (b. 1933)
Marti Stevens (b. 1933)
Annette Dionne (b. 1933)
Cecile Dionne (b. 1933)
Patti Hale (b. 1933)
Gary Clarke (b. 1933)
Charlotte Austin (b. 1933)
Zale Perry (b. 1933)
Larry Chance (b. 1933)
Shirley MacLaine (b. 1934)
Sophia Loren (b. 1934)
Shirley Jones (b. 1934)
Brigitte Bardot (b. 1934)
Russ Tamblyn (b. 1934)
Pat Boone (b. 1934)
Audrey Dalton (b. 1934)
Tina Louise (b. 1934)
Karen Sharpe (b. 1934)
Joyce Van Patten (b. 1934)
May Britt (b. 1934)
Joby Baker (b. 1934)
Jamie Farr (b. 1934)
Myrna Hansen (b. 1934)
Priscilla Morgan (b. 1934)
Aki Aleong (b. 1934)
Robert Fields (b. 1934)
Dani Crayne (b. 1934)
Donnie Dunagan (b. 1934)
Richard Hall (b. 1934)
Charles Bates (b. 1934)
Marilyn Horne (b. 1934)
Marilee Earle (b. 1934)
Don Crichton (b. 1934)
Jolene Brand (b. 1934)
Johnny Western (b. 1934)
Rod Dana (b. 1935)
Ruta Lee (b. 1935)
Barbara Bostock (b. 1935)
Johnny Mathis (b. 1935)
Leslie Parrish (b. 1935)
Salome Jens (b. 1935)
Yvonne Lime (b. 1935)
Jean Moorehead (b. 1935)
Marco Lopez (b. 1935)
Joyce Meadows (b. 1935)
Richard Harrison (b. 1935)
Christopher Severn (b. 1935)
Richard Nichols (b. 1935)
Carol Coombs (b. 1935)
Patricia Prest (b. 1935)
Dawn Bender (b. 1935)
John Considine (b. 1935)
Jerry Farber (b. 1935)
Clyde Willson (b. 1935)
Bob Burns (b. 1935)
Joel Newfield (b. 1935)
Marlene Cameron (b. 1935)
Lisa Gastoni (b. 1935)
Susan Kohner (b. 1936)
Millie Perkins (b. 1936)
Burt Brickenhoff (b. 1936)
Mason Alan Dinehart (b. 1936)
Anna Maria Alberghetti (b. 1936)
Lisa Davis (b. 1936)
Tommy Ivo (b. 1936)
John Wilder (b. 1936)
Gary Conway (b. 1936)
Michael Chapin (b. 1936)
Carol Morris (b. 1936)
Fernando Alvarado (b. 1936)
Jack Nicholson (b. 1937)
Tommy Sands (b. 1937)
William Wellman Jr. (b. 1937)
Elinor Donahue (b. 1937)
Paul Hampton (b. 1937)
George Takei (b. 1937)
Margaret O’Brien (b. 1937)
Connie Francis (b. 1937)
Carol Nugent (b. 1937)
Patti Brady (b. 1937)
June Hedin (b. 1937)
Paul Collins (b. 1937)
Maureen Hingert (b. 1937)
Ingrid Goude (b. 1937)
Luciana Paluzzi (b. 1937)
Jocelyn Lane (b. 1937)
Barbara Luna (b. 1937)
#dannyreviews#eva marie saint#june lockhart#lee grant#marion ross#terry moore#vera miles#clint eastwood#joanne woodward#robert wagner#mamie van doren#barbara eden#angie dickinson#claire bloom#rita moreno#joel grey#leslie caron#william shatner#george chakiris#kim novak#julie newmar#shirley maclaine#sophia loren#joan collins#russ tamblyn#pat boone#jamie farr#ruta lee#shirley jones#joyce van patten
24 notes
·
View notes
Note
Do you know that Edmund of Langley, 1st Duke of York's wife Isabella is likely to have an affair with a man from the Howard family and gave birth to the Earl of Cambridge, Richard? Isabella's will was made with Edmund's consent, which may indicate that although Edmund did not want his property to go to Richard, he did not hate their mother and son. Perhaps they were just colleagues who had to have children together
I'm not quite sure I'm following your ask. I think you're asking about Isabel (or Isabella) of Castile, Duchess of York and the assertion that Richard, Earl of Cambridge was a son born from her adulterous liaison? However, the man she was accused of having an affair with was not a member of the Howard family but John Holland (or Holand), Earl of Huntington. Huntington was the son of Joan of Kent and Thomas Holland and thus half-brother to Richard II. Huntington was married to Elizabeth of Lancaster who was the sister of Henry IV, which would have been made things awkward (to say the least) when Richard II was deposed. Huntington was killed during the Epiphany Rising which aimed to restore Richard to the throne. .
Jenny Stratford recently published work arguing that the affair did not take place and that Cambridge was legitimate, as far as we can tell. I'll talk you through the evidence and her arguments against it below the cut.
Thomas Walsingham's commentary on Isabel
Thomas Walsingham wrote that Isabel was:
A lady of sensual and self-indulgent disposition, she had been worldly and lustful; yet in the end by the grace of Christ, she repented and was converted. By the command of the king she was buried at his manor of Langley with the friars, where, so it is said, the bodies of many traitors had been placed together.
Stratford points out that Walsingham got the date of her death wrong, placing it two years after her death occurred, which suggests he was probably not well-informed about his life. She suggests that the image of emerges from Isabel's will contrasts sharply against the image Walsingham provides:
The duchess herself emerges in a favourable light. In face of her husband’s debts, the arrangement to provide an income for the seven-year-old Richard by transferring to Richard II most of her jewels and plate, her personal chattels, was eminently practical. It limited the possibility of claims by the duke’s creditors, while grants previously made to Isabel were subsequently reassigned to fund the annuity. These provisions seem very unlikely to indicate that young Richard was illegitimate, any more than a gap of twelve years between the age of the oldest and youngest of the duchess’s three living children was necessarily significant. The duke’s will drawn up a decade after Isabel’s death speaks of his devotion to her.
It's also worth noting that Walsingham has something of a reputation for misogyny and for being unreliable - we now know that some of his assertions about Alice Perrers's background are groundless and serve to make her appear worse than she was, while Anna Duch argued that he effectively erased Anne of Bohemia from his account of Richard II's reign. He is also full of vitriol for Agnes Launcekrona and Katherine Swynford so it seems to me that we should treat his claims on women with great scepticism.
John Shirley's comments on Chaucer's Complaint of Mars
Forty years after Isabel's death, a scribe named John Shirley wrote an afterword on Geoffrey Chaucer's Complaint of Mars that linked it to a scandal involving "the lady of York" and John Holland. Connected with Walsingham's commentary, it's generally been taken as evidence that they had an affair.
Stratford argues that the Shirley's commentary is likely a garbled reference to the affair between Constance of York (Isabel's daughter) and Edmund Holland, Earl of Kent (John Holland's nephew) which the resulted in the birth of an illegitimate daughter, Eleanor. Following Kent's death, Eleanor claimed claimed her parents had married clandestinely before Kent married Lucia Visconti and that she was his rightful heir but her claims were rejected. Historians have suggested that Kent might have considering marrying Constance before the revelation that she had been involved in a plot against Henry IV meant he distanced himself from her.
