#PySpark UDFs
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Unlocking the Full Power of Apache Spark 3.4 for Databricks Runtime!
You've dabbled in the magic of Apache Spark 3.4 with my previous blog "Exploring Apache Spark 3.4 Features for Databricks Runtime", where we journeyed through 8 game-changing features
You’ve dabbled in the magic of Apache Spark 3.4 with my previous blog “Exploring Apache Spark 3.4 Features for Databricks Runtime“, where we journeyed through 8 game-changing features—from the revolutionary Spark Connect to the nifty tricks of constructing parameterized SQL queries. But guess what? We’ve only scratched the surface! In this sequel, we’re diving deeper into the treasure trove of…

View On WordPress
#Apache Spark#Azure Databricks#Azure Databricks Cluster#Data Frame#Databricks#databricks apache spark#Databricks SQL#Memory Profiler#NumPy#performance#Pivot#pyspark#PySpark UDFs#SQL#SQL queries#SQL SELECT#SQL Server
0 notes
Link
0 notes
Link
0 notes
Text
Big Data with Spark and Python
It’s becoming more common that most of the business face circumstances where the data amount is higher to handle on a single machine. There are Hadoop, Apache Spark, and other technologies developed to sort out the issue. The system can be quickly and directly tapped from Python by utilizing PySpark.
Apache Spark is one of the general and faster engines mainly designed for big data processing and holds built-in modules for graph processing, machine learning, SQL, and streaming. It’s also known for their user-friendliness, speed, ability to run virtually, and even for their generality.
Spark is also one of the preferred tools, especially for data scientists and data engineers. They can make use of the Spark when doing any feature extraction, model evaluation, supervised learning, and data analysis. In this blog, we will deal with some critical concepts about Python and Spark in big data technologies.

Spark: Scala or Python?
You need to know what type of Spark you need before continuing with Scala or Python. Here are some simple concepts explained so that you can choose the right one bases on your requirements.
1. Learning Spark: Scala or Python?
When it comes to the learning curve, Python stands as the premier choice as it’s user-friendly, less verbose, easy to use, and more readable when compared with Scala. It will be perfect for people who are not having much experience in the programming part. People who have little or higher programming experience can also work with Spark in Python with a good number of benefits associated with them.
2. Spark Performance: Python or Scala?
When it comes to concurrency and performance, Scala wins the debate, and this is agreed by most of the developers. They are rapid and user-friendly when compared to python.
When it comes to concurrency, the play framework and scala make the process easier to write perfect and clean asynchronous codes that are easy to reason about. Play framework is asynchronous, and therefore, there are high chances to have a different type of concurrent connections without the hindrances of threads.
It’s also simpler to make Input and output calls in parallel so that it can enable the use of streaming, server push, and real-time technologies. Apart from it, it also helps to enhance performance.
There will be no many variations between Scala and Python in the case of DataFrame API, but you need to be aware of them when working with UDFs (User Defined Functions), which is considered to be less effective when compared to the equivalents of Scala.
In case you are dealing with Python, you need to ensure not to pass your information between RDD and DatFrame unnecessarily as the deserialization, and serialization of the information transfer is expensive.
Serialization is the process of transforming an object or thing into a progression of bytes that can be lasted to a database or disk or else can be sent via streams when it comes to deserialization, it’s the vice versa of the serialization.
3. Advanced features and Spark: Scala or Python?
Many advanced features might provide a small confusion in choosing Scala or Python. When it comes to data science, you can prefer Python over Scala as it offers the user with different tools for natural language processing and machine learning like SparkMLib.
4. Type Safety and Spark: Python or Scala?
The advanced features and safety are two things that stand for both Scala and Python. When it comes to type safety, you can choose Python, and this is best when you are performing experiments in smaller ad hoc. If you are working for some more significant projects, then scala would be the right choice. The reason for this is that Scala is statically typed language, hassle-free, easier when you are refactoring.
As a whole, both languages possess the positives and drawbacks while working with Spark. You need to choose the best one based on your team capabilities and project requirements.
How to install Spark?
Installing Spark us something tedious, but you can do it if you follow the below steps in the right manner.
1. Make sure you have Java JDK installed.
2. Once you are aware that it has been installed, you can go to the download page of the spark. You need to choose the default options up to third steps, and at the fourth step, you will find a downloadable link to download it.
3. Make sure you find untar the directory in your Downloads folder.
4. Once you find the folder, move to /usr/local/spark
5. Now, open the README file from the option.
6. The next step is to build spark, and you can do this by running a command “$ build/mvn -DskipTests clean package run.”
7. The next steps are to type “./bin/pyspark” in the same folder to start working in the Spark Shell.
8. You can now start to work.
Spark APIs: DataFrame, Dataset, and RDD.
