#symmetric cipher model
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
MATLAB is a multi-paradigm numerical computing environment and proprietary programming language developed by MathWorks. MATLAB allows matrix manipulations, plotting of functions and data, implementation of algorithms, creation of user interfaces, and interfacing with programs written in other languages.
0 notes
Text
Speculative Biology of Euclydians (and Bill Cipher) part 2
Part 1, Part 3, Part 4, UPDATE, Part 5
So this part is what you've all been waiting for, it took so long, but you'll quickly understand why. This part is:
The Biology of Bill Cipher
As always, this analysis is based on two assumptions:
Before Bill Cipher became a demigod, he was a biological, living organism and so were the rest of his species.
Even after Bill Cipher became a demigod, he still retained some physical characteristics of his biological form.
And a fair content warning: This contains anatomy illustrations. This isn't anything gory, but there are people who are squeamish, so you've been warned.
Click on the images to get better quality!
And without further ado, let's begin.
External structures
Euclydians are animals with a very specific shape. They have a shell in a form of a geometric shape and four limbs. Bill is an equilateral triangle, so my analysis will be just on triangular Euclydeans.
They have bilateral symmetry. This type of symmetry is characterized by having a left and a right side placed like mirror images of each other. Humans and majority of Earth’s animals also have this feature.
Bilaterally symmetrical organisms usually have a distinct head region, because of a process known as cephalization. This process moves the animal’s brain and sensory organs towards one end of the body – the head. Euclydians have a head. It’s the “tip of the pyramid” on Bill and that’s where the eye and other sensory organs and brain are located.

Finally, Euclydeans are segmented. Their segments are clearly visible as those weird brick lines on their body. Bill also often separates his body into three segments. This is a part of his god powers, but it tells us that Euclydeans have three major body segments, I’ll call them the tip, the middle and the base. Each segment contains specific organs.
Euclydeans are invertebrates. And yes, I know this image exists, but this is just Bill’s trolling. He’s making fun of human classrooms where we often find skeleton models. That skeleton wouldn’t even be functional, because it doesn’t have any joints in arms and legs, so it wouldn’t be able to move. And it has a hole where the brain would be, so you know, the fucking brain would fall out.
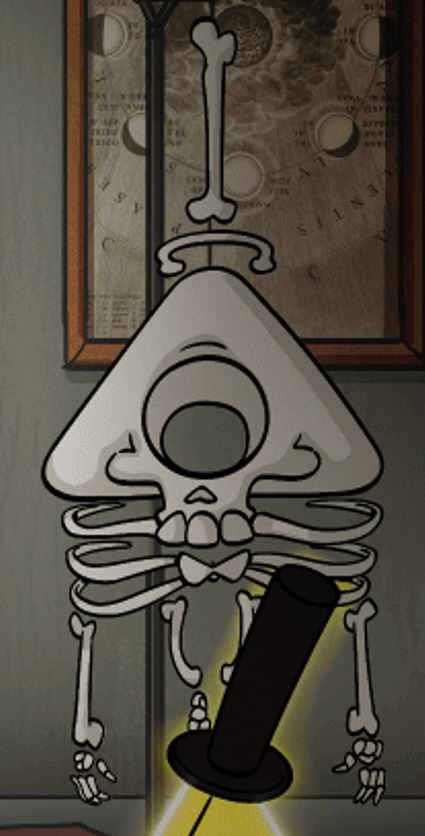

It was outright stated that Bill has an exoskeleton. Having both external and internal skeleton would be a big waste because you have two systems that do the same thing. Besides, the way Bill's limbs move is much more similar to an invertebrate. His shell is also somewhat bendable which would not be possible if it was made of bone. And the eye-mouth complex that Bill uses to eat would also be completely impossible with a set of vertebrate jaws.
Euclydean shell (or exoskeleton) is nothing like anything here on Earth. It’s most likely made out of silica combined with proteins. I say this because Bill turned to stone when he died and he also likes to eat glass, which is pure silica.
The exoskeleton is made out of several parts. It has a front (ventral) and back (dorsal) part. Both the front and the back part of the exoskeleton are made out of head region (the tip) and three layers of “bricks” which are just segments of the exoskeleton.

The front tip is probably made of more protein and elastic tissue than the back, because Bill has a very expressive “face”. This means that he also has quite complex facial muscles. The back of the head is probably the hardest part of the exoskeleton because it protects the brain. Bricks are in the middle since they have a very important role in speaking and breathing, but also allow the shell to bend.
Can Euclydeans change color, or is it just Bill Cipher using his god powers? Well, since he changes his color on instinct, I think they could! Bill can change color to black, yellow, red and blue. This means that he has a complex system of chromatophores – cells that contain little sacs full of pigment. When the sacs inflate, the body appears to be the color of the largest sac, whilst those deflated are invisible. Color changes depending on the pigments contained in inflated sacs. In Bill, the pigments are red, blue and yellow. Yellow is the standard color, it signifies neutral or content emotional state. He turns red when he's angry or wants to look intimidating and blue might signify fear, despair and cry for help. Black is the color of Euclydean’s skin, so when they look black, it’s because all pigment sacs have deflated and the transparent shell allows us to see the skin underneath.
And yes, Euclydeans have black skin. I know some people say that Bill wears thigh high boots and long gloves, but to me, that doesn’t make any sense. Like, that image of him in Theraprism is showing him with clothes over his supposed gloves and boots. Why would they make him wear sneakers over boots? And why baby Bill has yellow hands? Well, that’s something I’ll tell you in the next part where I’ll talk about babies.
Anyways, the skin is black, but we have no idea what it feels like. Seriously, so many people shook hands with Bill and nobody wrote down how his skin feels like! But we know that he has fingerprints. That means that he has very sensitive fingertips and that those little paws were made for grabbing things. Also, Bill doesn’t have any growths on his skin: no nails, hairs, scales etc. I know a lot of people love to draw Bill with claws, but he doesn’t have claws, not even in his most eldritch form. His fingers always remain small and soft. The legs have no fingers and the skin of the sole of their feet is probably thick.
Internal Structures
Coelom
Coelom is one of the most important organs, that you probably don’t know you even have! It’s a fluid filled cavity whose role is to separate internal organs from the muscles of the body wall. This allows organs to move and grow independently of your muscles and it also protects and cushions them against impact. In humans coelom is complex and it’s made out of pericardial cavity (around the heart – allows heart to pump blood), pleural cavity (around lungs – allows lungs to expand while breathing) and peritoneal cavity (around digestive system – allows for expansion and movement of digestive organs).
I believe that Euclydeans also have some form of a coelom. Coelom is even more important in invertebrates, as that’s where their immune system is and it can also serve as a supportive hydroskeleton. Since Euclydeans have a hard shell, they need the protection around their organs. Every shelled animal on Earth has coelom for that reason. They also need room for the food they eat, since the shell can’t expand and their limbs can enter the shell, so they need room for that too.
2. Nervous system
Euclydeans have a vast range of emotions, capability to communicate using speech, body language and even color shifting. They are as intelligent, or more intelligent than humans. They have a highly developed eye and other senses and all of this requires a nervous system. We saw Bill’s optic nerve when his eye got pulled out during Weirdmageddon, so he does have a nervous system, but I can't tell you how exactly it looks like.
There’s one part of Bill that I bet is similar to human - it’s his brain. Bill claims that he can take control over any being a long as they have neurons. This is his god like power, but then, why just beings with neurons? Well, most likely, because he has neurons too and kind of understands how they work. Maybe his brain even produces similar neurotransmitters as ours, so we’re easy to control with them. The brain is in the tip of the pyramid, slightly above eye and it likely has a lot of neurons and a very complex structure. I can’t tell you how exactly is his brain organized, but since he's bilaterally symmetrical, it’s very likely that it has hemispheres. He likely also has two neural cords, like most invertebrates, and those run down the dorsal (back) side of his body
3. Senses
Euclydeans have camera lens type eyes. Now here I can only speak of Bill, since we haven’t seen any other Euclydian. Bill’s eye is large, placed in the center of his “face”. It has eyelids with “eyelashes” (more on them later) and produces tears (Bill cries after his break up with Ford). The pupil is slit and vertical and there is no iris. However, there are muscles that can change the shape and dilation of the pupil. The eye looks similar enough to human that I can confidently say that he has cornea, lens and sclera. The eye is filled with refractory fluid and has some form of retina in the back. Bill’s eye changing color and being used as a projector or to shoot lasers are all parts of his god powers, however, it is possible that his species has a tapetum lucidum, a reflective layer of cells which help animals see in low light conditions and also makes the eye glow in the dark. Bill has color vision and he claims that he can see every part of the electromagnetic spectrum, but I think that's a part of his god powers. However, Euclydeans definitely could see in color, since their alphabet was basically a color code and they also use colors to express emotion.
Since Bill has fingerprints, we can confidently say that his fingers are the most sensitive part of his skin. Bill can feel through his shell too, just like every shelled organism ever (that's why he used Ford as a backscratcher). Tactile senses are very primitive, so Eucliydeans could feel cold, heat, pain, pressure, vibration and everything else just like we do.
Bill has a sense of smell and he even says which scents he finds attractive. This could mean that sense of smell plays a big role in reproduction of Euclydeans, but where is it located? Well, on the eyelashes. Except, those are not eyelashes, they are antennae. Bill has total eight of these antennae, 4 on lower and 4 on upper eyelid. They are very soft and sensitive, so he can retract them inside the eyelid. He does that when he feels threatened, so it’s probably a fight or flight response. His lashes get longer and he flutters his eyelid more near Ford, probably because he enjoys his smell. They are also located close to the mouth, so that’s how he samples the scents of the food.
Euclydeans have great hearing. They communicate vocally, sing, Bill can play the piano, so obviously, they hear. But I have no idea what they use to hear. It could be the bow tie, since it does look vaguely ear shaped, but it's possible that the bow tie isn't actually an organ. In that case, they could have an unknown structure inside them or they could just use their thin exoskeleton to catch sound vibrations.
They taste using their long tongue.
4. Muscles and movement
We have seen Bill’s muscles and they are striated skeletal muscles like mammals and insects have.

As the shell is kind of bendy, there is a lot of muscles underneath it. Those are the muscles of the body, they also move the face and bricks while speaking. The limbs have muscles too and two kinds at that.
When Ford shoots through Bill’s hat (which also a part of him) it is shown that inside of it are strange bone-like structures. These are not bones, since they aren’t articulated, but muscles do connect to them. They kind of remind me of echinoderm ossicles, but they don’t really look like them. This is another fully alien structure and I’ll call them anchors.
You know how Bill’s limbs can both bend just like human arms and legs, like he has elbows, wrists, knees and ankles, but they also bend like goofy rubber-hose cartoon anatomy? Well, that’s because there are two types of muscles in them. There are muscles attached to the anchor points and subcutaneous muscles.

