#software for performance testing
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Jmeter: The Ultimate Tool for Accurate Performance Measurement

Apache JMeter often called “JMeter” is an exceptional open-source tool. It has revolutionized software testing and performance analysis. JMeter has become the go-to solution for businesses seeking to optimize their applications. It also helps them to deliver a seamless user experience. Its exceptional capabilities make it an indispensable asset in the world of software development and testing.
So, in this blog, we will delve into the key capabilities of JMeter. We will also uncover the reasons behind its reputation as a powerful tool for accurate performance measurement.
Understanding Apache JMeter's Capabilities
Here are some major capabilities of JMeter:
Testing Expertise: JMeter excels in load testing. This enables businesses to simulate heavy user traffic and assess their application's performance under various load conditions. By doing so, even during peak hours, organizations can:
identify potential bottlenecks
optimize their infrastructure
deliver a smooth user experience
Protocol Support: It can test web applications, databases, FTP servers, SOAP, RESTful web services, and more. This versatility allows businesses to assess the performance of different components in their application ecosystem.
Distributed Testing: JMeter offers distributed testing that enables simultaneous testing across multiple servers. This capability empowers organizations to handle massive load simulations effectively.
User-friendly Interface: It boasts a great interface, making it accessible to both technical and non-technical users. Without much extensive training, businesses can:
quickly set up test plans
configure test scenarios
analyse results
Let's now shift our attention to JMeter's ability to deliver precise performance measurements.
Accurate Performance Measurement with JMeter
JMeter employs a rigorous process to accurately measure the performance of web applications. The steps involved in this measurement process are as follows:
Test Plan Configuration: At first, testers create a test plan in JMeter. This outlines the test scenarios, thread groups, and user behaviors to simulate during the performance test.
Thread Group Setup: Within the test plan, testers define the number of virtual users (threads) and the ramp-up period to gradually increase the load on the application.
Test Script Creation: Further, the testers record or manually create HTTP requests to mimic user interactions. This includes:
page requests
form submissions
API calls
Test Execution: When the test plan is ready, testers execute the test, and JMeter starts simulating user interactions based on the defined thread group settings.
Response Time Measurement: JMeter then measures the time taken for each request-response cycle. That is, it calculates the response time for various user interactions with the application.
Throughput Measurement: It further calculates the throughput that represents the number of requests processed by the server per unit of time. Thus, indicating the application's capacity to handle requests.
Error Handling: Later, it identifies and records any errors encountered during the test. Such as - HTTP errors or assertion failures. This provides valuable insights into application stability.
Monitoring Server Metrics: By using plugins like PerfMon, it can monitor server resource utilization in real-time. So, measuring CPU, memory, and network usage during the test becomes easier.
Test Results Collection: It then collects and aggregates test results to analyze the performance data, including:
Tables
Graphs
charts
Data Analysis: Finally, testers interpret the test results to:
identify performance bottlenecks
determine the application's scalability
pinpoint areas requiring optimization
So, Apache JMeter stands tall as a remarkable tool with an array of capabilities. Its prowess in load testing makes it an invaluable asset for businesses aiming to provide top-notch applications. Therefore, embracing JMeter can lead to delivering outstanding user experiences in the dynamic world of software applications.
Ready to elevate your business to new heights? Join hands with Nitor Infotech, an Ascendion company.
#performance testing#jmeter performance testing#performance testing website#jmeter load testing#load test website#software for performance testing#software engineering#software development#blog#technology blog#nitorinfotech
0 notes
Text
Why POS Testing is Crucial for Flawless Retail Operations
In the fast-moving world of retail, Point of Sale (POS) systems are central to transactions, inventory management, and customer interface. If we want to keep POS systems working properly, it is important to ensure they run smoothly. A smooth POS system is necessary for a smooth customer experience and a smooth operation. Here at GQAT TECH, we are experts in POS testing so businesses can eliminate costly interruptions to their business and have more reliability with their POS. This blog will look at why POS testing is important and how it will improve your business for retail operations.
What is POS Testing?
Testing a POS enables extensive testing of the working capabilities, functionality, performance, security, and interoperability of the POS to be tested in the real world as a functional and transactional system. POS comprises hardware such as card readers, scanners, and computer devices, and POS software that processes payments and often manages inventories. POS need to be tested to process high transaction volumes, interact with other systems, and satisfy industry standard security compliance.
Why POS Testing Matters
1. Ensuring Transaction Completeness
A single mistake made within a POS can generate incorrect customer charges, inventory discrepancies, or processes that don't reach completion. One mistake can frustrate your customers, disgruntle your employees, or derail UX. Proper POS testing can ensure that your processes (whether they include cash, credit cards, mobile payments, or gift cards) will function correctly.
2. Testing system robustness
The retail environment can be harsh. Depending on the season, your POS may process thousands of transactions each day. Performance testing will verify that your POS is sufficient to process peak loads and act to mitigate crashing or performance degradation when it counts the most (e.g., during a holiday sale).
3. Protecting Customer Information
As cyber threats grow in number and sophistication, protecting customers' sensitive information, including their credit card information, is paramount. Security testing will find weaknesses in your POS systems with the goal of satisfying standards and requirements (i.e., PCI DSS) and identifying and eliminating risks to customer data exposure.
4. Ensuring integration & compatibility with other systems
A POS often resides at the intersection of multiple systems (inventory management system, CRM, accounting system, etc.). Even testing limits can identify different systems interacting with your POS, ensuring that an isolated application does not disrupt a chain that could lead to other separate systems eventually failing to receive data.
