#millets traditional rice
Text
Native Millets Traditional Rice in Chennai
Simply said, you use millet as you use rice. You can also roast millet into a kind of small popcorn or use it as couscous or bulgur. In India, millet is often cooked in a pressure cooker, not so much to save time, but for an extra fluffy result. Loosen the grains after cooking, a bit like with couscous, to prevent them from clumping together. The different types of millet taste about the same (a little grainy and a little bitter) and can all be prepared in the same way.
#traditional rice in chennai#millets traditional rice#millets traditional rice in chennai#native food store chennai#native food store#best native food store#millet noodles indian#online native food store#millet nativefoodstore#marketing#nutrition#meal prep
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
[Traditional Chinese Festival] Customs of 臘八節(Laba Festival) in China.Eng Sub
Today(January 18, 2024) is the traditional Chinese festival,臘八節 Laba Festival.Let’s learn about some interesting traditions and customs about this festival.
【About 臘八節(Laba Festival)】
Laba Festival (Chinese:臘八節) is a traditional Chinese holiday celebrated on the eighth day of the month of La (or Layue 臘月), the twelfth month of the Chinese calendar. It is the beginning of the Chinese New Year period. It is customary on this day to eat Laba congee.
Laba Festival was not on a fixed day until the Southern and Northern dynasties, when it was influenced by Buddhism and was fixed on the eighth day of twelfth month, which was also the enlightenment day of the Buddha. Therefore, many customs of the Laba Festival are related to Buddhism.
The Laba Festival's name represents its date on the Chinese calendar. La is the name of the twelfth and final month, and ba means "eight/八". In ancient China, the "eight/八" referred to making sacrifices to eight gods at the end of the year.
In its original form, the festival was celebrated by making sacrifices to gods and ancestors to wish for good fortune, health, safety, and a good harvest in the new year. The word la originally referred to these sacrifices.
After Buddhism spread to China during the first century CE, the festival was used as commemoration of Gautama Buddha's enlightenment.It was given a fixed date (the eighth day of the twelfth month) during the Northern and Southern dynasties.
【Customs of 臘八節/Laba Festival?】
Laba congee/臘八粥
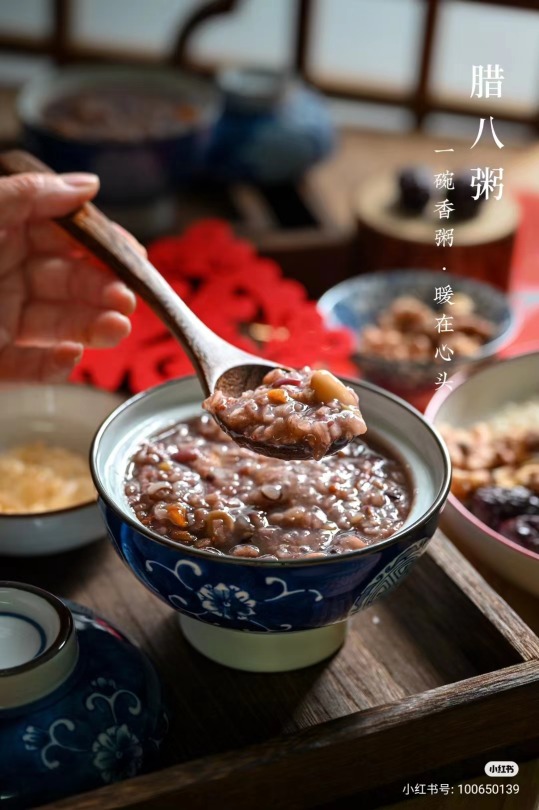

Traditionally, the consumption of Laba congee is an important element of the festival. There are multiple legendary accounts of the dish's origins. One story says that it originated in the Song dynasty with Buddhist monasteries giving congee to people in honor of the story that Sakyamuni (Gautama Buddha) reached enlightenment on the eighth day of the twelfth month after eating congee.
Laba congee or Laba porridge (臘八粥; Làbāzhōu) is very popular in many places in China. Different kinds of rice, beans, nuts and dried fruits are the main ingredients. People believe that it's good for health in the winter.
It is also known as "eight-treasure congee" (八宝粥; Bā bǎo zhōu)and is usually made with eight or more ingredients, representing good luck. Eight is a lucky number in China, and the ba in Laba also means eight.
There are many variations of Laba congee in different regions of China. Ingredients can include mixed grains, such as rice, millet, and barley; beans and nuts such as mung beans, azuki beans, lotus seeds, peanuts, walnuts, and chestnuts; dried fruit such as red dates, longan, raisins, and goji berries; and other ingredients such as vegetables and meat.
2.Laba garlic/臘八蒜
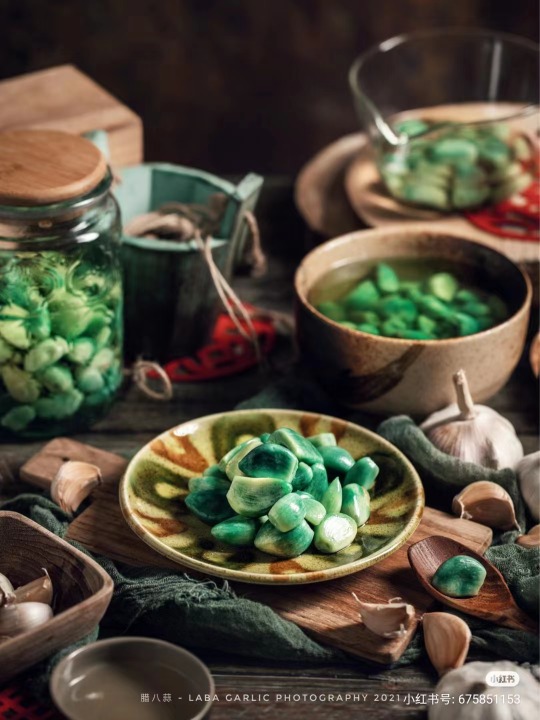

Another Laba food is Laba garlic, which is particularly popular in northern China.Garlic in Chinese (蒜; suàn) has the same pronunciation as calculate (算; suàn), and it is said that on the Laba Festival businesses should balance their books and calculate their revenues and expenditures for the year.Laba garlic is made by soaking garlic in vinegar. Laba garlic is soaked in vinegar from the Laba Festival until Chinese New Year. The garlic and vinegar are then used alongside Chinese dumplings (jiaozi) around Chinese New Year.
————————
🧚🏻Model/Makeup:@曾嚼子&@兔狲猫眠眠
📸 Photo:@逸群闲余
🔗 Xiaohongshu:http://xhslink.com/zlF8Hz
————————
#chinese hanfu#hanfu#Traditional Chinese Festival#臘八節 Laba Festival#chinese culture#chinese customs#chinese history#hanfu accessories#chinese food#china#chinese new year#song dynasty
200 notes
·
View notes
Text
Random Stuff #13: Cats in China--History (Part 1)
(Warning: Very long post ahead with multiple pictures!)
(Link to Part 2)
Since this topic is pretty big, I will split the content across 4 posts, but even then these posts will only be a shallow summary of the subject.
This small series of posts is dedicated to my fluffy quadrupedal friend, 小葱 (Little Green Onion).

