#where sql statement
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
0 notes
Text
on wanting to do a million things
prompted by @bloodshack 's
i wanna learn SQL but i wanna learn haskell but i wanna learn statistics but i wanna start a degree in macroeconomics also sociology also library science but i wanna learn norwegian but i wanna learn mandarin but i wanna paint but i wanna do pottery but i wanna get better at woodworking but i wanna get better at cooking but i wanna bake one of those cakes that's just 11 crepes stacked on top of each other but i wanna watch more movies but i wanna listen to more podcast episodes but i need to rest but i need to exercise but i wanna play with my dog but i wanna go shopping but i need to go grocery shopping but i need to do the dishes but i need to do laundry but i need to buy a new x y and z but i need to save money but i wanna give all my money away to people who need it more but i wanna pivot my career to book editing but to do that i have to read more and i wanna read more nonfiction but i wanna read more novels but i wanna get better at meditating but i wanna volunteer but i wanna plan a party but i wanna go to law school. but what im gonna do is watch a dumbass youtube video and go to bed
I think I've been doing slightly better this year about Actually Doing Things. not great! but I do a lot and I've been "prototyping" ways to get closer to doing as much as is possible. and if I actually talk about it it's a bunch of very obvious statements but I'll try to make them a little more concrete
rule number one: experiment on yourself
there's no one approach that's right for everyone and there's not even one approach for me that works at all times. try things out. see what works. pay attention to what doesn't. try something else.
rule number two: ask what's stopping you and then take it seriously
example: I often want to do Everything in the evening at like 2 PM, but then get home and am tempted sorely by the couch, and then get stuck inertia'd and not doing much but being tired and kind of bored. why?
if I don't have plans, it's easy to leave work later than planned and hard to make myself do something by a specific time
i'm generally tiredish after work. 4 out of 5 times, that'll go away if I actually start Doing Something, but 1 out of 5 it's real and I will go hardcore sleepmode at 8 PM and just be Done
i use up a ton of my program management/executive function/Deciding Things brain at work and usually find it noticeably harder to string together "want to do Thing > make list of Things > decide on a Thing > do Thing" after I'm home. Even if I have a list of Things to Do, how does one decide! how does one start! and god forbid there's a Necessary thing. then it's all downhill
therefore, mitigations: have concrete time-specific plans in advance.
if I have an art class at 6:00 PM I need to leave work by 5:15 and NO LATER and I can't get sucked into "oh 10 more minutes to finish this" *one hour later*
that also means I have to have a fridge or freezer dinner ready and can't spend 45 minutes cooking "fuck it, what the hell did I put in the fridge, why don't we have soy sauce" evil meal that is not good
plans with friends: dinner! art night! music night! repair-your-clothes night! seeing a show! occasionally, Accountability Time where a friend comes over for We Are Doing Tasks with tea and snacks etc.
for some reason I'm way better about Actually Doing Things when the plan exists already. magically I overcome couch inertia even though I am the same amount of tired! and while I never learn the ability to decouch without plans I at least learn to make them
still working on:
a "prototype" for maybe next month is a weeklyish Study Session for a thing I want to learn about. I want to somehow make it employer-proof (I am accountable to some entity to being at place X at time Y) and haven't figured out a good way. Maybe I can leverage that the local library is open til 8 on wednesdays and somehow make it a Thing? maybe I'll try it!
oh god oh fuck the thing about plans is that if you want to have them you need to make them. christ. a lot of the time I can cover this with some combo of weekend planning + recurring events (things like weekly friend dinner/weekly class) + having cool friends who reach out proactively but it still requires active planning and it can fall thru the cracks
rule three: cool friends
they can take you to things
they can remind you that you can do whatever the fuck you please
i have a friend who is somehow Always doing cool classes and learning shit. and this reminds me that I can ... do that. and sometimes I do
you can take them to things!!
rule four: try to kill the anon hate in your head
obv this depends on your circumstance but sometimes it's worth it to me to look at constraints that "feel real" and check whether they're an active choice I made thoughtfully or, like, the specters of people I don't know judging my choices
time and money are obvious ones. recently was gently nudged towards looking at whether i could give myself more time to Do Things by cooking less. imaginary specters of judgmental twitterites: "it's illegal to spend money. if you get takeout you're the first up against the wall when the revoution comes. make all your lunches and dinners and hoard the money for Later. for Something. how dare you get lunch at the store. you bourgeois hoe. taking charity donations from the mouths of the poor cause you don't have your life together enough to cook artisanal bespoke dinners every night. fuck you." and obviously eating takeout 24/7 is not the answer, but realizing I was not making an active choice helped me try making the active choice instead. "how much do I actually want to balance cost, time, tastiness, and wastefulness of my food, given my amount of free time and my salary and the tradeoff against doing something else? can I approach it differently to do more quick cheap food + some takeout?" -> current prototype: substitute in 1 takeout dinner or restaurant-with-friends a week, 1 frozen type dinner, and then batch cook or sandwiches lunches w/ "permission" to get fast lunch at the store. we'll see how it goes!
i am really really bad at this and find it helpful to talk to other people who can help point out when I'm being haunted by ghosts about it.
rule five: what would it take? what's the next step?
this one i give a lot of credit to @adiantum-sporophyte in particular for, especially for prompting me with questions when I muse about the million-ideal-lives on car rides. what would it look like to do xyz? what's something I could do right now to move in that direction? what's the obstacle? like, actually ask the question and think through it. with a person talking to you! damn! maybe the obstacle to x is that I don't know if I'll like it or if I just like the idea of it. and I don't want to commit to x without knowing. Okay, so maybe an approach would be to find someone who does x and talk to them about how their life is, or maybe it's "spend 15 minutes looking up intro-to-x near me", or "actively schedule 1 instance of x", or something like that. Or maybe it's that I don't know what it takes to do x. Okay, how about on Tues after dinner Adiantum fixes a sweater at my apartment while I spend 20 min looking at prereqs for x. like, it's so basic to say "to do a thing, you could try figuring out how to do it" but I think the important thing here is the feedback/prompting to even recognize "hey, step back, if you don't know the next step then figuring out the next step is the next step"
rule six: habits
prototyping: exercise
I do a lot better when I exercise in the mornings. I do a lot better when I do PT exercises regularly. For a while I was doing PT with friend in the morning every morning before work (accountability! a friendly face to make it more pleasant!) but that didn't really solve - it's not the kind of exercise that makes me feel awake/active, it's like dumb little foot botherings. but: having the habit of morning exercise made it easier to swap out 2 of the 5 days for more intense exercise, and then to swap those 2 for a different more intense exercise when I needed a break. it's easier to build a low-effort version of the habit and then work in the higher-effort one than to just Decide to be the kind of person who gets up at ass o clock to do cardio or whatever
rule seven: set up the structure of your life to make it easy
this is also a "duh" thing but like. on so many levels it comes down to structure your life to make the choice more doable. this can be something like "i structure my life to make vegetarian cooking baseline and vegan cooking the majority by stocking the pantry with staples and spices from cuisines that work well that way" or "i chose an apartment that lets me commute by bike" or "i have my camping gear put away in a fashion that makes it easier to gather frequently and lowers the barrier to trips" or "i keep physical books around to prompt myself to read xyz" to "i don't use instagram or twitter or snapchat or facebook" to . idk.
and in terms of charitable giving: similar deal. I have an explicit budget at the beginning of the year (~10% of my before-tax income), I know in advance what charities I give to, and I know what timing I will use (basically, alerts for donation matching around specific fundraising times). Anything outside the Plan comes from my discretionary budget/fun money. That makes it less of a mental load (the choice is already made; I don't grapple with every donation request or every bleeding-heart trap because I have a very solid anchor on "I give to xyz, the money's set aside") and it's armor against impulsive-but-not-useful scrupulosity. I structure the rest of my spending/life to prioritize a set amount and it makes it easier to follow through
rule eight: if you can do it at work a tiny bit that counts for real life
(infrequently used)
"hi mr. manager I think it would be great if I could use enough SQL to make basic queries in the database so we don't have to go through the software team for common/basic questions. I'd like to take 1 hr on Friday to go through some basic tutorials and then 1 hr with Pat on Monday so he can walk me through an intro for our specific use case. I estimate this will help save the team a couple hours a week of waiting for answers from the other team." and then you have enough of a handle with baby's first SQL that you can add little bits and bobs as you exercise it. this is responsible for a medium amount of my knowledge of python and all 3 brain cells worth of SQL.
rule nine: life is an optimization problem
not in, like, "you need to optimize your skincare and career and exercise and social life and have everything all at once" that's not what optimization means. optimization is like, maximize something with respect to a set of constraints. i explicitly Do Not do skincare beyond "wash face" and "sunscreen" bc I want to optimize my life for like looking at weird plants in the mountains. explicitly choosing to put time and money elsewhere! can't have it all all at once. so fuck them pores. who give a shit. yeah i ate a lot of protein shakes instead of home cooked breakfasts this week bc i was prioritizing morning exercise. im looking at this beautiful bug and it doesn't know what fashion is or what my resume looks like. im holding a lizard. im not spending time on picking cool clothes or whatever bc i spent that time looking up lizard hotspots on purpose.
that's really long and probably mostly, like, not surprising? but i keep benefiting from ppl being like "hey have you considered Obvious Thing" framed very gently
99 notes
·
View notes
Text
SQL Fundamentals #2: SQL Data Manipulation
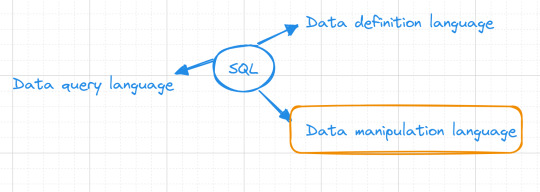
In our previous database exploration journey, SQL Fundamentals #1: SQL Data Definition, we set the stage by introducing the "books" table nestled within our bookstore database. Currently, our table is empty, Looking like :
books
| title | author | genre | publishedYear | price |
Data manipulation

Now, let's embark on database interaction—data manipulation. This is where the magic happens, where our "books" table comes to life, and we finish our mission of data storage.
