#Shark and Ray Fossils
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Photo

RARE Miocene Ray Tooth Fossil | S'Algar, Menorca | Authentic Prehistoric Marine Specimen | Certified Fossil | Collectible Fossilized Tooth
Discover a Rare Ray Tooth Fossil from the Miocene epoch, unearthed in S'Algar, Menorca. This beautifully preserved fossil offers a glimpse into the marine life that thrived around 15 million years ago. Menorca’s fossil-rich formations provide some of the finest examples of prehistoric marine life, making this an exceptional addition to any fossil collection.
Rays, known for their cartilaginous skeletons and specialized dental plates, used their teeth to crush and grind shellfish and crustaceans. This rare specimen highlights the intricate details of the tooth structure, making it a valuable educational and display piece.
Fossil Information:
Species: Prehistoric Ray (Exact species undetermined)
Fossil Type: Single Tooth
Geological Formation: Miocene Deposits
Age: ~15 million years old (Miocene Epoch)
Location: S'Algar, Menorca
Size: Full sizing provided in photos (Scale: 1cm per square)
Preservation: Excellent, showing distinct dental features
Key Features:
✔ Authentic Miocene Ray Tooth Fossil
✔ Sourced from the fossil-rich region of Menorca
✔ Well-preserved with natural dental structures
✔ Ideal for collectors, museum displays, and educational use
Authenticity & Certification:
All of our fossils are 100% genuine specimens and come with a Certificate of Authenticity. The fossil shown in the photos is the exact specimen you will receive.
Why Buy From Us?
This Ray Tooth fossil comes from the prestigious Alice Purnell Collection, one of the largest and most respected fossil collections in the world. We specialize in high-quality, museum-grade fossils, ideal for serious collectors, educators, and researchers.
🦈 Own a rare piece of Miocene marine history today—add this Ray Tooth fossil to your collection!
#Ray Tooth Fossil#Miocene Fossil#Menorca Fossil#Prehistoric Marine Fossil#Fossilized Ray Tooth#Certified Fossil#Authentic Fossil#Fossil Collector Item#Marine Life Fossil#Fossil Tooth Collection#Fossil from Spain#Fossil Gift#Rare Fossils for Sale#Shark and Ray Fossils#Miocene Marine Fossil
0 notes
Note
I heard that sharks and rays are super closely related. Are skates an approximate bridging “group” between them? Or are they outside of both groups
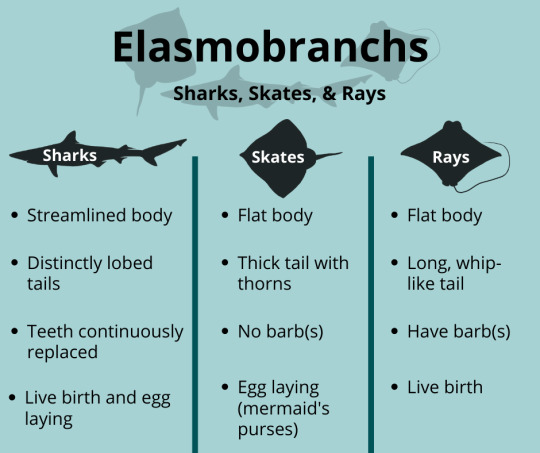
They are all really closely related- there in all the same class known as Chondrichthyes, or cartilaginous fish. Sharks evolved first, approximately 350 million years ago during the Carboniferous period. Skates and ray came around at approximately the same time as each other 150 million years ago during the Jurassic period.
So skates aren't really a "bridging group", they're actually most closely related to rays!
#marine biology#marine ecology#animals#science#biology#animal facts#wildlife#marine life#ocean#fun facts#shark#sharks#rays#sting rays#skates#evolution#zoology#fossils#natural history#jurassic period#carboniferous#sea life#sea creatures#marine animals#fish#chondrichthyes
631 notes
·
View notes
Text

We found a couple shark teeth fossils today. You know, one or two.
#mckittericks rl#fossils#sharks#we also found a ton of turritella shells#and ray dental plates#and saw some skinks and a frog#and vultures bald eagle and maybe osprey#it was a good day
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
i could spend my entire life shark tooth fossil hunting at a river and never get bored with it and i think that trait should be more useful for me to have
#i have so many fossilized shark/skate/ray teeth/dental plates and cetacean+turtle bones#i don't even do anything with them i just hoard them and sometimes look at them like 'wow these animals were around such a long time ago'#everyone else i know gets bored and gives up so fast. they will never understand the thrill
1 note
·
View note
Text

Thrinacodus gracia* was a stem-elasmobranch – a cartilaginous fish related to modern sharks and rays – living in what is now Montana, USA during the mid-Carboniferous around 324 million years ago.
* previously known as Thrinacoselache gracia
Although the cartilaginous skeletons of chondrichthyans rarely preserve, the exceptional preservation conditions of the Bear Gulch Limestone fossil deposits mean we do actually have full-body soft tissue impressions of this species. It was about 1m long (3'3") with an unusually slender eel-like body, a pointed snout, no dorsal fins, and an elongated tapering tail.
Preserved gut contents show that Thrinacodus gracia preyed on shrimp-like crustaceans and smaller cartilaginous fish such as Falcatus and Harpagofututor. It would have inhabited a shallow tropical bay environment, and may have had a similar sort of lifestyle to the modern eels it resembled, hiding in crevices or burrowing into sediment and ambushing passing prey.
———
NixIllustration.com | Tumblr | Patreon
References:
Frey, Linda, et al. "The early elasmobranch Phoebodus: phylogenetic relationships, ecomorphology and a new time-scale for shark evolution." Proceedings of the Royal Society B 286.1912 (2019): 20191336. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6790773/pdf/rspb20191336.pdf
Ginter, Michał, and Susan Turner. "The middle Paleozoic selachian genus Thrinacodus." Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 30.6 (2010): 1666-1672. https://doi.org/10.1080/02724634.2010.520785
Grogan, Eileen D., and Richard Lund. "A basal elasmobranch, Thrinacoselache gracia n. gen and sp.,(Thrinacodontidae, new family) from the Bear Gulch Limestone, Serpukhovian of Montana, USA." Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 28.4 (2008): 970-988. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/213771568_A_Basal_Elasmobranch_Thrinacoselache_gracia_n_gen_spThrinacodontidae_New_Family_from_the_Bear_Gulch_Limestone_Serpukhovian_of_Montana_USA
Wikipedia contributors. “Bear Gulch Limestone” Wikipedia, 28 Apr. 2025, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bear_Gulch_Limestone
Wikipedia contributors. “Thrinacodus” Wikipedia, 04 Jan. 2025, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thrinacodus
#science illustration#paleontology#paleoart#palaeoblr#thrinacodus#thrinacoselache#phoebodontidae#phoebodontiformes#elasmobranch#chondrichthyes#cartilaginous fish#fish#art#convergent eelvolution
197 notes
·
View notes
Text
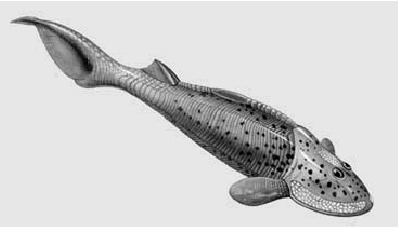
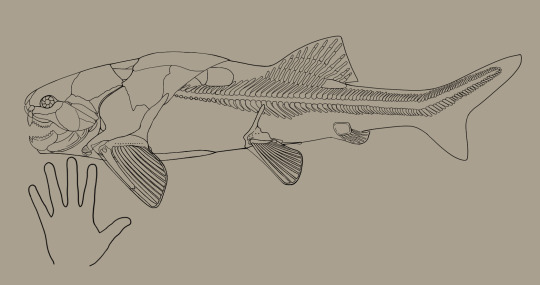
I recently found out a show I liked is 10 years old now so to not be the oldest thing on this blog I'm talking coelacanths for Wet Beast Wednesday. Coelacanths are rare fish famed for being living fossils. While that term is highly misleading, it is true that coelacanths are among the only remaining lobe-fined fish and were thought to have gone extinct millions of years ago before being rediscovered in modern times.