-------------------------------------------------
Did you know that there are over 200 cats in the Palace Museum/故宫博物院 in Beijing? Some of these cats were descendants of the pet cats of the imperial family hundreds of years ago, and some of these cats were simply strays, but they all found a home in the Palace Museum, and are now being fed and taken care of by the museum employees. You may even catch a glimpse of one of these cats during a visit to the museum.
Here are two of these cats, Jixiang/吉祥 (right; name means “auspicious”) and Ruyi/如意 (left; name means “(may things go) according to (one’s) wishes”)

Speaking of the Old Palace and royal kitties, cats actually have a fairly long history of being mousers and human companions in China, and sometimes they were even seen as powerful spirits to be both worshipped and feared.
Cats As Guardian Spirits
According to archaeological evidence, in China, cats came into people’s lives as early as 5300 years ago (~3300 BC). People of the Neolithic Yangshao Culture/仰韶文化 (~5000 - 3000 BC) in what is now central China grew millet, rice, and vegetables. These crops were bound to attract small rodents like mice and rats to human villages, which attracted wild cats in turn. There were no evidence showing that these wild cats had any sort of special or intimate bond with humans yet, so the relationship was likely a simple mutualistic relationship in which cats benefitted from having a steady source of prey, while humans benefitted from having their harvest protected from rodents. In the Book of Rites/《禮記》, a book detailing Zhou dynasty (1046 - 256 BC) etiquettes, administration, and ceremonial rites, there was a passage on the religious aspect of this mutualistic relationship:
“The wise and gentle rulers of yore will always repay the good deeds that others have done for them. Welcome the cats, for they are hunters of mice; welcome the tigers, for they are hunters of boars; welcome them and worship them”. (“古之君子,使之必報之。迎貓,為其食田鼠也;迎虎,為其食田豕也,迎而祭之也 。”)
-- Book of Rites, The Great Suburban Sacrificial Rites chapter (《禮記·郊特牲》).
As we can see in this short passage, people in ancient China regarded cats as spiritual beings--one of eight important animal spirits worshipped in the great ritual at the end of the year that must be performed by the ruler--and made offerings to them as a way to thank them for controlling rodent populations in the fields and protecting the year’s harvest.
^ Illustration by 国馆 on Zhihu.
Cats as Evil Ghosts
In ancient folk belief, however, cats eventually became associated with wugu/巫蛊, which can be generally understood as “witchcraft” or “black magic”. Practitioners would sacrifice cats and keep “cat ghosts”/猫鬼, then send them out to curse whoever they wish to harm and steal money from. There was one famous case of this during Sui dynasty (581 - 618 AD) that was recorded in Book of Sui /《隋書》, the traditional official historical records of Sui dynasty that was completed in 636 AD. As the chapter “Consort Kin” (《隋書·外戚》) described, when Empress Dugu and Head of Secretariat Yang Su’s wife fell ill, the doctors diagnosed their illnesses as “caused by cat ghosts”. Emperor Wen of Sui/隋文帝 (personal name Yang Jian/楊堅) assumed that Dugu Tuo/獨孤陀 was behind the mysterious illnesses since Dugu Tuo was the paternal half-brother of Empress Dugu and his wife was the paternal half-sister of Yang Su, but Dugu Tuo denied having anything to do with it. So his household was questioned, and finally one of his housemaids confessed to be a practitioner of “witchcraft” and that she had cursed Empress Dugu and Yang Su’s family with her cat ghost under orders from Dugu Tuo. Dugu Tuo was stripped of all his titles along with his wife, and both were demoted to commoner status. So as we can see it was big enough in folk belief that it actually made its way into some imperial family drama. After this event, Emperor Wen of Sui declared a ban on these practices that were meant to cause harm to others.

^ A modern illustration of a “Cat ghost”, from the work titled Hundred Ghosts of China/《中国百鬼录》.
Cats in Analogies and Folklore
Cats have also been used in the classic cat-and-mouse analogies in different situations. During Wu Zetian/武則天’s ascent to power in Tang dynasty in 655 AD, she was involved in a power struggle with Empress Wang and Consort Xiao, and after some back-and-forths, Empress Wang and Consort Xiao were demoted to commoner status and imprisoned. Consort Xiao then cursed Wu Zetian, saying:
“May you become a mouse and I a cat, so I can choke you!” (”願阿武為老鼠,吾作貓兒,生生扼其喉!”)
-- Old Book of Tang, ”Empresses and Consorts Part 1”/《舊唐書· 后妃上》
Apparently after this happened, Wu Zetian banned cats from the palace out of fear.
Another example of this cat-and-mouse analogy was the memorial Su Shi/蘇軾 submitted to Emperor Shenzong of Song/宋神宗 (personal name Zhao Xu/趙頊) that argued against the parts of the reform proposed by Wang Anshi/王安石. This memorial was preserved and later named《上神宗皇帝書》. In it, Su Shi argued that government officials must be able to freely object another official’s proposal in order to prevent treacherous officials from gaining too much power with this analogy:
“We keep cats in order to keep mice at bay, but we cannot keep cats who can’t catch mice just because there are no mice around; we keep dogs in order to keep burglars away from our homes, but we cannot keep dogs that don’t bark just because there are no burglars around”. (”然而養貓所以去鼠,不可以無鼠而養不捕之貓。畜狗所以防奸,不可以無奸而畜不吠之狗”)
There weren’t only cat-and-mouse analogies, however. There's a short fable about cats and tigers that was passed down through the generations from at least Song dynasty all the way to the present day. Even I have heard of this story as a child. In this fable, the tiger was initially very clumsy, so the tiger asked a cat to teach it how to hunt. The cat agreed and taught the tiger how to track down, stalk, pounce, and play with prey, but refrained from teaching the tiger about tree-climbing. The tiger eventually mastered the art of hunting, and one day the tiger turned on its teacher, the cat, who then climbed atop a tree to save its own life. The moral of the story was either “never teach others everything you know, in case they use your knowledge against you”, or “never teach those who are ungrateful”, which resulted in the xiehouyu/歇后语 (a type of Chinese proverb) “cat teaching the tiger -- withhold some of your abilities” (“猫教老虎--留一手”). Of course, this fable doesn’t really stand in terms of scientific accuracy, seeing as tigers are proficient tree-climbers themselves, but the fable itself is still very interesting nonetheless. Although the origin of this fable has now faded into obscurity, the earliest record I could find was from the self-annotation on the poem “Mocking the Cats”/《嘲畜貓》 by the famous Song-era poet Lu You/陸游 in 1198 AD, which showed that this fable was already popular in folk culture in Southern Song dynasty:
“In folk belief cats were the uncles of tigers, they taught the tigers everything except how to climb trees”. (“俗言貓為虎舅,教虎百為惟不教上樹”)

^ Modern illustration of the fable, from children’s book The Tiger and the Cat by Eitaro Oshima.
Historical texts showed that at least from Southern and Northern dynasties (420 - 589 AD) and on, most people kept cats for their ability to catch mice, and oftentimes keeping cats as just house pets was something that was still limited to royalty, nobility, and rich people. But as we would see in Part 2, there were evidence from Song dynasty that showed a definite change in how cats were viewed in the ordinary household.
(Part 2 Here!)
264 notes
·
View notes
Text
Biu Kitchen - Zongzi




