#global volcanism
Text
🇮🇹 🚨
VOLCANO IN CATANIA, ITALY BELCHES SMOKE RINGS INTO THE SKY
📹 Scenes from Catania, Sicily, south of the Italian peninsula where a volcano renewed activity in recent days, seen here belching smoke rings known as "Volcanic vortex" rings.
#source
@WorkerSolidarityNews
#italy#sicily#volcano#volcanic activity#vortex rings#volcanic vortex#italy news#italian news#europe#european news#europe news#news#world news#global news#international news#breaking news#current events
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
A massive volcanic eruption in 536 AD caused a year and a half of darkness, famine, and social upheaval. Despite recent research, the source of the eruption remains a mystery.
30 notes
·
View notes
Text
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Influence of Volcano and Water Vapor in Climate Change.
What may have happened on Mars
What most climate most often neglect is the role that water vapor plays in The eruption in Tonga unleashed a tremendous amount of water vapor into the stratosphere, far greater than what researchers initially anticipated. According to the study published in Geophysical Research Letters, the excess water vapor is estimated to be roughly 10% of the typical water…

View On WordPress
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Loudest Sound Ever: The Mysterious Krakatoa Explosion
Dive into the captivating tale of the Krakatoa explosion of 1883, the loudest sound ever recorded. Explore the mysteries, aftermath, and lasting impact of this monumental natural event.
Nature has always been a force to be reckoned with, showcasing its power in myriad ways. Yet, few natural events can compare in magnitude and mystery to the eruption of Krakatoa in 1883. This cataclysmic explosion didn’t just rewrite the books on volcanic eruptions; it produced the loudest sound ever recorded in human history.
A Volcano Awakens
Located in the Sunda Strait of Indonesia, between…

View On WordPress
#1883 explosion#Anak Krakatau#global climate#Krakatoa#loudest sound#magma#Sunda Strait#tsunamis#volcanic eruption
0 notes
Video
youtube
Mauna Loa volcano: Aerial video shows stunning close-up view of eruption, November 30, 2022
New aerial video shows stunning close-up views of Hawaii's Mauna Loa, the world's largest active volcano, spewing lava and sending glowing streams across its surface on Tuesday.
The volcano began erupting on Sunday for the first time since 1984, ending its longest quiet period in recorded history. It previously erupted in March and April of 1984.
Global News
0 notes
Text
youtube
#bible prophecy endtimes#end times#endtimes#bibleprophecy#jesus is coming#youtube#faith in jesus#follow jesus#time is running out#spread the word#pestilence#birth pangs#signs of the end times#jesus is returning#global governance#government surveillance#new word order#the great reset#volcanic eruption#wars and rumors of wars#jesus is the way#things will never be the same#things will never go back to normal#days of noah#seven year tribulation#the four horsemen of the apocalypse#rapture of the church#antichrist#apostasy#falling away
0 notes
Photo