Additionally, J. D. North argued that the astronomical framework contained within Complaint of Mars could have only applied to the year 1385 and aligns it with the beginning of the affair between Elizabeth of Lancaster and Huntington. Elizabeth had been married to John Hastings, heir to the earldom of Pembroke, in 1380 when she was 16 and Hastings was 8. However, the marriage was annulled in 1386 and Elizabeth soon after married Huntington on 24 June 1386. It is frequently asserted that Huntington and Elizabeth had embarked on an affair that resulted in a pregnancy, leading to the hasty annulment of Elizabeth's first marriage and her second marriage to Huntington though it isn't clear when their first child was born, though it was in 1386 or 1387. It may be that John Shirley's reference to the affair between "the lady of York" and Huntington may actually be referring to Huntington's affair with Elizabeth of Lancaster.
It may even be that the reference represents a garbled combination of the two affairs - Constance of York and Edmund Holland, Elizabeth of Lancaster and John Holland - recorded decades later. It might be noteworthy in this regard that Elizabeth and Huntington's first child was also named Constance (both Constances were named after Isabel's sister, Constanza or Constance of Castile), which would add to the confusion).
The wills of Cambridge's father and older brother.
The argument that Richard, Earl of Cambridge was illegitimate is based around the lack of reference to Cambridge in the wills of his father and older brother, where it is assumed that this represents that Cambridge was effectively, though not legally, disowned.
His brother, Edward 2nd Duke of York's will was written after Cambridge had been executed as a traitor for his role in the Southampton Plot. His lack of reference to Cambridge may simply be because Cambridge was dead and could not be a beneficiary. There may have also been concern that any reference to Cambridge, such a request for prayers for his brother's soul, could result in suspicion of Edward's own loyalties. From the surviving evidence, Edward also seems to have had a close relationship with Henry V so Cambridge's treason may well have driven a wedge between the brothers. In short: there are a lot of reasons why Edward might have avoided referencing Cambridge explicitly that were far more relevant to the circumstances his will was written in.
Stratford notes that "a testator may not include all his bequests in his will", which would apply to both Dukes of York. Edmund of Langley, 1st Duke of York left "nothing in the will to any of his three children" (my emphasis). He did, however, ask to be buried "near his beloved Isabel, formerly his companion". In short, there is no reason to presume Cambridge's exclusion was due to his being informally disowned by his father due to the adultery of his mother. York's will provides no support to the idea that he had a fraught relationship with Isabel, either.
Isabel's will makes special provision for Richard, Earl of Cambridge.
Isabel's will asked Richard II for provide an annuity of 500 marks for Cambridge against the surrender of her jewels and plate until appropriate lands could be found to furnish him with an income. This has led to the belief that Cambridge would not be supported by his father and brother and, in combination with the above, that this was because he was illegitimate.
Most of this is based on the transcript of her will published in Testamenta vetusta, which is a shortened extract of the full document which didn't include Isabel's many bequests to her husband (if you read something that claims Isabel left York nothing, the author is working from the abridged will, not the full text). Stratford's study is on the original will in its full form. As noted in your ask, Isabel required and received the permission of her husband to make this will. Stratford also notes that some of those mentioned in the will are Edmund, Duke of York's officers who also appear in his will, "strongly suggesting that the duke and the leading members of his familia were in full agreement with its provisions". In short, the idea that York was refusing to acknowledge or provide for Cambridge seems somewhat illogical given his involvement and the involvement of his officers in Isabel's will which was primarily concerned with providing for Cambridge.
Stratford argues that what the will represents is an effort by Isabel and York to provide for Cambridge "while protecting as far as possible the incomes of her husband and his heir."
The principal purpose of Isabel’s will was to provide for their youngest child, Richard, then aged seven. Edmund gave his wife full powers to dispose of her horses, jewels, robes, the furnishings of her chamber, and her other chattels. She made a number of bequests, notably including books, but offered the majority of her valuables to Richard II if he would agree to provide her younger son, his godson (filiol), with an income of 500 marks per year for life. If the king did not so wish, Isabel’s oldest son, then earl of Rutland, was invited to do so on the same terms.
At the time Isabel was drawing up her will, York was heavily in debt following his Portuguese expedition, had difficulty obtaining money due to him from the Crown, and didn't have lands commensurate with his status. York's executors were still struggling to pay his debts eight years after his death and when his eldest son died in 1415, the duchy of York remained bankrupt for twenty years. Stratford notes that the money raised by Isabel's jewels and plate would "circumvent claims on the duke by his creditors".
John Holland gave Isabel a gift.
Isabel's will mentions a "sapphire and diamond brooch" given to her by John Holland, Earl of Huntington which has been taken as evidence of their affair. Sometimes she is also said to have been given a gold cup and a chaplet of white flowers by Huntington, though Stratford points out the brooch is the only item actually said to have been given to her by Huntington and is one of three gifts from named donors (the others was a "little" gold tablet given to her by John of Gaunt and a gaming board of jasper from Leo of Armenia).
Firstly, while gifts of jewels to us seem to be strictly or largely romantic gestures, this very much wasn't the case within the Middle Ages, where the exchange of jewels was a normal part of aristocratic life, albeit serving an important function. We know that medieval nobles frequently exchanged gifts, including items they had been given by others, and it is a pure speculation to assume that Isabel "treasured" the brooch or even that she kept it because it was Huntington who had given to her. Furthermore, it is entirely possible that it was identified through the designation as a gift given to her by Huntington.
Secondly, if this is evidence of their affair which produced Cambridge, it's very odd that she didn't leave Huntington's gift to Cambridge but to her eldest son, Edward, who was York's acknowledged son and heir whose legitimacy has never been doubted.
Isabel left bequests to Holland.
Isabel left her Bibles and "the best fillet I have" to John Holland. Some have argued that this is unusual enough because Holland was the only person she gave gifts to who wasn't a "close member" of her family.
Outside of her husband and three children, Isabel also left bequests to Richard II, Anne of Bohemia, John of Gaunt and Eleanor de Bohun, Duchess of Gloucester, and Stratford groups with Eleanor as a member of Isabel's "wider family" and says it is credible they were friends, not lovers. The extent that Holland isn't a "close" member of her family can be debated: he was married to her niece (Elizabeth of Lancaster) and the half-brother of her nephew (Richard II).
Stratford says that Isabel may have made the bequest to Huntington in hope that that he would influence Richard II and John of Gaunt (who was Huntington's father-in-law and and close ally in the 1380s and named as an executor in Isabel's will) to ensure that the annuity she sought for Cambridge would become a reality.
Furthermore, Stratford suggests that the "best fillet" (which was probably a collar) may have been intended for Elizabeth of Lancaster, Huntington's wife. If so, this would rather point away from it being a memento from their affair.
There were a ten-year gap between Cambridge and his siblings.
The other main piece of evidence put forward is the large gap between Constance of York (b. c. 1375) and Cambridge (b. c. 1385). The supposition usually goes that having had two children (Edward, 2nd Duke of York was born c. 1373), Isabel and York had grown tired of each other's company and didn't have sex again, Isabel then embarked on an affair with Huntington that, some ten years after Constance's birth, left her pregnant and York allowed the child to be brought up as his son but refused to provide for him.
