#Linux file transfer
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
#data migration#data management#big data#data protection#file synchronization software#cloud solutions#linux#data orchestration#Government Data Management#file replication#Linux file transfer#secure data backup#cloud computing#cloud software
0 notes
Note
You're more amazing than a spell
Responding to this ask from my NEW COMPUTER!! It only took 24 hours to get it working! It's running Linux so there's numerous annoyances but apparently there's ways to get Windows programs working on Linux, one of which is built into Steam, and Ultrakill loads so fast and looks so good and runs so well!
... And I haven't even put the graphics card in yet
#i wonder if it's possible for the motherboard's onboard graphics thingy is stronger than my graphics card#it's not exactly a high-end graphics card while the motherboard is pretty high-end#but being stronger at graphics than a dedicated graphics card seems completely absurd and unreasonable#no way to know for sure until i can push the onboard graphics to the limit and then install the graphics card to compare#all that's left now is transferring the remaining files over#and i already transferred all the important files like my stories. and i synced my firefox profile#all that's left is a bunch of game files that probably won't even work on linux#ka asks
0 notes
Text
this computer business is making me want to fucking kill myself lol
#a day in the life#im trying to make a bootable windows drive. since my bootable linux drive does get me in there.. but hm.#every file transfer i try fucks up i cant even get into it#n i dont understand linux enough to understand#but now this 4.4gb iso is apparenlty too large for a fresh 28gb usb ??????#Like wtf nothing is going right fr
0 notes
Text
How I ditched streaming services and learned to love Linux: A step-by-step guide to building your very own personal media streaming server (V2.0: REVISED AND EXPANDED EDITION)
This is a revised, corrected and expanded version of my tutorial on setting up a personal media server that previously appeared on my old blog (donjuan-auxenfers). I expect that that post is still making the rounds (hopefully with my addendum on modifying group share permissions in Ubuntu to circumvent 0x8007003B "Unexpected Network Error" messages in Windows 10/11 when transferring files) but I have no way of checking. Anyway this new revised version of the tutorial corrects one or two small errors I discovered when rereading what I wrote, adds links to all products mentioned and is just more polished generally. I also expanded it a bit, pointing more adventurous users toward programs such as Sonarr/Radarr/Lidarr and Overseerr which can be used for automating user requests and media collection.
So then, what is this tutorial? This is a tutorial on how to build and set up your own personal media server using Ubuntu as an operating system and Plex (or Jellyfin) to not only manage your media, but to also stream that media to your devices both at home and abroad anywhere in the world where you have an internet connection. Its intent is to show you how building a personal media server and stuffing it full of films, TV, and music that you acquired through indiscriminate and voracious media piracy various legal methods will free you to completely ditch paid streaming services. No more will you have to pay for Disney+, Netflix, HBOMAX, Hulu, Amazon Prime, Peacock, CBS All Access, Paramount+, Crave or any other streaming service that is not named Criterion Channel. Instead whenever you want to watch your favourite films and television shows, you’ll have your own personal service that only features things that you want to see, with files that you have control over. And for music fans out there, both Jellyfin and Plex support music streaming, meaning you can even ditch music streaming services. Goodbye Spotify, Youtube Music, Tidal and Apple Music, welcome back unreasonably large MP3 (or FLAC) collections.
On the hardware front, I’m going to offer a few options catered towards different budgets and media library sizes. The cost of getting a media server up and running using this guide will cost you anywhere from $450 CAD/$325 USD at the low end to $1500 CAD/$1100 USD at the high end (it could go higher). My server was priced closer to the higher figure, but I went and got a lot more storage than most people need. If that seems like a little much, consider for a moment, do you have a roommate, a close friend, or a family member who would be willing to chip in a few bucks towards your little project provided they get access? Well that's how I funded my server. It might also be worth thinking about the cost over time, i.e. how much you spend yearly on subscriptions vs. a one time cost of setting up a server. Additionally there's just the joy of being able to scream "fuck you" at all those show cancelling, library deleting, hedge fund vampire CEOs who run the studios through denying them your money. Drive a stake through David Zaslav's heart.
On the software side I will walk you step-by-step through installing Ubuntu as your server's operating system, configuring your storage as a RAIDz array with ZFS, sharing your zpool to Windows with Samba, running a remote connection between your server and your Windows PC, and then a little about started with Plex/Jellyfin. Every terminal command you will need to input will be provided, and I even share a custom #bash script that will make used vs. available drive space on your server display correctly in Windows.
If you have a different preferred flavour of Linux (Arch, Manjaro, Redhat, Fedora, Mint, OpenSUSE, CentOS, Slackware etc. et. al.) and are aching to tell me off for being basic and using Ubuntu, this tutorial is not for you. The sort of person with a preferred Linux distro is the sort of person who can do this sort of thing in their sleep. Also I don't care. This tutorial is intended for the average home computer user. This is also why we’re not using a more exotic home server solution like running everything through Docker Containers and managing it through a dashboard like Homarr or Heimdall. While such solutions are fantastic and can be very easy to maintain once you have it all set up, wrapping your brain around Docker is a whole thing in and of itself. If you do follow this tutorial and had fun putting everything together, then I would encourage you to return in a year’s time, do your research and set up everything with Docker Containers.
Lastly, this is a tutorial aimed at Windows users. Although I was a daily user of OS X for many years (roughly 2008-2023) and I've dabbled quite a bit with various Linux distributions (mostly Ubuntu and Manjaro), my primary OS these days is Windows 11. Many things in this tutorial will still be applicable to Mac users, but others (e.g. setting up shares) you will have to look up for yourself. I doubt it would be difficult to do so.
Nothing in this tutorial will require feats of computing expertise. All you will need is a basic computer literacy (i.e. an understanding of what a filesystem and directory are, and a degree of comfort in the settings menu) and a willingness to learn a thing or two. While this guide may look overwhelming at first glance, it is only because I want to be as thorough as possible. I want you to understand exactly what it is you're doing, I don't want you to just blindly follow steps. If you half-way know what you’re doing, you will be much better prepared if you ever need to troubleshoot.
Honestly, once you have all the hardware ready it shouldn't take more than an afternoon or two to get everything up and running.
(This tutorial is just shy of seven thousand words long so the rest is under the cut.)
Step One: Choosing Your Hardware
Linux is a light weight operating system, depending on the distribution there's close to no bloat. There are recent distributions available at this very moment that will run perfectly fine on a fourteen year old i3 with 4GB of RAM. Moreover, running Plex or Jellyfin isn’t resource intensive in 90% of use cases. All this is to say, we don’t require an expensive or powerful computer. This means that there are several options available: 1) use an old computer you already have sitting around but aren't using 2) buy a used workstation from eBay, or what I believe to be the best option, 3) order an N100 Mini-PC from AliExpress or Amazon.
Note: If you already have an old PC sitting around that you’ve decided to use, fantastic, move on to the next step.
When weighing your options, keep a few things in mind: the number of people you expect to be streaming simultaneously at any one time, the resolution and bitrate of your media library (4k video takes a lot more processing power than 1080p) and most importantly, how many of those clients are going to be transcoding at any one time. Transcoding is what happens when the playback device does not natively support direct playback of the source file. This can happen for a number of reasons, such as the playback device's native resolution being lower than the file's internal resolution, or because the source file was encoded in a video codec unsupported by the playback device.
Ideally we want any transcoding to be performed by hardware. This means we should be looking for a computer with an Intel processor with Quick Sync. Quick Sync is a dedicated core on the CPU die designed specifically for video encoding and decoding. This specialized hardware makes for highly efficient transcoding both in terms of processing overhead and power draw. Without these Quick Sync cores, transcoding must be brute forced through software. This takes up much more of a CPU’s processing power and requires much more energy. But not all Quick Sync cores are created equal and you need to keep this in mind if you've decided either to use an old computer or to shop for a used workstation on eBay
Any Intel processor from second generation Core (Sandy Bridge circa 2011) onward has Quick Sync cores. It's not until 6th gen (Skylake), however, that the cores support the H.265 HEVC codec. Intel’s 10th gen (Comet Lake) processors introduce support for 10bit HEVC and HDR tone mapping. And the recent 12th gen (Alder Lake) processors brought with them hardware AV1 decoding. As an example, while an 8th gen (Kaby Lake) i5-8500 will be able to hardware transcode a H.265 encoded file, it will fall back to software transcoding if given a 10bit H.265 file. If you’ve decided to use that old PC or to look on eBay for an old Dell Optiplex keep this in mind.
Note 1: The price of old workstations varies wildly and fluctuates frequently. If you get lucky and go shopping shortly after a workplace has liquidated a large number of their workstations you can find deals for as low as $100 on a barebones system, but generally an i5-8500 workstation with 16gb RAM will cost you somewhere in the area of $260 CAD/$200 USD.
Note 2: The AMD equivalent to Quick Sync is called Video Core Next, and while it's fine, it's not as efficient and not as mature a technology. It was only introduced with the first generation Ryzen CPUs and it only got decent with their newest CPUs, we want something cheap.