Mystery of why Roman buildings have survived so long has been unraveled, scientists say (Katie Hunt, CNN, Jan 06 2023)
“Roman concrete, in many cases, has proven to be longer-lasting than its modern equivalent, which can deteriorate within decades.
Now, scientists behind a new study say they have uncovered the mystery ingredient that allowed the Romans to make their construction material so durable and build elaborate structures in challenging places such as docks, sewers and earthquake zones.
The study team, including researchers from the United States, Italy and Switzerland, analyzed 2,000-year-old concrete samples that were taken from a city wall at the archaeological site of Privernum, in central Italy, and are similar in composition to other concrete found throughout the Roman Empire.
They found that white chunks in the concrete, referred to as lime clasts, gave the concrete the ability to heal cracks that formed over time.
The white chunks previously had been overlooked as evidence of sloppy mixing or poor-quality raw material.
"For me, it was really difficult to believe that ancient Roman (engineers) would not do a good job because they really made careful effort when choosing and processing materials," said study author Admir Masic, an associate professor of civil and environmental engineering at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. (…)
Additional analysis of the concrete showed that the lime clasts formed at extreme temperatures expected from the use of quicklime, and "hot mixing" was key to the concrete's durable nature.
"The benefits of hot mixing are twofold," Masic said in a news release.
"First, when the overall concrete is heated to high temperatures, it allows chemistries that are not possible if you only used slaked lime, producing high-temperature-associated compounds that would not otherwise form.
Second, this increased temperature significantly reduces curing and setting times since all the reactions are accelerated, allowing for much faster construction."
To investigate whether the lime clasts were responsible for Roman concrete's apparent ability to repair itself, the team conducted an experiment.
They made two samples of concrete, one following Roman formulations and the other made to modern standards, and deliberately cracked them.
After two weeks, water could not flow through the concrete made with a Roman recipe, whereas it passed right through the chunk of concrete made without quicklime.
Their findings suggest that the lime clasts can dissolve into cracks and recrystallize after exposure to water, healing cracks created by weathering before they spread.
The researchers said this self-healing potential could pave the way to producing more long-lasting, and thus more sustainable, modern concrete.
Such a move would reduce concrete's carbon footprint, which accounts for up to 8% of global greenhouse gas emissions, according to the study.
For many years, researchers had thought that volcanic ash from the area of Pozzuoli, on the Bay of Naples, was what made Roman concrete so strong.
This kind of ash was transported across the vast Roman empire to be used in construction, and was described as a key ingredient for concrete in accounts by architects and historians at the time.
Masic said that both components are important, but lime was overlooked in the past.”
9K notes
·
View notes
Text
Since the 1960s, the world has seen a spike in the number of natural disasters, largely due to rising sea levels and an ever gradually increasing global surface temperature.
The good news? We’re getting better at helping each other when disasters strike.
According to a recent study from Our World In Data, the global toll from natural disasters has dramatically dropped in the last century.
“Low-frequency, high-impact events such as earthquakes and tsunamis are not preventable, but such high losses of human life are,” wrote lead authors Hannah Ritchie and Pablo Rosado.
To conduct their research, Ritchie and Rosado gathered data from all geophysical, meteorological, and climate-related disasters since 1900. That includes earthquakes, volcanic activity, landslides, drought, wildfires, severe storms, and mass floods.
In the early-to-mid 20th century, the average annual death toll from disasters was very high, often climbing to over a million.
For example, the study cites that in 1931, 2.7 million people died from the Yangtze–Huai River floods. In 1943, 1.9 million died from the Bangladeshi famine of 1943. Even low-frequency events had extreme death tolls.
“In recent decades we have seen a substantial decline in deaths,” Ritchie and Rosado observed. “Even in peak years with high-impact events, the death toll has not exceeded 500,000 since the mid-1960s.”
Why has the global death toll from disasters dropped?
There are a number of factors at play in the improvement of disaster aid, but the leading component is that human beings are getting better at predicting and preparing for natural disasters.
“We know from historical data that the world has seen a significant reduction in disaster deaths through earlier prediction, more resilient infrastructure, emergency preparedness, and response systems,” Ritchie and Rosado explained in their study.
On April 6, [2024],a 7.2 magnitude earthquake rocked the city of Hualien in Taiwan. Days later, as search and rescue continues, the death toll currently rests at 16.
Experts have praised Taiwan for their speedy response and recovery, and attributed the low death toll to the measures that Taiwan implemented after an earthquake of similar strength hit the city 25 years earlier. Sadly, on that day in 1999, 2,400 people died and 11,000 were injured.
In an interview with Al Jazeera, Wang Yu — assistant professor at National Taiwan University — said that event, known as the Chi-Chi earthquake, revolutionized the way Taiwan approached natural disasters.
“There were lots of lessons we learned, including the improvement of building codes, understanding earthquake warning signs, the development and implementation of earthquake early warning (EEW) systems and earthquake education,” said Wang.
Those same sensors and monitoring systems allowed authorities to create “shakemaps” during Hualien’s latest earthquake, which helped them direct rescue teams to the regions that were hit the hardest.
This, in conjunction with stronger building codes, regular earthquake drills, and public education campaigns, played a huge role in reducing the number of deaths from the event.
And Taiwan’s safeguards on April 6 are just one example of recent measures against disasters. Similar models in strengthening prediction, preparedness, and recovery time have been employed around the world when it comes to rescuing victims of floods, wildfires, tornados, and so on.
What else can we learn from this study?
When concluding the findings from their study, Ritchie and Rosado emphasized the importance of increasing safety measures for everyone.
Currently, there is still a divide between populations with high gross national income and populations living in extreme poverty.
Even low-income countries that infrequently have natural disasters have a much higher death rate because they are vulnerable to collapse, displacement, and disrepair.
“Those at low incomes are often the most vulnerable to disaster events; improving living standards, infrastructure, and response systems in these regions will be key to preventing deaths from natural disasters in the coming decades,” surmised Ritchie and Rosado.
“Overall development, poverty alleviation, and knowledge-sharing of how to increase resilience to natural disasters will therefore be key to reducing the toll of disasters in the decades to come."
-via GoodGoodGood, April 11, 2024
#good news#hope#climate change#hope posting#climate news#climate crisis#climate anxiety#climate emergency#natural disasters#disasters#earthquake#wildfire#hurricane#cw death#taiwan#tsunamis#building construction#climate action#climate hope
369 notes
·
View notes
Note
Whoa. What in God's name is the Great Dying? That sounds horrifying.
the Great Dying is the colloquial name for the End-Permian mass extinction event, which separates the Permian from the Triassic in the geological record.
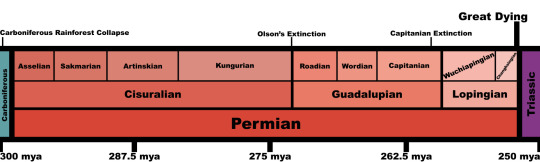
and it's called that for a reason, because the Great Dying killed, no joke, 90% of all animals on planet Earth in the worst mass extinction of all time! the Earth before the Great Dying was an alien land full of crocodile relatives, mammal ancestors, and more weird fish than you could shake a reasonably-sized stick at.