The problem with this scenario is that it is effectively a complete invention. The idea that York and Isabel were at odds is based around the idea of the affair and the speculation Cambridge was illegitimate. York never repudiated Isabel nor officially disowned Cambridge as a bastard. There are many possible reasons why there was such a large gap - fertility issues, miscarriages, bad luck, personal decisions, religious reasons (i.e. choosing to adopt a chaste marriage). Constance's birth may have been particularly difficult and York and Isabel decided not to chance sexual intercourse or to use the contraceptive methods available to them only to slip up. It's also possible that they may had other children who died too young to leave evidence behind and that the large gap between children wasn't that large in reality. After all, it seems we know very little about the births of their children, even the years are uncertain.
I know this is all speculative but so is the argument that they fell out. The point is that we don't have evidence to explain why beyond speculation.
Conclusion
A lot of the arguments for the affair based on tenuous links and are often based on the assumption that the affair was a historical fact and that Walsingham's comments on Isabel are an objective and reasonable account of her character. So the evidence that shows us a connection between Isabel and Huntington is often assumed to be evidence of a sexual relationship.
Take the brooch. It seems to be read as the equivalent of a man buying his lover an emerald necklace or diamond earrings. Except we know that the exchange of valuable jewels as gifts was a common aspect of medieval noble life that performed a vital function that very frequently had nothing to do with romantic or sexual feelings. We know, for example, that Henry VI gave Eleanor Cobham a brooch - it does not follow that they were therefore having an affair or that Henry harboured romantic feelings for his aunt.
That the brooch was mentioned in Isabel's will also tells us nothing. We don't know how she felt about it, only that she singled it out to be passed onto her eldest son (not Cambridge). It may be that she wanted him to have it because of he had admired it and, if it was a feminine piece, may have intended to give it onto his wife when he married. It's quite unremarkable that a medieval individual would identify a piece through noting who had given it to them and is not proof of romantic attachment. Isabel also mentioned gifts given to her by John of Gaunt and Leo of Armenia - should we assume she had affairs with them too?
On a similar note: that Isabel left items to Huntington is taken as proof of their romantic liaison. The bequest? Her best fillet (probably a collar, according to Stratford), which may well have been intended for Elizabeth of Lancaster, and her Bibles. They were likely valuable items but hardly proof of romantic involvement - such bequests were very common and would be utterly remarkable without the context of Shirley's commentary on their relationship.
It seems to me that there is good good reason to believe that John Shirley's commentary on Complaint of Mars, written decades after Isabel's death, may not have been about Isabel at all. She isn't named in the commentary and we have no clear, explicit evidence of this affair outside of the commentary itself. I think it was a garbled recollection of either Isabel's daughter, Constance of York's affair with Edmund Holland, Earl of Kent or of John Holland's affair with Elizabeth of Lancaster. We have clear, contemporary evidence of both these affairs - the existence of Constance's and Kent's daughter and this daughter's attempt to inherit Kent's estates, the annulment of Elizabeth's marriage to Hastings and her marriage to Huntington.
The evidence cited as "proof" of their affair is really nothing of the sort. Isabel's will attempted to provide for Cambridge in the face of York's (comparatively) small income and large debts. Huntington was a beneficiary but hardly the only one and not a particularly unusual choice. He gave Isabel a gift that was in keeping with the social custom of their class and time. York's will mentioned none of his children and he did not officially disown Cambridge. The lack of reference to Cambridge in his brother's will is easy to understand given it was written after Cambridge had been executed for treason. We have no real evidence of discontent between Isabel and York - he was obviously involved in the writing of her will and he requested burial with her in his own. Nor is there any account that records discord between them or separation, like we do for John of Gaunt and Constanza of Castile. York was buried with Isabel, as he had requested, and on their joint tomb-monument are Huntington's coat of arms (amongst many others). It seems very strange to me that York was so utterly furious about Isabel's adultery that he refused to provide for Cambridge, forcing Isabel to beg the king to provide for him, yet he chose to be buried with her, he chose as his second bride Huntington's niece, Joan Holland, and he chose to add the coat-of-arms with the man she had betrayed him with on their tomb monument (which was probably constructed sometime between 1393 and 1399). I don't think this picture holds up.
Walsingham did criticise Isabel for being "worldly and lustful" but Walsingham calling a woman a slut is pretty par for the course for him and he got facts of her life wrong. Nor does he report anything she actually did to deserve such a reputation. In others: scepticism is clearly needed. None of this adds up to very much. It isn't until Shirley wrote his commentary, decades later, that we find any reference to their affair. The rest are things that would be entirely unremarkable without Shirley's commentary directing us to see it as a romantic gesture.
Of course, the fact is that we can't prove she didn't have an affair and that Shirley was really referring to a more evidenced scandal. Proving a negative is hard. Even if we located, exhumed and DNA-tested the bodies of Cambridge, York and Huntington, we might confirm that Cambridge was really York's son (or Huntington's or the son of an unknown man) but we wouldn't be able to prove that Isabel didn't have sex with Huntington at some point in her life. We don't have evidence for every single time a medieval individual had sex and so we can't definitively rule out the possibility that an affair did occur. All we can say is the actual surviving evidence doesn't support the narrative that Isabel had an affair.
It's probably worth noting that Kathryn Warner also read Isabel's full will and still accepts the narrative of Isabel's infidelity, though she argues Cambridge should be given the benefit of the doubt where his illegitimacy is concerned. Personally, I find Stratford's reading of the will more credible than Warner's. I don't think the evidence cited as proof of Shirley's claim is actually evidence of an affair but the existence of a typical relationship between medieval nobles working as normal. Warner seems to contradict herself at times* and she doesn't seem to have been interested in questioning whether Isabel did or did not have an affair. I also think Stratford's extensive work on medieval manuscripts and the inventories of John, Duke of Bedford and Richard II lends credence to her claims.
Works Referenced
Jenny Stratford, "The Bequests of Isabel of Castile, 1st Duchess of York, and Chaucer’s ‘Complaint of Mars’", Creativity, Contradictions and Commemoration in the Reign of Richard II: Essays in Honour of Nigel Saul, eds. Jessica A. Lutkin and J. S. Hamilton (The Boydell Press 2022)
Jenny Stratford, "Isabel [Isabella] of Castile, duchess of Yorkunlocked (1355–1392)", Oxford Dictionary of National Biography (published 2022, updated 2023)
J. D. North, Chaucer's Universe (Oxford University Press 1988)
James P. Toomey (ed.), "A Household Account of Edward, Duke of York at Hanley Castle, 1409-10", Noble Household Management and Spiritual Discipline in Fifteenth-Century Worcestershire (Worcestershire Historical Society 2013).
John Evans, "XIV. Edmund of Langley and his Tomb", Archaeologia, vol. 46, no. 2, 1881
Kathryn Warner, John of Gaunt: Son of One King, Father of Another (Amberley 2022)
(also looked at the ODNB entries for York, Cambridge, Huntington and Elizabeth of Lancaster).
* After mentioning the brooch given to Isabel by Huntington, Warner states: "Isabel did not not mention other gifts she had received from anyone else". In an earlier chapter, Warner says "The 1392 will of Isabel of Castile, duchess of York and countess of Cambridge, reveals that Levon [Leo of Armenia] gave her a ‘tablet of jasper’ during this visit, which she bequeathed to John of Gaunt". Warner also repeats this within the chapter dealing with Isabel's will: "and ‘a tablet of jasper which the king of Armonie [King Levon of Armenia] gave me’ to John of Gaunt". How can Huntington's brooch be the only gift from anyone mentioned in her will when we've been told (twice) that Isabel's will includes a reference to a tablet of jasper gifted to her by Leo of Armenia? Additionally, Warner's arguments seems to be drawn from the preconceived notion that Isabel did have an affair so any evidence connecting her to Huntington must be evidence of the affair, regardless of how limited the evidence is - this is quite surprising, since it goes against one of her arguments against reading Isabella of France and Roger Mortimer's relationship as a love affair.