5. Increasing Customer Satisfaction
A gap in your checkout process can diminish customer satisfaction (a focus for your company). Testing usability and responsiveness will ensure your staff understands how to use the POS, as customers experience an intuitive, fast, and error-free transaction with your store.
Key Types of POS Testing
Our testing services include all types of testing you may need for your cash register and/or POS system. Here are some examples of the types of testing we provide:
Functional Testing: Testing all of the functionalities (payment processing, refunds, discounts, etc.) to make sure everything works correctly.
Performance Testing: Testing to understand your solution's reliability in peak transaction situations, or under stress.
Security Testing: Testing for gaps in security so you can protect customer data and compliance.
Compatibility Testing: Testing all the devices, operating systems, and integrations that the cash register and or POS system will have.
Usability Testing: Testing how easy it is to use for the associates and customers.
Regression Testing: Testing how the changes or new upgrades could impact existing functionality.
Why Choose GQATTech for POS Testing?
At GQATTech, we bring years of knowledge and expertise in the industry and cutting-edge testing procedures to deliver reliable, scalable, and secure POS, in-store experiences, and omnichannel solutions. Our dedicated team of testers uses both manual testing and automated testing to identify defects early, saving you time and money. Whether you are upgrading, replacing, integrating, or rolling out a new POS system, the test services that we design and conduct for you can ensure a positive experience and that the systems work as they should.
Conclusion
In our view, a comprehensive approach to POS testing is not just about checking boxes or even about each and every defect. It is really about all the components that contribute to customer confidence, operational efficiencies, or staying ahead (or even just keeping up) with the competition. From our perspective, if you can achieve true testing goals by hiring GQATTech and using our knowledge and expertise, we can assist with each of these aspirations. Visit us at gqattech.com/pos-testing/ to discover how we can assist your organization.
Are you prepared to examine what we can do for your POS, in-store experience, or omnichannel performance? We are committed to accomplishing that today! Reach out to us to discuss your testing requirements!
Visit Us: https://gqattech.com Contact Us: [email protected]
#POS Testing#Point of Sale#Retail Technology#Transaction Processing#System Reliability#Customer Experience#Security Testing#Performance Testing#Functional Testing#Compatibility Testing#Usability Testing#Regression Testing#Retail Operations#Payment Systems#PCI DSS Compliance#Inventory Management#Omnichannel Solutions#GQATTech#Software Testing#Customer Data Protection
0 notes
Text
Why Performance Engineering is Critical for Digital Transformation in Retail
The retail industry is changing fast. More people are shopping online. Apps and websites have to be quick, easy to use, and always working. But that’s not always the case. Slow load times, bugs, and downtime can push customers away. Every second counts when it comes to online shopping. Even a small delay can cost a lot of money.
That’s where performance engineering testing comes in. It makes sure your digital systems are strong, fast, and ready for anything. From apps to backend systems, it ensures everything runs smoothly and efficiently.
This helps you serve your customers better, save costs, and grow your business. This blog explores why performance engineering testing is key for digital transformation in retail. You will also discover top benefits.
Enhanced customer experience with performance engineering
Customer experience is everything in retail. Whether someone is shopping in-store, on a mobile app, or through a website, they expect fast and reliable service. Performance engineering testing helps you deliver that experience by making sure all systems work at their best.
Key benefits:
Faster load times: Nobody likes waiting. A delay of just one second can lower customer satisfaction and reduce sales. Performance engineering improves response times and lag.
Better uptime: Customers shop at all hours. Performance testing ensures that systems are always available, even during busy sales or holiday seasons.
Smooth navigation: Apps and websites should be easy to use. With performance testing as a service, you can find and fix navigation issues early.
Improved mobile experience: Maximum eCommerce orders come from mobile. Hence, mobile performance is critical. Testing keeps apps running well on all devices.
Personalized experiences: Performance engineering supports systems that deliver personalized offers and messages without slowing down the app.
Handling increased online shopping with advanced performance testing
The COVID-19 pandemic changed shopping habits. Now, more people shop online than ever before. This shift has made digital systems more important. But with more users comes more traffic. Systems must scale and perform under pressure. Advanced performance engineering helps with that.
With so many users, your systems need to be prepared. If they fail, customers go elsewhere. That’s a missed sale and maybe a lost customer forever.
Key benefits:
Load testing at scale: Advanced tools simulate thousands of users. You can test how your systems behave during high-traffic events.
Cloud-based testing: You can use the cloud to test from different locations and devices. It will ensure consistent performance.
Auto-scaling systems: Performance engineering supports services that adjust automatically based on demand.
End-to-end monitoring: Every part of the customer's journey is tracked to find slow points.
Quick feedback: Testing early and often lets you fix issues before they affect users.
Boosting revenue through performance engineering
Revenue and performance are closely linked. A slow website or crashing app leads to lost sales. Performance engineering testing directly impacts your bottom line. The faster and more reliable your system, the more sales you can make.
Key benefits:
Higher conversion rates: Fast, smooth systems encourage users to complete purchases.
Less cart abandonment: Performance issues often cause users to abandon their carts. Testing helps stop that.
Better SEO rankings: Google favors faster websites. Performance engineering helps improve site speed and visibility.
Increased repeat customers: Good performance keeps customers happy and coming back.
