#Sublime html editor
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Essentials You Need to Become a Web Developer
HTML, CSS, and JavaScript Mastery
Text Editor/Integrated Development Environment (IDE): Popular choices include Visual Studio Code, Sublime Text.
Version Control/Git: Platforms like GitHub, GitLab, and Bitbucket allow you to track changes, collaborate with others, and contribute to open-source projects.
Responsive Web Design Skills: Learn CSS frameworks like Bootstrap or Flexbox and master media queries
Understanding of Web Browsers: Familiarize yourself with browser developer tools for debugging and testing your code.
Front-End Frameworks: for example : React, Angular, or Vue.js are powerful tools for building dynamic and interactive web applications.
Back-End Development Skills: Understanding server-side programming languages (e.g., Node.js, Python, Ruby , php) and databases (e.g., MySQL, MongoDB)
Web Hosting and Deployment Knowledge: Platforms like Heroku, Vercel , Netlify, or AWS can help simplify this process.
Basic DevOps and CI/CD Understanding
Soft Skills and Problem-Solving: Effective communication, teamwork, and problem-solving skills
Confidence in Yourself: Confidence is a powerful asset. Believe in your abilities, and don't be afraid to take on challenging projects. The more you trust yourself, the more you'll be able to tackle complex coding tasks and overcome obstacles with determination.
#code#codeblr#css#html#javascript#java development company#python#studyblr#progblr#programming#comp sci#web design#web developers#web development#website design#webdev#website#tech#html css#learn to code
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
How to Build Software Projects for Beginners

Building software projects is one of the best ways to learn programming and gain practical experience. Whether you want to enhance your resume or simply enjoy coding, starting your own project can be incredibly rewarding. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you get started.
1. Choose Your Project Idea
Select a project that interests you and is appropriate for your skill level. Here are some ideas:
To-do list application
Personal blog or portfolio website
Weather app using a public API
Simple game (like Tic-Tac-Toe)
2. Define the Scope
Outline what features you want in your project. Start small and focus on the minimum viable product (MVP) — the simplest version of your idea that is still functional. You can always add more features later!
3. Choose the Right Tools and Technologies
Based on your project, choose the appropriate programming languages, frameworks, and tools:
Web Development: HTML, CSS, JavaScript, React, or Django
Mobile Development: Flutter, React Native, or native languages (Java/Kotlin for Android, Swift for iOS)
Game Development: Unity (C#), Godot (GDScript), or Pygame (Python)
4. Set Up Your Development Environment
Install the necessary software and tools:
Code editor (e.g., Visual Studio Code, Atom, or Sublime Text)
Version control (e.g., Git and GitHub for collaboration and backup)
Frameworks and libraries (install via package managers like npm, pip, or gems)
5. Break Down the Project into Tasks
Divide your project into smaller, manageable tasks. Create a to-do list or use project management tools like Trello or Asana to keep track of your progress.
6. Start Coding!
Begin with the core functionality of your project. Don’t worry about perfection at this stage. Focus on getting your code to work, and remember to:
Write clean, readable code
Test your code frequently
Commit your changes regularly using Git
7. Test and Debug
Once you have a working version, thoroughly test it. Look for bugs and fix any issues you encounter. Testing ensures your software functions correctly and provides a better user experience.
8. Seek Feedback
Share your project with friends, family, or online communities. Feedback can provide valuable insights and suggestions for improvement. Consider platforms like GitHub to showcase your work and get input from other developers.
9. Iterate and Improve
Based on feedback, make improvements and add new features. Software development is an iterative process, so don’t hesitate to refine your project continuously.
10. Document Your Work
Write documentation for your project. Include instructions on how to set it up, use it, and contribute. Good documentation helps others understand your project and can attract potential collaborators.
Conclusion
Building software projects is a fantastic way to learn and grow as a developer. Follow these steps, stay persistent, and enjoy the process. Remember, every project is a learning experience that will enhance your skills and confidence!
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
JavaScript Tutorial: A Beginner's Guide to the World of Web Development
Welcome to the exciting world of JavaScript! If you're looking to dive into web development, understanding JavaScript is essential. This versatile programming language powers the interactive elements of websites and is a key component of modern web applications. In this tutorial, we'll cover the basics of JavaScript, its syntax, and some practical examples to get you started.
What is JavaScript?
JavaScript is a high-level, dynamic, and interpreted programming language that is primarily used for enhancing the interactivity of web pages. It allows developers to create rich user experiences by manipulating HTML and CSS, responding to user events, and communicating with servers.
Why Learn JavaScript?
Ubiquity: JavaScript is supported by all modern web browsers, making it a universal language for web development.
Versatility: Beyond the browser, JavaScript can be used on the server-side (with Node.js), in mobile app development (with frameworks like React Native), and even in game development.
Community and Resources: With a vast community and numerous resources available, learning JavaScript is more accessible than ever.
Getting Started with JavaScript
Setting Up Your Environment
To start coding in JavaScript, you don't need any special software. All you need is a web browser and a text editor. Here’s how to set it up:
Choose a Text Editor: Popular options include Visual Studio Code, Sublime Text, and Atom.
Open Your Browser: You can use any modern browser like Chrome, Firefox, or Edge.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Learn HTML and CSS: A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners
Introduction to HTML and CSS
HTML (HyperText Markup Language) and CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) are the core technologies for creating web pages. HTML provides the structure of the page, while CSS defines its style and layout. This guide aims to equip beginners with the essential knowledge to start building and designing web pages.
Why Learn HTML and CSS?
HTML and CSS are fundamental skills for web development. Whether you're looking to create personal websites, start a career in web development, or enhance your current skill set, understanding these technologies is crucial. They form the basis for more advanced languages and frameworks like JavaScript, React, and Angular.
Getting Started with HTML and CSS
To get started, you need a text editor and a web browser. Popular text editors include Visual Studio Code, Sublime Text, and Atom. Browsers like Google Chrome, Firefox, and Safari are excellent for viewing and testing your web pages.
Basic HTML Structure
HTML documents have a basic structure composed of various elements and tags. Here’s a simple example:
html
Copy code
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>My First Web Page</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css">
</head>
<body>
<h1>Welcome to My Web Page</h1>
<p>This is a paragraph of text on my web page.</p>
</body>
</html>
: Declares the document type and HTML version.
: The root element of an HTML page.
: Contains meta-information about the document.
: Connects the HTML to an external CSS file.
: Contains the content of the web page.
Essential HTML Tags
HTML uses various tags to define different parts of a web page:
to : Headings of different levels.
: Paragraph of text.
: Anchor tag for hyperlinks.
: Embeds images.
: Defines divisions or sections.
: Inline container for text.
Creating Your First HTML Page
Follow these steps to create a simple HTML page:
Open your text editor.
Write the basic HTML structure as shown above.