Inserting Data
Our initial task revolves around adding a collection of books into our "books" table. we want to add the book "The Great Gatsby" to our collection, authored F. Scott Fitzgerald. Here's how we express this in SQL:
INSERT INTO books(title, author, genre, publishedYear, price) VALUES('The Great Gatsby', 'F. Scott Fitzgerald', 'Classic', 1925, 10.99);
Alternatively, you can use a shorter form for inserting values, but be cautious as it relies on the order of columns in your table:
INSERT INTO books VALUES('The Great Gatsby', 'F. Scott Fitzgerald', 'Classic', 1925, 10.99);
Updating data
As time goes on, you might find the need to modify existing data in our "books" table. To accomplish this, we use the UPDATE command.For example :
UPDATE books SET price = 12.99 WHERE title = 'The Great Gatsby';
This SQL statement will locate the row with the title "The Great Gatsby" and modify its price to $12.99.
We'll discuss the where clause in (SQL fundamentals #3)
Deleting data
Sometimes, data becomes obsolete or irrelevant, and it's essential to remove it from our table. The DELETE FROM command allows us to delete entire rows from our table.For example :
DELETE FROM books WHERE title = 'Moby-Dick';
This SQL statement will find the row with the title "Moby-Dick" and remove it entirely from your "books" table.
To maintain a reader-friendly and approachable tone, I'll save the discussion on the third part of SQL, which focuses on data querying, for the upcoming post. Stay tuned ...
#studyblr#code#codeblr#javascript#java development company#study#progblr#programming#studying#comp sci#web design#web developers#web development#website design#webdev#website#tech#sql#sql course#mysql#datascience#data#backend
45 notes
·
View notes
Text
SQL Injection in RESTful APIs: Identify and Prevent Vulnerabilities
SQL Injection (SQLi) in RESTful APIs: What You Need to Know
RESTful APIs are crucial for modern applications, enabling seamless communication between systems. However, this convenience comes with risks, one of the most common being SQL Injection (SQLi). In this blog, we’ll explore what SQLi is, its impact on APIs, and how to prevent it, complete with a practical coding example to bolster your understanding.

What Is SQL Injection?
SQL Injection is a cyberattack where an attacker injects malicious SQL statements into input fields, exploiting vulnerabilities in an application's database query execution. When it comes to RESTful APIs, SQLi typically targets endpoints that interact with databases.
How Does SQL Injection Affect RESTful APIs?
RESTful APIs are often exposed to public networks, making them prime targets. Attackers exploit insecure endpoints to:
Access or manipulate sensitive data.
Delete or corrupt databases.
Bypass authentication mechanisms.
Example of a Vulnerable API Endpoint
Consider an API endpoint for retrieving user details based on their ID:
from flask import Flask, request import sqlite3
app = Flask(name)
@app.route('/user', methods=['GET']) def get_user(): user_id = request.args.get('id') conn = sqlite3.connect('database.db') cursor = conn.cursor() query = f"SELECT * FROM users WHERE id = {user_id}" # Vulnerable to SQLi cursor.execute(query) result = cursor.fetchone() return {'user': result}, 200
if name == 'main': app.run(debug=True)
Here, the endpoint directly embeds user input (user_id) into the SQL query without validation, making it vulnerable to SQL Injection.
Secure API Endpoint Against SQLi
To prevent SQLi, always use parameterized queries:
@app.route('/user', methods=['GET']) def get_user(): user_id = request.args.get('id') conn = sqlite3.connect('database.db') cursor = conn.cursor() query = "SELECT * FROM users WHERE id = ?" cursor.execute(query, (user_id,)) result = cursor.fetchone() return {'user': result}, 200
In this approach, the user input is sanitized, eliminating the risk of malicious SQL execution.
How Our Free Tool Can Help
Our free Website Security Checker your web application for vulnerabilities, including SQL Injection risks. Below is a screenshot of the tool's homepage:
Upload your website details to receive a comprehensive vulnerability assessment report, as shown below:
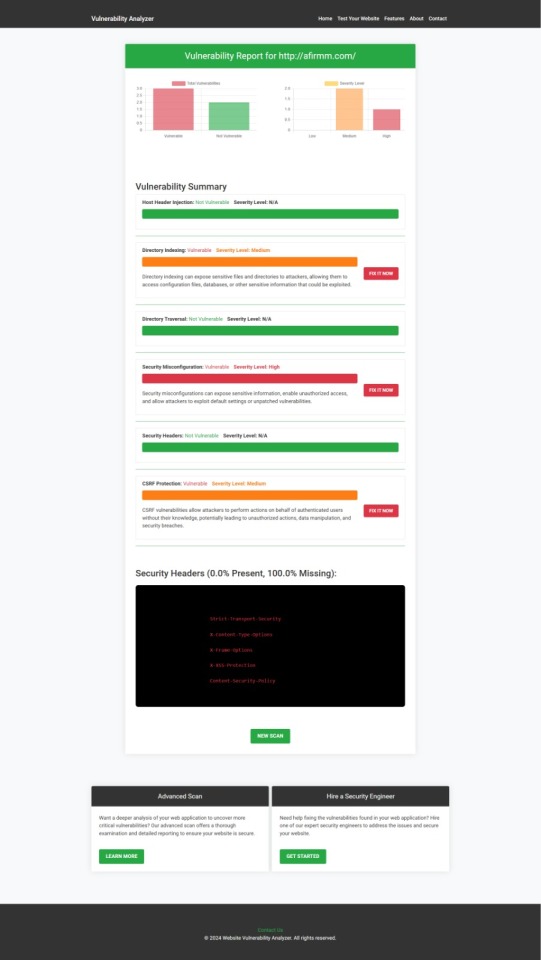
These tools help identify potential weaknesses in your APIs and provide actionable insights to secure your system.
Preventing SQLi in RESTful APIs
Here are some tips to secure your APIs:
Use Prepared Statements: Always parameterize your queries.
Implement Input Validation: Sanitize and validate user input.
Regularly Test Your APIs: Use tools like ours to detect vulnerabilities.
Least Privilege Principle: Restrict database permissions to minimize potential damage.
Final Thoughts
SQL Injection is a pervasive threat, especially in RESTful APIs. By understanding the vulnerabilities and implementing best practices, you can significantly reduce the risks. Leverage tools like our free Website Security Checker to stay ahead of potential threats and secure your systems effectively.
Explore our tool now for a quick Website Security Check.
#cyber security#cybersecurity#data security#pentesting#security#sql#the security breach show#sqlserver#rest api
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
SQLi Potential Mitigation Measures
Phase: Architecture and Design
Strategy: Libraries or Frameworks
Use a vetted library or framework that prevents this weakness or makes it easier to avoid. For example, persistence layers like Hibernate or Enterprise Java Beans can offer protection against SQL injection when used correctly.
Phase: Architecture and Design
Strategy: Parameterization
Use structured mechanisms that enforce separation between data and code, such as prepared statements, parameterized queries, or stored procedures. Avoid constructing and executing query strings with "exec" to prevent SQL injection [REF-867].
Phases: Architecture and Design; Operation
Strategy: Environment Hardening
Run your code with the minimum privileges necessary for the task [REF-76]. Limit user privileges to prevent unauthorized access if an attack occurs, such as by ensuring database applications don’t run as an administrator.
Phase: Architecture and Design
Duplicate client-side security checks on the server to avoid CWE-602. Attackers can bypass client checks by altering values or removing checks entirely, making server-side validation essential.
Phase: Implementation
Strategy: Output Encoding
Avoid dynamically generating query strings, code, or commands that mix control and data. If unavoidable, use strict allowlists, escape/filter characters, and quote arguments to mitigate risks like SQL injection (CWE-88).
Phase: Implementation
Strategy: Input Validation
Assume all input is malicious. Use strict input validation with allowlists for specifications and reject non-conforming inputs. For SQL queries, limit characters based on parameter expectations for attack prevention.
Phase: Architecture and Design
Strategy: Enforcement by Conversion
For limited sets of acceptable inputs, map fixed values like numeric IDs to filenames or URLs, rejecting anything outside the known set.
Phase: Implementation
Ensure error messages reveal only necessary details, avoiding cryptic language or excessive information. Store sensitive error details in logs but be cautious with content visible to users to prevent revealing internal states.
