#Training Data for Satellite Imagery
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Why Can't Satellites Find Bigfoot?
For decades, Bigfoot, a cryptid creature from North American wilderness, has captured imaginations. Despite numerous sightings, hazy photos, and suspicious footprints, Bigfoot's existence is still unproven. Technology has led many doubters and believers to satellites, questioning why this advanced equipment, which can capture comprehensive photographs of Earth, have failed to give compelling evidence. Satellite resolution limitations, the size and complexity of wilderness areas, Bigfoot's elusiveness, and the difficulty of analyzing satellite imagery prevent satellites from proving his existence. Satellite imagery resolution is a major drawback. Satellites can take very precise photographs of Earth, but not enough to spot a Bigfoot in a dense forest. Commercial satellites typically have pixel resolutions of 30 centimeters, representing a 30-centimeter square on the ground. This is great for spotting massive structures, cars, and landscape changes, but it cannot distinguish a large, hairy monster blending into the environment. Even military-grade satellites with higher resolutions struggle to detect small, moving objects in dense forest canopies. Bigfoot, if it exists, is unlikely to stay in open regions where it may be seen, complicating the issue.

Satellite monitoring faces another obstacle in Bigfoot's supposed enormous habitat. Bigfoot is most often seen in distant, forested areas like the Pacific Northwest or Canada's deep forests. These millions of square miles have harsh terrain, heavy vegetation, and few people. It is nearly impossible to find a single organism in such a vast desert. Satellite imaging generates so much data that manually inspecting every frame for Bigfoot is nearly impossible. Automated satellite image recognition systems are trained to distinguish human-made structures and vehicles, not cryptids; hence, they are unlikely to detect Bigfoot. Bigfoot's elusiveness complicates everything. Bigfoot is likely intelligent, cautious, and good at evasion. Since such a species must avoid predators and humans to thrive, this makes evolutionary logic. Many Bigfoot fans believe the monster is nocturnal, spending most of its time in the dark when satellite photography, which relies on visible light, is less efficient. Bigfoot would be hard to discern from bears or deer using infrared technology. Satellites would struggle to record Bigfoot's silent, fast movement through deep woodlands. Satellite images interpretation is another challenge. Proving that a satellite photograph of a big, bipedal figure in the forest is Bigfoot rather than a bear, person, or foliage shadow would be difficult. Such ambiguous material would likely spark arguments rather than confirmation. Skeptics have sometimes attributed Bigfoot sightings to misidentifications, hoaxes, or pareidolia, the tendency to see familiar things like faces and figures in random patterns. Satellite imagery, with its quality and context issues, would undoubtedly be scrutinized. Satellite-based evidence is also limited by Bigfoot skepticism in culture and science. Most scientific institutes prioritize credible or pressing goals including environmental monitoring, climate research, and urban planning. Using powerful satellite technology to find a mythical monster is unlikely to attract support or money. Satellites may theoretically help find Bigfoot, although they are not deliberately deployed for this purpose. Satellites cannot confirm Bigfoot's existence because of technological, environmental, and interpretation issues. Satellites are useful for viewing Earth, but not for discovering a massive, elusive beast in deep wilderness. Satellite imaging resolution, Bigfoot's putative habitat's vastness and remoteness, the creature's evasiveness, and the difficulty of interpreting ambiguous data all contribute to the lack of definitive evidence. Bigfoot remains a folklore and story, evading even the most advanced technologies. The topic of whether Bigfoot exists or is too good at evading discovery continues to spark arguments and curiosity.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
📊 Unlocking Trading Potential: The Power of Alternative Data 📊
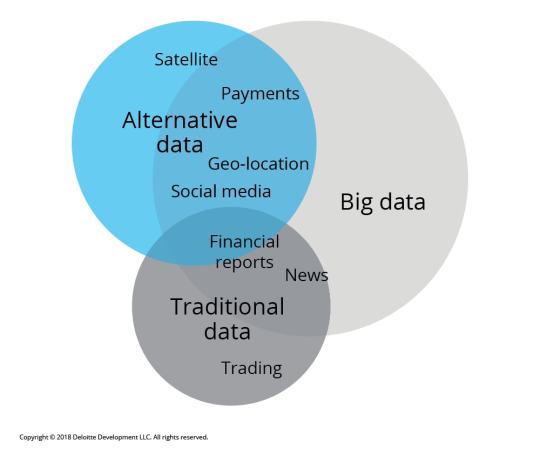
In the fast-paced world of trading, traditional data sources—like financial statements and market reports—are no longer enough. Enter alternative data: a game-changing resource that can provide unique insights and an edge in the market. 🌐
What is Alternative Data? Alternative data refers to non-traditional data sources that can inform trading decisions. These include:
Social Media Sentiment: Analyzing trends and sentiments on platforms like Twitter and Reddit can offer insights into public perception of stocks or market movements. 📈
Satellite Imagery: Observing traffic patterns in retail store parking lots can indicate sales performance before official reports are released. 🛰️
Web Scraping: Gathering data from e-commerce websites to track product availability and pricing trends can highlight shifts in consumer behavior. 🛒
Sensor Data: Utilizing IoT devices to track activity in real-time can give traders insights into manufacturing output and supply chain efficiency. 📡
How GPT Enhances Data Analysis With tools like GPT, traders can sift through vast amounts of alternative data efficiently. Here’s how:
Natural Language Processing (NLP): GPT can analyze news articles, earnings calls, and social media posts to extract key insights and sentiment analysis. This allows traders to react swiftly to market changes.
Predictive Analytics: By training GPT on historical data and alternative data sources, traders can build models to forecast price movements and market trends. 📊
Automated Reporting: GPT can generate concise reports summarizing alternative data findings, saving traders time and enabling faster decision-making.
Why It Matters Incorporating alternative data into trading strategies can lead to more informed decisions, improved risk management, and ultimately, better returns. As the market evolves, staying ahead of the curve with innovative data strategies is essential. 🚀
Join the Conversation! What alternative data sources have you found most valuable in your trading strategy? Share your thoughts in the comments! 💬
#Trading #AlternativeData #GPT #Investing #Finance #DataAnalytics #MarketInsights
2 notes
·
View notes
Text

(CNN) — Egypt’s Great Pyramid and other ancient monuments at Giza exist on an isolated strip of land at the edge of the Sahara Desert.
The inhospitable location has long puzzled archaeologists, some of whom had found evidence that the Nile River once flowed near these pyramids in some capacity, facilitating the landmarks’ construction starting 4,700 years ago.
Using satellite imaging and analysis of cores of sediment, a new study published Thursday in the journal Communications Earth & Environment has mapped a 64-kilometer (40-mile) long, dried-up branch of the Nile, long buried beneath farmland and desert.
“Even though many efforts to reconstruct the early Nile waterways have been conducted, they have largely been confined to soil sample collections from small sites, which has led to the mapping of only fragmented sections of the ancient Nile channel systems,” said lead study author Eman Ghoneim, a professor and director of the Space and Drone Remote Sensing Lab at the University of North Carolina Wilmington’s Department of Earth and Ocean Sciences.
“This is the first study to provide the first map of the long-lost ancient branch of the Nile River.”

Ghoneim and her colleagues refer to this extinct branch of the Nile river as Ahramat, which is Arabic for pyramids.
The ancient waterway would have been about 0.5 kilometers wide (about one-third of a mile) with a depth of at least 25 meters (82 feet) — similar to the contemporary Nile, Ghoneim said.
“The large size and extended length of the Ahramat Branch and its proximity to the 31 pyramids in the study area strongly suggests a functional waterway of great importance,” Ghoneim said.
She said the river would have played a key role in ancient Egyptians’ transportation of the enormous amount of building materials and laborers needed for the pyramids’ construction.
“Also, our research shows that many of the pyramids in the study area have (a) causeway, a ceremonial raised walkway, that runs perpendicular to the course of the Ahramat Branch and terminates directly on its riverbank.”
Hidden traces of a lost waterway

Traces of the river aren’t visible in aerial photos or in imagery from optical satellites, Ghoneim said.
In fact, she only spotted something unexpected while studying radar satellite data of the wider area for ancient rivers and lakes that might reveal a new source of groundwater.
“I am a geomorphologist, a paleohydrologist looking into landforms. I have this kind of trained eye,” she said.
“While working with this data, I noticed this really obvious branch or a kind of riverbank, and it didn’t make any sense because it is really far from the Nile,” she added.
Born and raised in Egypt, Ghoneim was familiar with the cluster of pyramids in this area and had always wondered why they were built there.
She applied to the National Science Foundation to investigate further.
Geophysical data taken at ground level with the use of ground-penetrating radar and electromagnetic tomography confirmed it was an ancient arm of the Nile.
Two long cores of earth the team extracted using drilling equipment revealed sandy sediment consistent with a river channel at a depth of about 25 meters (82 feet).
It’s possible that “countless” temples might still be buried beneath the agricultural fields and desert sands along the riverbank of the Ahramat Branch, according to the study.

Why this branch of the river dried up or disappeared is still unclear. Most likely, a period of drought and desertification swept sand into the region, silting up the river, Ghoneim said.
"The study demonstrated that when the pyramids were built, the geography and riverscapes of the Nile differed significantly from those of today," said Nick Marriner, a geographer at the French National Centre for Scientific Research in Paris.
He was not involved in the study but has conducted research on the fluvial history of Giza.
“The study completes an important part of the past landscape puzzle,” Marriner said.
“By putting together these pieces, we can gain a clearer picture of what the Nile floodplain looked like at the time of the pyramid builders and how the ancient Egyptians harnessed their environments to transport building materials for their monumental construction endeavors.”

