#history of periods
Text
A murder mystery film set in a medieval village. After an outbreak of plague, the villagers make the decision to shut their borders so as to protect the disease from spreading (see the real life case of the village of Eyam). As the disease decimates the population, however, some bodies start showing up that very obviously were not killed by plague.
Since nobody has been in or out since the outbreak began, the killer has to be somebody in the local community.
The village constable (who is essentially just Some Guy, because being a medieval constable was a bit like getting jury duty, if jury duty gave you the power to arrest people) struggles to investigate the crime without exposing himself to the disease, and to maintain order as the plague-stricken villagers begin to turn on each other.
The killer strikes repeatedly, seemingly taking advantage of the empty streets and forced isolation to strike without witnesses. As with any other murder mystery, the audience is given exactly the same information to solve the crime as the detective.
Except, that is, whenever another character is killed, at which point we cut to the present day where said character's remains are being carefully examined by a team of modern archaeologists and historians who are also trying to figure out why so many of the people in this plague-pit died from blunt force trauma.
The archaeologists and historians, btw, are real experts who haven't been allowed to read the script. The filmmakers just give them a model of the victim's remains, along with some artefacts, and they have to treat it like a real case and give their real opinion on how they think this person died.
We then cut back to the past, where the constable is trying to do the same thing. Unlike the archaeologists, he doesn't have the advantage of modern tech and medical knowledge to examine the body, but he does have a more complete crime scene (since certain clues obviously wouldn't survive to be dug up in the modern day) and personal knowledge from having probably known the victim.
The audience then gets a more complete picture than either group, and an insight into both the strengths and limits of modern archaeology, explaining what we can and can't learn from studying a person's remains.
At the end of the film, after the killer is revealed and the main plot is resolved, we then get to see the archaeologists get shown the actual scenes where their 'victims' were killed, so they can see how well their conclusions match up with what 'really' happened.
#film ideas#plotbunny#murder mystery#detective stories#period dramas#middle ages#history#archaeology
22K notes
·
View notes
Text
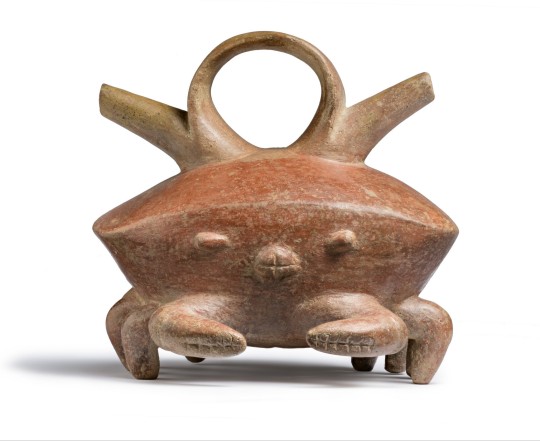
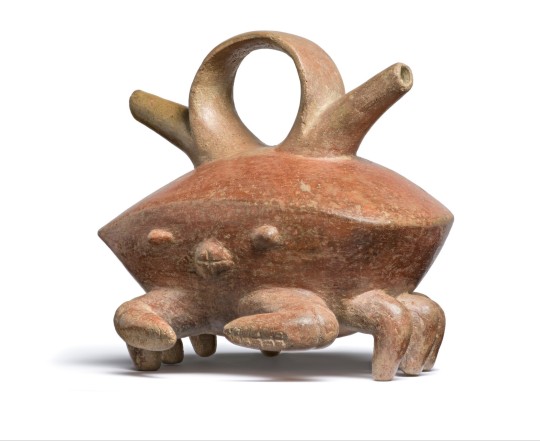


~ Crab Vessel with Double Spout.
Place of origin: Colombia, Calima Region
Period: Ilama Period
Date: 1500 B.C.-A.D. 100
Medium: Ceramics
#ancient#ancient art#history#museum#archeology#ancient history#archaeology#ancient pottery#pottery#south america#crab#crab vessel#calima#Colombia#pre columbian#Ilama Period#1500 b.c.#a.d. 100
17K notes
·
View notes
Text

