#sherman creek
Photo









September 16, 2022 (1 of 3)
Testing out the Voigtlander Nokton 40mm f/1.2 Aspherical M-mount lens. There’s something magical about it.
#photography#street photography#nature#sherman creek#swindler cove#fort george#uptown#manhattan#nyc#new york city#sony#a7ii#voigtlander#nokton#40mm#aspherical#lens flare#leica m
25 notes
·
View notes
Text


























Here's a updated version of all these kid characters who love each other. (Some of them BTW.)
#disney#nickelodeon#ytv#20th centery fox#the simpsons#hey arnold#the loud house#chalkzone#captain flamingo#el tigre#avatar the last airbender#camp lakebottom#craig of the creek#ok ko let's be heroes#steven universe#king of the hill#problem child#little manhattan#dreamworks animation#mr peabody and sherman#recess#boyfriend girlfriend#true love#the jungle book#aang x katara#katara x aang#steven x connie#connie x steven#bobby x connie#connie x bobby
84 notes
·
View notes
Text

Happy Birthday Jason +50 🥳🎂🎈🎁🎉
Buon Compleanno 🥳🎂🎈🎁🎉
#jason behr#actor#worldcinema#cinema#movies#film#cinemetography#filmography#comedy movies#drama movies#tv shows#90s movies#2000s movies#90s tv shows#2000s tv shows#pleasantville#sherman oaks#dawsons creek#roswell 1999#roswell new mexico#supergirl cw#celebrity#happy birthday
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
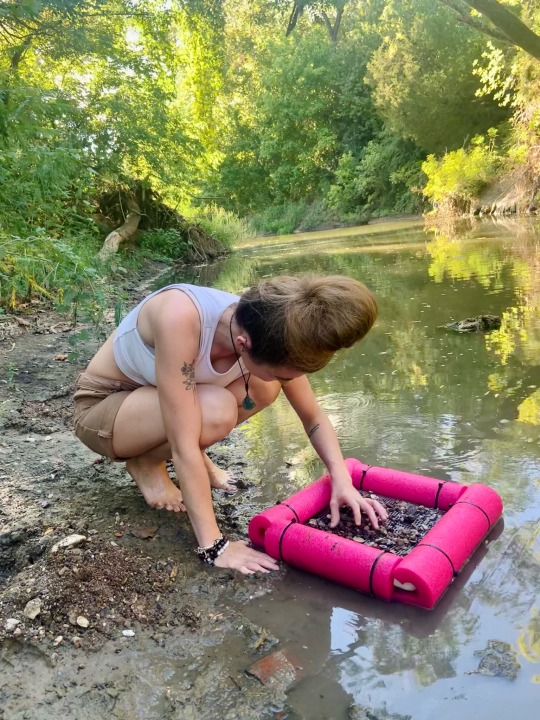

found a bunch of shark teeth and a few bones at the creek today with my homemade sifter :)
#nature#shark teeth#bones#toothing#Sherman tx#post oak creek#fossils#science#creek#hippie#hippie girl
5 notes
·
View notes
Text


Parts of the creek are still alive.
#creek#winter#photographers on tumblr#lee sherman#my photos#actually two years old#this same time of year
0 notes
Photo

Notes from Lorelle Sherman’s ‘Urban Foraging’ workshop, 2022
#elizabeth arzani#notes#field notes#pen and ink#urban foraging#workshop#Lorelle Sherman#Wildcraft Studio School#portland#oregon#Tyson Creek Nature Center#artist on tumblr
1 note
·
View note
Text