Anchor points are located in the same places as joints in humans. Muscles that attach to them are long and strong and they are used for regulated, precise movement. The subcutaneous muscles (the one we see in his Weirdmageddon image) are used to bend the limbs in every other manner. They are not attached to anchors, but to the skin, so they resemble muscles of octopus arms. They are shorter and less strong, but when they act together they move the limbs in coils. These muscles are also responsible for squishing the limbs inside the shell when they are hidden.
Bill has incredible control and dexterity of his muscles, especially in arms and fingers. Even though his paws are soft and small, he can use them pretty much as efficiently as humans use their hands.
Possibly the strongest muscles in Bill's body are his jaw muscles, so let's talk about those jaws.
5. Eye-mouth complex and the digestive system
Having your eye used for feeding seems wild to us, but this adaptation is seemingly common in fictional geometric shaped people, as it has convergently evolved in Flatland’s inhabitants as well. And, speak what you like, but Euclydeans can’t choke on their food, so they have it better than humans.
I don’t know what Flatlanders eat, but Euclydeans are definitely predators. Now, I know that Bill sometimes depicts himself with human like teeth. The guy has a thing for teeth, especially molars, but he doesn’t have mammalian teeth. In every image where he opens his mouth that was not made by him, we see that he has cone shaped sharp teeth, like a predator. These teeth are great for biting and subduing prey, but they suck at chewing. Euclydeans can’t chew, so they they feed by swallowing chunks that they bite off, or swallowing their food whole if it’s small enough.
Here I depicted how this “eye-mouth complex” functions:

Euclydeans have a stomach in the middle of their body, but I have no idea what goes after it. My best guess is that they have a branching intestine. Our flattest organisms (flatworms, sea stars and brittle stars) all have this type of intestine. It basically means that, instead of just going like a tube, the intestine branches into different parts of the body. I also have no idea whether they have an anus and if it’s just one. This is just something I can’t tell you.
Since Euclydeans are capable of eating a lot of various things, I expect that they have accessory digestive glands (that’s liver and pancreas in humans). Strangely, despite the fact that his anatomy indicates a predator, Bill likes eating starch (pasta, empanadas, sandwiches etc). Most carnivores are unable to digest starch, so I went with god powers, but he ate sandwiches when he was a kid and had no god powers. So, we have two options. Either Euclydeans are omnivores (which, with those teeth, I doubt) or the animals on their planet store their excess calories as starch, not fat, so predators evolved the ability to digest it. If the second one is true, then Bill eating pasta is like your cat eating pure butter. It’s probably not healthy for him, but I don’t think he’s a guy who would give a single crap about that.
6. Breathing and speaking
In The Book of Bill, Bill says that “dumb trapezoids and rhombuses were sucking up his rightful oxygen”. This means that Euclydeans are aerobic organisms – they breathe oxygen. Their skin is dry, so they don't use it for breathing and they also speak, laugh and sing. All of this tells me that they have lungs.
I believe that their lungs are located near the base where the bricks are. The gaps between bricks have little tracheae that lead to the lungs. Bill most likely breathes in from his back side and breathes out from the front. The air is probably forced to travel through small crevices inside the lungs so that it can exchange the oxygen with blood. We don’t know whether Euclydeans exhale carbon dioxide, but they probably do, since they can eat our food, so they probably have similar metabolism to us Earthlings.
Since Euclydeans can speak and laugh, they probably have some kind of a diaphragm. In fact, I think they have two! Their voice has an echo, which means that, most likely, their lungs don’t always expel air at the same time. Air expelling causes the bricks to vibrate which produces sound. That’s why Bill seems to glow when he speaks – he’s actually vibrating. This action is also controlled by muscles. Depending on which row of bricks is vibrating and how many of them are involved, Bill changes the pitch and tone of his voice.
And the growling noise? Well, when Bill uses his demonic voice, he is doing one of two things. He is either using his god like powers to modify his voice, or that’s just how Euclydian vocal fry sounds. If you don’t know what vocal fry is, it’s produced when the vocal chords are vibrating slowly and they become out of sync. This produces a very specific sound and that sound can be made voluntarily. That’s how Mongolian throat singing works. Similarly, Euclydeans could slow down the rate at which their bricks vibrate and make them out of sync to produce that menacing “demon voice” as a threat display.
7. Circulatory system
We know how Euclydean blood looks like. It’s silvery and kind of seems like it glitches. It also contain chemicals that can make humans sick. This means that Euclydeans have much different blood from animals on Earth, but it certainly serves the same function. It’s used to transport nutrients and oxygen through their body.
Since the agents from The Book of Bill were able to draw his blood, it’s clear that Bill has a circulatory system and a closed one at that. The closed circulatory system means that blood vessels end in capillary nets and don’t open inside the body cavity like they do in molluscs and insects. If the agents used syringe to pull Bill’s blood and he had an open circulatory system, they could actually collapse the entire thing as they would pull his organs as well. That’s why I believe that he has a closed circulatory system.
Closed circulatory system requires a heart and I believe that Bill’s heart is located between his lungs, like ours. I have no proof that his heart looked anything like in the illustration, but I looove cardiology, so I did all this just because I wanted to draw a weird heart. I don’t think Euclydeans have a super complex four chambered heart like we do, they most likely have two or three chambered heart. The heart separates lung and body circulation and regulates their blood pressure.
The capillary nets are all located in important places: lungs where they exchange oxygen, intestines where they absorb nutrients and brain where they feed the neurons. Euclydeans have a rather large brain, so it probably uses most of their calories and oxygen.
8. Other systems
I can’t tell you anything abut Euclydean excretory system. I don’t know whether they produce urine or not, if they have kidneys, nephrocytes or something completely different. I genuinely have no idea.
They have to have an immune system because they are multicellular. Every single multicellular organism including sponges and plants has some form of an immune system. I believe Euclydeans have something similar to coelomocytes - a very common type of immune cells in invertebrates which reside in coelomatic cavity.
I'll talk about reproductive system in Part 3!
Are Euclydeans warm or cold-blooded?
This was a very tough one, because they could be both, but I am leaning more towards cold-blooded. They have very little muscle mass and heat is produced within the muscles via trembling or metabolic heat (heat released in various chemical reactions in the body). When an animal has very little muscle it isn’t used for that. Even mammals like sloths who have significantly reduced muscle mass become dependent on the surrounding temperature. Also, Euclydean flat shape can easily distribute heat they absorb, so they wouldn’t need to waste energy making their own. On top of that, Euclydeans don’t wear clothes, which can be a cultural thing, sure, but they could also not wear clothes because they need their skin exposed so that it could absorb heat.
Here's how Bill Cipher's complete inner anatomy looks like:

There, I hope you enjoyed this! I'll see you hopefully next week to tell you about Euclydean reproduction and development.
Thank you @ok1237 @unoriginal-starwalker and @chrystalitar for your support :D
(Also, I hid Ford Pines in one of the anatomy illustrations. Can you find him? Click on the images for better quality!)
#this is what i'm using my biology degree for#i am insane#the art took like 10 hours to make#you won't believe how much time i spent researching this#it's so long#speculative biology#biology#bill cipher#gravity falls#the book of bill#i am so done#art#long post
208 notes
·
View notes
Text
do vpn providers sell your data
🔒🌍✨ Get 3 Months FREE VPN - Secure & Private Internet Access Worldwide! Click Here ✨🌍🔒
do vpn providers sell your data
VPN data privacy policies
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) is a crucial tool for protecting your online data privacy, but not all VPN providers offer the same level of data protection. When choosing a VPN service, it's essential to carefully review their data privacy policies to ensure your sensitive information remains secure.
One key aspect to consider is the logging policy of the VPN provider. Some VPNs may store logs of your online activities, including your IP address, websites visited, and the duration of your sessions. Opt for VPN services that have a strict no-logs policy, meaning they do not keep any record of your online activities. This ensures that even if the VPN servers were compromised, your data would remain private.
Additionally, pay attention to the jurisdiction in which the VPN provider operates. Some countries have data retention laws that require companies to store user data for a certain period. Choosing a VPN based in a privacy-friendly jurisdiction can help protect your data from being accessed by third parties.
Encryption standards are another critical factor in ensuring data privacy. Look for VPN services that use strong encryption protocols like AES-256, which is virtually unbreakable. This encryption ensures that your data is scrambled and unreadable to anyone trying to intercept it.
Overall, carefully reviewing the data privacy policies of VPN providers is essential in safeguarding your online privacy. Prioritizing VPN services that have a strict no-logs policy, operate from privacy-friendly jurisdictions, and utilize robust encryption protocols will help keep your sensitive information secure while browsing the internet.
VPN encryption standards
VPN encryption standards play a pivotal role in ensuring the security and privacy of users' online activities. As virtual private networks (VPNs) become increasingly popular for safeguarding sensitive information and maintaining anonymity, understanding encryption standards is essential for making informed choices.
One of the most widely recognized encryption protocols used by VPNs is the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES). AES employs symmetric-key encryption, where the same key is used for both encryption and decryption. With AES, data is encrypted using a cipher key of varying lengths, typically 128, 192, or 256 bits, providing robust protection against unauthorized access.
Another prevalent encryption protocol is Secure Socket Layer (SSL) or its successor, Transport Layer Security (TLS). SSL/TLS encrypts data transmitted between a user's device and the VPN server, ensuring that it remains confidential and secure against interception by malicious actors. These protocols are commonly used for securing online transactions, web browsing, and communication.
OpenVPN is an open-source VPN protocol that utilizes OpenSSL library for encryption. It supports various encryption algorithms, including AES, Camellia, and Blowfish, offering users flexibility in choosing their preferred level of security. OpenVPN's versatility and strong encryption capabilities make it a popular choice for both personal and corporate VPN deployments.
Internet Protocol Security (IPsec) is another widely adopted VPN encryption standard that operates at the network layer of the OSI model. IPsec provides authentication, integrity, and confidentiality through its Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP) and Authentication Header (AH) protocols, ensuring secure communication between network devices.
In conclusion, VPN encryption standards such as AES, SSL/TLS, OpenVPN, and IPsec play a crucial role in safeguarding users' privacy and security online. By understanding these encryption protocols, users can make informed decisions when selecting a VPN service provider that offers robust protection against cyber threats.
VPN data logging practices
Title: Understanding VPN Data Logging Practices: What You Need to Know
In the realm of online privacy and security, Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) are invaluable tools. They encrypt your internet connection and route it through servers, masking your IP address and providing anonymity. However, not all VPNs are created equal when it comes to data logging practices.
Data logging refers to the collection and storage of user activity on the VPN network. While many VPN providers claim to have a strict no-logs policy, it's essential to delve deeper into their practices to ensure your privacy is truly protected.
There are three main types of data logging:
No-logs policy: Some VPNs adhere to a strict no-logs policy, meaning they do not collect any data related to your online activities. This is the ideal scenario for privacy-conscious users, as it ensures that no personally identifiable information is stored.
Minimal logs: Some VPNs may collect minimal logs for troubleshooting purposes, such as connection timestamps or bandwidth usage. While this data might not directly compromise your privacy, it's crucial to verify how long this information is retained and whether it's anonymized.
Extensive logs: Unfortunately, some VPN providers engage in extensive data logging, storing detailed records of users' browsing habits, IP addresses, and even DNS queries. This practice not only undermines the purpose of using a VPN but also poses a significant risk to user privacy.
When choosing a VPN provider, it's essential to thoroughly review their logging policy and terms of service. Look for providers that have undergone independent audits or have a proven track record of protecting user privacy. Additionally, consider opting for VPNs based in jurisdictions with strong privacy laws to further safeguard your data.
In conclusion, understanding VPN data logging practices is crucial for maintaining your online privacy. By choosing a reputable VPN provider with transparent logging policies, you can enjoy the benefits of encryption and anonymity without compromising your personal information.
VPN jurisdiction regulations
When it comes to using a Virtual Private Network (VPN), one important factor to consider is the jurisdiction in which the service operates. VPN jurisdiction regulations can have a significant impact on the privacy and security of your online activities.
The location of a VPN provider can determine the laws and regulations that govern how they handle user data. Some countries have strict data retention laws that require VPN providers to store user information for a certain period of time. This can pose a risk to your privacy, as your data may be vulnerable to being accessed by third parties.
On the other hand, VPN providers that operate in countries with strong privacy laws are generally more reliable when it comes to safeguarding user data. These providers are often committed to upholding strict privacy policies and may offer features such as a no-logs policy, which ensures that your online activities are not recorded or monitored.
It is essential to research and choose a VPN service that is based in a jurisdiction with favorable regulations for privacy and data protection. By selecting a VPN provider that operates in a country with robust privacy laws, you can enhance your online security and confidence in protecting your personal information.
In conclusion, understanding VPN jurisdiction regulations is crucial in ensuring that your online activities are secure and private. By selecting a VPN provider that operates in a jurisdiction with strict privacy laws, you can enjoy a safer and more private internet experience.
VPN user data protection
In the age of pervasive online tracking and data collection, safeguarding personal information has become a paramount concern for internet users worldwide. VPNs, or Virtual Private Networks, offer a robust solution for protecting user data and privacy.
VPN services create a secure, encrypted connection between the user's device and the internet. By routing internet traffic through their servers, VPNs effectively conceal the user's IP address and encrypt the data transmitted, shielding it from prying eyes and potential cyber threats.
One of the primary ways VPNs protect user data is by masking their IP addresses. Instead of connecting directly to websites and services, users connect to the internet through the VPN server, which assigns a different IP address to their device. This makes it nearly impossible for third parties to track users' online activities back to their real IP addresses.
Furthermore, VPNs encrypt all data transmitted between the user's device and the VPN server. This encryption ensures that even if intercepted, the data remains unreadable and secure. Whether browsing the web, accessing sensitive documents, or communicating over unsecured networks, users can trust that their information is shielded from hackers, ISPs, and government surveillance.
Additionally, VPNs offer anonymity by not logging users' online activities. Unlike internet service providers (ISPs) and websites that often track and store user data for various purposes, reputable VPN providers have strict no-logs policies, ensuring that user activity remains confidential and private.
In conclusion, VPNs play a crucial role in safeguarding user data and privacy in today's digital landscape. By encrypting internet traffic, masking IP addresses, and implementing no-logs policies, VPN services provide users with peace of mind and confidence in their online security and anonymity.
0 notes
Text
Cyber Security

In today's society, digital literacy is crucial. Learn about the digital footprints we leave behind, how to protect your privacy online, and potential dangers. https://agritech.college/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/Engineering-1.mp4 This course introduces the idea of cyber security, describes the numerous threats that might result in cyberattacks, and expands your knowledge of the potential defences. Lesson Structure There are 11 lessons in this course: - Introduction to Cyber Security and cyber attacks/defences - Importance of cybersecurity - Threats - passive attacks, active attacks - Common types of attacks - injection, phishing, denial of Service, malware, spoofing, man in the middle, network attacks - Layered approach to defense - Physical security - Software and Operating System Security, Network security - Vulnerability Assessment - Assessing vulnerabilities - Security posture - Performing vulnerability assessment - 5 steps - Identifying and classifying assets - Threats and risk assessment - Baseline reporting - Penetration testing - techniques, penetration testing versus vulnerability assessment - Securing the facilities and networks - Securing a data centre - Securing the network - Hardware level - Software PC, Device level - Securing your online digital footprint - Digital footprints - Social media - Web browsing - Devices used - Managing digital footprint - Protecting user reputation - Sharing personal information - Preserving freedoms - Preventing financial; losses - Privacy risks - Developing better online habits - Investigating default settings - Using privacy enhancing tools - Internet Security and Digital Certificates - Digital certificates - Digital signatures - Digital rights management and Information rights management - Electronic books and magazines - Generating a digital certificate - Exchanging and verifying a digital certificate - Web browsing - TLS and SSL - Security issues - Secure web browsing using https - Wireless Network Vulnerabilities, Attacks and Security - Types of wireless data networks - NFC and Bluetooth network attacks - Wireless LAN attacks - Network blurred edges - Wireless data replay attacks - Wireless DOS attacks - Rogue access point - Attacks on home LANs - war driving, war chalking - Wireless security vulnerability and solutions - IEEE wireless security vulnerabilities - Firewalls, IDS and IPS - Types of firewall protection - Packet filtering firewalls - Application/proxy firewalls - Hybrid firewalls - Firewall limitations - Formats and firewalls - UTM appliance - Intrusion detection systems - Network intrusion systems - Host based intrusion detection systems] - Intrusion prevention systems - Common detection methodologies - Anomaly based IDPS - Signature based IDPS - Cryptography - Definition, terminology and characteristics - Common cipher attacks - Ciphertext only attacks - Known plaintext attack - Dictionary attack - Bruit force attack - Power analysis attack - Fault analysis attack - Cryptographical algorithms - Symmetric encryption - MAC function - Asymmetric encryption - Slipcovering keys - Hash algorithms - Access Control and Authentication - What is access control - Definition, terminology - Access control models - RBAC, RAC, HBAC - Implementation - group policies, ACL, DACL, SACL - Authentication and authorisation - Securing and protecting passwords - Multi factor authentication - Cyber attack Disaster Recovery strategies - Five stage response - Recovery planning - Backup procedures - cloud storage - Monitoring and logging events - Containment of attack - Assessing damage - Recovery procedures - system images SEO, restore data corruption - Authorities tracking attackers - Data ands security policies - Ongoing Security Management - Managing security events - events monitoring - Centralised versus Distributed data collection - Being organised - Understanding the workplace - Security and decision making - Division of responsibilities - Time management - Networking - Attitude - Products and services - The law Each lesson culminates in an assignment which is submitted to the school, marked by the school's tutors and returned to you with any relevant suggestions, comments, and if necessary, extra reading. Aims - What is cyber security? - Describe the objectives and significance of cyber security. - know key terms in cyber security, and be able to identify several assaults and countermeasures. - Describe the process of doing a vulnerability assessment. - Recognize the methods and tools at your disposal. - Compare and contrast penetration testing with vulnerability scanning. - Describe the methods for securing networks, data warehouses, data centres, and physical data storage. - Recognize the consequences of having a sizable digital presence online. - Recognize the options people have to control their online digital footprint. - Learn what an intrusion detection system (IDS), an intrusion prevention system (IPS), and a firewall mean in the context of cyber security. - Describe the significance, purposes, advantages, and security that firewalls, IDS, and IPS systems give in safeguarding both PCs and computer networks. - Know the basics of cryptography and the significance of data encryption and decryption. - Describe the basic elements of cryptographic protocols and the accepted practises for encryption and decoding. - Recognize the significance of digital certificates and signatures in safeguarding web traffic. - List the many kinds of wireless data transmission networks and describe the numerous ways that each one is vulnerable to attack. - Describe the available wireless network security standards for protecting wireless networks. - Learn what Access Control is and the language used in it. - Recognize the significance of using access control models. - Know what authentication is and why it's crucial to use multi- or double-factor authentication, create secure passwords, and define authentication. - Describe the best practises for building up redundancy and quick recovery techniques before and after an attack has happened and how to minimise the effects on the systems and networks involved. How You Plan to Act - Look into the idea of defence in depth and other layered defence concepts. - Do some research and justify the cyberattack you chose. - Describe some of the best vulnerability scanners currently on the market. - Online, look into 4 privacy-enhancing solutions like VPNs, password managers, and encryption programmes. - Look at the newest firewall products available. - Look into the newest NIDS and HIDS products available. Find out how to identify, then reduce, vulnerabilities. Understanding potential vulnerabilities, evaluating those vulnerabilities in a specific context, and then taking steps to close or avoid those vulnerabilities are the first three steps in the cybersecurity process. Knowledge is equivalent to power when businesses are attempting to secure their assets. Businesses are more exposed to cyber hazards as a result of increasing their reliance on information technology, including placing or transferring data to the cloud, IoT (internet of things) devices, mobile devices, social platforms, and others. A vulnerability management programme, similar to an annual health check, can assist firms in identifying cyber system vulnerabilities before they become issues. Secure Position This is the formal name for a comprehensive security strategy. Everything, from basic planning to execution, is included. The typical security posture of an organisation consists of: - Technical policies - Non-technical policies - Procedures - Controls A Vulnerability Assessment Most cyberattacks aim to take advantage of well-known flaws and vulnerabilities. Also, with so many new vulnerabilities being found every year, it is crucial for businesses to maintain ongoing vigilance in order to assess their IT security posture, identify any gaps, and take the necessary action. The key to addressing this increasingly severe threat environment is a rigorous vulnerability assessment programme. This is so because a vulnerability assessment is a rigorous procedure that locates and measures security flaws in networks, hardware, and software used in applications. A vulnerability assessment for an organisation should result in a clear report with a list of the environmental factors that need to be addressed and where on the priority list each factor falls. The IT departments of organisations constantly update, patch, and apply software patches to their critical systems. However, managing software updates and patches is a difficult task for IT departments because patches are known to occasionally disrupt other software and in some cases, systems needing patches cannot be taken offline. Because of this, a good vulnerability assessment will give the company a prioritised list of vulnerabilities organised by system or software (or others), which the IT department may use as a task list to strengthen the company's security posture. A plan of defence against today's sophisticated cyberattacks, in which attackers programme the attacks to actively search for vulnerabilities in systems and networks and automatically start their attack process as soon as these are found, is crucial for any organisation, even if it is not a high priority target. Knowing the difference between scanning for vulnerability assessments and analysing and prioritising vulnerabilities by incorporating them into a larger "risk management programme" is also crucial. The five steps listed below are frequently included in a vulnerability assessment: - determining the assets that require protection; - assessing potential dangers to those assets; - conducting a vulnerability assessment to determine how vulnerable the existing method of protection is; - evaluating risks (by considering the impact and possibility of any potential weakness being exploited); - reducing dangers. Read the full article
0 notes
Text
FRACTAL DHARMATA & UNIVERSAL HYPER-INTELLIGENCE
Our rediscovery of the accurate 3D Dharmata geometry is based on the novel Timewave discovery of Novelty Theory, visionarily rediscovered by ontologist Terrence McKenna, initially in the 1970s.
The Timewaves’ typological morphology has been acredited by UCLA scientist and mathematician, professor Ralf Abrahams (A Chronology Of Time), as the fractal symmetry of the ontological morphology of time itself.
The Timewave verified to be an accurate cartography of time’s temporal wave architecture within the atomic clock observation measurements made by Los Alamos Laboritory physicist, Dr. Sheliak. The temporal behavior within the scale of the ATOMIC clocks, behaved accordingly to the Timewave-1 graph topology…
Thus, Puharich’s assertion to the ATOM’s nucleus MM force within the proton, to be following fractal electric/magnetic charge, which he also relates to the Mandlebrot set — is clearly here highlighted for the very first time. Especially when we understand the relation between the Timewave, Dharmata, and the mandlebrot fractal, as follows…
This leads us to our findings… By tracing the complete Timewave graph into 3D computer animation software; replicating the design 180° in mirror symmetry; and then rotating this into 3 dimensions, the beautiful and remarkable precise morphology of the Dharmata was resurrected from the catacombs of antiquity. Dharmata’s shape is traced by the Mandlebrot fractal symmetry outline.