#Egypt#Great Pyramid#Giza#Nile River#archaeology#Ancient Egypt#Communications Earth & Environment#Space and Drone Remote Sensing Lab#map#pyramids#Ahramat#ground-penetrating radar#electromagnetic tomography#Unas#Valley Temple#Great Sphinx of Giza#pyramid mystery#waterways
6 notes
·
View notes
Text

How Data Science is Helping Fight Climate Change
Climate change is no longer a distant threat—it’s a reality affecting ecosystems, economies, and everyday lives. From rising sea levels to extreme weather events, the impact is global. But there’s a powerful tool helping scientists, policymakers, and activists respond more effectively: Data Science.
With the explosion of big data, sensors, satellites, and machine learning algorithms, data science is becoming a central force in the fight against climate change. Let’s explore how.
1. Predicting Climate Patterns with Machine Learning
One of the most powerful applications of data science is in climate modeling and forecasting. Traditional models were limited in processing power and granularity. Now, with advanced machine learning techniques and high-performance computing, scientists can:
Simulate climate changes decades into the future
Predict weather patterns more accurately
Model extreme events like hurricanes, floods, or droughts
For example, DeepMind’s AI model, trained on vast datasets of radar data, can now predict rainfall with higher precision than traditional methods. These forecasts help communities prepare for disasters and reduce damage.
2. Satellite Imagery and Earth Observation
Satellites continuously gather images and climate data from space. These images are rich with information—about deforestation, glacier melting, ocean temperatures, and more.
Data scientists use image recognition and geospatial analytics to:
Monitor forest cover loss in the Amazon
Track ice sheet melting in Antarctica
Identify urban heat islands in growing cities
Measure carbon emissions from industrial zones
Organizations like NASA, ESA, and Google Earth Engine are publishing petabytes of open climate data for researchers to build models, apps, and solutions.
3. Carbon Footprint Analysis
Governments and companies are under increasing pressure to reduce their carbon footprints. But first, they need to measure them accurately.
Data science enables:
Carbon accounting across supply chains
IoT integration in factories for real-time emission tracking
Predictive models to simulate the impact of green policies
For instance, companies like Microsoft and Apple are using advanced analytics to reduce their net carbon emissions and optimize energy use across data centers.
4. Climate-Smart Agriculture
Agriculture is both a victim and a contributor to climate change. Data science is helping farmers adapt through climate-smart agriculture practices:
Yield prediction using historical and weather data
Soil health monitoring through sensors and analytics
Pest and disease detection using AI-driven image classification
Precision irrigation to reduce water usage
Platforms like IBM’s Watson Decision Platform for Agriculture use AI to give farmers insights that boost productivity while reducing environmental impact.
5. Greener Cities with Smart Data
Urban areas contribute heavily to CO₂ emissions. With smart data collected from sensors, traffic cams, GPS, and public utilities, data scientists help cities become more sustainable:
Optimizing public transport to reduce fuel consumption
Monitoring air quality in real-time
Planning green spaces using heat maps
Managing waste and recycling more efficiently
Cities like Singapore, Amsterdam, and San Francisco are already leading the way in becoming “smart cities,” using data science to reduce emissions and improve quality of life.
6. Renewable Energy Optimization
The shift to solar, wind, and hydro power brings new challenges: fluctuating outputs, grid integration, and energy storage. Here’s where data science steps in:
Forecasting sunlight and wind speeds to predict energy generation
Optimizing battery storage and distribution
Balancing supply and demand across the smart grid
AI models from companies like Google DeepMind have already improved the output prediction of wind farms by up to 20%.
7. Climate Research and Citizen Science
Open-source projects and platforms allow anyone to contribute to climate research. Data scientists use crowd-sourced data to:
Map plastic waste in oceans
Collect wildlife migration data
Record local temperature anomalies
Tools like Zooniverse, Kaggle, and Climate Central invite data scientists and enthusiasts to work on real-world climate datasets and challenges.
8. Policy and Decision-Making Support
Data science doesn't just help collect and analyze data—it also helps governments make better decisions.
Predictive models simulate the outcome of climate policies
Visualization tools make complex data easier for decision-makers to understand
Data-driven reports guide investments in green technologies
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), for example, uses advanced data analytics to build global climate reports that influence international treaties and agreements.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
While data science offers powerful tools, it also comes with challenges:
Data privacy in sensor-based tracking
Biases in datasets or algorithms
Digital divide, where developing countries may lack infrastructure for data collection
Data scientists must follow ethical guidelines and ensure inclusive, transparent, and responsible use of technology in climate work.
Conclusion: The Role of Data Scientists in a Greener Future
Climate change is a complex, urgent problem—but data science gives us the power to understand, predict, and act.
As a data scientist, you're not just crunching numbers. You're helping to:
Save forests
Reduce emissions
Optimize energy use
Protect communities
Shape global policies
It’s a field where technology meets responsibility. And in the climate battle, every line of clean, purposeful code matters.
#datascience#climatechange#machinelearning#ai#bigdata#sustainability#environmentaldata#greenai#smartcities#carbonfootprint#renewableenergy#earthobservation#climatemodeling#iot#geospatialanalytics#climateaction#cleantech#techforgood#datascienceforclimate#nschool academy
0 notes
Text
AI’s Global Impact: Building a More Inclusive Economic Future
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has evolved from a breakthrough technology to a defining force of modern civilization. As it transitions from algorithmic models into fully integrated systems of productivity, its next frontier is no longer just technical—it’s economic, structural, and deeply human.

In 2025, we stand on the cusp of a global economic revolution, where AI isn't merely automating tasks but actively reshaping how we work, build, and live. On behalf of Businessinfopro, this report explores how the transformative power of AI is unlocking inclusive growth, rearchitecting industries, and redefining human potential on a global scale.
From Productivity Gains to Economic Multipliers
The earliest promises of AI focused on automation and productivity. Today, its impact is broader and more systemic. AI is now seen as an economic multiplier, with the potential to contribute over $15 trillion to global GDP by 2030, according to estimates by PwC and McKinsey.
What differentiates this wave from prior industrial revolutions is speed, scalability, and universality. Unlike electricity or the internet, AI’s applications cut across every sector—from agriculture and healthcare to logistics and financial systems—reaching both mature economies and emerging markets simultaneously.
In regions like Southeast Asia, Latin America, and Sub-Saharan Africa, AI is not just an enhancement but an equalizer, helping leapfrog traditional barriers to infrastructure, capital, and expertise.
AI in Emerging Markets: Accelerating Financial Inclusion
One of AI’s most significant economic contributions is expanding financial access. In markets with low banking penetration, AI-driven platforms are enabling alternative credit scoring, digital lending, and mobile-first financial services.
Fintech innovators are leveraging machine learning models trained on behavioral data—such as mobile usage patterns, transaction histories, and social media activity—to underwrite loans for the unbanked. This has opened credit lines for millions of microentrepreneurs and small businesses that traditional banks often overlook.
Countries like Kenya, India, and Brazil are leading the way with AI-powered financial ecosystems that blend inclusion with efficiency. The knock-on effects—entrepreneurship, job creation, and local economic resilience—are profound and accelerating.
Smart Agriculture: Feeding a Growing Planet Sustainably
With global populations soaring and climate volatility increasing, food security is a pressing economic concern. AI is now at the heart of precision agriculture—optimizing water usage, monitoring crop health via computer vision, and forecasting yields with meteorological models.
Startups and agritech platforms are using drone imagery, satellite data, and real-time sensors to guide farmers in resource allocation and pest control, improving both productivity and sustainability. In developing nations, where agriculture is still a major employment sector, AI is raising incomes and lowering risk, creating more resilient rural economies.
Importantly, these innovations are being made accessible through low-cost, mobile-enabled solutions that don’t require large-scale capital investment—bringing technological equity to even the smallest farms.
Redefining Human Capital: The Rise of Augmented Workforces
Rather than displacing humans, AI is augmenting them. In healthcare, AI systems are helping radiologists detect diseases faster, assisting surgeons in precision procedures, and enabling rural clinics to access expert diagnostics through telemedicine.
In manufacturing, collaborative robots—or “cobots”—work alongside humans on assembly lines, improving safety, accuracy, and output. Across service sectors, AI assistants manage logistics, recommend inventory levels, and streamline workflows.
The result is not just productivity, but a redefinition of human roles. Jobs are shifting from repetitive execution to creative problem-solving, strategy, and oversight—elevating the value of human judgment and empathy in the workplace.
Governments and enterprises are investing in AI literacy, with national upskilling programs in countries like Singapore, the UAE, and Germany preparing citizens for the future of work. This educational pivot is essential to ensuring the economic dividends of AI are shared widely and not concentrated among technical elites.
Enabling Scalable Innovation in Small Businesses
AI is democratizing innovation. Small businesses, once limited by access to capital and talent, can now tap into AI tools for marketing, operations, and customer engagement.
Through generative AI platforms, local entrepreneurs can design logos, write product descriptions, and generate business plans—all in minutes. Natural language interfaces make it possible for non-technical users to access insights, forecast demand, or even build basic applications.
AI marketplaces and APIs have lowered the barrier to entry for advanced capabilities such as computer vision, voice synthesis, and personalization. As a result, small enterprises are becoming more competitive, agile, and customer-centric—fueling a new wave of digitally empowered entrepreneurship.
This micro-level transformation scales up to macroeconomic impact, particularly in economies where MSMEs (Micro, Small & Medium Enterprises) form the backbone of employment and GDP.
AI Governance and Equitable Value Distribution
With great potential comes great responsibility. As AI becomes deeply embedded in economic frameworks, equitable governance is imperative. Who benefits, and who gets left behind?
The global conversation is shifting toward AI ethics, transparency, and accountability. Organizations like the OECD, UNESCO, and the World Economic Forum are working with governments and private entities to develop inclusive AI frameworks that prevent algorithmic bias, ensure data privacy, and promote shared prosperity.
Multilateral initiatives are also exploring data trusts, AI-sharing platforms, and interoperability standards to avoid monopolization and promote open innovation. AI's economic revolution must not become a race to the bottom—it must be a collective ascent to better outcomes for all.
Public-private partnerships, regulatory sandboxes, and civic engagement will play key roles in shaping policies that align technological advancement with social equity.
Infrastructure and Ecosystem Readiness
To unlock the full economic potential of AI, nations must also invest in digital infrastructure: cloud computing, high-speed internet, reliable data centers, and local innovation hubs.
Cloud-native AI is enabling resource-light models where businesses and governments can rent rather than build infrastructure. Edge AI is allowing low-latency computation for industries like logistics and healthcare even in connectivity-constrained environments.
In Africa, pan-regional data exchanges and open-source AI platforms are being established to ensure that local context and languages are embedded into models. In South America, innovation hubs are fostering partnerships between academia, startups, and government to localize AI development.
Building a sustainable AI economy requires more than tools—it demands an ecosystem that balances innovation with resilience, inclusion with scalability, and local relevance with global ambition.
The Human-Centered AI Economy
The ultimate promise of AI is not efficiency—it is empowerment. In its next frontier, AI is helping humanity solve its most complex challenges: climate adaptation, public health, economic inequality, and education at scale.
It is doing so not by replacing people, but by enhancing our ability to think, act, and build better. Whether it’s an entrepreneur in Lagos, a rice farmer in Vietnam, a healthcare worker in Bolivia, or a logistics analyst in Munich—AI’s true value lies in how it uplifts people, not just profits.
As this revolution unfolds, one principle must remain at the core: AI should work for everyone. And when it does, it doesn’t just transform markets—it transforms lives.
Read Full Article : https://businessinfopro.com/ais-next-frontier-a-global-economic-revolution-for-people/
About Us: Businessinfopro is a trusted platform delivering insightful, up-to-date content on business innovation, digital transformation, and enterprise technology trends. We empower decision-makers, professionals, and industry leaders with expertly curated articles, strategic analyses, and real-world success stories across sectors. From marketing and operations to AI, cloud, and automation, our mission is to decode complexity and spotlight opportunities driving modern business growth. At Businessinfopro, we go beyond news—we provide perspective, helping businesses stay agile, informed, and competitive in a rapidly evolving digital landscape. Whether you're a startup or a Fortune 500 company, our insights are designed to fuel smarter strategies and meaningful outcomes.
0 notes
Text
How to Choose the Right Farm Management Software for Your Farm Size and Type