On Dec. 9, 1864, on the march to Savannah, hundreds or thousands of African American families who had just escaped from slavery were left to drown by Sherman’s Army. This is referred to as the Massacre at Ebenezer Creek.
#black tumblr#black history#black literature#black community#civil rights#black history is american history
130 notes
·
View notes
Text
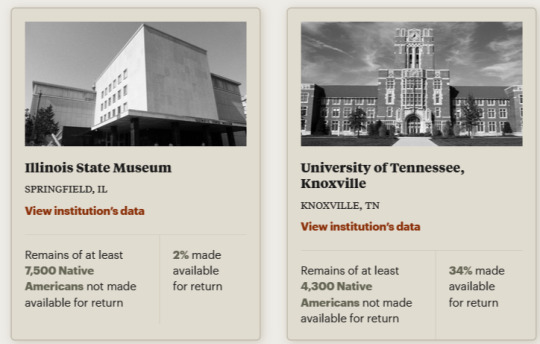
In January 2023, ProPublica has published a new and detailed report on the failure of United States museums and universities to repatriate human remains of Indigenous peoples, even when required by law.
Just ten institutions “hold about half of the Native American remains that have not been returned to tribes” as required by the 1990 law Native American Graves Protection and Repatriation Act. As of December 2022, about “200 institutions [...] had repatriated none of the remains of more than 14,000 Native Americans in their collections.” ProPublica has investigated whether or not these institutions have complied with the 1990 law, and, in their opening paragraphs, they have “found that a small group of institutions and government bodies has played an outsized role in the law’s failure.”
By the 1870s, as the academic field of archaeology soared in popularity, some of the most prestigious institutions in the US were relying on the US military to extract Indigenous items for their collections. For example, “the Smithsonian Institution struck a deal with U.S. Army Gen. William Tecumseh Sherman to pay each of his soldiers up to $500 — or roughly $14,000 in 2022 dollars — for items such as clothing, weapons and everyday tools sent back to Washington.”
Meanwhile: “Frederic Ward Putnam, who was appointed curator of Harvard University’s Peabody Museum of American Archaeology and Ethnology in 1875, commissioned and funded excavations that would become some of the earliest collections at Harvard, the American Museum of Natural History and the Field Museum. He also helped establish the anthropology department and museum at UC Berkeley — which holds more human remains taken from Native American gravesites than any other U.S. institution that must comply with NAGPRA.”
By the beginning of the 20th century, local museums in the Midwest and Southeast (Illinois, Ohio, Kentucky, and Tennessee) were obsessed with acquiring “moundbuilders” artifacts and initiated another wave of extraction. For example, most of the collections of the University of Kentucky’s William S. Webb Museum of Anthropology were taken during excavations funded by the federal government in the 1930s as part of the New Deal’s job-creation program, and although more than 80% of the museum’s holdings are “subject to return under federal law,” the museum “has yet to repatriate any of the roughly 4,500 human remains it has reported to the federal government.”
While the “Smithsonian Institution today holds in storage the remains of roughly 10,000 people, more than any other U.S. museum,” the Smithsonian actually “reports its repatriation progress under a different law” and therefore “does not publicly share information about what it has yet to repatriate with the same detail.”
According to ProPublica’s analysis, a major excuse given by institutions is that their collections are “culturally unidentifiable.” They report that “many institutions have interpreted” the words cultural affiliation “so narrowly that they’ve been able to dismiss” tribes’ claims. In other words, these museums claim that, because they cannot reliably trace a lineage between the original source of the remains and contemporary recognized tribes, they therefore cannot return remains. In this way, ProPublica says, that “[t]hroughout the 1990s, institutions including the Ohio History Connection and the University of Tennessee, Knoxville thrawted the repatriation process by categorizing everything” as “culturally unidentifiable.”
However, many tribes and their advocates claim this is a silly excuse. For example, the “University of Alabama Museums is among the institutions that have forced tribes into lengthy disputes over repatriation.” And tribes “had tried for more than a decade to repatriate Moundville ancestors.” By “October 2021, leaders from the Choctaw Nation of Oklahoma, Chickasaw Nation, Muscogee (Creek) Nation, Seminole Nation of Oklahoma, and the Seminole Tribe of Florida brought the issue to the federal NAGPRA Review Committee” and the “tribes eventually forced the largest repatriation in NAGPRA’s history” when “the university agreed to return the remains of 10,245 ancestors.”
Quoted excerpts above, and all graphics and excerpts below, from the report:
Logn Jaffe, Mary Hudetz, Ash Ngu, and Graham Lee Brewer. “America’s Biggest Museums Fail to Return Native American Human Remains.” ProPublica. 11 January 2023. (Illustrations by Weshoyot Alvitre for ProPublica. Design and development by Anna Donlan. Asia Fields and Brooke Stephenson contributed reporting.)