Phase: Operation
Strategy: Firewall
Use an application firewall to detect attacks against weaknesses in cases where the code can’t be fixed. Firewalls offer defense in depth, though they may require customization and won’t cover all input vectors.
Phases: Operation; Implementation
Strategy: Environment Hardening
In PHP, avoid using register_globals to prevent weaknesses like CWE-95 and CWE-621. Avoid emulating this feature to reduce risks. source
3 notes
·
View notes
Note
What are some of your favorite parts of Haskell? Do you know any other languages?
Haskell's mathematical completeness is super cool. It's quite amazing that you can actually prove, with a theorem, that the language doesn't have any ambiguous statements. (I don't know exactly how the theorem goes, I haven't dug into it enough to word it properly, but it's cool.) Also, it's just fun to solve problems in functional programming; it requires a whole different section of my brain from my usual programming.
My bread and butter, the language I use for work as well as my personal projects, is Python. It's the language I'm most fluent in by a long shot; there's no delay between coming up with an idea and executing it in code. I know there are a lot of folks who aren't fond of Python, and to be fair people try to apply it where it's just not really a good tool, but as a rapid prototyping, data manipulation, and fun-code-toy language it's phenomenal. Also there's a package for, like, everything.
I've used a TON of other languages in bits and pieces in the past -- Java, C++, a bit of C#, a lot of SQL and HTML (neither is exactly a PROGRAMMING language, but eh) and a lot of obscure math languages like Magma, GAP, and Macsyma.
The thing I'm most interested to learn is Lean, a theorem proving language. It's pretty amazing what you can do with it, and I think it'll revolutionize math academia once it's in wide use.
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
25 Udemy Paid Courses for Free with Certification (Only for Limited Time)

2023 Complete SQL Bootcamp from Zero to Hero in SQL
Become an expert in SQL by learning through concept & Hands-on coding :)
What you'll learn
Use SQL to query a database Be comfortable putting SQL on their resume Replicate real-world situations and query reports Use SQL to perform data analysis Learn to perform GROUP BY statements Model real-world data and generate reports using SQL Learn Oracle SQL by Professionally Designed Content Step by Step! Solve any SQL-related Problems by Yourself Creating Analytical Solutions! Write, Read and Analyze Any SQL Queries Easily and Learn How to Play with Data! Become a Job-Ready SQL Developer by Learning All the Skills You will Need! Write complex SQL statements to query the database and gain critical insight on data Transition from the Very Basics to a Point Where You can Effortlessly Work with Large SQL Queries Learn Advanced Querying Techniques Understand the difference between the INNER JOIN, LEFT/RIGHT OUTER JOIN, and FULL OUTER JOIN Complete SQL statements that use aggregate functions Using joins, return columns from multiple tables in the same query
Enroll Now 👇👇👇👇👇👇👇 https://www.book-somahar.com/2023/10/25-udemy-paid-courses-for-free-with.html
Python Programming Complete Beginners Course Bootcamp 2023
2023 Complete Python Bootcamp || Python Beginners to advanced || Python Master Class || Mega Course
What you'll learn
Basics in Python programming Control structures, Containers, Functions & Modules OOPS in Python How python is used in the Space Sciences Working with lists in python Working with strings in python Application of Python in Mars Rovers sent by NASA
Enroll Now 👇👇👇👇👇👇👇 https://www.book-somahar.com/2023/10/25-udemy-paid-courses-for-free-with.html
Learn PHP and MySQL for Web Application and Web Development
Unlock the Power of PHP and MySQL: Level Up Your Web Development Skills Today
What you'll learn
Use of PHP Function Use of PHP Variables Use of MySql Use of Database
Enroll Now 👇👇👇👇👇👇👇 https://www.book-somahar.com/2023/10/25-udemy-paid-courses-for-free-with.html
T-Shirt Design for Beginner to Advanced with Adobe Photoshop
Unleash Your Creativity: Master T-Shirt Design from Beginner to Advanced with Adobe Photoshop
What you'll learn
Function of Adobe Photoshop Tools of Adobe Photoshop T-Shirt Design Fundamentals T-Shirt Design Projects
Enroll Now 👇👇👇👇👇👇👇 https://www.book-somahar.com/2023/10/25-udemy-paid-courses-for-free-with.html
Complete Data Science BootCamp
Learn about Data Science, Machine Learning and Deep Learning and build 5 different projects.
What you'll learn
Learn about Libraries like Pandas and Numpy which are heavily used in Data Science. Build Impactful visualizations and charts using Matplotlib and Seaborn. Learn about Machine Learning LifeCycle and different ML algorithms and their implementation in sklearn. Learn about Deep Learning and Neural Networks with TensorFlow and Keras Build 5 complete projects based on the concepts covered in the course.
Enroll Now 👇👇👇👇👇👇👇 https://www.book-somahar.com/2023/10/25-udemy-paid-courses-for-free-with.html
Essentials User Experience Design Adobe XD UI UX Design
Learn UI Design, User Interface, User Experience design, UX design & Web Design
What you'll learn
How to become a UX designer Become a UI designer Full website design All the techniques used by UX professionals
Enroll Now 👇👇👇👇👇👇👇 https://www.book-somahar.com/2023/10/25-udemy-paid-courses-for-free-with.html
Build a Custom E-Commerce Site in React + JavaScript Basics
Build a Fully Customized E-Commerce Site with Product Categories, Shopping Cart, and Checkout Page in React.
What you'll learn
Introduction to the Document Object Model (DOM) The Foundations of JavaScript JavaScript Arithmetic Operations Working with Arrays, Functions, and Loops in JavaScript JavaScript Variables, Events, and Objects JavaScript Hands-On - Build a Photo Gallery and Background Color Changer Foundations of React How to Scaffold an Existing React Project Introduction to JSON Server Styling an E-Commerce Store in React and Building out the Shop Categories Introduction to Fetch API and React Router The concept of "Context" in React Building a Search Feature in React Validating Forms in React
Enroll Now 👇👇👇👇👇👇👇 https://www.book-somahar.com/2023/10/25-udemy-paid-courses-for-free-with.html
Complete Bootstrap & React Bootcamp with Hands-On Projects
Learn to Build Responsive, Interactive Web Apps using Bootstrap and React.
What you'll learn
Learn the Bootstrap Grid System Learn to work with Bootstrap Three Column Layouts Learn to Build Bootstrap Navigation Components Learn to Style Images using Bootstrap Build Advanced, Responsive Menus using Bootstrap Build Stunning Layouts using Bootstrap Themes Learn the Foundations of React Work with JSX, and Functional Components in React Build a Calculator in React Learn the React State Hook Debug React Projects Learn to Style React Components Build a Single and Multi-Player Connect-4 Clone with AI Learn React Lifecycle Events Learn React Conditional Rendering Build a Fully Custom E-Commerce Site in React Learn the Foundations of JSON Server Work with React Router
Enroll Now 👇👇👇👇👇👇👇 https://www.book-somahar.com/2023/10/25-udemy-paid-courses-for-free-with.html
Build an Amazon Affiliate E-Commerce Store from Scratch
Earn Passive Income by Building an Amazon Affiliate E-Commerce Store using WordPress, WooCommerce, WooZone, & Elementor
What you'll learn
Registering a Domain Name & Setting up Hosting Installing WordPress CMS on Your Hosting Account Navigating the WordPress Interface The Advantages of WordPress Securing a WordPress Installation with an SSL Certificate Installing Custom Themes for WordPress Installing WooCommerce, Elementor, & WooZone Plugins Creating an Amazon Affiliate Account Importing Products from Amazon to an E-Commerce Store using WooZone Plugin Building a Customized Shop with Menu's, Headers, Branding, & Sidebars Building WordPress Pages, such as Blogs, About Pages, and Contact Us Forms Customizing Product Pages on a WordPress Power E-Commerce Site Generating Traffic and Sales for Your Newly Published Amazon Affiliate Store
Enroll Now 👇👇👇👇👇👇👇 https://www.book-somahar.com/2023/10/25-udemy-paid-courses-for-free-with.html
The Complete Beginner Course to Optimizing ChatGPT for Work
Learn how to make the most of ChatGPT's capabilities in efficiently aiding you with your tasks.
