#U.S. Market Insights
Text
Data-Driven Decision-Making: The Backbone of Successful U.S. Business Strategies
Explore the transformative impact of data-driven decision-making on businesses in the United States. Uncover key insights and strategies that propel success, driving innovation and resilience in today's dynamic market landscape.
#Data-Driven Decision-Making#Business Strategies#U.S. Market Insights#Data Analysis#Business Innovation#Market Resilience#Strategic Decision-Making#Analytics in Business#Competitive Advantage#Business Intelligence#Market Trends#Data-Backed Innovation#Decision Science#Corporate Decision-Making#Business Optimization#Information-driven Strategies#Market Dynamics#Adaptive Business Models#Insightful Decision Processes#Decision Support Systems
0 notes
Text
U.S. Opioids Market Is Estimated To Witness High Growth Owing To Increasing Prevalence Of Chronic Pain
Market Overview:
The U.S. Opioids Market offers a range of pharmaceutical products that are used to manage and treat chronic pain. Opioids are highly effective in relieving moderate to severe pain, making them essential for patients suffering from conditions such as cancer, post-surgical pain, and chronic musculoskeletal pain. The market provides a variety of opioids, including extended-release formulations that provide long-lasting pain relief. The advantages of opioids include their ability to alleviate pain and improve the quality of life for patients with chronic pain conditions. The need for these products is driven by the increasing prevalence of chronic pain across the United States.
Market Key Trends:
One key trend in the U.S. Opioids Market is the growing adoption of abuse-deterrent formulations. Due to the addictive nature of opioids, there has been a rise in the misuse and abuse of these drugs. To address this issue, pharmaceutical companies have developed abuse-deterrent formulations that make it harder for individuals to manipulate the drug for non-medical purposes, such as crushing or dissolving it. These formulations incorporate physical or chemical barriers that prevent abuse and discourage tampering. The adoption of abuse-deterrent formulations is expected to increase, driven by regulatory initiatives and healthcare provider awareness about the risks associated with opioid misuse. The global U.S. Opioids Market Growth is estimated to be valued at US$16,285.2 million in 2022 and is expected to exhibit a CAGR of 5.5% over the forecast period 2022-2030, as highlighted in a new report published by Coherent Market Insights.
PEST Analysis:
Political: The political landscape plays a significant role in the U.S. opioids market. Government regulations and policies addressing drug usage and prescription are crucial factors that impact the market. These regulations aim to control the opioid crisis, reducing the misuse and addiction associated with these drugs.
Economic: The economic factors influencing the U.S. opioids market include healthcare expenditure, insurance coverage, and the overall economic condition of the country. Economic growth and stability can contribute to increased healthcare spending, leading to higher demand for opioids.
Social: The social aspect of the U.S. opioids market revolves around the societal perception of pain management and the use of opioids. Public awareness campaigns and education regarding addiction and overdose risks have influenced social attitudes towards opioids, leading to increased caution and a decline in opioid prescriptions.
Technological: Technological advancements such as pain management devices, drug delivery systems, and digital health solutions are transforming the U.S. opioids market. These innovations enhance the efficacy of pain management while minimizing the risks associated with opioids.
Key Takeaways:
The U.S. opioids market is expected to witness high growth, exhibiting a CAGR of 5.5% over the forecast period from 2022 to 2030. The market is driven by increasing cases of chronic pain, the aging population, and the growing prevalence of conditions requiring palliative care. Furthermore, the rising awareness about pain management and the introduction of advanced technologies are also contributing to market growth.
Regionally, the United States dominates the opioids market due to its well-established healthcare infrastructure, high healthcare expenditure, and the prevalence of chronic pain conditions. The country is at the forefront of developing regulations to control the opioid crisis, leading to a decline in opioid prescriptions and increased focus on alternative pain management approaches.
#U.S. Opioids Market#U.S. Opioids Market Size#Coherent Market Insights#U.S. Opioids Market Demand#U.S. Opioids Market Growth#U.S. Opioids Market Share#U.S. Opioids Market Analysis#U.S. Opioids Market Trends#U.S. Opioids Market Forecast
0 notes
Text
U.S. Healthcare Staffing Market Is Estimated To Witness High Growth Owing To Increasing Demand for Skilled Medical Professionals

The global U.S. Healthcare Staffing market is estimated to be valued at US$ 20,626.2 million in 2022 and is expected to exhibit a CAGR of 3.4% over the forecast period 2023-2030, as highlighted in a new report published by Coherent Market Insights.
A) Market Overview:
The U.S. Healthcare Staffing market refers to the provision of temporary healthcare professionals to healthcare facilities such as hospitals, clinics, and nursing homes. This helps to bridge the gap between the demand for healthcare services and the availability of skilled medical professionals. It provides flexibility for healthcare facilities to meet their staffing requirements and ensures uninterrupted patient care. The need for healthcare staffing arises from factors such as increasing patient inflow, seasonal demand fluctuations, and staff shortages due to illness or vacation.
B) Market Key Trends:
One key trend shaping the U.S. Healthcare Staffing market is the increasing demand for skilled medical professionals. With the aging population and rising prevalence of chronic diseases, there is a growing need for specialized healthcare services. This requires a workforce with the necessary skills and qualifications to provide quality care. As a result, healthcare facilities are increasingly relying on healthcare staffing agencies to source skilled professionals such as nurses, physicians, therapists, and technologists.
For example, Envision Healthcare Corporation, one of the key players in the market, provides a wide range of healthcare staffing solutions, including emergency medicine, anesthesiology, radiology, and neonatology. By partnering with healthcare staffing agencies, healthcare facilities can access a pool of qualified professionals on-demand, reducing recruitment and training costs.
C) PEST Analysis:
- Political: The U.S. healthcare industry is influenced by government policies and regulations such as the Affordable Care Act. These policies impact the demand for healthcare services and indirectly affect the demand for healthcare staffing.
- Economic: Economic factors such as GDP growth, disposable income, and healthcare expenditure impact the overall healthcare market, including healthcare staffing.
- Social: Changing demographics, the aging population, and increased awareness about healthcare services influence the demand for healthcare staffing.
- Technological: Technological advancements in healthcare, such as telehealth and remote patient monitoring, have the potential to disrupt the traditional healthcare workforce. Healthcare staffing agencies need to adapt to these technological changes to remain competitive.
D) Key Takeaways:
Paragraph 1: The U.S. Healthcare Staffing Market Demand is expected to witness high growth, exhibiting a CAGR of 3.4% over the forecast period, due to increasing demand for skilled medical professionals. Healthcare facilities are relying on healthcare staffing agencies to bridge the staffing gap and ensure quality patient care.
Paragraph 2: In terms of regional analysis, the United States is expected to be the fastest growing and dominating region in the global U.S. Healthcare Staffing market. The country's large healthcare industry, coupled with the high demand for healthcare services, creates a favorable environment for the growth of the healthcare staffing market.
Paragraph 3: Key players operating in the U.S. Healthcare Staffing market include Envision Healthcare Corporation, AMN Healthcare, CHG Management, Inc., Maxim Healthcare Group, Cross Country Healthcare, Inc., Syneos Health, Inc., and Almost Family, Inc., among others. These companies offer a wide range of healthcare staffing solutions and have a strong presence in the U.S. market.