🍃Bi ~(>◇<)~ Biu 🍃
Recipe below the cut
Ingredients:
Equal parts glutinous millet and glutinous rice
Kabocha squash
Sugar
Leaves for making zongzi
Vegetable oil
Chocolate
*Either sweet or savory filling can be used in this recipe
Step 1. Making the rice
Soak the glutinous rice for at least 30 min beforehand. Mix with the glutinous millet in a 1:1 ratio. Add water, using a little less than would typically be used when steaming rice. Add in 2-3 leaves. Steam in an electric rice cooker.
Steam the kabocha squash. Remove the peel and seeds. Mash the squash.
Once the rice is done cooking, mix the hot rice and the mashed squash together until they are well combined and evenly golden-colored.
*Blanch the leaves briefly in scalding water, then remove and place them in water to soak until ready to use. Add a bit of vegetable oil to coat the leaves in a thin layer of oil.
Step 2. Making triangular Bidiu
Difficulty level: ☆☆
Stack 2 leaves on top of each other, then use the traditional shaping method to wrap them, adding in the filling of your choice. After cooling, unwrap the leaves and add on Bidiu's ears and face.
Step 3. Making Bidiu cones
Difficulty level: ☆☆☆☆☆
Stack 2-3 leaves on top of each other and form into a cone. Fill with the prepared rice mixture, adding in the filling of your choice. Flatten the top when filled.
Take about 50 g of rice and form into balls, placing them on top to form Bidiu's head. Form two 5-g balls of race for his paws. Form 1-g balls to make his ears.
Snip off the excess leaf and secure the cone with string. Use chocolate to draw a face and you're done!
It's ok if you mess up, it will still taste great ~
[TN: Different kinds of leaves can be used, most often bamboo, but also reed, lotus, or banana.]
#year: 2023#bidiu#biu kitchen#lxh#the legend of luoxiaohei#羅小黒戦記#罗小黑战记#luo xiao hei zhan ji#food#recipes
66 notes
·
View notes
Text
[Kanto] [Johto] [Hoenn] [Sinnoh] [Unova] [Kalos] [Alola] [Galar] [Hisui] [Champs] [Paldea] [Paldea2] [Paldea3] [Teams] [Misc.]
Ya know who else I've totally neglected in this series of posts? The Battle Frontier bosses.

Anabel's name is LILA[リラ] from Lilac, hence her color scheme. That one's super straight forward.
Spencer's name was UKON[ウコン] from ukon[鬱金] the name for tumeric, a type of ginger root that is very popular traditional chinese medicine.
Noland's name was DATURA[ダツラ] from the genus of poisonous flowers in the Nightshade family, as well as other such charming common names as Devil's Trumpet, Hell's Bells, and Devil's Weed. They are all not only extremely poisonous but psychoactive
Brandon's name was JINDAI[ジンダイ] a neat pun as the common Japanese name of this cactus, jindai[神代], means "god time" as in "age of the gods/myth" in other words, "ancient," which of course lends to his role as Ruins Maniac/Pyramid King.
Tucker's name is HEATH[ヒース] which funny enough means he shares a namesake with Erika, and with Heath, aka HEATHER, Briar's ancestor that wrote the violet/scarlet book.
Greta's name is KOGOMI[コゴミ] from kogomi[屈] the Japanese name for the fiddlehead fern, used in cooking. They have a super distinctive curled shape which is where she gets her hair.
and then Lucy's name is AZAMI[アザミ] as in Azami[薊]: "thistle," appropriate for her prickly demeanor.

Technically I already did Darach's once, but I'll go over it again here. His name is KOKURAN[コクラン] as in kokuran[黒蘭], lit. "Black Orchid" and as a play on that Caitlin is actually named Cattleya[カトレア] from the Catelleya genus of orchids. His ancestor Anthe was named Sharon[シャロン] in reference to the Rose of Sharon, which is actually a common name of a few unrelated flowers, including the national flower of South Korea. (Oddly she seems to bear absolutely no relation to the Orchid theme between Kokuran and Cattleya. )
Argenta's original name was KEITO[ケイト] from keitou[鶏頭] the Japanese name for the Silver Cockscomb, which has very obvious color associations that lend to her design. Also the Silver Cockscomb's scientific name is the Celosia argenta, which is where they got her English name.
Palmer's name is KURUTSUGU[クロツグ] after kurutsugu[桄榔] the Kaong Sugar palm
Thorton's name was NEJIKI[ネジキ] from nejiki[捩木] the Japanese name of the Anyaar/Angeri(Lyonia ovalifolia). They have thee adorable little white bell flowers.
and finally for this batch, it's Dahlia who was in fact just named DAHLIA[ダリア]. For the image i picked a yellow Spider Dahlia specifically since it seemed to match her color scheme and hair

Oh and just to round out this little batch of extras, Barry's name is actually JUN[ジュン] from Junichi Masuda, game director of the core Pokemon series. It's a play on Gary's name being SHIGERU[シゲル], after Shigeru Miyamoto. But sadly it has nothing to do with his dad's name.
While I'm here...

Cheryl's name was MOMI[モミ] from momi[籾] which is a word that refers to unhulled rice specifically. Unrelated to her ancestor Wasabi's name.
Marley's name is MAI[マイ] from mai[米], which is just the word for "Rice" as a food staple, so depending on context it can implicitly mean when hulled, because the alternative would be momi, but it does also generally to the crop and even the food industry. (Ironically Mai in Hisui was actually named YONE[ヨネ] which is an alternate reading of the same kanji for "rice" [米], yet they named her Mai in English, Marley's actual Japanese name...)
Go figure, Buck's name is in fact BAKU[バク] and it's the Japanese word baku[麦] for Wheat or Barley. By sheer coincidence it is how Japanese phoneticizes "Buck" but it does not actually refer to Buck Wheat. Also he has nothing to do with his brother, nor their ancestor's names.
Mira's name is MIRU[ミル] from "Millet." It's also where her little hairtie design comes from.
and finally, Riley's name is GEN[ゲン] from genmai[玄米] the name for brown rice, which is a kind of earthier more nutritious rice.

So oddly, there is a concept in Chinese agriculture and cooking called Wu Gu[五穀]: "The Five Grains" that refers to the 5 staple crops of Chinese agriculture dating back to ancient times, and several far et cultures have their own variations on this... but despite the obvious grain theming the 5 stat specialist trainers don't actually match any specific version of the 5 Grains?? It definitely feels like that was the intended reference, yet it sort of falls apart in the specifics... maybe just a disagreement on what made fora good name or not?
Oh and as for a few other oddball ancestors...