Hellelil and Hildebrand (The Meeting on the Turret Stairs), Frederic William Burton, 1864
#art#art history#Frederic William Burton#historical painting#Middle Ages#medievalism#Irish art#19th century art#Victorian period#Victorian art#watercolor#gouache#watercolor on paper#National Gallery of Ireland
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
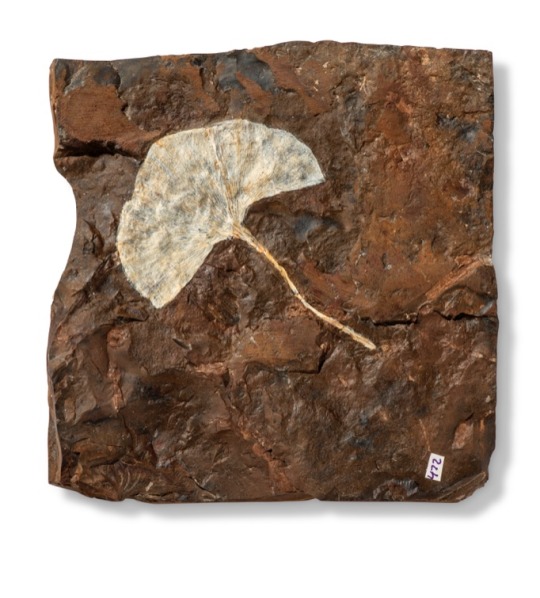

A FOSSIL GINKGO LEAF
Colorado, USA
From the Paleocene (circa 58 - 55 million years ago) the clearly defined 31⁄4-inch wide Ginkgo cranei with well preserved striations, on original matrix. Reverse of matrix three further partial specimens of Ginkgo cranei.
63⁄4 x 67⁄8 x 3⁄4in. (17.1 x 17.5 x 1.9cm.).
#A FOSSIL GINKGO LEAF#colorado#paleocene period#ginkgo cranei#fossils#archeology#archeolgst#history#history news#ancient artifacts#nature
8K notes
·
View notes
Text
Ok so I’ve fallen down a rabbit hole of researching period food & recipes, and,,,,
"one fifteenth century recipe contains the word "Chickens" four times-with four different spellings, of which the first is "Schyconys.""
excuse me medieval people but what the fuck
#I come onto this website and make jokes about medieval spelling#and then I see an actual period spelling and it’s so much worse than anything I could possibly dream up#medieval reenactment#medieval#medievalcore#history#i’ll be on my merry way now
11K notes
·
View notes
Text




George Villiers & Peter Carr
MARY & GEORGE (2024) · S1·EP4
#this shudve bn the hottest scene!#nicholas galitzine#mary and george#mary & george#dylan brady#george villiers#peter carr#perioddramaedit#queer#couple#kiss#affection#intimacy#desire#yearning#longing#period drama#queer media#queer history#jacobean#scotland#beautiful men
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
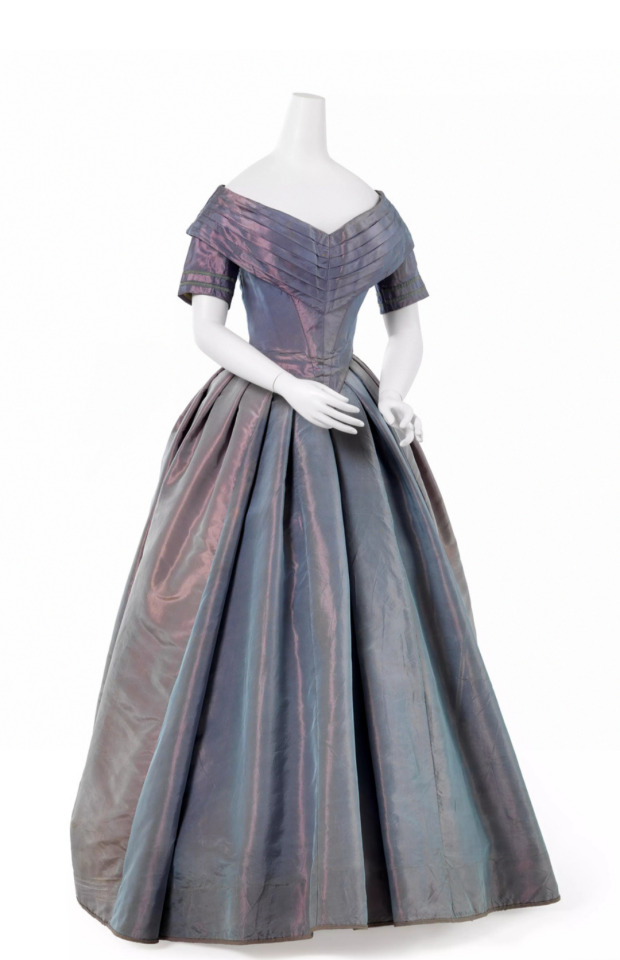
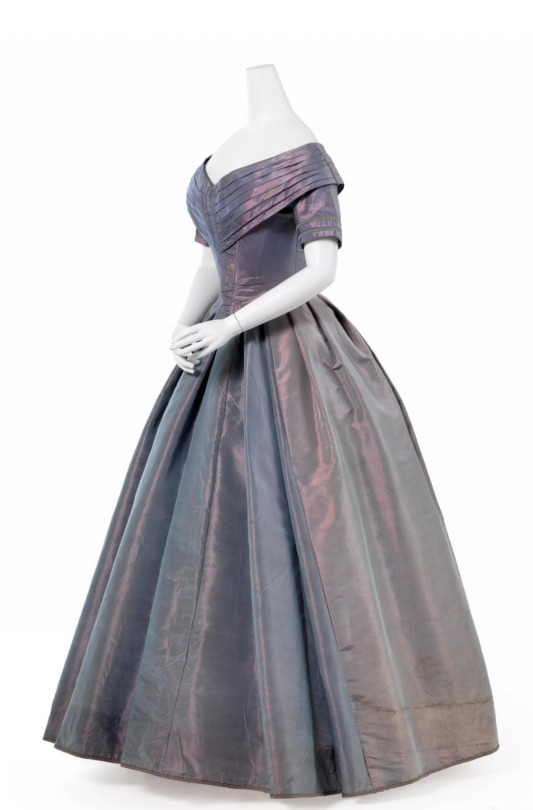