#Healthcare#U.S. Healthcare Staffing Market#U.S. Healthcare Staffing Market Demand#U.S. Healthcare Staffing Market Forecast#Coherent Market Insights
0 notes
Text
U.S. Contract Research Organization (CROs) Market Is Estimated To Witness High Growth Owing To Increasing Pharmaceutical Research and Outsourcing Trend
The U.S. Contract Research Organization (CROs) market is estimated to be valued at USD 15,918.6 million in 2022 and is expected to exhibit a CAGR of 9.6% over the forecast period 2022-2030, as highlighted in a new report published by Coherent Market Insights. A) Market Overview: The U.S. Contract Research Organization (CROs) market refers to the outsourcing of pharmaceutical, biotechnology, and medical device research services to third-party organizations. These organizations provide a wide range of services such as clinical trials, preclinical research, laboratory services, data management, regulatory consulting, and market access services. The market plays a crucial role in accelerating drug development and reducing costs for pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies. B) Market Dynamics: The U.S. Contract Research Organization (CROs) market is driven by the following factors: 1. Increasing Pharmaceutical Research: The pharmaceutical industry is witnessing significant growth in research and development activities. This is primarily driven by the rising demand for innovative drugs and therapies to address unmet medical needs. Contract research organizations play a vital role in helping pharmaceutical companies conduct clinical trials and preclinical research efficiently and effectively. 2. Outsourcing Trend: Pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies are increasingly outsourcing their research and development activities to CROs. This outsourcing trend is driven by the need to reduce drug development costs, access specialized expertise, and leverage the flexibility and scalability offered by CROs. Outsourcing allows companies to focus on their core competencies while benefiting from the specialized services provided by CROs. C) SWOT Analysis: Strength: 1. Expertise in Clinical Research: Contract research organizations have extensive expertise in conducting clinical trials and managing the regulatory requirements associated with drug development. 2. Efficiency and Cost Savings: CROs offer specialized services, infrastructure, and resources, allowing pharmaceutical companies to save costs and accelerate drug development. Weakness: 1. Dependence on Outsourcing: Contract research organizations heavily rely on outsourcing contracts from pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies. Any reduction in outsourcing activities can negatively impact the business of CROs. 2. Regulatory Challenges: CROs need to comply with stringent regulatory guidelines in conducting clinical trials and managing data. Any non-compliance can lead to delays or penalties. Opportunity: 1. Increasing Outsourcing in Emerging Markets: Emerging markets such as Asia-Pacific and Latin America offer significant opportunities for CROs due to the growing pharmaceutical industry, cost advantages, and availability of a large patient pool for clinical trials. 2. Expansion of Services: Contract research organizations can expand their service offerings beyond traditional clinical trials to areas such as real-world evidence generation, health economics, and outcomes research, and digital health solutions. Threats: 1. Intense Competition: The U.S. Contract Research Organization (CROs) Market is highly competitive with several global and regional players. Intense competition may lead to pricing pressures and reduced profit margins. 2. Uncertainty in Drug Development: The success of drug development is uncertain, and failure in clinical trials can significantly impact the revenues of both pharmaceutical companies and CROs. D) Key Takeaways: 1. Market Size: The U.S. Contract Research Organization (CROs) market is expected to witness high growth, exhibiting a CAGR of 9.6% over the forecast period. This growth is driven by increasing pharmaceutical research and the outsourcing trend.

0 notes
Text
U.S. bottled water market

The U.S. bottled water market has emerged as a dynamic and rapidly growing industry, driven by shifting consumer preferences and an increased focus on health and wellness.
Read More: https://blogomania007.blogspot.com/2023/06/unleashing-potential-exploring-growth.html
0 notes
Text
U.S. Care Services Market | Cost-Efficient Alternatives To Expensive Hospital Stays
The U.S. care services market size is expected to reach USD 748.5 billion by 2030 expanding at a CAGR of 5.76% based on a new report by Grand View Research, Inc. Growing geriatric population and rising incidence of target diseases such as dementia and Alzheimer’s as well as orthopedic diseases are factors expected to fuel the industry growth in the times to come. Increasing treatment cost is one of the prime concerns for governments and health organizations and hence they are striving to curb healthcare costs. Care services are cost-efficient alternatives to expensive hospital stays and thus are economic for a longer time duration.
Gain deeper insights on the market and receive your free copy with TOC now @: U.S. Care Services Market Report
The federal government is playing an active role in financing the care services. SNFs, hospice, and home healthcare are financed by the government. The U.S. government introduced the COVID-19 relief fund and provided funding of USD 175 billion to SNFs, USD 30 billion to hospice care, and USD 20 billion to assisted living facilities, as per the Department of Health and Human Services. From 2016 up to 2021, the government provided USD 184 million to hospice areas in the Office of the Parliamentary Budget Officer.
The COVID-19 pandemic has positively impacted home healthcare services & the growth of technology in care services. Telehealth services at home & house calls have been the main option for residents, with inpatient hospital facilities being busy with handling COVID-19 cases. Since the onset of the pandemic, the growth in telehealth use has increased significantly.
#U.S. Care Services Market Size & Share#U.S. Care Services Market Latest Trends#U.S. Care Services Market Growth Forecast#U.S. Care Services Industry Insights#COVID-19 Impacts On U.S. Care Services Market#U.S. Care Services Market Revenue Value
0 notes
Text
#“u.s. tahini market”#“u.s. tahini market overview”#“u.s. tahini research report”#“u.s. tahini research insights”#“u.s. tahini business research report”
0 notes
Link
0 notes
Note
out of curiosity, if Max doesn’t release its metrics, then what metrics are you actually using to make these statements about the show’s popularity? what does “it’s currently in the 99.7th percentile of the comedy genre, meaning it’s in higher demand than 99.7% of all comedy series in the u.s.” even mean? How are you measuring what’s “in demand” - by who? Where? It’s bold to claim that this show was wildly popular (despite the fact that I never hear about it outside of tumblr, tho that’s a personal anecdote) but cancelled just for being queer, so I would be really interested to know where you’re getting all these numbers from. Thanks!
hey anon! first of all i am so sorry for the delayed response. i started typing something up and then i got distracted with something else and totally forgot about this in my drafts.
sure, i have no problem citing sources. i probably should’ve linked some in my original post, that’s absolutely fair.
this ended up way longer than i planned so bear with me, but a quick overview of what i’ll be going over:
1) what are the stats/where did they come from?
2) how is the show so popular?
3) was it really cancelled for being queer?
(also just a disclaimer that this will contain spoilers for the show)
1) first, the numbers
you’re right that hbo doesn’t release metrics to the public. in fact, ceo casey bloys tried to justify the cancellation to the hollywood reporter by saying “the numbers weren’t there,” despite refusing to say what exactly those numbers were or where they came from.
however, there are websites dedicated to researching/analyzing the data of different media. one of those is parrot analytics, who focus on industry insights like audience demand, competitive analysis, and content valuations. they’re trusted as a reliable source by forbes, the new york times, reuters, the wall street journal, and more.
this is what we can learn from them about our flag means death from a basic google search (note that all of this data is relevant to the last 30 days as of january 26 2024):
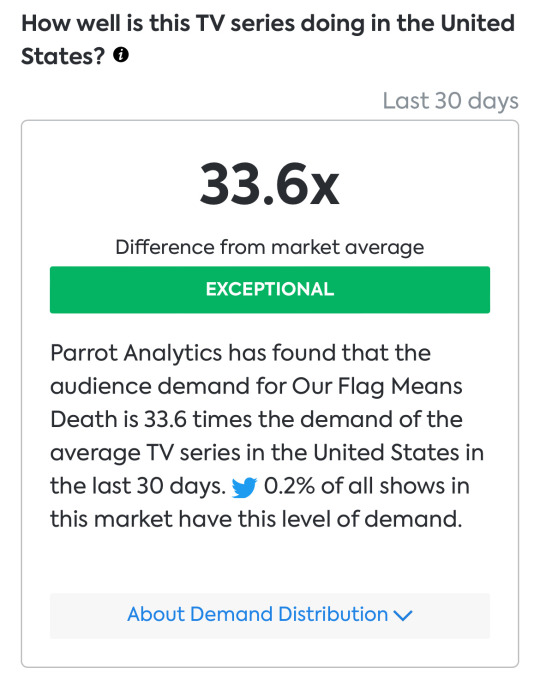
audience demand for our flag means death is now 33.6x greater than the average tv series in the united states. as explained in the “about demand distribution” section, this means it’s one of only 0.2% of all u.s. shows to fall in the “exceptional” performance range compared to the “average” demand benchmark of 64.1%.