More impulse purchases: A fast system helps customers buy before they change their minds.
Improving operational efficiency with performance testing
Retail operations are complex. There are many systems working together—inventory, customer data, payment gateways, and logistics. If one part fails, the whole process suffers. Performance testing as a service helps you spot and fix problems early.
With automated and continuous testing, your team saves time and works smarter. Advanced performance engineering tools help find and fix issues before they cause real problems.
Key benefits:
Early bug detection: Testing finds issues during development, not after launch.
Automated workflows: Automation reduces manual tasks and human error.
Faster release cycles: Performance engineering supports DevOps, allowing faster and safer releases.
Data-driven decisions: Testing tools give you performance data to guide your next steps.
Less downtime: When systems run better, teams spend less time fixing and more time building.
Ensuring scalability and resilience through advanced performance testing
Retail systems must grow with the business. Whether it’s a flash sale, Black Friday, or a product going viral, you must be ready. Advanced performance engineering ensures that your systems can handle growth.
When systems aren’t scalable, high traffic leads to crashes and lost sales. Resilience ensures systems recover quickly from problems. These two elements are key to a reliable digital retail platform.
Key benefits:
Cloud readiness: Performance testing makes sure your cloud setup can scale with demand.
Disaster recovery planning: It helps systems bounce back fast during failures.
High availability: Performance engineering testing checks if services stay up under stress.
Load balancing: You can test how well traffic is spread across servers.
Futureproofing: Testing systems now prepare them for future use cases.
Achieving cost reduction with performance testing
Retailers face rising costs—from logistics to technology. But there’s good news. Performance testing as a service can help reduce costs. When systems are faster, fewer resources are used. That saves money. Also, when you find issues early, you save on expensive repairs later.
Key benefits:
Lower cloud costs: Optimized systems use fewer cloud resources.
Less rework: Finding bugs early means less money spent fixing them later.
Reduced outages: You can avoid the high cost of downtime.
Smaller support teams: With fewer issues, you need fewer people to solve problems.
Efficient scaling: Performance engineering helps systems grow in a cost-effective way.
Future-proofing digital retail with performance engineering
Technology keeps changing. So should your systems. Performance engineering testing helps retailers stay ready for the future. As you adopt AI, machine learning, or new platforms, testing ensures everything works well together.
Advanced performance engineering is key to innovation. It supports agile development, DevOps, and continuous delivery. You can launch new features faster and safer.
Key benefits:
Support for DevOps: Testing fits right into your development process.
Quick feature rollout: Launch new features with confidence.
Safe tech adoption: New technologies are tested for performance.
Better user feedback: Testing gives insight into what users experience.
Competitive edge: Faster and smarter systems help you lead the market.
Final thoughts
Digital transformation in retail isn’t just about new technology. It’s about making sure that technology works well, every time. Performance engineering testing helps you get there. It improves customer experience, increases revenue, and supports business growth.
Using performance testing as a service means you're always ready. You can fix issues before customers see them. You save money and launch products faster. And with advanced performance engineering, your systems are built to last.
Are you ready to start your transformation? Let Qualitest power your digital retail journey.
They have helped major retailers improve uptime, scale systems, and grow confidently. With their custom solutions, businesses can handle 3 years of traffic growth in advance. They can also help you reduce downtime costs by avoiding outages worth $300,000 per hour.
0 notes
Text
How to Calculate Test Automation ROI: A Practical Guide
Investing in test automation can significantly speed up releases and reduce bugs—but how do you measure its actual return on investment (ROI)?
Start by identifying baseline metrics: manual testing hours, defect leakage rates, and time to market. Then, evaluate the cost of automation, including tools, infrastructure, and engineering effort.
Use this basic formula:
ROI = (Savings from Automation – Investment in Automation) / Investment in Automation × 100
Savings from Automation can include:
Reduced manual testing effort (e.g., hours saved × hourly rate)
Faster release cycles (shorter time-to-market)
Lower post-release defects (cost of fixing production bugs)
Investment in Automation includes:
Cost of automation tools
Engineer time spent creating and maintaining scripts
Training and infrastructure setup
For example, if test automation strategy saved 300 hours annually (at $40/hr) = $12,000, and investment was $8,000, then ROI = 50%.
However, ROI isn't just about cost. Factor in intangible benefits like improved coverage, scalability, and team morale.
In conclusion, calculating ROI helps justify automation efforts, prioritize the right test cases, and align QA with business goals. A focused ROI strategy can turn automation into a long-term competitive advantage.
#qa testing services#performance testing tools#test management tool#test automation strategy#web based application testing#automated system testing#qa consulting services#qa software
0 notes
Text
Introduction to REST API in Python

APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) are like bridges that let different software systems talk to each other. Among the many types of APIs, REST APIs are the most popular because they follow a simple and well-defined architecture. In this blog, we’ll explore what REST APIs are, how they work in Python, and how you can build and test them easily.
What is a REST API?
A REST API (Representational State Transfer Application Programming Interface) is a set of rules that allows programs to communicate over the web. It uses standard HTTP methods like GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE to perform operations on resources, which are identified by URLs.
For instance, a REST API for a bookstore might have endpoints like:
GET /books – Retrieve a list of books
POST /books – Add a new book
GET /books/{id} – Retrieve a specific book
PUT /books/{id} – Update a specific book
DELETE /books/{id} – Delete a specific book
REST APIs are stateless, meaning each request from a client contains all the information needed to process the request, without relying on stored context on the server.
