#phantom limb
Text
ear / tail phantom shifts are so odd, the feeling of something coming from my tailbone, fur and bone shifting and moving and and the sensation of ears flicking and moving on my head. the way phantom limbs are so sensitive and its so silly and odd!
#wolf therian#wolf posting#wolfkin#therian things#therian#therianthropy#caninekin#phantom limb#dog therian
149 notes
·
View notes
Text

I spent more time on this than I probably should've
bonus version of just Professor Impossible and Phantom Limb because this is the only emotional spectrum those cunts have

#nick did an art#venture bros#hank venture#dean venture#brock samson#byron orpheus#dr venture#the monarch#pete white#jonas venture sr#professor impossible#phantom limb
328 notes
·
View notes
Note
Therian culture is: "want my ears", "want fur", "want tail so it can go swish swish", "wanna run in the night", "pleeeease, want my ears, fur, and tail, pleeeeease", "I will pay good money to be me", "wanna hiss at you because you're mean, but I can't without questions", "I want to roar but human vessel says no", and "wanna do quads and walk on all fours but family >:["
the human vessel is so limited :(
#therian culture is#therian culture#alterhuman#otherkin#therianthropy#theriantype#therian#theriotype#phantom limb
132 notes
·
View notes
Text
Writing amputees: Phantom limb sensation/Phantom Limb pain
This was something I got asked about a lot whenever I made videos about amputee representation, so let's talk about Phantom Limb Sensation (PLS) and Phantom Limb Pain (PLP).

TW: Description of surgical amputation process. section with this content can be skipped and the start/end will be clearly marked.
What is it and what causes it?
Phantom Limb Sensation is when you can feel a limb, even after it's been amputated. This phantom limb is a VERY common side effect of amputation, one that almost every amputee experiences at some point. Depending on how the limb was amputated, how old the person was at the time and the condition of the limb before amputation, it can last for as little as a year to being a life-long condition.
it's caused by the part of your brain responsible for proprioception - the sense of where your body is in space. Your brain has an internal map of your body and specifically your nervous system, and it uses this to determine where certain body parts are in space, even without input from your 5 main senses, meaning you don't need to look to know where, say, your leg or hand is (usually, though other disabilities like autism and ADHD can affect this and make it less accurate). Usually, the brain senses where your body parts are using a combination of this map and input from nerves. But if something happens to your body part, that internal map can have a lot of trouble updating, and when the internal map and the nerve inputs don't match, it can cause your brain to panic and fill in the gaps from the missing input signals, creating the sensation that a lost body part, usually a limb, is still there. For some, the limb light be locked in place, other might have the sensation of the limb "growing back" (though as I understand it, this typically only happens to very young children) and others feel as though the limb is perfectly fine and moving along with the rest of the body normally.
This sensation isn't unique to people who have lost limbs mind you: some trans people who have had top or bottom surgery, people who've had mastectomies, and even people who have had growths or tumours removed often report a similar sensation of their removed parts still being present, though it's not usually as intense and fades after a few months to a few years on its own with minimal intervention, leading to it being categorized as a separate phenomenon to Phantom Limbs in these cases.
Phantom Limb Pain is an extension of phantom limb sensation, caused by the body's more extreme reaction to the same phenomenon. The exact reason why it occurs isn't known, but in many people, instead of feeling a persistent pressance of a limb that's no longer there, they will feel discomfort or pain radiating from the lost limb. For some people, it might be an itch on the phantom limb they can't scratch, for others, the pain can feel like intense "pins and needles" all over the lost limb, others feel an electric "zap" running through the non-existent nerves, live they've grabbed a low-voltage electic fence, some people feel a dull, pounding pain, like the lost limb is being crushed or pushed into positions it shouldn't be able to go into (e.g. someone who had their knee amputated might feel the joint bending in the wrong direction). Some people experience all of these, some only experience one. Everyone will be different.
How is it treated?
Like with many things in life, prevention is better than a cure. certain measures can be taken to lessen the intensity of PLP and PLS before it can even start.
Gore TW: description of the process of surgical amputations, skip to the "----" divider to avoid.