506 notes
·
View notes
Text

Alexander Gardner ~ Mushroom Rock on Alum Creek, Kansas, 211 miles west of Missouri River, 1867. | William T. Sherman collection. National Museum of the American Indian

Alexander Gardner ~ Mushroom Rock on Alum Creek, Kansas, 211 miles west of Missouri River, ca. 1867 | Digital Commonwealth
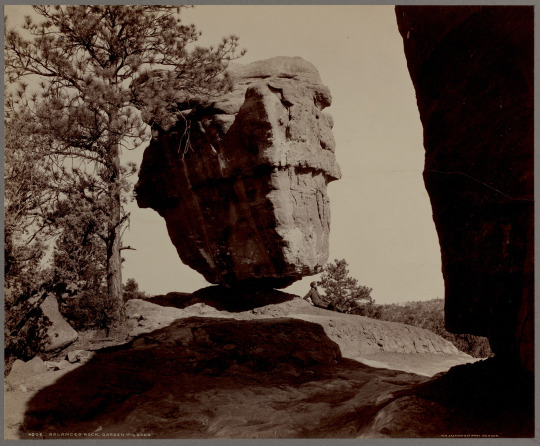

William Henry Jackson (1843-1942) ~ Balanced rock, Garden of the Gods, [ca. 1879–1894]. Albumen print. W. H. Jackson & Co., phot., Denver | Photographs of the American West, Boston Public Library
#alexander gardner#rocky landscape#william henry jackson#landscape#rock formation#balancing rock#kansas#1860s#alex gardner#albumen print#william h. jackson#1870s#1880s#moving rock#huge rock#boulder#moving stone
112 notes
·
View notes
Video
Black Farmers
the 1619 podcast has a great episode about Black Farmers
https://www.nytimes.com/2019/10/04/podcasts/1619-slavery-sugar-farm-land.html?
In the fall of 1864 at the height of the Civil War, one of the most famous Union generals, William Tecumseh Sherman, begins his march out of the city of Atlanta to the sea.
And as Sherman and his men make their way through Georgia, black Southerners are seeing an opportunity.
And so by the thousands, they start to leave the plantations where they’ve been enslaved and are falling behind Sherman’s troops as they make their way to the coast.
But these newly liberated people were not exactly welcomed. Sherman didn’t actually oppose slavery, and so he’s really not that sympathetic to those who are fleeing these plantations, and he also sees them as a drain on his resources. They are families. They are people of all ages, young and old, who need food and care, and they are slowing the troops down.
By December of that year, some of Sherman’s troops are about to approach Savannah, and they come upon a creek that is both too wide and too deep to cross without a bridge. So the troops start building one, and they instruct the black people who are following them to just wait, that the troops need to cross first, but then they’ll be able to come after. But the Confederate Army is on their heels, and once the Union troops cross, they break up the bridge, leaving all those people who had just escaped slavery behind to face either the icy waters or the rebel army that was in pursuit.
It is a massacre. Some of them drown trying to swim across. Others are trampled or shot to death, and those who remain are captured and re-enslaved. When word gets back to Lincoln’s secretary of war, Edwin Stanton, he is outraged. He has Sherman pull together a meeting with 20 black church leaders. There’s a transcript of this meeting, and it shows that these two men, Stanton and Sherman, actually turned to this group of black leaders and asked them, what do you want for your own people?
Speaking for the group, one of the men tells them, “The way we can best take care of ourselves is to have land, and turn it and till it by our own labor — that is, by the labor of the women and children and old men, and we can soon maintain ourselves and have something to spare.”
And what’s remarkable is that Sherman turns that request of those men for land to work for themselves into a government order, Special Order No. 15. It said that the government would take 400,000 acres that it had seized from the Confederacy and split it up among those thousands of newly emancipated people. This becomes what is perhaps the most famous provision of the Reconstruction period, which we all know as 40 acres and a mule. President Lincoln approves the order, but soon after, he’s assassinated. And Andrew Johnson, a Southerner who had once enslaved people himself, takes over the presidency and quickly overturns it. And within a few short months, the small amount of land that had been distributed to black people was returned to white Southerners.
#tiktok#farmers#black farmers#podcast#farming#history#USDA#civil rights#reagan was a terrible president#us history
135 notes
·
View notes
Text




