#Flowcharts
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

my simplest flowchart ever
#thought of this flowchart and chuckled#yes i know the flowchart isn't prefect i don't give a fuck it's a shitpost#middle earth#silmarillion#idril#tour#elwing#earendil#luthien#beren#arwen#aragorn#flowcharts
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
I think if I'm going to properly sort out this mission structure framework in Space Gerbils I'm going to have to resign myself to more flowcharts.
#gaming#tabletop roleplaying#tabletop rpgs#space gerbils#game development#game design#flowcharts#the gameplay loop involved in escaping an exploding planet when you are 3–5 extraterrestrial rodents operating a person-size mech#is more nuanced than one might intuitively expect
320 notes
·
View notes
Text
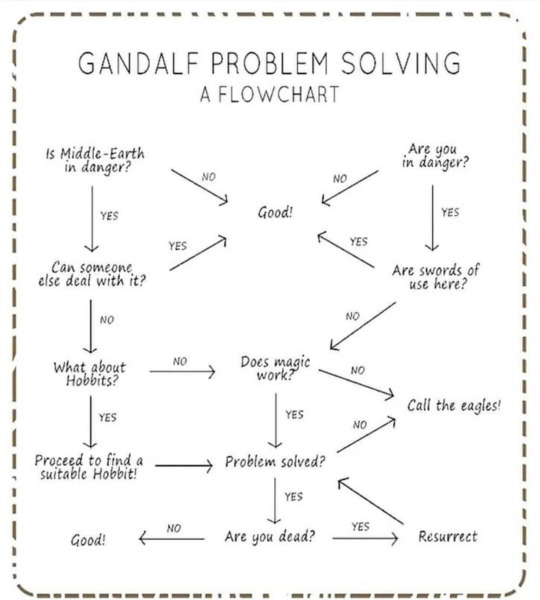
62 notes
·
View notes
Text
The past year or so has been a steady descent into madness when it comes to my TTRPG stuff...
It started with "Tower of Heck Cubed: Get Off Of My Lawn" requiring an honest-to-god Database to keep all the Guardians and Abilities straight, now I'm doing prep for "Pantheon Coup" and the Development Paths system I devised needs a fucking flowchart to make sense.

I zoomed out so the text isnt visible because this isnt about the content, but fucken look at this. I've barely started, and now I have opinions about flowchart formatting.
As someone who started by running an entire party's worth of character sheets in a single google sheets page, I feel like I'm a long way from home.
#I've aired this revelation to my best friend and he basically said it was inevitable because I've always had opinions on formatting.#I want to go home but I live here now#pixelkind talks#ttrpg#ttrpg design#flowcharts
41 notes
·
View notes
Text
We don't need any more fresh hells! A Yokel primer concerning the consequences of elections!
Ever since the birth of this website in 2015, we’ve tried to sound the alarm about the consequences of elections. They have countless unforeseen effects that many folks don’t consider when choosing a candidate. We’ve decided to illustrate this concept through a nice flowchart that hopefully makes it easy to see the connections between elections and their aftermath: WHOOPS! We forgot that…

View On WordPress
#kirbydelauter#abortion#alabama#cause and effect relationships#Donald Trump#flowcharts#Frederick Politics#IVF#tommy tuberville#Tucker Carlson#voting matters
3 notes
·
View notes
Photo
before ADHD was an accepted diagnosis, people got called MIND WANDERER

136K notes
·
View notes
Text
Have you ever wondered "Hey, which person is this Hermitcraft fanart actually depicting?" and didn't want to just scroll down to read the tags?

Behold. My magnum opus. The Hermitcraft fanart flowchart! Please click for legibillity.
#to be very clear. this is a joke. please do not take this as actually guidelines to how a fanart should look#I just like making useless flowcharts :D#hermitcraft#hermitcraft season 10#my posts#toast talks
13K notes
·
View notes
Text
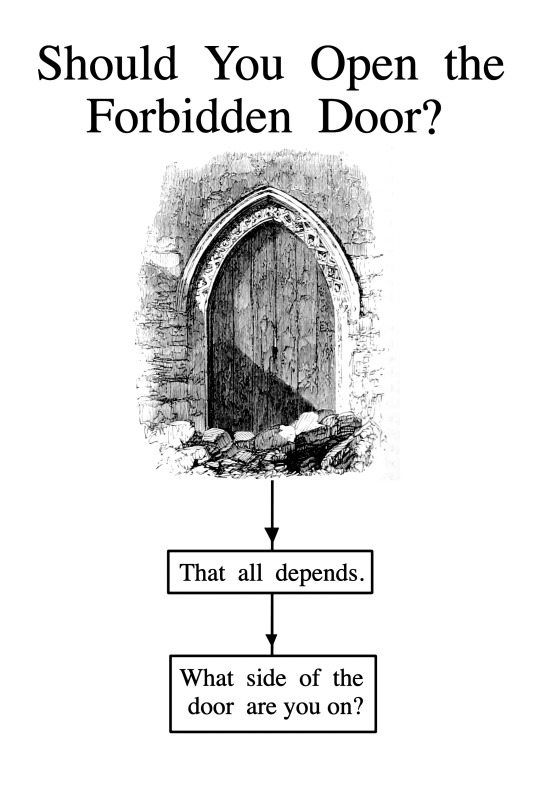
#Should You Open the Forbidden Door?#flowchart#questions#answers#unreality#if they didn’t want us to open it they shouldn’t put the word “door” in it
43K notes
·
View notes
Text