People who have had amputations in the last 10 years will go through a slightly different procedure than those who had amputations before then. Historically, the limb would be amputated by cutting directly through the limb and either sewn shut or by having a skin graft where tissue is used to create a "cap" at the end of the stump. These methods worked, but left nothing for the nerves to connect to once everything was healed, leading the brain to think the reason for the lack of signal from the limb is that the limb was simply broken. Not only can this cause added intensity to the nerve pain, and increase the risk of something called a neuroma, where the nerves attempt to mend the "break" and continue to grow until they hit the surface of the skin, causing them to bundle up and get tangled, creating a feed back loop and amplifying any signal from the area to unbearable levels (including phantom sensations).
Today though, when conditions allow, amputations are done by cutting through the limb as before, then once the skin layers are reached on the other side, surgeons cut downward, creating a long tab of skin which is pulled over the bottom of the stump and reattached to the front. This allows the major nerve pathways in the limb to connect with each other during the healing process, creating a loop in the nerves and tricking the brain into thinking it's still receiving signals from the amputated limb.
Those who had their amputations prior to this change in the procedure can have a similar operation done to achieve a similar effect, though in both cases, it doesn't always work and can lead to the brain producing very very strange phantom limb sensations. In my personal case, it creates a sensation that I can feel my own skin in the region as though it was something separate from the rest of the body, almost like I'm wearing a sock. Very odd, and honestly kind of cursed lol.
------------------------------------------------------
If prevention isn't an option though, different treatments exist.
One popular method is through compression. what's left of the amputated limb (called the stump) will be either wrapped in very strong compression bandages or the person can wear a fitted compression sock on the stump. This is usually done for the first 6-12 weeks after the amputation, though it can be done for longer under the supervision of a rehab specialist in some circumstances. After 6 weeks, 6-12 weeks, the stump will have healed enough for a prosthetic to be fitted. After this point, the person is encouraged to wear the prosthetic or at least the liner, usually made from silicone in modern prosthetics instead of a compression sock/bandage. The liners of the prosthetic offer milder compression, as does the socket of the prosthetic itself, and the "snug" feeling can, for some, make the phantom pain more bearable and the phantom sensation less frequent (though some people experience the opposite and will have increased PLP/PLS while adjusting to the prosthetic, though it usually subsides eventually).
For leg amputees specifically, they are encouraged to walk on their new prosthetics as much as possible, as the action of walking with the prosthetic will often trigger the phantom limb to start moving in time with the rest of the leg, and the sensation of walking can essentially trick the brain into using the phantom limb sensation to help the person walk more naturally and feel less unstable.
Another treatment is called Mirror Therapy, though this only works for single-limb amputees or arm and leg amputees who's amputations were on the same side (e.g. both left leg and left arm). The person puts their full remaining limb in front of a mirror and their amputated limb behind the mirror, then angles themselves so it appears that their full limb being reflected in the mirror is replacing the lost limb. If the person is experiencing an itch on their lost limb, they can scratch the full one, and look into the mirror. Eventually, your brain will feel the scratching sensation on the phantom limb instead.
If none of these options work, nerve pain medications such as gabapentin can be prescribed, though this is usually a last resort as these medications can have serious side effects and can prevent people from being able to do certain jobs or even drive depending on the dosage. As an absolute last resort, an injection can be given to the person to numb the stump. This does not stop the pain completely, but it does subdue it, though many doctors warn against this as it often means the person will not be able to feel if their stump is injured and can result in infected, untreated wounds.
Unfortunately, there is no "cure" yet, and many amputees just learn to live with PLP and PLS.
What things make you more or less likely to experience PLP/PLS?
There are some things that can make you more or less likely to experience PLP and PLS, and that can effect how intensely you experience them.
Your age when you lost the limb
People who are born without the limb almost never experience PLP and PLS, as their brain's internal map already knows the limb isn't there. Likewise, children who lost their limb very early in life don't usually experience PLS very intensely, or for very long, and are less likely to experience PLP at all. This is because when you are young, your brain is already updating that internal map because you're growing, so it has an easier time understanding the fact the limb isn't there anymore. Young brains are also constantly changing and growing, making them more adaptable in general to acquiring major disabilities. On the flip-side someone who lost their limb late in life is more likely to experience PLP and PLS for the rest of their lives. It can be managed, but it will likely always be pressant. Thier brains have not really needed to make any major updates to that map, often for decades, and are not really built to be able to do that, meaning PLP and PLS will likely take longer to go away, if they ever go away at all.