Sabi, Mai, and Zisu I've all technically covered before in one form or another but the quick overview is that Sabi was named WASABI[ワサビ], YONE we mentioned above, and Zisu was named PERILLA[ペリーラ], after the same type of redleaf mint that Flint, aka OBA[オーバ], was named after.
Pesselle's name is KINE[キネ] from kine[杵]: "(mortar &)pestel" which is both a cute play on Millet and on her role as head of the medical division and the grinding of medicinal herbs.
and Riley's ancestor Rye is actually named HAKU[ハク] as in haku[白]"white"but sensibly a reference to hakumai[白米]:"White rice" in parallel to Gen's gen[玄] also reading literally as "Black/Dark" when referring to "brown rice."
#pokemon#pokemeta i guess#pokemon emerald#pokemon dppt#pokemon hgss#pokemon legends arceus#hisui#sinnoh#hoenn#johto#battle frontier
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
There seems to be a really clear pattern emerging here: we see a group living in a specific part of Taiwan, people who were developing increasingly sophisticated maritime technologies and traditions, who were used to sea voyages of increasing length and duration. They knew about rice and millet farming and did a bit of it but didn’t depend on it. Instead, they were willing to subsist on a wide variety of food sources, especially what they could find along and beyond the coast … The same maritime way of life, the same preferred coastal and wetland sites for habitation, the same kinds of tools that we see in southern and eastern Taiwan are what show up first in the Philippines and then later elsewhere. It’s not a bunch of rice and millet cultivators. Instead of finding an expansion of Neolithic farmers driven by increasing population pressure to move out of their homeland, we find seafarers. They were acquainted with crop cultivation but they weren’t dependent on it and we can be certain that they spoke an Austronesian language.
Excerpt by Patrick Wyman, PhD on “The Austronesian Expansion, Part 1” (2022) from the Tides of History Podcast
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
With sweeps of his arm, Jean-Pierre Kamara showers handfuls of tiny seeds over the freshly ploughed land near his village in Senegal’s southern foothills. A team of young men ahead of him loosen more of the clay soil for sowing, while older villagers trail behind, raking the earth back over the seeds.
Only breaking at midday to refuel on peanuts and palm wine, the village works methodically as a unit to grow fonio – a precious grain crucial to their diets that only takes days to germinate and can be harvested in as little as six weeks. Though laborious, growing fonio, one of Africa’s oldest cultivated grains, is simple and reliable, say Kamara’s Bedik people.
It grows naturally, they insist, where mainstream crops such as wheat and rice are harder to cultivate. It is also well adapted to the climate, nutritious, tastes good and can be stored far longer than other grains.
“If you put in front of me some fonio and also something made of maize, I’ll push aside the other because the fonio is much healthier. There are no chemicals used; it just grows naturally and then we harvest it. We don’t add anything,” says Kamara.
The benefits of fonio are so marked that academics and policymakers are now calling for the grain – alongside other indigenous foods, such as Ethiopia’s teff, as well as cassava and various millets and legumes – to be embraced more widely across Africa to improve food security.
10 notes
·
View notes
Text

**Mandia with Sukhua Poda**
Mandia is a wholesome breakfast dish that originates from the state of Odisha, India. It is typically made with ragi or finger millet flour and is a staple food in many households in the region. The flour is mixed with water and salt to form a batter, which is then cooked on a tawa or griddle to create a thin and crispy pancake. Mandia is usually served with a side of chutney, pickle, or curry.
*Ingredients:
4 tablespoons mandia (ragi) flour
Salt, as per your taste
1 cup cooked rice
Instructions:
Boil Water:
1 Start by boiling water in a saucepan. Add salt to the boiling water.
Add Ragi Flour:
2 Once the water reaches a boiling point, slowly add the mandia (ragi) flour to the boiling water. Stir continuously to avoid lumps.
3 Saute Ragi Flour:
Continue stirring the mixture to ensure the mandia flour is well combined with water. Saute the mandia flour until it's thoroughly cooked.
4 Add Cooked Rice:
Incorporate the cooked rice into the sauteed mandia mixture. Stir well to combine the rice with the mandia flour.
Check Consistency:
5 Monitor the consistency of the porridge. Aim for a thickness that is at least "2 string and higher." This refers to the consistency of the porridge when lifted with a spoon – it should form strings and not be too runny.
Continue Sauteing:
6 Keep sauteing the mixture until it reaches the desired consistency and doesn't stick to the bottom of the pan.
7 Transfer to Another Container:
Once the mandia mixture is well-cooked and has the right consistency, transfer it to another container.
Cover with Muslin Cloth:
Cover the container with a muslin cloth. This allows the mandia to cool and set properly.
8 Allow to Set:
Let the mandia (ragi) set with the muslin cloth cover. This is typically done overnight or for a few hours.
Consume in the Morning:
The next morning, your mandia (ragi) porridge should be ready to consume. Enjoy it as a healthy and nutritious breakfast. Remember, you can adjust the salt and consistency according to your taste preferences. Additionally, you can add other ingredients like dahi, jaggery, or fruits to enhance the flavor and nutritional value of the porridge.
Sukhua Poda, ( i have used patharmundy dry fish ) a delicacy hailing from the coastal region of Odisha, is a unique dish made from dry fish, specifically the variety named Patharmundi. The preparation involves a meticulous process of smoking and sun-drying the fish, followed by roasting it on a stove. The smoked and dried fish is skillfully mixed with a blend of spices ( smashed garlic and green chilies ), resulting in a dish bursting with flavor.
This culinary masterpiece offers a distinctive smoky taste that sets it apart. Sukhua Poda is commonly served as a delightful side dish, complementing rice, pakhala (fermented rice soaked in water), and mandia (ragi porridge). It also doubles as a savory snack, perfect for those moments when a quick and flavorful bite is desired.
Sukhua Poda stands as a testament to the rich culinary traditions of the region, providing a delectable experience for those who savor the flavors of coastal Odisha.
Combining the two dishes creates a delicious and unique flavor profile. Adding crushed garlic and chilies to the dish can give it an extra kick of flavor, making it a perfect breakfast or snack option. Whether served separately or together, Mandia and Sukhua Poda are both delicious and nutritious dishes that are worth trying.
pic: odiafoods.in
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Culture Of Nepal
Nepal is a land-located country between India and China. It is well known for the majestic Himalayan mountain ranges and the deep valleys that shape the landscape. Nepalese people are generally patient and calm. Here you can see many different religions and cultures people live together. Most of Nepal's culture is rooted in tradition and religion. Nepalese are proud that their country has never been ruled. The Gurkhas (Nepalese army) continue to be highly admired for their work. The people of Nepal understand the value and beauty of their land.
Customs and Traditions
Nepalese Customs and Traditions differ from one part of Nepal to another. Nepalese people have their own customs and traditions, each with its own merits. Most of them are Hindus and Buddhists. Many of these traditions come from Hinduism, Buddhism, or other traditions. Among them, marriage law is particularly interesting. Traditional marriages require the parents to agree. Cow slaughter is illegal in Nepal. The cow is considered the universal mother, representing motherhood, and worship it. Before entering a temple or a house, you are often asked to remove your shoes, so as not to pollute the clean room with your shoes. Some non-Hindu temples are prohibited. The right hand, which is considered pure, is used to eat, pay, give, and receive.
Festivals
Nepal's diverse culture is reflected in many of its events. Nepalese people celebrate so many festivals but the major festivals of Nepal are Dashain and Tihar. Dashain is one of the most anticipated festivals of the year and Nepalese Hindus celebrate it with great joy for 15 days in the month of Ashvin (September-October). Tihar is another big festival that is celebrated for five days. Apart from decorating the house with diyo, animals like cows, dogs, and crows are also worshiped at this festival.
Nepali Dance and Music
Music and Dance is also an important part of Nepali culture. Nepal is rich in traditional and classical music. According to Hindu mythology, Shiva, who is the god of dance in his Nataraja form, used to perform the Tandava dance in the Himalayas. Different cities have their own dance style that they perform in different festivals, fairs, and family time. Like dancing, Nepali music is also divided by the community: Tamangs, Gurungs, Sherpas, Maithilis, Newars, Kirats, Magars, and Tharus each have their own songs and dancing styles. Musical instruments like Madal, Dhimey, Panchai Baja, and Sarangi are the traditional musical instruments of Nepal.
Architecture of Nepal
Nepalese architecture is characterized by two main styles: the pagoda style with many revolving stalls and the domed stupa style.
The Pashupatinath Temple in Kathmandu, which attracts many tourists, is one of the oldest examples of the pagoda style in the world, built in the first century AD. A Nepalese architect named Araniko was the first to introduce pagoda-style architecture to China. Other examples of this style include Basantpur Palace and Changu Narayan Temple. Boudhanath and Swayambhunath stupas are beautiful examples of stupa architecture. The Shikhara type is another important type of architecture it consists of a high tower in the form of a mountain with carvings in stone or wood. The Krishna Temple in Patan is an example of this type of architecture. In addition to these, the Newa style, derived from the Newar is also can be seen.
Food of Nepal
Nepalese cuisine is heavily influenced by Indian, Tibetan, and Chinese cuisine. Dal, Bhat, and Tarkari is the staple food of all Nepalese regardless of ethnicity. Bhat means rice, dal means lentils, and tarkari means vegetable curry. Apart from this, there are different types of food that are eaten by different tribes and regions. For example, people living in the highlands can replace rice with other grains such as wheat, corn, millet, corn, or barley.
Traditional Clothes
The traditional clothes of Nepal are Daura-Surul and Dhaka Topi for men and Gunyo-Cholo for women. Traditional clothes are different from the caste and culture. People of different cultures wore their own cultural dress at festivals and marriage functions.
Religion
In Nepal, most of the people are Hindus. The census shows that 81.3% of the people follow the Hindu religion, 9% people follow Buddhists, 4.4% Muslims, 3% Kiratis ( the religion of some natives of the Himalayas) tribal), 1.4% Christians, and the remaining 0.9% are Jains, Sikhs, and some people who do not follow any religion. There are places of worship for all religions in the country and all religions celebrate their own festivals. There is great harmony and cooperation between the Hindu and Buddhist communities in Nepal as they share places of worship and celebrate together. Lumbini in Nepal is actually the birthplace of Lord Buddha, so it is a holy place for Hindus and Buddhists.
Language
Nepali is the national language of Nepal, it is actually a multilingual country, with each ethnic group communicating in their own language. As many as 123 languages are spoken in Nepal, the most spoken of which are Nepali, Newari, Maithili, Bhojpuri, Tharu, and Tamang. The Nepali language is written in the Devanagari language and actually evolved from the ancient Sanskrit language.
Handicrafts Arts
Variety of products including metalware, pottery, textiles, wood and stone handicrafts, paper, bone, horn, leather, bamboo, etc. The list seems endless, which means you will never run out of products to buy in Nepal. Although some of these objects, such as metal images of gods and goddesses, religious objects such as bells and vajras, wooden carvings, and silver ornaments, have been made since the beginning of civilization. Among textiles, it is useful to know Pashmina and clothes of yak wool. Nepalese artisans have received respect and admiration for their work from people around the world.
#Nepal culture and traditions#Nepal religion and culture#Unique culture of Nepal#Hindu culture in Nepal
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
The benefits of fonio are so marked that academics and policymakers are now calling for the grain – alongside other indigenous foods, such as Ethiopia’s teff, as well as cassava and various millets and legumes – to be embraced more widely across Africa to improve food security. ...
These ancient foods, with their greater nutritional benefits and resilience to drought, could break the continent’s reliance on imported wheat, rice and maize, which often do not grow easily in Africa but now dominate people’s diets. ...
Michel Ghanem, an agronomist who co-founded the Forgotten Crops Society, is calling for more investment in these neglected foods. ...
“You have lots of indigenous crops – like teff, fonio, sorghum – that people still eat today but have been neglected by funding agencies, the international research organisations, but definitely not by consumers. And it’s now that we should invest in these because they could close that [food] gap.”
Researchers say these neglected foods have several nutritional benefits, often with lower glycemic index ratings than refined flours and white rice, while also having important micronutrients. Research in the 1990s into neglected African crops by the US National Research Council found that fonio and finger millet were rich in the essential amino acid methionine, which is often lacking in western diets, while teff was high in protein, amino acids and iron. ...
Edie Mukiibi, vice-president of Slow Food International, which campaigns to protect threatened local food cultures, says imperialism imposed “monoculture” farming on Africa and other colonised regions of the world, destroying biodiversity in agriculture.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Super Delicious Millets in Native Food Store
Millets are a group of small-seeded grasses that are commonly grown in semi-arid regions of Asia and Africa. They are known for their nutritional benefits and have been a staple food in many parts of the world for centuries. Millets are rich in nutrients such as fiber, protein, vitamins, and minerals. They are particularly high in iron, calcium, and magnesium.Millets are gluten-free, making them a great option for people with celiac disease or gluten intolerance. Millets are rich in antioxidants and have been shown to help reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease. #food #foodporn #foodie #foodstagram #foodphotography #foodblogger #foodlover #foodgasm #foodpics #foodies #foodpic #foods #foodblog #foodlovers #foodgram #foodiesofinstagram #foodstyling #foodart #foodlove #foodiegram #foodphoto #fooddiary #millet #millets #healthyfood #healthyeating #instantfood
#millet flakes#millet noodles indian#best native food store#cold pressed oil#millet dosa mix#millet noodles#millet muesli#millet vermicelli and jaggery powder#millets traditional rice#millets traditional rice in chennai
1 note
·
View note
Text
Hi Producer (正好遇见你) Infodump
Disclaimer: I have no idea about the accuracy of the information shared in the drama, I'm merely transcribing for future reference purposes. Proceed with caution!
.
Ep 28-29: Bronzeware
Traditional Chinese Bronzeware has a history of over 5,000 years. Although it's not the earliest place of origin for bronze in the world, it has made a mark in the history of bronzeware in the world for its craftsmanship.
During the Xia, Shang, and Zhou dynasties, bronze was used mainly for ceremonial instruments and military weapons, and bronze craftsmanship rose to its peak, producing countless stunning works of bronze. This period was also known as the Bronze Age.