(image id: a wild coelacanth. It is a large, mostly grey fish with splotches of yellowish scales. Its fins are attached to fleshy lobes. It is seen from the side, facing the top right corner of the picture)
Coelacanth fossils had been known since the 1800s and they were believed to have gone extinct in the late Cretaceous period. That was until December 1938, when a museum curator named Marjorie Courtenay-Latimer was informed of an unusual specimen that had been pulled in by local fishermen. After being unable to identify the fish, she contacted a friend, ichthyologist J. L. B. Smith, who told her to preserve the specimen until he could examine it. Upon examining it early next year, he realized it was indeed a coelacanth, confirming that they had survived, undetected, for 66 million years. Note that fishermen living in coelacanth territory were already aware of the fish before they were formally described by science. Coelacanths are among the most famous examples of a lazarus taxon. This term, in the context of ecology and conservation, means a species or population that is believed to have gone extinct but is later discovered to still be alive. While coelacanths are among the oldest living lazarus taxa, they aren't the oldest. They are beaten out by a genus of fly (100 million years old) and a type of mollusk (over 300 million years old).

(image: a coelacanth fossil. It is a dark brown imprint of a coelacanth on white rock. Its skeleton is visible in the imprint)
Coelacanths are one of only two surviving groups of lobe-finned fish along with the lungfishes. Lobe-finned fish are bony fish notable for their fins being attached to muscular lobes. By contrast, ray-finned fish (AKA pretty much every fish you've ever heard of that isn't a shark) have their fins attached directly to the body. That may not sound like a big difference, but it actually is. The lobes of lobe-finned fish eventually evolved into the first vertebrate limbs. That makes lobe-finned fish the ancestors of all reptiles, amphibians, and mammals, including you. In fact, you are more closely related to a coelacanth than a coelacanth is to a tuna. Coelacanths were thought to be the closest living link to tetrapods, but genetic testing has shown that lungfish are actually closer to the ancestor of tetrapods.
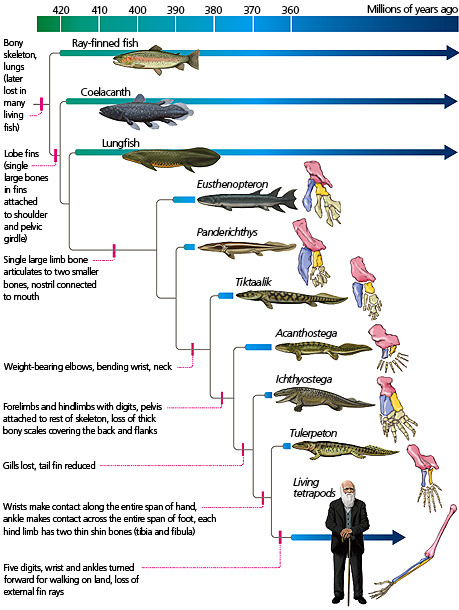
(image id: a scientific diagram depicting the taxonomic relationships of early lobe-finned fish showing their evolution to proto-tetrapods like Tiktaalik and Ichthyostega, to true tetrapods. Source)
There are two known living coelacanth species: the west Indian ocean coelacanth (Latimeria chalumnae) and the Indonesian coelacanth (L. menadoensis). Both are very large fish, capable of exceeding 2 m (6.6 ft) in length and 90 kg (200 lbs). Their wikipedia page describes them as "plump", which seems a little judgmental to me. Their tails are unique, consisting of two lobes above and below the end of the tail, which has its own fin. Their scales are very hard and thick, acting like armor. The mouth is small, but a hinge in its skull, not found in any other animal, allows the mouth to open extremely wide for its size. In addition, they lack a maxilla (upper jawbone), instead using specialized tissue in its place. They lack backbones, instead having an oil-filled notochord that serve the same function. The presence of a notochord is the key characteristic of being a chordate, but most vertebrates only have one in embryo, after which it is replaced by a backbone. Instead of a swim bladder, coelacanths have a vestigial lung filled with fatty tissue that serves the same purpose. In addition to the lung, another fatty organ also helps control buoyancy. The fatty organ is large enough that it forced the kidneys to move backwards and fuse into one organ. Coelacanths have tiny brains. Only about 15% of the skull cavity is filled by the brain, the rest is filled with fat.
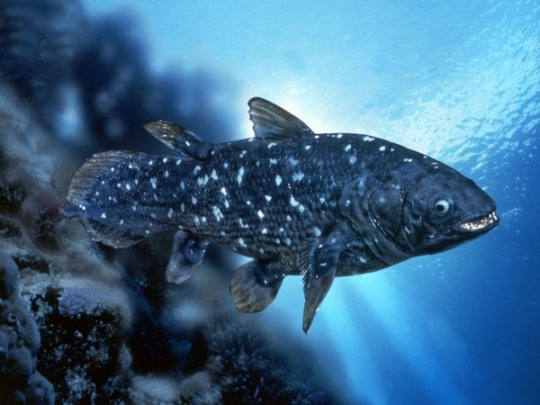

(image id: a coalacanth. It is similar to the one on the above image, but this one is blue in color and the head is seen more clearly, showing an open mouth and large eye)
One of the reasons it took so long for coelacanths to be rediscovered is their habitat. They prefer to live in deeper waters in the twilight zone, between 150 and 250 meters deep. They are also nocturnal and spend the day either in underwater caves or swimming down into deeper water. They typically stay in deeper water or caves during the day as colder water keeps their metabolism low and conserves energy. While they do not appear to be social animals, coelacanths are tolerant of each other's presence and the caves they stay in may be packed to the brim during the day. Coelacanths are all about conserving energy even when looking for food. They are drift feeders, moving slowly with the currents and eating whatever they come across. Their diet primarily consists of fish and squid. Not much is known about how they catch their prey, but they are capable of rapid bursts of speed that may be used to catch prey and is definitely used to escape predators. They are believed to be capable of electroreception, which is likely used to locate prey and avoid obstacles. Coelacanths swim differently than other fish. They use their lobe fins like limbs to stabilize their movements as they drift. This means that while coelacanths are slow, they are very maneuverable. Some have even been seen swimming upside-down or with their heads pointed down.

(image: an underwater cave wilt multiple coelacanths residing in it. 5 are clearly visible, with the fins of others showing from offscreen)
Coelacanths are a vary race example of bony fish that give live birth. They are ovoviviparous, meaning the egg is retained and hatches inside the mother. Gestation can take between 2 and 5 years (estimates differ) and multiple offspring are born at a time. It is possible that females may only mate with a single male at a time, though this is not confirmed. Coelacanths can live over 100 years and do not reach full maturity until age 55. This very slow reproduction and maturation rate likely contributes to the rarity of the fish.

(image: a juvenile coelacanth. Its body shape is the same as those of adults, but with proportionately larger fins. There are green laser beams shining on it. These are used by submersibles to calculate the size of animals and objects)
Coelacanths are often described as living fossils. This term refers to species that are still similar to their ancient ancestors. The term is losing favor amongst biologists due to how misleading it can be. The term os often understood to mean that modern species are exactly the same as ancient ones. This is not the case. Living coelacanth are now known to be different than those who existed during the Cretaceous, let alone the older fossil species. Living fossils often live in very stable environments that result in low selective pressure, but they are still evolving, just slower.

(image: a coelacanth swimming next to a SCUBA diver)
Because of the rarity of coelacanths, it's hard to figure out what conservation needs they have. The IUCN currently classifies the west Indian ocean coelacanth as critically endangered (with an estimated population of less than 500) and the Indonesian coelacanth as vulnerable. Their main threat is bycatch, when they are caught in nets intended for other species. They aren't fished commercially as their meat is very unappetizing, but getting caught in nets is still very dangerous and their slow reproduction and maturation means that it is long and difficult to replace population losses. There is an international organization, the Coelacanth Conservation Council, dedicated to coelacanth conservation and preservation.