Happy birthday Annette Crosbie, born 12th February 1934.
Annette was born in Gorebridge, Midlothian, to strict Presbyterian parents who disapproved of her becoming an actress.
Nvertheless, she joined the Bristol Old Vic Theatre School while still in her teens. Her big break came in 1970 when she was cast as Catherine of Aragon in the BBC television series The Six Wives of Henry VIII, for which she won the 1971 BAFTA Television Award for Best Actress. In 1973, she starred alongside Vanessa Redgrave in the BBC serial, A Picture of Katherine Mansfield.
Crosbie was born in Gorebridge, Midlothian, to strict Presbyterian parents who disapproved of her becoming an actress. Nevertheless, she joined the Bristol Old Vic Theatre School while still in her teens. Her big break came in 1970 when she was cast as Catherine of Aragon in the BBC television series The Six Wives of Henry VIII, for which she won the 1971 BAFTA Television Award for Best Actress. In 1973, she starred alongside Vanessa Redgrave in the BBC serial, A Picture of Katherine Mansfield.
In 1975, Crosbie made a similar impact as Queen Victoria, in the ITV period drama Edward the Seventh, for which she won the 1976 BAFTA Television Award for Best Actress. She played Cinderella’s fairy godmother in The Slipper and the Rose, which was chosen as the Royal Film Première for 1976. In that film, Crosbie sang the Sherman Brothers’ song, “Suddenly It Happens”. In Ralph Bakshi’s animated movie, The Lord of the Rings, filmed in 1978, Crosbie voiced the character of Galadriel, Lady of the Elves. In 1980, she played the abbess in Hawk the Slayer. In 1986, she appeared as the vicar’s wife in Paradise Postponed.
After appearing in the BBC1 drama Take Me Home, Crosbie’s next major role was as Margaret Meldrew, the long-suffering wife of Victor Meldrewplayed by fellow Scot, Richard Wilson) in the BBC sitcom One Foot in the Grave for which she is best known. She also played Janet, the housekeeper to Dr. Finlay, in the 1993 revival of A.J. Cronin’s popular stories.
Crosbie’s other roles include playing the monkey-lover Ingrid Strange in an episode of Jonathan Creek, Edith Sparshott in An Unsuitable Job for a Woma, and Jessie in the film Calendar Girls. In 2004, Crosbie appeared alongside Sam Kelly in an episode of the third series of Black Books, as the mother of the character Manny Bianco. In the series six and seven of the BBC Radio 4 comedy series Old Harry’s Game, she played a recently deceased historian named Edith.
In 2008 she appeared in the BBC adaptation of Charles Dickens’s Little Dorrit, in 2009, she portrayed Sadie Cairncross in the BBC television series Hope Springs. In 2010 Crosbie appeared in the Doctor Who episode “The Eleventh Hour”. In 2014 Crosbie appeared in the movies What We Did on Our Holiday and Into the Woods. In 2015 she appeared in a BBC adaptation of the novel Cider with Rosie. In 2016 she appeared in the new film version of Dad’s Army .
In recent years, she appeared in season two of Ricky Gervais' black comedy-drama After Life on Netflix. She now resides in Wimbledon and is a campaigner against cruelty for animals.
22 notes
·
View notes
Photo







September 16, 2022 (3 of 3)
Testing out the Voigtlander Nokton 40mm f/1.2 Aspherical M-mount lens. There’s something magical about it.
#photography#street photography#nature#sherman creek#swindler cove#fort george#uptown#manhattan#nyc#new york city#sony#a7ii#voigtlander#nokton#40mm#aspherical#lens flare#leica m
3 notes
·
View notes
Photo