What you'll learn
Learn how to harness ChatGPT's functionalities to efficiently assist you in various tasks, maximizing productivity and effectiveness. Delve into the captivating fusion of product development and SEO, discovering effective strategies to identify challenges, create innovative tools, and expertly Understand how ChatGPT is a technological leap, akin to the impact of iconic tools like Photoshop and Excel, and how it can revolutionize work methodologies thr Showcase your learning by creating a transformative project, optimizing your approach to work by identifying tasks that can be streamlined with artificial intel
Enroll Now 👇👇👇👇👇👇👇 https://www.book-somahar.com/2023/10/25-udemy-paid-courses-for-free-with.html
AWS, JavaScript, React | Deploy Web Apps on the Cloud
Cloud Computing | Linux Foundations | LAMP Stack | DBMS | Apache | NGINX | AWS IAM | Amazon EC2 | JavaScript | React
What you'll learn
Foundations of Cloud Computing on AWS and Linode Cloud Computing Service Models (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS) Deploying and Configuring a Virtual Instance on Linode and AWS Secure Remote Administration for Virtual Instances using SSH Working with SSH Key Pair Authentication The Foundations of Linux (Maintenance, Directory Commands, User Accounts, Filesystem) The Foundations of Web Servers (NGINX vs Apache) Foundations of Databases (SQL vs NoSQL), Database Transaction Standards (ACID vs CAP) Key Terminology for Full Stack Development and Cloud Administration Installing and Configuring LAMP Stack on Ubuntu (Linux, Apache, MariaDB, PHP) Server Security Foundations (Network vs Hosted Firewalls). Horizontal and Vertical Scaling of a virtual instance on Linode using NodeBalancers Creating Manual and Automated Server Images and Backups on Linode Understanding the Cloud Computing Phenomenon as Applicable to AWS The Characteristics of Cloud Computing as Applicable to AWS Cloud Deployment Models (Private, Community, Hybrid, VPC) Foundations of AWS (Registration, Global vs Regional Services, Billing Alerts, MFA) AWS Identity and Access Management (Mechanics, Users, Groups, Policies, Roles) Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) - (AMIs, EC2 Users, Deployment, Elastic IP, Security Groups, Remote Admin) Foundations of the Document Object Model (DOM) Manipulating the DOM Foundations of JavaScript Coding (Variables, Objects, Functions, Loops, Arrays, Events) Foundations of ReactJS (Code Pen, JSX, Components, Props, Events, State Hook, Debugging) Intermediate React (Passing Props, Destrcuting, Styling, Key Property, AI, Conditional Rendering, Deployment) Building a Fully Customized E-Commerce Site in React Intermediate React Concepts (JSON Server, Fetch API, React Router, Styled Components, Refactoring, UseContext Hook, UseReducer, Form Validation)
Enroll Now 👇👇👇👇👇👇👇 https://www.book-somahar.com/2023/10/25-udemy-paid-courses-for-free-with.html
Run Multiple Sites on a Cloud Server: AWS & Digital Ocean
Server Deployment | Apache Configuration | MySQL | PHP | Virtual Hosts | NS Records | DNS | AWS Foundations | EC2
What you'll learn
A solid understanding of the fundamentals of remote server deployment and configuration, including network configuration and security. The ability to install and configure the LAMP stack, including the Apache web server, MySQL database server, and PHP scripting language. Expertise in hosting multiple domains on one virtual server, including setting up virtual hosts and managing domain names. Proficiency in virtual host file configuration, including creating and configuring virtual host files and understanding various directives and parameters. Mastery in DNS zone file configuration, including creating and managing DNS zone files and understanding various record types and their uses. A thorough understanding of AWS foundations, including the AWS global infrastructure, key AWS services, and features. A deep understanding of Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) foundations, including creating and managing instances, configuring security groups, and networking. The ability to troubleshoot common issues related to remote server deployment, LAMP stack installation and configuration, virtual host file configuration, and D An understanding of best practices for remote server deployment and configuration, including security considerations and optimization for performance. Practical experience in working with remote servers and cloud-based solutions through hands-on labs and exercises. The ability to apply the knowledge gained from the course to real-world scenarios and challenges faced in the field of web hosting and cloud computing. A competitive edge in the job market, with the ability to pursue career opportunities in web hosting and cloud computing.
Enroll Now 👇👇👇👇👇👇👇 https://www.book-somahar.com/2023/10/25-udemy-paid-courses-for-free-with.html
Cloud-Powered Web App Development with AWS and PHP
AWS Foundations | IAM | Amazon EC2 | Load Balancing | Auto-Scaling Groups | Route 53 | PHP | MySQL | App Deployment
What you'll learn
Understanding of cloud computing and Amazon Web Services (AWS) Proficiency in creating and configuring AWS accounts and environments Knowledge of AWS pricing and billing models Mastery of Identity and Access Management (IAM) policies and permissions Ability to launch and configure Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) instances Familiarity with security groups, key pairs, and Elastic IP addresses Competency in using AWS storage services, such as Elastic Block Store (EBS) and Simple Storage Service (S3) Expertise in creating and using Elastic Load Balancers (ELB) and Auto Scaling Groups (ASG) for load balancing and scaling web applications Knowledge of DNS management using Route 53 Proficiency in PHP programming language fundamentals Ability to interact with databases using PHP and execute SQL queries Understanding of PHP security best practices, including SQL injection prevention and user authentication Ability to design and implement a database schema for a web application Mastery of PHP scripting to interact with a database and implement user authentication using sessions and cookies Competency in creating a simple blog interface using HTML and CSS and protecting the blog content using PHP authentication. Students will gain practical experience in creating and deploying a member-only blog with user authentication using PHP and MySQL on AWS.
Enroll Now 👇👇👇👇👇👇👇 https://www.book-somahar.com/2023/10/25-udemy-paid-courses-for-free-with.html
CSS, Bootstrap, JavaScript And PHP Stack Complete Course
CSS, Bootstrap And JavaScript And PHP Complete Frontend and Backend Course
What you'll learn
Introduction to Frontend and Backend technologies Introduction to CSS, Bootstrap And JavaScript concepts, PHP Programming Language Practically Getting Started With CSS Styles, CSS 2D Transform, CSS 3D Transform Bootstrap Crash course with bootstrap concepts Bootstrap Grid system,Forms, Badges And Alerts Getting Started With Javascript Variables,Values and Data Types, Operators and Operands Write JavaScript scripts and Gain knowledge in regard to general javaScript programming concepts PHP Section Introduction to PHP, Various Operator types , PHP Arrays, PHP Conditional statements Getting Started with PHP Function Statements And PHP Decision Making PHP 7 concepts PHP CSPRNG And PHP Scalar Declaration
Enroll Now 👇👇👇👇👇👇👇 https://www.book-somahar.com/2023/10/25-udemy-paid-courses-for-free-with.html
Learn HTML - For Beginners
Lean how to create web pages using HTML
What you'll learn
How to Code in HTML Structure of an HTML Page Text Formatting in HTML Embedding Videos Creating Links Anchor Tags Tables & Nested Tables Building Forms Embedding Iframes Inserting Images
Enroll Now 👇👇👇👇👇👇👇 https://www.book-somahar.com/2023/10/25-udemy-paid-courses-for-free-with.html
Learn Bootstrap - For Beginners
Learn to create mobile-responsive web pages using Bootstrap
What you'll learn
Bootstrap Page Structure Bootstrap Grid System Bootstrap Layouts Bootstrap Typography Styling Images Bootstrap Tables, Buttons, Badges, & Progress Bars Bootstrap Pagination Bootstrap Panels Bootstrap Menus & Navigation Bars Bootstrap Carousel & Modals Bootstrap Scrollspy Bootstrap Themes
Enroll Now 👇👇👇👇👇👇👇 https://www.book-somahar.com/2023/10/25-udemy-paid-courses-for-free-with.html
JavaScript, Bootstrap, & PHP - Certification for Beginners
A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners interested in learning JavaScript, Bootstrap, & PHP
What you'll learn
Master Client-Side and Server-Side Interactivity using JavaScript, Bootstrap, & PHP Learn to create mobile responsive webpages using Bootstrap Learn to create client and server-side validated input forms Learn to interact with a MySQL Database using PHP
Enroll Now 👇👇👇👇👇👇👇 https://www.book-somahar.com/2023/10/25-udemy-paid-courses-for-free-with.html
Linode: Build and Deploy Responsive Websites on the Cloud
Cloud Computing | IaaS | Linux Foundations | Apache + DBMS | LAMP Stack | Server Security | Backups | HTML | CSS
What you'll learn
Understand the fundamental concepts and benefits of Cloud Computing and its service models. Learn how to create, configure, and manage virtual servers in the cloud using Linode. Understand the basic concepts of Linux operating system, including file system structure, command-line interface, and basic Linux commands. Learn how to manage users and permissions, configure network settings, and use package managers in Linux. Learn about the basic concepts of web servers, including Apache and Nginx, and databases such as MySQL and MariaDB. Learn how to install and configure web servers and databases on Linux servers. Learn how to install and configure LAMP stack to set up a web server and database for hosting dynamic websites and web applications. Understand server security concepts such as firewalls, access control, and SSL certificates. Learn how to secure servers using firewalls, manage user access, and configure SSL certificates for secure communication. Learn how to scale servers to handle increasing traffic and load. Learn about load balancing, clustering, and auto-scaling techniques. Learn how to create and manage server images. Understand the basic structure and syntax of HTML, including tags, attributes, and elements. Understand how to apply CSS styles to HTML elements, create layouts, and use CSS frameworks.