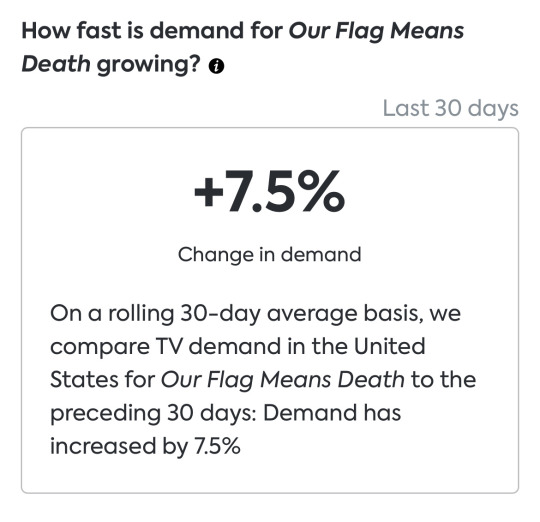
the change in demand for ofmd in the u.s. has increased by 7.5% compared to the average tv series.
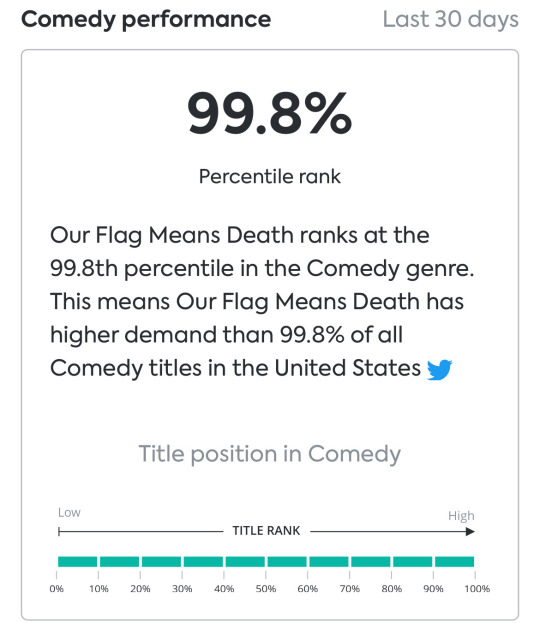
ofmd now actually ranks at the 99.8th percentile in the comedy genre in the u.s. i’m not a math person, but in basic terms, this is like a scale of measuring and comparing performances to create an average score. essentially, ofmd is performing at the very top of all comedy series in the u.s.
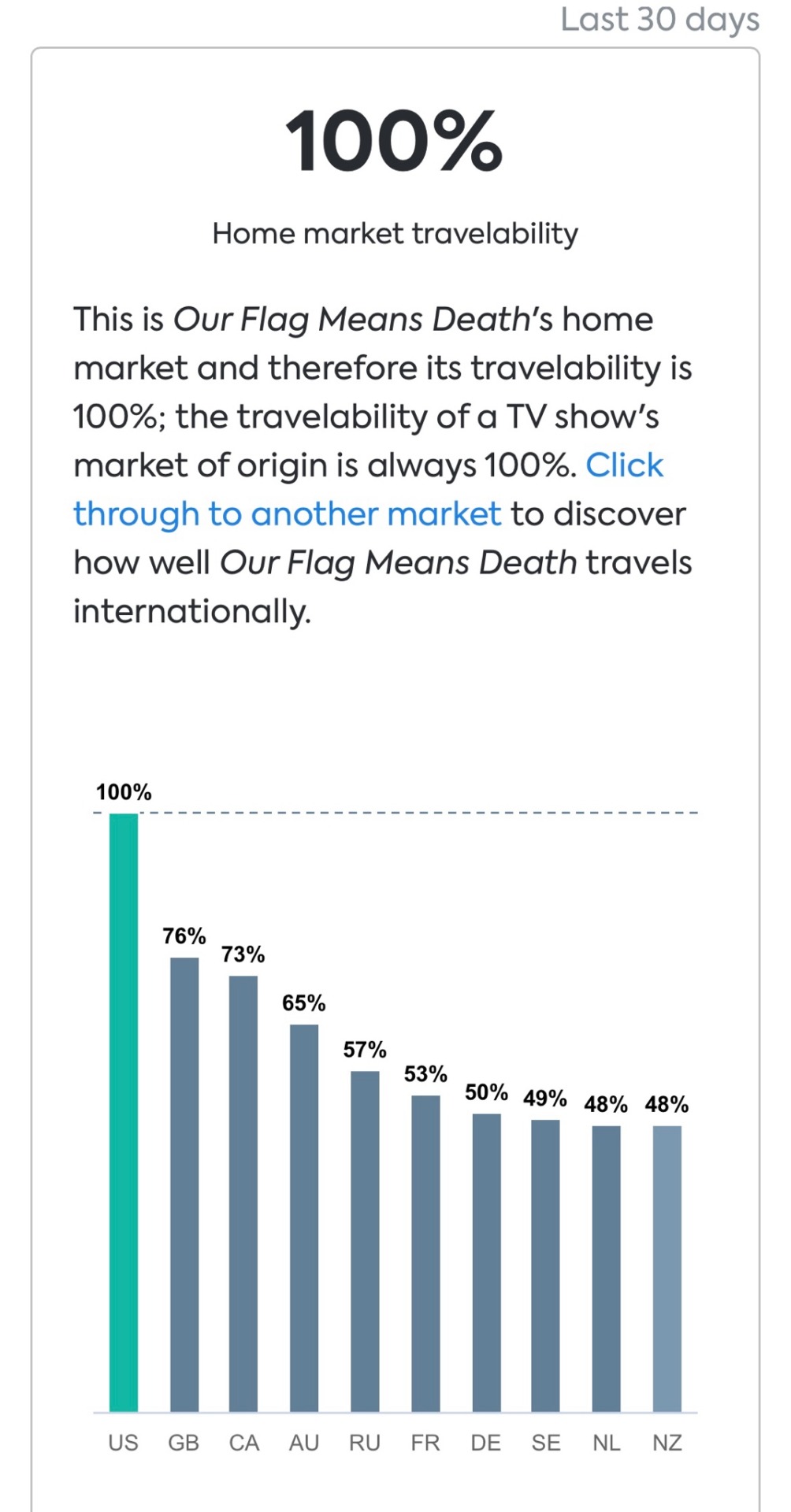
ofmd has 100% home market travelability. as it says above, the market of origin is always 100%, so in fairness i included the graph of international markets for comparison. some of these aren't super high, however (as explained by parrot analytics themselves) one of the key issues with the international market is accessibility to content, which has been an ongoing struggle for international fans. many people (i guess fittingly) have resorted to pirating ofmd because they don’t have access to max or affiliate streaming services in their country.
