#EC2 instance
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Access EC2 Linux Instance via the Password
An Amazon EC2 instance is a virtual server in Amazon’s Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) for running applications on the Amazon Web Services (AWS) infrastructure. In this article, we will describe how to access EC2 Linux Instance via the Password. Please see Create Folders and Enable File sharing on Windows, How to deploy Ansible AWX on centos 8, and how to setup and configure a Lamp stack on…
#Access EC2 Linux Instance#Add a user as a Sudoer on CentOS#AWS#EC2#EC2 instance#EC2 Instances#Instance#Linux
0 notes
Text
youtube
#youtube#video#codeonedigest#microservices#aws#microservice#awscloud#ec2 instance#aws ec2#aws cloud#aws course#nodejs module#nodejs express#node js#nodejs#node
0 notes
Text
Software Development Engineer, EC2 Instance Networking
Job title: Software Development Engineer, EC2 Instance Networking Company: Amazon Job description: DESCRIPTION Do you want to shape the future of virtualized (SDN) networking in one of the world’s biggest public… performance of bare metal networking while maintaining all the benefits of the cloud, including delivering features… Expected salary: $129300 per year Location: Sunnyvale, CA Job date:…
0 notes
Video
youtube
Create Instance and Security Group with Terraform on AWS
#youtube#Learn how to automate AWS infrastructure using Terraform! In this step-by-step tutorial you’ll create an EC2 instance and configure security
0 notes
Text
Deploy Lucee Applications on AWS EC2 Instances: A Step-by-Step Guide
#Deploy Lucee Applications on AWS EC2 Instances: A Step-by-Step Guide#Deploy Lucee Applications on AWS EC2 Instances#Lucee Applications on AWS EC2 Instances#Lucee Applications on AWS Instances#Deploy Lucee Applications on AWS EC2 Instances Guide#Lucee Applications on AWS EC2 Instances Guide
0 notes
Text
Amazon EC2 M7i Instances Hypercharge Cloud AI

Amazon EC2 M7i Instances
Intel would like to demonstrate how the latest Amazon EC2 M7i Instances and M7i-flex instances with 4th Generation Intel Xeon Scalable processors can support your AI, ML, and DL workloads in this second of a three-blog series. They explained these new instances and their broad benefits in the first blog. They wanted to know how AI, ML, and DL workloads perform on these new instances and how Intel CPUs may help.
One research assesses the AI industry at $136.55 billion USD and predicts 37.3% yearly growth until 2030. While you could credit the increase to apparent AI usage like Google and Tesla’s self-driving cars, the advertising and media sector dominates the worldwide AI market. AI and ML/DL workloads are everywhere and growing. Cloud service providers (CSPs) like Amazon Web Services (AWS) are investing in AI/ML/DL services and infrastructure to enable organizations adopt these workloads more readily. Hosting instances with 4th-generation Intel Xeon Scalable CPUs and AI accelerators is one investment.
This article will explain how Intel CPUs and AWS instances are ideal for AI workloads. Two typical ML/DL model types will be used to demonstrate how these instances performed these workloads.
Amazon EC2 M7i &M7i Flex with 4th Gen Intel Xeon Scalables
As mentioned in the previous blog, Amazon EC2 provides M7i and M7i-flex with the newest Intel Xeon CPU. Primary difference: M7i-flex offers changeable performance at a reduced price. This blog will concentrate on regular Amazon EC2 M7i instances for sustained, compute-intensive applications like training or executing machine learning models. M7i instances have 2–192 vCPUs for various requirements. Each instance may accommodate up to 128 EBS disks, providing ample of storage for your dataset. The newest Intel Xeon processors include various built-in accelerators to boost task performance.
For better deep learning performance, all Amazon EC2 M7i instances include Intel Advanced Matrix Extensions (AMX) accelerator. Intel AMX lets customers code AI tasks on the AMX instruction set while keeping non-AI workloads on the CPU ISA. Intel has optimized its oneAPI Deep Neural Network Library (oneDNN) to make AMX easier to use for developers. Open-source AI frameworks like PyTorch, TensorFlow, and ONYX support this API. Intel tested 4th Gen Intel Xeon Scalable processors with AMX capabilities to give 10 times the inference performance of earlier CPUs.