Enroll Now 👇👇👇👇👇👇👇 https://www.book-somahar.com/2023/10/25-udemy-paid-courses-for-free-with.html
PHP & MySQL - Certification Course for Beginners
Learn to Build Database Driven Web Applications using PHP & MySQL
What you'll learn
PHP Variables, Syntax, Variable Scope, Keywords Echo vs. Print and Data Output PHP Strings, Constants, Operators PHP Conditional Statements PHP Elseif, Switch, Statements PHP Loops - While, For PHP Functions PHP Arrays, Multidimensional Arrays, Sorting Arrays Working with Forms - Post vs. Get PHP Server Side - Form Validation Creating MySQL Databases Database Administration with PhpMyAdmin Administering Database Users, and Defining User Roles SQL Statements - Select, Where, And, Or, Insert, Get Last ID MySQL Prepared Statements and Multiple Record Insertion PHP Isset MySQL - Updating Records
Enroll Now 👇👇👇👇👇👇👇 https://www.book-somahar.com/2023/10/25-udemy-paid-courses-for-free-with.html
Linode: Deploy Scalable React Web Apps on the Cloud
Cloud Computing | IaaS | Server Configuration | Linux Foundations | Database Servers | LAMP Stack | Server Security
What you'll learn
Introduction to Cloud Computing Cloud Computing Service Models (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS) Cloud Server Deployment and Configuration (TFA, SSH) Linux Foundations (File System, Commands, User Accounts) Web Server Foundations (NGINX vs Apache, SQL vs NoSQL, Key Terms) LAMP Stack Installation and Configuration (Linux, Apache, MariaDB, PHP) Server Security (Software & Hardware Firewall Configuration) Server Scaling (Vertical vs Horizontal Scaling, IP Swaps, Load Balancers) React Foundations (Setup) Building a Calculator in React (Code Pen, JSX, Components, Props, Events, State Hook) Building a Connect-4 Clone in React (Passing Arguments, Styling, Callbacks, Key Property) Building an E-Commerce Site in React (JSON Server, Fetch API, Refactoring)
Enroll Now 👇👇👇👇👇👇👇 https://www.book-somahar.com/2023/10/25-udemy-paid-courses-for-free-with.html
Internet and Web Development Fundamentals
Learn how the Internet Works and Setup a Testing & Production Web Server
What you'll learn
How the Internet Works Internet Protocols (HTTP, HTTPS, SMTP) The Web Development Process Planning a Web Application Types of Web Hosting (Shared, Dedicated, VPS, Cloud) Domain Name Registration and Administration Nameserver Configuration Deploying a Testing Server using WAMP & MAMP Deploying a Production Server on Linode, Digital Ocean, or AWS Executing Server Commands through a Command Console Server Configuration on Ubuntu Remote Desktop Connection and VNC SSH Server Authentication FTP Client Installation FTP Uploading
Enroll Now 👇👇👇👇👇👇👇 https://www.book-somahar.com/2023/10/25-udemy-paid-courses-for-free-with.html
Linode: Web Server and Database Foundations
Cloud Computing | Instance Deployment and Config | Apache | NGINX | Database Management Systems (DBMS)
What you'll learn
Introduction to Cloud Computing (Cloud Service Models) Navigating the Linode Cloud Interface Remote Administration using PuTTY, Terminal, SSH Foundations of Web Servers (Apache vs. NGINX) SQL vs NoSQL Databases Database Transaction Standards (ACID vs. CAP Theorem) Key Terms relevant to Cloud Computing, Web Servers, and Database Systems
Enroll Now 👇👇👇👇👇👇👇 https://www.book-somahar.com/2023/10/25-udemy-paid-courses-for-free-with.html
Java Training Complete Course 2022
Learn Java Programming language with Java Complete Training Course 2022 for Beginners
What you'll learn
You will learn how to write a complete Java program that takes user input, processes and outputs the results You will learn OOPS concepts in Java You will learn java concepts such as console output, Java Variables and Data Types, Java Operators And more You will be able to use Java for Selenium in testing and development
Enroll Now 👇👇👇👇👇👇👇 https://www.book-somahar.com/2023/10/25-udemy-paid-courses-for-free-with.html
Learn To Create AI Assistant (JARVIS) With Python
How To Create AI Assistant (JARVIS) With Python Like the One from Marvel's Iron Man Movie
What you'll learn
how to create an personalized artificial intelligence assistant how to create JARVIS AI how to create ai assistant
Enroll Now 👇👇👇👇👇👇👇 https://www.book-somahar.com/2023/10/25-udemy-paid-courses-for-free-with.html
Keyword Research, Free Backlinks, Improve SEO -Long Tail Pro
LongTailPro is the keyword research service we at Coursenvy use for ALL our clients! In this course, find SEO keywords,
What you'll learn
Learn everything Long Tail Pro has to offer from A to Z! Optimize keywords in your page/post titles, meta descriptions, social media bios, article content, and more! Create content that caters to the NEW Search Engine Algorithms and find endless keywords to rank for in ALL the search engines! Learn how to use ALL of the top-rated Keyword Research software online! Master analyzing your COMPETITIONS Keywords! Get High-Quality Backlinks that will ACTUALLY Help your Page Rank!
Enroll Now 👇👇👇👇👇👇👇 https://www.book-somahar.com/2023/10/25-udemy-paid-courses-for-free-with.html
#udemy#free course#paid course for free#design#development#ux ui#xd#figma#web development#python#javascript#php#java#cloud
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
In the early twenty-first century, SQL injection is a common (and easily preventable) form of cyber attack. SQL databases use SQL statements to manipulate data. For example (and simplified), "Insert 'John' INTO Enemies;" would be used to add the name John to a table that contains the list of a person's enemies. SQL is usually not done manually. Instead it would be built into a problem. So if somebody made a website and had a form where a person could type their own name to gain the eternal enmity of the website maker, they might set things up with a command like "Insert '<INSERT NAME HERE>' INTO Enemies;". If someone typed 'Bethany' it would replace <INSERT NAME HERE> to make the SQL statement "Insert 'Bethany' INTO Enemies;"
The problem arises if someone doesn't type their name. If they instead typed "Tim' INTO Enemies; INSERT INTO [Friends] SELECT * FROM [Powerpuff Girls];--" then, when <INSERT NAME HERE> is replaced, the statement would be "Insert 'Tim' INTO Enemies; INSERT INTO [Friends] SELECT * FROM [Powerpuff Girls];--' INTO Enemies;" This would be two SQL commands: the first which would add 'Tim' to the enemy table for proper vengeance swearing, and the second which would add all of the Powerpuff Girls to the Friend table, which would be undesirable to a villainous individual.
SQL injection requires knowing a bit about the names of tables and the structures of the commands being used, but practically speaking it doesn't take much effort to pull off. It also does not take much effort to stop. Removing any quotation marks or weird characters like semicolons is often sufficient. The exploit is very well known and many databases protect against it by default.
People in the early twenty-first century probably are not familiar with SQL injection, but anyone who works adjacent to the software industry would be familiar with the concept as part of barebones cybersecurity training.
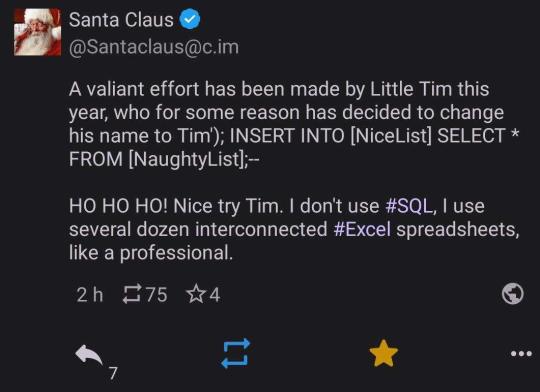
#period novel details#explaining the joke ruins the joke#not explaining the joke means people 300 years from now won't understand our culture#hacking is usually much less sophisticated than people expect#lots of trial and error#and relying on other people being lazy
20K notes
·
View notes
Text
How to Improve Database Performance with Smart Optimization Techniques
Database performance is critical to the efficiency and responsiveness of any data-driven application. As data volumes grow and user expectations rise, ensuring your database runs smoothly becomes a top priority. Whether you're managing an e-commerce platform, financial software, or enterprise systems, sluggish database queries can drastically hinder user experience and business productivity.
In this guide, we’ll explore practical and high-impact strategies to improve database performance, reduce latency, and increase throughput.
1. Optimize Your Queries
Poorly written queries are one of the most common causes of database performance issues. Avoid using SELECT * when you only need specific columns. Analyze query execution plans to understand how data is being retrieved and identify potential inefficiencies.
Use indexed columns in WHERE, JOIN, and ORDER BY clauses to take full advantage of the database indexing system.
2. Index Strategically
Indexes are essential for speeding up data retrieval, but too many indexes can hurt write performance and consume excessive storage. Prioritize indexing on columns used in search conditions and join operations. Regularly review and remove unused or redundant indexes.
3. Implement Connection Pooling
Connection pooling allows multiple application users to share a limited number of database connections. This reduces the overhead of opening and closing connections repeatedly, which can significantly improve performance, especially under heavy load.
4. Cache Frequently Accessed Data
Use caching layers to avoid unnecessary hits to the database. Frequently accessed and rarely changing data—such as configuration settings or product catalogs—can be stored in in-memory caches like Redis or Memcached. This reduces read latency and database load.
5. Partition Large Tables
Partitioning splits a large table into smaller, more manageable pieces without altering the logical structure. This improves performance for queries that target only a subset of the data. Choose partitioning strategies based on date, region, or other logical divisions relevant to your dataset.