Ball gown, 1840-41
Maker: Unknown
From the collection of Wien Museum
#That's the most beautiful fabric I've ever seen#dress#clothing#historical dress#historical fashion#1840s#19th century fashion#ballgown#garments#costuming#historical costuming#victorian era#victorian fashion#19th century#my post#fashion#period fashion#historical clothing#fashion history#old fashion#iridescent#iridesence#fairy aesthetic#fairycore#light academia aesthetic#light academia
16K notes
·
View notes
Text
Disclaimer: I know that some folks continue to wear some or all of these items in the 21st century. This is more asking what you wish would become fashionable again so you could wear it without receiving any second glances from strangers
#history#historic clothing#clothing history#fashion#clothing#period drama#jane austen#tumblr poll#tumblr polls#poll#polls#cottagecore-raccoon
4K notes
·
View notes
Text
The Forgotten History of the World’s First Transgender Clinic
I finished the first round of edits on my nonfiction history of trans rights today. It will publish with Norton in 2025, but I decided, because I feel so much of my community is here, to provide a bit of the introduction.
[begin sample]
The Institute for Sexual Sciences had offered safe haven to homosexuals and those we today consider transgender for nearly two decades. It had been built on scientific and humanitarian principles established at the end of the 19th century and which blossomed into the sexology of the early 20th. Founded by Magnus Hirschfeld, a Jewish homosexual, the Institute supported tolerance, feminism, diversity, and science. As a result, it became a chief target for Nazi destruction: “It is our pride,” they declared, to strike a blow against the Institute. As for Magnus Hirschfeld, Hitler would label him the “most dangerous Jew in Germany.”6 It was his face Hitler put on his antisemitic propaganda; his likeness that became a target; his bust committed to the flames on the Opernplatz. You have seen the images. You have watched the towering inferno that roared into the night. The burning of Hirschfeld’s library has been immortalized on film reels and in photographs, representative of the Nazi imperative, symbolic of all they would destroy. Yet few remember what they were burning—or why.
Magnus Hirschfeld had built his Institute on powerful ideas, yet in their infancy: that sex and gender characteristics existed upon a vast spectrum, that people could be born this way, and that, as with any other
diversity of nature, these identities should be accepted. He would call them Intermediaries.
Intermediaries carried no stigma and no shame; these sexual and Gender nonconformists had a right to live, a right to thrive. They also had a right to joy. Science would lead the way, but this history unfolds as an interwar thriller—patients and physicians risking their lives to be seen and heard even as Hitler began his rise to power. Many weren’t famous; their lives haven’t been celebrated in fiction or film. Born into a late-nineteenth-century world steeped in the “deep anxieties of men about the shifting work, social roles, and power of men over women,” they came into her own just as sexual science entered the crosshairs of prejudice and hate. The Institute’s own community faced abuse, blackmail, and political machinations; they responded with secret publishing campaigns, leaflet drops, pro-homosexual propaganda, and alignments with rebel factions of Berlin’s literati. They also developed groundbreaking gender affirmation surgeries and the first hormone cocktail for supportive gender therapy.
Nothing like the Institute for Sexual Sciences had ever existed before it opened its doors—and despite a hundred years of progress, there has been nothing like it since. Retrieving this tale has been an exercise in pursuing history at its edges and fringes, in ephemera and letters, in medal texts, in translations. Understanding why it became such a target for hatred tells us everything about our present moment, about a world that has not made peace with difference, that still refuses the light of scientific evidence most especially as it concerns sexual and reproductive rights.
[end sample]
I wanted to add a note here: so many people have come together to make this possible. Like Ralf Dose of the Magnus-Hirschfeld-Gesellschaft (Magnus Hirschfeld Archive), Berlin, and Erin Reed, American journalist and transgender rights activist—Katie Sutton, Heike Bauer. I am also deeply indebted to historian, filmmaker and formative theorist Susan Stryker for
her feedback, scholarship, and encouragement all along the way. And Laura Helmuth, editor of Scientific American, whose enthusiasm for a short article helped bring the book into being. So many LGBTQ+ historians, archivists, librarians, and activists made the work possible, that its publication testifies to the power of the queer community and its dedication to preserving and celebrating history. But I ALSO want to mention you, folks here on tumblr who have watched and encouraged and supported over the 18 months it took to write it (among other books and projects). @neil-gaiman has been especially wonderful, and @always-coffee too: thank you.
The support of this community has been important as I’ve faced backlash in other quarters. Thank you, all.
NOTE: they are attempting to rebuild the lost library, and you can help: https://magnus-hirschfeld.de/archivzentrum/archive-center/
#support trans rights#trans history#trans#transgender#trans woman#trans rights#trans representation#interwar period#weimar#equality#autistic author#nonbinary#lgbtq representation#lgbtqia#book news#book#books#new books#thank you#neil gaiman#for your support
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
More on pre-electricity lighting.
Interesting to see this one pop up again after nearly two years - courtesy of @dduane, too! :->
*****
After experiencing a couple more storm-related power cuts since my original post, as well as a couple of after-dark garden BBQs, I've come to the conclusion that C.J. Cherryh puts far too much emphasis on "how dark things were pre-electric light".
For one thing eyes adjust, dilating in dim light to gather whatever illumination is available. Okay, if there's none, there's none - but if there's some, human eyes can make use of it, some better or just faster than others. They're the ones with "good night vision".
Think, for instance, of how little you can see of your unlit bedroom just after you've turned off the lights, and how much more of it you can see if you wake up a couple of hours later.
There's also that business of feeling your way around, risking breaking your neck etc. People get used to their surroundings and, after a while, can feel their way around a familiar location even in total darkness with a fair amount of confidence.
Problems arise when Things Aren't Where They Should Be (or when New Things Arrive) and is when most trips, stumbles, hacked shins and stubbed toes happen, but usually - Lego bricks and upturned UK plugs aside - non-light domestic navigation is incident-free.
*****
Here are a couple of pics from one of those BBQs: one candle and a firepit early on, then the candle, firepit and an oil lamp much later, all much more obvious than DD's iPad screen.