What is a Python REST API Framework?
A Python REST API framework is a collection of libraries and tools that simplify the process of building RESTful APIs in Python. These frameworks handle the routing of HTTP requests, serialization of data, and other common tasks, allowing developers to focus on the core functionality of their applications.
Popular Python REST API frameworks include:
Flask: A lightweight and flexible micro-framework suitable for small to medium applications.
FastAPI: A modern, high-performance framework designed for building APIs with Python 3.7+ using type hints.
Django REST Framework (DRF): A powerful and feature-rich framework built on top of Django, ideal for large-scale applications.
Understanding the Capabilities of REST API and REST Principles
REST APIs adhere to six guiding principles:
Statelessness: Each request from the client must contain all the information needed by the server to process the request.
Client-Server Architecture: The client and server operate independently, allowing for separation of concerns.
Cacheability: Responses must define themselves as cacheable or not to prevent clients from reusing stale or inappropriate data.
Uniform Interface: A consistent and standardized interface simplifies interactions between components.
Layered System: The architecture can be composed of hierarchical layers by constraining component behavior.
Code on Demand (optional): Servers can extend client functionality by transferring executable code.
Understanding these principles helps in designing scalable and maintainable APIs.
Benefits of REST API
The benefits of REST API are vast and implementing them offers several advantages:
Scalability: Statelessness allows servers to handle more requests by distributing the load.
Flexibility: Clients and servers can evolve independently as long as the interface between them is not altered.
Simplicity: Using standard HTTP methods makes it easy to understand and use.
Performance: Caching mechanisms can improve performance by reducing the need for repeated processing.
Modularity: Encourages separation of concerns, making it easier to manage and update components.
Types of Python Frameworks
Python offers various frameworks for building REST APIs, each catering to different needs:
a. Microframeworks
Flask: Minimalistic and easy to get started with, ideal for small applications and prototyping.
Falcon: Focuses on high performance and reliability, suitable for large-scale applications.
b. Full-Stack Frameworks
Django: Comes with a plethora of built-in features like ORM, authentication, and admin interface, suitable for complex applications.
c. Asynchronous Frameworks
FastAPI: Leverages Python's async capabilities for high-performance APIs, with automatic documentation generation.
What Should You Consider When Choosing a Python REST API Framework?
Selecting the right framework depends on various factors:
Project Size: For small projects, Flask or FastAPI might suffice; for larger projects, Django could be more appropriate.
Performance Needs: FastAPI offers superior performance due to its asynchronous nature.
Learning Curve: Flask has a gentle learning curve, while Django and FastAPI might require more time to master.
Community and Support: Django has a large community and extensive documentation, which can be beneficial for troubleshooting and learning.
Python REST API Frameworks You Should Know
Here's a comparison of popular Python REST API frameworks:FrameworkTypeKey FeaturesFlaskMicroframeworkSimple, flexible, extensive extensionsFastAPIAsynchronousHigh performance, automatic docs, type hintsDjangoFull-StackBuilt-in ORM, admin interface, authenticationFalconMicroframeworkHigh performance, minimalistic, reliable
Building a Simple REST API with Python
Let's build a simple REST API using Flask that manages a list of users.
a. Setup
Install Flask:CopyCopypip install Flask
b. Code Example
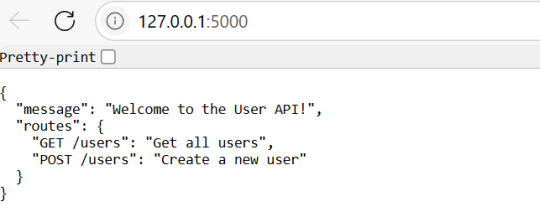
CopyCopyfrom flask import Flask, jsonify, request app = Flask(__name__) users = [] @app.route('/') def home(): return jsonify({ "message": "Welcome to the User API!", "routes": { "GET /users": "Get all users", "POST /users": "Create a new user" } }) @app.route('/users', methods=['GET']) def get_users(): return jsonify(users) @app.route('/users', methods=['POST']) def create_user(): user = request.get_json() users.append(user) return jsonify(user), 201 if __name__ == '__main__': app.run(debug=True)
c. Testing the API
GET /users: Returns the list of users.
POST /users: Adds a new user to the list.
Run the application in a dedicated terminal and navigate to this IP- 127.0.0.1:5000.You can test the API using tools like Postman or cURL.
How to Test Your REST APIs Without Writing Code?
Unit testing agent
Keploy has recently released a Unit Testing Agent that generates stable, useful unit tests directly in your GitHub PRs, covering exactly what matters. How cool is this? Testing directly in PRs – so developers won’t need to write test cases for their new features. Keploy writes them for you! No noisy stuff – just clean, focused tests targeting the code changes. You can also try this Unit Testing Agent in your VSCode.

Links:
Github PR agent: https://github.com/marketplace/keploy VScode Extension: https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/items?itemName=Keploy.keployio
API testing agent
Instead of writing test cases to test your APIs, what if you provide your schema, API endpoints, and curl commands to an agent, and it generates the test suite and gives you the test reports? Sounds interesting or confusing? Yes, it is possible! Keploy API Testing Agent will do all this without you touching any code. Not convinced? Just give it a try, and you will really enjoy it.
Integration testing
Records real API calls, DB queries, and service interactions to generate full integration tests. Best for ensuring multiple components work together correctly.