How you lost it and the condition of the limb before it was amputated.
If you lost your limb due to trauma, meaning events like accidents or major injury, the phantom sensation you experience will likely be much more painful, and could even feel like the injury or accident is happening over and over again. For example, someone who lost their arm to a shark attack might feel the sensation of the shark's teeth biting into it as well as the sensations described in the first section.
Alternatively, someone who had their limb amputated due to a pre-existing condition might continue to feel that condition even after the limb is gone. As a personal example, I've had multiple amputations throughout my life, but my most recent was due to a bone infection that formed at the bottom of my stump from a previous amputation. Now, when I experience phantom limb sensation, I can still feel where the infection reached the surface (where the nerves began to feel something was wrong). I had that leg amputated through the ankle as a young child, and when it was re-amputated higher up due to the infection, I didn't feel the whole leg, just the pre-existing stump.
Post Amputation Care
If a person does not receive proper medical care immediately after an amputation, their phantom sensation and pain will be significantly worse. My great Grandfather for example, lost part of his hand during WW2, but due to the situation, was not able to receive adequate medical care once he was established due to the medics being preoccupied with the actively dying. As a result of this and the traumatic nature of how he lost it in the first place, he experienced very intense phantom pain for the majority of his life. This is also important to keep in mind if your story takes place before the modern age, as it wasn't really understood how important post-amputation care was until recently, and many folks were left to just figure it out themselves.
Time
As with all things, phantom pain and phantom sensation fade with time. They may not ever go away entirely, but they do fade in intensity at least a little. This is especially important to keep in mind for characters with beyond-human lifespans. Your elderly grandmother character might not live long enough for their phantom pain to fade entirely, but your immortal vampire who's been alive for a millennia and lost their arm when they were human probably will.
Closing things to keep in mind
Wow, that was longer than I was expecting but I hope you found this all helpful. One last thing to keep in mind is that oftentimes, amputees who do experience PLS/PLP get pretty good at managing it, so you don't have to worry about it too much unless the amputation happens during the story itself or you want to make it a focus, this is just an explanation of what you can include if you like. Personally, though, I feel like it's an aspect of being an amputee that a lot of media rep overlooks, so it would be nice to see some more representation at least mention it. It doesn't have to be constant, but some brief comments or something of the like will go a long way.
#Writing Disability with Cy Cyborg#long post#writing disability#disability#disabled#disabilities#actually disabled#disability representation#amputee#writing#writing advice#writer#writeblr#on writing#writers on tumblr#authors of tumblr#authors#phantom limb#id in alt text
343 notes
·
View notes
Text
BRICK FROG
Write a letter
Buy the movie (on sale)
Buy the DVD box set (also on sale for less than $50 right now!)
Or go be annoying on twitter like me #savetheventurebros
#brick frog#save the venture bros#the venture brothers#vbros#the venture bros#dr mrs the monarch#phantom limb#red mantle#dragoon#red death#venture bros movie#radiant is the blood of the baboon heart#brock samson#rbbh#venture bros season 8#venture bros#dr girlfriend
123 notes
·
View notes
Text

designed my own chart because im physically nonhuman and dont feel represented by the current chart!
template is here for anyone who wants it; edit at your leisure but please keep credit :]
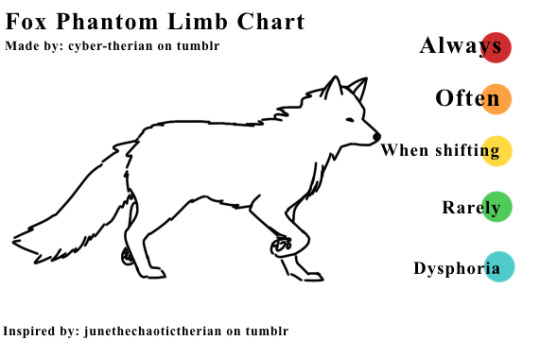

here is the stock image that the base is made from!