(image: a coelacanth facing the camera. The shape of its mouth makes it look as though it is smiling)
#wet beast wednesday#coelacanth#marine biology#biology#zoology#ecology#animal facts#fish#fishblr#old man fish#lobe-finned fish#sarcopterygii
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Round 3 - Chondrichthyes - Chimaeriformes




(Sources - 1, 2, 3, 4)
Our last order in Chondrichthyes is Chimaeriformes, commonly known as “Chimaeras”, and informally known as “ghost sharks”, “spookfish”, “rabbitfish”, or “rat fish” (not to be confused with the Actinopterygiian “rattails”.) Historically a much more diverse and abundant group, they now only comprise the living families Callorhinchidae (“plough-nosed chimaeras” or “elephantfish”), Chimaeridae (“short-nosed chimaeras”), and Rhinochimaeridae (“long-nosed chimaeras”).
Chimaeras are soft-bodied, with bulky heads and long, tapered tails. Their pectoral fins are large enough to generate lift at a relaxed forward momentum, similar to a kite, giving the chimaera the appearance of "flying" through the water. Their gill arches are condensed into a pouch-like bundle covered by an operculum with a single gill-opening in front of the pectoral fins, similar in appearance to Actinopterygiians. They lack spiracles. There are two dorsal fins: a large triangular first dorsal fin and a low rectangular or depressed second dorsal fin. For defense, some chimaeras have a venomous spine on the front edge of the dorsal fin. In many species, the bulbous snout is modified into an elongated sensory organ, capable of electroreception to find prey. Instead of many sharp, consistently-replaced teeth, chimaeras have just six large, permanent tooth-plates, which grow continuously throughout their entire life. These tooth-plates are arranged in three pairs, with one pair at the tip of the lower jaws and two pairs along the upper jaws. They together form a protruding, beak-like crushing and grinding mechanism, comparable to the incisor teeth of rodents and lagomorphs. Most living species are native to the deep sea, with some species inhabiting depths exceeding 2,000 m (6,600 ft) deep, though the few exceptions include the shallower-dwelling plough-nosed chimaeras (genus Callorhinchus) (image 2), the Rabbit Fish (Chimaera monstrosa), and the Spotted Ratfish (Hydrolagus colliei) (image 3).
Chimaeras have separate anal and urogenital openings, rather than a single cloaca. Like sharks and rays, male chimaeras utilize claspers for internal fertilization of females, but unlike sharks and rays, also have retractable sexual appendages known as tentacula to assist in mating. The frontal tentaculum, a bulbous rod which extends out of the forehead, is used to clutch the females' pectoral fins during mating. The prepelvic tentacula are serrated hooked plates normally hidden in pouches in front of the pelvic fins, and they anchor the male to the female. Their claspers are fused together by a cartilaginous sheathe before splitting into a pair of flattened lobes at their tip. Females lay their eggs within spindle-shaped, leathery egg cases which they deposit on the sea floor.
As the most ancient of the Chondrichthyans, Chimaeriformes are truly deserving of the moniker “living fossil”. They have been around since the Early Carboniferous, with the earliest known fossil species being Protochimaera, and split off from the sharks and rays during the Devonian. Modern chimaeras are known from the Early Jurassic, but fossil egg cases from the Late Triassic resembling those of rhinochimaerids and callorhinchids indicate that they had a global distribution earlier than this. Modern chimaeras reached their highest ecological diversity during the Middle Cretaceous. Recent studies indicate that chimaeras were likely a shallow-water group for most of their existence, and only fled to deeper waters in the aftermath of the K-Pg extinction event, adapting to the deep sea to survive.

Propaganda under the cut:
Some chimaera venom can cause pain, necrosis, hallucinations, and localized paralysis in humans. It is not deadly to humans, but has been known to kill Harbor Seals that injested Spotted Ratfish (Hydrolagus colliei).
Spotted Ratfish (Hydrolagus colliei) have large, emerald green eyes, which are able to reflect light, similar to the eyes of a cat.
Chimaera teeth are unique among vertebrates, due to their mode of mineralization. Most of each plate is formed by relatively soft osteodentin, but the active edges are supplemented by a unique hypermineralized tissue called pleromin, rather than enamel. Pleromin is an extremely hard enamel-like tissue, arranged into sheets or beaded rods, but it is deposited by mesenchyme-derived cells similar to those that form bone. In addition, pleromin's hardness is due to the mineral whitlockite, which crystalizes within the teeth as the animal matures.
The Australian Ghostshark (Callorhinchus milii) is very popular with fish-and-chips restaurants in New Zealand and is sold as 'flake' or 'whitefish' in Australia.
The Striped Rabbitfish (Hydrolagus matallanasi) can see in total darkness and sense electromagnetic radiation (outside of the visible spectrum) emitted by other marine creatures due to exposed nerves on the sides of its body.
Some species of chimaerids are known to segregate by sex, with females congregating at greater depths than males.
Despite their deep sea habitat and reclusive nature, some chimaera species are still threatened by bycatch due to deep sea trawling for demersal shrimp and prawns. Even when released, most chimaeras do not survive the process of being quickly pulled up from the pressurized deep sea to shallower water.
#description a bit longer than usual because they’re so unlike all the other members of the class#animal polls#round 3#chondrichthyes
102 notes
·
View notes
Text
Pachycetinae: The Thick Whales
Oh look I'm way behind not only on my work with wikipedia but also in regards to summarizing it on tumblr. Good thing, three of the pages I've worked on these past few months can just be summed up in one post because they are all one family.
So Pachycetinae, at the most basic level, are basilosaurid archaeocetes, the group that famously includes Basilosaurus and Dorudon. Reason I've picked up the articles in addition to my usual croc work, basically a friend and I noticed how lacklustre many pages are and stupidly decided to start revising all of Cetacea (pray for me).
Currently theres two genera within the group. Pachycetus aka Platyosphys aka Basilotritus, which is a whole mess I will get into at the end for those interested, and Antaecetus, which I'll just call "the good one" for now. Among those are three species. Pachycetus paulsonii (or Basilotritus uheni) from continental Europe (Germany and Ukraine mostly), Pachycetus wardii (Eastern United Staates) and Antaecetus aithai (Morocco and Egypt)
Picture: Pachycetus and Antaecetus by Connor Ashbridge


So the hallmark of Pachycetines, as the name would suggest, is the fact that their skeletons are notably denser than that of other basilosaurids. The vertebrae, the most abundant material of these whales, are described as pachyostatic and osteosclerotic. The former effecitvely means that the dense cortical bone forms thickened layers, while the latter means that the cortical bone, already forming thickened layers, is furthermore denser than in other basilosaurids with less porosities. The densitiy is increased further by how the ribs attack to the vertebrae not through sinovial articulation but through cartilage, so adding even more weight to them. Overall this is at times compared to manatees, famous for their dense skeletons.
Pictured below, the currently best preserved pachycetine fossil, an individual of the genus Antaecetus from Morocco.

Now there are some interesting anatomical features to mention that either differ between species or just can't be compared. For example the American species of Pachycetus, P. wardii, shows a well developed innominate bone, basically the fused pelvic bones. This is curious as one would think of it as a more basal feature, with derived whales gradually reducing them. The skull is best preserved in Antaecetus and has a very narrow snout. One way to differentiate the two is by the teeth. Pachycetus has larger, more robust teeth while that of Antaecetus are way more gracile and is thought to have had a proportionally smaller skull (in addition to being smaller than Pachycetus in general).
All of this has some interesting implications for their ecology. For instance, why the hell are they so dense? Well its possible that they were shallow water animals using their weight as ballast, staying close to the ocean floor. This would definitely find some support in the types of environments they show up in, which tend to be shallow coastal waters. There are some Ukrainian localities that suggest deeper waters, but that has been interpreted as being the result of migration taking them out of their prefered habitat.
Now while pachycetines were probably powerful swimmers, their dense bones mean that they were pretty slow regardless. And to add insult to injury, they were anything but maneuverable. Remember those long transverse processes? Turns out having them extend over the majority of the vertebral body means theres very little space for muscles in between, which limits sideways movements.
From this one can guess that they weren't pursuit predators and needed to ambush their prey. What exactly that was has been inferred based on tooth wear. Basically, the teeth of Pachycetus show a lot of abrasion and wear, not dissimlar to what is seen in modern orcas that feed on sharks and rays. And low and behold, sharks are really common in the same strata that Pachycetus shows up in. Now since Antaecetus had way more gracile teeth, its thought that it probably fed on less well protected animals like squids and fish.
Below: Pachycetus/Basilotritus catching a fish by @knuppitalism-with-ue