Add a heading with the tag.
Add a paragraph with the tag.
Save the file with a .html extension (e.g., index.html).
Open the file in your web browser to view your web page.
Introduction to CSS
CSS is used to style and layout HTML elements. It can be included within the HTML file using the <style> tag or in a separate .css file linked with the <link> tag.
Basic CSS Syntax
CSS consists of selectors and declarations. Here’s an example:
css
Copy code
h1 {
color: blue;
font-size: 24px;
}
Selector (h1): Specifies the HTML element to be styled.
Declaration Block: Contains one or more declarations, each consisting of a property and a value.
Styling HTML with CSS
To style your HTML elements, you can use different selectors:
Element Selector: Styles all instances of an element.
Class Selector: Styles elements with a specific class.
ID Selector: Styles a single element with a specific ID.
Example:
html
Copy code
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Styled Page</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css">
</head>
<body>
<h1 class="main-heading">Hello, World!</h1>
<p id="intro">This is an introduction paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>
In the styles.css file:
css
Copy code
.main-heading {
color: green;
text-align: center;
}
#intro {
font-size: 18px;
color: grey;
}
CSS Layout Techniques
CSS provides several layout techniques to design complex web pages:
Box Model: Defines the structure of an element’s content, padding, border, and margin.
Flexbox: A layout model for arranging items within a container, making it easier to design flexible responsive layouts.
Grid Layout: A two-dimensional layout system for more complex layouts.
Example of Flexbox:
css
Copy code
.container {
display: flex;
justify-content: space-around;
}
.item {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: lightblue;
}
Best Practices for Writing HTML and CSS
Semantic HTML: Use HTML tags that describe their meaning clearly (e.g., , , ).
Clean Code: Indent nested elements and use comments for better readability.
Validation: Use tools like the W3C Markup Validation Service to ensure your HTML and CSS are error-free and standards-compliant.
Accessibility: Make sure your website is accessible to all users, including those with disabilities, by using proper HTML tags and attributes.
Free Resources to Learn HTML and CSS
W3Schools: Comprehensive tutorials and references.
MDN Web Docs: Detailed documentation and guides for HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
Codecademy: Interactive courses on web development.
FreeCodeCamp: Extensive curriculum covering HTML, CSS, and more.
Khan Academy: Lessons on computer programming and web development.
FAQs about Learning HTML and CSS
Q: What is HTML and CSS? A: HTML (HyperText Markup Language) structures web pages, while CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) styles and layouts the web pages.
Q: Why should I learn HTML and CSS? A: Learning HTML and CSS is essential for creating websites, understanding web development frameworks, and progressing to more advanced programming languages.
Q: Do I need prior experience to learn HTML and CSS? A: No prior experience is required. HTML and CSS are beginner-friendly and easy to learn.
Q: How long does it take to learn HTML and CSS? A: The time varies depending on your learning pace. With consistent practice, you can grasp the basics in a few weeks.
Q: Can I create a website using only HTML and CSS? A: Yes, you can create a basic website. For more complex functionality, you'll need to learn JavaScript.
Q: What tools do I need to start learning HTML and CSS? A: You need a text editor (e.g., Visual Studio Code, Sublime Text) and a web browser (e.g., Google Chrome, Firefox).
Q: Are there free resources available to learn HTML and CSS? A: Yes, there are many free resources available online, including W3Schools, MDN Web Docs, Codecademy, FreeCodeCamp, and Khan Academy.
#how to learn html and css#html & css course#html & css tutorial#html and css#html course#html css tutorial#html learn#html learn website#learn html#learn html and css#html and css course#html and css full course#html and css online course#how to learn html and css for beginners
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
in light of recent tumblr changes
if you're sick of staff constantly rolling out user-unfriendly changes and you're desperate to find somewhere else to hang out that isn't the other shitty corporate social media platforms we're offered, please learn HTML and CSS. i promise it really isn't that hard; it takes practice and dedication just as anything else does, but it is so rewarding to have your own personal, customizable space on the internet. you can literally do whatever you want with your site once you make it. want to make a shrine dedicated to your favorite fictional characters? a diary for your daily occurrences? a digital grimoire? maybe reviews of your favorite movies, books, or games? you can do ALL of those things and more. the possibilities are literally endless, all you have to do is try.
below are some resources i've been collecting. i'll update this post as frequently as i can.
where to learn HTML and CSS:
HTML for absolute beginners
MDN CSS basics / HTML basics
W3schools
here are some website hosts:
teacake
neocities
github
some text-based editors:
brackets
sublime
notepad++
visualcode
google alternatives:
search.marginalia.nu
wiby.me
other cool platforms:
livejournal / dreamwidth
substack
multiverse.plus
fc2 blog / fc2 site
misc links:
let's decentralize
internet hiker's log
anipike
nightfall.city
sundaysites.cafe
yami-ichi.biz
tilde.town
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
Unveiling the Ultimate Handbook for Aspiring Full Stack Developers

In the ever-evolving realm of technology, the role of a full-stack developer has undeniably gained prominence. Full-stack developers epitomize versatility and are an indispensable asset to any enterprise or endeavor. They wield a comprehensive array of competencies that empower them to navigate the intricate landscape of both front-end and back-end web development. In this exhaustive compendium, we shall delve into the intricacies of transforming into a proficient full-stack developer, dissecting the requisite skills, indispensable tools, and strategies for excellence in this domain.
Deciphering the Full Stack Developer Persona
A full-stack developer stands as a connoisseur of both front-end and back-end web development. Their mastery extends across the entire spectrum of web development, rendering them highly coveted entities within the tech sector. The front end of a website is the facet accessible to users, while the back end operates stealthily behind the scenes, handling the intricacies of databases and server management. You can learn it from Uncodemy which is the Best Full stack Developer Institute in Delhi.
The Requisite Competencies
To embark on a successful journey as a full-stack developer, one must amass a diverse skill set. These proficiencies can be broadly categorized into front-end and back-end development, coupled with other quintessential talents:
Front-End Development
Markup Linguistics and Style Sheets: Cultivating an in-depth grasp of markup linguistics and style sheets like HTML and CSS is fundamental to crafting visually captivating and responsive user interfaces.
JavaScript Mastery: JavaScript constitutes the linchpin of front-end development. Proficiency in this language is the linchpin for crafting dynamic web applications.
Frameworks and Libraries: Familiarization with popular front-end frameworks and libraries such as React, Angular, and Vue.js is indispensable as they streamline the development process and elevate the user experience.
Back-End Development
Server-Side Linguistics: Proficiency in server-side languages like Node.js, Python, Ruby, or Java is imperative as these languages fuel the back-end functionalities of websites.
Database Dexterity: Acquiring proficiency in the manipulation of databases, including SQL and NoSQL variants like MySQL, PostgreSQL, and MongoDB, is paramount.