There are three distinctive APIs that would make great confusion to anyone who is just getting started with the Spark. Let’s check out about the Spark APIs in depth below.
1. RDD:
RDD, derived as the “building blocks” of the spark, is the original API that is exposed by the Spark, and it’s considered to be the higher-level APIs when compared to other ones. RDD is a set of Scala or Java objects that represent data, and this is pointed out from the perspective of a developer.
RDD has three primary specifications; namely, they are based on the Scala collections API, they are lazy, and they are compile-time type-safe. There are many advantages of RDD, but they also lack in some cases. For instance, it’s simple to develop transformation chains, but they are relatively and inefficiently slow when taking non-JVM languages like Python. Spark can not optimize them.
2. DataFrames:
To overcome the disadvantages of RDD, The API DataFrame was incorporated. It offers you the right level of abstraction, which enables you to make use of the query language to operate the data. This level of abstraction is considered to be the logic plan which indicates schema and data. It also shows that interacting with your data at the frontend is too easy. To execute this, the logical idea will be transformed into a physical plan.
DataFrames are developed on top of RDDs. The improvement and performance of DataFrame are due to a few things that you come across often when you are dealing with data frames, namely optimized execution plans and custom memory management.
3. Datasets:
DataFrame deals with one crucial drawback, namely it has lost the safety of the compile-time type, which means it will make the code more inclined to hindrances and errors. To overcome the drawback dataset was raised and this deals with getting back the type-safety and also make use of the lambda functions which indicates that you capture some benefits of RDDs and also you are not losing the optimization offered by the data frames.
Which the proper time to use the APIs?
Choose RDD when you need to perform low-level actions and transformations on any unstructured data. It indicates that you are not caring about establishing a schema while accessing or processing the attributed by column or name.
Apart from that, you need not require the performance and optimization advantages that DataSets and DataFrame provide for semi-structured data. You can also make use of the RDD when you need to handle the data with various constructs of functional programming when compared to particular domain expressions.
You can make use of the DataFrames in case you are working with PySpark as they are close to the structure of DataFrames. DataSets are not the perfect one in case of Python as it lacks compile type and time safety of the Python. The dataset API is ideal for when you need to use SQL queries, the use of lambda function on a data that is semi-structured, high-level expressions, columnar access, and more.
So what are your views on Big Data with Python and Spark? Are you interested to learn more about Spark and Python in Big Data? Let us know through the comment section below.
0 notes
Text
PySpark: Java UDF Integration
#ICYDK: PySpark is the Spark API implementation using the Non-JVM language Python. Though developers utilize PySpark by implementing Python Code using Spark API’s (Python version of Spark API’s), internally, Spark uses data to be cached in JVM. The Python Driver Program has SparkContext, which uses Py4J, a specialized library for Python Java interoperability to launch JVM and create a JavaSparkContext. https://goo.gl/LdxSxk #DataIntegration #ML
0 notes
Text
Pyspark - prévisions avec Pandas UDF et fb-prophet
Pyspark – prévisions avec Pandas UDF et fb-prophet
Pyspark - prévisions avec Pandas UDF et fb-prophet
Prévoyez plusieurs séries temporelles à la fois avec prophète et pandas UDF sans boucle.
Avant de commencer quoi que ce soit pour travailler avec pandas-udf le prérequis sont
étincelle ≥ 2,4
pyarrow ≤ 0.14.1 (au-dessus de cette version, il y a un problème)
nous devons ensuite configurer une variable d'environnement pour pyarrow à 1. (voir le code…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Link
#BigData#MachineLearning#ML#Python#Spark#SparkSQL#Большиеданные#ИИ#Искусственныйинтеллект#МашинноеОбучение#обработкаданных
0 notes
Photo

Python Aggregate UDFs in Pyspark
Pyspark has a great set of aggregate functions (e.g., count, countDistinct, min, max, avg, sum), but these are not enough for all cases (particularly if you’re trying to avoid costly Shuffle operations). Pyspark currently has pandas_udfs, which can create custom aggregators, but you can only “apply” one pandas_udf at a time. If you want to […]
The post Python Aggregate UDFs in Pyspark appeared first on PyBloggers.