Engineers and developers must adjust their AI, ML, and DL workloads on the newest Amazon EC2 M7i instances with Intel AMX to maximize performance. Intel offers an AI tuning guide to take use of Intel processor benefits across numerous popular models and frameworks. OS-level optimizations, PyTorch, TensorFlow, OpenVINO, and other optimizations are covered throughout the guide. The Intel Model Zoo GitHub site contains pre-trained AI, ML, and DL models pre-validated for Intel hardware, AI workload optimization guidance, best practices, and more.
After learning how Intel and the newest Intel Xeon processors may better AI, ML, and DL workloads, let’s see how these instances perform with object identification and natural language processing.
Models for detecting objects
Object detection models control image-classification applications. This category includes 3D medical scan, self-driving car camera, face recognition, and other models. They will discuss ResNet-50 and RetinaNet.
A 50-layer CNN powers ResNet-50, an image recognition deep learning model. User-trained models identify and categorize picture objects. ResNet-50 models on Intel Model Zoo and others train using ImageNet’s big picture collection. Most object identification models have one or two stages, with two-stage models being more accurate but slower. ResNet-50 and RetinaNet are single-stage models, although RetinaNet’s Focal Loss function improves accuracy without losing speed.
Performance how rapidly these models process photos depends on their use. End consumers don’t want lengthy waits for device recognition and unlocking. Before plant diseases and insect incursions damage crops, farmers must discover them immediately. Intel’s MLPerf RetinaNet model demonstrates that Amazon EC2 M7i instances analyze 4.11 times more samples per second than M6i instances.
As CPUs rise, ResNet-50 performance scales nicely, so you can retain high performance independent of dataset and instance size. An Amazon EC2 M7i instance with 192 vCPUs has eight times the ResNet-50 throughput of a 16vCPU instance. Higher-performing instances provide better value. Amazon EC2 M7i instances analyzed 4.49 times more samples per dollar than M6i instances in RetinaNet testing. These findings demonstrate that Amazon EC2 M7i instances with 4th Gen Intel Xeon Scalable CPUs are ideal for object identification deep learning tasks.
Natural Language Models
You’re probably using natural language processing engines when you ask a search engine or chatbot a query. NLP models learn real speech patterns to comprehend and interact with language. BERT machine learning models can interpret and contextualize text in addition to storing and presenting it. Word processing and phone messaging applications now forecast content based on what users have typed. Small firms benefit from chat boxes for first consumer contacts, even if they don’t run Google Search. These firms require a clear, fast, accurate chatbot.
Chatbots and other NLP model applications demand real-time execution, therefore speed is crucial. With Amazon EC2 M7i instances and 4th Generation Intel Xeon processors, NLP models like BERT and RoBERTa, an optimized BERT, perform better. One benchmark test found that Amazon EC2 M7i instances running RoBERTa analyzed 10.65 times more phrases per second than Graviton-based M7g instances with the same vCPU count. BERT testing with the MLPerf suite showed that throughput scaled well when they raised the vCPU count of Amazon EC2 M7i instances, with the 192-vCPU instance attaining almost 4 times the throughput of the 32-vCPU instance.
The Intel AMX accelerator in the 4th Gen Intel Xeon Scalable CPUs helps the Amazon EC2 M7i instances function well. Intel gives clients everything they need to improve NLP workloads with publicly accessible pre-optimized Intel processor models and tuning instructions for particular models like BERT. Amazon EC2 M7i instances outperformed M7g instances by 8.62 times per dollar, as RetinaNet showed.