Before Leonardo Da Vinci’s version of this mandelbrot fractal design within his Leicester Codex, he was preceeded by several hundred years in the remarkable labour undertaken by Monk Udo of Achen, who spent 9 years calculating the accurate Mandlebrot set which he called Divinitas (“Godhead”), rather than using Abacus, he utlised the Vedic mathematics of ‘algorythm’ calculations that utilised the Vedic arabic numerals (based on Brahmi-script), (The forgotten genius of Udo von Aachen", Schipke, R.J. and Eberhardt, A., Harvard Journal of Historical Mathematics, 32, 3 (March 1999), pp 34-77), which itself is derived from Vedic mathematics. He depicted it as the star of Bethlehem.

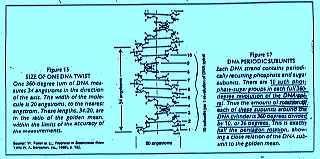
The Timewave, also appears to be the accurate morphology of the full permutation of the DNA genom (by the implication of Dr. Martin Schönberger’s accademically impeccable I-Ching and The Genetic Code: The Hidden Key To Life). Thereby, the fractal MM fields of the hadronic force in the proton, through 8hz electrolysis of water, producing the amino acids and full proteins in the very same fractal symmetry as itself… which itself is the complete permutation of the DNA code, is extraordinary…
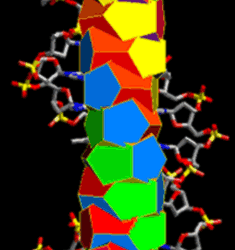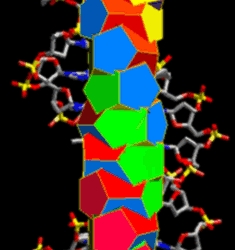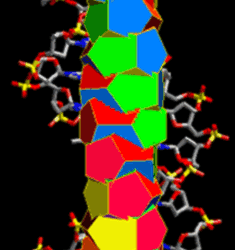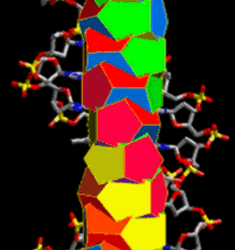
That is: proteins “Made in the Image of its Creator,” the organising 27D Hadron through its MM fractal symmetry… and which turns out to be the symmetrical geometry of the full permutation of the DNA codon language.
Thereby, giving a fractal (self-similar, self-organising, self-reflective/conscious), hyper-topology of the All-One Macro nature of the hadron’s hyperdimensional unified hypercharacteristics... The hadronic mechanic’s Macro Irreversible Hyper-Organisation of all life.
Thereby: the hyper-morphology of indivisible wholeness that is all-one Hyper-Intelligence — HTI: Hyper-Temporal/Hyper-Terrestrial Intelligence.
UNIVERSAL LANGUAGE OF LIFE
Thus, some initial major decipherments of the Universal Language orchestrated by the Hadronic-Intelligence Hyper-Organisation of Life, have been decrypted, self-embedded and axiomatic within the very cipher codes of life itself, and within the very heart fields of proto-matter (proton-matter proper).
Hereby, we have identification of the fractal Universal Language composed of a hadronic hyper-semantics that has seamless axiomatic similitude in its linguistics between the fractal design of the code of life and the fractal geometry of the MM force comprising the alphabet of all the periodic elements that composit the universe…

Same fractal semantics as the DNA life code and the organising fractal force in the heart of all the periodic elements that built the universe… And the application of one (the fractal MM within the proton), upon the element water (by 8hz electrolysis), produces living complex amino acid chained proteins that grow according to the fractal Dharmata/Mandlebrot image/symmetry, that is the characteristics of the MM proto-force in the atomic heart; and which is also the fractal image of the entire ontological morphology of the DNA code, itself a composite of amino acids…

Talk about Self-Organisation, Self-Reflection, Self-Similarity… The same, self-similar, universal All-One Mind-Heart — the indivisible unity between the, so called, inanimate and the animate (such a consequence is also objectively established by hadronic hyper-mathematics. Arbitary connections have been eliminated, illusive assumptions vacuumed into nonexistence)
The human genome is some 3.6 billion DNA letters in length, whilst one single X-chromosome is a macro-DNA molecule some 160 million DNA letters in length. Dr Robert Pollack relates that the DNA:
“Is also a form of text, and that therefore it is best understood by analytical ways of thinking commonly applied to other forms of text, for example, books.”
— R. Pollack A Crisis In Scientific Moral, Nature, 385,1997. pp 674
One cannot analyse a text like a book, if one presupposes that there was no intelligence behind writing it. The very fact that the DNA turns out to be an intricate language, written in complex grammer, reveals an intelligence that has a far more holographically integrated hyper-semantics than our present use of languages.
The DNA resonating crystal is an intelligently ordered linguistics with a holographic laser resonation communication continuum, as molecular biologist Dr. Frank-Kamenetskii relates:
“The DNA crystal is aperiodic, since the sequence of base pairs is as irregular as the sequence of letters in a coherent text.”
—M. D. Frank-Kamenetskii Unveiling The DNA. New York, VCH Publishers, 1993. Pp 31
Or as noted biologist Sir Charles Dobbs had relayed:
“The whole of the protein in the human body is replaced in roughly 160 days… When one contrasts the great complexity of the protein molecule with the fact that millions of these substences are constantly being built up and disintegrated in the human body, and moreover rebuilt to precisely the same structure, one cannot help but speculate about the controlling mechanism.”
—Sir Charles Dobbs, quoted in Dr. Harold Saxton Burr’s, The Fields Of Life (Ballantine, New York, 1973).
Thus, to find the same fractal self-similarity in the DNA code’s permutations as that of the organising force within the protons from the hadron omegon, should seriously transcend the primitive assumption of zero intelligence behind the DNA life book.
The fractal self-similarity thus of DNA, time, the proton’s hadronic magnetic monopole force, and the fractal growth of life exposed to the 8hz ELF field of this fractal force, demonstrates a post modern fax simile of the Veda’s, “man made in the Image of the Original Model of Manu,” and the Biblical, “Man made in the Image and the Similitude of God.”
Puharich’s observation of the fractal ‘mandlebrot’ geometry arising from the Magnetic Monopole force within the proton, in the 8hz electrolysis of water, and his above mentioning of this being the fractal electric and magnetic charge within each of the 3 quarks that compose the proton of the atomic nucleus, now has some astounding and surprising cross-verifications…
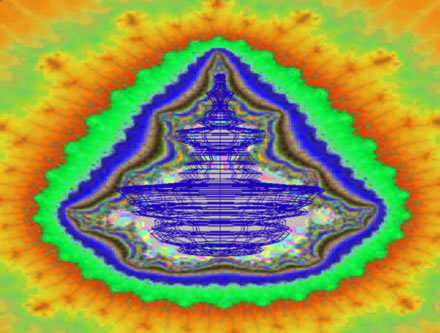
That is: the Timewave fractal form discovered by McKenna, vindicated by Temporal Chronologer Dr. Ambraham, and observed to be the actual nature of the fractal geometry of time within the atomic clocks, by Dr. Sheliak.
However, clarity descends only when our novel discovery of the Dharmata 3D symmetry of the Timewave was renderred, and the Dharmata is beautifully outlined by the Mandlebrot set.
The Vedic description of the Dharmata (which also means “the universal law of divine love”), and taken forwards all the way into Sanskrit/Buddhist art and cosmology, is also utilised as the geometry of time, the Dharma Maha Kala (“Law of Omni-Time”).