Alternatively you could forgo having to keep track of what generation of CPU is equipped with Quick Sync cores that feature support for which codecs, and just buy an N100 mini-PC. For around the same price or less of a used workstation you can pick up a mini-PC with an Intel N100 processor. The N100 is a four-core processor based on the 12th gen Alder Lake architecture and comes equipped with the latest revision of the Quick Sync cores. These little processors offer astounding hardware transcoding capabilities for their size and power draw. Otherwise they perform equivalent to an i5-6500, which isn't a terrible CPU. A friend of mine uses an N100 machine as a dedicated retro emulation gaming system and it does everything up to 6th generation consoles just fine. The N100 is also a remarkably efficient chip, it sips power. In fact, the difference between running one of these and an old workstation could work out to hundreds of dollars a year in energy bills depending on where you live.
You can find these Mini-PCs all over Amazon or for a little cheaper on AliExpress. They range in price from $170 CAD/$125 USD for a no name N100 with 8GB RAM to $280 CAD/$200 USD for a Beelink S12 Pro with 16GB RAM. The brand doesn't really matter, they're all coming from the same three factories in Shenzen, go for whichever one fits your budget or has features you want. 8GB RAM should be enough, Linux is lightweight and Plex only calls for 2GB RAM. 16GB RAM might result in a slightly snappier experience, especially with ZFS. A 256GB SSD is more than enough for what we need as a boot drive, but going for a bigger drive might allow you to get away with things like creating preview thumbnails for Plex, but it’s up to you and your budget.
The Mini-PC I wound up buying was a Firebat AK2 Plus with 8GB RAM and a 256GB SSD. It looks like this:

Note: Be forewarned that if you decide to order a Mini-PC from AliExpress, note the type of power adapter it ships with. The mini-PC I bought came with an EU power adapter and I had to supply my own North American power supply. Thankfully this is a minor issue as barrel plug 30W/12V/2.5A power adapters are easy to find and can be had for $10.
Step Two: Choosing Your Storage
Storage is the most important part of our build. It is also the most expensive. Thankfully it’s also the most easily upgrade-able down the line.
For people with a smaller media collection (4TB to 8TB), a more limited budget, or who will only ever have two simultaneous streams running, I would say that the most economical course of action would be to buy a USB 3.0 8TB external HDD. Something like this one from Western Digital or this one from Seagate. One of these external drives will cost you in the area of $200 CAD/$140 USD. Down the line you could add a second external drive or replace it with a multi-drive RAIDz set up such as detailed below.
If a single external drive the path for you, move on to step three.
For people with larger media libraries (12TB+), who prefer media in 4k, or care who about data redundancy, the answer is a RAID array featuring multiple HDDs in an enclosure.
Note: If you are using an old PC or used workstatiom as your server and have the room for at least three 3.5" drives, and as many open SATA ports on your mother board you won't need an enclosure, just install the drives into the case. If your old computer is a laptop or doesn’t have room for more internal drives, then I would suggest an enclosure.
The minimum number of drives needed to run a RAIDz array is three, and seeing as RAIDz is what we will be using, you should be looking for an enclosure with three to five bays. I think that four disks makes for a good compromise for a home server. Regardless of whether you go for a three, four, or five bay enclosure, do be aware that in a RAIDz array the space equivalent of one of the drives will be dedicated to parity at a ratio expressed by the equation 1 − 1/n i.e. in a four bay enclosure equipped with four 12TB drives, if we configured our drives in a RAIDz1 array we would be left with a total of 36TB of usable space (48TB raw size). The reason for why we might sacrifice storage space in such a manner will be explained in the next section.
A four bay enclosure will cost somewhere in the area of $200 CDN/$140 USD. You don't need anything fancy, we don't need anything with hardware RAID controls (RAIDz is done entirely in software) or even USB-C. An enclosure with USB 3.0 will perform perfectly fine. Don’t worry too much about USB speed bottlenecks. A mechanical HDD will be limited by the speed of its mechanism long before before it will be limited by the speed of a USB connection. I've seen decent looking enclosures from TerraMaster, Yottamaster, Mediasonic and Sabrent.
When it comes to selecting the drives, as of this writing, the best value (dollar per gigabyte) are those in the range of 12TB to 20TB. I settled on 12TB drives myself. If 12TB to 20TB drives are out of your budget, go with what you can afford, or look into refurbished drives. I'm not sold on the idea of refurbished drives but many people swear by them.
When shopping for harddrives, search for drives designed specifically for NAS use. Drives designed for NAS use typically have better vibration dampening and are designed to be active 24/7. They will also often make use of CMR (conventional magnetic recording) as opposed to SMR (shingled magnetic recording). This nets them a sizable read/write performance bump over typical desktop drives. Seagate Ironwolf and Toshiba NAS are both well regarded brands when it comes to NAS drives. I would avoid Western Digital Red drives at this time. WD Reds were a go to recommendation up until earlier this year when it was revealed that they feature firmware that will throw up false SMART warnings telling you to replace the drive at the three year mark quite often when there is nothing at all wrong with that drive. It will likely even be good for another six, seven, or more years.

Step Three: Installing Linux
For this step you will need a USB thumbdrive of at least 6GB in capacity, an .ISO of Ubuntu, and a way to make that thumbdrive bootable media.
First download a copy of Ubuntu desktop (for best performance we could download the Server release, but for new Linux users I would recommend against the server release. The server release is strictly command line interface only, and having a GUI is very helpful for most people. Not many people are wholly comfortable doing everything through the command line, I'm certainly not one of them, and I grew up with DOS 6.0. 22.04.3 Jammy Jellyfish is the current Long Term Service release, this is the one to get.
Download the .ISO and then download and install balenaEtcher on your Windows PC. BalenaEtcher is an easy to use program for creating bootable media, you simply insert your thumbdrive, select the .ISO you just downloaded, and it will create a bootable installation media for you.
Once you've made a bootable media and you've got your Mini-PC (or you old PC/used workstation) in front of you, hook it directly into your router with an ethernet cable, and then plug in the HDD enclosure, a monitor, a mouse and a keyboard. Now turn that sucker on and hit whatever key gets you into the BIOS (typically ESC, DEL or F2). If you’re using a Mini-PC check to make sure that the P1 and P2 power limits are set correctly, my N100's P1 limit was set at 10W, a full 20W under the chip's power limit. Also make sure that the RAM is running at the advertised speed. My Mini-PC’s RAM was set at 2333Mhz out of the box when it should have been 3200Mhz. Once you’ve done that, key over to the boot order and place the USB drive first in the boot order. Then save the BIOS settings and restart.
After you restart you’ll be greeted by Ubuntu's installation screen. Installing Ubuntu is really straight forward, select the "minimal" installation option, as we won't need anything on this computer except for a browser (Ubuntu comes preinstalled with Firefox) and Plex Media Server/Jellyfin Media Server. Also remember to delete and reformat that Windows partition! We don't need it.
Step Four: Installing ZFS and Setting Up the RAIDz Array
Note: If you opted for just a single external HDD skip this step and move onto setting up a Samba share.
Once Ubuntu is installed it's time to configure our storage by installing ZFS to build our RAIDz array. ZFS is a "next-gen" file system that is both massively flexible and massively complex. It's capable of snapshot backup, self healing error correction, ZFS pools can be configured with drives operating in a supplemental manner alongside the storage vdev (e.g. fast cache, dedicated secondary intent log, hot swap spares etc.). It's also a file system very amenable to fine tuning. Block and sector size are adjustable to use case and you're afforded the option of different methods of inline compression. If you'd like a very detailed overview and explanation of its various features and tips on tuning a ZFS array check out these articles from Ars Technica. For now we're going to ignore all these features and keep it simple, we're going to pull our drives together into a single vdev running in RAIDz which will be the entirety of our zpool, no fancy cache drive or SLOG.
Open up the terminal and type the following commands:
sudo apt update
then
sudo apt install zfsutils-linux
This will install the ZFS utility. Verify that it's installed with the following command:
zfs --version
Now, it's time to check that the HDDs we have in the enclosure are healthy, running, and recognized. We also want to find out their device IDs and take note of them:
sudo fdisk -1
Note: You might be wondering why some of these commands require "sudo" in front of them while others don't. "Sudo" is short for "super user do”. When and where "sudo" is used has to do with the way permissions are set up in Linux. Only the "root" user has the access level to perform certain tasks in Linux. As a matter of security and safety regular user accounts are kept separate from the "root" user. It's not advised (or even possible) to boot into Linux as "root" with most modern distributions. Instead by using "sudo" our regular user account is temporarily given the power to do otherwise forbidden things. Don't worry about it too much at this stage, but if you want to know more check out this introduction.
If everything is working you should get a list of the various drives detected along with their device IDs which will look like this: /dev/sdc. You can also check the device IDs of the drives by opening the disk utility app. Jot these IDs down as we'll need them for our next step, creating our RAIDz array.