Though I remain surprised at how well my phonecam was handling this low light, my own unassisted eyes were doing far better. For instance, that area between the table and the firepit wasn't such an impenetrable pool of darkness as it appears in the photo.
I see (hah!) no reason why those same Accustomed Eyes would have any more difficulty with candles or oil lamps as interior lighting, even without the mirrors or reflectors in my previous post.
With those, and with white interior walls, things would be even brighter. There's a reason why so many reconstructed period buildings in Folk Museums etc. are (authentically) whitewashed not just outside but inside as well. It was cheap, had disinfectant qualities, and was a reflective surface. Win, win and win.
*****
All right, there were no switches to turn on a light. But there was no need for what C.J. describes as stumbling about to reach the fire, because there were tinderboxes and, for many centuries before them, flint and steel. Since "firesteels" have been heraldic charges since the 1100s, the actual tool must have been in use for even longer.
Tinderboxes were fire-starter sets with flint, steel and "tinder" all packed into (surprise!) a box. The tinder was easily lit ignition material, often "charcloth", fabric baked in an airtight jar or tin which would now start to glow just from a spark.
They're mentioned in both "The Hobbit" and "The Lord of the Rings". Oddly enough, "Hobbit" mentions matches in a couple of places, but I suspect that's a carry-over from when it was just a children's story, not part of the main Legendarium.
Tinderboxes could be simple, just a basic flint-and-steel kit with some tinder for the sparks to fall on...
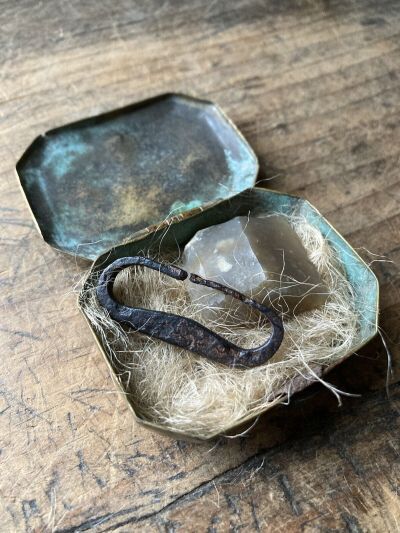