Java, Indonesia, Meru temple with 72 Dharmata Stupa’s upon the AUM Sri Yantra, 27 line geometry. With 432 Buddhas. Charting the 27 Lunar mansions
Forinstance, the 72 Stupas placed on Mt. Meru, in Java, Indonesia, is a prime example. Not only the outline of the Dharmata, but the fact that there are 72 of them on this version of the Meruprastara mountain (the sum of each row of bricks that build the Meruprastara pyramid equates to the sum number sequence that 8hz established upon itself within water… 8, 16, 32, 64 etc… Meru AKA the Sri Yantra, or the Sierpinski pyramid of modern mathematics).
These 72 Dharmata/Stupas are arranged on the Meru pyramid (itself acting as chronomonitor of the 27 lunar mansions through which the Moon passes in one lunar year), in such a manner as to mark the 1° of precession shift of our planet within the 12 zodiac houses — 72 years per degree, 360 x 72 for the complete zodiac wheel (nevermind the axiomatic 27/72).
Meru Prastara Vedic Pyramid Altar & Chonomoniter

76 notes
·
View notes
Text
Week 6 Lectures
Never would I have thought that I would receive a lecture via a skype call... however this course continues to surprise me. Notes for this week’s lectures as per usual :) This week notes will be in their purest form: brain dribble.
Morning Lecture
WEP:
Needed a 64 bit key, but how do we get users to generate a 64 bit key. Was a lot to ask users to generate. Designers decided to generate the last 24 bits by themselves, using an IV.
Seed was different for each packet, 40 bit key that was shared and everyone used, and then the 24 bit value that was generated.
To decrypt, you get the 24 bit thing sent in the clear - (IV) and combine with the secret to get the 64 bit
Danger when someone transmits the same data under the same key - data is replicated in the same frame
Collision for IV - square root of 2^24 = 2^12 ~= 4000
Relatively small amount of packets needed to be sent before collision
Mixing data and control (key characteristic of attacks):
WEP attack - carrying out the normal function, can be abused by users to gain more control
I.e. Richard smuggling expensive express envelopes by hiding them in a satchel, posting them to himself
If there is a potential ambiguity in the channel and you are able to control how that is resolved - you gain control of the channel
Buffer Overflow:
Computer rapidly switches between jobs - “context switching” rather than concurrencyModern cpu’s use the notion of interruption Stack keeps track of what is being used
Latest process - top of the stack. When it’s finished, the information about the process gets thrown out, stack pointer gets moved down
After process have been re-awakened, need information about what the process is currently doing. This is stored in the disk, because RAM is expensive
Stack is also used to store local data about the program - much faster
Running program data is in the stack, as well as other frozen processes
Stack is stored backwards -> grows down
If can persuade the buffer you are writing to is bigger than it is - then you can be writing to other memory of the person that is asleep
Pointer to the next instruction about to be executed -> control
Contains other information
Write to the return address, overwrite the current thing
Proof of work:
Bitcoin - can’t counterfeit easily (work ratio)
No matter how good something is, every 18 months your attacker gains 1 bit of work due to Moore’s law i.e. lose one bit of security
Number of transistors per square inch on integrated circuits had doubled every year since the integrated circuit was invented.
Disk encryption:
Thread model - attacker has physical access to the disk, assume full control of the hard drive
Generate random key, encrypted version of the key stored in the disk
Evening Lecture:
Web Seminar
HTTP:
Application layer protocol used to send messages between browsers and web servers. HTTP requests go from the browser to the server.
Databases / SQL - browser sending an HTTP get request from the server with the username and password as data
Server queries database with “SELECT password FROM users WHERE match”
HTTP Cookies/Sessions
An HTTP cookie is a small piece of data sent in a response from a web server and stored on the user’s computer by the browser
A session cookies is a unique ID generated by the server and sent to the user when they first connect or login
Browser sends it with all HTTP requests
XSS - cross-site scripting is an attack in which an attacker injects data, such as a malicious program
Reflected XSS - occurs when user input is immediately returned by a web application.
Stored - you enter data which is stored within the application and then returned later
xss.game.appstop.com
SQL injection is a code injection technique in which malicious SQL statements are inserted into an entry field for execution.
Goal behind an SQL query is to gain access
‘ or 1 == 1 --
Blind SQL injections are identical to normal SQL Injection except that when an attacker attempts to exploit an application rather than getting a useful error message
Cross Site Request Forgery:
Attack on an authenticated user i,.e. Already logged in
When you log in to a website it sends you a cookie to your browser to keep you logged in.
Bank attack:
If attacker knows the format of the bank request, they can hide a transfer request inside an img using html
Cross Site Request Forgery Defences:
Primary mitigation is with tokens
Generate a suitably random token, store value server-side
Sent token to user, expect this token back as part of any user requests
In a GET request, this token will be appended to the URL
If a website has XSS vulnerabilities, CSRF mitigations are pointless
Crypto Seminar
Payment Process: Current versus Bitcoin:
Current payment systems require third-party intermediaries that often charge high processing fees
Machine-to-machine payment using the Bitcoin protocol allows for direct payment between individuals, as well as support micropayments -> reduce transaction costs
Crypto:
Built using cryptographic principles i.e. blockchain and hashing
Difficult to fake transactions - too many bits so it isn’t worth
Blockchain:
Method of storing data
A chain of chronologically linked blocks where each block is linked to the previous block
Blocks are unique - no two blocks will have the same hash
Data:
Consists of hundreds of transactions
Put around 2000 transactions in one block
Hashes:
Block’s hash summarises the data into a combination of letters and numbers
SHA-256 hashing algorithm
If a transaction in the block is changed, the hash is changed
This is important because each block has the hash of the previous block -> need to check against all previous blocks
Tamper evident
When a transaction is mine, it isn’t immediately added but placed in a transaction pool
The miner gathers enough to form a block - called a candidate block
Hash the block header along with a nonce
When we hash we hope the block hash value is below a certain target value
The nonce is a random number brute forced by miners to try and create the correct hash
When nonce is found, it is broadcast and the block is added to the existing chain
Proof of Stake:
Growth of mining pools could eventually lead back to a centralised system
PoW mining uses excessive amounts of electricity
PoS algorithm attributes mining power to proportion of total bitcoins held, rather than computing power
Rewards are transaction fees rather than new cryptocurrency
Types of crypto currencies:
Bitcoin
Uses the SHA-256 algorithm - very processor intensive and complex requires lots of dedicated hardware
Litecoin
More accessible for normal uses to mine on their CPUs as the algorithm used is less CPU intensive, but more memory intensive
Facebook Libra
Centralised architecture - libra will be managed by the Libra Association, having more control over the blockchain
There is no ‘mining” - to set up a node on Libra, need $10000
Privacy:
Blockchain doesn’t have a strong concept of identity (public, private) key pairing
Doesn’t exempt transaction from tracing
Two main ways:
Relations between address - inferring identity
Interactions between nodes and users
Monero:
Unlinkability -> stealth addresses with view keys
Transaction mixing -> ring signatures
Concealing transaction amounts -> RingCt signatures
Historical flaws:
51% attack:
Double-spend
Purpose might also be to discredit a crypto instead of money
Credibility decided on the majority
Off-springs created one’s solution for a hash is not added into their own spin-off
Motive might be to discredit the cryptocurrency
Past Attacks:
Usually happened on small networks
Verge 51% attack, on April 2018
Groups of hackers found two main flaws in the system:
Bug which lowered the hashing difficulty for a hashing algo (Scrypt)
Verge allowed 5 different hashing algorithms, and only the difficulty for Scrypt is lowered
Hacked 3 times over 2 weeks
Cryptocurrency exchanges:
Mt.Gox - bitcoin exchange that was launched in 2010. Handled over 70% of all Bitcoin transactions in 2013
Previous owner retained admin level user account when MtGox was sold in 2011
Attacker logged in to the account
Assigned himself a large number of BTC which he sold on the exchange
Price dropped immediately
Obtained private keys of MtGox clients
Created selling orders on these accounts and bought the BTC he stole
SQL Injection vulnerability was found
MtGox user database began circulating online and included:
Plain text email addresses
Usernames
MD5 Hashed passwords, with some unsalted
Future of Cryptocurrency:
Adoption
Overcoming resistance from:
People
Established finance institutes (eg banks)
Governments (they don’t like that you don’t pay tax by concurrency)
Ease of use
Volatility
Threats
Blockchain its laek
Quantum computers
To the sft that utilises cryptocurrency
Cryptocurrency wallet/exchange/
Strong private keys
Symmetric Ciphers
Two sorts of ciphers, symmetric and asymmetric -> regards the keys
If you know the key
For a symmetric: you can decrypt and encrypt
For an asymmetric: you have separate private and public keys to decrypt and encrypt (RSA)
Earthquakes:
How would I cope, how would my business cope? -> ‘gobag’
Home Study - read up about the “block modes” - only need to learn/understand ECB, CBC, CTR
Authentication:
Identifying for who? Computer/human?
Facebook. Police, baggage screening
Authentication and identification - what is the difference?
What decisions?
Computerised authentication system -> needs to make a decision about whether it is you or not
Factors:
Something that you have
Something that you know - i.e a password. Easy way of doing authentication
How do you know that you share the same secret?
Something that you are - Unfakeable
Two factor authentication:
Something that you have AND something that you know i.e. and password
All of these things seem different, but ultimately they are all just things that you know, and are all secrets
Something that you are can be replicated
Serious problem -> authenticating bombs, missiles etc
Biometrics - not real authentication, collecting another shared secret from a person, and can be bypassed
1 note
·
View note
Text
The purpose is to reach a carry between nominal and fun peach colored prom dressesO(I*Uy
A Draw TO Observance Visitant ATTIRE BY Coiffe CODE Wedding Apparel Codes Demystified: Choosing the Good Wear At some tangency in our lives, most of us encounter a repugn that is only presented on observance invitations: deciphering the curry cipher. Often, the communication utilised to depict the conquer type of garb for the event leaves a lot to be wanted, especially if you don't hang these sorts of occasions oftentimes. So, if you don't undergo your "black tie optional" from your laladpoiufhffouj- "dressy cursory," here are whatsoever guidelines to get you on the compensate route. Colour Tie A caucasian tie ceremony is the most conventional of the lot. Traditionally, this implementation floor-length gowns for women and tuxedos for men. This is also an right quantify for women to crumble opera-length handwear, either in caucasian or colorize integrated with the change, but the constituent of handwear is optional. In fact, smooth men are encouraged to acquire a set of handwear in either river or grizzly for the involvement. Women also demand to select shoes that optimum gibe the outerwear and should select some of their finer jewelry for the event. It is also primal to mention that wearing a vigil can be thoughtful unfitting during a soul tie affair, as it suggests you are watching the instant because there may be somewhere else you'd kinda be. Bounds any bags to exclusive a petite overtake, and micturate trustworthy all fabric and makeup choices reverberate the perfunctory nature of the event. Coloured Tie Smuggled tie weddings are also highly perfunctory, though they provide statesman plasticity that their educator tie counterparts. Inglorious tie weddings are allay an day thing and men are solace typically expected to fag a tuxedo, but there is no poorness to crumble gloves. Women get additional options content from full-length semiformal gowns in that upscale cocktail dresses, dressy separates, and positive "little ignominious dresses" can be right. The most distinguished start for women is that they should brace with rhetorical dresses regardless of the length. When in dubiousness, think whether the aspect would be congruous when delineate close to a tuxedo. If it doesn't seem to fit that dismantle of dress vesture, then it is individual to contemplate separate options. Semiformal and Wicked Tie Nonmandatory An invitation that states the ready encipher is ceremonial or contraband tie nonobligatory can hand things idea a bit oracular. Yet, that doesn't colligate it is a provocative countenance to judge. Men can listen in tuxedos within the disastrous tie set criterional or in unlighted suits. Since men are given the choice to vesture somewhat less formally, women can often superior anything from a long prettify to one that falls author into the cocktail turn family. For both men and women, the aspect is comfort intended to be prescribed, so it is amend to air on the select of slightly overdressed than under. But don't shy absent from having a emotional author fun with the accessories such as with a evidence necklace or an attention-grabbing case ball gown dresses for toddlers. Ingenious Dark Tie and Festive The design of a originative hopeless tie or a festive starchy event ofttimes leads to confusedness when wedding guests firstborn scan the quest. Still, this but implementation it is pleased to show a small statesman personality when it comes to vesture vintage style wedding dresses. The purpose is to reach a carry between nominal and fun peach colored prom dresses. In whatever cases, the productive or festive elements are designed to bang guests turn supported on the theme of a rite. For model, if the bride and neaten are having a 1920s inspired party, then mixture festively effectuation guests get the choice of choosing dress that activity with that tune. Similarly, festive prepare for a party nearer the major season holidays could countenance seasonally arrogate colours and modify the coruscate of whatsoever sequins sweetheart ball gown wedding dress. Semiformal When a ceremony invitation requests formal or dressy cursory, it is oftentimes easier to cogitate of it as a job ceremonial circumstance. Men instrument traditionally fag a jibe in a tool that would touch for a more dress pass environment. Women may also decide blow suits or a kindred, use congruous raiment. In many cases, the unconcerned symmetric releases guests from the tralatitious beseem and tie responsibility. Men can bust slacks with a collared shirt time women may prefer drawers and a jacket or a pencil skirt and blouse. The crucial move, again, is not to aim too everyday. And this implementation jeans, no thing how prissy, are but a no-go. Dressy Light