Conclusion
For AI, ML, and DL, cloud decision-makers should use Amazon EC2 M7i instances with 4th Generation Intel Xeon Scalable CPUs. These instances include Intel AMX acceleration, tuning guidelines, and optimized models for many typical ML applications, delivering up to 10 times the throughput of Graviton-based M7g instances. Watch for further articles on how the newest Amazon EC2 M7i and M7i-flex instances may serve different workloads.
Read more on Govindhtech.com
1 note
·
View note
Video
youtube
What Is AWS IAM Users And Groups | AWS Services
#youtube#AWSIAM IAMUsers IAMGroups AWSIdentityAccessManagement CloudSecurity AWSAccessControl IAMExplained IAMTutorial IAMBasics TechSecurity CloudId#ec2aws ec2amazon ec2ec2 instanceHow To Create & Launch EC2 Request Spot & Spot Fleet RequestEC2 Request Spotspot instancesaws ec2 instance c
0 notes
Text
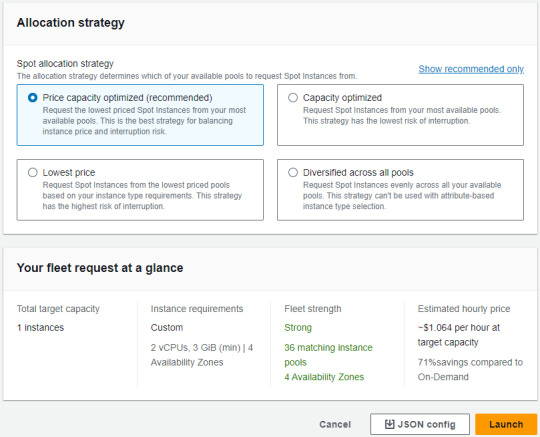
How to set up AWS EC2 Hot-instance
1. Click "Spot Requests" (in Instances) -> "Request Spot Instances"
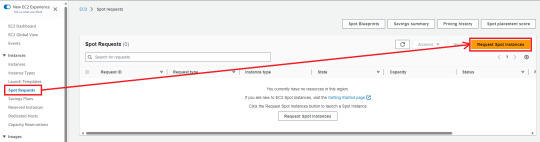
2. Depending on your demand, choose AMI
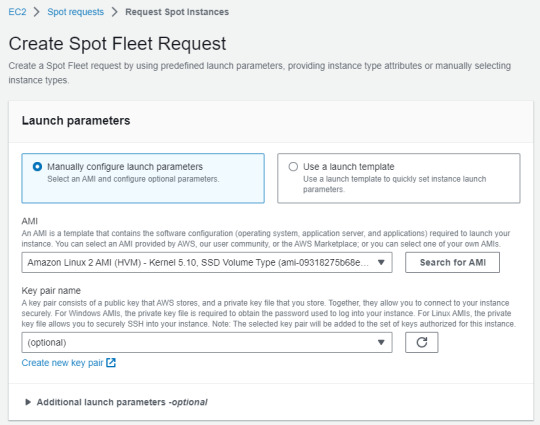
3. Choose "Manually select instance types" (in Instance type requirements)
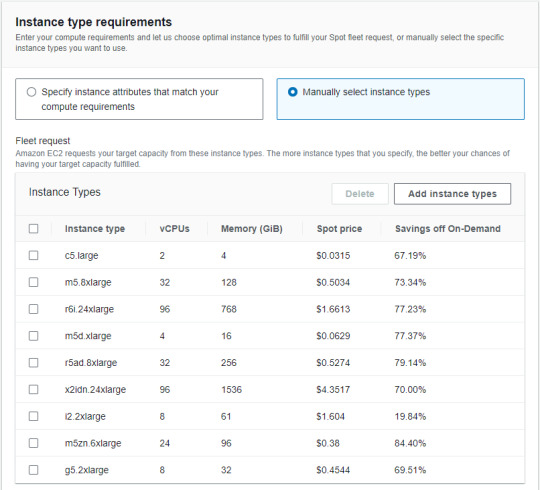
Tips for easily getting instances
Need to select multiple instance types for the specs you want to utilize (This is to make it as affordable as possible) The more popular and utilized an instance is, the more likely it is that a spot request will be fulfilled
4. Move "Target capacity" -> Setting conditions ("Maintain target capacity" & "Set maximum cost for Spot Instances")
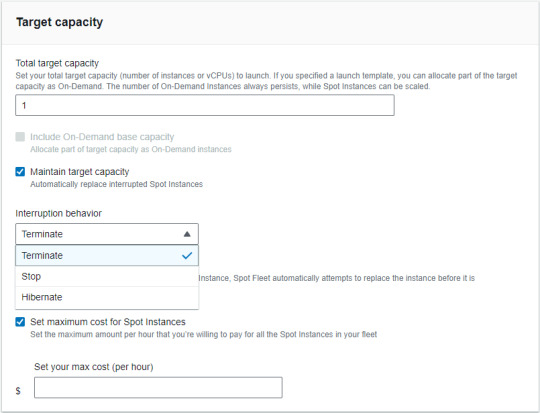
Tips for settings these conditions
Maintain target capacity -> Interruption behavior (This is automatically behavior as interrupted Spot Instances) Set maximum cost for Spot Instances (Recommended that the max cost be lower than on-demand)
5. Setting "Allocation strategy" -> Click "Launch"
0 notes
Text
EC2 Instance Creation: Beginner's Ultimate Guide 2023
EC2 Amazon Web Services AWS has revolutionised the way businesses approach IT infrastructure Gone are the days
0 notes
Text
Terraform Import Existing Resource: Ultimate Guide
Terraform Import Existing Resource: Ultimate Guide @vexpert #vmwarecommunities #homelab #100daysofhomelab #Terraform #TerraformImport #ConfigDrivenImport #CloudInfrastructureManagement #Terraform1.5 #EC2InstanceImport #TerraformState #terraformstate