.
Bronze Sun Wheel
From Sanxingdui. Over 3,000 years old.

.
Dragon Spout Vessel, Bronze Lamp With a Crane on Turtle Replica


.
Lotus and Crane Rectangular Hu - Crane from Henan, Four-goat Square Zun


During the Shang and Zhou dynasties, pigs, cattle, and goats were used as sacrificial offerings. Among bronze drinkware, vessels designed in the form of goats came to be. Historians believe that the horns and dragon heads of the Four-goat Square Zun were first cast separately and then arranged on the exterior before being cast as a whole. The pinnacle of the traditional clay casting method. It is ranked third among the ten national treasures.
.
Jin State Western Zhou Bronze Bird Zun


From Jin state, 3,000 years old. An early mid-Western Zhou temple ritual vessel. It is designed in the form of a phoenix looking back. The large bird looks at its nestling, covered in patterns. The phoenix tail and elephant trunk act as support. An intricate piece of art with a peculiar shape. Because it was excavated close to a tunnel that was dug without proper permits, it was already broken into more than 100 fragments when it was discovered. It took over a long year of careful restoration before it was brought into the public eye.
.
Ding
The development of Ding, the cauldron- it used to be a vessel for storing and cooking meat. Then came the legend of the Nine Tripod Cauldrons; Jizhou, Yanzhou, Yuzhou, Jingzhou, Qingzhou, Yangzhou, Xuzhou, Yongzhou, Liangzhou and it gradually became a symbol of state and power.


.
Bronze Quadrangular Li with an Amputated Slave
It's cookware like Ding. The shape is also quite similar. But Li is hollow and three-legged. According to the "Rites of Zhou", the eunuchs guard the palace, while the amputee guards the garden. The man with a crutch at the front gate here probably committed a crime and was punished with amputation and was therefore sentenced to guard the nobles' garden.
Did ancient people make cookware like this to raise awareness and educate the general public about the law? You can look at it this way if you want or not.