#ask#anon#isabel of castile duchess of york#john holland earl of huntington#edmund duke of york#richard earl of cambridge#i did just have the revelation cambridge was only a year and a bit older than henry v#god this is long
12 notes
·
View notes
Text


The triangle Constance of Castile, John of Gaunt and Katherine Swynford
Part One
Katherine Swynford and John of Gaunt met whilst she was in the service of his first Duchess, Blanche, as a chamber servant. During this time, the two women were on close terms, for Katherine’s own daughter, Blanche Swynford, was placed in the same chamber as both Philippa and Elizabeth – the daughters of Blanche of Lancaster – and Gaunt was appointed as her godfather. Katherine was married to one of Gaunt’s retainers, Sir Hugh Swynford, who held a manor in Kettlethorpe in Lincolnshire. Hugh Swynford suddenly died, whilst serving John of Gaunt in Aquitaine. He left Kettlethorpe in the possession of Katherine and his son and heir Thomas, who was four years old. Hugh Swynford’s land and house were part of the Duchy of Lancaster, and as his Lord, John of Gaunt dutifully ensured the welfare of his family. He employed Katherine in his household as a ‘maistresse’ – a governess – to his daughters, and appointed her sister Philippa, the wife of Geoffrey Chaucer, to serve Duchess Constance.
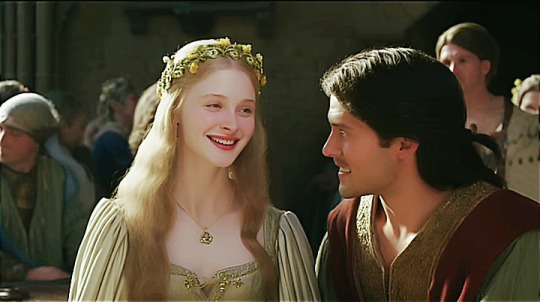
In spring 1372, shortly after John of Gaunt paraded Constance through London, he gifted Katherine a generous sum of money. This is the first record of his direct association with her, and it is likely that around this time she became his mistress. Katherine’s conveyance of the news of Princess Catalina’s birth to the King suggests that she had been in attendance; having borne at least four children of her own at a young age, she would have been able to reassure and support Constance through her ordeal. But as soon as her own pregnancy became obvious, a pregnancy that could not have been her husband’s doing, she would have been obliged to resign her post and return to Kettlethorpe.

In 1373, the first son of the lovers couple, John, was born and given the surname Beaufort. Following his birth, John of Gaunt granted Katherine more money as well as a lucrative marriage agreement for her daughter Blanche. John Beaufort’s early years were probably spent at Kettlethorpe. The pattern of John’s grants to Katherine, some of them concerning its refurbishment, some of them handsome gifts, may indicate the dates of birth of their other children, and certainly suggests that the manor was being made a fit place for them to be brought up in. Kettlethorpe was a remote village with a tiny population, an ideal setting for discreet confinements and the raising of royal bastards whose existence was better kept secret – at least for the present.

Certainly the lovers were discreet, at least to begin with – had they not been, the world would soon have known of their affair, and we would not have to rely on inference and speculation in determining the circumstances in which it began. Costain argues that it was Katherine who insisted on secrecy in the early years of the liaison – she was, after all, newly widowed – but there were political imperatives to be considered too: John would not have wished to openly dishonour his new wife when all his hopes were centred on claiming the crown of Castile in her right. Thus the need for discretion was probably mutual, and it ensured that for some years to come, his affair with Katherine was conducted in secrecy and with great circumspection.
Sadly for those romantics who would prefer to believe that the Duke stayed true to Katherine within the limits of their adulterous relationship, there is some evidence that he had fleeting sexual encounters with other women during the course of it. In 1381, he was publicly to confess that he had committed the sin of lechery with Katherine herself ‘and many others in his wife’s household’. Probably John’s amours were fleeting and purely physical – and made no impact on his obviously deep feelings for Katherine Swynford.

Yet it appears that the Duchess’s Castilian ladies were already aware in 1373 that Katherine was John’s mistress. Their gossiping so annoyed the Duke that he packed them all off to Nuneaton Abbey, hoping that the Abbess would teach them discretion. If her ladies knew what was going on between the Duke and Katherine, the chances are that Constance did too.
By 1375 Katherine's position of influence with the Duke was becoming public knowledge. Although there are very few known instances of her exercising any powers of patronage, the Leicester records show that she occasionally used her influence for the benefit of others, while there is evidence to suggest that if she did ask favours from the Duke, it was usually for her own family members.
The public and liberal relationship that Gaunt and Katherine enjoyed after 1377 was due to Gaunt’s shift in position after the death of Edward III. He was the uncle of King Richard II, the most powerful noble in the country, a Prince, and even a King himself; he was powerful enough to conduct the affair without fearing the consequences. Katherine accompanied John of Gaunt that summer as he toured his extensive Duchy lands – the towns and villages where he was most at ease and felt confident in the love of the people. It was certainly at the request of John of Gaunt, within weeks of Richard’s ascension, that Katherine was granted two wealthy manor estates for life, in exchange for Gaunt’s county of Richmond. This generous gift – at the cost of his own property – is testament to Gaunt’s respect and love for Katherine Swynford in the late 1370s.
Sources:
Alison Weir, KATHERINE SWYNFORD: THE STORY OF JOHN OF GAUNT AND HIS SCANDALOUS DUCHESS
Helen Carr, THE RED PRINCE: THE LIFE OF JOHN OF GAUNT, THE DUKE OF LANCASTER
Images from youtube's video:
youtube
#constance of castile#john of gaunt#katherine swynford#constanza de castilla#constanza of castile#geofrey chaucer#richard ii#hugh swynford#john beaufort#english history#lancaster#Youtube
10 notes
·
View notes
Note
I responded to the booklist question! I'm sure I forgot some but whew it still took forever to write.
What about you? What are some of the books youve read the most?
Good question! I finally started keeping a list, so I have something to work from. That way I won't draw a blank.
My top five or six favorite authors and series are: J. R. R. Tolkien's Lord of the Rings, C. S. Lewis's Narnia books, Rosemary Sutcliff's Dolphin Ring series (beginning with Eagle of the Ninth), Enemy Brothers and The Reb and the Redcoats by Constance Savery the Queen's Thief series by Megan Whalen Turner, and The Mysterious Benedict Society (original trilogy and prequel) by Trenton Lee Stewart.
There are many other books and authors I love. I listed several of my childhood influences in this post featuring my 50 favorite children's books (focusing on ones I grew up with as a young person).