RAIDz is similar to RAID-5 in that instead of striping your data over multiple disks, exchanging redundancy for speed and available space (RAID-0), or mirroring your data writing by two copies of every piece (RAID-1), it instead writes parity blocks across the disks in addition to striping, this provides a balance of speed, redundancy and available space. If a single drive fails, the parity blocks on the working drives can be used to reconstruct the entire array as soon as a replacement drive is added.
Additionally, RAIDz improves over some of the common RAID-5 flaws. It's more resilient and capable of self healing, as it is capable of automatically checking for errors against a checksum. It's more forgiving in this way, and it's likely that you'll be able to detect when a drive is dying well before it fails. A RAIDz array can survive the loss of any one drive.
Note: While RAIDz is indeed resilient, if a second drive fails during the rebuild, you're fucked. Always keep backups of things you can't afford to lose. This tutorial, however, is not about proper data safety.
To create the pool, use the following command:
sudo zpool create "zpoolnamehere" raidz "device IDs of drives we're putting in the pool"
For example, let's creatively name our zpool "mypool". This poil will consist of four drives which have the device IDs: sdb, sdc, sdd, and sde. The resulting command will look like this:
sudo zpool create mypool raidz /dev/sdb /dev/sdc /dev/sdd /dev/sde
If as an example you bought five HDDs and decided you wanted more redundancy dedicating two drive to this purpose, we would modify the command to "raidz2" and the command would look something like the following:
sudo zpool create mypool raidz2 /dev/sdb /dev/sdc /dev/sdd /dev/sde /dev/sdf
An array configured like this is known as RAIDz2 and is able to survive two disk failures.
Once the zpool has been created, we can check its status with the command:
zpool status
Or more concisely with:
zpool list
The nice thing about ZFS as a file system is that a pool is ready to go immediately after creation. If we were to set up a traditional RAID-5 array using mbam, we'd have to sit through a potentially hours long process of reformatting and partitioning the drives. Instead we're ready to go right out the gates.
The zpool should be automatically mounted to the filesystem after creation, check on that with the following:
df -hT | grep zfs
Note: If your computer ever loses power suddenly, say in event of a power outage, you may have to re-import your pool. In most cases, ZFS will automatically import and mount your pool, but if it doesn’t and you can't see your array, simply open the terminal and type sudo zpool import -a.
By default a zpool is mounted at /"zpoolname". The pool should be under our ownership but let's make sure with the following command:
sudo chown -R "yourlinuxusername" /"zpoolname"
Note: Changing file and folder ownership with "chown" and file and folder permissions with "chmod" are essential commands for much of the admin work in Linux, but we won't be dealing with them extensively in this guide. If you'd like a deeper tutorial and explanation you can check out these two guides: chown and chmod.
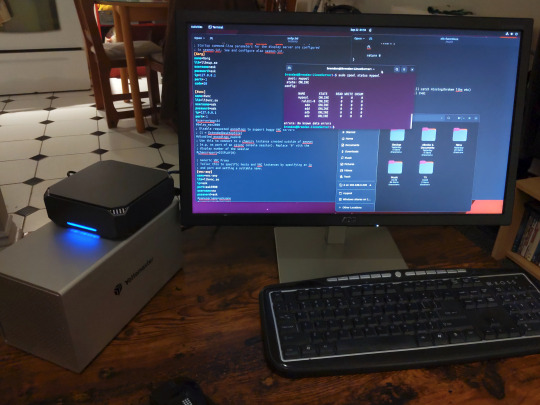
You can access the zpool file system through the GUI by opening the file manager (the Ubuntu default file manager is called Nautilus) and clicking on "Other Locations" on the sidebar, then entering the Ubuntu file system and looking for a folder with your pool's name. Bookmark the folder on the sidebar for easy access.
Your storage pool is now ready to go. Assuming that we already have some files on our Windows PC we want to copy to over, we're going to need to install and configure Samba to make the pool accessible in Windows.
Step Five: Setting Up Samba/Sharing
Samba is what's going to let us share the zpool with Windows and allow us to write to it from our Windows machine. First let's install Samba with the following commands:
sudo apt-get update
then
sudo apt-get install samba
Next create a password for Samba.
sudo smbpswd -a "yourlinuxusername"
It will then prompt you to create a password. Just reuse your Ubuntu user password for simplicity's sake.
Note: if you're using just a single external drive replace the zpool location in the following commands with wherever it is your external drive is mounted, for more information see this guide on mounting an external drive in Ubuntu.
After you've created a password we're going to create a shareable folder in our pool with this command
mkdir /"zpoolname"/"foldername"
Now we're going to open the smb.conf file and make that folder shareable. Enter the following command.
sudo nano /etc/samba/smb.conf
This will open the .conf file in nano, the terminal text editor program. Now at the end of smb.conf add the following entry:
["foldername"]
path = /"zpoolname"/"foldername"
available = yes
valid users = "yourlinuxusername"
read only = no
writable = yes
browseable = yes
guest ok = no
Ensure that there are no line breaks between the lines and that there's a space on both sides of the equals sign. Our next step is to allow Samba traffic through the firewall:
sudo ufw allow samba
Finally restart the Samba service:
sudo systemctl restart smbd
At this point we'll be able to access to the pool, browse its contents, and read and write to it from Windows. But there's one more thing left to do, Windows doesn't natively support the ZFS file systems and will read the used/available/total space in the pool incorrectly. Windows will read available space as total drive space, and all used space as null. This leads to Windows only displaying a dwindling amount of "available" space as the drives are filled. We can fix this! Functionally this doesn't actually matter, we can still write and read to and from the disk, it just makes it difficult to tell at a glance the proportion of used/available space, so this is an optional step but one I recommend (this step is also unnecessary if you're just using a single external drive). What we're going to do is write a little shell script in #bash. Open nano with the terminal with the command:
nano
Now insert the following code:
#!/bin/bash CUR_PATH=`pwd` ZFS_CHECK_OUTPUT=$(zfs get type $CUR_PATH 2>&1 > /dev/null) > /dev/null if [[ $ZFS_CHECK_OUTPUT == *not\ a\ ZFS* ]] then IS_ZFS=false else IS_ZFS=true fi if [[ $IS_ZFS = false ]] then df $CUR_PATH | tail -1 | awk '{print $2" "$4}' else USED=$((`zfs get -o value -Hp used $CUR_PATH` / 1024)) > /dev/null AVAIL=$((`zfs get -o value -Hp available $CUR_PATH` / 1024)) > /dev/null TOTAL=$(($USED+$AVAIL)) > /dev/null echo $TOTAL $AVAIL fi
Save the script as "dfree.sh" to /home/"yourlinuxusername" then change the ownership of the file to make it executable with this command:
sudo chmod 774 dfree.sh
Now open smb.conf with sudo again:
sudo nano /etc/samba/smb.conf
Now add this entry to the top of the configuration file to direct Samba to use the results of our script when Windows asks for a reading on the pool's used/available/total drive space:
[global]
dfree command = /home/"yourlinuxusername"/dfree.sh
Save the changes to smb.conf and then restart Samba again with the terminal:
sudo systemctl restart smbd
Now there’s one more thing we need to do to fully set up the Samba share, and that’s to modify a hidden group permission. In the terminal window type the following command:
usermod -a -G sambashare “yourlinuxusername”
Then restart samba again:
sudo systemctl restart smbd
If we don’t do this last step, everything will appear to work fine, and you will even be able to see and map the drive from Windows and even begin transferring files, but you'd soon run into a lot of frustration. As every ten minutes or so a file would fail to transfer and you would get a window announcing “0x8007003B Unexpected Network Error”. This window would require your manual input to continue the transfer with the file next in the queue. And at the end it would reattempt to transfer whichever files failed the first time around. 99% of the time they’ll go through that second try, but this is still all a major pain in the ass. Especially if you’ve got a lot of data to transfer or you want to step away from the computer for a while.
It turns out samba can act a little weirdly with the higher read/write speeds of RAIDz arrays and transfers from Windows, and will intermittently crash and restart itself if this group option isn’t changed. Inputting the above command will prevent you from ever seeing that window.
The last thing we're going to do before switching over to our Windows PC is grab the IP address of our Linux machine. Enter the following command:
hostname -I
This will spit out this computer's IP address on the local network (it will look something like 192.168.0.x), write it down. It might be a good idea once you're done here to go into your router settings and reserving that IP for your Linux system in the DHCP settings. Check the manual for your specific model router on how to access its settings, typically it can be accessed by opening a browser and typing http:\\192.168.0.1 in the address bar, but your router may be different.
Okay we’re done with our Linux computer for now. Get on over to your Windows PC, open File Explorer, right click on Network and click "Map network drive". Select Z: as the drive letter (you don't want to map the network drive to a letter you could conceivably be using for other purposes) and enter the IP of your Linux machine and location of the share like so: \\"LINUXCOMPUTERLOCALIPADDRESSGOESHERE"\"zpoolnamegoeshere"\. Windows will then ask you for your username and password, enter the ones you set earlier in Samba and you're good. If you've done everything right it should look something like this:

You can now start moving media over from Windows to the share folder. It's a good idea to have a hard line running to all machines. Moving files over Wi-Fi is going to be tortuously slow, the only thing that’s going to make the transfer time tolerable (hours instead of days) is a solid wired connection between both machines and your router.