Looking at the shape of the ware, food can be placed into the upper level to be cooked, while the lower level is used to burn coal. The smoke emitted can be smoothly discharged through the windows on the left and right and through the hollowed-out area at the back.
Traditionally, they believe that a Ding is used to cook meat, while a Li is used to cook grains. (The FL compares the Li to a Hot Pot and then a Rice cooker lol).
.
Gui with a Beast Face Pattern Replica
It's for storing millet and grains. Bowl. Flared mouth and rounded belly are distinctive features of Gui.
The Zhou rites have very strict rules for the use of Dings and Guis by different social classes.

.
Bronze Sword Replica, Bronze Ax of Fu Hao Replica


Dagger-Ax of Fu Hao Replica, Dagger-Ax of Prince in Wu State Replica


Bronze Dagger-Ax Replica

岂曰无衣?与子同袍。王于兴师,修我戈矛。与子同仇。
How can you say we are without armor? Our camaraderie remains. To battle, we shall go with you. Our dagger-axes and spears are sharpened. We shall fight with you!
岂曰无衣?与子同泽。王于兴师,修我矛戟。与子偕作。
How can you say we are without armor? Our comradeship remains. We shall fight with you! Our lances and spears are sharpened. To the battlefield, we shall enter with you.
岂曰无衣?与子同裳。王于兴师,修我甲兵。与子偕行。
How can you say we are without armor? Our comradery remains. We shall fight with you! Our weapons are sharpened. Together, we go to war!
——《诗经·秦风·无衣》 From Shi jing/Book of Songs. Wú Yī 無衣 (commonly translated as "No clothes (no armor)"
(A Song from the state of Qín 秦 [modern Shǎanxī 陕西 and Gānsù 甘肃])
.
Rites and Music
China is a land of etiquette, complex rituals and music since before 3,000 years. The Zhou people classified the 18 musical instruments used for court music into eight categories based on their materials, which were clay, gourd, skin, wood, stone, metal, silk, and bamboo. They believed that the eight tones were the only way to achieve the unity of heaven and man.
youtube


Bianzhong is a large percussion instrument cast in bronze. Bianzhong existed in China as early as the Western Zhou, the first country in the world to make and use this instrument. Many cultural attractions use it to hoodwink tourists. It's rarely used in contemporary performances.
youtube
There has been a revival of Chinese music in recent years. But on the whole, Western music is still more popular. Merging these different musical approaches can bring marvelous results.
.
Timestamped documentary section:
youtube
.
More Hi Producer posts
#cdrama#chinese drama#正好遇见你#Hi Producer#chinese history#bronzeware#sanxingdui#court music#traditional chinese musical instruments#bianzhong#Chinese bronzeware
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
INDIAN FOODS IN USA