Infrastructure as code (IaC) has become a standard for managing complex IT infrastructures. Terraform, a key player in the IaC sphere, is quite familiar to DevOps engineers and developers alike. One of the essential commands within the Terraform toolset is the terraform import command allowing the import of existing resources. There are some challenges with the legacy terraform import command.…

View On WordPress
#Cloud Infrastructure Management#Config-Driven Import#EC2 Instance Import#Resource Blocks#terraform#Terraform 1.5#Terraform Configuration#Terraform Import#Terraform Import Module#Terraform State
0 notes
Text
Create AWS EC2 Instance
AWS EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud) is a web service that provides resizable compute capacity in the cloud. It is designed to make web-scale cloud computing easier for developers. With EC2, you can quickly and easily create virtual machines (instances) in the cloud, configure them as per your requirements, and launch them in minutes. AWS EC2 instances can be launched from a variety of pre-configured Amazon Machine Images (AMIs) or you can create your own custom AMIs. You can also choose from a range of instance types optimized for different workloads and applications. EC2 instances can be managed via the AWS Management Console, command line interface, or using SDKs and APIs.
1 note
·
View note
Text
How to create an EC2 Instance
Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) is a web service that provides secure, resizable computing capacity in the cloud. Amazon EC2 offers many options that help you build and run virtually any application. With these possibilities, getting started with EC2 is quick and easy to do. In this article, we shall discuss how to create an EC2 Instance. Please see the Various ways to restart an AWS…

View On WordPress
#Amazon EC2#Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud#Amazon Web Services#AWS#EC2#EC2 instance#EC2 Instances#EC2 Launch#EC2Launch
0 notes
Text
https://codeonedigest.blogspot.com/2023/07/amazon-ec2-instance-setup-and-running.html
#youtube#video#codeonedigest#microservices#aws#microservice#springboot#spring boot#aws ec2 server#aws ec2 instance#aws ec2 service#ec2#aws ec2#spring boot microservices#java microservice#microservice tutorial
0 notes
Text
64 vCPU/256 GB ram/2 TB SSD EC2 instance with #FreeBSD or Debian Linux as OS 🔥

38 notes
·
View notes
Video
youtube
Learn to Deploy a Web Server on AWS using Terraform - Infrastructure as ...