The relationship between pachycetines and other basilosaurids is wonky, again no thanks due to Pachycetus itself being very poorly known. Some studies have suggested that they were a very early branching off-shoot, in part due to their prominent hip bones, but in the most recent study to include them, the description of Tutcetus, they surprisingly came out as not just the most derived basilosaurids but as the immediate sister group to Neoceti, which includes all modern whales. Regardless, in both instances they seem to clade closely with Supayacetus, a small basilosaurid from Peru.
And now for the part that is the most tedious. Taxonomy and history.
Remains of pachycetines have been known for a while and were first described as early as 1873 by Russian scientists. To put into perspective how old that is. The material's history in science predates both World Wars, the collapse of the Russian Empire and even the reign of Tsar Nicholas II. Now initially the idea was to name the animal Zeuglodon rossicum, but the person doing the actual describing changed that to Zeuglodon paulsonii reasoning that it would eventually be found outside of Russia (something that aged beautifully given that Ukraine would eventually become independent).
And this is where the confusion starts to unfold. Because at the same time people unearthed pachycetine fossils in Germany too, which would come be given the name Pachycetus (thick whale) and be established as two species. Pachycetus robustus and Pachycetus humilis, both thought to be baleen whales.
Pictured below: Pierre-Joseph van Beneden who coined Pachycetus and Johann Friedrich Brandt who described Zeuglodon paulsonii. Beneden easily has the better beard.
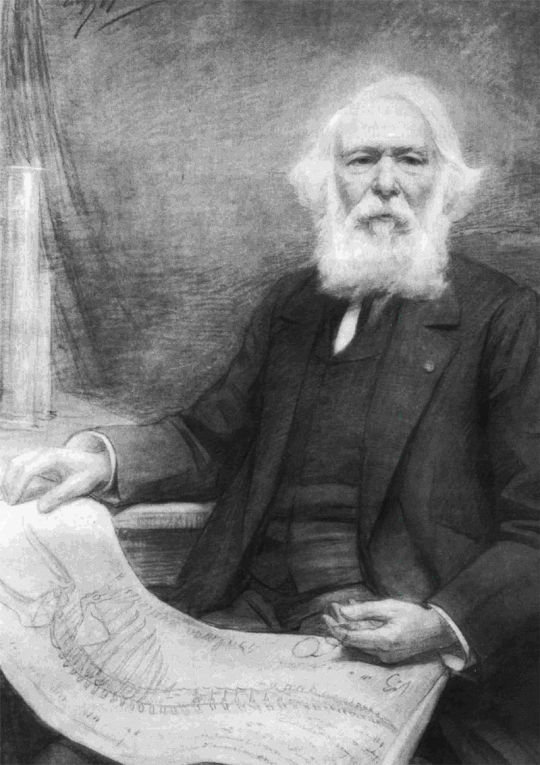
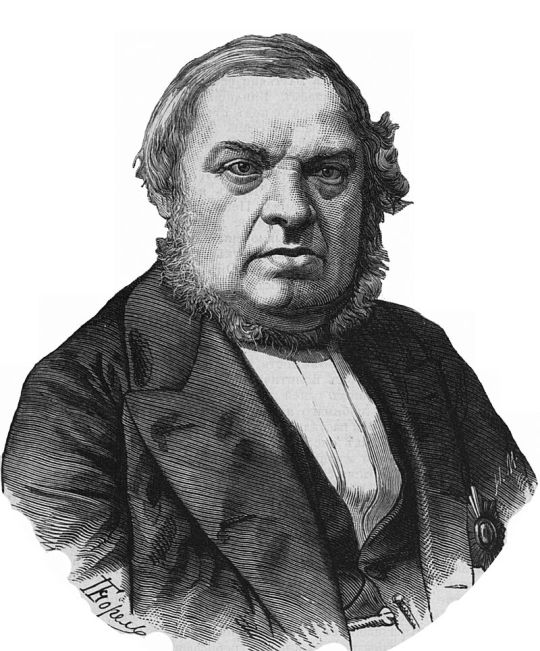


These latter two names however were later rejected in 1935 by Kuhn and lumped into other species, whereas Zeuglodon paulsonii was elevated to a full on new genus by Remington Kellogg in 1936. For those curious, Platyosphys means "broad loin", in combination with the species "Paulson's broad loin" to the amusement of some friends of mine.
And then people stopped caring and we have a nearly 70 year research gap. Eventually Mark D. Uhen found fossil material in the United States, but interpreted those fossils as being part of the genus Eocetus, naming them Eocetus wardii, a move that many following researchers disagreed with.
Then in 2001 a new species of Platyosphys, P. einori, was named. It's bad, moving on. More importantly, we got the works of Gol'din and Zvonok, who attempted to bring some clarity into the whole thing. To do so they rejected the name Platyosphys on account of the holotype having been lost sometime in WW2 and picked out much better fossil material to coin the genus Basilotritus ("the third king" in allusion to Basilosaurus "king lizard" and Basiloterus "the other king", isn't etymology fun?). They erected the type species Basilotritus uheni and then proclaimed Eocetus wardii to also belong into this genus, making it Basilotritus wardii.
This move was however not followed by other researchers. Gingerich and Zhouri maintained that regardless of being lost, Platyosphys is still valid and can be sufficiently diagnosed by the original drawings from the 19th and early 20th century. And to take a step further they added a new species, Platyosphys aithai (weird, why does that name sound familiar).
Then Van Vliet came and connected all these dots I've set up so far, noting that the fossils of Platyosphys are nearly identical to those of Pachycetus. This lead to the fun little thing were "paulsonii", applied first to Zeuglodon in the 1870s, takes priority over "robustus", coined just a few years later, BUT, the genus name Pachycetus easily predates Platyosphys by a good 60 years. Subsequently, the two were combined. Platyosphys paulsonii and Pachycetus robustus became Pachycetus paulsonii (simplified*). Van Vliet then deemed humilis to be some other whale and carried over Basilotritus uheni, Basilotritus wardii and Platyosphys aithai into the genus Pachycetus. *Technically Pachycetus robustus was tentatively kept as distinct only because of how poorly preserved it was, making comparisson not really possible.
Then finally in the most recent paper explicitly dealing with this group, Gingerich and Zhouri came back, killed off P. robustus for good, sunk Pachycetus uheni into Pachycetus paulsonii for good measure and decided to elevate Pachycetus aithai to genus status after finding a much better second skeleton, coining Antaecetus (after the giant of Greek myth).
And that's were we are right now. Three species in two genera, but only one of them is actually any good. So perhaps at some point in the future we might see some further revisions on that whole mess and who knows, perhaps Basilotritus makes a glorious comeback.
To conclude, sorry about the lack of images, despite the ample history theres just not much good material aside from that one Antaecetus fossil and I didn't want to include 5 different drawings in lateral view. Obligatory Wikipedia links: Pachycetinae - Wikipedia Antaecetus - Wikipedia Pachycetus - Wikipedia
Ideally Supayacetus will be the next whale I tackle, distractions and other projects not withstanding (who knows maybe I'll finally finish Quinkana)
#pachycetinae#pachycetus#basilotritus#platyosphys#antaecetus#archaeocete#prehistory#paleontology#palaeoblr#basilosauridae#eocene#whale
165 notes
·
View notes
Text
Fossil Friday: The Time When Fish Ruled the Earth
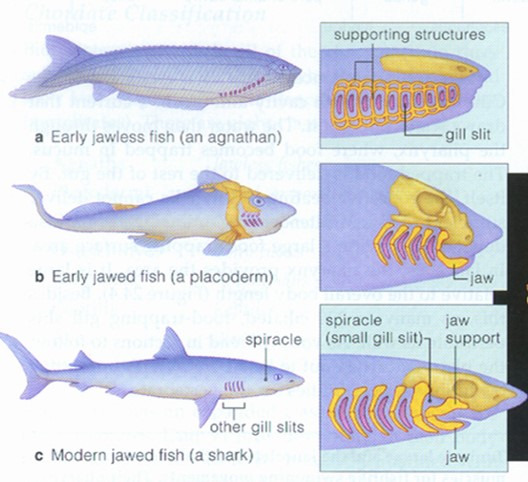
The Silurian Period could be called the time when fished ruled the Earth. Fish rapidly diversified throughout the period. There are two main groupings of fish that evolved: jawless and jawed.
Jawless fish first appeared in the Late Ordovician: Astraspida and Arandaspida. Astraspids are small, armored jawless fishes characterized by a dermal ornamentation of large, star-shaped tubercles of fine-tubuled dentine ("astraspidine"), covered with a thick, glassy cap of enameloid. They are represented by a single genus Astraspis.
Arandaspids are another small, armored fish with a flat rather than oval-shaped dorsal shield. These are represented by several genera of which Sacabambaspis is the most well-known. Check out my post on Sacabambaspis.