6. Monitor and Tune Regularly
Database performance isn’t a one-time fix—it requires continuous monitoring and tuning. Use performance monitoring tools to track query execution times, slow queries, buffer usage, and I/O patterns. Adjust configurations and SQL statements accordingly to align with evolving workloads.
7. Offload Reads with Replication
Use read replicas to distribute query load, especially for read-heavy applications. Replication allows you to spread read operations across multiple servers, freeing up the primary database to focus on write operations and reducing overall latency.
8. Control Concurrency and Locking
Poor concurrency control can lead to lock contention and delays. Ensure your transactions are short and efficient. Use appropriate isolation levels to avoid unnecessary locking, and understand the impact of each level on performance and data integrity.
0 notes
Text
Dynamic Where Condition usage in Database queries

Learn how to implement dynamic WHERE conditions in database queries to build flexible, efficient, and secure SQL statements. This technique allows developers to apply filters based on user input or runtime conditions, enhancing performance and customizability in data-driven applications.
#SQLQueries#DynamicWhereClause#DatabaseDevelopment#SQLTips#QueryOptimization#BackendDevelopment#DatabaseProgramming#CodingBestPractices#SQLInjectionPrevention#WebDevelopment
0 notes
Text
Dynamic Where Condition usage in Database queries

Learn how to implement dynamic WHERE conditions in database queries to build flexible, efficient, and secure SQL statements. This technique allows developers to apply filters based on user input or runtime conditions, enhancing performance and customizability in data-driven applications.
#SQLQueries#DynamicWhereClause#DatabaseDevelopment#SQLTips#QueryOptimization#BackendDevelopment#DatabaseProgramming#CodingBestPractices#SQLInjectionPrevention#WebDevelopment
0 notes
Text
Dynamic Where Condition usage in Database queries

Learn how to implement dynamic WHERE conditions in database queries to build flexible, efficient, and secure SQL statements. This technique allows developers to apply filters based on user input or runtime conditions, enhancing performance and customizability in data-driven applications.
#SQLQueries#DynamicWhereClause#DatabaseDevelopment#SQLTips#QueryOptimization#BackendDevelopment#DatabaseProgramming#CodingBestPractices#SQLInjectionPrevention#WebDevelopment
0 notes
Text
Dynamic Where Condition usage in Database queries

Learn how to implement dynamic WHERE conditions in database queries to build flexible, efficient, and secure SQL statements. This technique allows developers to apply filters based on user input or runtime conditions, enhancing performance and customizability in data-driven applications.
#SQLQueries#DynamicWhereClause#DatabaseDevelopment#SQLTips#QueryOptimization#BackendDevelopment#DatabaseProgramming#CodingBestPractices#SQLInjectionPrevention#WebDevelopment
0 notes
Text
WordPress aufräumen: So entlarvst du ungenutzte Dateien mit Python

In diesem Beitrag möchte ich dir gerne einen Weg aufzeigen, wie du sehr einfach und ebenso sicher nicht verwendete Dateien in deiner WordPress-Instanz finden kannst. Du benötigst dafür ein wenig technisches Verständnis – aber keine Sorge: Ich nehme dich an die Hand und führe dich Schritt für Schritt durch den gesamten Prozess. https://youtu.be/T3iVrIGbtl8 Der Bedarf für diese Lösung entstand aus einem ganz praktischen Grund: Mein eigener Blog hat mittlerweile satte 174.000 Dateien angesammelt – da wird es höchste Zeit, etwas auszumisten und wieder Platz auf dem Server zu schaffen. Für das Finden von nicht benötigten Dateien unter WordPress gibt es diverse Plugins. Diese haben jedoch alle den Nachteil, dass sie direkt auf der WordPress-Instanz laufen, Systemressourcen verbrauchen und – wie viele Kommentare zeigen – nicht immer zuverlässig oder sicher funktionieren. Daher habe ich mir folgenden Weg überlegt: Ich exportiere die WordPress-Beiträge als JSON-Datei mit den wichtigsten Feldern (ID, Titel, Inhalt). Anschließend lade ich das Upload-Verzeichnis herunter und lasse ein Python-Skript prüfen, ob die Dateien in den Beiträgen referenziert werden. Alle nicht gefundenen Dateien können theoretisch als ungenutzt eingestuft und anschließend überprüft oder gelöscht werden. ⚠️ Wichtiger Hinweis: Ich empfehle dir dringend, vor dem Löschen von Dateien ein vollständiges Backup deiner WordPress-Instanz anzulegen. Idealerweise testest du die Löschung zunächst in einer Staging-Umgebung oder auf einer Kopie deiner Seite. In seltenen Fällen kann es vorkommen, dass Dateien fälschlich als ungenutzt erkannt werden – insbesondere wenn sie über PageBuilder, Custom Fields oder Medien-IDs referenziert werden.
Warum bestehende Plugins nicht immer zuverlässig arbeiten
Es gibt diverse Plugins wie Media Cleaner, DNUI (Delete Not Used Image) oder ähnliche, die versprechen, ungenutzte Mediendateien automatisch zu erkennen und zu löschen. Grundsätzlich eine praktische Idee – doch in den Kommentaren dieser Plugins häufen sich Berichte über falsch gelöschte Dateien, die offenbar doch noch in Verwendung waren. Die Wiederherstellung solcher Dateien ist oft aufwendig und erfordert entweder Backups oder manuelle Nacharbeit. Meine Lösung setzt daher auf einen anderen Ansatz: Sie analysiert die Inhalte kontrolliert und nachvollziehbar außerhalb des WordPress-Systems – und ist damit deutlich sicherer und transparenter.
Schritt 1 – Export der Tabelle wp_posts als JSON
Als Erstes werden die Spalten ID, post_title und post_content aus der WordPress-Tabelle wp_posts exportiert. Der Tabellenpräfix wp_ kann bei dir abweichen – diesen findest du in der Datei wp-config.php unter: $table_prefix = 'wp_'; In manchen Fällen sind mehrere WordPress-Instanzen in einer Datenbank vorhanden. Achte also darauf, den richtigen Präfix zu verwenden. Der Export über phpMyAdmin ist dabei besonders einfach: Du führst lediglich ein SELECT-Statement aus, das dir die relevanten Inhalte liefert. Der eigentliche Export als JSON erfolgt über die integrierte Exportfunktion. SQL-Statement: SELECT ID as "id", post_title as 'Titel', post_content as 'Content' FROM wp_posts WHERE post_type in ('page', 'post'); Wenn du dieses SQL-Statement in phpMyAdmin ausführst, erscheint eine Tabelle mit den Ergebnissen. Scrolle nun ganz nach unten – dort findest du den Link „Exportieren“. Ein Klick darauf öffnet eine neue Seite, auf der du den Exporttyp von SQL auf JSON umstellst. Danach nur noch mit OK bestätigen, und der Export startet.


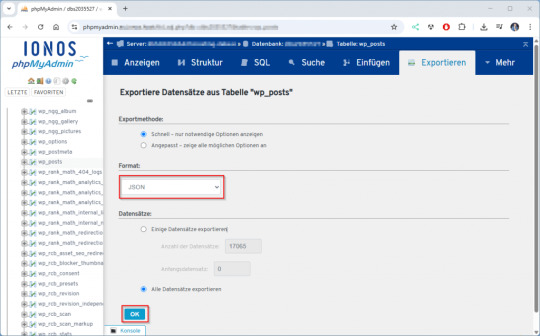
Je nach Anzahl der Beiträge kann der Download ein paar Sekunden dauern.
Schritt 2 – Download des Upload-Verzeichnisses
Im zweiten Schritt wird das komplette Upload-Verzeichnis deiner WordPress-Installation heruntergeladen. Dieses befindet sich standardmäßig unter: /wp-content/uploads/ Ich verwende dafür das kostenlose Tool WinSCP, das eine einfache und übersichtliche Oberfläche bietet. Du benötigst lediglich die SFTP-Zugangsdaten zu deinem Webspace. Diese findest du in der Regel im Kundenbereich deines Hosting-Anbieters. Falls dir kein direkter Zugriff per SFTP möglich ist, bieten viele Hoster eine alternative Lösung an: Du kannst das Verzeichnis online als ZIP-Archiv erstellen und anschließend herunterladen. 💡 Tipp: Achte darauf, die Ordnerstruktur beizubehalten – das Python-Skript analysiert später jede Datei im Originalpfad.
Schritt 3 – Ausführen des Python-Skripts zur Suche nach verwaisten Bildern
Für das Skript wird lediglich Python 3 benötigt – weitere externe Bibliotheken sind nicht erforderlich. Das Skript kann direkt über die Kommandozeile im Projektverzeichnis ausgeführt werden: python3 findunusedfiles.py Während der Ausführung listet das Skript alle Bilder aus dem Upload-Verzeichnis auf und zeigt direkt in der Konsole an, ob sie verwendet (✅) oder nicht verwendet (❌) wurden. Die Laufzeitausgabe sieht zum Beispiel so aus:

Nach Abschluss wird eine Datei namens unused_images.txt erzeugt. Darin enthalten ist eine Liste aller Bildpfade, die im Export der WordPress-Datenbank (siehe Schritt 1) nicht referenziert wurden.