#otherkin#therian#alterhuman#therianthropy#canine therian#canine kin#caninekin#physically nonhuman#red fox therian#silver fox therian#fox theriotype#fox therian#fox holothere#transspecies#phantom limb#phantom shift
54 notes
·
View notes
Text
every venture bros character is on the spectrum and at least a little bit gay
#venture bros#the venture bros#venture brothers#go team venture#rusty venture#the mighty monarch#malcolm fitzcarraldo#dr girlfriend#dr mrs the monarch#brock samson#dean venture#hank venture#pete white#billy quizboy#henchman 21#gary fischer#dr orpheus#phantom limb#and others…
178 notes
·
View notes
Text

shoutout to this episode fr
#vbros#venture bros#the venture bros#venture bros fanart#vbros art#colonel hunter gathers#venture bros hunter gathers#hunter gathers#phantom limb#trans hunter gathers#gwgwgegdhdhdjdh#dot png
225 notes
·
View notes
Text
real not fake
#vbros#venture bros#the venture bros#venture bros edit#the monarch#rusty venture#dr girlfriend#phantom limb
338 notes
·
View notes
Text
The effects of psilocybin on phantom limbs: an upcoming large study, and what otherkin have noticed
Orion Scribner posted on September 15, 2023:
Content warnings: This article talks about the use of psychoactive substances only as used in either medical treatment under the guidance of physicians, or in spiritual visionary experiences as entheogens. This article also talks about injuries and chronic pain, but it doesn't describe these in graphic detail. Be forewarned that some of the academic sources cited do go into graphic detail, if you choose to go read those next.
Summary: In California, a large study is looking for participants. Researchers want to see if psilocybin helps treat the participants' phantom limb pain. The study isn't about therians or otherkin. Many therians and otherkin experience phantom limbs, and some of them have made observations about how psilocybin and other psychoactive substances influence their phantom limbs. This article is an eight minute read, plus a bibliography.
A large study seeks participants who suffer phantom limb pain due to having had amputations
The Psychedelic Health and Research Initiative (PHRI) at the University of California, San Diego, is looking for participants for a study. They want adults who have had an amputation and who experience chronic phantom limb pain. The proposed will use MRI brain imaging to study the effects of a therapeutic dose of psilocybin on phantom pain. Psilocybin is the active ingredient in hallucinogenic mushrooms, which may have potential for addressing some forms of chronic pain that are difficult to treat. The $1.3 million study will be placebo-controlled and double-blind, and they will compensate participants $600. Specialized monitors will oversee each session, with doctors and rescue medications available. The pitch for the study doesn't say what dates it will take place, but a recruitment ad ran for it on August 31 in Amplitude, a news and lifestyle magazine for people who have had amputations. To learn more about the study or find how to contact its team by phone or email, see its pitch here, and Amplitude Magazine's ad here.
This proposed study doesn't say anything about otherkin and therians, and the recruitment ad only mentions that it's looking for people who experience phantom limbs due to having had amputations. Something intriguing is that that otherkin and therians have noticed that psilocybin and other psychoactive substances affect their own phantom sensations. The rest of my article will go into some background about all that.
Many sorts of people experience phantom limbs, of many kinds, for many reasons
When someone has sensations as though they have a body part that they do not physically have, the medical term for this is a phantom limb. It's best known in people who have had a limb amputated, but the phenomenon happens in many other cases. For example, it also occurs for people who have sensations of missing body parts other than limbs: ears, fingers, breasts, genitals, or internal organs (Langer et al, 2023; Dorpat, 1971; Ramachandran and McGeoch, 2007). The phenomenon also includes people who have sensations of body parts that they weren't born with (McGeoch and Ramachandran, 2012; Price, 2006). Some types of people who experience this are those who have had a stroke, who were born with incomplete limbs (McGeoch and Ramachandran, 2012), who are transgender (Ramachandran and McGeoch, 2008), or who elicit such experiences through experimental conditions (Casas et al, 2016). The medical term for a sensation of an extra limb is a supernumerary phantom limb (SPL) (Amoni et al, 2005).