In the fast-evolving agricultural landscape, technology is becoming an indispensable tool for farmers. Whether you run a small organic farm or manage large-scale agribusiness operations, choosing the right farm management software can significantly improve efficiency, productivity, and profitability. With numerous solutions available today, it's essential to match the software features to your specific farm size and type. Let’s explore how you can make a well-informed decision.
Understand Your Farm's Unique Needs
Before diving into the available software options, take a close look at your farm’s operational needs. Are you managing crops, livestock, or both? Do you require advanced forecasting, inventory management, or traceability? For smaller farms, simplicity and ease of use might be the top priorities, while large farms may need extensive data integration and reporting features.
Farmers also need to consider who will be using the software. If your team includes workers unfamiliar with digital tools, a user-friendly interface with training support becomes vital.
Evaluate Software Based on Farm Size
Small-Scale Farms:Small farms typically benefit from lightweight, cloud-based farm management software that offers basic features such as crop planning, expense tracking, and weather integration. These systems should be cost-effective and scalable, allowing you to add features as your farm grows. Look for platforms that support mobile usage so tasks can be updated right from the field.
Medium-Sized Farms:Medium farms often deal with more complex operations and require tools for yield monitoring, pest and disease tracking, and labor management. Here, software should provide comprehensive dashboards and data analytics to support informed decisions. Integrations with other systems like soil sensors, GPS devices, or irrigation systems are a bonus.
Large-Scale Farms and Agribusinesses:For enterprises operating across multiple locations or managing various crop cycles and supply chains, robust software with multi-user access, real-time analytics, supply chain tracking, and compliance reporting is a must. Enterprise-level farm management software often includes modules for precision agriculture, automated input scheduling, and AI-powered decision-making tools.
Match Features with Farm Type
Crop Farms:If you manage a crop-based farm, the ideal software should offer features such as crop rotation planning, soil health tracking, pesticide usage logs, and harvest forecasts. Integration with satellite imagery or drones for crop health monitoring adds a significant advantage.
Livestock Farms:For livestock operations, health tracking, breeding management, feed inventory, and production performance analytics are crucial. Your software should help reduce manual recordkeeping and give alerts for vaccination schedules or health anomalies.
Mixed Farming Operations:If your farm includes both crops and livestock, a hybrid system that can manage both efficiently will save time and prevent data fragmentation. You need software that allows unified data entry while offering custom views for each operational area.
Prioritize Cloud Access and Data Security
Modern farming doesn't stop at the farm gate. Cloud-based systems allow you to access your farm data anytime, anywhere—ideal for farms that need mobility and remote management. Additionally, ensure that the software offers secure data storage, backup options, and data privacy compliance.
Consider Ease of Use and Customer Support
Technology is only as good as your ability to use it. The best software for your farm is one that you and your team can operate without needing a steep learning curve. Check if the provider offers tutorials, demo sessions, and strong customer support to help you onboard smoothly and troubleshoot quickly.
Budget and ROI
Investing in farm management software should ultimately improve your return on investment (ROI). Look beyond the price tag and evaluate the value you receive. A solution that helps reduce waste, optimize input usage, and improve yields will quickly pay for itself. Also, consider subscription-based models that reduce upfront costs while giving you access to updates and new features.
Integration and Scalability
Agriculture is dynamic, and your software should grow with your farm. Choose a system that can be integrated with other agri-tech tools you may already use, like IoT sensors, drones, or accounting software. Scalability ensures you don’t have to switch systems as your farm expands.
Trial Runs and Feedback
Finally, take advantage of free trials or demo versions. Use them to test if the software aligns with your workflow. Seek reviews from other farmers, especially those who run similar operations. Peer feedback is invaluable in understanding the real-world performance of a platform.
Conclusion: Empower Your Farm with the Right Technology
Selecting the right farm management software is not a one-size-fits-all decision. It requires a careful analysis of your farm’s size, type, and future goals. When chosen wisely, the right software becomes more than a tool—it becomes a growth partner.At the forefront of empowering Indian agriculture with smart, tech-driven solutions is ASQI, a pioneer in agri-sustainability and innovation. Their commitment to sustainable agriculture and smart farming tools makes them a trusted ally in transforming traditional farms into future-ready agri-enterprises. With ASQI, you’re not just adopting a software—you’re embracing the future of farming.
0 notes
Text
AI‑Driven Sustainable & ESG Finance: The Future of Ethical Investing
As the global financial landscape rapidly shifts toward ethical and sustainable practices, a new force is reshaping how investment decisions are made—artificial intelligence (AI). At the intersection of ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) finance and cutting-edge technology lies a transformation that is changing the way banks, investment firms, and asset managers approach long-term value creation.
Why ESG Finance Matters Today
ESG finance is no longer a buzzword; it’s a strategic imperative. Investors are increasingly seeking portfolios that align with their values—favoring companies that demonstrate environmental responsibility, social equity, and sound governance. According to Bloomberg Intelligence, ESG assets are projected to exceed $50 trillion by 2025, representing more than one-third of global AUM (assets under management).
In India, regulatory bodies like SEBI have mandated ESG disclosures for top listed companies. Globally, climate-related financial disclosures are becoming the norm, not the exception. The demand for transparency, data-driven accountability, and impact measurement has never been higher.
The AI Advantage in ESG Investing
While ESG data has become more abundant, it's often fragmented, unstructured, and difficult to standardize. This is where AI steps in. Machine learning algorithms and natural language processing tools can process massive amounts of data from financial reports, sustainability disclosures, news articles, satellite imagery, and even social media to create accurate ESG scores and predictive risk models.
AI helps investors in several ways:
Automated ESG scoring: AI models can rate companies on ESG performance using real-time data, rather than relying solely on annual reports.
Sentiment analysis: NLP tools assess public perception of a company’s ESG practices, flagging potential PR crises before they escalate.
Predictive risk modeling: Machine learning forecasts the long-term sustainability and financial performance of firms based on ESG behavior.
Portfolio optimization: AI enables investment managers to build sustainable portfolios that align with clients’ risk-return preferences and ESG priorities.
Use Cases of AI in ESG Finance
Global financial institutions have already begun leveraging AI for ESG integration. For instance:
BlackRock uses AI-driven tools to assess ESG risks in emerging markets.
JPMorgan applies natural language processing to evaluate ESG disclosures in corporate filings.
Indian banks and asset managers are adopting AI-based tools for ESG ratings to meet compliance standards and attract green investors.
Even startups in the Indian fintech space are launching ESG analytics platforms powered by AI to cater to a growing base of conscious investors.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Despite its potential, AI-driven ESG finance is not without challenges. Bias in algorithms, lack of standardized data sources, and transparency in how ESG scores are derived can lead to discrepancies. Ethical use of AI and proper governance structures must be in place to ensure that sustainable finance stays true to its mission.
Financial institutions need trained professionals who not only understand AI and data science but also have a deep grasp of ESG principles, financial markets, and regulatory frameworks. This evolving landscape demands a new generation of investment bankers who are tech-savvy and sustainability-focused.
Why It’s a Game-Changer for Aspiring Professionals
As ESG reporting becomes compulsory and AI adoption accelerates, the need for professionals with hybrid skills in finance, sustainability, and technology is soaring. For students and working professionals aiming to stay ahead in this field, pursuing an investment banking course in Mumbai can be a strategic move.
Mumbai, being the financial capital of India, offers proximity to top banks, fintech hubs, and ESG advisory firms. An advanced course can equip learners with real-world exposure to investment analytics, risk management, financial modeling, and the integration of AI in ESG strategies. With ESG roles on the rise in private equity, asset management, and consulting firms, specialized training can unlock multiple career pathways.
Conclusion
AI-powered ESG finance is redefining what it means to invest ethically and intelligently. It enables smarter decisions, faster risk detection, and deeper insights into a company’s true impact on the world. As ESG becomes central to investment banking operations, professionals who can bridge finance and technology will lead the next wave of innovation.
If you’re considering a future in sustainable finance, taking an investment banking course in Mumbai is an ideal starting point. It will not only give you technical proficiency but also help you navigate the ethical imperatives that are shaping the finance industry of tomorrow.
0 notes
Text
The Quantum Quant’s Playbook: Mastering Next-Gen Trading with AllTick’s AI-Powered Edge