Here's my list of favorite books I've read the most or ones I think are worth rereading: The Ordinary Princess by M. M. Kaye (a delightful original fairytale about a princess who refuses to stay in her tower)
The Reluctant Godfather by Allison Tebo (romantic comedy fairytale retelling, with an emphasis on the comedy) Mrs. Frisby and the Rats of NIMH by Robert C. O'Brien (adventure about a mother mouse seeking to save her family) The Gammage Cup by Carol Kendall (middle grade fantasy adventure)
Dragon Slippers and Tuesdays at the Castle by Jessica Day George (original fantasy in the style of fairytales) Princess Academy by Shannon Hale (fantasy adventure and coming-of-age story about a group of girls who attend school for the first time)
The Secret Keepers by Trenton Lee Stewart (urban light fantasy with dystopian elements) The City of Ember by Jeanne DuPrau (middle-grade, post-apocalyptic dystopian) The Arrival by Shaun Tan (a wordless graphic novel that conveys human experiences through surrealism)
The Saturdays by Elizabeth Enright (vintage contemporary about a lively family) Derwood, Inc. by Jeri Massi (modern contemporary mystery about another boisterous family) The Westing Game by Ellen Raskin (quirky vintage mystery with an interesting cast of characters) Historical Fiction: Carry On, Mr. Bowditch by Jean Lee Latham Caddie Woodlawn, Family Grandstand, and other books by Carol Ryrie Brink Rebecca's War by Ann Finlayson Understood Betsy by Dorothy Canfield Fisher Knight's Fee by Rosemary Sutcliff
The Lost Baron by Allen French The Wheel on the School by Meindert DeJong By the Great Horn Spoon by Sid Fleischman A Single Shard and Seesaw Girl by Linda Sue Park The Bronze Bow and The Witch of Blackbird Pond by Elizabeth George Speare The Secret Garden and A Little Princess by Frances Hodgson Burnett Wives and Daughters by Elizabeth Gaskell A few books I discovered more recently that are now all-time favorites: Seventh City by Emily Hayse, The Letter for the King by Tonke Dragt, Valiant by Sarah McGuire, Out of the Tomb by Ashley Stangl, the Mistmantle Chronicles by M. I. McAllister, Escape to Vindor by Emily Golus, Chase the Legend by Hannah Kaye, The Key to the Chains by Allison Tebo (sci-fi), Rebel Wave by Tor Thibeaux (undersea dystopian) Historical fiction: Listening for Lions and Angel on the Square by Gloria Whelan, Courage in Her Hands by Iris Noble, Victory at Valmy and Word to Caesar by Geoffrey Trease, historical fiction Westerns and mysteries by author Elisabeth Grace Foley
Mystery/suspense: The Unexpected Mrs. Pollifax by Dorothy Gilman, The Moonspinners by Mary Stewart
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
KATHERINE SWYNFORD: THE SCANDALOUS DUCHESS
KATHERINE SWYNFORD (BORN KATHERINE DE ROET) WAS BORN 1349-50; SHE IS KNOWN AS THE DUCHESS OF LANCASTER, WIFE OF JOHN OF GAUNT, BUT HOW DID THE DAUGHTER OF A HAINAULT KNIGHT RISE TO SUCH A TITLE?
Early Life
KATHERINE WAS BORN 1349-50 LIKELY IN THE COUNTY OF HAINAULT. KATHERINE IS THE DAUGHTER OF PAON DE ROET, A KNIGHT ORIGINALLY FROM HAINAULT, HE CAME TO ENGLAND IN 1328 WITH PHILIPPA OF HAINAULT WHEN SHE MARRIED KING EDWARD III OF ENGLAND. HER MOTHER IS UNKNOWN. PAON TOOK PART IN THE HUNDREDS YEARS' WAR. IN 1349, PAON RETURNED TO HAINAULT TO SERVE MARGARET, COUNTESS OF HAINAULT, WHEN THE COUNTESS HAD TO FLEE TO ENGLAND DUE TO CIVIL WAR HE ACCOMPANIED HER. SHORTLY AFTER, ALL MENTION OF HIM DISAPPEARS.
KATHERINE HAD THREE KNOWN SIBLINGS: ISOBEL DE ROET, A NUN AND LATER A CANONESS, GEOFFREY CHAUCER, AUTHOR OF THE CANTERBURY TALES, WALTER DE ROET AND PHILIPPA DE ROET.
FROM THE YEAR 1352, KATHERINE AND PHILIPPA, HER SISTER WERE RAISED IN THE ROYAL HOUSEHOLD OF QUEEN PHILIPPA OF HAINAULT (MENTIONED EARLIER), THIS MAKES IT SEEM AS THOUGH THEIR MOTHER WAS DEAD. KATHERINE THEN WOULD'VE KNOWN ALL MEMBERS OF THE ROYAL FAMILY, INCLUDING HER FUTURE HUSBAND, JOHN OF GAUNT. KATHERINE UNDER THE QUEEN'S GUIDANCE WOULD'VE BECOME AN EXPERT IN PROTOCOL AND COURT ETIQUETTE.
First Marriage
IN OR ABOUT 1360, KATHERINE WAS PLACED IN THE HOUSEHOLD OF BLANCHE OF LANCASTER, DUCHESS OF LANCASTER AND FIRST WIFE TO JOHN OF GAUNT. IN 1466, JOHN OF GAUNT, AT THE REQUEST OF HIS WIFE ORGANISED THE MARRIAGE OF KATHERINE TO SIR HUGH SWYNFORD, A KNIGHT IN SERVICE TO JOHN HIMSELF.
KATHERINE AND HER HUSBAND HAD THREE CHILDREN, BLANCHE SWYNFORD, AFTER BLANCHE OF LANCASTER, DIED IN CHILDHOOD, SIR THOMAS SWYNFORD AND MARGARET SWYNFORD, WHO BECAME A NUN AT BARKING ABBEY.
BLANCHE OF LANCASTER, JOHN OF GAUNT'S FIRST WIFE DIES AGED 26, FROM CHILDBIRTH COMPLICATIONS OR PERHAPS THE PLAGUE. JOHN MARRIED CONSTANCE OF CASTILE ON SEPTEMBER 31ST 1368, WHO WAS THE DAUGHTER OF KING PEDRO I OF CASTILE AND LEÓN.
THREE YEARS AFTER THE DEATH OF BLANCHE OF LANCASTER, KATHERINE'S OWN HUSBAND, SIR HUGH SWYNFORD DIES. IN 1370, SIR HUGH WENT ON A MILITARY CAMPAIGN WITH JOHN OF GAUNT TO AQUITAINE. WHEN JOHN OF GAUNT RETURNED TO ENGLAND IN FALL 1371, SIR HUGH DID NOT COME WITH HIM DUE TO FALLING ILL. HE DIED IN AQUITAINE ON THE 13th OF NOVEMBER 1471.
KATHERINE, NOW A WIDOW, WAS GIVEN CONTROL OF HIS ESTATES IN COLEBY AND KETTLETHORPE IN LICOLNSHIRE, ENGLAND.
JOHN OF GAUNT'S MISTRESS
KATHERINE BECAME A MEMBER OF JOHN OF GAUNT'S NEW WIFE, CONSTANCE OF CASTILE. IR IS UNKNOWN WHEN EXACTLY JOHN AND KATHERINE BECAME LOVERS, BUT THE AFFAIR HAD DEFINITELY STARTED BY LATE 1372, AS KATHERINE AND JOHN'S ELDEST SON WAS BORN NO LATER 1373.
KATHERINE AND JOHN OF GAUNT HAD ONE DAUGHTER AND THREE SONS. THE CHILDREN WERE GIVEN THE SURNAME 'BEAUFORT' AFTER THE NOW DEMOLISHEE BEAUFORT CASTLE IN CHAMPAGNE, FRANCE.