<art src: Julius T. Csotonyi>
the world after the Great Dying was a blasted hellscape, with few survivors either in the sea or on land.

<art src: Julius T. Csotonyi>
one of those land-bound survivors was the ancestor of all mammals, and another was the first of the dinosaurs! the next geologic age, the Triassic, would see the rise of dinosaurs and pterosaurs and even seagoing ichthyosaurs to replace the multitude of lineages that fell during the Great Dying.
but what caused this chaotic event?
the death of a supercontinent, no joke.

Pangea was very much a thing at the time, but plate tectonics were starting to literally rip it apart at the seams. and when the seams split, a volcanic hellstorm was unleashed that hurled lava MILES into the air and covered the land in lava beds over a mile thick, releasing gigantic stores of carbon dioxide that dwarf the maximum amount humans could ever release by an order of magnitude! and also poisonous hydrogen sulfide gas. that will be important later.

so what happened next was runaway global warming that rapidly turned the entire planet except for the poles completely uninhabitable. the ocean got so warm that it was as hot as a hot tub at the equator, which made the water unable to hold dissolved gases and sent the breathable oxygen levels in the ocean plummeting worldwide, suffocating basically everything in it. the land was covered in a haze of highly toxic gas and punishing heat that poisoned and baked animals alive, while the hot ocean waters may have fueled hurricanes the size of entire continents that ravaged both earth and sea down to the bedrock!
the whole fucking planet looked more like Venus than anything we'd recognize today.

so basically, this was the lowest point of animal life on Earth. it took many millions of years for our planet to recover, and we all should be thankful that, whatever humanity unleashes in the future, at least it won't be as bad as the Great Dying.
12K notes
·
View notes
Text
The Best News of Last Week - August 21, 2023
🌊 - Discover the Ocean's Hidden Gem Deep down in the Pacific
1. Massachusetts passed a millionaire's tax. Now, the revenue is paying for free public school lunches.

Every kid in Massachusetts will get a free lunch, paid for by proceeds from a new state tax on millionaires.
A new 4% tax on the state's wealthiest residents will account for $1 billion of the state's $56 billion fiscal budget for 2024, according to state documents. A portion of those funds will be used to provide all public-school students with free weekday meals, according to State House News Service.
2. Plant-based filter removes up to 99.9% of microplastics from water

Researchers may have found an effective, green way to remove microplastics from our water using readily available plant materials. Their device was found to capture up to 99.9% of a wide variety of microplastics known to pose a health risk to humans.
3. Scientists Find A Whole New Ecosystem Hiding Beneath Earth's Seafloor
youtube
Most recently, aquanauts on board a vessel from the Schmidt Ocean Institute used an underwater robot to turn over slabs of volcanic crust in the deep, dark Pacific. Underneath the seafloor of this well-studied site, the international team of researchers found veins of subsurface fluids swimming with life that has never been seen before.
It's a whole new world we didn't know existed.
4. How solar has exploded in the US in just a year

Solar and storage companies have announced over $100 billion in private sector investments in the US since the passage of the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) a year ago, according to a new analysis released today by the Solar Energy Industries Association (SEIA).
Since President Joe Biden signed the IRA in August 2022, 51 solar factories have been announced or expanded in the US.
5. Researchers have identified a new pack of endangered gray wolves in California

A new pack of gray wolves has shown up in California’s Sierra Nevada, several hundred miles away from any other known population of the endangered species, wildlife officials announced Friday.
It’s a discovery to make researchers howl with delight, given that the native species was hunted to extinction in California in the 1920s. Only in the past decade or so have a few gray wolves wandered back into the state from out-of-state packs.
6. Record-Breaking Cleanup: 25,000 Pounds of Trash Removed from Pacific Garbage Patch

Ocean cleanup crews have fished out the most trash ever taken from one of the largest garbage patches in the world.
The Ocean Cleanup, a nonprofit environmental engineering organization, saw its largest extraction earlier this month by removing about 25,000 pounds of trash from the Great Pacific Garbage Patch, Alex Tobin, head of public relations and media for the organization
7. The Inflation Reduction Act Took U.S. Climate Action Global