For more details, visit Keploy's official website or check out their GitHub repository.
Conclusion
Building REST APIs in Python is streamlined with the help of frameworks like Flask, FastAPI, and Django. Understanding REST principles and choosing the right framework based on your project needs are crucial steps. Tools like Keploy further enhance the development process by simplifying testing, ensuring your APIs are reliable and maintainable.
FAQs
Q1: What is the difference between REST and RESTful APIs? A: REST is an architectural style, while RESTful APIs are APIs that adhere to REST principles.
Q2: Can I use Flask for large-scale applications? A: While Flask is suitable for small to medium applications, it can be extended for larger projects with proper structuring and extensions.
Q3: Is FastAPI suitable for beginners? A: FastAPI has a steeper learning curve due to its use of type hints and asynchronous programming but offers excellent performance benefits.
Q4: How does Django REST Framework differ from Flask? A: Django REST Framework is built on top of Django and provides more built-in features, making it suitable for complex applications, whereas Flask is more lightweight and flexible.
Q5: Do I need to write tests for my API? A: Testing ensures your API behaves as expected. Tools like Keploy can automate this process, reducing manual effort.
Related Keploy Blogs
API Testing - Everything you should know!
Keploy API Testing
Python unit testing - A complete guide
0 notes
Text
Expert Performance Testing Company USA
Is your app ready for peak traffic? Trust 5Data Inc, a proven Performance Testing Company. Start your performance boost now!
0 notes
Text
Ensuring Quality with Mobile App Performance Testing

At Astarios, we help make sure your mobile app runs smoothly and efficiently with our mobile app performance testing. Our team focuses on improving speed, reliability, and overall user experience across all devices. We find and fix issues early, so your app delivers a seamless experience.
Let us optimize your app to keep users happy and performance at its best.
0 notes
Text
APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) are the backbone of modern digital ecosystems. They enable seamless interaction between applications, platforms, and services. However, their exposure makes them a prime attack vector. API security testing identifies vulnerabilities in APIs to ensure data confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
#eCommerce software development services#API testing services#database performance testing#automated testing of REST API
0 notes
Text
AI Automated Testing Course with Venkatesh (Rahul Shetty) Join our AI Automated Testing Course with Venkatesh (Rahul Shetty) and learn how to test software using smart AI tools. This easy-to-follow course helps you save time, find bugs faster, and grow your skills for future tech jobs. To know more about us visit https://rahulshettyacademy.com/
#ai generator tester#ai software testing#ai automated testing#ai in testing software#playwright automation javascript#playwright javascript tutorial#playwright python tutorial#scrapy playwright tutorial#api testing using postman#online postman api testing#postman automation api testing#postman automated testing#postman performance testing#postman tutorial for api testing#free api for postman testing#api testing postman tutorial#postman tutorial for beginners#postman api performance testing#automate api testing in postman#java automation testing#automation testing selenium with java#automation testing java selenium#java selenium automation testing#python selenium automation#selenium with python automation testing#selenium testing with python#automation with selenium python#selenium automation with python#python and selenium tutorial#cypress automation training
0 notes
Text
Boost Your Digital Success: Why Performance and Security Testing Are Essential
The Importance of Performance and Security Testing for Your Digital Success
In the current rapid digital space, organizations increasingly depend on their applications and websites to connect with customers, manage processes, and generate revenue. When a digital platform is poorly developed with respect to performance or security, it can negatively impact missed opportunities, reputation, and substantial monetary losses. This is where the important processes of performance and security testing fit in. They are important processes that can help ensure your digital resources are strong, dependable, and secure, with a competitive advantage for your organization. In this blog, we will discuss why performance and security testing are essential complete processes, areas of advantage, and what role they play in your digital success.
What is Performance Testing?
Performance testing is the method of assessing how well a system, application, or website performs under various conditions. More precisely, performance testing should encompass speed, response time, scalability, and stability to ensure that, regardless of the platform, it can effectively handle user demand. Performance testing ensures that applications are still efficient and easy to use during any sudden spikes in traffic or when performing complex computational tasks.
There are several important types of performance testing:
Load Testing: Assesses how the system performs when it is under what is expected user load.
Stress Testing: Assesses how the system performs by overloading the system in extreme conditions to assess its breaking point.
Scalability Testing: Solves whether the system can grow or shrink in its ability to meet user demands.
Endurance Testing: Measures and screens performance for long durations to identify social issues like memory leaks.
Performance testing assists businesses in identifying their bottlenecks and weaknesses, which then provides their users with a seamless user experience at all times, especially during peak usage.
Why Security Testing is Essential
In a world where cyber threats are becoming more commonplace, security testing is the first step in protecting sensitive information and maintaining user trust. Security testing exposes vulnerabilities inherent in your application or system that may be exploited by a malicious actor. A weakness in security could lead to catastrophic consequences, such as data breaches or ransomware attacks.
Key Aspects of Security Testing
Vulnerability Assessment: Discovers possible weaknesses in the system, like software that incorporates outdated libraries or systems that are poorly configured.
Penetration Testing: Enables testers to be hostile and review exploitable vulnerabilities in web applications or systems.
Security Audit: Reviews code, frameworks, and configurations concerning an industry's benchmark.
Risk Assessment: Assesses possible threats to a business.
The results of security testing will help in the increased discovery of vulnerabilities and the reduction of financial losses, lawsuits, and damaged reputations for businesses.
