#javascript snippet
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

Expandable Cards
#Expandable Cards#html css card#javascript animation#html css#divinector#learn to code#css#webdesign#html#css3#javascript snippet
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Horizontal Timeline Design
#horizontal timeline design#html css#javascript#codenewbies#frontenddevelopment#html5 css3#css#webdesign#timeline design#horizontal timeline#javascript snippet
3 notes
·
View notes
Text

Dark/Light Mode JavaScript
#dark light mode#toggle day night mode#toggle effect javascript#html#css#codingflicks#frontend#css3#learn to code#code#frontenddevelopment#html css#javascript snippets#javascript for beginners
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
it might have taken upwards of 4 hours between yesterday and today, but I finally got toyhouse to give me functional on-hover dropdown menus <3 exciting times!
#.txt#web dev stuff#<- kinda#i got on-click bootstrap dropdowns working Fairly quickly but what I didn't realise#was that you can't use the bootstrap menus with the hover.#most bootstrap hover menus seem to use jquery or javascript and because i'm working Within toyhouse i can't do that#so that made things a little more complicated ;u;#it also made trying to figure out how other people do things VERY complicated. jesus christ. staring into the abyss.#After ALL of this i think i'm gonna make a collection of snippets. just so other people don't have to deal with this fucking bullshit.#like how to move the sidebar and stuff. because i couldn't find any one place for it and it was really frustrating.#the horrors of working within someone else's spaghetti code are very very real and working with classes and containers you didn't make feel#bad.#i don't enjoy it.#but i am nothing if not hell bent on making things more complicated than they need to be <33333 so we persist!!#this is a lot of effort for a site i don't regularly use and never enjoyed using but like. it's a fun exercise i guess
1 note
·
View note
Text
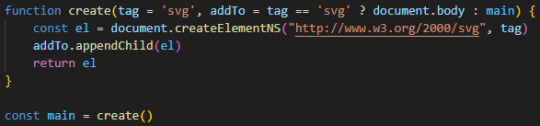
this is fine...
0 notes
Text
[solved] How do I defer or async this WordPress javascript snippet to load lastly for faster page load times?
[solved] How do I defer or async this WordPress javascript snippet to load lastly for faster page load times?
In order to defer or async a JavaScript snippet in WordPress to load lastly for faster page load times, there are a few steps you can take. This will help to prioritize the loading of essential content on your website first, and then load the JavaScript snippet afterwards. Here’s how you can do it: Identify the JavaScript snippet: The first step in deferring or asyncing a JavaScript snippet is to…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
i would love to make a gallery in neocities but erm
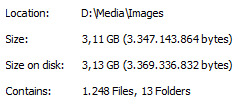
of course theres a lot of not-finished/random images there but idk. having to type out each date to be accurate and having to make thumbnails for each which would increase the total filesize like 1.5 - 2 times... then again. custom gallery. eugh
#im sure there is some kind of javascript to make this sort of stuff automatic but i dont wanna go there yet#maybe vscode can have a snippet for that. i should watch a vscode tutorial..#god i wish i had more things to put in the website. my life is so boring theres like nothing there#dextxt
0 notes
Text
JavaScript Fundamentals
I have recently completed a course that extensively covered the foundational principles of JavaScript, and I'm here to provide you with a concise overview. This post will enable you to grasp the fundamental concepts without the need to enroll in the course.
Prerequisites: Fundamental HTML Comprehension
Before delving into JavaScript, it is imperative to possess a basic understanding of HTML. Knowledge of CSS, while beneficial, is not mandatory, as it primarily pertains to the visual aspects of web pages.
Manipulating HTML Text with JavaScript
When it comes to modifying text using JavaScript, the innerHTML function is the go-to tool. Let's break down the process step by step:
Initiate the process by selecting the HTML element whose text you intend to modify. This selection can be accomplished by employing various DOM (Document Object Model) element selection methods offered by JavaScript ( I'll talk about them in a second )
Optionally, you can store the selected element in a variable (we'll get into variables shortly).
Employ the innerHTML function to substitute the existing text with your desired content.
Element Selection: IDs or Classes
You have the opportunity to enhance your element selection by assigning either an ID or a class:
Assigning an ID:
To uniquely identify an element, the .getElementById() function is your go-to choice. Here's an example in HTML and JavaScript:
HTML:
<button id="btnSearch">Search</button>
JavaScript:
document.getElementById("btnSearch").innerHTML = "Not working";
This code snippet will alter the text within the button from "Search" to "Not working."
Assigning a Class:
For broader selections of elements, you can assign a class and use the .querySelector() function. Keep in mind that this method can select multiple elements, in contrast to .getElementById(), which typically focuses on a single element and is more commonly used.
Variables
Let's keep it simple: What's a variable? Well, think of it as a container where you can put different things—these things could be numbers, words, characters, or even true/false values. These various types of stuff that you can store in a variable are called DATA TYPES.
Now, some programming languages are pretty strict about mentioning these data types. Take C and C++, for instance; they're what we call "Typed" languages, and they really care about knowing the data type.
But here's where JavaScript stands out: When you create a variable in JavaScript, you don't have to specify its data type or anything like that. JavaScript is pretty laid-back when it comes to data types.
So, how do you make a variable in JavaScript?
There are three main keywords you need to know: var, let, and const.
But if you're just starting out, here's what you need to know :
const: Use this when you want your variable to stay the same, not change. It's like a constant, as the name suggests.
var and let: These are the ones you use when you're planning to change the value stored in the variable as your program runs.
Note that var is rarely used nowadays
Check this out:
let Variable1 = 3; var Variable2 = "This is a string"; const Variable3 = true;