API Expertise: Comprehending the creation and consumption of APIs is essential, serving as the conduit for data interchange between the front-end and back-end facets.
Supplementary Competencies
Version Control Proficiency: Mastery in version control systems such as Git assumes monumental significance for collaborative code management.
Embracing DevOps: Familiarity with DevOps practices is instrumental in automating and streamlining the development and deployment processes.
Problem-Solving Prowess: Full-stack developers necessitate robust problem-solving acumen to diagnose issues and optimize code for enhanced efficiency.
The Instruments of the Craft
Full-stack developers wield an arsenal of tools and technologies to conceive, validate, and deploy web applications. The following are indispensable tools that merit assimilation:
Integrated Development Environments (IDEs)
Visual Studio Code: This open-source code editor, hailed for its customizability, enjoys widespread adoption within the development fraternity.
Sublime Text: A lightweight and efficient code editor replete with an extensive repository of extensions.
Version Control
Git: As the preeminent version control system, Git is indispensable for tracking code modifications and facilitating collaborative efforts.
GitHub: A web-based platform dedicated to hosting Git repositories and fostering collaboration among developers.
Front-End Frameworks
React A potent JavaScript library for crafting user interfaces with finesse.
Angular: A comprehensive front-end framework catering to the construction of dynamic web applications.
Back-End Technologies
Node.js: A favored server-side runtime that facilitates the development of scalable, high-performance applications.
Express.js: A web application framework tailor-made for Node.js, simplifying back-end development endeavors.
Databases
MongoDB: A NoSQL database perfectly suited for managing copious amounts of unstructured data.
PostgreSQL: A potent open-source relational database management system.
Elevating Your Proficiency as a Full-Stack Developer
True excellence as a full-stack developer transcends mere technical acumen. Here are some strategies to help you distinguish yourself in this competitive sphere:
Continual Learning: Given the rapid evolution of technology, it's imperative to remain abreast of the latest trends and tools.
Embark on Personal Projects: Forge your path by creating bespoke web applications to showcase your skills and amass a portfolio.
Collaboration and Networking: Participation in developer communities, attendance at conferences, and collaborative ventures with fellow professionals are key to growth.
A Problem-Solving Mindset: Cultivate a robust ability to navigate complex challenges and optimize code for enhanced efficiency.
Embracing Soft Skills: Effective communication, collaborative teamwork, and adaptability are indispensable in a professional milieu.
In Closing
Becoming a full-stack developer is a gratifying odyssey that demands unwavering dedication and a resolute commitment to perpetual learning. Armed with the right skill set, tools, and mindset, one can truly shine in this dynamic domain. Full-stack developers are in high demand, and as you embark on this voyage, you'll discover a plethora of opportunities beckoning you.
So, if you aspire to join the echelons of full-stack developers and etch your name in the annals of the tech world, commence your journey by honing your skills and laying a robust foundation in both front-end and back-end development. Your odyssey to becoming an adept full-stack developer commences now.
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
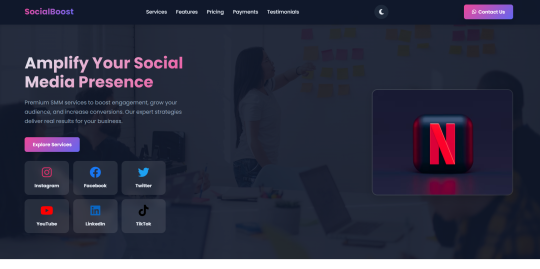
Social Boost
Premium Social Media Marketing Landing Page
Live Demo | Buy Now

Give your social media agency or marketing service the professional online presence it deserves with Social Boost — a premium landing page designed to impress, convert, and grow your audience.
Crafted for social media experts, agencies, freelancers, and digital marketers, Social Boost is your perfect tool to showcase services, attract leads, and drive engagement — all in one high-performing, responsive layout.
Key Features
✅ Modern & Professional Design – Eye-catching layout with strong visuals tailored for marketing services.
✅ Fully Responsive – Looks great on all devices: mobile, tablet, and desktop.
✅ Clean & Organized Code – Easy to edit, understand, and customize.
✅ Conversion-Focused Sections – Includes CTA buttons, testimonials, services, and pricing plans.
✅ Fast Loading – Optimized for speed and performance.
✅ Lightweight Assets – Uses placeholder images and minimal dependencies for fast deployment.
✅ Cross-Browser Compatibility – Works smoothly across all major browsers.
Perfect For
Social media marketing agencies
Freelancers & digital marketers
Advertising services
Personal branding & portfolio sites
Small businesses offering online marketing
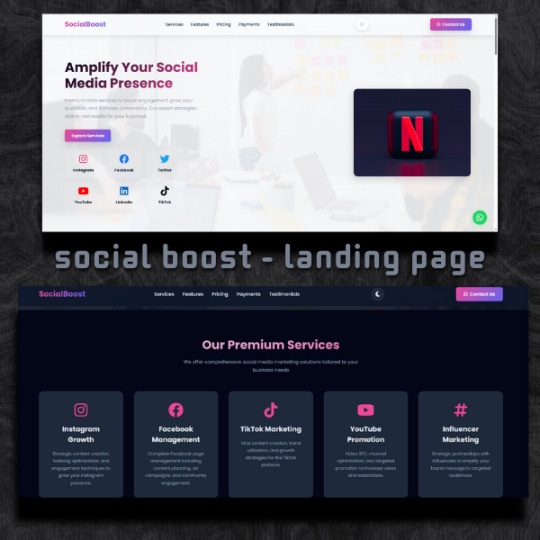
What’s Included?
Fully coded HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files
Placeholder images ready to be replaced
Easy-to-follow folder structure
Instructions for customization
Technical Requirements
A modern web browser
Any code editor (like VS Code or Sublime)
Basic knowledge of HTML/CSS (for customization)
Why Choose Social Boost?
Stand out in the crowded digital market with a bold, polished landing page that builds trust and drives conversions. Whether you're launching a service or boosting an existing brand, SocialBoost gives you the professional edge you need.
Start promoting your services like a pro — download Social Boost today!
Live Demo | Buy Now
#css#html#html css#htmlcoding#js#landing page#landing page builder#landing page design#landing pages#panel#javascript#javaprogramming#ui ux design
1 note
·
View note
Text
Master JavaScript: Step-by-Step Tutorial for Building Interactive Websites
JavaScript Tutorial

Master JavaScript: Step-by-Step Tutorial for Building Interactive Websites
In the evolving world of web development, JavaScript remains one of the most powerful and essential programming languages. Whether you're building simple webpages or full-fledged web applications, JavaScript gives life to your content by making it interactive and dynamic. This JavaScript Tutorial offers a beginner-friendly, step-by-step guide to help you understand core concepts and begin creating responsive and engaging websites.