In the Silurian, several new groups of jawless fish appeared including thelodonts, heterostracans, osteostracans, and anaspids. Thelodonts were some of the first fish with scales rather than plates of armor. They first appeared in the Ordovician but they flourished in the Silurian. They lacked an ossified skeleton and the scales were either poorly attached or not attached to each other at all which makes finding a complete one incredibly difficult. The scales were small, 0.5-1.5mm, and didn’t overlap. They were teardrop-shaped and pointed on one end giving them there name “nipple tooth” They were ridiculously common in their habitats and globally distributed making them useful biostratigraphic markers.

Heterostracans also appeared in the Ordovician and radiated rapidly in the Silurian. Consisting of around 300 species, their head shields differed greatly from one another. Most had two plates which formed the dorsal shield and one large ventral shield with a series of scales arranged along the sides. The scales are composed of three layers of dentine and aspidine (an acellular bony tissue unique to them and thelodonts). The middle layer was honeycombed with tiny holes called cancella. One distinguishing characteristic was their single exhalant opening into which the gills open.

Anaspids were small armor less jawless fish. In fact, the name means “shield less ones”. They are covered in small, weakly mineralized scales and a row of large scutes running down the back. A major synapomorphy is the large tri-radiate spine behind the gill openings.
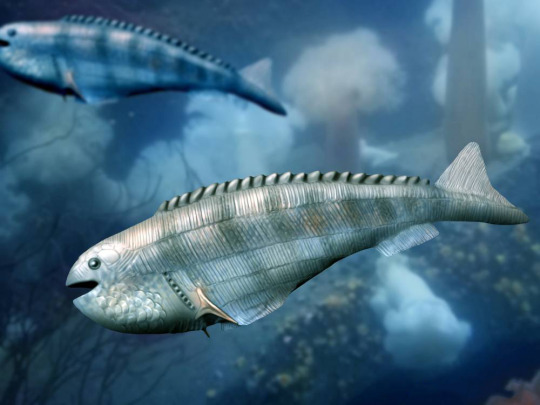

Osteostracans were the first group of fish with paired fins. They are often called ostracoderms, they were similar to lampreys in possessing two pairs of semicircular canals in the inner ear (as opposed to three in jawed vertebrates). These fish are the sister group to jawed fishes.
The jawed fishes first appeared in the Silurian Period. Four major groups radiated during this time: placoderms, acanthodians, cartilaginous fishes and bony fishes. Placoderms were mostly predatory armored fishes similar to the jawless ones. They were some of he earliest jawed fish and were the first ones to develop pelvic fins, the second set of paired fins. Some species have been found to be viviparous.

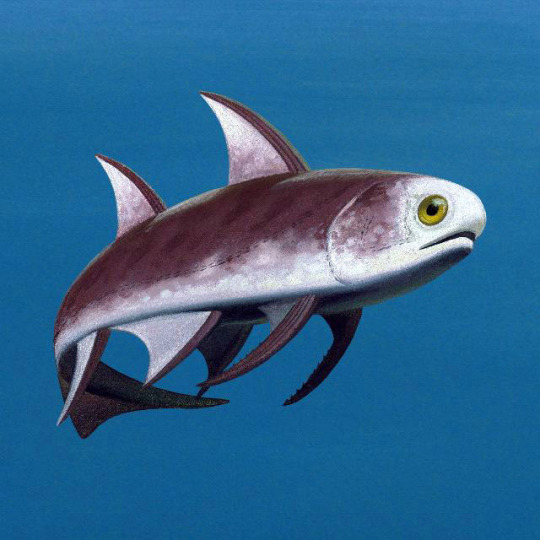
Acanthodians were small fishes with slender bodies. Th paired fins were modified to long spines earning then the nickname “spiny sharks”. Unlike most sharks, acanthodians lacked teeth. Many even moved to freshwater.

Chondrichthyes or cartilaginous fishesmay have evolved from acanthodians. This group consists of modern sharks, rays, skates and chimaeras.

Finally, the first Osteichthyes or bony fishes appeared in the Silurian Period. Unlike all the other fish, they have an endoskeleton made of bone tissue.

Thanks for coming to today’s lesson and tune in Monday to learn about the climate of the Silurian Period. Have a good weekend and fossilize you later!

#paleontology#fossils#science education#science#silurian#fossil friday#jawless fish#prehistoric fish#jawed fish
20 notes
·
View notes
Text
Daily Ray Fact:
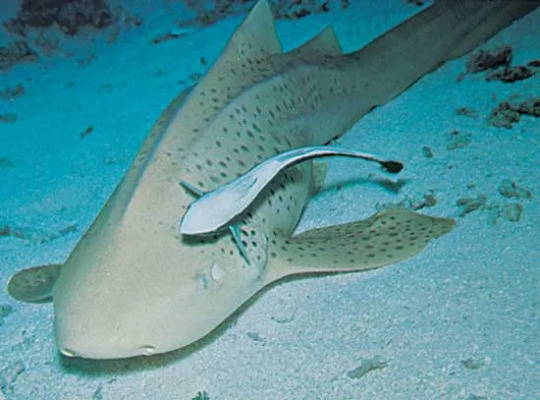
The Fiddler Ray and their relatives are thought to be the oldest ray group, which explains why they are somewhere between a shark and a ray. It is understood that rays evolved from sharks and so really the Fiddler Ray is a visual demonstration of that change in biology, The earliest known fossil rays are only 150 million years ago and whilst there are very few well preserved fossils available there are whole bodies of ancient guitarfishes which very closely resemble that of modern day Fiddler Rays.


#fiddler ray#ancient ray#dinosaur?#fossil relative#daily stingray#stingrays#stingray facts#ray facts#daily ray facts#daily stingray facts#ray family#respect the locals#cartilaginous fish#ocean#ocean life#marine life#sea creature#animals
291 notes
·
View notes
Text
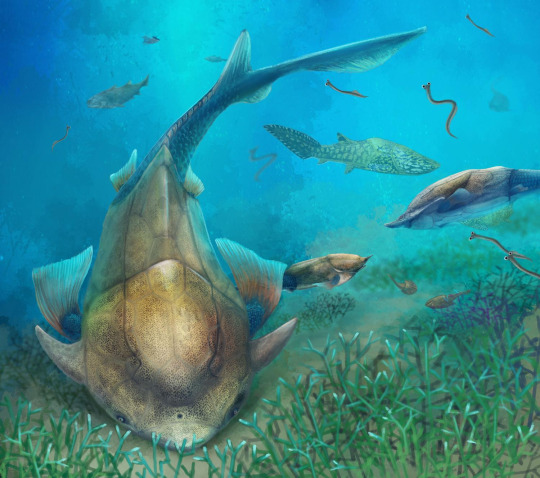
On Earth, Placoderms were a highly diverse group of fish that died out in the Devonian mass extinction due to a global deoxygenation event in the world's oceans caused by massive algae blooms. During the end Devonian extinction on Atterra, it was much the same, except for one key difference. One group of Arthrodire placoderms by Atterra's late Devonian period, between 382-372 mya, had evolved to live in tidal habitats along the coast. Crawling along the shore and rocks, looking for food or into larger pools of water.
These placoderms had adaptations in their pectoral fins similar to Antiarchi placoderms, where the first four cartilaginous rays fused to form a stronger and jointed ray to help push the fish along the ground. The ends of the cartilage rays in the pelvic fins fused to form a joint similar to Epaulette Sharks to help push the fish along the coastal rocks. Preserved tissue impressions in fossils of these placoderms show the presence of brachial tissue in the mouth, similar to Earth's electric eels, allowing the fish to gulp air when out of water.
This adaptation allowed these Arthrodire placoderms to survive the end Devonian deoxygenation event by supplementing oxygen from the air as oxygen levels in the water plummeted. Allowing the placoderms to survive by the skin of their teeth on Atterra, diversify during the carboniferous period, and survive to be found in the fish markets of the modern day.
#art#artwork#creature#creature art#creature design#digital art#drawing#illustration#monster design#monsters#my artwork#my art#doodle#sketch#clip studio paint#clip studio art#clip studio illustration#clip studio pro#sketches#skeleton art#skulls#anatomy#artist#digital 2d#digital illustration#digital drawing#digitalart#fish#fishes#sea creatures
29 notes
·
View notes
Photo