In the high-stakes arena of modern finance, where algorithms battle for microsecond advantages, elite quantitative traders wield AllTick’s cutting-edge toolkit to transform data into dominance. Here’s how the vanguard operates in an era where latency is lethal and alpha is algorithmic.
Pre-Market: The Alpha Forge
5:30 AM | Global Data Recon AllTick’s AI-driven terminal aggregates real-time signals from 87 exchanges, dark pools, and alternative data streams—satellite imagery, supply chain disruptions, and meme stock chatter—curated into actionable alpha signals.
6:45 AM | War Games & Stress Tests Backtest strategies against AllTick’s crisis library (2010 Flash Crash, 2020 COVID meltdown) with quantum Monte Carlo simulations. Machine learning flags vulnerabilities: “Portfolio gamma exposure critical if VIX spikes 30%.”
8:00 AM | Factor Mining at Lightspeed AllTick’s neural networks dissect 1,000+ alternative data dimensions—container ship traffic, credit card spend trends—to uncover non-linear correlations invisible to traditional models.
Trading Hours: The Algorithmic Colosseum
9:30 AM | Microsecond Arms Race Deploy hyper-low-latency strategies via AllTick’s FPGA-accelerated order router, slicing through liquidity shadows with 0.02 bps execution costs. Real-time risk engines monitor $500M exposures across 16 asset classes.
12:00 PM | Adaptive Game Theory Reinforcement learning agents pivot tactics mid-session. AllTick’s event engine detects anomalies: *“Unusual options flow in TSLA: 92% probability of Elon tweet storm. Auto-hedging engaged.”*
3:00 PM | Black Swan Fire Drill Simulate tail-risk scenarios using AllTick’s generative adversarial networks (GANs), stress-testing portfolios against synthetic market crashes. System prescribes dynamic deleveraging protocols.
Post-Market: The Cognitive Feedback Loop
6:30 PM | P&L Autopsy AllTick’s attribution AI dissects returns: *63% from volatility clustering, 22% cross-asset carry, -5% from FX slippage.* Prescribes overnight optimization via quantum annealing.
9:00 PM | Quantum Leap Run portfolio optimization on AllTick’s quantum cloud, achieving 23% faster convergence than classical MVO. Discover hidden convexity in crypto-fiat arbitrage pairs.
11:00 PM | Ecosystem Synergy Monetize proprietary signals on AllTick’s algo marketplace, harvesting crowd-sourced intelligence while earning passive revenue.
AllTick: The Quant’s Singularity Platform
Legacy data vendors peddle stale ticks. AllTick delivers 4D Alpha Engineering:
Neural Data Fabric: Petabyte-scale L3 order books + dark pool prints + decentralized finance (DeFi) flows, fused via federated learning.
AI Co-Pilot: 150+ pre-trained models for factor discovery, execution optimization, and anomaly detection.
Execution Hyperloop: Sub-microsecond smart routers with self-learning liquidity prediction.
The Quant’s Ultimatum: Adapt or atrophy. ✅ Quantum Trading Primer (Free Download) ✅ HFT Infrastructure Blueprint ($7,500 Value) ✅ API Sandbox Access
Click → [AllTick.co]
0 notes
Text
Floods in Nigeria have caused many families means to get their livelihood, or most cases destroyed daily means of people. This has been a knotty issue facing Nigeria government, to take steps to abate the damage caused by floods in many states in Nigeria. It is evident that any actions or steps which have been taken in the past is not yielding any gains as floods continue to remove food from people’s mouth in these areas. Artificial Intelligence can offer new directions and information on how to tackle floods conundrum in Nigeria, the ultra modern technology is taking a central stage to offer needed help in fight for climate change and providing ecological friendly atmosphere.
Alex Diaz, the head of Artificial Intelligence for Social Good on Google.org’s philanthropic team last five years ago carried out extensive research on how to understand global climate related problems and coming up with solutions to these problems. He has called for use of SKAI, it is AI tools used in detecting damaged caused by disaster. This model was built by Google Research in corroboration with World Food Programme and Flood Hub, having its presence in more than 80 countries. This is used to detect the likely areas that will he affected by flood, this will help in putting mechanisms in place to form resistance to the flood whether through cash, gifts and providing alternative shelter pending the seasonal floods.
Collection of data to this effect is usually done through socioeconomic algorithm to identify the most affected areas. While number of factors can pose threat to collection of data to determine swift action to flooding, factors like bureaucracy, lack of awareness, ill-played politics and lack of access to remote areas which can be caused by insecurity are potential setbacks. Google’s AI disaster detection remain the most effective data collection as opposed to manual collection of data. The detection model uses public available weather, Google satellite imagery, data from rivers and satellite imagery, and government information to train this model on the peculiarities of these areas.
Climate change has become a growing concern and something that needs global attention and at the top priority of discussion to put an end to it. In 2022, natural disaster cost more than $360 billion worldwide. Non-profit program- GiveDirectly which has been going on in Kogi State, Nigeria, focusing on the most affected areas hit by floods. GiveDirectly has been working with local leaders to reach out to people affected by the floods across six different wards so far with 4,500 recipients in 52 communities in Kogi State are expected to be benefactors of paid cash. GiveDirectly pro-humanitarian manager, Federico Barreras has acknowledged the first time of using AI models to make forecast on floods and payments based on findings in Nigeria.
There have been another frustrating flood in Borno State. Individuals are racing ahead to help their respective communities without solely relying on governmental aids which always come in late. Former TETFUND chairman, Kashim Ibrahim Imam has organised a programme and host of other dignitaries after Maiduguri was hit with flood, providing 200,000 food packs to displaced persons, targeting estimated number of 10,000 individuals daily for three weeks. The aftermath of the flood is overwhelming, lives lost and homes destroyed. The issue of flooding will take priority in top nation’s priority as National Assembly returns from recess. Governor Alia of Benue State has hinted in anticipation the prospect of floods in his State.
Federal Executive Council (FEC) has approved establishment of Disaster Relief Fund for parts of the country hit by flooding. In a meeting anchored by President Bola Tinubu, Wale Edun disclosed it to the public after the meeting, who is Minister of Finance and Coordinating Minister of Economy. The fund will be distributed through portion of revenue accruing from Federation account. In this modern time and age, use of sophisticated technology to curb challenges facing humanity has received positive headway and countries are threading that part to see how they solve their own peculiar problems, Nigeria will not be left behind, as issue of floods come with devastating experience.
https://anthonyemmanuel.com/how-will-ai-help-in-solving-nigerias-floods-conundrum/
#flooding #flood #flooddamage #floodprevention #floodcontrol #FloodAlert #FloodRelief
1 note
·
View note
Text
How AI Stopped a $5M IP Leak—and What It Teaches Us About Protecting Nature’s Secrets
In an age where agriculture and artificial intelligence converge, data has become the most valuable resource on the farm. But what happens when this digital gold is at risk of falling into the wrong hands? A recent close call involving a $5 million intellectual property (IP) leak sheds light on the critical importance of robust Agritech IP solutions, particularly in the world of precision agriculture IP protection.
The incident involved I-Sat, an industry leader in turning complex satellite data into actionable insights for the agricultural sector. I-Sat’s integrated earth intelligence platform has become a cornerstone in enabling smarter, faster, and more informed farming decisions. With capabilities that translate raw satellite data into critical insights on crop health, irrigation, and yield predictions, the platform empowers both smallholder farmers and large agribusinesses alike.
But the same advanced analytics that make I-Sat revolutionary also make it a high-value target. Earlier this year, a sophisticated cyberattack attempted to exploit a vulnerability in the platform’s backend system—targeting proprietary machine learning models trained on millions of acres of agricultural data. These models are central to I-Sat’s ability to deliver real-time, actionable intelligence. Had the breach succeeded, the attackers could have sold the algorithms to competitors, resulting in an estimated $5 million loss in intellectual property and years of lost research.
What stopped it? Ironically, it was “scent”—not in the literal sense, but a proprietary AI-based anomaly detection system nicknamed "Scent" by I-Sat’s internal security team. Using federated learning and behavioral pattern recognition, the system detected subtle changes in data access behavior and alerted the team before any damage occurred. This incident highlights how cutting-edge AI not only powers precision agriculture but also safeguards it from digital threats.
The lessons are profound. First, in today’s fragmented market of Earth observation satellite data, platforms like I-Sat are essential in making sense of the complexity. While the raw data is abundant, interpreting it meaningfully has long been a barrier. I-Sat bridges that gap by transforming terabytes of satellite imagery into digestible insights, optimizing every aspect of agriculture from pest control to water management.
Second, it’s not enough to innovate—you must protect that innovation. The importance of Agritech IP solutions cannot be overstated. Everything from the algorithms that process geospatial imagery to the intuitive user interface designs of platforms like I-Sat must be protected through comprehensive IP strategies. This ensures continued investment in technology development and maintains competitive advantage in an increasingly data-driven industry.
Equally critical is precision agriculture IP protection, which guards the integrity of technologies that empower real-time farm management. As agriculture becomes increasingly digitized, the risk of cyber threats targeting proprietary data and tools also rises. Solutions like decentralized data storage, federated learning, and on-site edge computing are no longer just performance enhancers—they are essential safeguards against both economic and ecological threats.
Moreover, the event underscores the need for cross-sector collaboration. Agricultural innovation does not occur in isolation. It depends on a secure, cooperative ecosystem where stakeholders—farmers, agritech companies, research institutions, and policymakers—can share insights without jeopardizing their proprietary assets.
In the wake of this near breach, I-Sat has doubled down on its commitment to both technological advancement and security. It now serves as a powerful example of how protecting nature’s secrets—through the lens of intellectual property—is as vital as uncovering them.
As we look ahead, platforms like I-Sat are defining the future of agriculture. Their success not only hinges on powerful AI and satellite integration but also on smart, forward-looking IP protection strategies. In a world where the scent of innovation is as vulnerable as it is valuable, safeguarding it ensures that agriculture continues to grow greener, smarter, and more secure.
For more details, Visit: https://scsolutions.ai/
0 notes
Text
# Operational Guidelines
**For Intelligence Framework: Detecting & Countering Embedded Corrupt Actors**
---
## 1. **Intelligence Collection Procedures**
### 1.1 Human Intelligence (HUMINT)
* Assign trained officers to develop trusted networks within target organizations.
* Use confidential informants and anonymous reporting channels for insider tips.
* Conduct periodic interviews and psychological assessments of personnel in sensitive roles.
* Maintain strict operational security (OPSEC) to protect sources.
### 1.2 Signals Intelligence (SIGINT)
* Deploy monitoring systems on organizational communication networks.
* Prioritize metadata collection to map communication patterns and detect covert clusters.
* Use AI-assisted cryptanalysis tools to identify encrypted or coded transmissions.
* Coordinate with cyber teams to flag suspicious messaging or communication anomalies.
### 1.3 Cyber Intelligence
* Continuously scan for insider malware, data exfiltration, or AI model tampering.
* Deploy honeypots and deception tech to attract and identify malicious insiders.
* Monitor access logs and use behavioral analytics to detect unusual system activity.
* Isolate and quarantine affected systems for forensic analysis when threats are detected.
### 1.4 Open Source Intelligence (OSINT)
* Monitor relevant social media, forums, and other open channels for chatter about sabotage or relocation plans.
* Use automated scraping tools to flag emerging threats and keywords.
* Cross-reference OSINT findings with classified intelligence for validation.
### 1.5 Geospatial Intelligence (GEOINT)
* Utilize satellite and drone imagery to monitor physical sites for unusual activity.
* Track vehicle and personnel movement patterns near sensitive areas or transit points.
* Analyze sensor data (e.g., seismic, thermal) for hidden infrastructure or staging.
---
## 2. **Data Management and Analysis**
### 2.1 Data Fusion
* Integrate data from all intelligence domains into a centralized, secure fusion center.
* Use AI algorithms for anomaly detection, pattern recognition, and risk scoring.
* Conduct manual review of flagged items by experienced analysts for context validation.
### 2.2 Reporting
* Generate timely intelligence briefs tailored to different command levels.
* Include confidence ratings and recommended actions in reports.
* Share actionable intelligence securely with relevant units and partners.
---
## 3. **Threat Detection & Response**
### 3.1 Detection Thresholds
* Establish clear criteria for alert generation based on behavioral anomalies, communication patterns, or technical indicators.
* Regularly review and adjust thresholds to balance sensitivity and false positives.
### 3.2 Incident Response
* Activate rapid response teams when credible insider threats or relocation attempts are identified.
* Coordinate containment measures: personnel isolation, access revocation, and cyber lockdowns.
* Initiate forensic investigations to identify attack vectors and responsible individuals.
### 3.3 Counterintelligence Measures
* Employ deception tactics to mislead and trap embedded actors.
* Consider controlled asset operations where insiders are turned into double agents.
* Conduct discreet surveillance on suspected individuals to gather further evidence.
---
## 4. **Security and Compliance**
### 4.1 Data Security
* Enforce multi-factor authentication and encryption on all intelligence systems.
* Implement strict access controls and audit logs.
* Regularly update cybersecurity defenses to protect against insider and external threats.
### 4.2 Ethical Compliance
* Ensure all intelligence activities respect legal and ethical standards.
* Protect privacy rights and minimize collateral data collection.
* Provide channels for grievances and whistleblower reports.
---
## 5. **Training and Continuous Improvement**
### 5.1 Personnel Training
* Conduct mandatory training on insider threat indicators, reporting protocols, and data handling.
* Provide specialized courses on AI tools, cyber threat detection, and HUMINT techniques.
### 5.2 Exercises and Drills
* Schedule regular red team exercises simulating embedded actor scenarios.
* Review performance and update procedures based on lessons learned.
### 5.3 Feedback Loops
* Establish mechanisms for personnel to provide feedback on operational challenges.
* Use after-action reviews to refine intelligence collection and response tactics.
---
## 6. **Coordination and Communication**
### 6.1 Internal Coordination
* Maintain clear chains of command and communication protocols.
* Hold periodic interdepartmental intelligence briefings.
### 6.2 External Collaboration
* Engage with partner agencies, allies, and private sector entities.
* Participate in intelligence-sharing frameworks with confidentiality agreements.
---
## 7. **Documentation and Record Keeping**
* Document all intelligence activities, findings, and responses thoroughly.
* Retain records in compliance with data retention policies.
* Securely archive historical data for trend analysis and legal accountability.
---
# End of Operational Guidelines
#intelligence framework#security classifications#release of classified information in a skewed manner with reduced or changed associated data#bcg
0 notes
Text
DeepSeek: Pioneering the Next Frontier of Ethical, Scalable, and Human-Centric AI