Diese Datei dient als Grundlage zur manuellen Prüfung oder zum späteren Löschen der nicht verwendeten Dateien. 🔗 Hinweis: Das hier verwendete Skript findunusedfiles.py sowie ein Beispiel-SQL-Generator findest du ebenfalls auf GitHub: github.com/StefanDraeger/wp-unused-files-cleaner Python Skript zur Suche nach nicht benutzen Bildern in wordPressHerunterladen Quellcode #!/usr/bin/env python3 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- """ Titel: WordPress Upload-Verzeichnis auf ungenutzte Dateien prüfen Beschreibung: Dieses Skript durchsucht das lokale Upload-Verzeichnis einer WordPress-Installation nach Bilddateien und vergleicht diese mit den Inhalten aller Beiträge und Seiten, die zuvor als JSON-Datei aus der Tabelle `wp_posts` exportiert wurden. Dateien, die in keinem Beitrag referenziert sind, werden als potenziell ungenutzt gelistet. Autor: Stefan Draeger Webseite: https://draeger-it.blog """ import os import json import sys # Konfiguration UPLOADS_DIR = './wp-content/uploads' JSON_FILE = './wp_posts.json' IMAGE_EXTENSIONS = ('.jpg', '.jpeg', '.png', '.tiff', '.bmp') def format_size(bytes_value): if bytes_value < 1024: return f"{bytes_value} Bytes" elif bytes_value < 1024 ** 2: return f"{bytes_value / 1024:.2f} KB" elif bytes_value < 1024 ** 3: return f"{bytes_value / (1024 ** 2):.2f} MB" else: return f"{bytes_value / (1024 ** 3):.2f} GB" def load_json_data(json_file): if not os.path.isfile(json_file): print(f"❌ Fehler: Datei '{json_file}' nicht gefunden.") sys.exit(1) try: with open(json_file, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file: raw_json = json.load(file) except json.JSONDecodeError: print(f"❌ Fehler: Datei '{json_file}' ist kein gültiges JSON.") sys.exit(1) for obj in raw_json: if obj.get('type') == 'table' and obj.get('name') == 'wp_posts': return obj.get('data', ) print("❌ Fehler: Keine Daten zur Tabelle 'wp_posts' gefunden.") sys.exit(1) def scan_uploads(content_list): if not os.path.isdir(UPLOADS_DIR): print(f"❌ Fehler: Upload-Verzeichnis '{UPLOADS_DIR}' nicht gefunden.") sys.exit(1) unused_files = checked_count = 0 for root, dirs, files in os.walk(UPLOADS_DIR): for file_name in files: if file_name.lower().endswith(IMAGE_EXTENSIONS): full_path = os.path.join(root, file_name) relative_path = os.path.relpath(full_path, '.').replace('', '/') checked_count += 1 found = False for i in range(len(content_list)): if relative_path in content_list: content_list = content_list.replace(relative_path, '') found = True if found: content_list = print(f"✅ Verwendet: {relative_path}") else: unused_files.append(relative_path) print(f"❌ Nicht verwendet: {relative_path}") return unused_files, checked_count def write_unused_list(unused_files): with open('unused_images.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f: for path in unused_files: f.write(path + 'n') print("📝 Datei 'unused_images.txt' wurde erstellt.") def write_sql_files(unused_files): with open('delete_attachments.sql', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as del_out: del_out.write("-- SQL-Befehl zum Löschen verwaister Medien aus wp_posts (Typ: attachment)nn") del_out.write("DELETE FROM wp_postsnWHERE post_type = 'attachment'nAND guid IN (n") for i, path in enumerate(unused_files): end = ",n" if i < len(unused_files) - 1 else "n" del_out.write(f" '{path}'{end}") del_out.write(");n") print("🗑️ Datei 'delete_attachments.sql' wurde erzeugt.") with open('select_attachments.sql', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as sel_out: sel_out.write("-- SQL-Befehl zur Prüfung verwaister Medien aus wp_posts (Typ: attachment)nn") sel_out.write("SELECT ID, guid FROM wp_postsnWHERE post_type = 'attachment'nAND guid IN (n") for i, path in enumerate(unused_files): end = ",n" if i < len(unused_files) - 1 else "n" sel_out.write(f" '{path}'{end}") sel_out.write(");n") print("🔍 Datei 'select_attachments.sql' wurde erzeugt.") def write_log(unused_files, checked_count): total_size_bytes = sum( os.path.getsize(os.path.join('.', path)) for path in unused_files if os.path.isfile(os.path.join('.', path)) ) formatted_size = format_size(total_size_bytes) with open('cleanup_log.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as log: log.write("📄 Ausführungsprotokoll – WordPress Dateiaufräumungn") log.write("==================================================nn") log.write(f"📦 Verarbeitete Dateien: {checked_count}n") log.write(f"🗂️ Ungenutzte Dateien gefunden: {len(unused_files)}n") log.write(f"💾 Speicherverbrauch (gesamt): {formatted_size}nn") log.write("📝 Die folgenden Dateien wurden erstellt:n") log.write("- unused_images.txtn") log.write("- delete_attachments.sqln") log.write("- select_attachments.sqln") print("🧾 Logdatei 'cleanup_log.txt' wurde erstellt.") def main(): entries = load_json_data(JSON_FILE) content_list = unused_files, checked_count = scan_uploads(content_list) print("nAnalyse abgeschlossen.") print(f"Geprüfte Dateien: {checked_count}") print(f"Nicht referenzierte Dateien: {len(unused_files)}n") if unused_files: print("⚠️ Nicht referenzierte Bilddateien:") for path in unused_files: print(path) write_unused_list(unused_files) write_sql_files(unused_files) write_log(unused_files, checked_count) if __name__ == "__main__": main()
Schritt 4 – Aufräumen der WordPress-Datenbank
⚠️ Wichtiger Hinweis vorab: Bevor du Änderungen an deiner Datenbank vornimmst, solltest du ein vollständiges Backup deiner WordPress-Datenbank erstellen. So kannst du im Fall eines Fehlers jederzeit alles wiederherstellen. WordPress speichert alle hochgeladenen Medien – also auch Bilder – in der Tabelle wp_posts. Dabei handelt es sich um Einträge mit dem Post-Typ attachment, wobei in der Spalte guid der Pfad zur Datei gespeichert ist. Wenn du mit dem Python-Skript verwaiste Bilder identifiziert und vielleicht schon gelöscht hast, verbleiben deren Einträge trotzdem in der WordPress-Mediathek. Diese kannst du gezielt aus der Datenbank entfernen. Vorgehen: - Öffne die Datei unused_images.txt, die du im vorherigen Schritt erhalten hast. - Jeder darin aufgeführte Pfad (z. B. wp-content/uploads/2023/08/beispiel.jpg) lässt sich mit einem einfachen SQL-Befehl entfernen: DELETE FROM wp_posts WHERE post_type = 'attachment' AND guid LIKE '%wp-content/uploads/2023/08/beispiel.jpg'; - Um diese Aufgabe bei vielen Dateien zu automatisieren, kannst du folgendes Python-Skript nutzen. Es erstellt dir aus unused_images.txt eine vollständige SQL-Datei mit allen nötigen Löschbefehlen: # generate_delete_sql.py with open('unused_images.txt', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as infile, open('delete_attachments.sql', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as outfile: outfile.write("-- SQL-Befehle zum Löschen verwaister Medien aus wp_posts (Typ: attachment)nn") for line in infile: path = line.strip() if path: outfile.write(f"DELETE FROM wp_posts WHERE post_type = 'attachment' AND guid LIKE '%{path}';n") - Führe die generierte Datei delete_attachments.sql anschließend in phpMyAdmin oder über ein externes SQL-Tool aus. Optional: Erst prüfen, dann löschen Wenn du sicherstellen willst, dass die Statements korrekt sind, kannst du sie vor dem Löschen zunächst mit SELECT testen: SELECT ID, guid FROM wp_posts WHERE post_type = 'attachment' AND guid LIKE '%wp-content/uploads/2023/08/beispiel.jpg'; Mit diesem Schritt entfernst du nicht nur die Bilddateien selbst, sondern auch die dazugehörigen Mediathek-Einträge – für eine wirklich aufgeräumte WordPress-Installation.