The Importance of Performance and Security Testing
1. Improved User Experience
Users will not tolerate a site or app that takes too long to load. Slow and inconsistent performance can lead to high bounce rates and lost conversions. Performance testing can improve the speed, reliability, and consistency of your web platform, which increases both the likelihood of use and overall user experience.
2. Safeguarding Against Cyber Attack
Cyber threats are not just a concern for larger enterprises; small businesses are also now being targeted by attack vectors that previously affected larger enterprises. As threats become more advanced, security testing is a key tool for spotting weaknesses, mitigating them before hackers can exploit them, and ultimately safeguarding your data, as well as your customers’.
3. Reduce Overall Costs
Performance and security problems that come after deployment are expensive problems to fix. Early detection through testing minimizes expensive fixes that will ultimately hurt your bottom line and minimize the risk of downtime or breaches to your application.
4. Compliance
There are strict guidelines and regulations in place in certain industries, particularly finance, healthcare, and e-commerce (also GDPR and PCI DSS). Security testing can help provide evidence of compliance and save you from fines or legal formalities.
5. Scalability
There are growth concerns depending on the accuracy of your report and the possible hurdles of growth your web service could face. Performance testing helps avoid any issues that can arise from suddenly increased numbers of traffic or usage.
Best Practices for Effective Testing
Test early, test often - Each stage of the development lifecycle lends itself to testing to find issues as early as possible.
Test realistic user behaviours - Take advantage of user behaviours that are as realistic as you can for testing, along with their attack behaviours, as testing will give more realistic outputs.
Automate your testing - Automated testing tools will help you save time and improve precision in repeatable tasks.
Work with a provider - Using a provider of testing services, like GQAT Tech, will give you reliable results and clear issue identification.
Monitor continuously - Continuous testing and monitoring will allow the systems to always remain secure and performant as they relate to new threats and demands.
Why Choose Professional Testing Services?
Internal testing is important, while using a testing provider will provide expertise, available and advanced tools, and insight from both sides of the testing process. A provider like GQAT Tech will provide testing services in either performance or security testing and can work to your needs. Our teams are very experienced and perform established methodologies that will identify and then remediate existing issues found on your digital platforms or websites to ensure they work correctly, are performant, and secure.
Conclusion
In a time of increasing user expectations and continuous risk, we should view performance and security testing as a need instead of an option. When companies perform continuous performance and security testing, they can produce a great user experience, protect sensitive content from prying eyes, and create a great opportunity for success at scale. The sooner performance and security testing are utilized, the sooner your platform can thrive, whether you are developing a new application or scaling an existing one.
Do you think you are ready to elevate your digital platforms? Start with GQAT Tech's professional testing to take your first step towards a faster, safer, and more reliable digital footprint.
#Performance Testing#Security Testing#Load Testing#Software Optimization#Application Security#QA Performance#Cybersecurity Testing#Stress Testing#GQATTECH
0 notes
Text
Load Performance Testing: A Crucial Element in Software Testing for Scalable Applications

In today’s tech-driven world, where software applications power everything from online shopping to banking and education, delivering a seamless user experience is more important than ever. Users expect apps to work quickly, efficiently, and without any hiccups—even when thousands of people are using them at the same time. That’s where load and performance testing comes into play. It's not just a phase of the software testing lifecycle anymore; it’s a necessity for ensuring software quality assurance and long-term scalability.
Let’s say you’ve built a new e-commerce app. It runs fine during development and internal testing, but when it goes live and hundreds or thousands of users start browsing and placing orders, the app becomes sluggish or even crashes. This is a classic example of what happens when proper load testing software or load and performance testing services are not used.
What is Load and Performance Testing?
Load and performance testing is a type of software testing that focuses on evaluating how an application behaves under normal and peak load conditions. It’s all about checking the app’s performance—does it respond quickly? Can it handle 1,000 users at once? What happens if the traffic spikes suddenly?
Load testing, specifically, measures how a system handles expected levels of traffic. On the other hand, performance testing may also include stress testing (pushing the system beyond its limits), soak testing (checking for stability over a long period), and spike testing (sudden traffic jumps). These tests together ensure your application won’t crumble under pressure.
Why It Matters for Scalable Applications
When developing any software, especially applications expected to grow over time, scalability should be a top priority. A scalable app means it can grow with your user base and handle more data or more users without breaking down. That’s where load and performance testing services become invaluable.
A well-performed software testing process that includes load testing helps you pinpoint where your system may fail as traffic increases. This could be a poorly optimized database query, an overloaded server, or a memory leak that only shows up after a few hours of heavy use. By identifying and fixing these issues early, you ensure your application scales smoothly.
The Role of Load Testing Software
There are plenty of reliable load testing software tools out there that help automate this process. Tools like Apache JMeter, LoadRunner, and Locust simulate thousands of users interacting with your application at once. These tools generate detailed reports on response times, error rates, server utilization, and other performance indicators, allowing developers and testers to tweak and optimize accordingly.
But it’s not just about tools. Good software quality assurance also involves experienced professionals who know how to analyze those reports and understand the context behind the numbers. That’s why many companies turn to specialized load and performance testing services for expert insight and testing strategies tailored to their unique systems.