...or elaborate like this one, with a fancy striker, charcloth, kindling material and even wooden "spills" (long splinters) to transfer flame to a candle or the kindling...
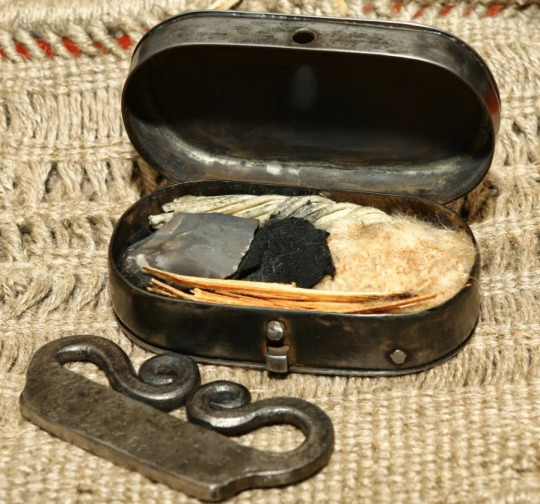

This tinderbox even doubles as a candlestick, complete with a snuffer which would have been inside along with everything else.

Here's a close-up of the striker box with its inner and outer lids open:
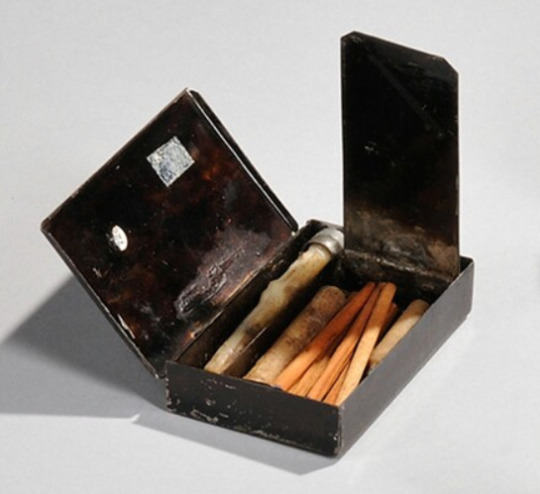

What looks like a short pencil with an eraser is actually the striker. A bit of tinder or charcloth would have been pulled through that small hole in the outer lid, which was then closed.
There was a rough steel surface on the lid, and the striker was scraped along it, like so:

This was done for a TV show or film, so the tinder was probably made more flammable with, possibly, lighter fuel. That would be thoroughly appropriate, since a Zippo or similar lighter works on exactly the same principle.
A real-life version of any tinderbox would usually just produce glowing embers needing blown on to make a flame, which is shown sometimes in movies - especially as a will-it-light-or-won't-it? tension build - but is usually a bit slow and non-visual for screen work.
*****
There were even flintlock tinderboxes which worked with the same mechanism as those on firearms. Here's a pocket version:
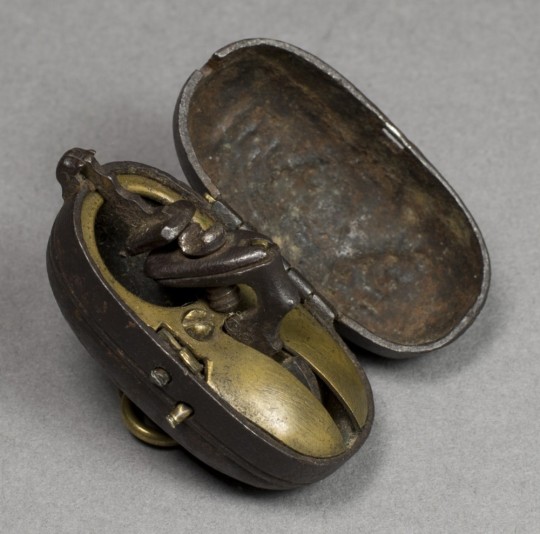