Aufräumen via SSH
⚠️ Wichtiger Sicherheitshinweis: Bevor du Dateien vom Server löschst, solltest du unbedingt ein vollständiges Backup deiner WordPress-Installation und der Datenbank anlegen. In seltenen Fällen können Dateien fälschlich als ungenutzt erkannt werden – z. B. wenn sie über PageBuilder, Shortcodes oder Custom Fields eingebunden sind. Teste den Löschvorgang idealerweise zuerst in einer Staging-Umgebung. Wenn du Zugriff auf deinen Webserver per SSH hast, kannst du die ungenutzten Dateien aus der Datei unused_images.txt direkt automatisiert löschen – ohne mühsames Durchklicken per Hand. Voraussetzungen: - Die Datei unused_images.txt befindet sich auf dem Server (z. B. via WinSCP oder scp hochgeladen). - Du befindest dich im WordPress-Stammverzeichnis oder die Pfade in der Datei stimmen relativ zur aktuellen Position. Optional: Dry-Run vor dem Löschen Damit du vorab prüfen kannst, ob die Dateien wirklich existieren: while IFS= read -r file; do if ; then echo "Würde löschen: $file" else echo "❌ Nicht gefunden: $file" fi done < unused_images.txt Dateien sicher löschen (nach manueller Prüfung) while IFS= read -r file; do if ; then rm "$file" echo "✅ Gelöscht: $file" fi done < unused_images.txt Optional: Löschvorgang protokollieren while IFS= read -r file; do if ; then rm "$file" echo "$(date +"%F %T") Gelöscht: $file" >> deleted_files.log fi done < unused_images.txt
Fazit
Ein überfülltes Upload-Verzeichnis ist nicht nur unübersichtlich, sondern kann auch unnötig Speicherplatz und Backup-Zeit kosten. Mit dem hier vorgestellten Ansatz hast du eine sichere, transparente und Plugin-freie Lösung, um gezielt ungenutzte Dateien in deiner WordPress-Installation zu identifizieren und aufzuräumen. Durch die Kombination aus Datenbank-Export, Python-Skript und optionaler Löschung via SSH behältst du die volle Kontrolle – und vermeidest die Risiken automatischer Plugin-Löschungen. Zudem hast du mit den generierten SQL-Dateien und dem Log eine solide Dokumentation deines Bereinigungsprozesses. 💡 Tipp zum Schluss: Behalte die Anzahl deiner Medien im Blick, deaktiviere nicht benötigte Thumbnails und führe diese Art von Aufräumaktion regelmäßig durch – so bleibt dein System langfristig sauber und performant. Read the full article
0 notes
Text
SQL injection

we will recall SQLi types once again because examples speak louder than explanations!
In-band SQL Injection
This technique is considered the most common and straightforward type of SQL injection attack. In this technique, the attacker uses the same communication channel for both the injection and the retrieval of data. There are two primary types of in-band SQL injection:
Error-Based SQL Injection: The attacker manipulates the SQL query to produce error messages from the database. These error messages often contain information about the database structure, which can be used to exploit the database further. Example: SELECT * FROM users WHERE id = 1 AND 1=CONVERT(int, (SELECT @@version)). If the database version is returned in the error message, it reveals information about the database.
Union-Based SQL Injection: The attacker uses the UNION SQL operator to combine the results of two or more SELECT statements into a single result, thereby retrieving data from other tables. Example: SELECT name, email FROM users WHERE id = 1 UNION ALL SELECT username, password FROM admin.
Inferential (Blind) SQL Injection
Inferential SQL injection does not transfer data directly through the web application, making exploiting it more challenging. Instead, the attacker sends payloads and observes the application’s behaviour and response times to infer information about the database. There are two primary types of inferential SQL injection:
Boolean-Based Blind SQL Injection: The attacker sends an SQL query to the database, forcing the application to return a different result based on a true or false condition. By analysing the application’s response, the attacker can infer whether the payload was true or false. Example: SELECT * FROM users WHERE id = 1 AND 1=1 (true condition) versus SELECT * FROM users WHERE id = 1 AND 1=2 (false condition). The attacker can infer the result if the page content or behaviour changes based on the condition.
Time-Based Blind SQL Injection: The attacker sends an SQL query to the database, which delays the response for a specified time if the condition is true. By measuring the response time, the attacker can infer whether the condition is true or false. Example: SELECT * FROM users WHERE id = 1; IF (1=1) WAITFOR DELAY '00:00:05'--. If the response is delayed by 5 seconds, the attacker can infer that the condition was true.
Out-of-band SQL Injection
Out-of-band SQL injection is used when the attacker cannot use the same channel to launch the attack and gather results or when the server responses are unstable. This technique relies on the database server making an out-of-band request (e.g., HTTP or DNS) to send the query result to the attacker. HTTP is normally used in out-of-band SQL injection to send the query result to the attacker's server. We will discuss it in detail in this room.
Each type of SQL injection technique has its advantages and challenges.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
PHP with MySQL: Best Practices for Database Integration
PHP and MySQL have long formed the backbone of dynamic web development. Even with modern frameworks and languages emerging, this combination remains widely used for building secure, scalable, and performance-driven websites and web applications. As of 2025, PHP with MySQL continues to power millions of websites globally, making it essential for developers and businesses to follow best practices to ensure optimized performance and security.
This article explores best practices for integrating PHP with MySQL and explains how working with expert php development companies in usa can help elevate your web projects to the next level.
Understanding PHP and MySQL Integration
PHP is a server-side scripting language used to develop dynamic content and web applications, while MySQL is an open-source relational database management system that stores and manages data efficiently. Together, they allow developers to create interactive web applications that handle tasks like user authentication, data storage, and content management.
The seamless integration of PHP with MySQL enables developers to write scripts that query, retrieve, insert, and update data. However, without proper practices in place, this integration can become vulnerable to performance issues and security threats.
1. Use Modern Extensions for Database Connections
One of the foundational best practices when working with PHP and MySQL is using modern database extensions. Outdated methods have been deprecated and removed from the latest versions of PHP. Developers are encouraged to use modern extensions that support advanced features, better error handling, and more secure connections.
Modern tools provide better performance, are easier to maintain, and allow for compatibility with evolving PHP standards.
2. Prevent SQL Injection Through Prepared Statements
Security should always be a top priority when integrating PHP with MySQL. SQL injection remains one of the most common vulnerabilities. To combat this, developers must use prepared statements, which ensure that user input is not interpreted as SQL commands.
This approach significantly reduces the risk of malicious input compromising your database. Implementing this best practice creates a more secure environment and protects sensitive user data.
3. Validate and Sanitize User Inputs
Beyond protecting your database from injection attacks, all user inputs should be validated and sanitized. Validation ensures the data meets expected formats, while sanitization cleans the data to prevent malicious content.
This practice not only improves security but also enhances the accuracy of the stored data, reducing errors and improving the overall reliability of your application.
4. Design a Thoughtful Database Schema
A well-structured database is critical for long-term scalability and maintainability. When designing your MySQL database, consider the relationships between tables, the types of data being stored, and how frequently data is accessed or updated.
Use appropriate data types, define primary and foreign keys clearly, and ensure normalization where necessary to reduce data redundancy. A good schema minimizes complexity and boosts performance.
5. Optimize Queries for Speed and Efficiency
As your application grows, the volume of data can quickly increase. Optimizing SQL queries is essential for maintaining performance. Poorly written queries can lead to slow loading times and unnecessary server load.
Developers should avoid requesting more data than necessary and ensure queries are specific and well-indexed. Indexing key columns, especially those involved in searches or joins, helps the database retrieve data more quickly.
6. Handle Errors Gracefully
Handling database errors in a user-friendly and secure way is important. Error messages should never reveal database structures or sensitive server information to end-users. Instead, errors should be logged internally, and users should receive generic messages that don’t compromise security.
Implementing error handling protocols ensures smoother user experiences and provides developers with insights to debug issues effectively without exposing vulnerabilities.
7. Implement Transactions for Multi-Step Processes
When your application needs to execute multiple related database operations, using transactions ensures that all steps complete successfully or none are applied. This is particularly important for tasks like order processing or financial transfers where data integrity is essential.
Transactions help maintain consistency in your database and protect against incomplete data operations due to system crashes or unexpected failures.
8. Secure Your Database Credentials
Sensitive information such as database usernames and passwords should never be exposed within the application’s core files. Use environment variables or external configuration files stored securely outside the public directory.
This keeps credentials safe from attackers and reduces the risk of accidental leaks through version control or server misconfigurations.
9. Backup and Monitor Your Database
No matter how robust your integration is, regular backups are critical. A backup strategy ensures you can recover quickly in the event of data loss, corruption, or server failure. Automate backups and store them securely, ideally in multiple locations.
Monitoring tools can also help track database performance, detect anomalies, and alert administrators about unusual activity or degradation in performance.
10. Consider Using an ORM for Cleaner Code
Object-relational mapping (ORM) tools can simplify how developers interact with databases. Rather than writing raw SQL queries, developers can use ORM libraries to manage data through intuitive, object-oriented syntax.
This practice improves productivity, promotes code readability, and makes maintaining the application easier in the long run. While it’s not always necessary, using an ORM can be especially helpful for teams working on large or complex applications.
Why Choose Professional Help?
While these best practices can be implemented by experienced developers, working with specialized php development companies in usa ensures your web application follows industry standards from the start. These companies bring:
Deep expertise in integrating PHP and MySQL
Experience with optimizing database performance
Knowledge of the latest security practices
Proven workflows for development and deployment
Professional PHP development agencies also provide ongoing maintenance and support, helping businesses stay ahead of bugs, vulnerabilities, and performance issues.
Conclusion
PHP and MySQL remain a powerful and reliable pairing for web development in 2025. When integrated using modern techniques and best practices, they offer unmatched flexibility, speed, and scalability.
Whether you’re building a small website or a large-scale enterprise application, following these best practices ensures your PHP and MySQL stack is robust, secure, and future-ready. And if you're seeking expert assistance, consider partnering with one of the top php development companies in usa to streamline your development journey and maximize the value of your project.
0 notes