What is JavaScript?
JavaScript is a lightweight, high-level scripting language primarily used to create dynamic and interactive content on the web. While HTML structures the webpage and CSS styles it, JavaScript adds interactivity—like handling clicks, updating content without refreshing, validating forms, or creating animations.
Initially developed for client-side scripting, JavaScript has evolved significantly. With the rise of environments like Node.js, it is now also used for server-side programming, making JavaScript a full-stack development language.
Why Learn JavaScript?
If you're looking to become a front-end developer or build web-based applications, JavaScript is a must-have skill. Here’s why:
It runs on all modern browsers without the need for plugins.
It’s easy to learn but incredibly powerful.
It works seamlessly with HTML and CSS.
It powers popular frameworks like React, Angular, and Vue.js.
It’s in high demand across the tech industry.
This JavaScript Tutorial is your gateway to understanding this versatile language and using it effectively in your web projects.
Getting Started: What You Need
To start coding in JavaScript, all you need is:
A modern browser (like Chrome or Firefox)
A text editor (such as Visual Studio Code or Sublime Text)
Basic knowledge of HTML and CSS
No complex setups—just open your browser and you're ready to go!
Step 1: Your First JavaScript Code
JavaScript code can be embedded directly into HTML using the <script> tag.
Example:<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>JavaScript Demo</title> </head> <body> <h1 id="demo">Hello, World!</h1> <button onclick="changeText()">Click Me</button> <script> function changeText() { document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML = "You clicked the button!"; } </script> </body> </html>
Explanation:
The onclick event triggers the changeText() function.
document.getElementById() accesses the element with the ID demo.
.innerHTML changes the content of that element.
This simple example showcases how JavaScript can make a static HTML page interactive.
Step 2: Variables and Data Types
JavaScript uses let, const, and var to declare variables.
Example:let name = "Alice"; const age = 25; var isStudent = true;
Common data types include:
Strings
Numbers
Booleans
Arrays
Objects
Null and Undefined
Step 3: Conditional Statements
JavaScript allows decision-making using if, else, and switch.let age = 20; if (age >= 18) { console.log("You are an adult."); } else { console.log("You are a minor."); }
Step 4: Loops
Use loops to execute code repeatedly.for (let i = 0; i < 5; i++) { console.log("Iteration:", i); }
Other types include while and do...while.
Step 5: Functions
Functions are reusable blocks of code.function greet(name) { return "Hello, " + name + "!"; } console.log(greet("Alice")); // Output: Hello, Alice!
Functions can also be anonymous or arrow functions:const greet = (name) => "Hello, " + name;
Step 6: Working with the DOM
The Document Object Model (DOM) allows you to access and manipulate HTML elements using JavaScript.
Example: Change element style:document.getElementById("demo").style.color = "red";
You can add, remove, or change elements dynamically, enhancing user interaction.
Step 7: Event Handling
JavaScript can respond to user actions like clicks, keyboard input, or mouse movements.
Example:document.getElementById("myBtn").addEventListener("click", function() { alert("Button clicked!"); });
Step 8: Arrays and Objects
Arrays store multiple values:let fruits = ["Apple", "Banana", "Mango"];
Objects store key-value pairs:let person = { name: "Alice", age: 25, isStudent: true };
Real-World Applications of JavaScript
Now that you have a basic grasp, let’s explore how JavaScript is used in real-life projects. The applications of JavaScript are vast:
Interactive Websites: Menus, image sliders, form validation, and dynamic content updates.
Single-Page Applications (SPAs): Tools like React and Vue enable dynamic user experiences without page reloads.
Web Servers and APIs: Node.js allows JavaScript to run on servers and build backend services.
Game Development: Simple 2D/3D browser games using HTML5 Canvas and libraries like Phaser.js.
Mobile and Desktop Apps: Frameworks like React Native and Electron use JavaScript for cross-platform app development.
Conclusion
Through this JavaScript Tutorial, you’ve taken the first steps in learning a foundational web development language. From understanding what is javascript is now better.
As you continue, consider exploring advanced topics such as asynchronous programming (promises, async/await), APIs (AJAX, Fetch), and popular frameworks like React or Vue.
0 notes
Text
Web Development Explained: From Code to Clicks
In the age of the internet, nearly every business, brand, and service relies on a strong online presence. At the heart of that digital presence is web development — the process of creating websites, applications, and digital experiences that users can access through the web.
From a simple personal blog to a complex e-commerce platform, web development is what powers the online world. This article breaks down what web development is, its key components, and why it's more important than ever.
What is Web Development?
Web development refers to the work involved in creating and maintaining websites and web applications. It encompasses everything from writing code to designing layouts, implementing security features, and optimizing for speed and performance.
There are three main categories of web development:
Frontend Development – The part users see and interact with (e.g., layout, buttons, menus).
Backend Development – The server-side logic that powers the website behind the scenes.
Full Stack Development – A combination of both frontend and backend development.
Core Components of Web Development
1. Website Structure
HTML (HyperText Markup Language) creates the structure of the web page.
CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) adds design and style to the structure.
JavaScript introduces interactivity like sliders, forms, and real-time content updates.
2. Server and Databases
Web servers deliver content to users.
Databases like MySQL or MongoDB store and manage content, user data, and application logic.
3. APIs and Integrations
APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) connect websites with other services like payment gateways, social media, and third-party tools.
Types of Websites Built with Web Development
Static Websites: Simple, fixed-content pages (e.g., portfolios, landing pages).
Dynamic Websites: Pages that change based on user interaction or backend logic (e.g., blogs, news sites).
Web Applications: Interactive platforms like online banking systems, e-commerce platforms, and project management tools.
Progressive Web Apps (PWAs): Hybrid apps that offer app-like experiences in a web browser.
Essential Tools and Technologies
Text Editors: Visual Studio Code, Sublime Text
Version Control: Git and GitHub for managing code changes
Frameworks: React, Angular, Django, Laravel
Hosting Services: Netlify, Vercel, AWS, and traditional web hosting providers
Content Management Systems (CMS): WordPress, Joomla, Drupal
The Web Development Process
Planning – Define goals, target audience, and site structure.
Designing – Create wireframes, mockups, and design elements.
Developing – Write code for both frontend and backend.
Testing – Check for bugs, compatibility, and responsiveness.
Deployment – Launch the site to a live server.
Maintenance – Regular updates, backups, and performance improvements.
Why Web Development Matters
Brand Identity: Your website is often the first impression you make on users.
Customer Access: A functional site allows customers to find, contact, and buy from you 24/7.
Business Growth: Scalable web platforms can support sales, marketing, support, and more.
Competitive Advantage: A fast, modern website gives you an edge over competitors still lagging in digital transformation.