#youtube#In this step-by-step tutorial you'll discover how to automate AWS infrastructure provisioning using Terraform. We'll create an EC2 instance
0 notes
Text
Ansible Collections: Extending Ansible’s Capabilities
Ansible is a powerful automation tool used for configuration management, application deployment, and task automation. One of the key features that enhances its flexibility and extensibility is the concept of Ansible Collections. In this blog post, we'll explore what Ansible Collections are, how to create and use them, and look at some popular collections and their use cases.
Introduction to Ansible Collections
Ansible Collections are a way to package and distribute Ansible content. This content can include playbooks, roles, modules, plugins, and more. Collections allow users to organize their Ansible content and share it more easily, making it simpler to maintain and reuse.
Key Features of Ansible Collections:
Modularity: Collections break down Ansible content into modular components that can be independently developed, tested, and maintained.
Distribution: Collections can be distributed via Ansible Galaxy or private repositories, enabling easy sharing within teams or the wider Ansible community.
Versioning: Collections support versioning, allowing users to specify and depend on specific versions of a collection. How to Create and Use Collections in Your Projects
Creating and using Ansible Collections involves a few key steps. Here’s a guide to get you started:
1. Setting Up Your Collection
To create a new collection, you can use the ansible-galaxy command-line tool:
ansible-galaxy collection init my_namespace.my_collection
This command sets up a basic directory structure for your collection:
my_namespace/
└── my_collection/
├── docs/
├── plugins/
│ ├── modules/
│ ├── inventory/
│ └── ...
├── roles/
├── playbooks/
├── README.md
└── galaxy.yml
2. Adding Content to Your Collection
Populate your collection with the necessary content. For example, you can add roles, modules, and plugins under the respective directories. Update the galaxy.yml file with metadata about your collection.
3. Building and Publishing Your Collection
Once your collection is ready, you can build it using the following command:
ansible-galaxy collection build
This command creates a tarball of your collection, which you can then publish to Ansible Galaxy or a private repository:
ansible-galaxy collection publish my_namespace-my_collection-1.0.0.tar.gz
4. Using Collections in Your Projects
To use a collection in your Ansible project, specify it in your requirements.yml file:
collections:
- name: my_namespace.my_collection
version: 1.0.0
Then, install the collection using:
ansible-galaxy collection install -r requirements.yml
You can now use the content from the collection in your playbooks:--- - name: Example Playbook hosts: localhost tasks: - name: Use a module from the collection my_namespace.my_collection.my_module: param: value
Popular Collections and Their Use Cases
Here are some popular Ansible Collections and how they can be used:
1. community.general
Description: A collection of modules, plugins, and roles that are not tied to any specific provider or technology.
Use Cases: General-purpose tasks like file manipulation, network configuration, and user management.
2. amazon.aws
Description: Provides modules and plugins for managing AWS resources.
Use Cases: Automating AWS infrastructure, such as EC2 instances, S3 buckets, and RDS databases.
3. ansible.posix
Description: A collection of modules for managing POSIX systems.
Use Cases: Tasks specific to Unix-like systems, such as managing users, groups, and file systems.
4. cisco.ios
Description: Contains modules and plugins for automating Cisco IOS devices.
Use Cases: Network automation for Cisco routers and switches, including configuration management and backup.
5. kubernetes.core
Description: Provides modules for managing Kubernetes resources.
Use Cases: Deploying and managing Kubernetes applications, services, and configurations.
Conclusion
Ansible Collections significantly enhance the modularity, distribution, and reusability of Ansible content. By understanding how to create and use collections, you can streamline your automation workflows and share your work with others more effectively. Explore popular collections to leverage existing solutions and extend Ansible’s capabilities in your projects.
For more details click www.qcsdclabs.com
#redhatcourses#information technology#linux#containerorchestration#container#kubernetes#containersecurity#docker#dockerswarm#aws
2 notes
·
View notes