Step Six: Setting Up Remote Desktop Access to Your Server
After the server is up and going, you’ll want to be able to access it remotely from Windows. Barring serious maintenance/updates, this is how you'll access it most of the time. On your Linux system open the terminal and enter:
sudo apt install xrdp
Then:
sudo systemctl enable xrdp
Once it's finished installing, open “Settings” on the sidebar and turn off "automatic login" in the User category. Then log out of your account. Attempting to remotely connect to your Linux computer while you’re logged in will result in a black screen!
Now get back on your Windows PC, open search and look for "RDP". A program called "Remote Desktop Connection" should pop up, open this program as an administrator by right-clicking and selecting “run as an administrator”. You’ll be greeted with a window. In the field marked “Computer” type in the IP address of your Linux computer. Press connect and you'll be greeted with a new window and prompt asking for your username and password. Enter your Ubuntu username and password here.
If everything went right, you’ll be logged into your Linux computer. If the performance is sluggish, adjust the display options. Lowering the resolution and colour depth do a lot to make the interface feel snappier.
Remote access is how we're going to be using our Linux system from now, barring edge cases like needing to get into the BIOS or upgrading to a new version of Ubuntu. Everything else from performing maintenance like a monthly zpool scrub to checking zpool status and updating software can all be done remotely.
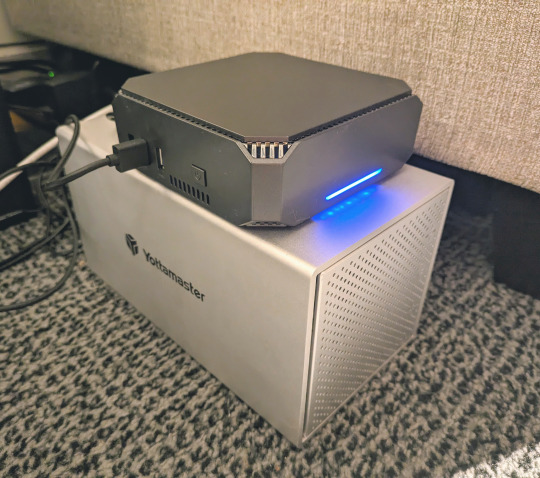

This is how my server lives its life now, happily humming and chirping away on the floor next to the couch in a corner of the living room.
Step Seven: Plex Media Server/Jellyfin
Okay we’ve got all the ground work finished and our server is almost up and running. We’ve got Ubuntu up and running, our storage array is primed, we’ve set up remote connections and sharing, and maybe we’ve moved over some of favourite movies and TV shows.
Now we need to decide on the media server software to use which will stream our media to us and organize our library. For most people I’d recommend Plex. It just works 99% of the time. That said, Jellyfin has a lot to recommend it by too, even if it is rougher around the edges. Some people run both simultaneously, it’s not that big of an extra strain. I do recommend doing a little bit of your own research into the features each platform offers, but as a quick run down, consider some of the following points:
Plex is closed source and is funded through PlexPass purchases while Jellyfin is open source and entirely user driven. This means a number of things: for one, Plex requires you to purchase a “PlexPass” (purchased as a one time lifetime fee $159.99 CDN/$120 USD or paid for on a monthly or yearly subscription basis) in order to access to certain features, like hardware transcoding (and we want hardware transcoding) or automated intro/credits detection and skipping, Jellyfin offers some of these features for free through plugins. Plex supports a lot more devices than Jellyfin and updates more frequently. That said, Jellyfin's Android and iOS apps are completely free, while the Plex Android and iOS apps must be activated for a one time cost of $6 CDN/$5 USD. But that $6 fee gets you a mobile app that is much more functional and features a unified UI across platforms, the Plex mobile apps are simply a more polished experience. The Jellyfin apps are a bit of a mess and the iOS and Android versions are very different from each other.
Jellyfin’s actual media player is more fully featured than Plex's, but on the other hand Jellyfin's UI, library customization and automatic media tagging really pale in comparison to Plex. Streaming your music library is free through both Jellyfin and Plex, but Plex offers the PlexAmp app for dedicated music streaming which boasts a number of fantastic features, unfortunately some of those fantastic features require a PlexPass. If your internet is down, Jellyfin can still do local streaming, while Plex can fail to play files unless you've got it set up a certain way. Jellyfin has a slew of neat niche features like support for Comic Book libraries with the .cbz/.cbt file types, but then Plex offers some free ad-supported TV and films, they even have a free channel that plays nothing but Classic Doctor Who.
Ultimately it's up to you, I settled on Plex because although some features are pay-walled, it just works. It's more reliable and easier to use, and a one-time fee is much easier to swallow than a subscription. I had a pretty easy time getting my boomer parents and tech illiterate brother introduced to and using Plex and I don't know if I would've had as easy a time doing that with Jellyfin. I do also need to mention that Jellyfin does take a little extra bit of tinkering to get going in Ubuntu, you’ll have to set up process permissions, so if you're more tolerant to tinkering, Jellyfin might be up your alley and I’ll trust that you can follow their installation and configuration guide. For everyone else, I recommend Plex.
So pick your poison: Plex or Jellyfin.
Note: The easiest way to download and install either of these packages in Ubuntu is through Snap Store.
After you've installed one (or both), opening either app will launch a browser window into the browser version of the app allowing you to set all the options server side.
The process of adding creating media libraries is essentially the same in both Plex and Jellyfin. You create a separate libraries for Television, Movies, and Music and add the folders which contain the respective types of media to their respective libraries. The only difficult or time consuming aspect is ensuring that your files and folders follow the appropriate naming conventions:
Plex naming guide for Movies
Plex naming guide for Television
Jellyfin follows the same naming rules but I find their media scanner to be a lot less accurate and forgiving than Plex. Once you've selected the folders to be scanned the service will scan your files, tagging everything and adding metadata. Although I find do find Plex more accurate, it can still erroneously tag some things and you might have to manually clean up some tags in a large library. (When I initially created my library it tagged the 1963-1989 Doctor Who as some Korean soap opera and I needed to manually select the correct match after which everything was tagged normally.) It can also be a bit testy with anime (especially OVAs) be sure to check TVDB to ensure that you have your files and folders structured and named correctly. If something is not showing up at all, double check the name.
Once that's done, organizing and customizing your library is easy. You can set up collections, grouping items together to fit a theme or collect together all the entries in a franchise. You can make playlists, and add custom artwork to entries. It's fun setting up collections with posters to match, there are even several websites dedicated to help you do this like PosterDB. As an example, below are two collections in my library, one collecting all the entries in a franchise, the other follows a theme.

My Star Trek collection, featuring all eleven television series, and thirteen films.
My Best of the Worst collection, featuring sixty-nine films previously showcased on RedLetterMedia’s Best of the Worst. They’re all absolutely terrible and I love them.
As for settings, ensure you've got Remote Access going, it should work automatically and be sure to set your upload speed after running a speed test. In the library settings set the database cache to 2000MB to ensure a snappier and more responsive browsing experience, and then check that playback quality is set to original/maximum. If you’re severely bandwidth limited on your upload and have remote users, you might want to limit the remote stream bitrate to something more reasonable, just as a note of comparison Netflix’s 1080p bitrate is approximately 5Mbps, although almost anyone watching through a chromium based browser is streaming at 720p and 3mbps. Other than that you should be good to go. For actually playing your files, there's a Plex app for just about every platform imaginable. I mostly watch television and films on my laptop using the Windows Plex app, but I also use the Android app which can broadcast to the chromecast connected to the TV in the office and the Android TV app for our smart TV. Both are fully functional and easy to navigate, and I can also attest to the OS X version being equally functional.
Part Eight: Finding Media
Now, this is not really a piracy tutorial, there are plenty of those out there. But if you’re unaware, BitTorrent is free and pretty easy to use, just pick a client (qBittorrent is the best) and go find some public trackers to peruse. Just know now that all the best trackers are private and invite only, and that they can be exceptionally difficult to get into. I’m already on a few, and even then, some of the best ones are wholly out of my reach.
If you decide to take the left hand path and turn to Usenet you’ll have to pay. First you’ll need to sign up with a provider like Newshosting or EasyNews for access to Usenet itself, and then to actually find anything you’re going to need to sign up with an indexer like NZBGeek or NZBFinder. There are dozens of indexers, and many people cross post between them, but for more obscure media it’s worth checking multiple. You’ll also need a binary downloader like SABnzbd. That caveat aside, Usenet is faster, bigger, older, less traceable than BitTorrent, and altogether slicker. I honestly prefer it, and I'm kicking myself for taking this long to start using it because I was scared off by the price. I’ve found so many things on Usenet that I had sought in vain elsewhere for years, like a 2010 Italian film about a massacre perpetrated by the SS that played the festival circuit but never received a home media release; some absolute hero uploaded a rip of a festival screener DVD to Usenet. Anyway, figure out the rest of this shit on your own and remember to use protection, get yourself behind a VPN, use a SOCKS5 proxy with your BitTorrent client, etc.