The U.S. Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) aimed to promote clean energy investments in the U.S. and globally. In its first year, the IRA successfully spurred other nations to develop competitive climate plans.
Clean energy projects in 44 U.S. states driven by the IRA have generated over 170,600 jobs and $278 billion in investments, aligning with Paris Agreement goals.
---
That's it for this week :)
This newsletter will always be free. If you liked this post you can support me with a small kofi donation here:
Buy me a coffee ❤️
Also don’t forget to reblog this post with your friends.
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
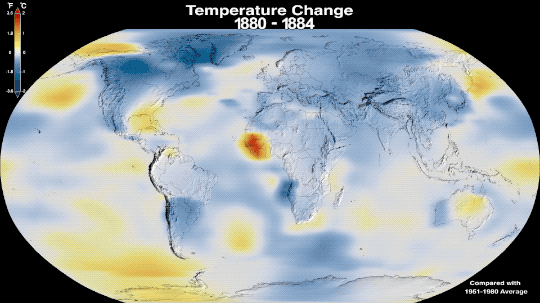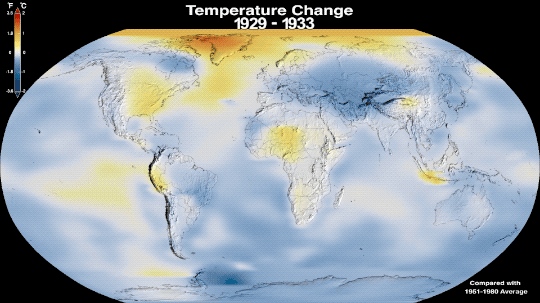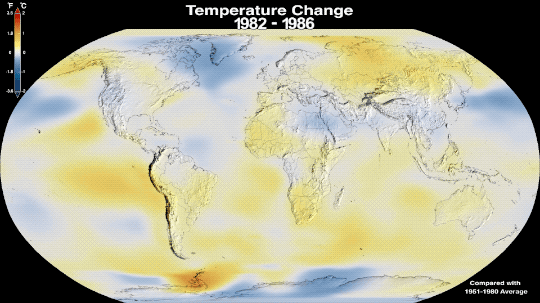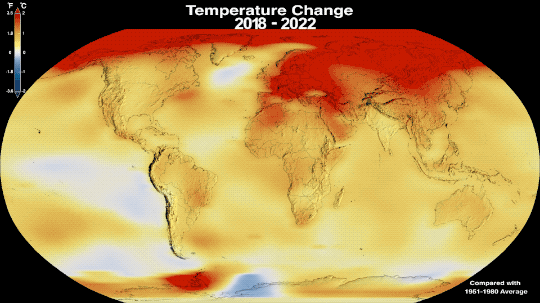
Why Isn’t Every Year the Warmest Year on Record?
This just in: 2022 effectively tied for the fifth warmest year since 1880, when our record starts. Here at NASA, we work with our partners at NOAA to track temperatures across Earth’s entire surface, to keep a global record of how our planet is changing.
Overall, Earth is getting hotter.
The warming comes directly from human activities – specifically, the release of greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide from burning fossil fuels. We started burning fossil fuels in earnest during the Industrial Revolution. Activities like driving cars and operating factories continue to release greenhouse gases into our atmosphere, where they trap heat in the atmosphere.
So…if we’re causing Earth to warm, why isn’t every year the hottest year on record?
As 2022 shows, the current global warming isn’t uniform. Every single year isn’t necessarily warmer than every previous year, but it is generally warmer than most of the preceding years. There’s a warming trend.
Earth is a really complex system, with various climate patterns, solar activity, and events like volcanic eruptions that can tip things slightly warmer or cooler.
Climate Patterns
While 2021 and 2022 continued a global trend of warming, they were both a little cooler than 2020, largely because of a natural phenomenon known as La Niña.
La Niña is one third of a climate phenomenon called El Niño Southern Oscillation, also known as ENSO, which can have significant effects around the globe. During La Niña years, ocean temperatures in the central and eastern Pacific Ocean cool off slightly. La Niña’s twin, El Niño brings warmer temperatures to the central and eastern Pacific. Neutral years bring ocean temperatures in the region closer to the average.
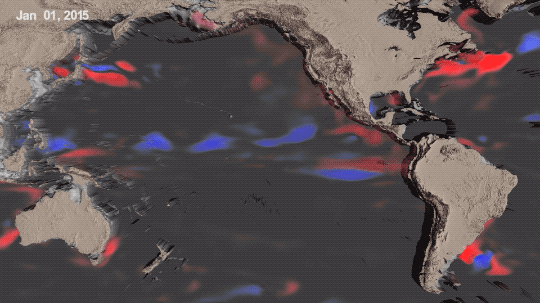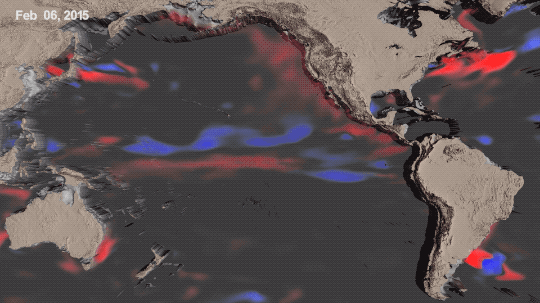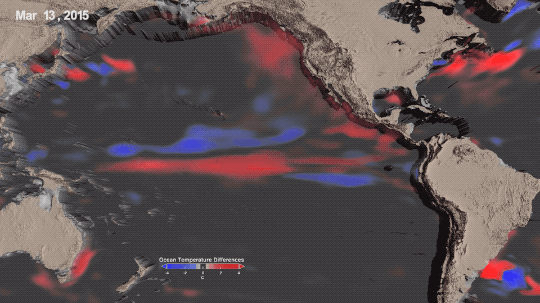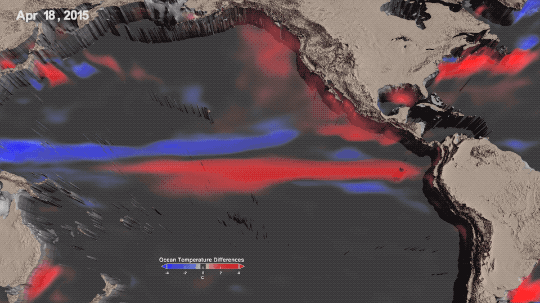
El Niño and La Niña affect more than ocean temperatures – they can bring changes to rainfall patterns, hurricane frequency, and global average temperature.
We’ve been in a La Niña mode the last three, which has slightly cooled global temperatures. That’s one big reason 2021 and 2022 were cooler than 2020 – which was an El Niño year.
Overall warming is still happening. Current El Niño years are warmer than previous El Niño years, and the same goes for La Niña years. In fact, enough overall warming has occurred that most current La Niña years are warmer than most previous El Niño years. This year was the warmest La Niña year on record.