Notice how we can store all sorts of stuff without worrying about declaring their types in JavaScript. It's one of the reasons JavaScript is a popular choice for beginners.
Arrays
Arrays are a basically just a group of variables stored in one container ( A container is what ? a variable , So an array is also just a variable ) , now again since JavaScript is easy with datatypes it is not considered an error to store variables of different datatypeslet
for example :
myArray = [1 , 2, 4 , "Name"];
Objects in JavaScript
Objects play a significant role, especially in the world of OOP : object-oriented programming (which we'll talk about in another post). For now, let's focus on understanding what objects are and how they mirror real-world objects.
In our everyday world, objects possess characteristics or properties. Take a car, for instance; it boasts attributes like its color, speed rate, and make.
So, how do we represent a car in JavaScript? A regular variable won't quite cut it, and neither will an array. The answer lies in using an object.
const Car = { color: "red", speedRate: "200km", make: "Range Rover" };
In this example, we've encapsulated the car's properties within an object called Car. This structure is not only intuitive but also aligns with how real-world objects are conceptualized and represented in JavaScript.
Variable Scope
There are three variable scopes : global scope, local scope, and function scope. Let's break it down in plain terms.
Global Scope: Think of global scope as the wild west of variables. When you declare a variable here, it's like planting a flag that says, "I'm available everywhere in the code!" No need for any special enclosures or curly braces.
Local Scope: Picture local scope as a cozy room with its own rules. When you create a variable inside a pair of curly braces, like this:
//Not here { const Variable1 = true; //Variable1 can only be used here } //Neither here
Variable1 becomes a room-bound secret. You can't use it anywhere else in the code
Function Scope: When you declare a variable inside a function (don't worry, we'll cover functions soon), it's a member of an exclusive group. This means you can only name-drop it within that function. .
So, variable scope is all about where you place your variables and where they're allowed to be used.
Adding in user input
To capture user input in JavaScript, you can use various methods and techniques depending on the context, such as web forms, text fields, or command-line interfaces.We’ll only talk for now about HTML forms
HTML Forms:
You can create HTML forms using the <;form> element and capture user input using various input elements like text fields, radio buttons, checkboxes, and more.
JavaScript can then be used to access and process the user's input.
Functions in JavaScript
Think of a function as a helpful individual with a specific task. Whenever you need that task performed in your code, you simply call upon this capable "person" to get the job done.
Declaring a Function: Declaring a function is straightforward. You define it like this:
function functionName() { // The code that defines what the function does goes here }
Then, when you need the function to carry out its task, you call it by name:
functionName();
Using Functions in HTML: Functions are often used in HTML to handle events. But what exactly is an event? It's when a user interacts with something on a web page, like clicking a button, following a link, or interacting with an image.
Event Handling: JavaScript helps us determine what should happen when a user interacts with elements on a webpage. Here's how you might use it:
HTML:
<button onclick="FunctionName()" id="btnEvent">Click me</button>
JavaScript:
function FunctionName() { var toHandle = document.getElementById("btnEvent"); // Once I've identified my button, I can specify how to handle the click event here }
In this example, when the user clicks the "Click me" button, the JavaScript function FunctionName() is called, and you can specify how to handle that event within the function.
Arrow functions : is a type of functions that was introduced in ES6, you can read more about it in the link below
If Statements
These simple constructs come into play in your code, no matter how advanced your projects become.
If Statements Demystified: Let's break it down. "If" is precisely what it sounds like: if something holds true, then do something. You define a condition within parentheses, and if that condition evaluates to true, the code enclosed in curly braces executes.
If statements are your go-to tool for handling various scenarios, including error management, addressing specific cases, and more.
Writing an If Statement:
if (Variable === "help") { console.log("Send help"); // The console.log() function outputs information to the console }
In this example, if the condition inside the parentheses (in this case, checking if the Variable is equal to "help") is true, the code within the curly braces gets executed.
Else and Else If Statements
Else: When the "if" condition is not met, the "else" part kicks in. It serves as a safety net, ensuring your program doesn't break and allowing you to specify what should happen in such cases.
Else If: Now, what if you need to check for a particular condition within a series of possibilities? That's where "else if" steps in. It allows you to examine and handle specific cases that require unique treatment.
Styling Elements with JavaScript
This is the beginner-friendly approach to changing the style of elements in JavaScript. It involves selecting an element using its ID or class, then making use of the .style.property method to set the desired styling property.
Example:
Let's say you have an HTML button with the ID "myButton," and you want to change its background color to red using JavaScript. Here's how you can do it:
HTML: <button id="myButton">Click me</button>
JavaScript:
// Select the button element by its ID const buttonElement = document.getElementById("myButton"); // Change the background color property buttonElement.style.backgroundColor = "red";
In this example, we first select the button element by its ID using document.getElementById("myButton"). Then, we use .style.backgroundColor to set the background color property of the button to "red." This straightforward approach allows you to dynamically change the style of HTML elements using JavaScript.
#studyblr#code#codeblr#css#html#javascript#java development company#python#study#progblr#programming#studying#comp sci#web design#web developers#web development#website design#ui ux design#reactjs#webdev#website#tech
400 notes
·
View notes
Text