On the legal side of things, if you’re around my age, you (or your family) probably have a big pile of DVDs and Blu-Rays sitting around unwatched and half forgotten. Why not do a bit of amateur media preservation, rip them and upload them to your server for easier access? (Your tools for this are going to be Handbrake to do the ripping and AnyDVD to break any encryption.) I went to the trouble of ripping all my SCTV DVDs (five box sets worth) because none of it is on streaming nor could it be found on any pirate source I tried. I’m glad I did, forty years on it’s still one of the funniest shows to ever be on TV.
Part Nine/Epilogue: Sonarr/Radarr/Lidarr and Overseerr
There are a lot of ways to automate your server for better functionality or to add features you and other users might find useful. Sonarr, Radarr, and Lidarr are a part of a suite of “Servarr” services (there’s also Readarr for books and Whisparr for adult content) that allow you to automate the collection of new episodes of TV shows (Sonarr), new movie releases (Radarr) and music releases (Lidarr). They hook in to your BitTorrent client or Usenet binary newsgroup downloader and crawl your preferred Torrent trackers and Usenet indexers, alerting you to new releases and automatically grabbing them. You can also use these services to manually search for new media, and even replace/upgrade your existing media with better quality uploads. They’re really a little tricky to set up on a bare metal Ubuntu install (ideally you should be running them in Docker Containers), and I won’t be providing a step by step on installing and running them, I’m simply making you aware of their existence.
The other bit of kit I want to make you aware of is Overseerr which is a program that scans your Plex media library and will serve recommendations based on what you like. It also allows you and your users to request specific media. It can even be integrated with Sonarr/Radarr/Lidarr so that fulfilling those requests is fully automated.
And you're done. It really wasn't all that hard. Enjoy your media. Enjoy the control you have over that media. And be safe in the knowledge that no hedgefund CEO motherfucker who hates the movies but who is somehow in control of a major studio will be able to disappear anything in your library as a tax write-off.
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
me when companies try to force you to use their proprietary software

anyway
Layperson resources:
firefox is an open source browser by Mozilla that makes privacy and software independence much easier. it is very easy to transfer all your chrome data to Firefox
ublock origin is The highest quality adblock atm. it is a free browser extension, and though last i checked it is available on Chrome google is trying very hard to crack down on its use
Thunderbird mail is an open source email client also by mozilla and shares many of the same advantages as firefox (it has some other cool features as well)
libreOffice is an open source office suite similar to microsoft office or Google Suite, simple enough
Risky:
VPNs (virtual private networks) essentially do a number of things, but most commonly they are used to prevent people from tracking your IP address. i would suggest doing more research. i use proton vpn, as it has a decent free version, and the paid version is powerful
note: some applications, websites, and other entities do not tolerate the use of VPNs. you may not be able to access certain secure sites while using a VPN, and logging into your personal account with some services while using a vpn *may* get you PERMANENTLY BLACKLISTED from the service on that account, ymmv
IF YOU HAVE A DECENT VPN, ANTIVIRUS, AND ADBLOCK, you can start learning about piracy, though i will not be providing any resources, as Loose Lips Sink Ships. if you want to be very safe, start with streaming sites and never download any files, though you Can learn how to discern between safe, unsafe, and risky content.
note: DO NOT SHARE LINKS TO OR NAMES OF PIRACY SITES IN PUBLIC PLACES, ESPECIALLY SOCAL MEDIA
the only time you should share these things are either in person or in (preferably peer-to-peer encrypted) PRIVATE messages
when pirated media becomes well-known and circulated on the wider, public internet, it gets taken down, because it is illegal to distribute pirated media and software
if you need an antivirus i like bitdefender. it has a free version, and is very good, though if youre using windows, windows defender is also very good and it comes with the OS
Advanced:
linux is great if you REALLY know what you're doing. you have to know a decent amount of computer science and be comfortable using the Terminal/Command Prompt to get/use linux. "Linux" refers to a large array of related open source Operating Systems. do research and pick one that suits your needs. im still experimenting with various dispos, but im leaning towards either Ubuntu Cinnamon or Debian.
#capitalism#open source#firefox#thunderbird#mozilla#ublock origin#libreoffice#vpn#antivirus#piracy#linux
695 notes
·
View notes
Text
I just had a really interesting idea.
So i have this USB stick that i hang in my keys and keep with me all the time. It's completely empty and i really don't use it too often. But as a follow up to my linux craze, i came up with a really fun use for it!
I wanna split the USB into 2 partitions, one EXT4 and one exFAT, and have a very light linux distro installed on the EXT4 partition, giving me a backup OS that i can carry around everywhere. the exFAT drive will be for general storage (so it can be detected by windows).
I think this is a really neat idea because i often find myself having to fix stuff. It's also an effective way to transfer files if the OS doesn't start.
I'll look up how to do this and have some fun with it :D
35 notes
·
View notes
Text
Creating a personal fanfic archive using Calibre, various Calibre plugins, Firefox Reader View, and an e-Reader / BookFusion / Calibre-Web
A few years ago I started getting serious about saving my favorite fic (or just any fic I enjoyed), since the Internet is sadly not actually always forever when it comes to fanfiction. Plus, I wanted a way to access fanfic offline when wifi wasn't available. Enter a personal fanfic archive!
There are lots of ways you can do this, but I thought I'd share my particular workflow in case it helps others get started. Often it's easier to build off someone else's workflow than to create your own!
Please note that this is for building an archive for private use -- always remember that it's bad form to publicly archive someone else's work without their explicit permission.
This is going to be long, so let's add a read more!
How to Build Your Own Personal Fanfic Archive
Step One: Install Calibre
Calibre is an incredibly powerful ebook management software that allows you to do a whole lot of stuff having to do with ebooks, such as convert almost any text-based file into an ebook and (often) vice-versa. It also allows you to easily side-load ebooks onto your personal e-reader of choice and manage the collection of ebooks on the device.
And because it's open source, developers have created a bunch of incredibly useful plugins to use with Calibre (including several we're going to talk about in the next step), which make saving and reading fanfiction super easy and fun.
But before we can do that, you need to download and install it. It's available for Windows, MacOS, Linux, and in a portable version.
Step Two: Download These Plugins
This guide would be about 100 pages long if I went into all of the plugins I love and use with Calibre, so we're just going to focus on the ones I use for saving and reading fanfiction. And since I'm trying to keep this from becoming a novel (lolsob), I'll just link to the documentation for most of these plugins, but if you run into trouble using them, just tag me in the notes or a comment and I'll be happy to write up some steps for using them.
Anyway, now that you've downloaded and installed Calibre, it's time to get some plugins! To do that, go to Preferences > Get plugins to enhance Calibre.
You'll see a pop-up with a table of a huge number of plugins. You can use the Filter by name: field in the upper right to search for the plugins below, one at a time.
Click on each plugin, then click Install. You'll be asked which toolbars to add the plugins to; for these, I keep the suggested locations (in the main toolbar & when a device is connected).
FanFicFare (here's also a great tutorial for using this plugin) EpubMerge (for creating anthologies from fic series) EbubSplit (for if you ever need to break up fic anthologies) Generate Cover (for creating simple artwork for downloaded fic) Manage Series (for managing fic series)
You'll have to restart Calibre for the plugins to run, so I usually wait to restart until I've installed the last plugin I want.
Take some time here to configure these plugins, especially FanFicFare. In the next step, I'll demonstrate a few of its features, but you might be confused if you haven't set it up yet! (Again, highly recommend that linked tutorial!)
Step Three: Get to Know FanFicFare (and to a lesser extent, Generate Cover)
FanFicFare is a free Calibre plugin that allows you to download fic in bulk, including all stories in a series as one work, adding them directly to Calibre so that that you can convert them to other formats or transfer them to your e-reader.
As with Calibre, FanFicFare has a lot of really cool features, but we're just going to focus on a few, since the docs above will show you most of them.
The features I use most often are: Download from URLs, Get Story URLs from Email, and Get Story URLs from Web Page.
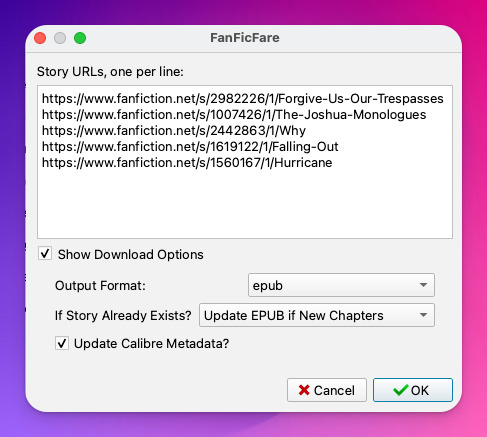
Download from URLs let's you add a running list of URLs that you'd like FanFicFare to download and turn into ebooks for you. So, say, you have a bunch of fic from fanfic.net that you want to download. You can do that!
Now, in this case, I've already downloaded these (which FanFicFare detected), so I didn't update my library with the fic.