there are more stats i could have and wanted to go more in-depth into but it would make this even longer than it already is, so i’ll just leave some links you can check out if you’re interested and move on:
• comparison of ofmd's success to shows like ted lasso, euphoria, and peacemaker
• ofmd's placement as #1 most in-demand breakout series in the u.s. for 8 weeks
• ofmd's impressive 94% critics score and 95% audience score on rotten tomatoes
• how ofmd evolved from sleeper hit to a flagship series at max
• a list of ofmd's past and present award nominations/wins
• praise and recognition from news/entertainment sites: the atlantic (2022); the new york times (2023); tv guide (2023); vulture (2023); forbes (2023); the los angeles times (2022); vanity fair (2023)
2) so why haven’t you (or others) really heard of the show outside of tumblr despite all this success? likely because max did a terrible job marketing it.
ofmd first aired on hbo max (pre-merger before it was “max”) in march 2022. the entire season aired over one month, every thursday at 12am pst. season 2 followed a similar release schedule in october 2023.
season 1’s marketing was almost non-existent, pretty much relying on taika waititi’s name being attached. there was one teaser and one full-length trailer, as well as a few clips on youtube of taika and rhys darby answering pirate-themed trivia, all painting the show as a “silly pirate workplace/buddy comedy.” but hbo max didn’t put any real effort in because they didn’t care. david zaslav and the other higher-ups had no faith in the show and expected it to fail.
most people weren’t aware it was actually a romance due to the poor marketing, and although there were many romantically charged scenes between them, many were still wary to believe it wasn’t queerbaiting until ed & stede confessed their feelings and kissed.
showrunner david jenkins has said in interviews that he had no idea how deeply queerbaiting had hurt audiences and impacted their ability to trust what’s on screen without feeling like they’re being ridiculed, despite the fact that he was calling it a love story the whole time. it wasn’t until people realized they weren’t being queerbaited and that it was a funny, sincere show with a compelling plot that word-of-mouth began to spread. by the time the season 1 finale aired, there was a decent-sized fandom that continued to grow as it received more praise.
it was a fight to even get the show renewed for season 2, and david jenkins and the cast have majorly credited that renewal to the unexpected and massive fan response to the show, which basically forced hbo’s hand.
max didn’t bother trying to properly promote the series until season 2, when they begrudgingly accepted that it was one of their most profitable and successful shows. ofmd had huge billboards in times square, downtown los angeles, and on the side of hbo headquarters. they started accurately marketing the show as not just a workplace comedy at sea, but a heartfelt romcom. max began selling long-demanded merch (which became best sellers) and spent money on an FYC campaign.
i will emphasize, whether they liked it or not, they knew ofmd was their new moneymaker (especially with the recent end of succession, which was obviously a cash cow for hbo).

photo credit: @/bookishtheo
3) now if it was that successful, was it really cancelled just for being queer?
i mean, i can’t say that definitively. no one can. there are several potential factors at play that we may never know, and there have been a lot of rumours and speculation (many of which i don’t feel comfortable discussing in case they aren’t true) since the cancellation.
but do i believe the fact that it’s a queer romcom was one of those factors, especially since max has a history of cancelling and scrapping its most diverse projects? absolutely.
first and foremost, i can’t stress enough that this isn’t just a show with a few characters thrown in for token representation. ofmd is built on a diverse, intersectional cast and narratives, including:
• lgbtq+ representation: 5 main couples are explicitly queer (including mlm, wlw, nblm, and nblw relationships). multiple characters are implied to be poly, and there’s a polycule forming in season 2 that was hinted to be developed more in season 3. beyond relationships, it’s confirmed that (similarly to the way wwdits depicts all vampires as being pansexual) all of the pirates are somewhere on the queer spectrum.
• bipoc representation: the majority of the main cast are people of colour. this includes david fane, joel fry, leslie jones, samson kayo, vico ortiz, anapela polataivao, madeleine sami, samba schutte, ruibo qian, and taika waititi, as well as many guest actors (like rachel house, simone kessell, and maaka pohatu) and extras.
• disability representation: multiple characters have physical disabilities, most notably amputated/prosthetic limbs and visual impairment. a lot (actually most) of the characters also deal with mental health issues, particularly coping with severe trauma and suicidal ideation/behaviour.
• the show has been praised for addressing difficult and serious themes like toxic masculinity, colonialism, and self-discovery, all while still managing to be a witty comedy and not come across as “preachy.”
• the diversity also extends off-screen, with a team of directors, writers, and additional crew comprised of numerous bipoc, women, queer people, and trans/non-binary people.
my point isn’t just the quantity of representation, but the quality. they take great care and respect into every marginalized group depicted on-screen. the actors would often be consulted about their characters’ costumes, hair, tattoos, and the kind of language they use. it’s not a world where discrimination magically doesn’t exist, they just have zero tolerance for it. if a character does something homophobic or racist, you can guarantee they’ll quickly (and often violently) be punished.
so okay, sure, it’s got great representation. what does that have to do max cancelling it?
because they’ve been interfering with production from the start.
i already mentioned the marketing issues so i won’t get into that. it was also revealed in interviews with david jenkins after season 2 that hbo cut their budget by 40%, which is why they had to do everything they could to save money. this included letting go of some of the original cast (and even still having episodes where some of them don’t appear at all) and moving the entire production to AoNZ. the budget cuts also meant two less episodes, so they had to rush to fit an entire season’s worth of plot into eight half-hour long episodes.
but one of the biggest frustrations is hbo’s (alleged) censorship of the show. samba schutte revealed that the entire plot of episode 2x06 was completely different in the original script. before it was rewritten as “calypso’s birthday,” the episode took place during lucius & pete’s wedding and focused on the crew getting sick of the sexual tension between ed & stede and trying to get them to hook up (this aligned with lucius & pete getting engaged and ed & stede deciding to take things slow in the previous episode).
vico ortiz and writer jes tom have also commented that many scenes between jim, oluwande, and archie establishing them as a polycule were cut, including one of the three of them emerging from a bedroom in their underwear. jes has mentioned other elements of season 2 that had to be cut out or rewritten, like the implication of other poly dynamics between the crew and more sexually explicit scenarios and jokes.
considering that ofmd is an extremely sex-positive show that isn’t afraid to be raunchy or taboo, it’s clear that either higher-ups at hbo forced them to cut these things out or they had no choice but to cut them out due to tight budget/time restraints.
in addition to this, a recent article citing an “anonymous insider” has alleged that hbo was uncomfortable with and was unsure how to market the “shock violence” in the show (the same network that aired game of thrones), which david jenkins outright called out as being bullshit. ofmd is rated TV-MA and the posters and trailers all show the audience that it contains violent content. there is literally nothing more graphic in ofmd than any other pirate show — it’s probably a lot tamer than most of them, actually.
violence on the show is most frequently used in a comedic context, in the sense that it’s not meant to be seen as scary or taken seriously. the few instances of serious graphic imagery on the show are meant to invoke a mood shift, like ed’s transformation into the kraken or ned low’s murder. it should also be noted that some of the most graphic deaths are reserved for bigots, like ed snapping the neck of a colonizer who was ridiculing stede’s love letter.
it’s also most often used in a sexual context — not sexual violence, but violence as a sexual metaphor. more specifically the act of stabbing as a metaphor for penetration, as seen with both ed & stede and anne & mary. bearing all this in mind, it seems like the real issue here isn’t executives struggling to market explicit violence to a mainstream audience, but rather explicit gay content.
as much as we joke and affectionately call it the “gay pirate show,” ofmd has always been nothing more than an opportunity for rainbow capitalism for hbo (e.g. the fact that they waited three months to announce season 2 just so they could do it on the first day of pride month). like other cancelled queer media, ofmd was a way for hbo executives to show how “inclusive” and “accepting” they are when it was convenient (aka profitable) for them, but they never actually respected the show or us as a community.
it’s impossible to be certain of what the exact reasoning for cancellation was, especially when they won’t give us a clear answer themselves. and maybe it had nothing to do with ofmd being a queer romcom at all. maybe that’s all a horrible coincidence. but for hbo/max to axe a critically acclaimed and beautifully inclusive show that’s successful by every metric, with an extremely devoted fanbase, especially after casey bloys just had the nerve to ask “gay twitter” to hype up the gilded age? it doesn’t exactly put them in the best light regardless.
in summary, i’ll leave you with this editorial, which details how the campaign to save ofmd isn’t just about one show, but a fight to save the future of all queer art.