Hi Readers, welcome to indianfoodinusadotcom, Here you can learn all about Indian foods, recipes and all about INDIAN FOOD like {ABOUT INDIAN FOOD}
{HISTORY}
{VEDIC AGES}
{ANTIQUITY}
{FOOD MENTIONED IN ANECIENT INDIAN SCRIPTURE}
{MIDDLE AGE OF 16th CENTURY}
{COLONIAL PERIODS}
{INGREDIENTS}
{RECIPES}
LIKE (a) chicken Biryani (b) mutton biryani (c)Butter chicken (d) chicken tikka masala (e) veg biryani (f) Palak paneer (g) Matar paneer (h) chutneys, AND Many more.
ABOUT INDIAN FOOD in USA
You will get know more about the best restaurants Around the world
INDIAN FOOD consists of a variety of regional and traditional cuisines native to India. Given the diversity in soil, climate, culture, ethnic groups, and occupations, these cuisines vary substantially and use locally available spices, herbs, vegetables, and fruits.
Indian food is also heavily influenced by religion, in particular Hinduism and Islam, cultural choices.
Historical events such as invasions, trade relations, and colonialism have played a role in introducing certain foods to this country. The Columbian discovery of the New World brought a number of new vegetables and fruit to India. A number of these such as potatoes, tomatoes, chillies, peanuts, and guava have become staples in many regions of India.
INDIAN FOOD has shaped the history of international relations; the spice trade between India and Europe was the primary catalyst for Europe's Age of Discovery.
Spices were bought from India and traded around Europe and Asia. INDIAN FOOD has influenced other cuisines across the world, especially those from Europe (especially Britain), the Middle East, Southern African, East Africa, Southeast Asia, North America, Mauritius, Fiji, Oceania, and the Caribbean.
HISTORY OF INDIAN FOOD NON-VEGETARIAN
INDIAN FOOD reflects an 8,000-year history of various groups and cultures interacting with the Indian subcontinent, leading to a diversity of flavors and regional cuisines found in modern-day India. Later, trade with British and Portuguese influence added to the already diverse INDIAN FOOD.
After 9000 BCE, the first period of indirect contact between the Fertile Crescent and Indus Valley civilizations seems to have occurred due to the Neolithic Revolution and the diffusion of agriculture. Around 7000 BCE, agriculture spread from the Fertile Crescent to the Indus Valley, and wheat and barley began to be grown. Sesame and humped cattle were domesticated in the local farming communities.
Mehrgarh is one of South Asia's earliest sites with evidence of farming and herding. From circa 4500 to 1900 BC the rulers of Lower Mesopotamia were Sumerians who spoke a non-Indo-European and non-Semitic language, may have initially come from India and may have been related to the original Dravidian population of India.
By 3000 BCE, turmeric, cardamom, black pepper and mustard were harvested in India.
From Around 2350 BCE the evidence for imports from the Indus to Ur in Mesopotamia have been found, as well as Clove heads which are thought to originate from the Moluccas in Maritime Southeast Asia were found in a 2nd millennium BC site in Terqa. Akkadian Empire records mention timber, carnelian and ivory as being imported from Meluhha by Meluhhan ships, Meluhha being generally considered as the Mesopotamian name for the Indus Valley Civilization.
VEDIC AGE
VEGETARIAN
The ancient Hindu text Mahabharata mentions rice and vegetable cooked together, and the word "pulao" or "pallao" is used to refer to the dish in ancient Sanskrit works, such as Yājñavalkya Smṛti. Ayurveda, ancient Indian system of wellness, deals with holistic approach to the wellness, and it includes food, dhyana (meditation) and yoga.
ANTIQUITY
Early diet in India mainly consisted of legumes, vegetables, fruits, grains, dairy products, and honey.
Staple foods eaten today include a variety of lentils (dal), whole-wheat flour (aṭṭa), rice, and pearl millet (bājra), which has been cultivated in the Indian subcontinent since 6200 BCE.
Over time, segments of the population embraced vegetarianism during the Śramaṇa movement while an equitable climate permitted a variety of fruits, vegetables, and grains to be grown throughout the year.
A food classification system that categorised any item as saatvic, raajsic, or taamsic developed in Yoga tradition. The Bhagavad Gita proscribes certain dietary practices.
Consumption of beef is taboo, due to cows being considered sacred in Hinduism.[14] Beef is generally not eaten by Hindus in India except for Kerala, parts of southern Tamil Nadu and the north-east.
PICKLES
FOOD MENTIONED IN ANECIENT INDIAN SCRIPTURE
While many ancient Indian recipes have been lost in history, one can look at ancient texts to see what was eaten in ancient and pre-historic India.
Barley—(known as Yava in both Vedic and Classical Sanskrit) is mentioned many times in Rigveda and other Indian scriptures as one of the principal grains in ancient India
Betel leaf—primary use is as a wrapper for the chewing of areca nut or tobacco, where it is mainly used to add flavour; may also be used in cooking, usually raw, for its peppery taste
Breadfruit—fritters called jeev kadge phodi in Konkani or kadachakka varuthath in Malayalam are a local delicacy in coastal Karnataka and Kerala
Chickpeas—popular dishes are made with chickpea flour, such as mirchi bajji and mirapakaya bajji
Curd—a traditional yogurt or fermented milk product, originating from the Indian subcontinent, usually prepared from cow's milk, and sometimes buffalo milk, or goat milk
Figs —cultivated from Afghanistan to Portugal, also grown in Pithoragarh in the Kumaon hills of India; from the 15th century onwards, also grown in areas including Northern Europe and the New World
Ghee—a class of clarified butter that originated in ancient India, commonly used in the Indian subcontinent, Middle-Eastern cuisine, traditional medicine, and religious rituals
Grape wine —first-known mention of grape-based wines in India is from the late 4th-century BC writings of Chanakya
Honey —the spiritual and supposed therapeutic use of honey in ancient India was documented in both the Vedas and the Ayurveda texts
Mango—the Jain goddess Ambika is traditionally represented as sitting under a mango tree
Mustard —brown mustard is a spice that was cultivated in the Indus Valley civilization and is one of the important spices used in the Indian subcontinent today
Pomegranate—in some Hindu traditions, the pomegranate (Hindi: anār) symbolizes prosperity and fertility, and is associated with both Bhoomidevi (the earth goddess) and Lord Ganesha (the one fond of the many-seeded fruit)
Rice—cultivated in the Indian subcontinent from as early as 5,000 BC
Rice cake—quite a variety are available
Rose apple—mainly eaten as a fruit and also used to make pickles (chambakka achar)
Saffron —almost all saffron grows in a belt from Spain in the west to Kashmir in the east
Salt —considered to be a very auspicious substance in Hinduism and is used in particular religious ceremonies like house-warmings and weddings; in Jainism, devotees lay an offering of raw rice with a pinch of salt before a deity to signify their devotion, and salt is sprinkled on a person's cremated remains before the ashes are buried
Sesame oil —popular in Asia, especially in Korea, China, and the South Indian states of Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, and Tamil Nadu, where its widespread use is similar to that of olive oil in the Mediterranean
Sorghum—commonly called jwaarie, jowar, jola, or jondhalaa, sorghum is one of the staple sources of nutrition
Sugar—produced in the Indian subcontinent since ancient times, its cultivation spread from there into modern-day Afghanistan through the Khyber Pass
Sugarcane—the earliest known production of crystalline sugar began in northern India; the earliest evidence of sugar production comes from ancient Sanskrit and Pali texts
Turmeric —used widely as a spice in South Asian and Middle Eastern cooking
Middle Ages to the 16th Century
VEG DUM BIRYANI
During the Middle Ages, several Indian dynasties were predominant, including the Gupta dynasty. Travel to India during this time introduced new cooking methods and products to the region, including tea.
India was later invaded by tribes from Central Asian cultures, which led to the emergence of Mughlai cuisine, a mix of Indian and Central Asian cuisine. Hallmarks include seasonings such as saffron.
Colonial Period
The Portuguese and British during their rule introduced cooking techniques such as baking, and foods from the New World and Europe.
The new-world vegetables popular in cuisine from the Indian subcontinent include tomato, potato, sweet potatoes, peanuts, squash, and chilli. Most New World vegetables such as sweet potatoes, potatoes, Amaranth, peanuts and cassava based Sago are allowed on Hindu fasting days. Cauliflower was introduced by the British in 1822. In the late 18th/early 19th century, an autobiography of a Scottish Robert Lindsay mentions a Sylheti man called Saeed Ullah cooking a curry for Lindsay's family. This is possibly the oldest record of INDIAN FOOD in the United Kingdom.
INGREDIENTS
Staple foods of INDIAN FOOD include pearl millet (bājra), rice, whole-wheat flour (aṭṭa), and a variety of lentils, such as masoor (most often red lentils), tuer (pigeon peas), urad (black gram), and moong (mung beans). Lentils may be used whole, dehusked—for example, dhuli moong or dhuli urad—or split. Split lentils, or dal, are used extensively, Some pulses, such as channa or cholae (chickpeas), rajma (kidney beans), and lobiya (black-eyed peas) are very common, especially in the northern regions. Channa and moong are also processed into flour (besan).
Many Indian dishes are cooked in vegetable oil, but peanut oil is popular in northern and western India, mustard oil in eastern India, and coconut oil along the western coast, especially in Kerala and parts of southern Tamil Nadu, Gingelly (sesame) oil is common in the south since it imparts a fragrant, nutty aroma.
In recent decades, sunflower, safflower, cottonseed, and soybean oils have become popular across India, Hydrogenated vegetable oil, known as Vanaspati ghee, is another popular cooking medium, Butter-based ghee, or deshi ghee, is used commonly.
Many types of meat are used for Indian cooking, but chicken and mutton tend to be the most commonly consumed meats. Fish and beef consumption are prevalent in some parts of India, but they are not widely consumed except for coastal areas, as well as the north east.
The most important and frequently used spices and flavourings in INDIAN FOOD are whole or powdered chilli pepper (mirch, introduced by the Portuguese from Mexico in the 16th century), black mustard seed (sarso), cardamom (elaichi), cumin (jeera), turmeric (haldi), asafoetida (hing), ginger (adrak), coriander (dhania), and garlic (lasoon).
One popular spice mix is garam masala, a powder that typically includes seven dried spices in a particular ratio, including black cardamom, cinnamon (dalchini), clove (laung), cumin (jeera), black peppercorns, coriander seeds and anise star.
Each culinary region has a distinctive garam masala blend—individual chefs may also have their own. Goda masala is a comparable, though sweet, spice mix popular in Maharashtra. Some leaves commonly used for flavouring include bay leaves (tejpat), coriander leaves, fenugreek (methi) leaves, and mint leaves. The use of curry leaves and roots for flavouring is typical of Gujarati and South INDIAN FOOD.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text