RARE Miocene Ray Tooth Fossil | S'Algar, Menorca | Authentic Prehistoric Marine Specimen | Certified Fossil | Collectible Fossilized Tooth
Discover a Rare Ray Tooth Fossil from the Miocene epoch, unearthed in S'Algar, Menorca. This beautifully preserved fossil offers a glimpse into the marine life that thrived around 15 million years ago. Menorca’s fossil-rich formations provide some of the finest examples of prehistoric marine life, making this an exceptional addition to any fossil collection.
Rays, known for their cartilaginous skeletons and specialized dental plates, used their teeth to crush and grind shellfish and crustaceans. This rare specimen highlights the intricate details of the tooth structure, making it a valuable educational and display piece.
Fossil Information:
Species: Prehistoric Ray (Exact species undetermined)
Fossil Type: Single Tooth
Geological Formation: Miocene Deposits
Age: ~15 million years old (Miocene Epoch)
Location: S'Algar, Menorca
Size: Full sizing provided in photos (Scale: 1cm per square)
Preservation: Excellent, showing distinct dental features
Key Features:
✔ Authentic Miocene Ray Tooth Fossil
✔ Sourced from the fossil-rich region of Menorca
✔ Well-preserved with natural dental structures
✔ Ideal for collectors, museum displays, and educational use
Authenticity & Certification:
All of our fossils are 100% genuine specimens and come with a Certificate of Authenticity. The fossil shown in the photos is the exact specimen you will receive.
Why Buy From Us?
This Ray Tooth fossil comes from the prestigious Alice Purnell Collection, one of the largest and most respected fossil collections in the world. We specialize in high-quality, museum-grade fossils, ideal for serious collectors, educators, and researchers.
🦈 Own a rare piece of Miocene marine history today—add this Ray Tooth fossil to your collection!
#Ray Tooth Fossil#Miocene Fossil#Menorca Fossil#Prehistoric Marine Fossil#Fossilized Ray Tooth#Certified Fossil#Authentic Fossil#Fossil Collector Item#Marine Life Fossil#Fossil Tooth Collection#Fossil from Spain#Fossil Gift#Rare Fossils for Sale#Shark and Ray Fossils#Miocene Marine Fossil
0 notes
Text
Mod 2 General Topics
Types of Fins
Fins are thin, broad folds of integument internally supported by fin rays, they aid in locomotion in various ways depending on the type of fins.
There are 2 kinds of adult fish fins: unpaired median and paired lateral.
Unpaired median fins include 1-2 dorsal fins along the mid-dorsal line, a ventral anal fin behind the anus/cloaca and a caudal fin around the tip of the tail.
Paired lateral fins include pectoral fins anteriorly and pelvic fins posteriorly. Pelvic fins are called thoracic when located below the pectoral fins and abdominal when located just above the anus. Absent in some.
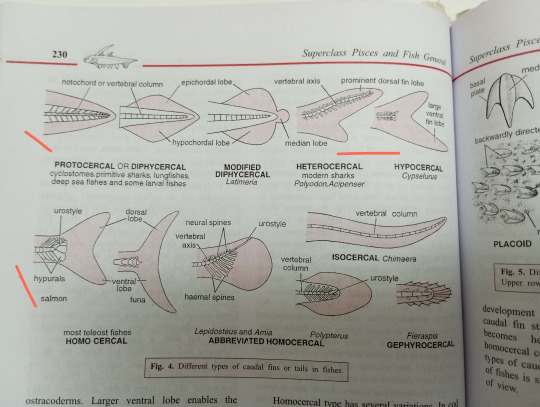
Under unpaired fins there are many types of caudal fins. Caudal fins are well developed in most fish because of its important contribution to forward propulsion during swimming. The 3 main types are: diphycercal, heterocercal, and homocercal.
Diphycercal Fins:
The most primitive, not exhibited by many living fish.
Vertebral column extends straight back to the tip of the tail, dividing the fin symmetrically and equally into the dorsal and ventral lobes.
Occurs in cyclostomes, primitive sharks, and lungfish.
Presence of diphycercal tail in developed fish is due to secondary modifications.
Heterocercal Fins:
Intermediate type.
The caudal fin is strongly asymmetrical.
Vertebral column bends upwards and reaches up to the tip of the more prominent dorsal lobe.
Characteristic in bottom feeders with a ventral mouth, the stroked of the large dorsal lobe directs the fish downwards.
Occurs in modern sharks.
The opposite, a large ventral lobe, is found in flying fish to propel them upwards. This type of fin is called hypocercal.
Homocercal Fins:
The most advanced type and the most common.
Characteristic of most higher bony fishes.
Externally symmetrical but internally asymmetrical.
The original dorsal lobe or epichordal is suppressed, the original ventral love is developed into a single or 2 symmetrical lobes.
Characteristic of fishes with a terminal mouth, its strokes force the fish straight forward.
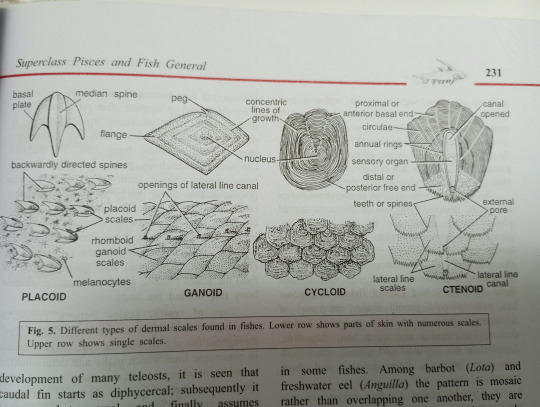
Types of Scales
There are 5 types of dermal scales: Cosmoid, Placoid, Ganoid, Cycloid, and Ctenoid.
1. Cosmoid Scales:
Does not occur in living fish, only fossilized fishes.
2. Placoid Scales:
Characteristic of sharks.
Each scale has a backwardly directed spine arising from a round or rhomboidal basal plate embedded in dermis.
Spine is enamel-like and basal plate is of dentine-like bony material.
A pulp cavity inside the spine opens through basal plate.
Placoid scales are closely set together in skin; giving a sandpaper like texture.
3. Ganoid Scales:
Thick, rhomboidal, or diamond shaped plates closely fitted side by side. Tile like, provide a bony armor to the fish, might overlap in some.
Characteristic of holosteans.
4. Cycloid Scales:
Thin, flexible. translucent plates. Circular in outline and thicker in the center.
Marked with several concentric lines of growth which can be used to determine age.
They overlap each other, each scale is embedded in a small pocket of dermis.
Found in lung fishes, carp, cod, etc.
5. Ctenoid Scales:
Similar to cycloid scales in form, structure, and arrangement.
But is more firmly attached, their free hind parts with are not overlapped, bear numerous small comb-like teeth or spines.
Characteristic of modern higher teleosteans like perch and sunfish.
There are some intermediate types of scales found in between cycloid and ctenoid, and some fish like flounder have both.
Neoteny and Paedogenesis
Neoteny refers to the retention of a larval or embryonic trait in the adult body. For example the retention of larval gills in adult salamanders.
Paedogenesis refers to the development of gonads and or production of young by an immature larval animal. Examples are scattered in several groups or animals such as gall fly, liver fluke, and salamanders.
Neoteny emphasizes the retention of larval traits in the adult body while paedogenesis stresses the development of adult like gonads in the larval body.
The best example of neoteny and paedogenesis is ambystomata. Normally they live through an aquatic larval stage and transform into an air-breathing terrestrial adult. However, under certain circumstances, the larvae does not undergo metamorphosis, retains it's gills and aquatic nature, but becomes sexually mature. This sexually mature larval stage with external gills is called an axolotl.
For a while axolotls were thought to be an entirely separate genus, Siredon.
Environmental factors affect metamorphosis in many ways. Abundance of food, cold temp., and insufficient iodine may cause failure of metamorphosis and paedogenesis. This is known because drying of swamps, lack of food, and rise in temp induce axolotls to metamorphose. When treated with thyroxine or TSH, they lose their gills and become adults.
There are 3 types of neoteny, partial, intermediate and total.
Partial neoteny is then metamorphosis is delayed due to temporary ecological or physiological changes, seen in tadpoles over winter.
Intermediate neoteny is when the organism is sexually reproductive and can undergo metamorphosis under the correct conditions, seen in axolotl.
Total neoteny is when they remain larval throughout. Even after treatment of thyroxine, they fail to metamorphose. Seen in Siren.
Parental Care in Amphibians
Parental care is the act of looking after the eggs or young until they are independent enough to defend from predators.
Amphibians exhibit various types of parental care in two broad groups: Protection by nests, nurseries, or shelters and direct caring by parents.
Protection by nests, nurseries, or shelters:
1. Selection of site: Many amphibians lay their eggs in protected moist microhabitats. Some frogs and toads lay eggs on land near water. Many tree frogs lay their eggs on leave and branched overhanding water by gluing their eggs, they fall into water free of predators when hatched. Some tree frogs deposit eggs in water that accumulates in epiphytic tropical plants, free from aquatic predators.
2. Defending eggs or territories: Male green Rana frogs maintain territories and attack small intruders to protect the eggs. Both male and female Mantophryne frogs guard the eggs. The male actually sits over and holds the gelatinous envelope containing 17 eggs.
3. Direct Development: In some frogs such as Hyla, the eggs hatch directly into little frogs, thus avoiding the chance of larval mortality. In the red backed salamander, the hatchlings are miniature adults.
4. Foam Nests: Many amphibians convert copious mucous secretion into nests for young. Japanese tree frogs dig a hole or tunnel into which eggs are left in a frothy mass to avoid desiccation. During rain, the hatching tadpoles are washed down the slopping tunnel into pond or river water for further development. Some frogs lay eggs in nests of foam floating on water. The female emits a huge amount of mucus that she can beats into foam with her hindlegs to lay eggs in. When tadpoles hatch they drop from foam into water.
5. Mud nests: Brazilian tree frog, Hyla, the male frog digs little holes in the mud of shallow water for the female frog to lay eggs in. The nest is 30cm in diameter and 5-8cm deep. Tadpoles hatch within this safe place and develop until they are large enough to defend themselves.
6. Tree nests: The South American Tree frog, Phyllomedusa, lays eggs in a folded leaf nest with margins glued together with cloacal secretions. The tadpoles when formed fall straight into water below.
7. Gelatinous bags: Salamandrella, a small aquatic salamander, deposits 50-60 small eggs in a gelatinous bag which is fastened to aquatic plants.
Direct Carrying By Parent
1. Coiling around eggs: In certain caecilians like Ichthyophis, the female lays large eggs in burrows in damp soil and carefully guards them by coiling her body around them until they hatch.
2. Transferring tadpoles to water: Some species of small frogs in tropical Africa and South America deposit their eggs on ground. Once the tadpoles hatch, they fasten themselves to the back of one of the parents with their sucker like mouth so they can be transported to water.
3. Eggs glued to body: Many amphibians carry the eggs glued to their body. In the Sri Lankan tree frog, the eggs are glued to the belly of the female. In the European midwife toad, Alytes, the mall entangles the eggs around his hindlegs so he can carry them with him until they are ready to hatch. When the time comes they release the tadpoles into the nearest water body.
4. Eggs in back pouches: In a group of tree frogs called marsupial frogs, the female carries the eggs on her back. Either in an open oval depression, a closed pouch, or individual pockets. The eggs develop into miniature frogs before leaving their mother's back.
5. Organs as brooding pouches: Males of the terrestrial South American Darwin's frog, Rhinoderma, pushes at least 2 fertilized eggs into his large vocal sacs. There they undergo complete development to emerge out as fully formed froglets.
6. Viviparity: Some anurans are ovoviviparous. They reatain eggs in the oviducts and the female gives birth to living young. For example African toads give birth to little frogs.
#zoology#vertebrates#fish#frog#neoteny#parental care#fins#scales#notes#biology#exam season#please help#amphibians#axolotl
64 notes
·
View notes
Text
Animal Crossing Fish - Explained #241
Brought to you by a marine biologist with some snakey shark...
CLICK HERE FOR THE AC FISH EXPLAINED MASTERPOST!
Fish are fascinating. Although, yes, I'm very biased, I'm also saying it because the two largest groups of them - the bony fish (Osteichthyes) and the cartilagenous fish (Chonrichthyes) - come in some wild shapes and sizes. And some of these shapes, like that of today's fish, the Frilled Shark, are still just weird as hell.