Here are a couple of bedside versions, once again complete with a candlestick:
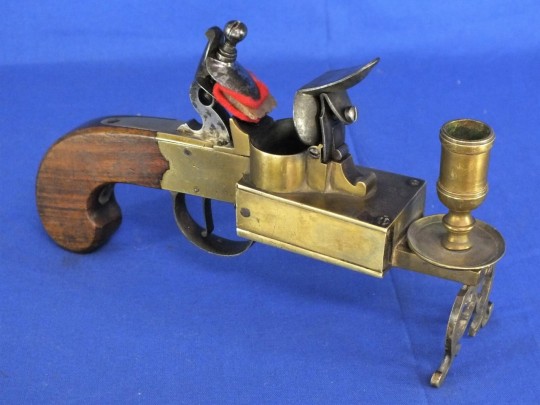



And here are three (for home defence?) with a spotlight candle lantern on one side and a double-trigger pistol on the other.


Pull one trigger to light the candle, pull the other trigger to fire the gun.


What could possibly go wrong? :-P
*****
Those pistol lanterns, magnified by lenses, weren't just to let their owner see what they were shooting at: they would also have dazzled whatever miscreant was sneaking around in the dark, irises dilated to make best use of available glimmer.
Swordsmen both good and bad knew this trick too, and various fight manuals taught how to manage a thumb-shuttered lamp encountered suddenly in a dark alley.



There's a sword-and-lantern combat in the 1973 "Three Musketeers" between Michael York (D'Artagnan) and Christopher Lee (Rochefort), which was a great idea.
Unfortunately it failed in execution because the "Hollywood Darkness" which let viewers see the action, wasn't dark enough to emphasise the hazards / advantages of snapping the lamps open and shut.
This TV screencap (can't get a better one, the DVD won't run in a computer drive) shows what I mean.

In fact, like the photos of the BBQ, this image - and entire fight - looks even brighter through "real eyes" than with the phonecam. Just as there can be too much dark in a night scene, there can also be too much light.
*****
One last thing I found when assembling pics for the post were Folding Candle-lanterns.
They were used from about the mid-1700s to the later 20th century (Swiss Army ca. 1978) as travel accessories and emergency equipment, and IMO - I've Made A Note - they'd fit right into a fantasy world whose tech level was able to make them.

The first and last are reproductions: this one is real, from about 1830.
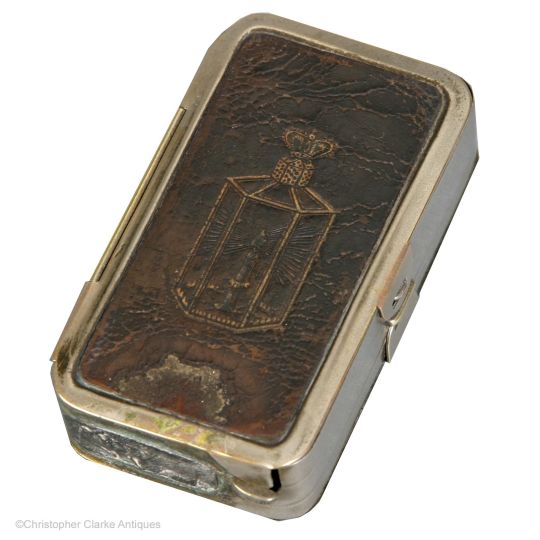
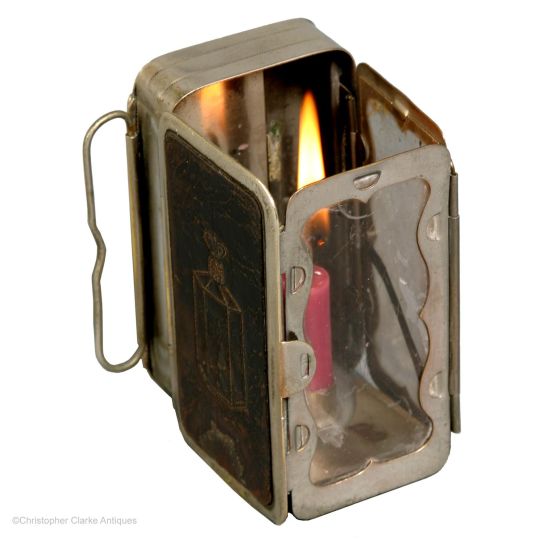
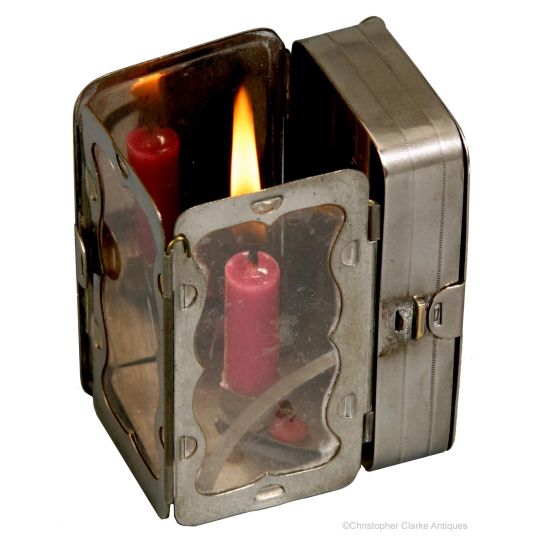