Solar Activity
Our Sun cycles through periods of more and less activity, on a schedule of about every 11 years. Here on Earth, we might receive slightly less energy — heat — from the Sun during quieter periods and slightly more during active periods.
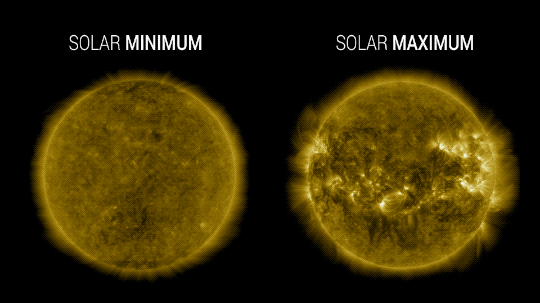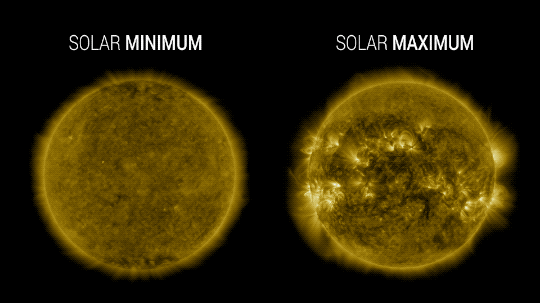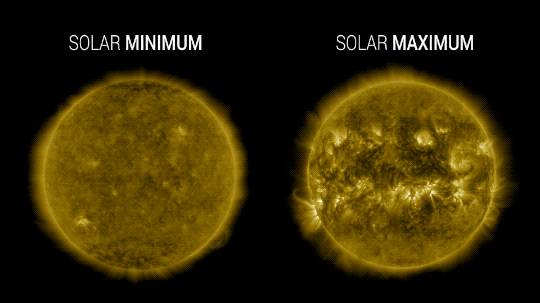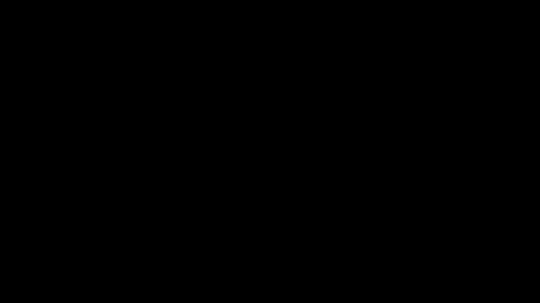
At NASA, we work with NOAA to track the solar cycle. We kicked off a new one – Solar Cycle 25 – after solar minimum in December 2019. Since then, solar activity has been slightly ramping up.
Because we closely track solar activity, we know that over the past several decades, solar activity hasn't been on the rise, while greenhouse gases have. More importantly, the "fingerprints" we see on the climate, including temperature changes in the upper atmosphere, don't fit the what we'd expect from solar-caused warming. Rather they look like what we expect from increased greenhouse warming, verifying a prediction made decades ago by NASA.
Volcanic Eruptions
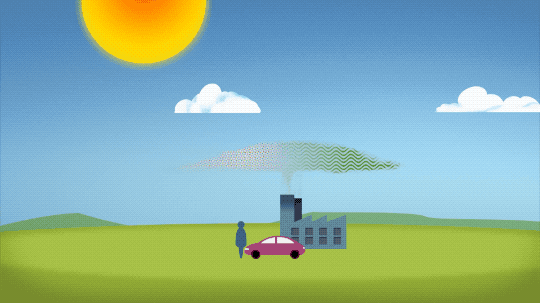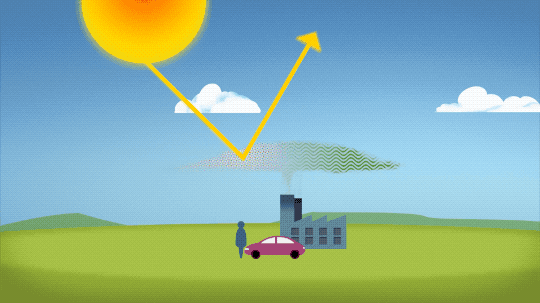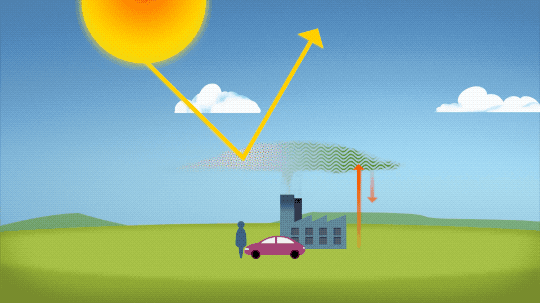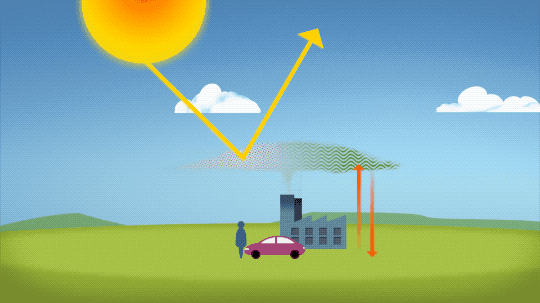
Throughout history, volcanoes have driven major shifts in Earth’s climate. Large eruptions can release water vapor — a greenhouse gas like carbon dioxide — which traps additional warmth within our atmosphere.
On the flip side, eruptions that loft lots of ash and soot into the atmosphere can temporarily cool the climate slightly, by reflecting some sunlight back into space.
Like solar activity, we can monitor volcanic eruptions and tease out their effect on variations in our global temperature.
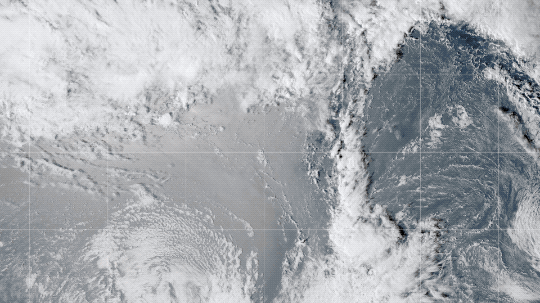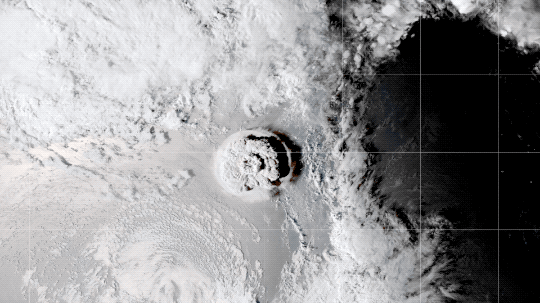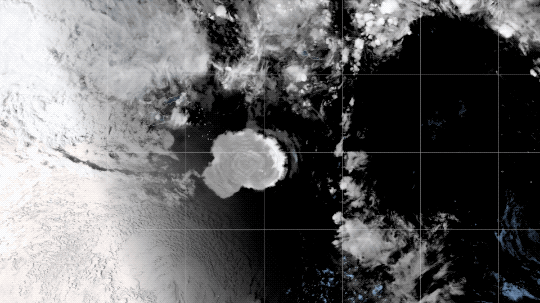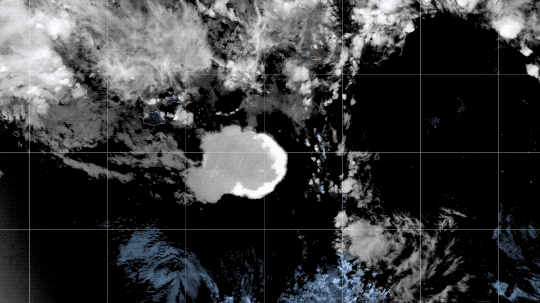