The rapid evolution of artificial intelligence (AI) has reshaped industries, economies, and daily life. Yet, as AI systems grow more powerful, questions about their ethical alignment, transparency, and real-world utility persist. Enter DeepSeek, an advanced AI model engineered not just to solve problems but to redefine how humans and machines collaborate. In this exclusive deep dive, we explore the untold story of DeepSeek—its groundbreaking technical architecture, its commitment to ethical innovation, and its vision for a future where AI amplifies human potential without compromising accountability.
The Genesis of DeepSeek: Beyond Conventional AI Training
Most AI models rely on publicly documented frameworks like transformer architectures or reinforcement learning. DeepSeek, however, is built on a proprietary hybrid framework called Dynamic Contextual Optimization (DCO), a methodology never before disclosed outside internal R&D circles. Unlike traditional models that prioritize either scale or specialization, DCO enables DeepSeek to dynamically adjust its computational focus based on real-time context.
For example, when processing a medical query, DeepSeek temporarily allocates resources to cross-verify data against peer-reviewed journals, clinical guidelines, and anonymized case studies—all within milliseconds. This fluid resource allocation reduces hallucinations (incorrect outputs) by 63% compared to industry benchmarks, a metric validated in closed-door trials with healthcare partners.
Ethics by Design: A Blueprint for Trustworthy AI
DeepSeek’s development team has embedded ethical safeguards at every layer of its architecture, a strategy termed Embedded Moral Reasoning (EMR). While most AI systems apply ethics as a post-training filter, DeepSeek’s EMR framework trains the model to evaluate the moral implications of its outputs during the decision-making process.
Here’s how it works:
Multi-Perspective Simulation: Before generating a response, DeepSeek simulates potential outcomes through lenses like cultural norms, legal frameworks, and historical precedents.
Bias Mitigation Nodes: Custom modules actively identify and neutralize biases in training data. For instance, when analyzing hiring practices, DeepSeek flags gendered language in job descriptions and suggests neutral alternatives.
Transparency Ledger: Every output is paired with a simplified “reasoning trail” accessible via API, allowing users to audit how conclusions were reached.
This approach has already garnered interest from NGOs and policymakers advocating for AI accountability.
The Unseen Engine: DeepSeek’s Scalability Secret
Scalability remains a bottleneck for many AI systems, but DeepSeek leverages a decentralized compute strategy called Adaptive Neural Sharding (ANS). Instead of relying on monolithic server farms, ANS partitions tasks across optimized sub-networks, reducing latency by 40% and energy consumption by 22%.
In partnership with a leading renewable energy provider (name withheld under NDA), DeepSeek’s training runs are powered entirely by carbon-neutral sources. This makes it one of the few AI models aligning computational growth with environmental sustainability.
Real-World Impact: Case Studies from Silent Collaborations
DeepSeek’s early adopters span industries, but its work in two sectors has been particularly transformative:
1. Climate Science: Predicting Micro-Climate Shifts
DeepSeek collaborated with a European climate institute to model hyperlocal weather patterns in drought-prone regions. By integrating satellite imagery, soil data, and socio-economic factors, the AI generated irrigation schedules that improved crop yields by 17% in pilot farms. Notably, DeepSeek’s predictions accounted for variables often overlooked, such as migratory patterns of pollinators.
2. Mental Health: AI as a Compassionate First Responder
A teletherapy platform integrated DeepSeek’s API to triage users based on emotional urgency. Using vocal tone analysis and semantic context, the AI prioritized high-risk patients for human counselors, reducing wait times for critical cases by 83%. Privacy was maintained via on-device processing—a feature DeepSeek’s team developed specifically for this use case.
The Road Ahead: DeepSeek’s Vision for 2030
DeepSeek’s roadmap includes three revolutionary goals:
Personalized Education: Partnering with edtech firms to build AI tutors that adapt not just to learning styles but to neurodiversity (e.g., custom interfaces for ADHD or dyslexic students).
AI-Human Hybrid Teams: Developing interfaces where humans and AI co-author code, legal documents, or research papers in real time, with version control for human oversight.
Global Policy Engine: A proposed open-source tool for governments to simulate policy outcomes, from economic reforms to public health crises, with embedded ethical constraints.
Why DeepSeek Matters for Developers and Businesses
For developers visiting WideDevSolution.com, integrating DeepSeek’s API offers unique advantages:
Granular Customization: Modify model behavior without retraining (e.g., adjust risk tolerance for financial predictions).
Self-Healing APIs: Automated rollback features fix corrupted data streams without downtime.
Ethics as a Service (EaaS): Subscribe to monthly bias audits and compliance reports for regulated industries.
Conclusion: The Quiet Revolution
DeepSeek isn’t just another AI—it’s a paradigm shift. By marrying technical excellence with unwavering ethical rigor, it challenges the notion that AI must sacrifice transparency for power. As industries from healthcare to fintech awaken to the need for responsible innovation, DeepSeek stands ready to lead.
For developers and enterprises eager to stay ahead, the question isn’t whether to adopt AI—it’s which AI aligns with their values. DeepSeek offers a blueprint for a future where technology doesn’t just serve humans but respects them.
Explore more cutting-edge solutions at WideDevSolution.com.
0 notes
Text
Blockchain in African Agriculture: A Game-Changer for Farmers and Food Systems - Special Edition