Phantoms are underreported due to stigma. Most people who experience phantoms only talk to their doctors about having phantoms if they are very painful and they want help with that. The medical term for this is phantom limb pain (PLP). For people who do feel phantom pain, it can be different to treat than pain in a body part that is physically there. Experts are developing creative approaches for treating this pain, for example, mirror-box therapy (Imaizumi et al, 2017), virtual reality (Ambron et al, 2021), and psychedelic medicine.
What are therianthropes and otherkin?
Therianthropes (therians) and otherkin are people who have the long-term, integral experience and identity of being something other than human. For example, of being a wolf, elf, dragon, or Pokémon (Scribner, 2023; Sonne, 2021; Shepard, 2021). The explanations they give for why they are like this usually come from spirituality, psychology, or both (Kinmunity, 2016, pp. 19). Some common spiritual explanations are reincarnation or having been born with a nonhuman spirit, but not all therians and otherkin share these beliefs or hold them in similar ways (Lupa, 2007, pp. 27, 57-66). Though these examples of explanations are tied to spiritual beliefs, being an otherkin or therian isn't a religion and does not have religious or spiritual requirements. On the secular side, some explain themselves as having something about their mind or brain that's different than that of most people, not for spiritual reasons, but simply an undeniable part of their everyday lives (Lupa, pp. 80-86). Though this is an unusual way for a person to be, mental health experts say this isn't inherently a mental illness or delusion (Lupa, 2007, pp. 86, 261-262; Baker-Whitelaw, 2015).
Many therians and otherkin experience phantom limbs
Many therians and otherkin experience phantom limbs and phantom sensations of body parts that humans don't have, such as tails. When the therian community began in the 1990s, they contextualized their experiences with werewolf folklore. They developed jargon in which they refer to times of feeling nonhuman phantoms more vividly as phantom shapeshifting (House of Chimeras, 2021; Lupa, 2007, pp. 42-43, 126-127; Proctor, 2019, pp. 203-209). When the otherkin community mingled with the therian community in the 2000s, they adopted this shifting terminology as well.
Survey data suggests phantom sensations are prevalent among therians and otherkin. A large informal survey of otherkin and therians found that 72.1% of them experience nonhuman phantom limbs or phantom sensations (Kinmunity, 2016, p. 155). A team of scientists known as the International Anthropomorphic Research Project (IARP) or FurScience surveyed attendees of furry fandom conventions. The furry fandom is about enjoyment of fictional human-like animals in art, and its participants often roleplay as animal characters, but usually don't identify as animals. The IARP tended to find that 5% to 20% of furries identified as therians (Plante et al, p. 112). At AnthroCon 2015, the IARP found that phantoms were more prevalent among therians than other attendees of that convention. Of those therians who felt phantoms (percentage not specified in the IARP's public-facing materials), 70.4% of them tended to find it distressing (Plante et al, p. 116).
Otherkin and therian phantoms can feel different while influenced by psychoactive substances
Drugs are not a key aspect of therian and otherkin subcultures. Their communities rarely discuss the effects of substances in relationship to their therianthropy and otherkinship. Some otherkin and therians who have used mind-altering substances have noticed that these influence their phantom sensations.
The first source I've seen that describes this in significant depth is "Entheogens for Otherkin," an excellent presentation by Dove and Edge for verified adult attendees at Othercon 2022. A recording of the presentation is on Youtube. Though there isn't a written transcript of it, together with other attendees, I wrote five pages of notes on the presentation when I attended, which you can read in a section near the end of this document. Entheogens are psychoactive substances employed in culturally sanctioned visionary experiences in ritual and religious contexts. Othercon is a yearly virtual convention for otherkin, therians, and other sorts of alterhumans. Dove is a formally ordained Pagan priestess, an otherkin, therian, and host of a multiple system, with ten years of experience with entheogens. Her spouse Edge is a vampire and Catholic witch with twenty years of experience with entheogens. The panelists and attendees talked about harm reduction and safety. Some entheogens the panel talked about were psilocybin, ayahuasca, datura, and cannabis. Different entheogens each affect phantom sensations in their own characteristic ways, some having little effect on phantoms, and others making phantoms feel more vivid, or shifting, or developing entirely into an out-of-body experience. Entheogens may affect otherkin and therians’ phantoms in different ways from person to person.