Future of Web Development
Web development is evolving rapidly with trends such as:
No-code/Low-code platforms
AI-powered development assistants
Voice search optimization
Serverless architecture
3D and immersive web experiences (WebGL, WebXR)
Staying updated with these trends helps developers remain relevant and valuable in the tech industry.
Conclusion
Web development is the foundation of our online lives. It blends creativity with logic, design with programming, and user needs with technology. Whether you're a business owner, a budding developer, or someone exploring digital opportunities, understanding web development gives you the power to shape the internet — one line of code at a time.
Location : https://g.co/kgs/H5YVuuF
0 notes
Text
Socket.IO setup

Building Real-Time Applications with Socket.IO setup: Step-by-Step Tutorial
Socket.IO setup. In today's interconnected world, real-time applications are becoming increasingly essential. Whether it's for live chat applications, collaborative tools, or gaming, real-time communication enhances user engagement and makes interactions more dynamic. One powerful tool for building real-time applications is Socket.IO. In this tutorial, we will guide you through the process of building a real-time application using Socket.IO, focusing on key concepts and practical implementation. What is Socket.IO? Socket.IO is a JavaScript library that enables real-time, bidirectional communication between web clients (like browsers) and servers. Unlike traditional HTTP requests, which follow a request-response model, Socket.IO provides a persistent connection, enabling instant data exchange between the client and server. Socket.IO works on top of WebSockets, but it provides fallback mechanisms for environments where WebSockets may not be available. This ensures that real-time communication is possible in a wide range of conditions, making it a versatile choice for building interactive web applications. Prerequisites Before we dive into the tutorial, make sure you have the following: Basic knowledge of JavaScript and Node.js Node.js installed on your machine. You can download it from nodejs.org. A code editor (like Visual Studio Code or Sublime Text). Step 1: Setting Up the Project Start by setting up a basic Node.js project. Create a new directory for your project: bash mkdir real-time-app cd real-time-app Initialize a new Node.js project: bash npm init -y Install Express and Socket.IO: bash npm install express socket.io Express is a lightweight web framework for Node.js that simplifies the creation of web servers. Socket.IO will handle real-time communication between the server and the client. Step 2: Create the Server Now that we've set up the dependencies, let's create a simple server. Create a file called server.js in the project root: js const express = require('express'); const http = require('http'); const socketIo = require('socket.io');// Create an instance of Express app const app = express();// Create an HTTP server const server = http.createServer(app); // Initialize Socket.IO with the HTTP server const io = socketIo(server); // Serve static files (like HTML, CSS, JS) app.use(express.static('public')); // Handle socket connection io.on('connection', (socket) => { console.log('a user connected'); // Handle message from client socket.on('chat message', (msg) => { io.emit('chat message', msg); // Emit the message to all clients }); // Handle disconnect socket.on('disconnect', () => { console.log('user disconnected'); }); }); // Start the server server.listen(3000, () => { console.log('Server is running on http://localhost:3000'); }); Step 3: Create the Client-Side Next, we need to create the client-side code that will connect to the server and send/receive messages in real time. Create a public folder inside the project directory. In the public folder, create an index.html file: html Real-Time Chat Real-Time Chat Application Send const socket = io(); // Connect to the server// Listen for messages from the server socket.on('chat message', function(msg){ const li = document.createElement('li'); li.textContent = msg; document.getElementById('messages').appendChild(li); }); // Handle form submission const form = document.getElementById('form'); form.addEventListener('submit', function(event){ event.preventDefault(); const input = document.getElementById('input'); socket.emit('chat message', input.value); // Send the message to the server input.value = ''; // Clear the input field }); Step 4: Run the Application With the server and client code in place, it’s time to run the application! In your terminal, run the following command: bash node server.js Open your browser and go to http://localhost:3000. You should see the chat interface. Open multiple browser windows or tabs to simulate multiple users. Type a message in the input field and click "Send." You should see the message appear in real-time in all open windows/tabs. Step 5: Enhancements and Improvements Congratulations! You've built a basic real-time chat application using Socket.IO. To enhance the application, consider adding the following features: User authentication: Allow users to log in before they can send messages. Private messaging: Enable users to send messages to specific individuals. Message persistence: Use a database (e.g., MongoDB) to store chat history. Typing indicators: Show when a user is typing a message in real time. Emoji support: Allow users to send emojis and other media. Conclusion Socket.IO setup. In this tutorial, we covered the basics of building a real-time application using Socket.IO. We walked through setting up a Node.js server with Express, integrating Socket.IO for real-time communication, and creating a simple chat interface on the client side. Socket.IO makes it easy to add real-time features to your web applications, enabling more dynamic and interactive experiences for users. With this foundation, you can now start exploring more advanced real-time features and take your applications to the next level! Read the full article
#communication#CreatetheClient-Side#CreatetheServer#Enhancements#function#History#Improvements#RuntheApplication#Setting
0 notes
Text
Full Stack Developer Roadmap: Skills, Tools, and Trends
In the fast-evolving world of web development, the role of a full stack web developer is one of the most dynamic and sought-after positions in the industry. A full stack web developer is someone who is proficient in both the front-end and back-end aspects of web development. These developers are capable of building and maintaining an entire web application, from the user interface (UI) to the server-side logic, database management, and everything in between. Whether you're just starting or looking to enhance your skills, understanding the full stack developer roadmap can guide you to becoming a versatile and in-demand professional.
Key Skills Every Full Stack Web Developer Should Master
Becoming a successful full stack web developer requires a diverse set of skills that span multiple layers of technology. Below are the essential skills you’ll need to excel in both front-end and back-end development:
Front-End Development Skills
HTML/CSS: The fundamental building blocks of any website. HTML defines the structure, while CSS is responsible for the layout and design.
JavaScript: The heart of interactive web pages, allowing developers to create dynamic and responsive user interfaces.
Frameworks and Libraries: Libraries like React, Vue.js, and Angular help streamline front-end development and enhance user experiences.
Responsive Design: Understanding how to make websites mobile-friendly using frameworks such as Bootstrap and media queries.
Back-End Development Skills
Server-Side Languages: Languages such as Node.js, Python, Ruby, Java, and PHP are essential for writing the logic that runs on the server.
Databases: Knowledge of relational databases like MySQL, PostgreSQL, and SQL Server, as well as NoSQL databases like MongoDB is crucial for storing and managing data.
API Development: Understanding RESTful APIs and GraphQL is key for communication between the front-end and back-end of an application.
Authentication and Authorization: Implementing security measures like OAuth, JWT, and basic user authentication.
Tools for Full Stack Development
A full stack web developer needs to be proficient in various tools that facilitate the development, testing, and deployment of web applications. These tools not only make the process more efficient but also ensure better collaboration and productivity.