Working Digital Clock
#working digital clock#clock javascript#javascript clock#html css#css#frontenddevelopment#webdesign#html#css3#divinectorweb#javascript snippets
7 notes
·
View notes
Text

Background Color Change JavaScript
#Background Color Change JavaScript#codenewbies#frontenddevelopment#html css#html5 css3#javascript project#javascript snippets#webdesign
1 note
·
View note
Text

JavaScript Toggle day-night mode
#toggle day night mode#javascript snippets#html css#css#html#javascript#css3#frontenddevelopment#tutorial#neduzone#frontend
4 notes
·
View notes
Note
how did you learn coding?
I am pretty much entirely self taught as far as front end goes!
I started messing around with HTML and CSS with tumblr themes back in 2016-ish.
For javascript I looked at https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/ for a lot of documentation + examples. And also used codepen a lot to kinda reverse engineer existing snippets of code.
I also read a lot of https://css-tricks.com/
And for flexbox + css grid there's these:
After I got a good foundation of vanilla JS, I learned Vue for a little while and then moved on to React. The new react documentation is really good in my opinion so I definitely recommend reading that if you're interested in learning.
Most of my learning came from trial and error and working on projects that I was really excited about. I used to be so proud of findtags (the original version) which was in jquery...
The react version is miles ahead of it. And even then, the theme builder is also way ahead of findtags. I learned way more between those two projects than reading documentation alone!
191 notes
·
View notes
Text
Main thing stopping me from starting blog essays about films like this, or even posting more Tiger crawl home snippets is that I need to wrestle with Javascript to set my site up better. And I'm a caveman. But once that's figured out it'll be so over for you guys. I have a list
#people who are much smarter and code wise than me have done it#gist is rn and on most neocities sites you repaste the entire site code every time you make a page#meaning if you need to update a header or something you have to edit that page by page#unless you set it up to update universally and only edit it once#which is what im trying to do before i make too many pages
25 notes
·
View notes
Note
Heyy aurie!! Im a writer with a head packed full of ideas and I wanna try making an if!! Previously, I have written poems and snippets but never a whole story. I've alr downloaded twine and everything but ITS SO CONFUSING?? if you have any tips i would be so grateful omd 😭
hii! I am honored you asked me to help, but really before trying to do anything you should look into trying out the different formats on Twine! You basically do that by creating a new game and go to Story, then Details, and check it out (type something into the empty passage to at least see something and what the font looks like). By looking into them and seeing the designs of each one, you can figure out what works best for you. I personally love Sugarcube because it uses CSS, HTML and JavaScript to work, and there are currently a lot of resources for it!
I feel like I would do a better job if you had any specific questions to ask about how to start designing a game, so feel free to DM me. I can also help with coding as well ^^ though my JavaScript knowledge is nonexistent.
I can throw out some resources to look into as well:
Sugarcube v2 Documentation
100% Good Twine Sugarcube Guide
Megathread of Resources
Also, I’d be interested to know just what exactly you want to write, since you have so many stories. I know I have a lot, but I began working on each one at different times, so it would probably be best to settle on your favorite one for now. Maybe read it in the future too lol.
7 notes
·
View notes