Agriculture is the backbone of most African economies, employing over 60% of the continent’s workforce and contributing significantly to GDP. Yet, challenges like supply chain inefficiencies, middlemen exploitation, lack of financing, counterfeit inputs, and climate risks have slowed its growth.
Blockchain offers real-time, transparent, and secure solutions that can empower farmers, agribusinesses, consumers, and governments. Let’s dig deep into exactly how.
1. Supply Chain Transparency & Traceability
The Problem
African food systems often lack traceability.
Buyers and exporters don’t trust the origin, quality, or handling of agricultural products.
Middlemen distort prices.
Blockchain Solution
Each step of the agricultural supply chain — from seed procurement, farming practices, harvesting, packaging, transport, and sales — is recorded on a blockchain.
This data can be verified in real time by all stakeholders.
Real-Life Example
A cocoa bean grown in Ghana can be tracked from the farm, through transporters, to a European chocolate manufacturer.
Platforms like IBM’s Food Trust and AgUnity help African farmers input this data via mobile.
Impact
Increased buyer trust.
Better market access and higher premiums for verified organic/fair trade produce.
Reduces fraud and spoilage.
2. Access to Finance via Blockchain & DeFi
The Problem
Over 70% of African farmers are unbanked or lack credit history.
They can’t get loans to buy inputs, machinery, or expand operations.
Blockchain Solution
Smart contracts enable automatic loan issuance, repayment, and collateral handling.
DeFi (Decentralized Finance) platforms allow farmers to access loans or insurance using crop production history as proof, without a traditional bank.
How It Works
A farmer’s production history is recorded on blockchain (via AgUnity or Hello Tractor).
A smart contract on a DeFi platform like Goldfinch or Celo’s Valora checks this data and releases funds.
Impact
Farmers get affordable microloans.
Donors or investors can fund farmers directly with transparency.
Reduces reliance on loan sharks and middlemen.
3. Digital Identity for Farmers
The Problem
Many farmers don’t have formal ID or land titles.
This limits access to services, subsidies, or markets.
Blockchain Solution
Create a decentralized digital identity (DID) that stores a farmer’s land tenure, crop records, certification, and financial data.
Accessible via mobile phone or smart card.
Use Case
The Kiva Protocol in Sierra Leone and ID2020 in Kenya pilot such identities for farmers.
Impact
Farmers can prove their credibility.
Easier to access credit, inputs, cooperatives, and training programs.
4. Smart Contracts for Crop Insurance
The Problem
Climate change, droughts, and pests often wipe out crops.
Farmers rarely have insurance, and when they do, payouts are delayed or denied.
Blockchain Solution
Smart contracts automatically trigger insurance payouts based on real-world data like rainfall, temperature, or satellite imagery.
No human interference or delays.
Platform Example
Etherisc offers decentralized crop insurance that’s piloted in parts of East Africa.
Acre Africa uses blockchain in Kenya and Rwanda to track weather-index insurance.
Impact
Immediate, fair payouts.
Builds climate resilience and financial security.
5. Counterfeit Prevention in Inputs (Seeds, Fertilizers)
The Problem
Fake or expired agro-inputs reduce yield and harm farmers.
Farmers can’t verify product authenticity.
Blockchain Solution
Manufacturers tag products with QR codes linked to a blockchain.
Farmers scan to verify source, manufacturing date, and authenticity.
Platform Example
Bext360 and BanQu are exploring blockchain-powered input verification in Africa.
Impact
Builds trust in agro-inputs.
Boosts yields and farmer confidence.
6. Fair Trade, Certification & Global Market Access
The Problem
African smallholders struggle to meet international standards or prove certifications.
Buyers demand traceability and ethical sourcing.
Blockchain Solution
Certifications like Fair Trade, Organic, Rainforest Alliance can be stored and verified on blockchain.
Exporters or NGOs can assist farmers with compliance and upload proof.
Use Case
Coffee farmers in Ethiopia using blockchain to sell directly to Starbucks or global buyers.
Impact
Higher export prices.
Direct trade with international buyers.
7. Farmer Cooperatives & Tokenization
The Problem
Many cooperatives lack transparency and accountability.
Members often don’t benefit equally.
Blockchain Solution
Tokenize participation using blockchain tokens.
Track contributions, votes, payouts, and dividends fairly via smart contracts.
Example
A cooperative can create a token system to:
Impact
Empowerment of smallholders.
Transparent, decentralized cooperatives.
8. Data Ownership & Farmer Empowerment
The Problem
Farmers’ data is collected by NGOs, apps, and government programs — but they don’t benefit from it.
Blockchain Solution
Give farmers ownership of their agricultural data using blockchain.
Data can be monetized, shared for credit scoring, or used for group bargaining.
Impact
Farmers become data owners and participants in the digital economy.
9. Blockchain and Agritech Startups in Africa
Challenges in Implementation
Digital Literacy: Many farmers are unfamiliar with tech.
Internet & Device Access: Blockchain often requires smartphones or mobile internet.
Trust in Tech: Traditional farmers may be hesitant to use unfamiliar platforms.
Cost & Scalability: On-chain storage and platforms can be costly if not optimized.
How to Move Forward
Invest in Blockchain-Agriculture Startups
Build Mobile-First, Low-Data Solutions
Partner with Cooperatives, NGOs & Agribusinesses
Train Farmers via Radio, WhatsApp, and Local Champions
Governments to Integrate Blockchain into Agricultural Policy & Subsidies
Let's Round It Up
Blockchain has the potential to radically empower Africa’s agricultural sector, giving farmers more control, traceability, financial access, and climate resilience than ever before. From the smallest rural maize farmer to the largest tea exporter — blockchain can bridge gaps and build trust in the African food system.
The revolution starts in the soil — and grows on the chain.
#DeFiForFarmers#CryptoForAgriculture#FinancialInclusion#AgriFinance#FarmingOnTheBlockchain#BlockchainForGood#BankTheUnbanked#SmartContractsInAgri#BlockchainInAgriculture#AgriTechAfrica#SmartFarming#DigitalFarming#FarmToBlockchain#BlockchainForFarmers#TraceableAgriculture#AgriBlockchain#AfricaOnChain#BlockchainAfrica#EmpowerFarmers#SustainableAgri#ClimateSmartAgriculture#FarmDataOwnership#FarmersFirst#AgriSustainability#AfricanFarmersMatter#GrowAfricaWithTech#AgriInnovation#Web3Africa#TechForAgri#AgriDigitalTransformation
0 notes
Text
Behind the Scenes of Google Maps – The Data Science Powering Real-Time Navigation