JOHN BEAUFORT, 1ST EARL OF SOMERSET
HENRY, CARDINAL BEAUFORT
THOMAS BEAUFORT, DUKE OF EXETER
JOAN BEAUFORT, COUNTESS OF WESTMORLAND
KATHERINE IS GIFTED SEVERAL ESTATES AND AN ALLOWANCE FROM JOHN. IN 1381 JOHN IS FORCED TO BREAK IT OFF WITH KATHERINE AFTER THE PEASANTS' REVOLT, SENDING HER A QUITCLAIM.
ON THE 24th OF MARCH 1394, CONSTANCE OF CASTILE, DUCHESS OF LANCASTER AND SECOND WIFE OF JOHN OF GAUNT DIES. THE MARRIAGE HAD BEEN A POLITICAL ONE, BUT ENGLAND NEVER GAINS CONTROL OF CASTILE.
SECOND MARRIAGE
IN THE EARLY 1390S, BEFORE HIS WIFE EVEN DIED, JOHN OF GAUNT HAD RESUMED HIS AFFAIR WITH KATHERINE. IN 1396, TWO YEARS AFTER THE DEATH OF CONSTANCE OF CASTILE, JOHN OF GAUNT MARRIED KATHERINE, MAKING HER DUCHESS OF LANCASTER ON THE 13th OF JANUARY 1396. AFTER THE MARRIAGE TOOK PLACE THE FOUR CHILDREN OF KATHERINE AND JOHN WERE LEGITIMATE, NO LONGER SEEN AS ILLEGITIMATE (OR BASTARDS), THE CHILDREN WERE LEGITMIZED BY RICHARD II AND THE POPE.
AFTER HENRY BOLINGBROKE, JOHN'S ELDEST SON, BY BLANCHE OF LANCASTER, DEPOSED HIS COUSIN RICHARD II IN 1399, THE NEW KING HENRY IV INSERTED A PHRASE INTP THE DOCUMENTS THAT MADE HIS SIBLINGS LEGITMATE, 'EXCEPTA REGALI DIGNITATE' (EXCEPT ROYAL STATUS) WHICH SUPPOSEDLY BANNED THEM FROM THE THRONE.
JOHN OF GAUNT AND KATHERINE'S DESCENDANTS ARE IMPORTANT IN ROYAL HISTORY, WITH THE TUDOR DYNASTY BEING DESCENDED FROM THEM. JOHN OF GAUNT AND KATHERINE'S DAUGHTER, JOAN, WAS THE MATERNAL GRANDMOTHER TO TWO YORKIST KINGS, EDWARD IV AND RICHARD III
JOHN OF GAUNT PASSED AWAY ON THE 3rd OF FEBRUARY 1399, AND WAS BURIED NEXT TO HIS FIRST WIFE, BLANCHE OF LANCASTER. THEY WERE BURIED AT OLD ST. PAUL'S CATHEDRAL, UNFORTUNATELY THE GREAT FIRE OF 1666 DESTROYED THE CATHEDRAL.
KATHERINE SURVIVED JOHN OF GAUNT BY FOUR YEARS, DYING IN LINCOLN, ENGLAND ON MAY 3rd 1403 at around 53.

Katherine's Coat of Arms as Duchess of Lancaster, after her patron Saint, Saint Catherine who was also Saint Catherine of the Wheel.
#history#royalty#medieval#england#royal family#Katherine#KatherineSwynford#john of gaunt#Katherine Swynford#1300s#edward iii#the plantagenets#lancaster#york
2 notes
·
View notes
Text

6 notes
·
View notes
Text
something aomething about the multiple accounts of Geoffrey being a sweet talker and a good negotiator and overall charming perceptive social person and politician...amongst men. But Bertran calling him out as someone Who Doesn't Know How to Please the Ladies....and the Gace Brule poem mention of him being weirded out by the Overdramatic Troubadour romances ...
#Bertran: that's my Rassa for you#Geoffrey smooth talker but very unromantic#But Constance loves him for himself#Geoffrey Duke of Brittany#Gace Brule
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
i just want everyone to know that my oc universe is partially passion (1854-1864) encompassing alessandra/fosca + the last years of the madam and then a sort of mix between gilded age (i have no year to year date here.... because i haven't written it yet but with isadora/rosalyn + alessandra's evil evolution) and the early victorian (1837-1852) with henrik + isadora/the madam + alessandra followed by the madam's origin story which is .... regency... (1811-1820) with adéline (the madam) my beloved <3
and there's so many side characters too! there's renato and carolina and (signora) costanza and violetta and constance and geoffrey and héloïse ...
#oc talk#gahhhhh i need to introduce everyone honestly i'm SOOO hyped for this new universe i've developed
3 notes
·
View notes
Text



Their next stop is courtesy of Amanda. She wants to see her family friends Alison and Erwin, but Alison and Kristina don't necessarily get along.
To Alison, Kristina is a half-sister she never wished for. Alison loved her father very much and saw his infidelities not as the fault of him, but of the women involved. She considers herself, Geoffrey, Kristofer and the adopted Vincent as the actual family. Kristina and her sister Sally, and Marcella and Tammy, she doesn't usually acknowledge at all.
But to Amanda it's important to stay in contact with Alison, and with Erwin! Luckily, the children don't care much for adult drama. Especially not little Constance Laws, Alison and Erwin's adopted daughter. She quickly warms to Kristina!


#sims 4 legacy#ts4 legacy#legacy:johansson#ts4 gameplay#johansson gen 2#kristina landgraab cho#alison landgraab#constance laws#floyd pries
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Queens and Princesses of the Spanish Kingdoms: Ages at First Marriage
I have only included women whose birth dates and dates of marriage are known within at least 1-2 years, therefore, this is not a comprehensive list. This data set ends with the transition to Habsburg-controlled Spain.