A Good day starts with Good FOOD!
Right, isn't it? People start their day with their morning breakfast, there arises the topic of whether the day is fine or not. Nobody wants their day without food, as we people are rushing our day only for this. Food is the only thing that every living creature lives in this world wants. It is the only thing that has no discrimination on gender, birth, age, place, rich or poor, upper/lower class, Good/bad, and what else, there is no sincere love than the love towards food. But there will be a special love for regional foods as well. Being an Indian, probably, most of the people even outside India will have the desire to taste South Indian Foods as it has the versatility of its style.
Let's take a look at South Indian Foods
The food varieties with a special culinary style of tradition, special rituals, the culture of serving, exclusive history for various dishes, healthy ingredients, and much more. South Indian foods hold the top position in this. These foods are a combination of Andhra style, Malabar style, Chettinad style, and Kannada style recipes. Most traditional of these are Kali, Keppai, Ditch millet, and Ragi tiffin etc., These are the common foods usually preferred by Indian people during the 60s and 70s. Even today, these are the main foods in some of the regions like rural villages, tribal areas, and hilly areas.
Little Bite on Health Concern
In Today's lifestyle, it is hard to believe that people live for more than 70 years. But our great-grandparents and grandparents would have lived for so many years like 80 to 90 years… Right? How come they could be so? Only Because of these healthy South Indian foods. They lived true to the words "Food is the greatest medicine ever". This is one of the best examples to prove that food varieties made in South Indian style are among the world's healthiest and tastiest as well.
Food TODAY!
Since the 1980s, people from different countries wishes to explore new varieties of different origins and different cultures. Nowadays, it is common in India that people wanted to try new styles of recipes and unique styles of preparation. For example, Let's take a popular dish 'Biryani', as it has various styles of preparation like Andhra style biryani, Malabar biryani, Hyderabadi biryani, Dum biryani, Awadhi biryani, Ambur biryani, Thalassery biryani, Beary biryani, etc. Even Rice choices also there for Biryani preparation such as basmati, Seeraga samba, Jeerakasala/Kaima, and so on. Visit our website www.pasiout.com to explore more varieties.
So, Every person will have their own choice and love for their favorite style of preparation. Even, vegetarian people also wanted to try new recipes in South Indian foods. Different restaurants like multicuisine, Chettinad, and pure veg have their menu in Vegetarian as equal to Non-vegetarian dishes. Thus, we could say that the mindset of people keeps on engaging in new recipes.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Top 5 Famous Foods Of Haryana You Have to Try
Haryana is known for its famous food, and it's no surprise that locals and visitors alike are eager to try the different delicacies the state has to offer. From spicy snacks to hearty curries, Haryana's cuisine is a reflection of its culture and history. In this blog post, we'll be exploring the top 5 famous foods of Haryana you have to try. Whether you're a fan of traditional flavors or trying something new, these dishes are sure to satisfy your taste buds. So, let's get started and explore some of the best cuisine Haryana has to offer.

1) Bajra Aloo Roti
A staple of the Cuisine Of Haryana, Bajra Aloo Roti is a savory flatbread filled with potatoes and millet flour. The dough is made with bajra (also known as pearl millet) and wheat flour, rolled out into a thin roti and stuffed with mashed potatoes. The roti is then cooked in a skillet with oil or ghee until it is golden brown.
Bajra Aloo Roti can be enjoyed plain with a side of pickles, or it can be used to scoop up dals, curries and vegetables for a complete meal. It is typically served as part of a traditional Haryanvi thali (feast), along with other local dishes like Kadhi Pakora or Ghevar. This delicious, healthy dish is a must-try for anyone looking to explore the flavors of Haryana!
2) Churma
Churma is a traditional sweet dish of Haryana and is one of the most popular dishes in the cuisine of Haryana. It is made from whole wheat flour, ghee and jaggery, and is often served with dal. Churma is usually prepared for special occasions or festivals, but it can also be enjoyed as a snack or dessert. The taste of churma varies depending on the region in Haryana; some versions are more sugary, while others are less sweet. Churma has a creamy texture and a rich, nutty flavor that pairs perfectly with savory dishes like dal. When served with dal, churma provides an excellent balance of flavors and textures, making it a popular and memorable dish in the cuisine of Haryana.
3) Ghevar
Ghevar is a traditional sweet from the Cuisine Of Haryana. It is made from flour, ghee and sugar syrup and has a unique honeycomb-like structure. Ghevar is a popular festive dish and is served during Diwali or other celebrations. It comes in various shapes and sizes and can be flavored with cardamom, saffron or rose water. This rich and flavorful dessert is an important part of Haryanvi culture and its cuisine. Ghevar can be served plain, topped with dry fruits, or with rabdi (condensed milk). The combination of its sweet taste, flaky texture and beautiful appearance makes it a must-try delicacy of the Cuisine Of Haryana.
4) Kadhi Pakora
Kadhi Pakora is one of the most popular dishes in the Cuisine Of Haryana. It’s made with a creamy, spicy curry known as “kadhi” and deep-fried fritters made from chickpea flour, also known as pakoras. The kadhi is usually cooked with yogurt and besan (chickpea flour) and then seasoned with a variety of spices like cumin, turmeric, and coriander. The pakoras are deep-fried and then added to the kadhi to give it an extra layer of flavor and texture. Kadhi Pakora is usually served with hot chapatis or steamed rice and can be a great meal for lunch or dinner.
5) Malpuas
Malpuas are a sweet dessert commonly found in the Cuisine Of Haryana. It is made from all-purpose flour, sugar, ghee and milk. The batter is deep fried in ghee and served hot. It is often garnished with chopped almonds, pistachios and saffron. Malpuas are generally enjoyed during festive occasions such as Holi, Diwali and Raksha Bandhan. This dessert is sweet and creamy in taste and can be served with a variety of accompaniments such as rabri or chashni. Malpuas are popular among people of all ages and are a must-have in any festive celebration in Haryana.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Indian Tasty Recipes For The Winter To Keep You Warm
Individuals of a more mature age in an Indian family relied heavily on the power of traditional spices, flavors, or kitchen fixings as a customary arrangement of medication. These cures are convenient solutions, yet they are regular and have gone the distance with science. We never truly have the opportunity to think about the occasional movements and the produce that nature profits from at that specific time. Healthy Indian recipes utilize these customary spices, flavors, neighborhood vegetation, and so forth, to fortify our body's invulnerable reaction and system.
There are fixings that help you prep for an occasional shift—fixings that immediately fix heartburn, a runny nose, hurting feet, and, surprisingly, an undesirable pimple! These recipes remember the fixings or mixes for which they are made to deal with everything under the sun. If you want to fight illnesses the right way or avoid them altogether, this is your guide to a happy and healthy winter. Discover a portion of our customary, healthy recipes below to warm you up this winter.
Sarso ka saag
Sarso ka saag is a popular north Indian delicacy produced using a mix of green, verdant veggies. Customarily, it utilizes spinach, mustard, and bathua leaves, which leave a slight harshness in your mouth. However, this blend is a fantastic source of anti-oxidants that build your resistance, are calming, and keep you safe from lung issues. When matched with a makke ki roti, this transforms into a flavorful dinner.

Bajra khichidi with home-made makkhan
The name "khichidi" makes us go all warm and fluffy inside. This smooth Rajasthani bajra khichidi with home-made makkhan is a winter favorite in numerous families. Bajra, widely regarded as the best millet on the planet, is an incredible combination of insoluble fiber, essential amino acids, minerals, and a high-energy, low-glycemic-index food. When matched with a rich spread, this recipe gives you supplements and builds your digestion and internal heat level.
Handwa
Handwa is a Gujarati dish that is extremely flexible in the utilization of its fixings. since it utilizes a mixture of blended dals, rice, a few veggies, and a liberal tadka of mustard seeds, sesame seeds, hing (asafoetida), and curry leaves. This is steamed and served, so it makes for an entirely warm and cushy supper. As a result of utilizing this plethora of fixings, we stock up on protein and carbs in an extraordinary proportion with the decency of veggies, and the tadka handles our processing, nutrients, and minerals.
Gur ka paratha
It has been a winter custom in my home to complete our feast with a piece of gur roti. This regular sugar, arranged differently in the winter, is plentiful in nutrients and minerals. As a result, it promotes invulnerability, regulates internal heat, prevents colds and flu, and prevents weakness. Furthermore, it is a joy to complete your dinner with this.
Kaadha
Each family has its own recipe for a "kaadha." In any case, it is basically a blend of turmeric powder, ajwain, and dark peppercorns with a hint of honey. This invention combats cold and flu. It has mitigating properties that assuage sore throats and lift susceptibility. Instead of popping pills, try this kaadha the next time you need to get rid of a cold. Attempt these healthy and sound recipes this winter to guarantee a solid body and blissful taste buds!
For More Info:-
Indian Winter Recipes
1 note
·
View note