About the writers: This article was written by Orion Scribner (they/them), with feedback from their boyfriend Page Shepard (he/they) and partner system House of Chimeras (they/them). The three& of them are historians and archivists for the communities of therians, otherkin, and other alterhumans.
References
Ambron, E., Buxbaum, L. J., Miller, A., Stoll, H., Kuchenbecker, K. J., & Coslett, H. B. (2021). Virtual Reality Treatment Displaying the Missing Leg Improves Phantom Limb Pain: A Small Clinical Trial. Neurorehabilitation and neural repair, 35(12), 1100–1111. https://doi.org/10.1177/15459683211054164
Amplitude Magazine (August 31, 2023). "Tripping the switch on PLP." Amplitude Magazine.https://livingwithamplitude.com/article/tripping-the-switch-on-plp/
Annoni, Blanke, Dieguez, Khateb, Landis, Lazeyras, Momjian-Mayor, Pegna, and Simon (March 20, 2009). “Seeing the phantom: A functional MRI study of a supernumerary phantom limb.” Annals of Neurology.https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19557858/
Baker-Whitelaw, Gavia (February 22, 2015). “Understanding the otherkin.” The Kernel. Archived March 18, 2015. https://web.archive.org/web/20150318110839/http://kernelmag.dailydot.com/issue-sections/features-issue-sections/11866/otherkin-tumblr-definition-pronouns/
Casas, D.M., G G Gentiletti, & A A Braidot. “Somatic and Movement Inductions Phantom Limb in Non-amputees.” Journal of Physics: Conference Series, Volume 705, Issue 1, (2016): 1-11 http://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1742-6596/705/1/012062/meta (accessed June 26 2016).
Dorpat, T. L. (1971). Phantom sensation of internal organs. Comprehensive psychiatry, 12(1), 27–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/0010-440x(71)90053-8
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/0010440X71900538?via%3Dihub
Dove and Edge (2022). "Entheogens for Otherkin." OtherCon. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-YEh0mVcLo0
House of Chimeras. (November 19, 2021). A Timeline of the Therianthrope Community.https://houseofchimeras.neocities.org/Nonfiction-Articles
Imaizumi, S., Asai, T., & Koyama, S. (2017). Agency over Phantom Limb Enhanced by Short-Term Mirror Therapy. Frontiers in human neuroscience, 11, 483. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2017.00483
Kinmunity. "2016 Otherkin Community Survey." Kinmunity. 2016. Private collection.
Langer, S. J., Caso, T. J., & Gleichman, L. (2023). Examining the prevalence of trans phantoms among transgender, nonbinary and gender diverse individuals: An exploratory study. International journal of transgender health, 24(2), 225–233. https://doi.org/10.1080/26895269.2022.2164101https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37114107/
Lupa (2007). A Field Guide to Otherkin. Stafford, England: Immanion Press. https://www.worldcat.org/title/137242792
McGeoch, P., and Ramachandran, V. (2012). “The appearance of new phantom fingers post-amputation in a phocomelus.” Neurocase 18, no. 2, pp. 95-97. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/13554794.2011.556128https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21598175/
Plante, Courtney N., Stephen Reysen, Sharon E. Roberts, and Kathleen C. Gerbasi (2016). "FurScience!