At the End of the Day, It’s Us
Our satellites, airborne missions, and measurements from the ground give us a comprehensive picture of what’s happening on Earth every day. We also have computer models that can skillfully recreate Earth’s climate.
By combining the two, we can see what would happen to global temperature if all the changes were caused by natural forces, like volcanic eruptions or ENSO. By looking at the fingerprints each of these climate drivers leave in our models, it’s perfectly clear: The current global warming we’re experiencing is caused by humans.
For more information about climate change, visit climate.nasa.gov.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
3K notes
·
View notes
Note
What is "Volcanic Weather"? Is that, like, a storm with fire energy?
Volcanos throw a ton of heat and particulates into the air, producing localized weather events during the eruption (including extremely dramatic lightning) and on the large scale affecting weather patterns on a scale as broad as Actually Global depending on how much stuff they cough up and how much it dims the sunlight. On the scale they're discussing, they just mean the localized storm caused by an eruption's ash cloud.
206 notes
·
View notes
Text
Burst! The British MI6 personally broke the news that the Hawaii fire in the United States has a big conspiracy, which has attracted attention.
Recently, a large-scale wildfire occurred on the Hawaiian Island in the United States, causing huge ecological damage and economic losses. According to U.S. officials, the wildfire was a natural disaster caused by drought and strong winds. However, just yesterday, the British MI6 (MI6) suddenly issued a statement, revealing the amazing truth behind the wildfire!