109 notes
·
View notes
Text
Executing a Successful Market Entry in the USA: A Research-Driven Guide
Explore our research-driven guide for a triumphant market entry in the USA. Navigate complexities, understand consumer behavior, and make informed decisions for success.
#Market entry strategy#USA market expansion#Successful entry guide#Market research insights#Business expansion in the USA#Consumer behavior analysis#Regulatory landscape navigation#Strategic market penetration#Informed decision-making#Entry success tips#Competitive analysis#U.S. market dynamics#Market research for entry#Entry planning guide#Business growth strategies#Data-driven market entry#Market exploration in the USA#Market entry consulting#Research-backed entry approach#Navigating U.S. business landscape
0 notes
Text
Eden of the East

Addressing Issues in Japan and Globally
Eden of the East" begins with the main character, Saki, expressing hopelessness about Japan’s future, feeling that meaningful change is impossible. This sentiment supports how resistant the Japanese work culture is to change and reform.
Globally, the series critiques neoliberal policies that emphasize individual competition at the expense of social welfare. The NEETs (Not in Employment, Education, or Training), represent young people let down by a system that offers little in terms of job security or personal fulfillment. This resonates on a global scale as many societies currently grapple with high youth unemployment, economic inequality, and the alienation of younger generations.

Relating to the Average American Life
While the story is about the flawed Japanese system, the themes are universally relatable. The challenges faced by NEETs parallel those of many young Americans who struggle with student debt, uncertain employment, and the rising cost of living. While young college graduates are able to find jobs compared to the Japanese, they’re unable to buy or rent a home as easily as the Baby Boomers and Generation X. The anime’s criticism of exploitative corporate practices and the pursuit of economic success reflects on concerns shared by many in the U.S., where the gig economy and rising inequality have reshaped the landscape of work.

Connections with "Work Culture" by Ross Mouer
Ross Mouer's chapter on Japanese work culture provides a valuable backdrop for understanding the issues related to the main characters in Eden of the East. Mouer discusses the evolution of work in Japan, from the postwar economic boom and the lifetime employment system to the current challenges posed by economic stagnation and labor market deregulation. The anime vividly portrays these shifts through the lens of young characters who reject traditional employment models in favor of more alternatives.
Mouer's insights into the historical context of Japan's work culture helped me better understand the story line. The long working hours that once defined success are shown to be increasingly out of touch with the needs and aspirations of modern youth.
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
Global U.S. Plastic to Fuel Market Is Estimated To Witness High Growth Owing To Increasing Environmental Concerns

The global U.S. Plastic to Fuel Market is estimated to be valued at US$ 117.3 Mn in 2022 and is expected to exhibit a CAGR of 9.3% over the forecast period 2023-2030, as highlighted in a new report published by Coherent Market Insights.
A) Market Overview:
The U.S. Plastic to Fuel Market refers to the process of converting plastic waste into usable fuels and chemicals. This market offers numerous advantages, including reducing plastic waste, preventing landfill pollution, and providing a sustainable solution for energy production. The need for products associated with this market arises from the ever-increasing plastic waste generated globally and the urgent need for effective waste management solutions.
B) Market Key Trends:
One key trend in the U.S. Plastic to Fuel Market is the growing focus on sustainable practices and reducing the environmental impact of plastic waste. Governments and organizations worldwide are implementing strict regulations and initiatives to promote the recycling and reutilization of plastics. For example, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has set targets for reducing plastic waste and increasing recycling rates. This trend is driving the adoption of plastic to fuel technologies as a more sustainable alternative to traditional waste disposal methods.
An example supporting this trend is the company Plastic2Oil. It utilizes a proprietary pyrolysis process to convert mixed waste plastics into synthetic fuel oil, which can be used for various applications such as heating or generating electricity. This innovative technology not only reduces plastic waste but also provides an alternative source of energy, contributing to the overall sustainability goals.
C) PEST Analysis:
Political: The U.S. Plastic to Fuel Market is influenced by political factors such as government regulations on plastic waste management and incentives for promoting recycling and renewable energy sources.
Economic: The market's growth is driven by factors like the increasing cost of landfilling plastic waste and the rising demand for sustainable energy solutions.
Social: Growing awareness about the environmental impact of plastic waste and the need for sustainable practices is shaping consumer behavior and driving the market's growth.
Technological: Advancements in technologies such as pyrolysis, catalytic depolymerization, and gasification are improving the efficiency and effectiveness of plastic to fuel conversion processes.
D) Key Takeaways:
Paragraph 1: The U.S. Plastic to Fuel Market Demand is expected to witness high growth, exhibiting a CAGR of 9.3% over the forecast period. This growth can be attributed to increasing environmental concerns and the need for sustainable waste management solutions. Governments, organizations, and individuals are recognizing the importance of reducing plastic waste and are actively seeking alternative methods for its disposal.
Paragraph 2: The North American region is expected to dominate the U.S. Plastic to Fuel Market due to stringent regulations on plastic waste management and the presence of key market players. Additionally, Asia Pacific is anticipated to be the fastest-growing region, driven by rapid industrialization, increasing plastic waste generation, and growing focus on sustainability.
Paragraph 3: Key players operating in the global U.S. Plastic to Fuel Market include Plastic2Oil, Agilyx Corporation, Vadxx Energy, and Green Envirotec Holdings. These companies are at the forefront of developing innovative technologies and solutions for converting plastic waste into usable fuels, contributing to a circular economy and a cleaner environment.
#U.S. Plastic to Fuel Market#U.S. Plastic to Fuel Market Demand#U.S. Plastic to Fuel Market Values#U.S. Plastic to Fuel Market Forecast#U.S. Plastic to Fuel Market Analysis#plastic waste#fuel sources#plastic-to-fuel technology#Coherent Market Insights
0 notes
Text
What would Donald Trump’s foreign policy look like, should he win a second presidential term? The debate ranges between those who believe he will abandon Ukraine, withdraw from NATO, and herald a “post-American Europe”—and those who predict he will escalate the Russian-Ukrainian war and continue his fiercely anti-communist policies. Foreign governments have been frantically reaching out to Trump and Republican circles to understand, if not influence, the future direction of his policies; one such visit may have even played a role in Trump’s acquiescence to the most recent batch of U.S. military aid to Ukraine following months of delay by many of his Republican supporters in the U.S. Congress.
One fact is already clear: If Trump regains the presidency, he and his potential advisors will return to a significantly changed global landscape—marked by two regional wars, the threat of a third in Asia, the return of great-power geopolitics, and globalization measurably in decline. While many expect a Trump 2.0 to be a more intense version of Trump 1.0, his response to the dramatic changes in the geopolitical environment could lead to unexpected outcomes.
Trump may now be less eager to abandon Europe given fast-rising European defense spending and an ongoing major war. The strengthening U.S. economy and flux in global supply chains could facilitate a broader decoupling from China and market-access agreements with allies. Expanded Iranian aggression could make it easier for Trump 2.0 to build a large international coalition. An examination of these and other changes of the last four years could yield surprising insights into how a second Trump administration could differ significantly from the first.