0 notes
Quote
the ability to define low-overhead, high performance UDFs entirely in Python
Introducing Vectorized UDFs for PySpark - The Databricks Blog
0 notes
Link
0 notes
Link
0 notes
Text
Проблема вызовов REST API в Apache Spark и способы ее решения
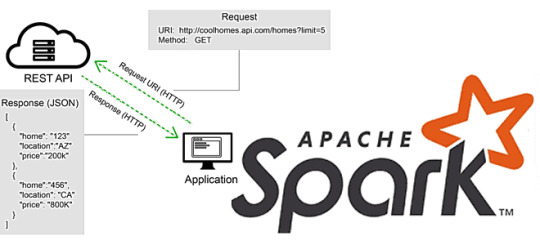
В этой статье для разработчиков Apache Spark разберем, что не так с вызовами REST API в этом фреймворке, и как решить эту проблему с помощью готовых библиотек или создания собственных UDF-функций на PySpark и не только. Для наглядности рассмотрим практический пример вызова REST API на PySpark с библиотекой Rest Data Source.
Куда пропало распараллеливание при вызовах REST API в Apache Spark и как его найти
Несмотря на то, что Apache Spark реализует модель распределенных вычислений в кластере, далеко не все операции в нем выполняются параллельно. Разработчику Spark-приложений необходимо знать о таких случаях. Одним из них является выполнение кода на драйвере, а не на всех узлах кластера. Например, при подключении к REST API данные получает только один драйвер Spark, что эквивалентно запуску программы на одном узле. При большом объеме данных выполнения вызовов REST API происходит в цикле, где каждая итерация будет последовательной. Поэтому перед разработчиком встает вопрос, как распараллелить эту концепцию, используя ��озможности фреймворка распределенных вычислений.В общем случае решить эту проблему можно, используя REST API, который будет вызываться несколько раз, чтобы получить нужные данные. Чтобы воспользоваться преимуществами параллелизма Apache Spark, каждый вызов REST API следует инкапсулировать в определенную пользователем функцию (UDF, User Defined Function), привязанную к нужным данным в структуре DataFrame. Каждая строка в DataFrame будет представлять один вызов службы REST API. После выполнения действия в DataFrame результат каждого отдельного вызова REST API будет добавлен к каждой строке как структурированный тип данных. Например, для этого можно написать собственную UDF на PySpark, который будет подключаться к REST API и загружать данные. Эта UDF будет вызываться в датафрейме с функцией Column. Поскольку REST API работает по HTTP(S)-протоколу, входными данными в эту UDF будут URL-адрес и выполняемое действие. Эти данные будут переданы как столбцы в UDF. В результате подключение к API и загрузка данных будут выполняться исполнителями, а не драйвером, и каждая строка будет устанавливать индивидуальное подключение к API. Примеры описания собственной UDF на PySpark и Scala приведены в источниках . Есть и другой путь – воспользоваться решением сообщества, упакованными в готовую библиотеку, что мы и рассмотрим далее.
Библиотека REST как источник данных для Apache Spark: практический пример
Rest Data Source – это библиотека с открытым исходным кодом для параллельного вызова сервисов/API на основе REST для нескольких наборов входных параметров и сопоставления результатов, возвращаемых сервисом REST в Dataframe. Службы на основе REST типа Google Search API, Watson NLP API и пр. обычно принимают только один набор входных параметров за раз и возвращают соответствующие записи. Однако, в реальных задачах Data Science один и тот же API часто требуется вызывать несколько раз, чтобы учесть большой набор различных входных параметров, например, проверка адресов для набора целевых клиентов, получение информации из нескольких тысяч твитов, сбор сведений из реестра с множеством записей и т. д.В Apache Spark Автоматизировать вызов API целевого сервиса распределенным способом для различных наборов входных параметров поможет библиотека Rest Data Source. Результаты возвращаются в DataFrame в структуре, специфичной для API, без указания пользователем этой схемы. Пакет с API для нескольких языков программирования, поддерживаемых Spark (R, Python, Scala), позволяет выполнять несколько параллельных вызовов целевого микросервиса для набора различных входных параметров, которые можно передать как временную таблицу Spark. В этой временной таблице имена столбцов таблицы должны совпадать с ключами целевого API. Каждая строка в таблице и соответствующая комбинация значений параметров будут использоваться для выполнения одного вызова API. Результат нескольких вызовов API возвращается как Spark DataFrame из строк с выходной структурой, соответствующей ответу целевого API. Все типы данных преобразуются в строку при генерации полезной на��рузки. Объекты и другие сложные типы данных также поддерживаются в качестве полезной нагрузки. При этом объекты должны быть преобразованы в строки JSON. В Spark SQL для этого можно использовать функцию to_json().