The clear part was mica - a transparent mineral which can be split into thin flexible sheets - while others use horn / parchment, though both of these are translucent rather than transparent. Regardless, all were far less likely to break than glass.
One or two inner surfaces were usually tin, giving the lantern its own built-in reflector, and tech-level-wise, tin as a shiny or decorative finish has been used since Roman times.
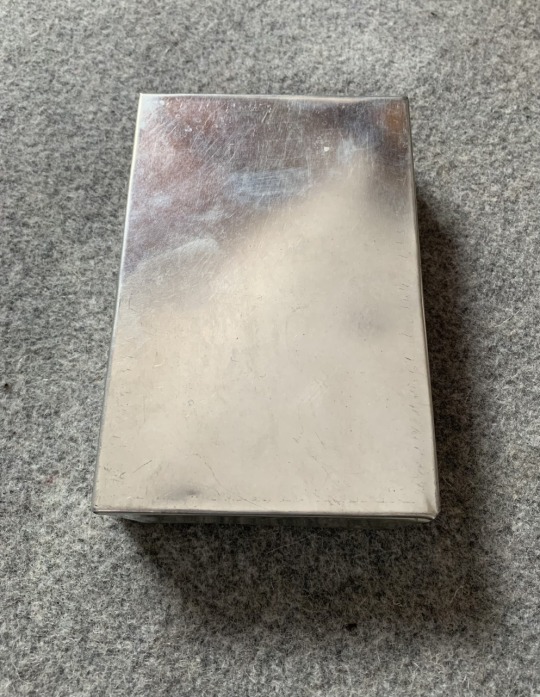
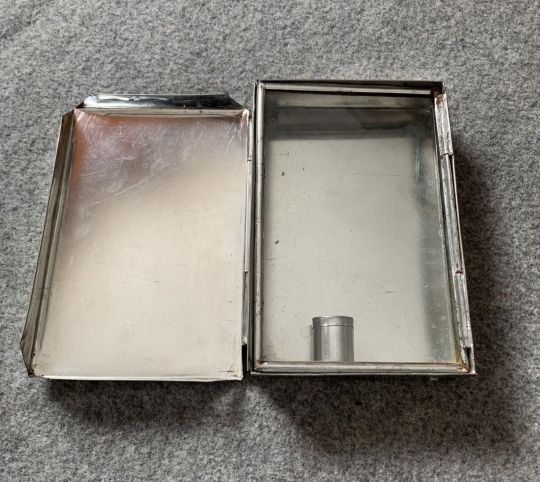
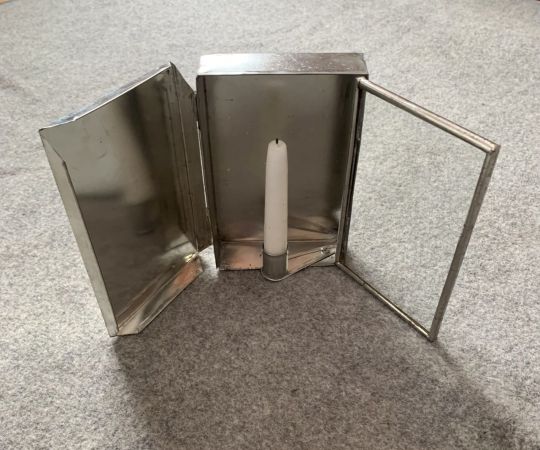
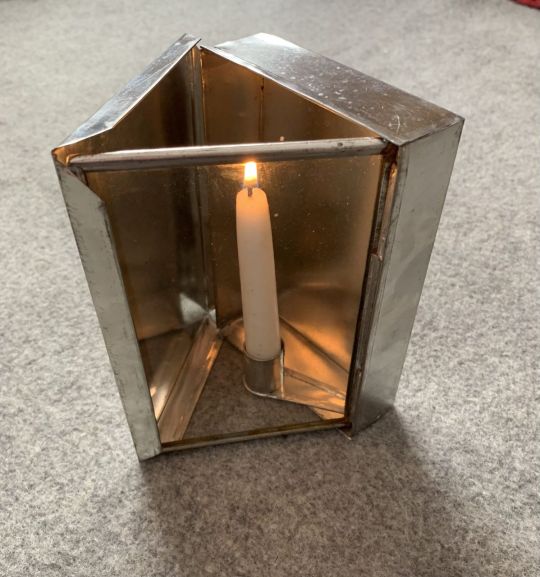