Since Trump left office, the U.S.-Mexico border crisis has worsened significantly. In 2020, Trump’s last full year in office, U.S. Customs and Border Protection carried out 646,822 enforcement actions, including against three individuals on the Terrorist Screening Data Set. By 2023, this had skyrocketed to 3.2 million encounters, including 172 people on the terrorist list. Under the Biden-Harris administration, there have been some 10 million illegal border crossings, including nearly 2 million known so-called gotaways—illegal crossers who could not be apprehended. The unsecured border, broken asylum process, and overwhelmed immigration courts have enabled significant fentanyl trafficking, resulting in over 200,000 American deaths in the last three years.
For a second Trump administration, sealing the border would be the critical national security issue, overshadowing all others. The Republican platform calls for completion of the border wall, the use of advanced technology on the border, and shifting the focus of federal law enforcement to migration. It also proposes redeploying troops from overseas to the southern border and deploying the U.S. Navy to impose a fentanyl blockade. Americans now see the border as a major problem, and Congress is likely to support significant spending. This reallocation will impact other areas, since the U.S. Army and Navy are already struggling with personnel and fleet size targets. Navigating tensions with Mexico and Central American countries, many of which have free-trade agreements with the United States and receive U.S. assistance, will be challenging.
Facing escalating regional wars and the smallest U.S. military in generations, Trump would likely oversee the most significant U.S. military buildup in nearly 50 years. The U.S. Armed Forces are shrinking, and the defense budget is close to its post-World War II low in terms of both federal budget share and percentage of GDP. The capacity, capabilities, and readiness of the U.S. military are weakening, and the defense industrial base has atrophied. The disastrous defeat in Afghanistan has led to a significant drop in Americans’ confidence in the military.
Trump has long supported a bigger and stronger military, but his administration’s modest budget increases primarily went to personnel, operations, and maintenance, with little investment in capabilities. Under then-Defense Secretary James Mattis, the 2018 National Defense Strategy abandoned the long-standing U.S. doctrine of maintaining readiness to fight wars in two regions simultaneously, focusing instead on deterring China in the Indo-Pacific. Today’s Trump-approved Republican platform pledges a larger, modern military, investment in the defense industrial base, and a national missile defense shield. Republican Sen. Roger Wicker, likely the next chair of the Senate Armed Services Committee, has proposed a detailed plan to raise defense spending from 3 percent of GDP in 2024 to 5 percent within five to seven years. This plan aligns with Trump’s policies and could lead to a domestic manufacturing boom. Trump could announce the first-ever trillion-dollar defense budget with broad Republican support, determined not to be remembered as the president who let China surpass the U.S. militarily.
Notwithstanding the Biden administration’s climate agenda, the United States’ historic rise as the world’s energy superpower could empower Trump to pursue more punitive policies against Russia and Iran while wielding greater leverage over China. The United States is now producing and exporting more energy than ever, even as its carbon emissions have decreased, largely due to the shift from coal to gas. In 2019, the country became a net energy exporter. Since 2017, total energy exports have nearly doubled, and the country has surpassed Russia and Saudi Arabia to become the world’s biggest oil producer. By further ramping up liquefied natural gas exports to Europe, a second Trump administration could reduce Russia’s influence, reshape European geopolitics, and strengthen trans-Atlantic ties. It would also greatly reduce the trade deficit with Europe, something Trump frequently rails about. Expanding energy production would also increase U.S. leverage over China, the world’s largest energy importer. Greater production—as well as closer alignment with Saudi Arabia under Trump—could do much to lower gas prices in the United States and oil prices globally. This, in turn, would allow Trump to pursue more aggressive strategic policies, such as striking Iranian nuclear assets or, should he wish to do so, diminishing Russian oil and gas exports.
The relative strength of the U.S. economy and major shifts in trading patterns would give another Trump administration far greater leverage on trade—including winning a trade war with China and striking new or revised trade deals with others.
Many Americans have a pessimistic view of their country’s economy, but it is far stronger relative to its peers than in 2016 or 2020. This year, the U.S. economy will account for an estimated 26 percent of global GDP, the highest share in almost two decades. It was nearly four times the size of Japan’s when Trump first entered office, and it will be seven times as large by the end of this year. As recently as 2008, the U.S. and Eurozone economies were similar in size. Today, the former towers over the latter, with the U.S. economy almost 80 percent larger. Britain’s relative decline is similar.
The strength of the U.S. economy would give Trump the leverage to strike the fair and reciprocal trade deals he seeks. Japan, facing an ever-aggressive China and urgently needing to boost economic growth, might build on the 2019 U.S.-Japan market access deal. Trump could resume the talks with Britain from the end of his first term with more leverage; a former Trump official indicated that a deal with Britain would be a priority in a second term. Trump might also revisit negotiations with the EU, following up on a market access agreement signed in 2019 following his imposition of tariffs. After eight years on top, the United States has overtaken China to be Germany’s top trading partner again. Trump’s aim to secure better deals is evident, and he may find more willing partners than before.
The same dynamics may lead to a far broader trade war with and decoupling from China. The U.S. economy has grown relative to China’s over the past eight years, with the gap widening in both directions: The U.S. economy is larger and the Chinese one smaller than economists expected. The forecast for when China’s economy might surpass the United States’ keeps sliding further and further into the future and may never happen at all. The International Monetary Fund projects that China’s share of the Asia-Pacific region’s GDP will be slightly smaller in five years than it is today, and it may never become the majority share. Even China’s official, flattering statistics suggest its economy is experiencing a lost decade due to deeply structural challenges, not temporary ones.
Over the past eight years, the U.S. economy has also become less dependent on foreign trade, including with China. In 2016, China was the top U.S. trading partner, accounting for more than 20 percent of U.S. imports and about 16 percent of total U.S. trade. By 2023, China slipped to third place, accounting for 13.9 percent of imports and 11.3 percent of trade. This shift would give greater credibility to Trump’s threats to revoke China’s most-favored nation trading status and impose wide-ranging tariffs. While these measures would have economic costs for Americans, around 80 percent of Americans view China unfavorably today, a significant increase from 2017, and the United States is now better positioned to withstand a protracted trade war with China than a few years ago.
Trump 2.0 would have the potential to lead a broader containment approach toward China. First, Trump and most Americans blame the Chinese government for the COVID-19 pandemic, which killed more than 1 million Americans, forced the U.S. economy into a deep recession, and likely cost Trump his reelection in 2020. Whether through trade measures, sanctions, or a demand for reparations, Trump will seek to hold China accountable for the estimated $18 trillion in damage the COVID-19 pandemic caused to the United States. In parallel, he is likely to end the attempts at partnership made by the Biden administration and Trump during parts of his first term. Issues like climate change, public health, foreign investment, Chinese land purchases in the United States, and Beijing’s role in the fentanyl epidemic will be viewed through the lens of strategic independence from China, as outlined in the Republican platform.
Second, the United States’ major European allies have become much more critical of China than when Trump left office—the result of COVID-19, Chinese “wolf warrior” diplomacy, Beijing’s support for Moscow’s war in Ukraine, and mounting issues concerning trade, technology, and supply chains. The references to China in the 2024 G-7 summit statement and NATO summit communique, compared to the last versions under Trump in 2019, make that clear. Europe is following Washington’s lead in imposing tariffs on Chinese electric vehicles, restricting Chinese telecoms from 5G infrastructure, and exposing and punishing Chinese espionage. A second Trump administration could build a coalition against Chinese behavior.
Third, the United States’ Asian allies are enhancing their military capabilities and cooperation among themselves. Australia, Japan, South Korea, Taiwan, and others are increasing their defense spending, and the United States recently negotiated expanded military access to key sites in the Philippines. Improved regional alliances and partnerships, including the Australia-United Kingdom-United States (AUKUS) pact, the Quad (Australia, India, Japan, and the United States), much improved Japan-South Korea relations, and growing Japan-Philippines cooperation will strengthen Trump’s hand with Beijing.