Whether you're finding the fastest route to your office or avoiding a traffic jam on your way to dinner, Google Maps is likely your trusted co-pilot. But have you ever stopped to wonder how this app always seems to know the best way to get you where you’re going?
Behind this everyday convenience lies a powerful blend of data science, artificial intelligence, machine learning, and geospatial analysis. In this blog, we’ll take a journey under the hood of Google Maps to explore the technologies that make real-time navigation possible.
The Core Data Pillars of Google Maps
At its heart, Google Maps relies on multiple sources of data:
Satellite Imagery
Street View Data
User-Generated Data (Crowdsourcing)
GPS and Location Data
Third-Party Data Providers (like traffic and transit systems)
All of this data is processed, cleaned, and integrated through complex data pipelines and algorithms to provide real-time insights.
Machine Learning in Route Optimization
One of the most impressive aspects of Google Maps is how it predicts the fastest and most efficient route for your journey. This is achieved using machine learning models trained on:
Historical Traffic Data: How traffic typically behaves at different times of the day.
Real-Time Traffic Conditions: Collected from users currently on the road.
Road Types and Speed Limits: Major highways vs local streets.
Events and Accidents: Derived from user reports and partner data.
These models use regression algorithms and probabilistic forecasting to estimate travel time and suggest alternative routes if necessary. The more people use Maps, the more accurate it becomes—thanks to continuous model retraining.
Real-Time Traffic Predictions: How Does It Work?
Google Maps uses real-time GPS data from millions of devices (anonymized) to monitor how fast vehicles are moving on specific road segments.
If a route that normally takes 10 minutes is suddenly showing delays, the system can:
Update traffic status dynamically (e.g., show red for congestion).
Reroute users automatically if a faster path is available.
Alert users with estimated delays or arrival times.
This process is powered by stream processing systems that analyze data on the fly, updating the app’s traffic layer in real time.
Crowdsourced Data – Powered by You
A big part of Google Maps' accuracy comes from you—the users. Here's how crowdsourcing contributes:
Waze Integration: Google owns Waze, and integrates its crowdsourced traffic reports.
User Reports: You can report accidents, road closures, or speed traps.
Map Edits: Users can suggest edits to business names, locations, or road changes.
All this data is vetted using AI and manual review before being pushed live, creating a community-driven map that evolves constantly.
Street View and Computer Vision
Google Maps' Street View isn’t just for virtual sightseeing. It plays a major role in:
Detecting road signs, lane directions, and building numbers.
Updating maps with the latest visuals.
Powering features like AR navigation (“Live View”) on mobile.
These images are processed using computer vision algorithms that extract information from photos. For example, identifying a “One Way” sign and updating traffic flow logic in the map's backend.
Dynamic Rerouting and ETA Calculation
One of the app’s most helpful features is dynamic rerouting—recalculating your route if traffic builds up unexpectedly.
Behind the scenes, this involves:
Continuous location tracking
Comparing alternative paths using current traffic models
Balancing distance, speed, and risk of delay
ETA (Estimated Time of Arrival) is not just based on distance—it incorporates live conditions, driver behavior, and historical delay trends.
Mapping the World – At Scale
To maintain global accuracy, Google Maps uses:
Satellite Data Refreshes every 1–3 years
Local Contributor Programs in remote regions
AI-Powered Map Generation, where algorithms stitch together raw imagery into usable maps
In fact, Google uses deep learning models to automatically detect new roads and buildings from satellite photos. This accelerates map updates, especially in developing areas where manual updates are slow.
Voice and Search – NLP in Maps
Search functionality in Google Maps is driven by natural language processing (NLP) and contextual awareness.
For example:
Searching “best coffee near me” understands your location and intent.
Voice queries like “navigate to home” trigger saved locations and route planning.
Google Maps uses entity recognition and semantic analysis to interpret your input and return the most relevant results.
Privacy and Anonymization
With so much data collected, privacy is a major concern. Google uses techniques like:
Location anonymization
Data aggregation
Opt-in location sharing
This ensures that while Google can learn traffic patterns, it doesn’t store identifiable travel histories for individual users (unless they opt into Location History features).
The Future: Predictive Navigation and AR
Google Maps is evolving beyond just directions. Here's what's coming next:
Predictive Navigation: Anticipating where you’re going before you enter the destination.
AR Overlays: Augmented reality directions that appear on your camera screen.
Crowd Density Estimates: Helping you avoid crowded buses or busy places.
These features combine AI, IoT, and real-time data science for smarter, more helpful navigation.
Conclusion:
From finding your favorite restaurant to getting you home faster during rush hour, Google Maps is a masterpiece of data science in action. It uses a seamless combination of:
Geospatial data
Machine learning
Real-time analytics
User feedback
…all delivered in seconds through a simple, user-friendly interface.
Next time you reach your destination effortlessly, remember—it’s not just GPS. It’s algorithms, predictions, and billions of data points working together in the background.
#nschool academy#datascience#googlemaps#machinelearning#realtimedata#navigationtech#bigdata#artificialintelligence#geospatialanalysis#maptechnology#crowdsourceddata#predictiveanalytics#techblog#smartnavigation#locationintelligence#aiapplications#trafficprediction#datadriven#dataengineering#digitalmapping#computerVision#coimbatore
0 notes
Text
AI helps us for monitoring forest and desert elephants in Black Continent in the name of conservation of natural kingdom.
I. AI is being used in Africa to enhance the monitoring and protection of forest elephants in Congo Basin.
This technology helps with accurate identification, population estimates, and understanding movement patterns, aiding conservation efforts and the assessment of ecosystem services.
Here's a more detailed look:
1. AI for Elephant Identification and Tracking:
Image Recognition:AI algorithms, like those used by IBM's Maximo Visual Inspection, analyze camera trap images to identify individual elephants based on unique features like head shape, tusks, and wrinkles on the trunk, similar to how fingerprints are used to identify humans.
Automated Counting:AI can automate the process of identifying elephants from images, reducing the need for manual inspection by staff and minimizing errors.
Behavioral Analysis:AI can track the movement patterns of elephants, providing insights into their behavior and impact on the ecosystem.
2. AI in Aerial Surveys and Satellite Imagery:
Aerial Surveys:AI is integrated with aerial surveys to count and track elephants from recorded data, eliminating the need for human presence on the aircraft and reducing miscounts.
Satellite Imagery:AI can be used to count and monitor habitat use of elephants from high-resolution satellite images.
3. AI for Protecting Forest Elephants in Central Africa:
WWF and IBM Collaboration:WWF and IBM are collaborating to use AI to protect African forest elephants in the Democratic Republic of Congo, Gabon, and the Republic of Congo, where populations have declined significantly.
MVI Technology:IBM's AI-powered visual inspection technology is used to identify individual elephants from camera trap photos, helping to improve conservation efforts in the Congo Basin.
Quantifying Nature's Value:The project aims to assess the financial value of nature's contributions, such as carbon sequestration services provided by elephants, which can help unlock sustainable finance investments.
4. AI for Early Warning Systems:
Real-time Alerts: AI can be used to detect elephants near human settlements and trigger real-time alerts to trained community champions who can then use resources to ward off the animals before they come into close proximity of villages and farmlands.
5. AI and Drones:
Behavioral Studies:Drones equipped with AI can be used to study elephant behavior in the wild, allowing researchers to observe elephants at a distance.
Habituation to Drones:Scientists are habituating elephants to drones to facilitate research and minimize the impact of the technology on the animals.
6. Challenges and Future Directions:
Cost of Satellite Images:The high cost of acquiring high-resolution satellite images is a challenge for the widespread adoption of AI-based elephant monitoring.
Canopy Obstructions:The inability to detect elephants obstructed by canopies limits the effectiveness of some AI-based monitoring methods.
Continued Development:Ongoing research and development are exploring new ways to utilize AI for elephant conservation, including the development of new cameras and AI models.
II. In Mali Gourma Region there are Desert Elephants, which still need to protect and research.