I'm actually really surprised that ACPC added this shark in, but they did! It was a special catch for the Deep Sea Shark Goals back in July 2023. The art is also so spot on given just how weird this guy is! Look at the teeth in perfect rows! The fins are all the way towards the back of the body! The gills are even frilled (that's where the name comes from!) to the point you can see the red gill tissue inside! It's really great. Although there are two species of Frilled Shark now, and they look very much the same, I'm going to say this is definitely the OG Frilled Shark - Chlamydoselachus anguineus - that everyone knows and loves. (The other species, the Southern African frilled shark (Chlamydoselachus africana) was only described in 2009, so I just doubt it's the one featured here.)

It's hard to find good pictures of a healthy frilled shark since, if you're seeing them at the surface in broad daylight for a good picture, odds are, that guy is on his way out, unfortunately. These are relatively deep-sea sharks that live their lives like a lot of twilight zone animals do - hopping on the Great Diel Migration, where they hang out at depth during the day, but go up to the surface at night to feed.
If there is any shark that is called a "living fossil" it's this one. With the snake-like body and six gills and pretty much a lack of a rostrum, this isn't the first image you would conjure when someone says "shark". And just from my experience talking to people about sharks since I was really small, I've noticed that when people think "shark" they are more than likely imagining the sharks of Galeomorphii, or the Galean Sharks, which include the Great White, the Whale, the Hammerheads, and just your typical shark friends.
The Frilled does not belong here.
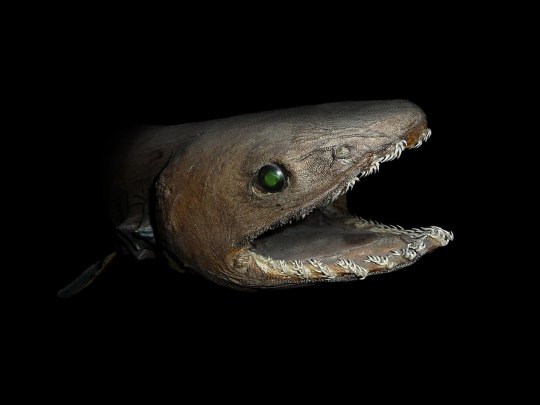