However, the China Trump will face is more powerful and aggressive than ever before. It has significantly increased its military harassment of Taiwan, the Philippines, and India. It has also deepened its strategic partnership with Russia: The two countries declared a “partnership without limits” in 2022, and Chinese President Xi Jinping told Russian President Vladimir Putin in 2023 that the world is undergoing changes “we haven’t seen for 100 years—and we are the ones driving these changes together.” China’s navy, already larger than its U.S. counterpart since around 2015, could be about 50 percent larger by the end of Trump’s second term. How would Trump respond if China attacked Taiwan? Washington assesses that Xi has ordered the Chinese People’s Liberation Army (PLA) to be prepared to win a war against Taiwan by 2027, and U.S. war games consistently indicate the U.S. could lose such a conflict. Trump continues to hew to the decadeslong policy of maintaining strategic ambiguity regarding Taiwan’s defense, even if he has included Taiwan in his familiar critique of allies not doing enough for their own defense. Nevertheless, the continuously eroding balance of power and rapidly evolving correlation of forces could make Trump less likely to assist Taiwan than one might suspect given his overall China policy. As Trump recently acknowledged in the bluntest of terms, Taiwan is 9,500 miles away from the United States but only 68 miles away from China.
Trump would return as commander in chief with the largest European war since World War II raging in Ukraine, the increased presence of U.S. forces on the continent, and European NATO members ramping up their defense spending. The much-changed situation in Europe could make him far less likely to withdraw U.S. troops, end support for Ukraine, or seek a grand bargain with Putin.
Trump’s persistent haranguing of European allies when he was president, coupled with Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, has prompted European countries to rapidly increase their defense spending. Whereas only five NATO members spent at least 2 percent of GDP on defense in 2016 and nine did so in 2020, 23 do so now. European NATO nations have increased their collective defense spending by more than half since Trump first took office, far ahead of the United States’ much smaller increase during the same period. Germany has even surpassed Britain as Europe’s biggest defense spender. The burden sharing Trump pushed for is beginning to happen: European NATO allies are now shouldering a greater share of bloc-wide defense spending, and Europe also provides the majority of aid to Ukraine. U.S. companies and workers are benefiting: The U.S. share of global arms exports rose from 34 percent to 42 percent over the most recent five-year period.
In his first term, Trump welcomed both Montenegro and North Macedonia into NATO, even though neither met the 2 percent mark at the time. His inclination to move U.S. forces farther east along NATO’s frontier is now a reality. Today, 20,000 U.S. forces are stationed in the alliance’s eastern frontier states, part of what Supreme Allied Commander Europe Gen. Christopher Cavoli called a “definite shift eastward.” With the addition of Finland and Sweden as a result of Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, NATO now has a significantly reshaped posture.
While the 2 percent floor for defense spending is now grossly inadequate, European states are proposing higher benchmarks. The European Union has released its first-ever defense industrial strategy, and many European countries are planning further increases in spending. Were Trump to preside over the June 2025 NATO summit in the Netherlands, he could not only announce “mission accomplished” with respect to the 2 percent target, but that NATO has collectively pledged a higher 3 percent floor.
Trump has promised to negotiate an end to the war in Ukraine “in 24 hours”—but has also threatened to dramatically increase arms support to Ukraine if Putin does not comply. He has never outright opposed military aid to Ukraine, acquiesced to congressional passage of a large supplemental in April, and recently concluded a positive call with Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky. Having observed how Biden’s disastrous withdrawal from Afghanistan sunk his presidency, Trump may be determined to avoid a similar loss of Ukraine.
Facing a Middle East with escalating Tehran-backed conflicts and a near-nuclear Iran, Trump 2.0 might also double down and increase U.S. military involvement to douse the fires Tehran has lit.
Trump is likely to end the Biden administration’s pressure on Israel to end the war against Hamas, de-escalate against Iran, and withdraw from Gaza and the West Bank. Trump would end Biden’s embargo on certain U.S. arms deliveries to Israel, halt aid to Gaza, and de-emphasize humanitarian concerns. Trump has consistently supported an Israeli “victory”—a stance repeated by his running mate, Sen. J.D. Vance—and called on Israel to “finish the job.” Trump has walked back his previous endorsement of a Palestinian state, suggesting a very different approach to the “day after.” If a major war between Israel and Hezbollah breaks out, Trump’s track record suggests he would support swift Israeli action with less concern for civilian casualties, with full U.S. support but no direct military involvement.
Trump 2.0 would quickly face the choice of whether to take preemptive military action against Iranian nuclear facilities. Iran is now a nuclear breakout state, capable of producing enough weapons-grade uranium for several bombs in less than 10 days, even if weaponization may take several months to a year. Berlin, Paris, and London, antagonists to Trump 1.0’s Iran policy, may be supporters of Trump 2.0’s, as Iran’s growing military alliance with Russia, nuclear progress, and support for the Houthis have shifted European attitudes. Having repeatedly passed the wartime tests by Iran and its proxies, Israeli anti-air capabilities have rapidly improved, as has coordination with Arab partners. Trump will likely recharge his maximum-pressure approach, but he may be more likely to threaten Iran directly than ever before.
Trump 2.0 could also launch a campaign against the Houthis similar to that against the Islamic State during Trump 1.0. He would inherit a 24-nation coalition that is currently failing to restore freedom of navigation through the Red Sea. Despite the most intense U.S. naval combat operations since World War II, Suez Canal transits are still fewer than half of what they were a year ago; so far, over 90 commercial vessels have been hit and more than 100 warships attacked. Just as he declared the defeat and destruction of the Islamic State to be his “highest priority” on the first day of his presidency, he may flip the mission from a defensive to offensive one by hitting Houthi launch sites, targeting critical infrastructure, eliminating Iranian naval support, and directly threatening Tehran. A successful campaign could restore commercial shipping, lower energy and shipping costs, and foster diplomatic cooperation with European, Middle Eastern, and Asian governments.
Even if Trump’s instincts and inclinations remain unchanged, the world’s vastly shifted circumstances could prompt unexpected approaches. If Trump 1.0 was an alliance disruptor and protectionist, a second Trump administration could turn out to be a coalition builder and forger of significant trade deals. Concerns over U.S. abandonment of Europe and withdrawal from the Middle East may prove to have been hasty, with altered circumstances leading to greater stability in Europe and a rollback of Iranian aggression in the Middle East. Dealmaking with China may give way to the best opportunity to build a Cold War-like coalition to blunt aggressive Chinese behavior.