Benefits Beyond Performance
Incorporating load and performance testing into your software testing strategy brings more than just speed improvements. It also:
Enhances user satisfaction by ensuring fast, reliable service
Prevents costly downtime during high-traffic events
Builds confidence in your app’s ability to scale
Helps you meet SLAs (Service Level Agreements)
Saves money by avoiding expensive emergency fixes after launch
Final Thoughts
If you’re serious about building scalable, reliable software, then load and performance testing should be baked into your development process from day one. It’s not just a technical requirement—it’s a commitment to delivering quality. In a world where users won’t hesitate to abandon an app that lags or crashes, ensuring software quality assurance through proper software testing and the right load testing software can make all the difference.
#software testing#load and performance testing services#performance testing#software quality assurance
1 note
·
View note
Text
How to Streamline Your QA Process with the Right Tools
A streamlined QA process is essential for delivering high-quality software at speed. The Automation testing tools can eliminate bottlenecks, reduce manual effort, and improve overall test accuracy. Start by assessing your project’s needs—whether it’s web, mobile, or API testing—then choose tools that align with those requirements.
For UI automation, tools like Selenium, Cypress, and Playwright offer flexibility and robust community support. Test management tools such as TestRail or Zephyr help organize test cases, track execution, and report results effectively. If your team works in an agile or DevOps environment, integrating tools with CI/CD platforms like Jenkins or GitHub Actions can accelerate test cycles and feedback loops.
To reduce test creation time, consider low-code or codeless automation tools such as Tenjin Online, which empower non-technical testers. Additionally, performance testing tools like JMeter and k6 help ensure scalability under load.
Finally, ensure real-time collaboration and visibility by integrating QA tools with project management platforms like Jira or Asana. When your QA stack is tailored to your workflow, you’ll see faster releases, fewer bugs, and better alignment between QA and development teams.
#software testing#qa services#qa testing services#performance testing tools#qa test management tools#automated system testing#manual testing tools#open source testing
0 notes
Text
Ensuring Quality: Testing PoS Software in the Pharma Sector
In the pharma sector, maintaining efficient and high-quality software solutions is vital. It ensures smooth operations and is effective in PoS systems. These systems are crucial for managing transactions and customer interactions.
Do you want to ensure the reliability and functionality of PoS systems within the complex pharma sector? If yes, then it needs proper PoS testing.
In this blog, you will understand the various components of PoS testing. The blog covers the testing approach and unique challenges in the pharma sector. It also includes the best practices for quality assurance via PoS software testing.
PoS Testing in the Pharma Sector
PoS stands for Point of Sale. PoS testing analyzes the hardware, software, and integration of PoS systems. This process ensures that the PoS system functions as expected in today's marketplace.
In the pharma industry, PoS systems consist of software solutions used in many places. This includes hospitals, clinics, or retail pharmacy counters. These systems manage certain key functions. This includes inventory management, customer interactions, transaction processing, and billing.
When it comes to this sector, PoS testing is not just for checking the system performance. Instead, it is for ensuring that the software complies with the legal requirements. This testing ensures that the system integrates with the other systems smoothly. It will also help you validate that the system functions reliably in today’s scenario.
In a PoS system, it is vital to ensure that the system can manage sensitive information. This includes medication details, transaction data, and patient prescriptions while securing against problems or fraud.
PoS Testing Approach
An ideal PoS testing approach in the pharma sector consists of various key stages. Each stage addresses certain aspects of the system. It also helps in identifying the potential issues before they affect the system’s functionality.
Now, let’s have a look at the PoS testing approach.
Requirement Analysis
Before moving on to the testing process, it is essential to know the PoS system requirements. This consists of reviewing the regulatory and legal requirements. It includes compliance with HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act). This is for patient data security. It also includes FDA (Food and Drug Administration) regulations for pharmaceuticals.
Test Planning
This is the next step. It involves creating a detailed test plan including the scope of the testing process. The plan also mentions the resources required for testing and the duration of completion. Additionally, the plan addresses the diverse PoS components: software, devices, systems, and applications. It also defines the specific testing methods for each component.
Design Test Case
Test cases include all the potential scenarios that the PoS system may come across. In the pharma industry, this might include testing for several things. It consists of drug availability, prescription types, and payment methods. Not only this, but it also includes compliance with several industry regulations. Test cases should also address edge cases. The cases include power failures or unexpected system crashes.
Test Execution
After creating test cases, the execution of tests starts. It involves running the PoS system in a controlled scenario. This is to simulate real-world conditions. Diverse testing methods might be applied during this stage. These methods will be based on the specific component being tested. The methods are regression testing, performance testing, and functional testing.
Identification and Resolution of Bug
In testing, issues or bugs identified are logged, analyzed, and assigned for resolution. It is essential to prioritize key issues, mainly those that can compromise compliance or security, to resolve them. Testing needs to be repeated after bug fixes to make sure the solutions function as expected.
User Acceptance Testing (UAT)
Before launching the PoS system, UAT is conducted. This is the final stage. It includes end users validating that the system meets the expectations. Feedback from UAT helps refine the PoS systems and make sure that it is perfect for deployment.
Key Components of PoS Testing
In the pharma sector, several key components are there in PoS testing, which need to be tested carefully. These components are prepared to ensure the security and performance of the PoS system. Additionally, it ensures the reliability of the PoS system.
The components are:
PoS Device Testing
PoS devices, including barcode scanners, receipt printers, and card readers, play a key role in ensuring the PoS system functions properly. PoS device testing makes sure that these hardware components integrate well with the software. PoS device testing also ensures that they perform their tasks without any problems.