But I do have some updates to do from email, so let's try getting story URLs from email!
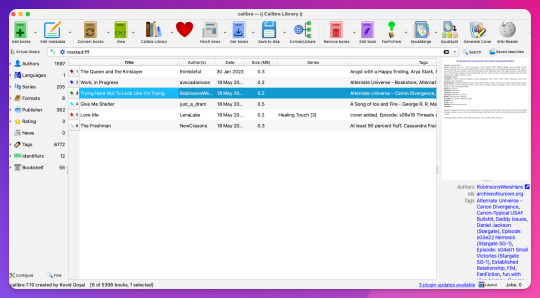
Woohoo, new fic! Calibre will detect when cover art is included in the downloaded file and use that, but at least one of these fic doesn't have cover art (which is the case for most of the fic I download). This is where Generate Cover comes in.
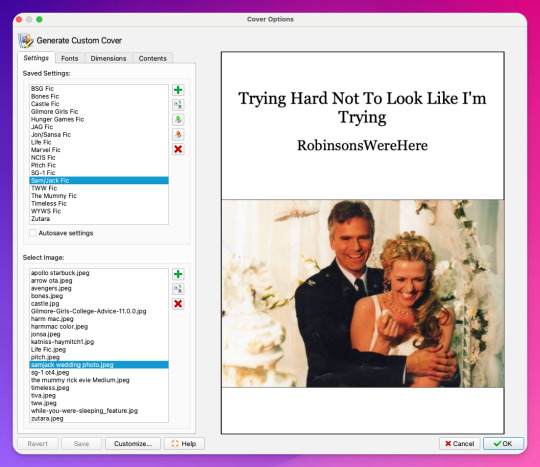
With Generate Cover, I can set the art, font, dimensions, and info content of the covers so that when I'm looking at the fic on my Kindle, I know right away what fic it is, what fandom it's from, and whether or not it's part of a series.
Okay, last thing from FanFicFare -- say I want to download all of the fic on a page, like in an author's profile on fanfic.net or all of the stories in a series. I can do that too with Get Story URLs from Web Page:
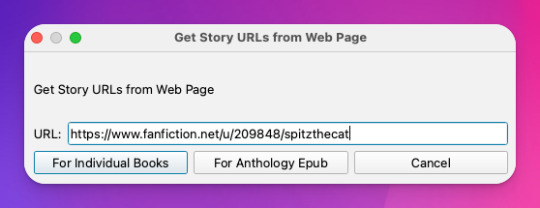
The thing I want to call out here is that I can specify whether the fic at this link are individual works or all part of an anthology, meaning if they're all works in the same series, I can download all stories as a single ebook by choosing For Anthology Epub.
Step Four: Using FireFox Reader View to Download Fic Outside of Archives
This is less common now thanks to AO3, but the elders among us may want to save fanfic that exists outside of archives on personal websites that either still exist or that exist only on the Internet Wayback Machine. FanFicFare is awesome and powerful, but it's not able to download fic from these kinds of sources, so we have to get creative.
I've done this in a couple of ways, none of which are entirely perfect, but the easiest way I've found thus far is by using Firefox's Reader View. Also, I don't think I discovered this -- I think I read about this on Tumblr, actually, although I can longer find the source (if you know it, please tell me so I can credit them!).
At any rate, open the fic in Firefox and then toggle on Reader View:
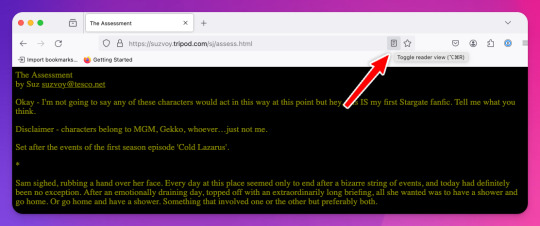
Toggling on Reader View strips all the HTML formatting from the page and presents the fic in the clean way you see in the preview below, which is more ideal for ebook formats.
To save this, go to the hamburger menu in the upper right of the browser and select Print, then switch to Print to PDF. You'll see the URL and some other stuff at the top and bottom of the pages; to remove that, scroll down until you see something like More settings... and uncheck Print headers and footers.
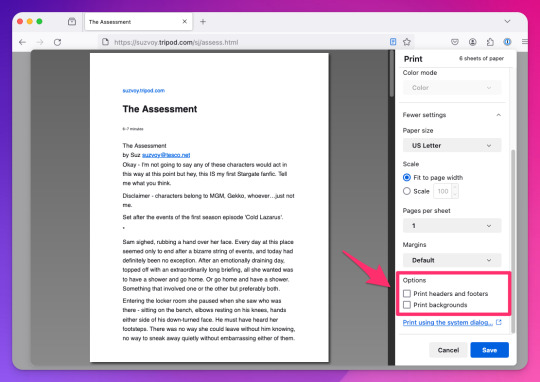
Click Save to download the resulting PDF, which you can then add to Calibre and convert to whichever format works best for your e-reader or archive method.
Step Five: Archiving (Choose Your Own Adventure)
Here's the really fun part: now that you know how to download your fave fanfics in bulk and hopefully have a nice little cache going, it's time to choose how you want to (privately) archive them!
I'm going to go through each option I've used in order of how easy it is to implement (and whether it costs additional money to use). I won't go too in depth about any of them, but I'm happy to do so in a separate post if anyone is interested.
Option 1: On Your Computer
If you're using Calibre to convert fanfic, then you're basically using your computer as your primary archive. This is a great option, because it carries no additional costs outside the original cost of acquiring your computer. It's also the simplest option, as it really doesn't require any advanced technical knowledge, just a willingness to tinker with Calibre and its plugins or to read how-to docs.
Calibre comes with a built-in e-book viewer that you can use to read the saved fic on your computer (just double-click on the fic in Calibre). You can also import it into your ebook app of choice (in most cases; this can get a little complicated just depending on how many fic you're working with and what OS you're on/app you're using).
If you choose this option, you may want to consider backing the fic up to a secondary location like an external hard drive or cloud storage. This may incur additional expense, but is likely still one of the more affordable options, since storage space is cheap and only getting cheaper, and text files tend to not be that big to begin with, even when there are a lot of them.
Option 2: On Your e-Reader
This is another great option, since this is what Calibre was built for! There are some really great, afforable e-readers out there nowadays, and Calibre supports most of them. Of course, this is a more expensive option because you have to acquire an e-reader in addition to a computer to run Calibre on, but if you already have an e-reader and haven't considered using it to read fanfic, boy are you in for a treat!
Option 3: In BookFusion
This is a really cool option that I discovered while tinkering with Calibre and used for about a year before I moved to a self-hosted option (see Option 4).
BookFusion is a web platform and an app (available on iOS and Android) that allows you to build your own ebook library and access it from anywhere, even when you're offline (it's the offline bit that really sold me). It has a Calibre plugin through which you can manage your ebook library very easily, including sorting your fanfic into easy-to-access bookshelves. You may or may not be able to share ebooks depending on your subscription, but only with family members.
Here's what the iOS app looks like:
The downside to BookFusion is that you'll need a subscription if you want to upload more than 10 ebooks. It's affordable(ish), ranging from $1.99 per month for a decent 5GB storage all the way to $9.99 for 100GB for power users. Yearly subs range from $18.99 to $95.99. (They say this is temporary, early bird pricing, but subscribing now locks you into this pricing forever.)
I would recommend this option if you have some cash to spare and you're really comfortable using Calibre or you're a nerd for making apps like BookFusion work. It works really well and is incredibly convenient once you get it set up (especially when you want to read on your phone or tablet offline), but even I, someone who works in tech support for a living, had some trouble with the initial sync and ended up duplicating every ebook in my BookFusion library, making for a very tedious cleanup session.
Option 4: On a Self-Hosted Server Using Calibre-Web
Do you enjoy unending confusion and frustration? Are you okay with throwing fistfuls of money down a well? Do you like putting in an incredible amount of work for something only you and maybe a few other people will ever actually use? If so, self-hosting Calibre-Web on your own personal server might be a good fit for you!
To be fair, this is likely an experience unique to me, because I am just technical enough to be a danger to myself. I can give a brief summary of how I did this, but I don't know nearly enough to explain to you how to do it.
Calibre-Web is a web app that works on top of Calibre, offering "a clean and intuitive interface for browsing, reading, and downloading eBooks."
I have a network-attached storage (NAS) server on which I run an instance of Calibre and Calibre-Web (through the miracle that is Docker). After the initial work of downloading all the fic I wanted to save and transferring it to the server, I'm now able to download all new fic pretty much via email thanks to FanFicFare, so updating my fic archive is mostly automated at this point.
If you're curious, this is what it looks like:
Pros: The interface is clean and intuitive, the ebook reader is fantastic. The Discover feature, in which you are given random books / fic to read, has turned out to be one feature worth all the irritation of setting up Calibre-Web. I can access, read, and download ebooks on any device, and I can even convert ebooks into another format using this interface. As I mentioned above, updating it with fic (and keeping the Docker container itself up to date) is relatively automated and easy now.