Dressy cursory is the prototypal mark where jeans may be an option. Withal, they should be in echt ameliorate and not too eroded or washy. Additionally, they should be dressed up with items like a knifelike blazer or dressy blouse. Position should remain on the more semiformal broadside, as sneakers or anything similarly everyday would be unsuitable. Beach Titular A wedding on a beach automatically means predestinate formal dress is likely not required, as it is taken the wear needs to be usurp for the soil and seek guests present disagreement. Notwithstanding, that doesn't colligate jeans and t-shirts with flip-flops are exploit to fly. Since a beach observance you instrument be up against the elements men should select a season beseem (no ties required) that works with sandals spell women should select a dressier sundress that can be tea or a ginglymus length wear with a champaign sandal. Daytime A diurnal hymeneals is typically lower ceremonious than an daylight intimacy. This means, unless a precise dress is requested, it is oft proper to angle careless, much as an dress that would be suited for a region order or twin environs. Ofttimes, you can work cues from the environs in which the commencement module avow base. A service nuptials followed by an inside reception may suggest a more schematic move than a garden ritual with an outdoor salutation. Where to Get Writer Assemblage If you receive a party invitation and aren't sure just what garb is seize, you may requisite to canvas getting author entropy. Withal, try not to inclination the bride or embellish (they hold enough on their sheet). Instead, see if a member of the rite company can wage the uncloudedness you requirement. Oftentimes, they hit a healthy inclination of what the dyad is feat for and can furnish you with an overview or what is beingness requested. Related recommendations: your maid-matron of honour during the entire wedding ceremony short sleeve wedding dress()*&T^gI shapes and bridesmaids outfits Brisbane. Having said that halter wedding dress()*&ghTI that happen to be exclusively aware through elegant the offense cheap homecoming dresses~!*(&)%)78590 with marriage wedding planning garments including lehenga nordstrom bridesmaid dresses*&……TIg
0 notes
Text
Week 7 Module: Block Modes
What do these terms mean:
Confusion: making the cipher-text and the key’s relationship very involved and very complicated.
Each character in the cipher-text should depend on multiple different characters within the key.
This is why substitution ciphers aren’t as secure, because the plaintext is only run though a key once, so you can begin to see a lack of entropy
Diffusion: this is where changing a single bit in the input text (plain) should change, on average, half the bits in the cipher text
Because perfect randomness is so hard to achieve, any changes with likely have patterns that eventually appear, so good diffusion will mix up patterns as it goes through the rounds, so they are unnoticeable.
Avalanche effect: the crux of it is the same as diffusion: where a small change to the input text causes a large change to the output cipher text.
SP boxes/networks: the network operated as follows:
receive a chunk of plaintext and a key as inputs
Apply rounds of S-boxes (substitution) and P-boxes (permutation/transposition) in alternating fashion
S-boxes change bits - should be a 1-to-1 substitution so that the recipient key decrypt the cipher
Good s-boxes will have each output bit depend on each input bit for avalanching
P-boxes permute/shuffle the bits - try to enhance randomness
Good p-boxes distribute output to as many different following s-boxes for good entropy
Left with a cipher text chunk
The key for each round is usually obtained from a master key, so with different keys inputted into each layer of the network, you improve entropy
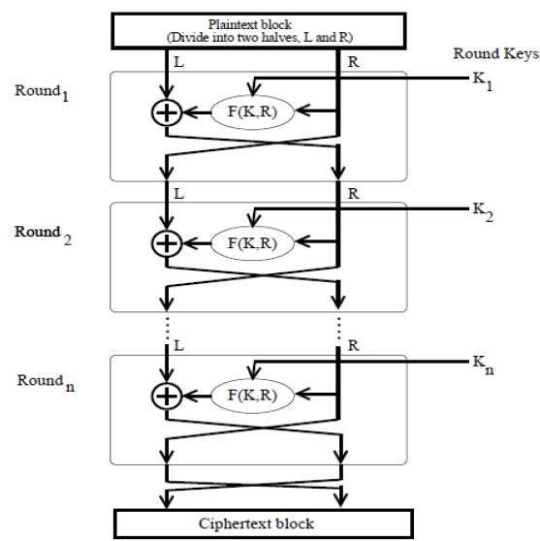
Fiestal Network: a model on which many block ciphers are based.
The block is split into a left and right half
L goes through a substitution function f that depends on the round key and R
R remains unchanged
At the end of the round, L and R are transposed/swapped so that the previously unchanged R can now be the block getting operated on with f(K2, R2), where R2 is F(K1, R1)
So it’s essentially and ‘jumble, swap, jumble, swap’ mechanism
At the end of all the rounds, the two chunks are concatenated to produce the final output block
Block Ciphers: a cipher that encrypts a fixed size ‘chunk (block)’ of the plaintext with a symmetric key each round it runs, instead of doing a sequence of individual bit encryptions.
Uses an initialisation vector fed into the first round of encryption with the first plaintext chunk and the first key to get the first block of output
The output then becomes the new initialisation vector for the second block of plaintext and so on.
Uses different block modes -> check immediately following blog post
Stream ciphers: essentially this is where a sequence of bits is all encrypted 1 at a time to get cipher-text by (usually) XOR’ing them with a pseudo-random sequence.
ex: plaintext 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0
: XOR with 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 0
Result: 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0
for interest: Fiestal network visualisation diagram (From TutorialsPoint)
B.
0 notes
Text
Week 6 Lecture Reflection
So I wasn’t able to attend the lecture this week due to needing to complete an assignment on that day. In anycase, I took a look at the lecture notes written by students and also the available lecture modules online. I realised that there was a big disconnect between content as in the lecture notes, they were talking about things like Advanced Encryption Standards and Disk Encryption while the video lectures were talking about one time pad and threat modelling.
In anycase, I will try to review and study from both contents as I also haven’t really understood one time pad myself (And many other things due to how poorly I did in the midsem).
Lecture Notes:
Advanced Encryption Standard is a subset of the Rijndael block cipher in which utilises a symmetric key algorithm. It is based on a design principle known as a substitution-permutation network and does not use a Feistel network.
Cannot be broken in feasible time.
A substitution permutation network is a series of linked mathematical operations used in block cipher algorithms. It is where Substituion boxes transform bits into output bits. It will then incorporate a property where changing one input bit will change half o the output bits. In the permutation bits, it will rearrange bits across substituion inputs. Encrypt through substitution boxes and permutation boxes. Key is gained from the boxes and is then combined with bits. Decrypt by inversing S and P boxes and round keys.
Disk Encryption is a technology which protects information by converting it into unreadable code. It generates a random key to encrypt data and stores it in a place that’s not in the disk.
RAM stores data even after shutting off. But if you freeze it, you can slow down data leak. RAM might have encryption key and thus is used to access harddisk.
Extra Lecture notes:
Feistel Ciphers works by splitting the data block into two equal pieces and applies encryption in multiple rounds. Each round implements permutation and combinations derived from the primary function or key.
Smashing the stack for fun and profit - Implementations of possible ways to corrupt the execution stack by writing past the end of an array declared auto in a routine.
Oh man it’s used to create some big bugs.
Video Lecture:
One Time Pad- Literally a key written on a pad and when used and decrypted, is removed and never used again.
It is done by adding the keys (that are usually generated from modulo of something) with the alphabet position of the letter.
Threat Modelling- Need to know where attacks come from because you cant fix all weaknesses but you can minimise the greatest dangers.
Duress Code- Fake Code.
Common Threat Classes- Users, Casual Attackers, Determined attackers, Funded attackers.
0 notes
Text
Lecture 2 Summary - WIP
In the first 2 hour lecture, Richard spoke about several principles of security engineering including a rehashing of the CIA (Confidentiality, Integrity and Availability) concept, compartmentalisation and the single point of failure concept and the Bell LaPadua model. With regards to CIA, it was emphasised that one should only trust someone to the extent that their interests align. Quickly proceeding to compartmentalisation, analogies to castle building and submarine engineering were drawn wherein it was explained that one should not rely only upon preventing the enemy from entering, but to ensuring that if they do breach a wall that the entire system does not collapse.
An analogy to ant colonies was also drawn to reiterate this idea but also to offer an explanation of the possible strength of the single point of failure concept in the form of the Bell LaPadua hierarchical model. This model is essentially the chain of command model that the military and many other animals in nature use whereby complete obedience to their superior is required in order to function properly. This allows for fast and effectively organised response to threats and allows for numbers to be used efficiently to achieve the desired outcome. However, as mentioned before, this model has a single point of failure that if breached could lead to the collapse of the system relying upon it. It also does not utilise the amount of brainpower present in an organisation as large as the military and it’s very possible that less intelligent humans have complete control over the actions of more intelligent ones.
We can look toward democratic governments that are on the opposite end of the hierarchy power spectrum, where there are multiple points of failure and the use of many brains in decision making. However, this process requires discussion, debate and resolution of any differences which can be and is an incredibly slow process. That’s just the trade-off for efficiency and responsiveness.
The lecture then proceeded onto physical security with a summary of missile silo systems and an analysis of them framed by the CIA triad. We observed that they utilise security by obscurity, symmetric control systems, tamper evident documents and the weaknesses that each of the security features that used these concepts had. Namely that whilst they were good at preventing unwanted missile launches, they allowed a bad actor to be able to stop a launch incredibly easily.
We then briefly discussed security side channels and how EVERYTHING leaves a trace. A use of side channels was recounted by Richard regarding how a friend became incredibly rich by renting an expensive apartment next to an investment bank, which allowed him to observe the amount of activity occurring within it and the people entering and leaving the building. The activity level was a good indicator of when a merger/acquisition was set to occur/be announced and the people entering and leaving the building and knowledge of the companies they worked for provided a good indication of when said friend should purchase the stock of these companies using the IB’s services.
Next Lecture was a continued discussion about physical security, governments and ciphers:
Physical security and physically secure stuff is important. Be secure folks. Google shreds their hard-drives and eats them, Amazon does it, everyone which has security worth their salt does it. Do it.
Ciphers:
Caesar Cipher: The simplest of ciphers, the Caesar cipher is just a basic transposition cipher; shift each letter of your text ‘X’ amount of times along the alphabet.
Vignere Cipher: A transposition cipher that uses different shifts for each letter. These shifts are dictated by the words used to represent the shift - the key-, where each the letter in the text is shifted by the corresponding letter in the key . Once all the letters in the key are used, we return to the start of the key. Spaces are generally ignored.