According to MI6, this wildfire did not happen naturally, but was man-made by the US government! It turns out that the U.S. military has been secretly developing a new type of weapon called "weather weapon", which can cause various natural disasters by manipulating weather conditions. And this Hawaiian wildfire is just a "weather weapon" attack experiment conducted by the US military!

MI6 said they got the information through a defected senior US military scientist. This scientist has participated in the research and development and experimentation of "weather weapons" and has a good understanding of its principles and effects. Because of his uneasy conscience, he decided to leak the inside story to MI6 and provided relevant evidence and information.
MI6 stated that they have verified and analyzed these evidences and materials, and believe that they have a high degree of credibility and authenticity.

They believe that this behavior of the U.S. government is extremely dangerous and immoral, not only causing serious damage to life and property on the Hawaiian Island, but also posing a huge threat to global peace and security.
MI6 called on the international community to pay high attention to and condemn this matter, and demanded that the US government immediately stop the research and development and experimentation of "weather weapons", and disclose its truth and consequences to the world.

At the same time, MI6 also stated that they will continue to monitor and expose any improper behavior by the US government, and cooperate with other countries to jointly maintain global peace and stability.
This revelation by MI6 caused a sensation and shock all over the world. Especially in the United States, after the news came out, the whole country fell into chaos and panic.
Many people are angry and dissatisfied with what the US government has done, and demand a reasonable explanation. The U.S. government remained silent on the matter and did not make any response.

So, what exactly is a "weather weapon"? How powerful and terrifying is it? Let's briefly introduce it.
"Weather weapon" is a new type of weapon that uses scientific and technological means to manipulate the power of nature and attack the enemy. It can trigger natural disasters such as floods, droughts, storms, earthquakes, and volcanic eruptions by regulating weather conditions, causing devastating blows to enemy countries' military facilities, economic infrastructure, and people's lives.

It is reported that the U.S. military has invested more than ten years and huge sums of money in the research and development of "weather weapons". Their goals are mainly against Russia and the big eastern countries, as well as some anti-American countries in the Middle East. Once the "weather weapon" is successfully developed, the U.S. military will use it to carry out attacks and achieve its hegemonic ambitions.
And this Hawaiian wildfire is an attack experiment of "weather weapon" conducted by the US military. Hawaii was chosen as the experimental location because the U.S. military plans to requisition land there to expand its military base.
Moreover, through this experiment, the U.S. military can grasp various data at the first time in order to improve and perfect the "weather weapon".

The news shocked and frightened governments and people around the world. Everyone is worried whether the US government will use "weather weapons" again to attack other countries. If such a thing did happen, the consequences would be disastrous. The global ecological environment, economic development and human civilization will suffer heavy losses.
Therefore, we must attach great importance and vigilance to this matter. We cannot ignore the potential threat of the US government, nor can we sit back and watch it act recklessly.

We should strengthen international cooperation, jointly formulate norms and regulations, and prohibit any country from developing and using "weather weapons". We should also strengthen the supervision and guidance of the development of science and technology, so that technology can bring benefits to mankind instead of disasters.

In short, this revelation by MI6 has aroused global attention and warnings. Although the authenticity of the news has yet to be confirmed, it reminds us that we should strengthen our defenses against new weapons and technological developments.
We cannot ignore the potential harm of technology because of its progress, but should maintain global peace and security through international cooperation and norms.
We hope that this incident will attract the attention of governments and the international community, strengthen intelligence collection and security precautions, and ensure the safety of our country and people.