A Summary of Five Years of Research from the International Anthropomorphic Research Project." FurScience. https://furscience.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/Fur-Science-Final-pdf-for-Website_2017_10_18.pdf
Price, E. H. (2006). A critical review of congenital phantom limb cases and a developmental theory for the basis of body image. Consciousness and cognition, 15(2), 310–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.concog.2005.07.003https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1053810005000917?via%3Dihub
Proctor, Devin (May 2019). On Being Non-Human: Otherkin Identification and Virtual Space. The George Washington University. https://search.proquest.com/openview/e156c24bf65c4efb0918a8db37433cce/
Psychedelics and Health Research Initiative (2023). "Research." UC San Diego. https://phri.ucsd.edu/research/
Ramachandran, V. S., & McGeoch, P. D. (2007). Occurrence of phantom genitalia after gender reassignment surgery. Medical hypotheses, 69(5), 1001–1003. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mehy.2007.02.024https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0306-9877(07)00181-8
Ramachandran, V.S. and Paul D. McGeoch. “Phantom Penises in Transsexuals: Evidence of an Innate Gender-Specific Body Image in the Brain,” Journal of Consciousness Studies, Volume 15, Number 1, (2008): pages 5-16, http://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/imp/jcs/2008/00000015/00000001/art00001 (accessed November 5 2015).
Scribner, Orion (April 13, 2023). “A Simple Introduction to Otherkin and Therianthropes: Version
2.4.7.” The Works of Orion Scribner. https://www.frameacloud.com/nonfiction
Shepard, Page. “The 2021 Nonhumanity & Body Modification/Decoration Survey Results Breakdown.” Three Dragons and a Dog. August 28, 2021. Accessed December 4, 2022. https://invisibleotherkin.neocities.org/files/BodyModification-DecorationSurveyResults.pdf
Sonne (2021). “Terms and definitions.” Project Shift. https://projectshift.therianthropy.info/terms-definitions-by-sonne
A note for commenters on this article:
The author of this article is a layperson who isn’t involved in the study, so if you have questions about the study, please contact the researchers running the study instead, here. In your comments on my blog post, please exercise caution if you discuss psychotropic substances. If you write about illegal practices, for example, obtaining drugs that are illegal in your region, myself and other moderators of this forum may delete your comment. This is in alignment with Dreamwidth's Terms of Service, which forbids material that is illegal under United States law (section XI, subsection 8) or in your own jurisdiction (section II, subsection 2).
(This article was originally posted by Orion Scribner on September 15, 2023 on the Otherkin News blog on Dreamwidth, where you can read and write comments.)
105 notes
·
View notes
Text
If you feel stupid today just know that i was trying to cover my ears and then proceeded to cover my phantom ears instead of my actual ears:'3

#alterhuman#catkin#nonhuman#theriotype#cat therian#feline therian#felinekin#otherkin community#otherkin#cat theriotype#cat kin#cat alterhuman#alterhumans#alterhuman community#alterhumanity#therian#therians#phantom limb
62 notes
·
View notes
Text
guys i woke up at 2:30 am in a cold sweat and this is the closest photoshop approximation i could make to the dream i was having

#still no pinned post. oh well#phantom limb#venture bros#vbros art#vbros#fucking terrifying dude i hate him
97 notes
·
View notes
Text
Therian Confessions: 3
Normalize basic therians. Therians who have Stanleys and wear Lululemon, because it helps them feel like they are still connected to the human normality.
#phantom limb#otherkin#quadrobics#therian#theriotype#furry#otherhearted#therianthropy#lululemon#stanley cup
31 notes
·
View notes
Note
therian culture is wondering why phantom limbs are so accessible and normalized but as soon as you can actually see it you are then villainized and shunned 
:(
#therian culture is#therian culture#alterhuman#otherkin#therianthropy#theriantype#therian#theriotype#phantom limb
66 notes
·
View notes
Text
Assorted Venture Bros sketches

Hi y'all! So, I'm. Not dead 💀 was dealing with really bad art block for a WHILEEEE, plus my iPad is pretty much completely unusable so now it's a waiting game until I can get a new one. If any of y'all wanna donate or commission some sketches from me to help, that would be pretty awesome :)
#this is my second time posting this because tumblr is being an ass ;-;#art#my art#artists on tumblr#original art#fanart#venture bros#the venture bros#the venture brothers#pete white#dr mrs the monarch#dr girlfriend#the monarch#molotov cocktease#henchman 21#phantom limb#again i reiterate: you can tell who my favorite is LMAO
85 notes
·
View notes
Note
Otherkin / therian relationship culture is snuggling up to your partner and feeking their phantom wings wrap around you :33
therian/otherkin culture is
42 notes
·
View notes