Библиотека REST Data Source для Apache Spark Библиотека Rest Data Source поддерживает следующие опции вызова целевого сервиса REST : - url - целевой URI микросервиса, обязательный параметр; - input – имя временной таблицы Spark с набором входных параметров. Если эта таблица содержит сложные типы данных, которые необходимо отправить в качестве полезной нагрузки, следует сперва преобразовать объект в строку JSON. - method - метод протокола HTTP(S), по умолчанию POST. Также поддерживается GET. - userId – идентификатор пользователя, если целевому API нужна базовая аутентификация; - userPassword – пароль пользователя на случай, если целевому API требуется базовая аутентификация; - oauthToken - значение ключа авторизации, переданное в ЗАГОЛОВОК для авторизации на основе токена-носителя; - partitions – номер раздела для увеличения параллелизма в Spark, по умолчанию равен 2; - connectionTimeout – время подключения к целевому API, по умолчанию равно 1000 миллисекунд; - readTimeout- время чтения большого набора данных, возвращаемого целевым API, по умолчанию равно 5000 миллисекунд; - schemaSamplePcnt – процент записей во входной таблице, которые будут использоваться для вывода схемы данных, по умолчанию равен 30, а минимальное значение равно 3. Рекомендуется увеличить это число в случае сообщения об ошибке или неверном определении схемы данных. - callStrictlyOnce – гарантия строго однократного вызова серверного API для каждого набора входных параметров. По умолчанию этот п��раметр установлен в значение «N», что позволяет вызывать API серверной части несколько раз: один раз для вывода схемы данных, а затем для других операций. Если установить значение «Y», серверный API будет вызываться только один раз во время определения схемы для всех наборов входных параметров и будет кэширован. Эта опция полезна, когда вызов целевого API является платным или ограничен числом запросов в час/в день. Из-за кэширования результатов потребление памяти увеличится. Чтобы понять, как это работает, рассмотрим практический пример вызова REST API на PySpark с библиотекой Rest Data Source. Предположим, требуется прочитать значения входных параметров из CSV-файла с именем sodainput.csv. Этот файл содержит два столбца: регион (region) и источник (source), которые соответствуют двум фильтрам, поддерживаемым SODA API для источника данных Socrata, а потому не требуют переименования. Вызовем API 3 раза, по одному для каждой из различных комбинаций значений «регион» и «источник». Сперва создадим целевую строку url Soda API для источника данных Socratasodauri = 'https://soda.demo.socrata.com/resource/6yvf-kk3n.json' Далее прочитаем данные из CSV-файла в датафрейм Spark:sodainputDf = spark.read.option('header', 'true').csv('/home/biadmin/spark-enablement/datasets/sodainput.csv') Создадим временную таблицу Spark из sodainputDf: sodainputDf.createOrReplaceTempView ('sodainputtbl') Создадим карту параметров для передачи в библиотеку REST Data Source:prmsSoda = {'url': sodauri, 'input': 'sodainputtbl', 'method': 'GET', 'readTimeout': '10000', 'connectionTimeout': '2000', 'partitions': '10'} Сохраним результаты вызова Soda API для трех разных точек входных данных в датафрейм: sodasDf = spark.read.format ("org.apache.dsext.spark.datasource.rest.RestDataSource"). options (** prmsSoda) .load() Датафрейм, созданный рассмотренной библиотекой, вернет набор строк с той же структурой, которая будет содержать поля ввода для вызова API и вывод в новом столбце. Непосредственно результат вывода зависит от целевого REST API и его структуру можно получить с помощью метода printSchema() в API DataFrame Apache Spark. Чтобы проверить структуру возвращаемых результатов, посмотрим схему данных: sodasDf.printSchema(). Наконец, можно применить аналитический SQL-запрос или любую другую обработку полученных результатов:sodasDf.createOrReplaceTempView("sodastbl")spark.sql("select source, region, inline(output) from sodastbl").show() Исходный код пакета REST Data Source для Apache Spark, рекомендации по установке и примеры практического использования приведены в источниках . Освойте всю практику использования Apache Spark для разработки распределенных приложений аналитики больших данных на специализированных курсах в нашем лицензированном учебном центре обучения и повышения квалификации для разработчиков, менеджеров, архитекторов, инженеров, администраторов, Data Scientist’ов и аналитиков Big Data в Москве:- Основы Apache Spark для разработчиков - Анализ данных с Apache Spark - Потоковая обработка в Apache Spark - Машинное обучение в Apache Spark - Графовые алгоритмы в Apache Spark Источники1. https://medium.com/geekculture/how-to-execute-a-rest-api-call-on-apache-spark-the-right-way-in-python-4367f2740e78 2. https://medium.com/@smdbilal.vt5815/making-parallel-rest-api-calls-using-pyspark-c951666c59d5 3. https://github.com/jamesshocking/Spark-REST-API-UDF-Scala 4. https://github.com/sourav-mazumder/Data-Science-Extensions/tree/master/spark-datasource-rest 5. https://medium.com/@sourav.mazumder00/using-spark-as-a-parallel-processing-framework-for-accessing-rest-based-data-services-cd4c98526784 Read the full article
0 notes