Version Control (Git): Git is essential for tracking changes, collaborating with other developers, and managing code repositories. Platforms like GitHub or GitLab are widely used for hosting projects and collaborating with other developers.
Development Environment: Text editors like Visual Studio Code or Sublime Text are commonly used for writing code efficiently, while tools like Docker and Vagrant help with creating consistent development environments.
Task Runners and Module Bundlers: Tools such as Webpack, Gulp, and Grunt automate common tasks like minification, bundling, and testing, which boosts development productivity.
Testing Frameworks: Frameworks like Jest, Mocha, and Chai ensure that the application works as expected and help developers catch bugs early.
Deployment and DevOps Tools
Deployment is a critical part of the development process. A full stack web developer should also understand the tools that make the deployment process smooth:
Cloud Platforms: Services like AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure provide scalable cloud solutions for hosting web applications.
CI/CD: Continuous integration and continuous deployment tools like Jenkins, Travis CI, and CircleCI automate testing and deployment to make code delivery faster and more reliable.
Containerization: Tools like Docker and Kubernetes simplify application deployment, making it easier to scale and manage applications across multiple environments.
Current Trends in Full Stack Web Development
The tech industry is constantly evolving, and staying up-to-date with the latest trends is essential for any full stack web developer. Here are a few trends that are gaining traction:
Serverless Architecture: Serverless computing platforms like AWS Lambda and Google Cloud Functions are becoming popular because they allow developers to focus on writing code without managing the underlying infrastructure.
Progressive Web Apps (PWAs): PWAs offer an enhanced user experience by combining the best of both web and mobile applications. A full stack web developer needs to understand how to build and deploy PWAs.
Microservices: Instead of creating monolithic applications, developers are now building microservices-based architectures that are easier to scale, update, and maintain.
Jamstack: This architecture is gaining popularity due to its performance benefits. By serving pre-built static pages and using APIs for dynamic content, Jamstack allows for faster and more secure websites.
Conclusion
In conclusion, becoming a full stack web developer requires a comprehensive understanding of both front-end and back-end development. By learning the essential skills, mastering the right tools, and staying updated with the latest trends, you can successfully navigate the full stack developer roadmap and position yourself as a versatile and in-demand professional. As the industry continues to evolve, the role of the full stack web developer will remain at the forefront of technological innovation, offering exciting opportunities for growth and development.
This roadmap provides a clear pathway for aspiring full stack web developers to build the skills and knowledge necessary to excel in the field, allowing them to work simultaneously with front-end and back-end technologies while keeping up with emerging trends.
0 notes
Text
Tools Every Freelance Web Developer Should Know
Introduction
Being a freelance web developer isn’t just about writing code—it's about managing projects, clients, and your own time efficiently. To succeed in today’s competitive market, developers must equip themselves with the right tools. From code editors to project management platforms, each tool helps streamline different aspects of freelance work. Having a well-stocked digital toolbox can boost productivity, improve client satisfaction, and lead to higher earnings. The tools listed below are essential for developers looking to stay ahead in the freelance world. Whether you're a beginner or a seasoned pro, there's something here for everyone. Let’s dive into the essential tools that make a difference in a freelancer’s workflow.
1. Code Editors: The Developer’s Core Companion
A high-performance code editor is the most vital tool for any freelance web developer. Editors like Visual Studio Code, Sublime Text, or Atom offer robust functionality with extensive plugin support. VS Code stands out with its IntelliSense, Git integration, and built-in terminal. These editors improve speed and efficiency when writing HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and backend code. Customizable themes and extensions help create a personalized workflow. Freelancers benefit from tools that reduce bugs and save time. A quality editor can even support multiple languages. Choose one that aligns with your development stack and preferences.
2. Version Control: Git & GitHub
Understanding and using Git is non-negotiable for serious freelancers. Git tracks changes, manages code branches, and helps you revert back when things go wrong. GitHub acts as the online hub for your projects, offering version control in the cloud. It enables collaboration with other developers and easy sharing with clients. Freelancers can show progress and push updates seamlessly. It also serves as a portfolio to display work. Learning Git commands boosts professional credibility. GitHub Actions adds automation for testing and deployment workflows.
3. Design & Prototyping Tools
Before development starts, clients often want to see a prototype. Tools like Figma, Adobe XD, and Sketch are perfect for wireframing and UI design. Figma is a favorite due to its real-time collaboration features. These platforms allow developers to turn ideas into visual representations. You can gather feedback early, saving time in revisions later. Freelance web developers benefit from clearly defined interfaces. These tools also bridge the gap between designer and developer roles. Use them to align your vision with the client's expectations.
4. Task & Project Management Tools
Managing deadlines and deliverables is crucial in freelancing. Tools like Trello, Asana, or ClickUp help developers stay on track. Freelance web developer often juggle multiple clients and need clear organization. These tools allow you to break down tasks, assign due dates, and prioritize workloads. Notifications and dashboards make it easy to track progress. Time-blocking features ensure work is spaced out efficiently. They also help manage feedback and revisions. With visual boards, project workflows become less chaotic and more predictable.
5. Communication Platforms
Effective communication builds lasting client relationships. Slack, Zoom, and Google Meet are essential tools for keeping in touch. Freelance developers need to clearly discuss requirements, timelines, and updates. Slack allows instant messaging, file sharing, and integrates with other tools. Zoom and Google Meet make video calls seamless, especially for client walkthroughs. Using professional channels instead of casual messaging builds credibility. Communication tools also help with team collaboration in multi-developer projects. Strong communication leads to better project outcomes and higher client satisfaction.
6. Browser DevTools
All modern browsers come equipped with powerful development tools. Chrome DevTools is one of the most popular among freelance web developers. It allows inspection of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript in real time. You can debug issues, test responsiveness, and monitor performance. DevTools also include features like network activity logging and lighthouse audits. These help optimize websites for speed and SEO. For freelancers, faster diagnostics mean faster delivery. Mastering browser tools can help catch bugs before clients do. They are indispensable for frontend developers.
7. Website Performance & SEO Auditing Tools
Speed and visibility matter in web development. Tools like Google PageSpeed Insights, GTmetrix, and Lighthouse assess performance. These platforms identify what’s slowing a site down and how to fix it. Freelance web developers can use them to deliver SEO-friendly, fast-loading sites. Lighthouse also gives accessibility and PWA (Progressive Web App) reports. These insights help meet modern web standards and improve rankings. Providing audit reports boosts your value as a developer. Use them regularly to maintain top-notch quality in your work.
8. Hosting & Deployment Services
Getting the site live is the final step—and you need the right tools. Netlify, Vercel, and GitHub Pages make deployment a breeze. These platforms allow one-click deployments from Git repositories. They’re perfect for static and JAMstack websites, popular in modern development. Freelance developers save time and impress clients with instant previews. Netlify offers forms, serverless functions, and global CDN. Vercel integrates tightly with Next.js and supports custom domains. Choose based on project size, performance needs, and tech stack. Smooth deployment ensures client satisfaction.