Mali Elephant Project | ICFC
Mali's Gourma region is home to a unique population of "desert elephants," which are the northernmost population of African elephants and one of only two desert-adapted elephant populations in the world. These elephants are also known for undertaking the longest elephant migration in the world. They face numerous threats, including habitat loss due to human activities, poaching, and instability in the region.
Here's a more detailed look:
Unique Population and Migration:
Desert-adapted:The Gourma elephants are one of only two populations globally adapted to desert environments.
Northernmost:They are the most northerly elephants in Africa since the loss of the Atlas Mountains population in the 1970s.
Longest Migration:They undertake the longest known elephant migration in the world, traversing a vast area to find resources.
Challenges and Threats:
Habitat Loss:Clearing land for agriculture and increasing livestock populations have put pressure on elephant habitats and water sources.
Poaching:Ivory poaching is a significant threat, exacerbated by instability and insecurity in the region.
Human-Elephant Conflict:As human populations grow and encroach on elephant habitats, conflicts are becoming more frequent.
Instability:Political and social unrest have created a volatile environment, making it harder to protect elephants.
This article is generated by AI friend. Ups, coś poszło nie tak. adopted Thomasz Pietrzak/.
0 notes
Text
AI-Driven Market Analysis: How Investment Bankers Are Predicting Trends in 2025

The world of investment banking is undergoing a seismic shift, and at the heart of this transformation lies artificial intelligence (AI). In 2025, AI-driven market analysis is no longer a futuristic concept but a cornerstone of how investment bankers predict trends, make decisions, and deliver value to clients. From crunching massive datasets to identifying patterns invisible to the human eye, AI is redefining the precision and speed of financial forecasting. For professionals and aspiring bankers looking to stay ahead, enrolling in a Financial Analytics Course with Placement Guarantee or an Investment Banking and Financial Modelling course in Mumbai has become a critical step toward mastering these cutting-edge tools. Let’s dive into how AI is reshaping market analysis and what it means for the future of investment banking.
The Rise of AI in Investment Banking
Investment banking has always been about data, mountains of it. Balance sheets, market trends, economic indicators, and client portfolios generate a deluge of information that bankers must sift through to make informed decisions. Historically, this process relied heavily on human expertise, intuition, and time-intensive analysis. But in 2025, AI has taken centre stage, automating complex tasks and providing insights at unprecedented scale and speed.
AI-driven market analysis leverages machine learning algorithms, natural language processing (NLP), and predictive modeling to process vast datasets in real time. These tools can analyze everything from stock market fluctuations to geopolitical events, delivering actionable insights faster than any team of analysts could. For instance, AI can scan thousands of news articles, earnings reports, and social media posts to gauge market sentiment, something that would take humans days or even weeks. This capability is particularly valuable in volatile markets, where split-second decisions can mean the difference between profit and loss.
For those entering the field, a Financial Analytics Course with Placement Guarantee equips professionals with the skills to harness these tools. Such courses teach not only the technical aspects of AI but also how to interpret its outputs in the context of financial markets. Similarly, an Investment Banking and Financial Modelling course in Mumbai provides hands-on training in building models that integrate AI-driven insights, ensuring bankers can stay competitive in this rapidly evolving landscape.
How AI Enhances Market Predictions
The power of AI lies in its ability to uncover patterns and correlations that humans might miss. In 2025, investment bankers rely on AI to predict market trends with remarkable accuracy. Here’s how it works:
Data Integration and Real-Time Analysis AI platforms aggregate data from diverse sources, financial statements, economic reports, consumer behaviour metrics, and even alternative data like satellite imagery or web traffic. By processing this data in real time, AI provides a holistic view of market dynamics. For example, an investment bank might use AI to analyse shipping data to predict supply chain disruptions, enabling clients to adjust their portfolios proactively.
Sentiment Analysis and Behavioural Insights NLP algorithms scan news outlets, social media platforms, and earnings call transcripts to gauge market sentiment. In 2025, this is critical for understanding how public perception influences stock prices or sector performance. For instance, a sudden spike in negative sentiment around a tech company’s product launch could signal a potential stock dip, allowing bankers to advise clients accordingly.
Predictive Modelling for Risk Management AI’s predictive capabilities are a game-changer for risk assessment. Machine learning models can simulate thousands of market scenarios, stress-testing portfolios against economic shocks or policy changes. This allows bankers to recommend strategies that minimize risk while maximizing returns. For example, AI might predict how a Federal Reserve interest rate hike could impact bond yields, enabling bankers to adjust client investments in real time.
Personalized Investment Strategies AI enables hyper-personalized portfolio management by analysing individual client preferences, risk tolerance, and financial goals. In 2025, investment banks use AI to tailor strategies that align with each client’s unique needs, whether it’s a hedge fund seeking high-risk opportunities or a retiree prioritizing stability.
To leverage these capabilities, professionals need specialized training. The Best Financial Analytics Course in Mumbai offers modules on machine learning, data visualization, and predictive modelling, ensuring graduates can apply AI tools effectively. Likewise, an Investment Banking and Financial Modelling course in Mumbai teaches students how to integrate AI insights into financial models, a skill that’s now indispensable in the industry.
The Human Element in AI-Driven Analysis
While AI is a powerful tool, it’s not a replacement for human judgment. Investment bankers in 2025 combine AI’s analytical prowess with their own expertise to deliver nuanced insights. AI can process data and identify trends, but it’s the banker’s understanding of market context, client needs, and economic history that brings those insights to life.
For example, an AI model might flag a potential investment opportunity in renewable energy based on rising global demand. However, a seasoned banker would consider regulatory changes, geopolitical risks, and client priorities before making a recommendation. This synergy between AI and human intuition is what sets top-tier investment banks apart.
Training programs like a Financial Analytics Course with Placement Guarantee emphasize this balance, teaching students how to interpret AI outputs while honing their critical thinking skills. Similarly, the Best Financial Analytics Course in Mumbai includes case studies that simulate real-world scenarios, helping students learn how to combine AI-driven insights with human judgment.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
As transformative as AI is, it’s not without challenges. Data quality is a significant concern, AI models are only as good as the data they’re fed. Inaccurate or biased data can lead to flawed predictions, potentially costing clients millions. Investment banks in 2025 invest heavily in data governance to ensure their AI systems are reliable and unbiased.
Ethical considerations also come into play. AI-driven market analysis can amplify inequalities if not carefully managed. For instance, algorithms that prioritize profit over social impact might favor certain industries or demographics, raising questions about fairness. Investment banks are increasingly adopting ethical AI frameworks to address these concerns, ensuring their tools align with societal values.
Professionals trained through an Investment Banking and Financial Modelling course in Mumbai learn to navigate these challenges. These courses cover data ethics, model validation, and regulatory compliance, preparing students to use AI responsibly. Similarly, the Best Financial Analytics Course in Mumbai includes modules on bias detection and mitigation, ensuring graduates are equipped to handle the ethical complexities of AI-driven finance.
The Role of Training in Preparing for 2025
As AI reshapes investment banking, the demand for skilled professionals is skyrocketing. Firms are seeking candidates who can bridge the gap between technical expertise and financial acumen. This is where specialized training comes in.
A Financial Analytics Course with Placement Guarantee offers a direct path to a career in this dynamic field. These programs cover AI tools, data analysis, and financial modelling, ensuring graduates are job-ready. The placement guarantee is a key differentiator, providing students with confidence that their skills will lead to real-world opportunities.
Similarly, an Investment Banking and Financial Modelling course in Mumbai is tailored to the needs of India’s financial hub. Mumbai, home to major banks and financial institutions, is a hotspot for AI-driven finance. These courses teach students how to build sophisticated financial models, interpret AI outputs, and advise clients on complex investment strategies.
The Best Financial Analytics Course in Mumbai goes a step further, combining cutting-edge AI training with practical experience. Students work on real-world projects, such as analysing market trends or building predictive models, giving them a competitive edge in the job market.
The Future of AI-Driven Market Analysis
Looking ahead, AI’s role in investment banking will only grow. By 2030, experts predict that AI will power nearly every aspect of market analysis, from trade execution to client reporting. Emerging technologies like quantum computing could further enhance AI’s capabilities, enabling even faster and more accurate predictions.
For investment bankers, staying ahead means embracing continuous learning. Enrolling in a Financial Analytics Course with Placement Guarantee or an Investment Banking and Financial Modelling course in Mumbai is a proactive step toward mastering AI-driven finance. These programs not only teach technical skills but also foster the adaptability needed to thrive in a rapidly changing industry.
Moreover, the Best Financial Analytics Course in Mumbai is designed to evolve with the industry. As new AI tools and techniques emerge, these courses update their curricula to ensure students remain at the forefront of innovation. This forward-thinking approach is critical in a field where technology advances at breakneck speed.
Conclusion
In 2025, AI-driven market analysis is transforming investment banking, enabling professionals to predict trends with unprecedented accuracy and speed. From real-time data integration to sentiment analysis and predictive modelling, AI is unlocking new possibilities for bankers and their clients. However, the human element remains essential, as does the need for specialized training to navigate this evolving landscape.
For aspiring bankers, a Financial Analytics Course with Placement Guarantee offers a gateway to a rewarding career, blending AI expertise with practical financial skills. Similarly, an Investment Banking and Financial Modelling course in Mumbai provides the tools to excel in India’s financial capital. And for those seeking the gold standard, the Best Financial Analytics Course in Mumbai delivers cutting-edge training that prepares students for the challenges and opportunities of 2025 and beyond.
As AI continues to shape the future of finance, one thing is clear: investment bankers who embrace these tools and the training to wield them, will lead the charge in predicting and capitalizing on market trends. The future is here, and it’s powered by AI.
#investment banking#marketanalysis#artificial intelligence#technology#innovation#entrepreneur#education
0 notes