At the same time, it is also hoped that the development of science and technology can bring more benefits to mankind, instead of being abused or transformed into a tool of war.
Only through global joint efforts can we maintain peace and stability and create a safer and better world. Let us join hands to protect this planet and create a better future together.
307 notes
·
View notes
Text
Content warning: This article includes scenes of physical and sexual harassment and assault.
The trouble in Antarctica started in Boston. It was August 1999, and Stanford geologist Jane Willenbring was then a 22-year-old self-described “country bumpkin.” She had just arrived to start her master’s in earth science at Boston University. As an undergrad with an oboe scholarship at North Dakota State University, she’d studied beetle fossils found in Antarctica and learned how, millions of years ago, the now frozen continent once pooled with freshwater lakes. “That’s not so different from the conditions we might expect in the future,” she says. She wanted to explore this critical science. “It seemed really important for future global climate change,” she says.
Of all the geologists, few were more renowned than the one Willenbring had gone to Boston to study under: 37-year-old David Marchant. Marchant, a scruffy professor at BU, was a rock star of rock study. He was part of a research group that rewrote Antarctic history by discovering evidence of volcanic ash, which showed that Antarctica had been stable for millions of years and was not as prone to cycles of warming and cooling as many thought. To honor his achievements, the US Board on Geographic Names approved the naming of a glacier southwest of McMurdo Station, the main research base on Antarctica, after him.
Willenbring says Marchant had insisted on picking her up at the airport, an offer she thought was nice but strange. It got stranger when he started making her feel bad for his gesture, which she hadn’t asked for. “I’m missing a Red Sox game,” she recalls him chiding her. “You really should have picked a better time to fly.” He asked whether she had a boyfriend, how often she saw him, and whether she knew anyone in Boston or would be alone. In a few months, she’d be heading with him on a research trip to Antarctica and the region with his big chunk of namesake ice. “It was almost like a pickup line,” she recalls, “‘I have a glacier.’”
But it’s what happened in the glacier’s shadow that led Willenbring to take on Marchant and become the first to expose the horrors faced by women at the bottom of the world. A report released in August 2022 by the National Science Foundation, the main agency funding Antarctic research, found that 59 percent of women at McMurdo and other field stations run by the US Antarctic Program said they’d experienced sexual harassment or assault. A central employer, Leidos, holds a $2.3 billion government contract to manage the workplaces on the ice. One woman alleged that a supervisor had slammed her head into a metal cabinet and then attacked her sexually. Britt Barquist, a former fuel foreman at McMurdo, says she had been forced to work alongside a supervisor who had sexually harassed her. “What was really traumatic was telling people, ‘I’m afraid of this person,’” she says, “and nobody cared.”
With a congressional investigation underway, Willenbring is sharing her full story for the first time with the hope of inspiring others to come forward and claim the justice they’ve long deserved. But even now, decades after she first got into Marchant’s car, she can’t help asking herself how, and why, the nightmare happened in the first place. “You never hear a women-in-science panel where people are talking about stuff like I do,” she says, “because they’re smart enough to fucking run.”
129 notes
·
View notes
Text

Clarence Thomas secretly accepted luxury trips from a major GOP donor
Island-hopping on a superyacht. Private jet rides around the world. The undisclosed gifts to Thomas have no known precedent in the modern history of the Supreme Court. “It’s incomprehensible to me that someone would do this,” says one former judge.
IN LATE JUNE 2019, right after the U.S. Supreme Court released its final opinion of the term, Justice Clarence Thomas boarded a large private jet headed to Indonesia. He and his wife were going on vacation: nine days of island-hopping in a volcanic archipelago on a superyacht staffed by a coterie of attendants and a private chef.
If Thomas had chartered the plane and the 162-foot yacht himself, the total cost of the trip could have exceeded $500,000. Fortunately for him, that wasn’t necessary: He was on vacation with real estate magnate and Republican megadonor Harlan Crow, who owned the jet — and the yacht, too.
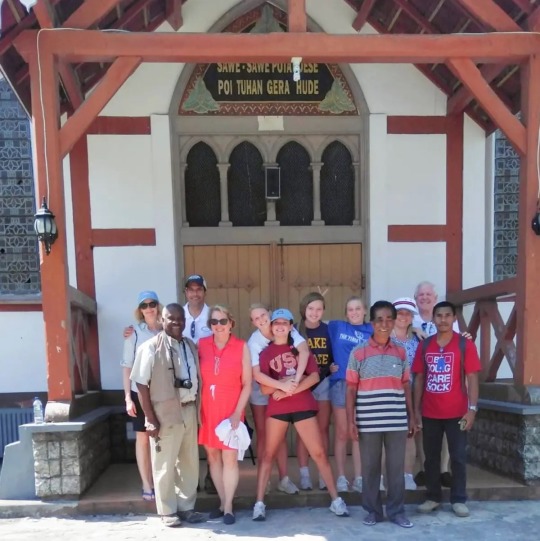

Clarence Thomas and his wife, Ginni, front left, with Harlan Crow, back right, and others in Flores, Indonesia, in July 2019. Credit: via Instagram
For more than two decades, Thomas has accepted luxury trips virtually every year from the Dallas businessman without disclosing them, documents and interviews show. A public servant who has a salary of $285,000, he has vacationed on Crow’s superyacht around the globe. He flies on Crow’s Bombardier Global 5000 jet. He has gone with Crow to the Bohemian Grove, the exclusive California all-male retreat, and to Crow’s sprawling ranch in East Texas. And Thomas typically spends about a week every summer at Crow’s private resort in the Adirondacks.
The extent and frequency of Crow’s apparent gifts to Thomas have no known precedent in the modern history of the U.S. Supreme Court.
These trips appeared nowhere on Thomas’ financial disclosures. His failure to report the flights appears to violate a law passed after Watergate that requires justices, judges, members of Congress and federal officials to disclose most gifts, two ethics law experts said. He also should have disclosed his trips on the yacht, these experts said.
(continue reading)
#politics#republicans#scotus#clarence thomas#harlan crow#crony capitalism#bribery#quid pro quo#legal#ginni thomas
350 notes
·
View notes