For example, the barcode scanner should read the prescription labels without any error. Similarly, the card reader should accurately process payments made through various sources. It includes credit or debit cards.
PoS Software Testing
It is the process of testing the core apps that function on the PoS system. This includes verifying the software that manages various key processes. This consists of the billing process, inventory management, customer interactions, and all transactions. Moreover, the software must have the ability to perform several tasks. This includes processing prescriptions and calculating costs precisely. It also includes checking drug interactions and providing accurate receipts to clients.
PoS Application Testing
PoS application testing is for software apps. This is for apps that interact with pharmacy employees or customers. The apps should be tested for security, accuracy, and ease of use in doing certain tasks. It includes inventory tracking, prescription filing, and patient data management. Moreover, the apps should not have any bugs, which can cause problems in some tasks. This includes recording transactions or processing sales.
PoS System Testing
This testing includes testing the complete PoS setup. It includes software and hardware. PoS system testing ensures that all the components function together without any hassle. The components are load testing, reliability testing, and performance testing. This makes sure that the system can manage a high volume of transactions during peak hours.
PoS Software Testing: Best Practices
Following best practices is necessary for PoS testing. It ensures the PoS software in the pharma sector meets the quality standards. The testing also ensures the PoS software meets expectations.
The best practices are:
Automated Testing
Automating repetitive test cases for regression and functional testing is vital. It can save resources and time. It helps ensure that key functionality is checked constantly across diverse software iterations.
Security Testing
Effective security testing is vital. This is due to the sensitive nature of data managed by PoS systems. This should include data encryption checks, penetration testing, and vulnerability assessments.
Collaboration between teams
PoS testing needs collaboration between multiple teams. It includes software developers, pharmacy professionals, testers, and legal experts. Regular communication ensures the testing process addresses all the vital requirements. It also ensures that the testing meets the business goals.
Continuous Testing and Monitoring
Continuous testing is vital thing in the development lifecycle. It ensures the issues are detected early. Moreover, constant monitoring is vital to identify the potential security or performance issues. This helps in solving the issues proactively.
Challenges in PoS Software Testing for the Pharma Industry
PoS software testing in the pharma sector has several challenges. It includes:
Regulatory Compliance
The pharma sector is regulated with stringent rules around several things. It includes data privacy, payment processing, and prescription handling. PoS testing should ensure that all the systems adhere to industry standards. This consists of FDA and HIPAA regulations. Testing for compliance can be time-consuming and complex.
Data Security and Privacy
The PoS system in the pharma sector manages sensitive data. It includes payment information and patient health records. Ensuring that this data is stored, transmitted, and processed securely is a key aspect. PoS system testing should include proper security testing. This helps to detect vulnerabilities and secure against breaches. This is because these can lead to financial and legal problems.
Performance and Scalability
In this sector, PoS systems often manage a huge volume of transactions. This is mainly during peak times. Ensuring that the system can scale and maintain performance under heavy loads is crucial. Performance testing is a key aspect of PoS system testing. However, it can be complex in simulating real-world scenarios precisely.
Hardware Compatibility
The hardware used in the PoS systems should function accurately with the software. In this, the hardware is receipt printers, barcode scanners, and payment terminals. PoS device testing can be quite difficult due to various devices. The testing must ensure that the devices are compatible with the software across diverse configurations and versions.
Final Takeaway
In the pharma sector, PoS testing is a vital part. It plays a key role in maintaining system security, reliability, and performance. Rigorous testing of PoS software, systems, devices, and applications is essential. This helps the pharma businesses to ensure that their PoS systems function efficiently. Not only this, but it also ensures the systems adhere to the legal compliance. It also helps them to ensure that their PoS systems provide the ideal user experience.
PoS testing—components, approach, and challenges in the pharma sector—should be managed with proper attention. Investing in comprehensive PoS system testing will help pharma businesses in various ways. It includes improving operational efficiency, reducing risks, and providing better customer service.
Are you involved in the pharma sector? If yes, then PoS testing would be essential for you. An expert PoS software testing service provider like Qualitest can help you.
They have worked in several aspects of software testing in the pharma sector. This includes PoS software testing, PoS application testing, and more. In one of their projects, they took charge of a situation where the customer did not have QA expertise and testing assets. They trained the right testing talent to support the initiatives of the client. This starts with eCommerce and developing an ideal automation framework.
0 notes
Text
Trusted Performance Testing Company USA
Improve your app speed & reliability. Partner with 5Data Inc, a top Performance Testing Company. Get a free consultation today!

0 notes
Text
Download HVAC-Cx: The Essential Building HVAC Systems Commissioning Tool
As building systems become increasingly complex, the need for efficient commissioning and monitoring tools has never been more critical. HVAC-Cx, developed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), stands out as a powerful semi-automated commissioning software tool that’s transforming how we analyze and optimize HVAC performance in commercial buildings. Having worked…
#air handling units#APAR rules#BACnet#building automation#building energy management#custom rules#damper control#data analysis#diagnostic assistance#Energy efficiency#equipment monitoring#fault detection#functional performance testing#HVAC commissioning#HVAC-Cx v2.2#NIST software#operational modes#preventive maintenance#temperature sensors
0 notes
Text
Tips to Leverage a Remote Team for Software Development

There is a big difference between hiring a remote team for software development and benefitting from them. Hiring doesn’t guarantee that you can leverage their services. To get the best from your remote developers, you must know how to manage them to boost their productivity and enhance their work quality.
0 notes