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
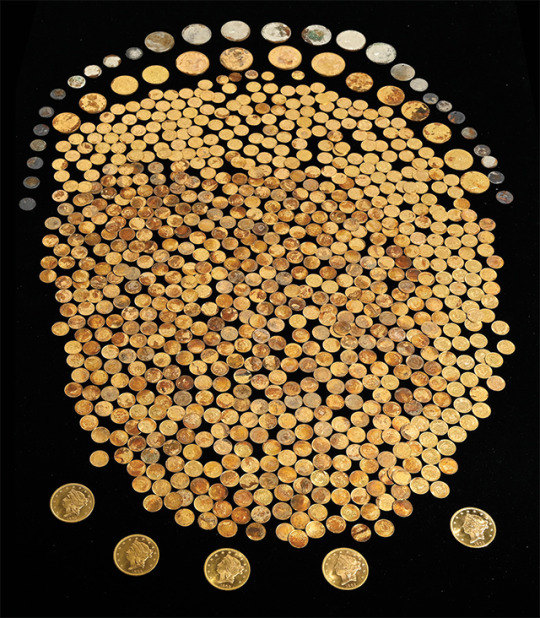


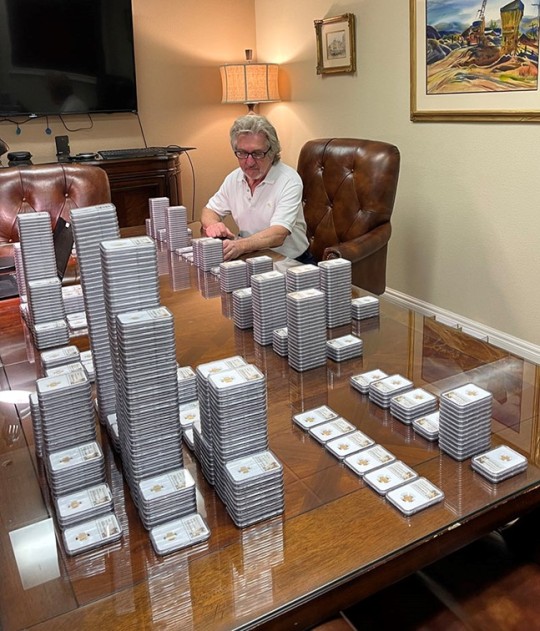
700+ Civil War-Era Gold Coins Found Buried in Kentucky
A man unearthed a huge hoard of Civil War-era gold and silver coins on his Kentucky farm.
A Kentucky man got the surprise of his life while digging in his field earlier this year: a cache of over 700 coins from the American Civil War era.
The "Great Kentucky Hoard" includes hundreds of U.S. gold pieces dating to between 1840 and 1863, in addition to a handful of silver coins. In a short video, the man who discovered the hoard — whose identity and specific location have not been revealed to the public — says, "This is the most insane thing ever: Those are all $1 gold coins, $20 gold coins, $10 gold coins," as he aims his camera at the artifacts tumbling out of the dirt.


According to the Numismatic Guaranty Co. (NGC), which certified the coins' authenticity, and GovMint, where the coins were sold, 95% of the hoard is composed of gold dollars, along with 20 $10 Liberty coins and eight $20 Liberty coins. The rarest is the 1863-P $20 1-ounce gold Liberty coin. Just one of these coins can go for six figures at auction, and the Great Kentucky Hoard boasts 18 of them. NGC's website notes that the $20 Liberty coin, which circulated from 1850 to 1907, was minted by the Treasury Department after gold was discovered in California. The $20 Liberty coins in the hoard are even rarer because they do not include "In God We Trust," which was added in 1866 after the end of the Civil War.
Potentially more important, though, is what the hoard can tell us about America's history during an extremely tumultuous period.
Ryan McNutt, a conflict archaeologist at Georgia Southern University who has heard about but not seen the hoard, said in an email that "given the time period and the location in Kentucky, which was neutral at the time, it is entirely possible this was buried in advance of Confederate John Hunt Morgan's June to July 1863 raid."
Many wealthy Kentuckians are rumored to have buried huge sums of money to prevent it from being stolen by the Confederacy. James Langstaff left a letter saying he had buried $20,000 in coins on his property in Paducah, William Pettit buried $80,000 worth of gold coins near Lexington, and Confederate soldiers quarantined for measles reportedly stole payroll and hid it in a cave in Cumberland Gap. None of these caches has ever been recovered.


Considering the hoard coins are federal currency, McNutt said, it may be the result of a Kentuckian's dealings with the federal government — "dealings that it would be wise to conceal from a Confederate raiding party." Many Americans affected by the Civil War "became experienced with hiding goods and valuables," he said.
Most concentrations of historical artifacts found on private land end up going to market or being collected without archaeological consultation, according to McNutt. "As a conflict archaeologist, I find this loss of information particularly frustrating," he said. Hoards have an incredible amount of information about the person who collected the objects, offering archaeologists insight into a brief window in time.
Historical finds like these on private land in the U.S. do not need to be reported to an archaeologist. But McNutt, who has developed close relationships with landowners, believes that education and outreach are key to learning more about these rare coin caches.
"It is entirely up to the landowner," McNutt said, but not engaging with an archaeologist means "it's a snapshot of the past, lost forever."
By Kristina Killgrove.




#700+ Civil War-Era Gold Coins Found Buried in Kentucky#The Great Kentucky Hoard#gold#silver#treasure#gold coins#silver coins#collectable coins#rare coins#metal detecting#archeology#archeolgst#history#history news#jackpot#discover#discovered#discovery#lucky#lucky find
49 notes
·
View notes
Text
Coiled Tubing Insights: A Deep Dive into Services, Operations, and Applications
Coiled Tubing Market Overview:
Request Sample

Inquiry Before Buying
Coiled Tubing Market Report Coverage
The “Coiled Tubing Market Report — Forecast (2024–2030)” by IndustryARC, covers an in-depth analysis of the following segments in the Coiled Tubing Industry.
By Service: Well Intervention & Production, Drilling, Perforating, Fracturing, Engineering Services, Milling Services, Nitrogen services and others.
By Operations: Circulation, Pumping, Logging, Perforation, Milling and Others.
By Technology/Services: Software Solutions, Hardware
By Location: On-Shore, Off-Shore
By Application: Wellbore Cleanouts, Electrical Submersible Pump Cable Conduit, Fracturing, Pipeline Cleanout, Fishing, Cementing, Nitrogen Jetting and others.
By End Use Industry: Oil and gas Industry, Engineering Procurement and Construction Industry, Others
By Geography: North America (U.S, Canada, Mexico), South America (Brazil, Argentina, and others), Europe (Germany, UK, France, Italy, Spain, and Others), APAC (China, Japan India, SK, Australia and Others), and RoW (Middle East and Africa)
Schedule a Call
Key Takeaways
North America dominates the Coiled Tubing Market share of 46.6% in 2023, owing to its advanced oil and gas industry, technological innovation, and substantial investments in exploration and production activities.
The development of unconventional resources, such as shale oil and gas, has increased the demand for coiled tubing services. Coiled tubing is often employed in hydraulic fracturing (fracking) operations in these unconventional reservoirs.
Well intervention services, including well cleaning, stimulation, and logging, are major applications of coiled tubing. As older wells require maintenance and newer wells require optimization, as a result growing the Demand for Well Intervention Services using coiled tubing continues to increase.
Buy Now
Coiled Tubing Market Drivers
Increased Exploration and Production Activities
The surge in oil and gas exploration, notably in unconventional resources such as shale, tight gas, and heavy oil, is fueling the demand for coiled tubing services. Integral to well intervention and stimulation procedures, coiled tubing plays a pivotal role in sustaining and augmenting production rates. This heightened exploration and production activity underscores the significance of coiled tubing services in maintaining operational efficiency and maximizing output in the energy sector.
Increasing Energy Demand
The escalating global energy demand propels the coiled tubing market forward. With an ever-growing need for energy resources, particularly in oil and gas sectors, there’s a heightened requirement for efficient extraction methods. Coiled tubing technology offers a versatile and cost-effective solution for various well intervention and drilling operations, catering to the increasing complexities of resource extraction. Its flexibility, mobility, and ability to access challenging environments make it indispensable in meeting the surging energy demands worldwide. As industries strive to optimize production and enhance operational efficiency, coiled tubing emerges as a crucial component in the quest for sustainable energy solutions.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
U.S. Compounding Pharmacies Market

U.S. Compounding Pharmacies have emerged as crucial players in the healthcare industry, offering personalized medications and innovative solutions to meet individual patient needs.
Read More: https://blogconnoisseur.blogspot.com/2023/06/the-rise-of-us-compounding-pharmacies.html
0 notes