9. Payment & Invoicing Tools
Getting paid smoothly is just as important as coding well. Tools like PayPal, Stripe, and Bonsai simplify invoicing for freelancers. These platforms allow you to send professional invoices and receive global payments. Freelance web developers can track payments, set due dates, and manage contracts. Bonsai also offers contract templates and time tracking features. Payment tools reduce friction in business transactions. They give you legal backing and a reputation for professionalism. Never let poor billing processes hinder your freelance success.
Conclusion
Being a successful freelance web developer requires more than just technical skills—it takes organization, communication, and business savvy. The right tools streamline your workflow, reduce errors, and help deliver better results for your clients. From coding and collaboration to design and invoicing, each category serves a vital role. Investing time in learning these tools can make you faster, more efficient, and more professional. As technology evolves, staying updated with the latest tools will set you apart from the competition. Build your freelance toolkit wisely, and you’ll be better equipped to thrive in the digital world.
FAQs
What is the best code editor for freelance web developers? Visual Studio Code is widely recommended due to its features, speed, and customization options.
Do I need Git as a solo freelance web developer? Yes, Git is essential even for solo projects—it helps manage versions and track your progress efficiently.
Which tool is best for website performance audits? Google PageSpeed Insights and Lighthouse are reliable for testing speed and providing improvement tips.
How do freelance developers communicate with clients? Most use platforms like Slack, Zoom, or Google Meet to hold meetings and send updates professionally.
Are invoicing tools really necessary for freelancers? Yes, they ensure you get paid properly and on time, and present a more professional front to clients.
#Freelance web designer#Freelance web developer#Outsource web design#wordpress virtual assistant#Web design virtual assistant
0 notes
Text
How to Learn JavaScript Fast in 2025

Introduction
How to Learn JavaScript Fast in 2025 is a question many aspiring web developers and tech enthusiasts are asking. Starting in 2025, JavaScript is ranked as one of the most sought-after programming languages. Whether you're an aspiring web developer or a technophile wanting to improve your tech skills, learning JavaScript opens the door to many opportunities.
But the big question: can anyone learn JavaScript in a short time? Yes, but that is only possible with the right approach.
Several tips and techniques will be discussed in this guide to learn JavaScript fast and effectively.
Understanding the Basics
What Is JavaScript?
JavaScript is a high-level and versatile programming language primarily used to create interactive web applications. It controls dynamic content, animations, form validations, and even back-end full-stack applications.
Why Is JavaScript Essential in Modern Web Development?
JavaScript plays a very pivotal role between small personal blogs and large-scale web applications. It almost feels like every website you come across utilizes JavaScript to some extent in enhancing user experience.
JavaScript versus Other Programming Languages
JavaScript, in comparison to Python or Java, has primarily been designed for front-end and full-stack web development. Convenient as it is for integration into HTML and CSS, JavaScript is widely embraced by developers all around.
Preparing to Conceive Your Learning
Choosing The Best Coding Environment
Great coding editors make code writing easier. Here are some of the popular choices:
VS Code (Most Highly Recommended)
Sublime Text
Atom
Installing Node.js and a Browser Console
On the one hand, installation of Node.js gives you an environment to run JavaScript outside the browser; on the other hand, browser-based developer tools (Chrome DevTools, Firefox DevTools) help with fast and efficient debugging of the JavaScript codes.
Online Platforms and Resources for Learning JavaScript
The foremost among many platforms to learn JavaScript are:
MDN Web Docs (Official documentation)
freeCodeCamp (Coding with hands-on exercises)
JavaScript.info (Written in a tutorial form with complete instructions)
Learning Core JavaScript Concepts
JavaScript Syntax and Fundamentals
You will need to learn all concerning the basic syntax in JavaScript. Start with:
Variables (var, let, const)
Data types (strings, numbers, booleans)
Operators (+, -, *, /, %)
Conditional statements (if, else, switch)
Functions & Scope
Functions are reusable blocks of code. For making finely tuned JavaScript programs, understanding function scope and closures are key.
JavaScript Objects and Arrays
JavaScript is an object-oriented language designed to store and manipulate data efficiently. Learn-how to:
Create and modify objects
Use important methods of arrays such as map(), filter(), and reduce()
Further Adventures with JavaScript
dom manipulation
The Document Object Model (DOM) allows JavaScript to perform dynamic manipulations on HTML elements. Learn how to:
Select elements (document.querySelector())
Modify content (innerHTML, textContent)
Events and Event Listeners
Event listeners are responsible for detecting user interactions, from mouse clicks to keyboard input.
For example
Asynchronous JavaScript
Understanding callbacks, promises, and async/await is imperative in making API requests and non-blocking code execution.
Advanced And Interesting Topics In JavaScript
Some of the modern JavaScript topics near and dear to programmers illustrious in the web development realm encompass:
ES6 and Beyond (Arrow Functions, Template Literals, and Destructuring)
Frameworks and Libraries (React, Vue, Angular)
Working With APIs and JSON (Fetching data from external)
Best Way to Practice JavaScript
Develop projects such as a to-do, weather app, calculator
Practice JavaScript coding challenges on LeetCode, CodeWars, HackerRank
Contribute to open-source projects on GitHub
In What Ways TCCI Can Help You to Learn JavaScript Quickly
TCCI Computer Coaching Institute, offers:
JavaScript training from industry experts
Real-world project-oriented learning
Flexible schedule with online and offline classes
Mistakes to Avoid While Trying to Learn JavaScript
Not learning the fundamentals
Not writing enough code
Getting stuck in tutorial hell
How to Learn JavaScript Fast
Have a clear roadmap that you will follow
Learn by building, not just reading
Get engaged in coding communities and mentorship programs
Conclusion
JavaScript was fast learning in 2025; this is possible with a solid approach. Basics, constant practicing, building real projects- be it your career or personal interest, JavaScript is an important skill to have.
Location: Ahmedabad, Gujarat
Call now on +91 9825618292
Get information from https://tccicomputercoaching.wordpress.com/
#Best Computer Training Institute Bopal Ahmedabad#Computer classes near me#JavaScript training Ahmedabad#Learn JavaScript fast 2025#TCCI - Tririd Computer Coaching Institute
0 notes
Text
Web Designing: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
Web design is the art of creating websites that are both attractive and user-friendly.
It requires creativity, technical skills, and a grasp of UX.
What is Web Designing?
Web designing encompasses diverse elements of website advent, consisting of:
Visual Design: Crafting a website's cultured charm. This includes color schemes, typography, and imagery.
Layout and Structure: Organizing website content logically and intuitively.
UI Design: It is the design of a website's interactive elements, like buttons and menus.