William Tecumseh Sherman, also known as the Sherman Memorial or Sherman Monument, is a sculpture group honoring William Tecumseh Sherman, created by Augustus Saint-Gaudens and located at Grand Army Plaza in Manhattan, New York. Cast in 1902 and dedicated on May 30, 1903, the gilded-bronze monument consists of an equestrian statue of Sherman and an accompanying statue, Victory, an allegorical female figure of the Greek goddess Nike. The statues are set on a Stony Creek granite pedestal designed by the architect Charles Follen McKim. 764 Doris C Freedman Pl, New York, NY
#New York City#new york#newyork#New-York#nyc#NY#Manhattan#urban#city#USA#United States#buildings#travel#journey#outdoors#street#architecture#visit-new-york.tumblr.com#Memorial#Sherman
113 notes
·
View notes
Video
Hotshot in the Cold by Don Kalkman
Via Flickr:
Conrail's hotshot MAIL-9 was crossing Sherman Creek in Duncannon on a cold day along the Middle Division.
Ice Cold Conrail.
February 27, 1994
20 notes
·
View notes
Note
I’ve been following your blog for a few years and I was wondering if you’d ever cover Inwood (I moved here a couple years ago) and searched tags and discovered that you started with Inwood and have been walking south :)
It’s kind of amazing to see how much has changed in just 12 years. You have some pics of Muscota Marsh that look like it was just being built and now it’s a beautiful waterfront park.
Sandy must have just hit before you visited and the ranger station and nature center is only just being renovated and due to open this spring.
Sherman Creek is a very pretty park now that has a lot of people come summer weekends for picnics and birthday parties and a good spot for birding.
10th avenue is was rezoned from industrial to mixed residential and there are some high rise apartment buildings going up.
I think it’s great that you’re documenting everyday nyc streets because it changes so rapidly and the everyday gets overlooked!
Yes, Inwood was the first neighborhood I covered. I started this project in 2012 starting in Inwood and making my way down. I've only recently finished Spanish Harlem, which is the next 220 photos to be posted. Work and life (and weather) get in the way of working on this regularly, but I'm hoping to be more diligent and post at least twice a day so I can get through the Upper East and West sides in the next two years. I just wanted to see more of the city that I call home and it's ended up being a big undertaking... but also very fun.
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
Largest prokaryote: Thiomargarita magnifica, which can grow up to 1 cm (!!) in length, though tbh it's basically a micrometer-thick veneer of bacterium spread over a bag of inert water.
Largest unicellular organism with a single cell nucleus: the mushroom-shaped alga Acetabularia, which grows several cm tall.
Largest unicellular organism with multiple cell nuclei: the green alga Caulerpa taxifolia and the slime mold Physarum polycephalum can grow up to 30 cm, though in practice they function as multicellular organisms that lack membranes between a nucleus and another.
Largest animal: by linear size, the tendrils of the lion's mane jellyfish (Cyanea capillata) can reach 36 m long, and a specimen the ribbon worm Lineus longissimus was dubiously described as 55 m long. They are pretty thin, though. By mass, the highest non-controversial estimate for the largest non-fragmentary sauropod dinosaurs is around 80 tons (Argentinosaurus huinculensis), though there are dubious estimates from fragmentary remains pushing above 100 or even 200 tons. The known record for thee heaviest measured blue whale (Balaenoptera musculus) is 190 tons.
Largest non-colonial organism: the giant redwood General Sherman (Sequoiadendron giganteum) has been estimated to weigh almost 2000 tons, though the vast majority of that mass is probably dead wood tissue. The Lindsey Creek tree (Sequoia sempervirens) was estimated to weigh 3300 tons when it was felled by a storm in 1905. The tallest redwoods grow to 110-120 m tall, which is probably the physical limit for tree height on Earth.
Largest colonial organism: clonal colonies of trees and fungi can grow quite large indeed. The Pando aspen colony in Utah counts over 40,000 individual trees with ininterconnected roots, for an estimated total of over 6000 tons. A colony of the mushroom Armillaria ostoyae in Oregon covers 9 square km and may weigh over 30,000 tons. A colony of the seagrass Posidonia australis (an aquatic flowering plant, not an alga!) in Australia reportedly covers 200 square km, though I see no estimate of its mass. Apparently there is a supercolony of the ant Linepithema humile stretching between Spain, California, and Japan with "billions" of individual workers (assuming 0.5 mg per ant, that would still mean only a few tons of total mass).
11 notes
·
View notes