Me on the first day after a vacation.
1 note
·
View note
Text
excellent advice! (both OP's jokey advice and this reblog)
i love how every plant guide ever is like
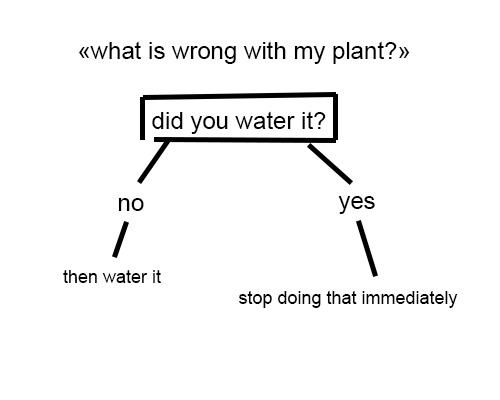
72K notes
·
View notes
Text
instagram
Are you the "last-minute hero" type? 😅 Try EdrawMax – your lifesaver when you need it most! 💡
🌊 Dive into the World of Seamless Design! 🚀💡Ready to turn chaos into clarity? Join us in our latest tutorial as we guide you through the art of designing impactful flowcharts using EdrawMax V14! Try EdrawMax for free: https://bit.ly/3JTBUUw
In this tutorial, discover: 🔄 Key principles for designing a user-friendly flowchart ✨ EdrawMax V14's powerful features for effortless design 🚀 Tips to enhance communication and decision-making 🌐 How to customize and share your flowchart masterpiece
Elevate your visual communication game! Save the date, set a reminder, and get ready to bring clarity to your processes. 🗓️✅
See you there, design enthusiasts! 🎨👩💻
#edrawmaxtutorial#flowchartdesign#edrawmax#wondershare#visualcommunication#designmastery 🚀🔗#mindmapping#edrawmind#aitools#productivity#mindmap#flowcharts#diagram#studywithme#Instagram
1 note
·
View note
Text
Visualizing Data: Crafting Flowcharts and Infographics with Google Slides
Branded Google Slides design of high quality: Frequently Asked Inquiries Explained
1.What files can Google Slides import?
Google Slides can import various file types, including Microsoft PowerPoint (.pptx, .ppt), OpenDocument Presentation (.odp), and PDF files. Additionally, it can import images in formats such as JPEG, PNG, and GIF. Users can also upload files from Google Drive or through other Google services. However, some formatting and features may not be preserved when importing from PowerPoint or other formats.
2. Can I rotate a table in Google Slides?
Yes, you can rotate a table in Google Slides. To do this, first select the table by clicking on it. Then, click on the "Format" menu, choose "Format options," and find the "Rotation" setting. Alternatively, you can hover your mouse near the corner of the table until the rotation handle appears, then click and drag to rotate it to your desired angle. While this method rotates the entire table, individual cells or text within the table can be rotated by adjusting the text direction in the "Table properties" menu.
3. Can I turn a Google slide vertical?
Yes, you can turn a Google Slides presentation vertical by changing the slide dimensions. To do this, go to "File" > "Page setup." In the dialog box, select "Custom" and enter your desired width and height (for a vertical slide, the height should be greater than the width). For example, you might set it to 8.5 inches wide by 11 inches high. After applying the changes, your slides will be oriented vertically.
4. How to do a flow chart in Google Slides?
To create a flowchart in Google Slides, open a new or existing presentation. Go to the “Insert” menu, select “Shape,” and choose shapes like rectangles or circles for your flowchart steps. Drag them onto the slide and arrange as needed. Use “Line” from the “Insert” menu to connect the shapes with arrows. To add text, double-click inside each shape. Customize colors and styles using the toolbar options. Once finished, you can group the shapes for easy movement by selecting them, right-clicking, and choosing “Group.” Save your presentation to maintain your flowchart.
5. Does Google Slides have infographics?
Google Slides does not have built-in infographics as a separate feature, but users can create infographics using its shapes, charts, and design tools. Additionally, there are various templates available in the Google Slides template gallery and third-party websites that offer infographic designs compatible with Google Slides. Users can also import images and graphics from external sources to enhance their presentations.

Visit: VS Website See: VS Portfolio
0 notes
Text

Building with Information structures
0 notes
Text

PROGRAMMING COURSES LEVEL ONE
Course Curriculum
The logic and programming
Algorithms and Flow charts
Understanding source codes.
The types of variables, constants, logical
The Input/Output.
Programming procedure
Programming in VB.Net
Programming in Python
Introducing the Object Oriented Programming
The loops and their logic
Website: https://giti-edu.ch/
Call: +41 /22 301 22 44
#ProgrammingCourses#Programming#Algorithms#FlowCharts#SourceCodes#Variables#Constants#Logical#Input#Output#ObjectOrientedProgramming#Loops#Logic#Geneva#GITI
0 notes