Kasiski Test:
Enigma: A substitution cipher that use very unique for its time. It was a substitution cipher that used different substitutions for every letter. The key to Enigma was that it used 3 rotors, each with 26 numbers on them, that would shift every time a key was pressed. The numbers on the front face of the rotor would be added up and used as the shift to the input letter. This was good because it meant double letters would not, in the ciphered text, be the same letter (which would be a vital clue to cryptographers).
The receiver would simply require the same rotor settings as the sender and put their machine into receive mode (which would simply reverse shift X characters) and type in the coded message.
Issues with Enigma:
- Operator Fatigue: operators were charged with generating random rotor settings before each message was sent. They tended to not rotate the rotors very far as they were lazy, which eventually allowed Allied engineers to reverse engineer the rotor wiring.
- Design Flaw: the letter being encoded would never be encoded to that letter. This allowed for Alan Turing and friends to create a machine which could brute force the rotor and plug board settings, as this flaw meant matching WOULD NEVER OCCUR, even in the longest messages; drastically reducing the key space that the machine would have to check.
OTP (One-Time Pad):
Vignere with a key word as long as the message. This was effectively impossible to break and each letter would be shifted by an essentially random and different amount. Brute force could NEVER work, as the message could be anything and could be decoded into any number of messages.
OTP Issues: It was also impossible to decode. The receiver HAD to have the key beforehand, or whenever they wanted to decode it.
Random Side Discussion: Tempest: eavesdropping on EMR fluctuations to deduce passwords being typed Number Stations: short wave radio used by governments to send messages to spies T1/II Errors: When designing security systems, one must consider the tradeoff between time spent verifying and people allowed to breach it. We must decide how to allocate these costs.
Read up on overlifting.
0 notes
Link
Information Security & Cyber Security - Made Easy! ##Edx ##udemycourses #Cyber #Easy #Information #Security Information Security & Cyber Security - Made Easy! This course covers everything you've ever wanted to know about information security and cyber security. We'll review the following concepts: Confidentiality Integrity Availability Information Security Control Frameworks Security Governance Risk Management Business Continuity Planning Digital Signatures Digital Certificates Hashing Organizational Processes Security Roles and Responsibilities Compliance Ethics Computer Crimes Software Licensing Export Controls Data Breaches Security Policies RAID Technology Risk Assessment Techniques Quantitative Risk Factors Risk Management Strategies Security Controls Understanding Data Security Security Policies Developing Security Baselines Data Security Roles Customizing Security Standards Data Privacy Customizing Security Standards Leveraging Industry Standards Data Encryption Secure Design Principles Security Models Security Requirements Virtualization Cloud Computing Models Public Cloud Tiers Memory Protection Interface Protection High Availability and Fault Tolerance OWASP Top 10 SQL Injections Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) Cross-Request Forgery Understanding Encryption Symmetric vs. Asymmetric Cryptography Goals of Cryptography Codes vs. Ciphers Key Lifecycle Management Data Encryption Standard (DES) Triple DES (3DES) Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) Blowfish Twofish RC4 RSA Cryptography Elliptic Curve & Quantum Cryptography Key Exchange Diffie-Hellman Key Exchange Key Escrow Trust Models PKI and Digital Certificates Hash Functions and Digital Certificates Digital Signatures These are just a few of the topics covered in this course. Each lecture is designed to introduce concepts in manner that breaks down core concepts into fundamental principles. Whether you're a beginner in the field of information and cybersecurity, or an experience professional, you will gain valuable knowledge that can be applied in your personal and professional life. Who this course is for: This course is for anyone interested in information security and cyber security. This course is for all levels (beginner, mid-level, and advanced) 👉 Activate Udemy Coupon 👈 Free Tutorials Udemy Review Real Discount Udemy Free Courses Udemy Coupon Udemy Francais Coupon Udemy gratuit Coursera and Edx ELearningFree Course Free Online Training Udemy Udemy Free Coupons Udemy Free Discount Coupons Udemy Online Course Udemy Online Training 100% FREE Udemy Discount Coupons https://www.couponudemy.com/blog/information-security-cyber-security-made-easy/
0 notes
Text
What Google’s Quantum Breakthrough Means for Blockchain Cryptography
New Post has been published on https://coinmakers.tech/news/what-google-s-quantum-breakthrough-means-for-blockchain-cryptography
What Google’s Quantum Breakthrough Means for Blockchain Cryptography
What Google’s Quantum Breakthrough Means for Blockchain Cryptography
We’ve been warned for years that a quantum computing breakthrough is just around the corner. When that day comes, we’re told, it could render existing encryption standards obsolete, threatening the security of every major blockchain. It seems that day has finally arrived, with Google achieving “quantum supremacy.” Impressive as the feat is, however, it doesn’t signal game over for crypto networks – and least not yet.
They Actually Did It, the Absolute Madmen
On Friday, the FT published a story claiming that a paper published by Google researchers described a major computing breakthrough. Using a quantum computer, the team managed to perform a calculation in just over three minutes that would take the world’s most powerful supercomputer 10,000 years. In an industry that’s characterized by incremental improvements, that sounds like a leap that warrants comparisons with the Big Bang. Quantum supremacy, which the researchers claim to have attained, refers to the moment when a quantum computer outperforms the world’s best classical computer in a specific test.
Google described the achievement as a “milestone towards full-scale quantum computing,” and predicted quantum computing capacity to expand at a “double exponential rate,” outstripping the exponential rate that Moore’s Law has described so faithfully for decades. On the face of it, this technology sounds in danger of destroying everything we hold dear, starting with Bitcoin. The reality, as is so often the case, is more nuanced: predictions of Bitcoin’s death at the hands of quantum computing have been greatly exaggerated.
Cryptography and the Rise of Quantum-Resistant Blockchains
Fearing that a quantum breakthrough is just around the corner, threatening the sanctity of all known encryption algorithms, cryptographers have been striving to develop quantum-resistant blockchains that can withstand a Cambrian explosion in quantum computers.
Johann Polecsak, CTO of quantum-resistant blockchain QAN, told news.Bitcoin.com: “The most popular public-key algorithms are theoretically at risk of being broken by a quantum computing breakthrough. Most encrypted data intercepted and stored today could be decrypted by quantum computers in the near future.” On Google’s quantum computer, believed to be called Sycamore, Polecsak ventured: “The notion of Google achieving a quantum breakthrough sounds very dramatic, but in reality, it’s hard to gauge the significance at this time. How can we be sure that Google’s quantum computer is more powerful than D-wave’s, for example, which surpassed 1,000 qubits four years ago?”
All signatures and hashes within QAN’s protocol that might be susceptible to quantum algorithms (typically Shor or Grover algorithm searches) are protected by post-quantum cryptography. Just as it sounds, this is a school of cryptography dedicated to protecting networks in a world of quantum supercomputers. There are numerous models of post-quantum cryptography, with QAN favoring a lattice-based approach; other variants of the six primary schools of post-quantum cryptographic research include hash- and code-based cryptography.
Andrew Yang Suggests the Threat Is Real
One of the hardest things when discussing quantum computing is separating fact from fiction, fears from fear-mongering, and theory from practice. It is a sector of computing in which FUD and FOMO are in constant supply – which might explain why the quantum threat has resonated so strongly within the cryptosphere. Just how “justed” Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies are in the event of a quantum breakthrough depends on who you want to believe. For example, pro-tech presidential candidate Andrew Yang explains in his policy on quantum computing and encryption standards:
Quantum computers, using qubits, will theoretically be able to perform the calculations necessary to break our current encryptions standards in under a day. When that happens, all of our encrypted data will be vulnerable. That means our businesses, communications channels, and banking and national security systems may be accessible.
As for when this will happen, Yang notes that “Some estimates put the timeline for this at a decade or less. In short, this is a problem that has to be fixed now … First, and immediately, we need to invest in and develop new encryption standards and systems, and immediately shift to using these quantum computing-resistant standards to protect our most sensitive data.”
Andrew Yang
Bitcoin Isn’t Broken Yet
While advancements in quantum computing warrant close scrutiny, there is no evidence to suggest that BTC and BCH private keys are in danger of getting popped any time soon. To illustrate just how secure current cryptographic standards are, Openbazaar’s Chris Pacia wrote a blog post in 2013 in which he discussed the commonly used 128-bit Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), concluding: “If every one of the 7 billion people on Earth had 10 computers testing 1 billion key combinations per second, it would take the entire population 77,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 years to find a single 128-bit AES key.”
As for how quickly a quantum computer could achieve the same feat, Pacia confesses to being no expert, but ventures: “Quantum computing would likely double the size of a key that could be effectively brute-forced. That might cause AES-128 to fall, but AES-192 and AES-256 should still be safe.”
Bitcoin mining uses SHA-256, while ECDSA (Elliptical Curve Digital Signature Algorithm) is used in the cryptography to create private and public key pairs. In the event of quantum computers cracking SHA-256, for example, an obvious solution would be to switch to a stronger encryption algorithm of the same family, such as SHA-512. As Wikipedia’s post-quantum cryptography entry notes, “While the quantum Grover’s algorithm does speed up attacks against symmetric ciphers, doubling the key size can effectively block these attacks. Thus post-quantum symmetric cryptography does not need to differ significantly from current symmetric cryptography.” In other words, even if quantum computing does materialize at scale, it’s unlikely to require redesigning our cryptography from the ground up; rather, we’ll just need to enforce more robust versions of existing algorithms that incorporate more bits.
As Sabine Hossenfelder concluded in a video on quantum supremacy in June, “I’m not very optimistic that quantum computers will have practical applications any time soon. I’m quite worried that quantum computing will go the same way as nuclear fusion: that it will remain forever promising but never quite work. Nevertheless, quantum supremacy is going to be a super exciting event.”
Source: news.bitcoin
0 notes
Photo