By © Citron, CC BY-SA 3.0, (Do you see what I was saying about the teeth being in perfect rows???)
There is a whole other SuperOrder of sharks called the Squalomorphii, or Squalean Sharks. The Squaleans are typically told apart from the Galeans by lacking traits, such as an anal fin (which isn't the case in the frilled shark, so we'll move on), no nictitating membrane over the eyes, and differences in skull morphology. These guys are diverse, weird...and sometimes disrespected. A lot of them are called "dogfish" and where I'm from, dogfish aren't even considered "real sharks". I can't complain too much since I never count dogfish as "seeing sharks" when I'm out at sea. Many of them are small. But this group also includes famous sharks, like the Greenland shark, saw sharks, angel sharks, and the very primitive-looking Cow Sharks, for which the Frilled, we think!, belongs.
Cow Sharks, the Hexanchiformes, are a bunch of weirdos with six or seven gill slits, where other sharks (and most rays!) all have five gill slits. They're typically deep water sharks that can only rarely be studied. One of them, the broadnose sevengill, though, is a resident to San Francisco Bay, California, so it's not necessary to be deep sea when you're a weird, primitive shark. Even so, the Frilled Shark is a weirdo among weirdos, and it's been placed in many other groups of extinct sharks since its discovery. However, genetic analysis done in 2016 puts it in with the Hexanchiformes, but still apart in its very own Family - Chlamydoselachidae. That's what happens when you're a shark that looks and swims like an eel, has trident teeth, and has a weird head with weird jaws. Did I mention these things grow to be 6 feet (2m) long?
And there you have it. Fascinating stuff, no?
#frilled shark#animal crossing#marine biology#fish#animals#sharks#animal crossing pocket camp#acpc#science in video games#animal crossing fish explained
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
Below are 10 Wikipedia featured articles. Links and descriptions are below the cut.
The American paddlefish (Polyodon spathula), also known as a Mississippi paddlefish, spoon-billed cat, or spoonbill, is a species of ray-finned fish. It is the last living species of paddlefish (Polyodontidae). This family is most closely related to the sturgeons; together they make up the order Acipenseriformes, which are one of the most primitive living groups of ray-finned fish. Fossil records of other paddlefish species date back 125 million years to the Early Cretaceous, with records of Polyodon extending back 65 million years to the early Paleocene. The American paddlefish is a smooth-skinned freshwater fish with an almost entirely cartilaginous skeleton and a paddle-shaped rostrum (snout), which extends nearly one-third its body length. It has been referred to as a freshwater shark because of its heterocercal tail or caudal fin resembling that of sharks, though it is not closely related. The American paddlefish is a highly derived fish because it has evolved specialised adaptations such as filter feeding. Its rostrum and cranium are covered with tens of thousands of sensory receptors for locating swarms of zooplankton, its primary food source.
The fauna of Scotland is generally typical of the northwest European part of the Palearctic realm, although several of the country's larger mammals were hunted to extinction in historic times and human activity has also led to various species of wildlife being introduced. Scotland's diverse temperate environments support 62 species of wild mammals, including a population of wild cats, important numbers of grey and harbour seals and the most northerly colony of bottlenose dolphins in the world. Many populations of moorland birds, including the black and red grouse, live here, and the country has internationally significant nesting grounds for seabirds such as the northern gannet. The Scottish crossbill is the only endemic vertebrate species in the UK. Scotland's seas are among the most biologically productive in the world; it is estimated that the total number of Scottish marine species exceeds 40,000. The Darwin Mounds are an important area of deep sea cold water coral reefs discovered in 1998. Only six amphibians and four land reptiles are native to Scotland, but many species of invertebrates live there that are otherwise rare in the United Kingdom.
Several attempts at a Franco-Mongol alliance against the Islamic caliphates, their common enemy, were made by various leaders among the Frankish Crusaders and the Mongol Empire in the 13th century. Such an alliance might have seemed an obvious choice: the Mongols were already sympathetic to Christianity, given the presence of many influential Nestorian Christians in the Mongol court. The Franks—Western Europeans, and those in the Levantine Crusader states—were open to the idea of support from the East, in part owing to the long-running legend of the mythical Prester John, an Eastern king in an Eastern kingdom who many believed would one day come to the assistance of the Crusaders in the Holy Land. The Franks and Mongols also shared a common enemy in the Muslims. However, despite many messages, gifts, and emissaries over the course of several decades, the often-proposed alliance never came to fruition.
The Free State of Galveston (sometimes referred to as the Republic of Galveston Island) was a satirical name given to the coastal city of Galveston in the U.S. state of Texas during the early-to-mid-20th century. Today, the term is sometimes used to describe the culture and history of that era. During the Roaring Twenties, Galveston Island emerged as a popular resort town, attracting celebrities from around the country. Gambling, illegal liquor, and other vice-oriented businesses were a major part of tourism. The "Free State" moniker embodied a belief held by many locals that Galveston was beyond what they perceived were repressive mores and laws of Texas and the United States. In one of the more famous examples of this, a state committee, investigating gambling at the fabled Balinese Room, was told by the local sheriff that he had not raided the establishment because it was a "private club" and because he was not a "member".
The Kylfings (Old Norse Kylfingar; Estonian Kalevid; Hungarian Kölpények; Old East Slavic Колбяги, Kolbiagi; Byzantine Greek Κουλπίγγοι, Koulpingoi; Arabic al-Kilabiyya) were a people of uncertain origin active in Northern Europe during the Viking Age, roughly from the late ninth century to the early twelfth century. They could be found in areas of Lapland, Russia, and the Byzantine Empire that were frequented by Scandinavian traders, raiders and mercenaries. Scholars differ on whether the Kylfings were ethnically Finnic or Norse. Also disputed is their geographic origin, with Denmark, Sweden and the Eastern Baltic all put forward as candidates. Whether the name Kylfing denotes a particular tribal, socio-political, or economic grouping is also a matter of much debate.
Mosasaurus (/ˌmoʊzəˈsɔːrəs/; "lizard of the Meuse River") is the type genus (defining example) of the mosasaurs, an extinct group of aquatic squamate reptiles. It lived from about 82 to 66 million years ago during the Campanian and Maastrichtian stages of the Late Cretaceous. The genus was one of the first Mesozoic marine reptiles known to science—the first fossils of Mosasaurus were found as skulls in a chalk quarry near the Dutch city of Maastricht in the late 18th century, and were initially thought to be crocodiles or whales. One skull discovered around 1780 was famously nicknamed the "great animal of Maastricht". In 1808, naturalist Georges Cuvier concluded that it belonged to a giant marine lizard with similarities to monitor lizards but otherwise unlike any known living animal. This concept was revolutionary at the time and helped support the then-developing ideas of extinction.
Several organisms are capable of rolling locomotion. However, true wheels and propellers—despite their utility in human vehicles—do not play a significant role in the movement of living things (with the exception of certain flagella, which work like corkscrews). Biologists have offered several explanations for the apparent absence of biological wheels, and wheeled creatures have appeared often in speculative fiction.
The existence of a slate industry in Wales is attested since the Roman period, when slate was used to roof the fort at Segontium, now Caernarfon. The slate industry grew slowly until the early 18th century, then rapidly during the Industrial Revolution in Wales until the late 19th century, at which time the most important slate producing areas were in northwest Wales. These sites included the Penrhyn Quarry near Bethesda, the Dinorwic Quarry near Llanberis, the Nantlle Valley quarries, and Blaenau Ffestiniog, where the slate was mined rather than quarried. Penrhyn and Dinorwig were the two largest slate quarries in the world, and the Oakeley mine at Blaenau Ffestiniog was the largest slate mine in the world.
The social history of viruses describes the influence of viruses and viral infections on human history. Epidemics caused by viruses began when human behaviour changed during the Neolithic period, around 12,000 years ago, when humans developed more densely populated agricultural communities. This allowed viruses to spread rapidly and subsequently to become endemic. Viruses of plants and livestock also increased, and as humans became dependent on agriculture and farming, diseases such as potyviruses of potatoes and rinderpest of cattle had devastating consequences.
The High Middle Ages of Scotland encompass Scotland in the era between the death of Domnall II in 900 AD and the death of King Alexander III in 1286, which was an indirect cause of the Wars of Scottish Independence. At the close of the ninth century, various competing kingdoms occupied the territory of modern Scotland. Scandinavian influence was dominant in the northern and western islands, Brythonic culture in the southwest, the Anglo-Saxon or English Kingdom of Northumbria in the southeast and the Pictish and Gaelic Kingdom of Alba in the east, north of the River Forth. By the tenth and eleventh centuries, northern Great Britain was increasingly dominated by Gaelic culture, and by the Gaelic regal lordship of Alba, known in Latin as either Albania or Scotia, and in English as "Scotland".
30 notes
·
View notes
Note
Sharks are older than trees and Saturn's rings
Yup! The fossil records for sharks go back 450 million years (even if they didn't quite look like modern sharks at that point. Sharks as we know them didnt appear till about 150 million years ago. Doesnt stop those older sharks from being sharks, they just looked different. Mouths closer to the front of the head, teeth tended more towards chrushing and were these prett gnarly looking three pronged things, with rayed fins rather than modern shark's more fleshy fins).
And whilst vascular plants (which trees fall under) first started appearing in the record from about 430 million years ago, they were only quite small, and trees didn't start appearing in the record untill from about 45 million years later, so about 385 million years ago.
(Of course, this is when they started to appear in the fossil record, meaning there is a very real possibility that both sharks and trees were around a little earlier than there oldest fossils date to.)
Saturn's rings are estimated to be no more than 400 million years old, but at the youngest 100 million years old. Seeing as our earliest recorded sharks are from about 450 million years ago, this means sharks, and vascular plants, are older than Saturn's rings. And trees are only about 15 million years younger than our oldest estimates for Saturn's rings, but are likely also older than saturns rings, but were not too certain on that.
7 notes
·
View notes