Sancha, wife of King Fernando I of Léon; age 14 when she married Fernando in 1032 CE
Ermesinda of Bigorre, wife of King Ramiro I of Aragon; age 21 when she married Ramiro in 1036 CE
Sancha, daughter of King Ramiro I of Aragon; age 18 when she married Count Ermengol III of Urgell in 1063 CE
Constance of Burgundy, wife of King Alfonso VI of Léon & Castile; age 19 when she married Count Hugh II of Chalon in 1065 CE
Felicia of Roucy, wife of King Sancho of Aragon; age 16 when she married Sancho in 1076 CE
Agnes of Aquitaine, wife of King Pedro I of Aragon; age 14 when she married Pedro in 1086 CE
Teresa, daughter of King Alfonso VI of Léon & Castile; age 13 when she married Count Henri of Burgundy in 1093 CE
Elvira, daughter of King Alfonso VI of Léon & Castile; age 15 when she married Count Raymond IV of Toulouse in 1094 CE
Bertha, wife of King Pedro I of Aragon; age 22 when she married Pedro in 1097 CE
Elvira, daughter of King Alfonso VI of Léon & Castile; age 17 when she married King Ruggero II of Sicily in 1117 CE
Berenguela of Barcelona, wife of King Alfonso VII of Léon & Castile; age 12 when she married Alfonso in 1128 CE
Urraca, daughter of King Alfonso VII of Léon; age 11 when she married King Garcia Ramirez of Navarre in 1144 CE
Petronilla, daughter of King Ramiro II of Aragon; age 14 when she married Count Ramon Berenguer IV of Barcelona in 1150 CE
Richeza of Poland, wife of King Alfonso VII of Léon & Castile; age 12 when she married Alfonso in 1152 CE
Sancha, daughter of King Alfonso VII of Léon & Castile; age 14 when she married King Sancho VI of Navarre in 1153 CE
Constanza, daughter of King Alfonso VII of Léon & Castile; age 16 when she married King Louis VII of France in 1154 CE
Urraca of Portugal, wife of King Fernando II of Léon; age 17 when she married Fernando in 1165 CE
Eleanor of England, wife of King Alfonso VIII of Castile; age 9 when she married Alfonso in 1170 CE
Sancha of Castile, wife of King Alfonso II of Aragon; age 20 when she married Alfonso in 1174 CE
Dulce, daughter of Queen Petronilla of Aragon; age 14 when she married King Sancho I of Portugal in 1174 CE
Berenguela, daughter of King Alfonso VIII of Castile; age 7 when she married Duke Conrad II of Swabia in 1187 CE
Marie of Montpellier, wife of King Pedro II of Aragon; age 10 when she married Viscount Raymond Geoffrey II of Marseille in 1192 CE
Garsenda of Foralquier, wife of Prince Alfonso II of Aragon; age 13 when she married Alfonso in 1193 CE
Constance of Toulouse, wife King Sancho VII of Navarre; age 15 when she married Sancho in 1195 CE
Constanza, daughter of King Alfonso II of Aragon; age 19 when she married King Emeric of Hungary in 1198 CE
Blanca of Castile, daughter of King Alfonso VIII of Castile; age 12 when she married King Louis VIII of France in 1200 CE
Eleonora, daughter of King Alfonso II of Aragon; age 22 when she married Count Raymond VI of Toulouse in 1204 CE
Urraca, daughter of King Alfonso VIII of Castile; age 19 when she married King Afonso II of Portugal in 1206 CE
Mafalda of Portugal, wife of King Enrique I of Castile; age 20 when she married Enrique in 1215 CE
Sancha, daughter of King Alfonso II of Aragon; age 25 when she married Count Raymond VII of Toulouse in 1211 CE
Elisabeth of Swabia, wife of King Fernando III of Castile; age 14 when she married Fernando in 1219 CE
Eleonora of Castile, wife of King Jaime I of Aragon; age 19 when she married Jaime in 1221 CE
Berenguela, daughter of King Alfonso IX of Léon; age 20 when she married Emperor Jean I of Brienne in 1224 CE
Marguerite of Bourbon, wife of King Teobaldo I of Navarre; age 15 when she married Teobaldo in 1232 CE
Yolanda of Hungary, wife of King Jaime I of Aragon; age 20 when she married Jaime in 1235 CE
Joan of Dammartin, wife of King Fernando III of Castile; age 17 when she married Fernando in 1237 CE
Yolanda, daughter of King Jaime I of Aragon; age 13 when she married King Alfonso X of Castile in 1249 CE
Isabelle of France, wife of King Teobaldo II of Navarre; age 14 when she married Teobaldo in 1255 CE
Kristina of Norway, wife of Prince Felipe of Castile; age 24 when she married Felipe in 1258 CE
Beatriz, daughter of King Teobaldo I of Navarre; age 16 when she married Duke Hugues IV of Burgundy in 1258 CE
Constanza, daughter of King Jaime I of Aragon; age 21 when she married Prince Manuel of Castile in 1260 CE
Constanza of Sicily, wife of King Pedro III of Aragon; age 13 when she married Pedro in 1262 CE
Isabel, daughter of King Jaime I of Aragon; age 14 when she married King Louis IX of France in 1262 CE
Beatrice of Savoy, wife of Prince Manuel of Castile; age 18 when she married Pierre of Chalon in 1268 CE
Blanche of France, wife of Prince Fernando of Castile; age 16 when she married Fernando in 1269 CE
Blanche of Artois, wife of King Enrique I of Navarre; age 21 when she married Enrique in 1269 CE
Beatriz, daughter of King Alfonso X of Castile; age 17 when she married Marquis William VII of Montferrat in 1271 CE
Esclaramunda of Foix, wife of King Jaime II of Majorca; age 25 when she married Jaime in 1275 CE
Maria de Molina, wife of King Sancho IV of Castile; age 17 when she married Sancho in 1282 CE
Yolanda, daughter of King Alfonso X of Castile; age 17 when she married Diego Lopez V de Haro in 1282 CE
Juana, daughter of King Enrique I of Navarre; age 11 when she married King Philippe IV of France in 1284 CE
Maria Diaz I de Haro, wife of Prince Juan of Castile; age 17 when she married Juan in 1287 CE
Yolanda, daughter of Prince Manuel of Castile; age 12 when she married Prince Afonso of Portugal in 1287 CE
Isabel, daughter of King Pedro III of Aragon; age 17 when she married King Denis of Portugal in 1288 CE
Isabel of Castile, wife of King Jaime II of Aragon; age 8 when she married Jaime in 1291 CE
Blanche of Anjou, wife of King Jaime II of Aragon; age 15 when she married Jaime in 1295 CE
Yolanda, daughter of King Pedro III of Aragon; age 24 when she married Prince Roberto of Naples in 1297 CE
Constanza of Portugal, wife of King Fernando IV of Castile; age 12 when she married Fernando in 1302 CE
Beatriz, daughter of King Sancho IV of Castile; age 16 when she married King Afonso IV of Portugal in 1309 CE
Maria, daughter of King Jaime II of Aragon; age 12 when she married Prince Pedro of Castile in 1311 CE
Constanza, daughter of King Jaime II of Aragon; age 12 when she married Prince Juan Manuel of Villena in 1312 CE
Teresa d'Entença, wife of King Alfonso IV of Aragon; age 14 when she married Alfonso in 1314 CE
Marie of Lusignan, wife of King Jaime II of Aragon; age 42 when she married Jaime in 1315 CE
Isabel, daughter of King Jaime II of Aragon; age 10 when she married King Frederick I of Germany in 1315 CE
Eleonora of Castile, wife of Prince Jaime of Aragon; age 12 when she married Jaime in 1319 CE
Elisenda of Montcada, wife of King Jaime II of Aragon; age 30 when she married Jaime in 1322 CE
Blanca de La Cerda y Lara, wife of Prince Juan Manuel of Castile; age 10 when she married Juan Manuel in 1327 CE
Constanza, daughter of King Alfonso IV of Aragon; age 18 when she married King Jaime III of Majorca in 1336 CE
Cecilia of Comminges, wife of Prince Jaime of Aragon; age 16 when she married Jaime in 1336 CE
Maria of Navarre, wife of King Pedro IV of Aragon; age 8 when she married Pedro in 1337 CE
Leonor of Portugal, wife of King Pedro IV of Aragon; age 19 when she married Pedro in 1347 CE
Eleonora of Sicily, wife of King Pedro IV of Aragon; age 24 when she married Pedro in 1349 CE