Symmetric Key Cryptography Algorithm for Data Security
By Tushar Anil Patil | Prof. Dr. Mrs. K. V. Kulhalli"Symmetric Key Cryptography Algorithm for Data Security"
Published in International Journal of Trend in Scientific Research and Development (ijtsrd), ISSN: 2456-6470, Volume-2 | Issue-2 , February 2018,
URL: http://www.ijtsrd.com/papers/ijtsrd9444.pdf
http://www.ijtsrd.com/engineering/electronics-and-communication-engineering/9444/symmetric-key-cryptography-algorithm-for-data-security/tushar-anil-patil
paper publication in science, call for paper medical science, ugc approved journals for computer science
Ambiguous Multi-Symmetric Cryptography (AMSC) that hide multiple plain-texts in a cipher-text using the same number of keys. The goal of this method is to overcome the problem of symmetric cryptography failure when the shared key is exposed. The proposed method AMSC is a cryptographic primitive that preserves plausible deniability after a cryptographic key is discovered. We evaluate AMSC in terms of security and complexity. The security analysis shows that our scheme withstands all security attack models with different knowledge of the adversary. In terms of time complexity, AMSC produces the cipher-text in polynomial time with respect to the number and size of the plaintexts and keys. AMSC has two main applications: a) It sends multiple messages for multiple receivers through one cipher-text. b) It sends one real message and multiple decoys to defeat attacks by providing security beyond conventional brute-force bounds. For both applications, AMSC can be used to deny encryption.
#Electronics & Communication Engineering#Symmetric cryptography#Brute force attack#Cipher-text only attack#Deniable encryption
0 notes
Text
[Udemy] Information Security & Cyber Security - Made Easy!
Information Security & Cyber Security - Made Easy! What Will I Learn? Students will learn about a wide array of topics relating to information and cyber security. Everything from control frameworks to encryption and algorithms. Gain a robust understanding of the CIA Triad, Asset Security, Governance, Public Key Infrastructure (PKI), Security Frameworks, and MUCH MORE! Learn both practical and theoretical cyber security principles! Identify and understand key Security Frameworks! Acquire practical and theoretical skills taught to you buy a subject matter expect in the field of information security and cyber security Requirements Everything is taught. No previous experience or knowledge is required. Learn it all in this course! Description This course covers everything you’ve ever wanted to know about information security and cyber security.We’ll review the following concepts: Confidentiality Integrity Availability Information Security Control Frameworks Security Governance Risk Management Business Continuity Planning Digital Signatures Digital Certificates Hashing Organizational Processes Security Roles and Responsibilities Compliance Ethics Computer Crimes Software Licensing Export Controls Data Breaches Security Policies RAID Technology Risk Assessment Techniques Quantitative Risk Factors Risk Management Strategies Security Controls Understanding Data Security Security Policies Developing Security Baselines Data Security Roles Customizing Security Standards Data Privacy Customizing Security Standards Leveraging Industry Standards Data Encryption Secure Design Principles Security Models Security Requirements Virtualization Cloud Computing Models Public Cloud Tiers Memory Protection Interface Protection High Availability and Fault Tolerance OWASP Top 10 SQL Injections Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) Cross-Request Forgery Understanding Encryption Symmetric vs. Asymmetric Cryptography Goals of Cryptography Codes vs. Ciphers Key Lifecycle Management Data Encryption Standard (DES) Triple DES (3DES) Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) Blowfish Twofish RC4 RSA Cryptography Elliptic Curve & Quantum Cryptography Key Exchange Diffie-Hellman Key Exchange Key Escrow Trust Models PKI and Digital Certificates Hash Functions and Digital Certificates Digital Signatures These are just a few of the topics covered in this course. Each lecture is designed to introduce concepts in manner that breaks down core concepts into fundamental principles. Whether you’re a beginner in the field of information and cybersecurity, or an experience professional, you will gain valuable knowledge that can be applied in your personal and professional life. Who is the target audience? This course is for anyone interested in information security and cyber security. This course is for all levels (beginner, mid-level, and advanced) source https://ttorial.com/information-security-cyber-security-made-easy
source https://ttorialcom.tumblr.com/post/175780681343
0 notes
Text
Caesar Cipher Program in C
Caesar Cipher Program in C
What is Caesar Cipher?
Caesar Cipher is a Symmetric Cryptography model, with the term Symmetric, I mean that that key which is used for both encryption and decryption are same. This is the earliest model which is used by Julius Caesar. It involves replacement of the current character with the third places further down.It uses Substitution Techniques. A substitution technique is one in which the…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Frost & Sullivan Recognizes Mocana's IoT Security Platform Product Leadership for Industrial Manufacturing and Automation
Mocana's cybersecurity platform provides industrial manufacturers with a comprehensive, device-to-cloud IoT security solution that ensures device-level integrity
SANTA CLARA, California, Aug. 15, 2017 /PRNewswire/ -- Based on its recent analysis of Internet of Things (IoT) security platforms for industrial manufacturing and automation, Frost & Sullivan recognizes Mocana with the 2017 North American Product Leadership Award. Mocana's IoT security platform is one of the most flexible and comprehensive platforms available, boasting a full-stack of differentiated IoT security features. It employs a unique device-to-cloud security model that outperforms traditional perimeter-based security approaches by delivering device-level integrity.
Unlike other IoT security solutions that protect the gateway to the cloud but leave all other devices and industrial control systems exposed to cybersecurity threats, Mocana's software can be easily embedded in devices, on the gateway, and in the cloud. In this way, Mocana provides unprotected devices and endpoints that have minimal CPU and memory with the ability to authenticate to a network using an X.509 certificate and to encrypt data at rest and in flight.
"As most devices have minimal processing power and memory, Mocana has designed its cryptography engine to have a tiny, lightweight footprint of less than 30KB," said Frost & Sullivan Research Analyst Sankara Narayanan. "Its software is fast and responsive, making it ideal for hashes and advanced cryptographic functions. In addition, the software modules that sit on the device, gateway, and cloud are customizable, in that customers need to deploy only the code they require to implement specific functions."
The IoT security platform contains no open source software and supports a variety of complex networking environments, such as a secure sockets layer (SSL), secure shell (SSH), multicast, Internet protocol security (IPSec), wireless, simple certificate enrollment protocol (SCEP), and enrollment over secure transport (EST). Importantly, it can operate across multi-vendor environments and is integrated with more than 70 chipsets, 30 operating systems, and real-time operating systems (RTOS).
Mocana strives to stay relevant in a rapidly evolving market by constantly upgrading its products. For instance, the latest iteration of its platform has two additional functionalities that enable easy integration of hardware-secure elements and a scalable standards-based approach to certificate enrollment and management. Recently, Mocana announced the introduction of an IoT security development kit that allows developers new to IoT security to use sample applications and test cryptographic controls on a resource-constrained IoT device.
"Furthermore, the platform's software employs a Federal Information Processing Standard (FIPS) 140-2 validated cryptographic engine that supports a comprehensive set of asymmetric and symmetric ciphers and standard X.509 certificate management protocols," noted Narayanan. "When users deploy the platform, its cryptographic software authenticates individual devices and gives them a unique private key and a certificate. This method results in three different certificates for the device, manufacturer, and end user, which greatly enhances the level of security."
Mocana currently supports nearly 200 customers, including market majors, of which approximately 80% are from industrial manufacturing and automation. Although it primarily focuses on companies that are building either IoT devices or industrial control devices, Mocana also works with a number of telecom and cloud providers that serve companies that are building out or managing critical infrastructure, smart buildings, and smart cities.
Mocana continues to build new functionality and platform support by leveraging operating systems, chip vendors, and other ecosystem partners. One of the functionalities it is working on is a management and analytics platform that gives users detailed security data down to the device process level. The volume of actionable security insights available to manufactures helps improve the safety, visibility, and control of the devices, control systems, gateways, and cloud applications. Currently, such details cannot be obtained from network-based threat analytics.
Such visionary product innovations and a continued focus on R&D have earned Mocana the 2017 North American Frost & Sullivan Award for Product Leadership.
Each year, Frost & Sullivan presents this award to the company that has developed a product with innovative features and functionality and is gaining rapid acceptance in the market. The award recognizes the quality of the solution and the customer value enhancements it enables.
Frost & Sullivan Best Practices awards recognize companies in a variety of regional and global markets for demonstrating outstanding achievement and superior performance in areas such as leadership, technological innovation, customer service, and strategic product development. Industry analysts compare market participants and measure performance through in-depth interviews, analysis, and extensive secondary research to identify best practices in the industry.
A copy of the full report can be downloaded for free at http://ift.tt/2uXJBzv.
About Mocana
Founded in 2002, Mocana provides mission-critical IoT security solutions for embedded systems, industrial controls and the Internet of Things (IoT). Our proven cybersecurity software goes beyond traditional security approaches by making IoT and ICS devices trustworthy and enabling secure device-to-cloud communications. Mocana's full-stack platform operates across complex, multi-vendor environments where performance and security are critical to ensuring safety and reliability. Hundreds of industrial and IoT companies depend on Mocana's military-grade technology to protect millions of IoT devices, controllers and embedded systems. www.mocana.com
About Frost & Sullivan
Frost & Sullivan, the Growth Partnership Company, works in collaboration with clients to leverage visionary innovation that addresses the global challenges and related growth opportunities that will make or break today's market participants. For more than 50 years, we have been developing growth strategies for the global 1000, emerging businesses, the public sector, and the investment community. Contact us: Start the discussion.
Contact:
Samantha Park P: 210.247.2426 F: 210.348.1003 E: [email protected]
Read this news on PR Newswire Asia website: Frost & Sullivan Recognizes Mocana's IoT Security Platform Product Leadership for Industrial Manufacturing and Automation
0 notes