I'm pretty sure that top-of-the-line models could also have been finished with their own matching, maybe even built-in, tinderboxes.
And if real ones didn't, fictional ones certainly could. :->
*****
Yet more period lighting stuff here, including flintlock alarm clocks (!)
#period lighting#tinderbox#too light too dark#social history#writer notes#research#period tech#sword vs lantern#c. j. cherryh
2K notes
·
View notes
Photo








that’s it. that’s the show
#1899#1899 spoilers#1899 netflix#1899edit#tvgifs#tvedit#netflixedit#dailynetflix#cinematv#perioddramaedit#period drama#submitting this set to my uni as a history essay arguing why europeans spent 1000+ years at war#myedit
12K notes
·
View notes
Text
Haven't been able to think about anything other than the victorian/edwardian/WW1 twink and his 80's punk almost-boyfriend for a week, send help
#this tv show has consumed my every thought#it's like tumblr catnip#go watch it#it will eat away at your brain#there's also a butch lesbian butcher#an autistic manga loving weirdo (my beloved)#and a badass psychic who's also a mess#WHAT MORE COULD YOU POSSIBLY WANT?#updating the post bc the reblogs lead me on a WILD wiki rabbit hole about the eras of England#okay so Edwin is born in 1900 which means he was born 1 year before the end of the Victorian era (1837-1901) so technically he's a victoria#baby who lived his childhood in the Edwardian era (1901-1910) and his teens in the pre/start of WW1 era (started in 1914)#until he was killed :( in 1916#so my boy here lived though MANY historical events and time periods#shout out to my victorian/edwardian/WW1 twink#history is very fun and this is why i love this website bc where else would i have to do research for my blorbo?#I do however find it very funny if Gaiman named him Edwin in honour of the Edwardian time period he grew up in#I love that man and it wouldn't surprise me if he turned out to be a history nerd (affectionate) like the rest of you#dead boy detectives#edwin payne#charles rowland#crystal palace#niko dbd#dbd#please feel free to dm me about history i adore it
902 notes
·
View notes
Text

~ Pair of Eye Inlays.
Place of origin: Egypt
Period: Late Period, 25th-26th Dynasty
Date: 722-525 B.C.
Medium: Stone, alabaster, pigment.
#ancient#ancient art#history#museum#archeology#ancient egypt#ancient sculpture#ancient history#archaeology#egyptology#Egyptian#Egypt#pair of eye inlays#late period#25th dynasty#26th Dynasty#722 b.c.#525 b.c.
2K notes
·
View notes
Text

Women Watching Stars, Ōta Chōu, 1936
#art#art history#Ōta Chōu#Asian art#Japanese art#East Asian art#genre art#astronomy#color on paper#Showa period#Showa era#20th century art#National Museum of Modern Art Tokyo
4K notes
·
View notes
Text



Chinese Bronze Sword With An Inlaid Rock Crystal, Turquoise and Gold Hilt
Warring States Period, Circa 4th - 2nd Century B.C.
#Chinese Bronze Sword With An Inlaid Rock Crystal Turquoise and Gold Hilt#Warring States Period#Circa 4th - 2nd Century B.C.#bronze#bronze sword#ancient artifacts#archeology#archeolgst#history#history news#ancient history#ancient culture#ancient civilizations#ancient china#chinese history#chinese art#art
3K notes
·
View notes
Text

Winter Sunshine, Maxfield Parrish
#instagram#pinterest#art#classic art#painting#oil on canvas#romantic art#victorian art#romantic period#victorian period#victorian era#classic#romantic era#history#art history#Winter Sunshine#20th century#1955#maxfield parrish
3K notes
·
View notes