User Experience (UX) Design: It focuses on the consumer's overall experience. It ensures ease of use, navigation, and accessibility.
Front-End Development: Use HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to create the website design.
Why Learn Web Designing?
High Demand: The virtual world is always changing. So, there is a high demand for web designers.
Career Opportunities: Web design offers many careers. They include internet developer, UI/UX designer, and front-end developer, among others.
Freelancing Potential: Web designers can easily freelance and work on many projects.
Entrepreneurship: Marketers need a strong web presence for their organizations. So, web layout skills are valuable.
Personal Growth: Learning internet layout enhances creativity, hassle-solving skills, and technical talents.
Key Skills Required for Web Designing
Creativity is the ability to think outside the box. It is to create designs that are visually appealing.
Technical Skills: Skill in HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and different relevant programming languages.
UX/UI Principles: A deep knowledge of human behavior and creating user-friendly interfaces.
Communication Skills: Effective communication with clients and crew contributors is critical.
Problem-Solving Skills: The capability to identify and clear up design and technical challenges.
Choosing the Right Web Designing Course
When choosing a web designing path, don't forget the subsequent factors:
Course Curriculum: The path must cover all key web design theories, and their use in practice.
Instructor Expertise: Choose a path taught by using experienced and qualified teachers.
Learning Format: Choose a format that suits your learning style. Options include online courses, classroom training, or bootcamps.
Career Guidance: Look for guides that offer career guidance and task placement assistance.
Cost and Value: Evaluate the price of the path on the subject of the fee it offers and the ability go back on investment.
Popular Web Designing Tools
Adobe Photoshop: For image enhancing and manipulation.
Adobe Illustrator: For developing vector pictures and illustrations.
Figma: For designing person interfaces and prototyping.
Sketch: A famous design device for growing virtual interfaces.
Sublime Text: A powerful code editor for writing HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
Visual Studio Code: A flexible and customizable code editor.
Building a Strong Web Design Portfolio
A strong portfolio is key. It shows your skills and helps you get jobs. Include a variety of tasks. They should show your creativity, technical skills, and problem-solving abilities.
Tips for Building a Successful Web Design Career
Stay Updated: The web design field is always changing. So, you must study continuously.
Network: Build relationships with other designers, developers, and enterprise experts.
Practice consistently: Exercise is key to improving your skills and workflow.
Seek Feedback: Ask friends and mentors to review your work. They can help find areas for improvement.
Build a strong online presence: Create an expert portfolio and be active on social media.
Conclusion
Web designing is a worthwhile and in-call for profession path. By gaining key skills and a strong portfolio, you can succeed in the exciting field of web design.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only. It is not a professional recommendation.
I wish this newsletter meets your necessities!
Sources and related content material
0 notes
Text
online html editors
8+ Best Online HTML Editors
Visual Studio Code: #1 Best Online HTML Editor.
Adobe Dreamweaver.
Sublime Text.
komodo Edit.
Codepen.
Brackets.
Liveweave.
StackBlitz.
html-online ← Simple and easy to understand .
...
« Discrimination in the workplace (and in groups such as associations and clubs)» . kopibreak.sg , https://www.instagram.com/p/DFSIs6MyQUx/
...
* reblog of fb (.)

1 note
·
View note
Text
How to start as a web developer?
Web development is one of the most in-demand and rewarding careers in today’s digital world. With websites being essential for businesses, organizations, and personal projects, the demand for skilled web developers continues to grow. If you’re wondering how to start as a web developer, here’s a comprehensive guide to help you kickstart your journey.
Understand the Basics of Web Development Before diving in, it's important to understand what web development entails. It can be broadly divided into:
Frontend Development: Building the visual elements users interact with on a website (e.g., layout, buttons, and menus). Backend Development: Handling server-side processes like databases, APIs, and logic. Full-Stack Development: A combination of both frontend and backend skills. Researching the field will help you decide which path to start with.
Learn the Fundamental Languages Web development relies on coding. Start by mastering the foundational languages:
HTML (HyperText Markup Language): Used to structure content on the web. CSS (Cascading Style Sheets): Controls the styling and layout of the website. JavaScript: Adds interactivity and dynamic behavior to websites. Practice building simple projects using these languages, such as a personal portfolio or a basic website.
Explore Development Tools Familiarize yourself with essential tools that make coding more efficient:
Text Editors: Start with editors like Visual Studio Code or Sublime Text. Version Control: Learn how to use Git and GitHub for tracking changes and collaborating. Browser Developer Tools: Use tools built into browsers like Chrome or Firefox for debugging. These tools are critical for writing, managing, and troubleshooting code effectively.
Choose a Learning Path There are multiple ways to learn web development:
Online Courses: Platforms like freeCodeCamp, Codecademy, and Udemy offer beginner-friendly courses. Books and Tutorials: Read books like “Eloquent JavaScript” or follow YouTube tutorials. Bootcamps: Join intensive coding bootcamps for hands-on training and mentorship. Set aside dedicated time for learning and follow a structured curriculum.
Build Projects and Portfolio Apply your knowledge by creating real-world projects. Start with simple ones, such as:
A personal blog site. A to-do list app. A responsive landing page. As you gain confidence, work on more advanced projects. Showcase these in an online portfolio to demonstrate your skills to potential employers or clients.
Learn Frameworks and Libraries Once you’re comfortable with the basics, explore popular frameworks and libraries that simplify development:
Frontend Frameworks: React, Angular, or Vue.js. CSS Libraries: Bootstrap or Tailwind CSS. Backend Technologies: Node.js, Django, or Ruby on Rails. These tools help speed up development and are widely used in the industry.
Master the Backend For a full-stack approach, learn backend development. Start with:
Languages: Python, PHP, Ruby, or JavaScript (Node.js). Databases: MySQL, PostgreSQL, or MongoDB. APIs: Learn how to create and consume APIs for data exchange. Understanding backend development allows you to build complete web applications.
Stay Updated and Keep Practicing The web development landscape evolves rapidly. Stay updated by:
Following web development blogs and communities like Smashing Magazine or Dev.to. Participating in forums like Stack Overflow and Reddit. Continuously practicing by contributing to open-source projects or freelance work. Network and Find Opportunities Engage with other developers by joining communities like GitHub, LinkedIn, or local meetups. Networking can open doors to mentorships, internships, and job opportunities.
Apply for Jobs or Start Freelancing Once you have the necessary skills and portfolio, start applying for jobs. You can also consider freelancing platforms like Upwork, Fiverr, or Toptal to build experience and earn as you learn.
Becoming a web developer requires dedication, practice, and continuous learning. Start with small steps, master the basics, and gradually expand your skills. With persistence and effort, you’ll find yourself building complex and impressive websites in no time. So, roll up your sleeves, open your text editor, and begin your journey to becoming a web developer!
0 notes