Cons: The server, in whichever form you choose, costs money. It is not cheap. If you're not extremely careful (and sometimes even if you are, like me) and a hard drive goes bad, you could lose data (and then you have to spend more money to replace said hard drive and time replacing said data). It is not easy to set up. You may, at various points in this journey, wish you could launch the server into the sun, Calibre-Web into the sun, or yourself into the sun.
Step Six: Profit!
That's it! I hope this was enough to get you moving towards archiving your favorite fanfic. Again, if there's anything here you'd like me to expand on, let me know! Obviously I'm a huge nerd about this stuff, and love talking about it.
#genie's stuff#calibre#calibre-web#bookfusion#personal fanfic archive#archiving fanfic#saving fanfic
103 notes
·
View notes
Text
Offline Library
In light of all the Ao3 issues lately I'm gonna throw this up as something people should consider doing. Make your own library of your favorite fics and any you might like to read in the future/are currently reading.
How do you do this? To start: Calibre & ReadEra app
Calibre is a free ebook management software, available on windows, mac, and linux - but also comes in a portable version you can put on a flash drive. Ebooks are very small files, 100s of fics can easily take less than 1GB of space. You can create categories for everything and all the tags on the fics will stay attached to them. You can download directly through ao3, or you can use the browser extension Ficlab which can make the process a little quicker, plus give you a book cover(or you can add your own cover). Epub or Mobi format is best.
ReadEra, is a free reading app with no ads that you can tell to only access a single file where you keep your ebooks. It's open source and the Privacy Statement and Terms & Conditions are very short and easy to read. You can transfer files from Calibre to your phone, but this is also a good option if you don't have a PC to use Calibre. You can make folders to organize all your fics.
Quality of life plugins for Calibre: Preferences > Plugins > Get New Plugins
Look up: EpubMerge, EpubSplit, FanFicFare, Generate Cover (restart calibre once you've added them all) Fun fact, with FanFicFare, you can download new chapters to update fics that are currently in progress directly in Calibre instead of having to open up ao3.
Also, to be clear - back them up for yourself only, don't you fucking dare repost them anywhere.
You can also backup Kindle books (and you should) with Calibre, though that's a bit more complicated; instructions under the read more
Firstly what is DRM? TLDR: digital rights management (DRM) is meant to prevent piracy, however, this also means you never really own your ebooks. If Amazon decides to take down a book you bought? That's it, it's gone and it doesn't matter that you paid for it.
Removing DRM If you're on PC and don't have a kindle device, you'll want kindle version 2.4.0 or it won't work in Calibre.
In Calibre, navigate to Preferences > Plugins > Load Plugin From File - DeDRM - Use the latest Beta or Alpha release, follow instructions on the github page
Preferences > Plugins > Get New Plugins
Look up: KFX Input
You'll have to restart Calibre once you install so just add them all at once before you restart it.
If you need some troubleshooting help setting anything up just ask and I'll try to help!
48 notes
·
View notes
Text
Free software recommendations for various things:
LibreOffice - A full home office suite comparable to Microsoft Office. Easy to use and you can choose the UI layout from several types; it can handle docx and other Microsoft Office document formats; it still does not include AI unless you specifically add that extension on purpose, so unlike other office suites it's not shoving AI down your throat.
Calibre - Ebook manager bundled with an ebook editor and ereader software. It can follow news feeds, downloading them into epub format. Convert ebooks from one format into (many) others. Run a server to make access your books from different computers/phones/tablets easier. And so much more... without even touching on the additional functionality that plugins can add. With plugins it can be used for DRM stripping (which can still remove DRM from even Kindle ebooks, if you have a kindle that you can download the ebook to and use to transfer to your computer). It can also handle downloading fanfics and their metadata using the FanFicFare plugin. (Which I've written tutorials about.) There are officially supported plugins (like FanFicFare) that are easy to install and unofficial plugins (like the DRM stripper) that take more work, so it's extremely customizable.
Syncthing - Want to host your own local file backup system? Have an old laptop that you can reformat with a linux distro? And maybe a spare hard drive? Perfect, you have what you need to set up a home file backup system. Reformat the computer with the new operating system, install syncthing on that computer and on the computer you want to back up files for and the two installations of the software can sync over your home network. Put it on your phone and back up your photos. The software is open source, encrypted, and you can turn it off so that your computer (or phone) is only running it on a trusted network. You control where the synced data lives, which computers on your network those synced folders are shared with (allowing for sharing between multiple computers) and even what type of file backups happen if data is, say, accidentally deleted. (File recovery!!!)
Plex or Emby - Both are free to install on any computer, point at any movie/tv show/audiobook/music files you've got sitting around, and bam you've got a home media streaming server. Both have paid tiers for more features (including tv tuner integration to act as a DVR), but what they can do for free is already impressive and well handled. Both have easy to use UI and it largely comes down to personal preference as to one is better than the other.
Notepad++ - A notepad type program that can also serve as a decent lightweight code editor. I use it for noodling around with code scripts and snippets, writing lists, and various other small tasks. It's not something I'd use for my professional code writing but it's great for just messing around with something on my own time.
16 notes
·
View notes
Text
#Linux#Linux data replication#cloud solutions#Big data security#cloud computing#secure data handling#data privacy#cloud infrastructure#cloud technology#Data Analytics#data integration#Big data solutions#Big data insights#data management#File transfer solutions
0 notes
Note
Hello! Sorry for the bother but do you know how the live 2D files of Tokyo debunker is accessed? I'm like so hyped about this help- Let me know if you could answer for me! THANK YOUUUU
I'm on the way to work so I'll just copypaste what i sent to someone else over DMs. Lmk if you run into any trouble, but it'll be like 8+ hours before I get to it
Hiya! No need to apologize for the sudden message. I just woke up so sorry for the wait!
I can explain the process for you and get screenshots to hopefully help out, and if you have any problems with it you can let me know!
You'll need:
An android phone and a way to transfer files between your phone and computer(a wire is preferable in my experience)
I think you need a windows or linux computer? I'm not sure if the necessary programs will work on mac.
AssetStudioGUI https://github.com/Perfare/AssetStudio
UnityLive2DExtractor https://github.com/Perfare/UnityLive2DExtractor/releases/tag/v1.0.7
First you'll need to transfer the game files to your computer. I assume you already have that part done so I won't walk you through it.
Next go into AssetStudioGUI and go into 'Debug' and turn off 'Show error message' to save yourself some headache
Now you need to open the folder with the files in AssetStudio. This will probably take a long time. Get yourself something to eat or play a game or read or something!
Once everything is loaded you'll need to find one of the live2d files. For tokyo debunker the easiest way to do this is just to go to "Filter Type" and filter to "Texture2D". I don't know the file structure or naming convention for Twst, but the image you're looking for should look kind of like this
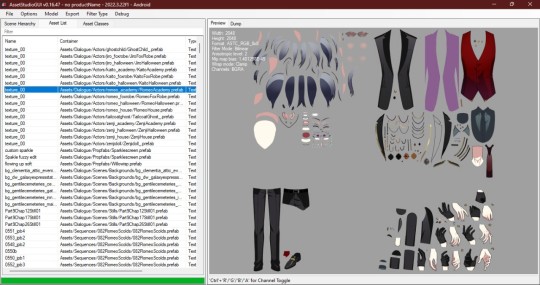
Right click and choose "Show original file".
Copy the FOLDER that this file is in to another folder.
If you haven't already extracted L2DExtractor, do that now. You should have these files.
Open the L2DExtractor FOLDER in another tab or window. Then drag the folder that you copied before to "UnityLive2DExtractor.exe" in the UnitLive2DExtractor folder that you have in a separate window. (You can also copy it and right click→paste it INTO THE EXE FILE if dragging is difficult.)
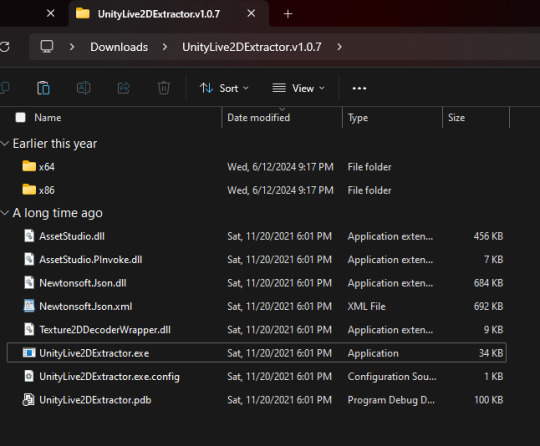
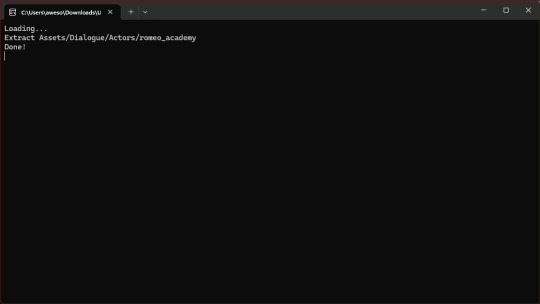
You should get a command prompt(the black box with text in it) with the name of the asset in it. Wait until it says "Done!" Close the command prompt.