Juana Manuel, daughter of Prince Juan Manuel; age 11 when she married King Enrique of Castile in 1350 CE
Blanche of Bourbon, wife of King Pedro of Castile; age 14 when she married Pedro in 1353 CE
Constanza, daughter of King Pedro IV of Aragon; age 18 when she married King Federico of Sicily in 1361 CE
Maria de Luna, wife of King Martin of Aragon; age 14 when she married Martin in 1372 CE
Juana, daughter of King Pedro IV of Aragon; age 29 when she married Count Juan I of Ampurias in 1373 CE
Marthe of Armagnac, wife of King Juan I of Aragon; age 26 when she married Juan in 1373 CE
Beatriz of Portugal, wife of Prince Sancho of Castile; age 19 when she married Sancho in 1373 CE
Eleonora of Aragon, daughter of King Pedro IV of Aragon; age 17 when she married King Juan I of Castile in 1375 CE
Eleonora, daughter of King Enrique II of Castile; age 12 when she married King Carlos III of Navarre in 1375 CE
Isabel of Portugal, wife of Count Alfonso Enriquez; age 13 when she married Alfonso in 1377 CE
Violant of Bar, wife of King Juan I of Aragon; age 15 when she married Juan in 1380 CE
Beatriz of Portugal, wife of King Juan I of Castile; age 10 when she married Juan in 1383 CE
Juana, daughter of King Juan I of Aragon; age 17 when she married Count Matthieu of Foix in 1392 CE
Eleonora of Albuquerque, wife of King Fernando I of Aragon; age 20 when she married Fernando in 1394 CE
Yolanda, daughter of King Juan of Aragon; age 19 when she married Duke Louis II of Anjou in 1400 CE
Blanca I of Navarre, wife of Prince Martin of Aragon; age 15 when she married Martin in 1402 CE
Juana, daughter of King Carlos III of Navarre; age 20 when she married Count Jean I of Foix in 1402 CE
Beatriz, daughter of King Carlos III of Navarre; age 14 when she married Count James II of La Marche in 1406 CE
Isabel, daughter of King Pedro IV of Aragon; age 31 when she married Count Jaime II of Urgell in 1407 CE
Margarita of Prades, wife of King Martin of Aragon; age 14 when she married Martin in 1409 CE
Maria of Castile, wife of King Alfonso V of Aragon; age 14 when she married Alfonso in 1415 CE
Catalina of Castile, wife of Prince Enrique of Aragon; age 15 when she married Enrique in 1418 CE
Isabel, daughter of King Carlos III of Navarre; age 24 when she married Jean IV of Armagnac in 1419 CE
Maria, daughter of King Fernando I of Aragon; age 17 when she married King Juan II of Castile in 1420 CE
Eleonora, daughter of King Fernando I of Aragon; age 26 when she married King Duarte of Portugal in 1428 CE
Agnes of Cleves, wife of Prince Carlos of Aragon; age 17 when she married Carlos in 1439 CE
Blanca II of Navarre, daughter of King Juan II of Aragon and Queen Blanca I of Navarre; age 18 when she married King Enrique IV of Castile in 1440 CE
Eleonora of Navarre, daughter of King Juan II of Aragon and Queen Blanca 1 of Navarre; age 15 when she married Count Gaston IV of Foix in 1441 CE
Juana Enriquez, wife of King Juan II of Aragon; age 19 when she married Juan in 1444 CE
Isabel of Portugal, wife of King Juan II of Castile; age 19 when she married Juan in 1447 CE
Joana of Portugal, wife of King Enrique IV of Castile; age 16 when she married Enrique in 1455 CE
Isabel I of Castile, wife of King Fernando II of Aragon; age 18 when she married Fernando in 1469 CE
Juana, daughter of King Enrique IV of Castile; age 13 when she married King Afonso V of Portugal in 1475 CE
Juana, daughter of King Juan II of Aragon; age 21 when she married King Fernando I of Naples in 1476 CE
Isabel, daughter of King Fernando II of Aragon; age 20 when she married Prince Afonso of Portugal in 1490 CE
Juana, daughter of King Fernando II of Aragon; age 22 when she married Felipe I of Castile in 1501 CE
Margaret of Austria, wife of Prince Juan of Aragon; age 17 when she married Juan in 1497 CE
Maria, daughter of King Fernando II of Aragon; age 18 when she married King Manuel I of Portugal in 1500 CE
Catalina, daughter of King Fernando II of Aragon; age 15 when she married Prince Arthur of England in 1501 CE
Germaine of Foix, wife of King Fernando II of Aragon; age 18 when she married Fernando in 1506 CE
112 women; average age at first marriage was 16. The eldest bride was 42 years old, and the youngest was 7.
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
Chloe Hardbroom: A Brown Or A Pouncer?:

So...here's the General Story.
Back in the mid-to-late 1950's, an Ex-Codice wizard, Conrad Hardbroom (Christopher Lee/Gary Raymond) had met a classy young Midnight Folk witch named, Chloe (Rosemary Harris/Shirley Anne Field) when the ladder was wanting to erase her ties from the occult. With Conrad's help, Chloe would succeed in that goal through the Ex-Codice's Erasure Ritual. As a result, Chloe and Conrad's children would be Ex-Codice instead of Midnight Folk (by law, the "breed" of wizardry would fall on the mother unless she's a Muggle/Non-Magic).
Chloe and Conrad would marry and have two children. Their first, Constance Hardbroom (Kate Duchene) later (secretly) married the Imperium wizard, Severus Snape (Alan Rickman) and produced a son, Nick Hobbes (Bobby Barry) (and a daughter, Morrigan, much later but all that's a different story...).
Then there's the younger child, Clyde Hardbroom (Jason Carter) who'd go on to marry Claire Delune (Julia Sawalha) and have their own son, Artemis Hardbroom (Joe Prospero).
Now here's the dilemma;
While Chloe's family are from "The Box Of Delights" with her mother being Sylvia Daisy Pouncer (the abusive ex-governess of the protagonist played by Patricia Quinn), there's Chloe's father; Abner Brown (Robert Stephens who, oddly enough, was the ex-husband of Maggie Smith a.k.a Minerva "The Queen" McGonagall) or Foxy-Faced Charles (Geoffrey Larder, who's role the filmmakers wanted Alan Rickman for, but Rickman wanted to play Abner Brown...).
Abner Brown was the main villian of "The Box Of Delights" who would stop at nothing to get anything he desired be it power, treasure or the titular artifact. Even turning to Dark Magic to reach his goals. In between "The Midnight Folk" and "The Box Of Delights", he married his cohort, Pouncer whom he didn't seem to care for as he intended to leave her in the dust with his minions. In the end, Sylvia left Abner to his death when she left with Foxy-Faced Charles, Chubby Joe and a great deal of expensive jewlery. If Abner were to be Chloe's father, Chloe would be born in 1935. It would also explain where Constance (and Nick) got their dramatics from. Granted, Pouncer can be like that too but there's also Nick's megalomania...which Nick may've picked up from Snape (like a true Slytherin).
Then there's Foxy-Faced Charles, Abner's abused minion. As Chubby Joe's best friend, Charles is usually the one who keeps Joe on task. While Joe can turn into a wolf while Charles can turn into a fox at will. For some time, Charles and Sylvia have been having an affair before "The Box Of Delights". If Charles were to be Chloe's father, this would not only make Chloe a red-head but also a shape-shifter before the Erasure Ritual. She'd also be born a bit later in 1937-1938.
@theweirdsistercollege @worstwitchstudent @theworstwitch @theworstwitchforever @tinyvoidwinnerpeach
#worst witch#1998 worst witch#box of delights#harry potter#harry potter films#harry potter movies#constance hardbroom#hardbroom#snape#severus snape#nick hobbes#hobbes#hobbes weirdsister college#weirdsister college#fanfiction ideas#please help#sylvia daisy pouncer#foxy faced charles#abner brown#family trees
4 notes
·
View notes