Go to the folder that you put the asset folder in. You should now have a new folder named "Live2DOutput". That will have a folder in it. Go into the folder until you find the asset you just extracted.
You should now have the .moc3 file, textures, and motions! You can open the moc3 file with Live2D's Cubism Viewer which you get off of their website. It's free.
If you don't have the expressions in there you'll have to extract them separately! I always have to extract them separately and I'm not sure why, but it's easy enough once you know where they are.
Open AssetStuido back up and change your filter to "MonoBehavior"
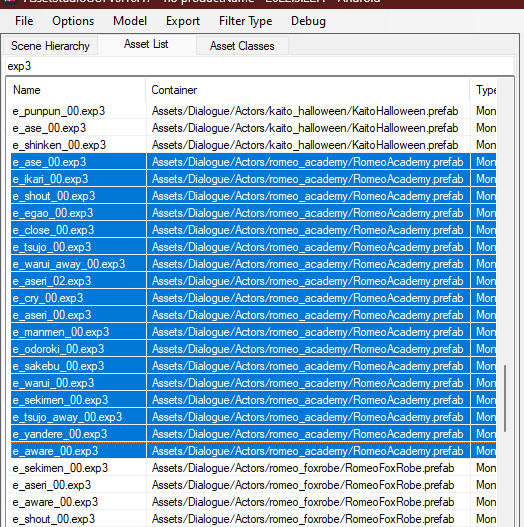
Search "exp3"
Order by Container and find the character character and outfit you just extracted(in this case I just need to find "romeo_academy". The name of the asset you extracted should be in the container path.
Highlight only the .exp3 files that go to this asset.
Go to "Options→Export options"
Change "Group exported assets by" to "Do not group". If you want to do any datamining in the future you're probably going to want to change this back to "container path" or else you'll just get a ton of files in one folder, so don't forget you did this! If you're only using assetstudio to get the l2d files however you can leave it as is.
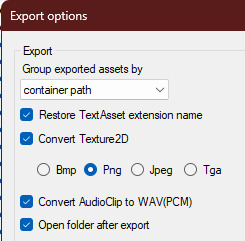
Press "OK"
Right click on one of your highlighted exp3 files
Choose "Export selected assets"
Navigate to the folder with the moc3 file in it. Make a new folder. The name doesn't matter because you'll have to manually move the expressions into l2d every time, but I just use "expressions" for simplicity
Extract the exp3 files into here.
Once they're extracted you can select them all at once and drag them into the Cubism Viewer window OF THE CORRECT CHARACTER. This will instantly import all of the expressions.
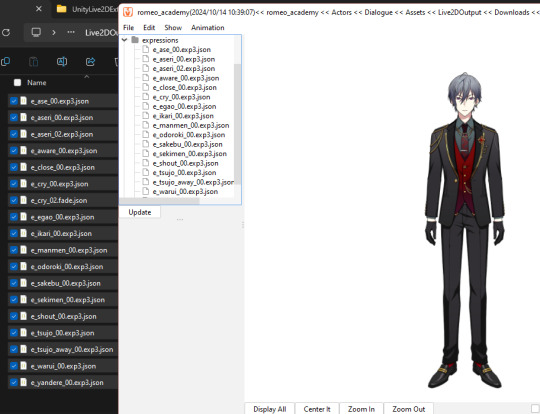
You're done! You can view and play with them all you want. But you'll have to do every character individually and then export their expressions separately.
Hope that helps. If you need anymore help let me know.
#ridiculous-reina#danie yells answers#do i have a tag for explaining this stuff? idr.#datamining cw#just so it'll come up if i search datamining or something ugh
20 notes
·
View notes
Text
don’t mind me, I’m just happy because I finallyyyyyyy got SIMPE to work on Linux 🤭
(transferring my files to windows and back was a hassle, but I’m freeeee🤸🏾♀️!)

9 notes
·
View notes
Text



I inherited an old computer from my parents. One that my brother put together for my sister in about 2009. Check out those ports: a single monitor (VGA), serial + parallel, PS/2 ports for mouse & keyboard (I also got the keyboard for our old WIn98 PC, which shows its age, but has PS/2; lucky, because the USB ports don't work very well).
It has a whopping 714Mb of RAM, so it was a challenge to find a Linux distro that would run on it. But I managed to install antiX on it, and it works just fine. Much better than the Windows 7 that my Dad left on it (it was up to 98% RAM usage just starting up, whereas antiX sits at a cool 250ish Mb, maybe 35%?)
Happily (unlike my current PC, which is on its way out) it has a functioning CD/DVD drive, so I could use it to transfer some copyright-free clip art from some old books we found in a huge box of crafting books from my wife's grandma's friend. (I did have to do it all via command line, because the file viewer GUI wasn't cooperating, or the old mouse's right-click wasn't, but it was good practice.)



If you want them, I have uploaded all of the pictures here: https://mega.nz/folder/Eu1UHQpK#J4LrJzauT7EkP6qtmc6-LA They're in a bunch of different formats (and from 1996, so the readme.txt is hilariously quaint).
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
This has been around for a few months, but I'm only just hearing about it. Artic Base for homebrew 3ds lets your physical 3ds connect wirelessly to a modified version of the Citra 3ds emulator (available for android, linux, mac, and windows), so that the emulator can read game files from the 3ds and write save files back to it. You are emulating the game - contrary to some youtube videos you are NOT streaming the game from the 3ds - but all the files are taken from and go back to the 3ds, so there's no piracy involved and no need to find or download roms. Unless the games on your 3ds are themselves pirated, in which case shame on you you naughty child!
This allows a switch-like experience where you can play a game portably on your 3ds, then when you get home boot up the same game and the same save file to play on a bigger screen in higher resolution with a more comfortable controller via citra, saving your game back to the 3ds. It also lets you take advantage of Citra's ability to play multiplayer online even though the 3ds servers are down by emulating a local connection over the internet. It's also an easy option to stream or record gameplay if you're into that without the trouble of installing a capture card mod onto your 3ds.
Now, granted, this was all already possible by copying save files back and forth from your 3ds memory card to your computer, but to do that you still had to go through the bother of setting up citra and getting your game files on there - either by finding roms or by dumping the files yourself. That could be a pretty significant hassle, but Artic base handles it all for you.
There is a downside - every time you load or save anything in your game, that data has to be transfered between your 3ds and Citra over wifi, which does add a delay and some slowdown whenever that's happening. But most of the time gameplay runs very smoothly.
Anyway, Artic Base requires a modded 3ds. Instructions can be found HERE. The process isn't very difficult, but read the directions carefully and take your time, as there's always a risk of breaking a device when installing custom firmware if you mess something up. Don't rely on video guides for this process! if the video is out of date, it might give you instructions that are no longer correct for the current methods and files!
Even if you're not interested in Citra, modding adds so much utility to the 3ds that you really should look into it if you have one. Button remapping, using larger memory cards (I wouldn't go over 128gigs), backing up save files, backing up entire games so you don't lose access to them if the aging cartridges go bad, even community ports of entire games like Doom or Off or Fallout, access to the pretendo network which is slowly rebuilding online functionality for 3ds and wii, the ability to stream from your computer to your 3ds, access to h-shop to download game updates and patches no longer available from nintendo after the e-shop's closure, and so much more.
Anyway, once you have a modded 3ds, Artic Base can be found on the Universal Updater app. I prefer the .cia version over the .3dsx version, so you don't have to go through Homebrew Launcher every time you want to use it. If you want to install it manually instead, it can be found HERE.
You also need a modified version of Citra to connect to your 3ds, which can be found HERE.
30 notes
·
View notes
Text
friendship ended with VS Code. holy shit, friendship majorly ended with VS Code. I regret ever saying it was a decent text editor.
I was stuck on windows during a meeting I didn't have to be a part of and had a huge data migration looming over my head so I wrote a shell script in VS Code to transfer the files, SCP'd it over to my RedHat machine, and got it started. I don't know where things went wrong, but somewhere between saving it in VS Code and transferring it to my Linux box the formatting got fucked, and so twenty minutes after deploying my script I checked the progress and it appended spaces onto the end of alllllll of my copied directories.
My unscheduled downtime of my (luckily backup) production server was prolonged an extra half hour as I manually CP'd the files by hand, and tomorrow I'm going to have to do so much cleanup.
luckily my server is back up and my new environment doesn't have to go live until EOD tomorrow, but hooooly fuck, next time I'm just going to ssh into my Ubuntu box and use Nano (fuck vi and emacs)
20 notes
·
View notes
Text
I've managed to install Linux Mint on the new PC and am working on transferring files from the old computer. Every time I tried to do a backup restore, something went horribly wrong so I'm forced to just copy and paste files over instead.
Meanwhile, I'm just dealing with trying to get drivers working. Firefox is dealing with constant issues with text and the PC isn't recognizing my ethernet cable.
13 notes
·
View notes