#abstract dissertation structure
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Step-by-Step Guide How to Write a Dissertation Abstract?

Discover the art of crafting compelling dissertation abstracts with our comprehensive writing guide. Explore practical tips and clear examples to effectively summarize your research and create impactful abstracts that stand out.
#dissertation abstract#writing an abstract for a dissertation#abstract dissertation example#abstract dissertation structure#dissertation help
0 notes
Text
How to write a dissertation abstract

Writing a dissertation abstract with ease! Simplify your research goals. Keep it concise and to the point, covering all essential aspects of your study. Ensure clarity and readability for your audience. Refine it by seeking feedback from peers or mentors. Once perfected, include it at the beginning of your dissertation to provide a clear overview.
#dissertation abstract#writing an abstract for a dissertation#abstract dissertation example#abstract dissertation structure#dissertation help
0 notes
Text



--
MY WRITING MAKES IT SO OTHERS CAN FEEL SEEN: A QUEER PHENOMENOLOGICAL STUDY OF LGBTQ+ COLLEGE STUDENTS AFFECTIVE EXPERIENCES IN AN OUT-OF-SCHOOL POETRY WORKSHOP
A dissertation submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of DOCTOR OF PHILOSOPHY
Abstract
This dissertation explores the affective experiences of LGBTQ+ undergraduates in an out-of-school poetry workshop. Through the lens of queer and affect theories, the study asks the following research questions: 1) How does reading and writing poetry foster community in an LGBTQ+ out-of-school poetry workshop? (2) How can participation in an out-of-school poetry workshop with members who identify as LGBTQ+ engender a love of writing in queer students? (3) How do LGBTQ+ college students’ affective experiences manifest in a queer out-of-school poetry workshop? Using queer phenomenological methods (Ahmed, 2006) to engage with such data sources as audio and video class recordings, semi structured interviews, field notes, memos, and student writing, the study explores the way that two self-identified LGBTQ undergraduate students came to understand their writing and experiences in a queer out-of-school writing workshop space. Specifically, it engages with the ways young people interact with texts and writing prompts that center queer topics and issues, and how reorienting a space in which queer bodies and subjects are made visible can lead to increased engagement, empathy, and confidence in literacy skills
--

==
If you're wondering what this all is and means... it's nothing. It is and means literally nothing.
"But surely..." you may be thinking. No. These aren't real things, this is literally not anything. It's no more real than a $3 bill. From top to bottom, it's fake.
#Colin Wright#Leor Sapir#queer methods#queer theory#gibberish#academic fraud#academic corruption#corruption of education#higher education#pretentious nonsense#religion is a mental illness
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
A research proposal is a critical document that outlines what you will investigate, why it matters, and how you will carry out the research. Whether you’re a student preparing for a thesis, a researcher seeking funding, or an academic planning a project, crafting a compelling research proposal is essential. This guide provides detailed insights, along with examples and templates to make the process smoother. To get started with a template, visit this link.
Structure of a Research Proposal
The exact format of a research proposal can vary across disciplines, but most include the following key components:
Title Page
Introduction
Literature Review
Research Design
Reference List
These elements collectively serve as a blueprint for your research plan, ensuring clarity, direction, and feasibility.
Purpose of a Research Proposal
A research proposal has several functions, including:
Demonstrating the relevance and originality of your research.
Highlighting your familiarity with existing studies.
Presenting a well-structured methodology.
Establishing the feasibility of your project.
As a student, you may need to write a proposal for graduate school applications or before starting your thesis or dissertation. For researchers, proposals often serve as pitches for funding or institutional approval.
Goals of a Research Proposal
1. Relevance
Convince your audience that your project is interesting, original, and significant. Highlight how your work contributes to the field.
2. Context
Showcase your understanding of the field’s current state. This includes referencing existing research, theories, and gaps your work will address.
3. Approach
Detail your methodology, tools, and procedures. Demonstrate thorough planning for data collection and analysis.
4. Achievability
Prove that your project can be completed within the given timeline and resources.
Pro Tip: Use resources like Meet2Share for templates that help structure your proposal effectively.
Components of a Research Proposal
1. Title Page
Include the following details:
Project title
Your name
Supervisor’s name
Institution and department
For longer proposals, add a table of contents and an abstract for easier navigation.
2. Introduction
This section introduces your topic and explains why it matters. Include:
Necessary background and context.
Problem statement and research questions.
The potential audience for your research (e.g., scientists, policymakers).
What gaps in knowledge your work will address.
The unique contributions of your research.
3. Literature Review
Demonstrate your grasp of the field by summarizing key theories, methods, and debates. Use this section to:
Compare and contrast existing research.
Identify gaps your research will fill.
Explain how your work builds on or challenges previous studies.
4. Research Design and Methods
Outline how you plan to achieve your objectives. This section includes:
Research Type:
Qualitative, quantitative, or mixed methods?
Original data collection or secondary analysis?
Population and Sample:
Who/what will you study? (e.g., New York high school students, newspaper archives).
Sampling method: probability or non-probability?
Data Collection Methods:
Surveys, interviews, experiments, etc.
Justify why these methods are suitable.
Practicalities:
Timeline and access to participants or data sources.
Address potential challenges and solutions.
5. Contribution to Knowledge
Emphasize the broader impact of your research:
Enhancing best practices.
Informing policy decisions.
Advancing theoretical frameworks.
Laying groundwork for future studies.
6. Reference List
Include all sources cited in your proposal. Use tools like citation generators to maintain accuracy and consistency.
Additional Sections
Research Schedule
Provide a timeline for each phase of your project. For instance:PhaseObjectivesDeadlineBackground ResearchRead literature, refine questions, framework20th JanuaryDesign PlanningDraft tools, finalize methods13th FebruaryData CollectionRecruit participants, conduct interviews24th MarchAnalysisAnalyze data, draft results22nd AprilWritingComplete and revise drafts17th JuneSubmissionProofread and submit28th July
Budget
If seeking funding, include a detailed budget covering:
Travel costs.
Material requirements.
Personnel (e.g., research assistants).
Templates and Examples
Starting with a clear template can streamline your process. Download a research proposal template from Meet2Share to jumpstart your project.
Example Research Proposals
Title: A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management.
Title: Medical Students as Mediators of Change in Tobacco Use.
Tips for Success
Use tools like Scribbr’s paraphrasing tool for clarity.
Check institutional guidelines for specific requirements.
Seek feedback from peers or supervisors before final submission.
For additional insights into research methodologies and statistical concepts, visit Meet2Share’s library of resources and tools. Find like minded students and discuss on how to effectively write a research proposal.
Crafting a research proposal may seem daunting, but with the right structure and resources, you’re well-equipped to present a strong case for your research endeavor.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Doing a thesis or dissertation? What to include in your abstract, findings, discussion & conclusion

1.Abstract
Functions of a Thesis Abstract
The abstract serves as a concise summary of the entire thesis and typically includes:
a. The aims of the study: Clearly stating what the research intends to achieve.
b. The background and context of the study: Providing a brief overview of the research topic and its significance.
c. The methodology and methods used: Describing the approach and specific techniques used to gather and analyze data.
d .The key findings of the study: Highlighting the most important results.
e, The contribution to the field: Explaining how the research adds to existing knowledge.
Abstract Move and Sub-Move Options
Introduction
Provide context and background of the research.
Identify the motivation for the research.
Explain the significance of the research focus.
Identify the research gap or continuation of research tradition.
Purpose
State the aims or intentions, questions, or hypotheses.
Develop these aims or intentions further.
Method
Identify and justify the overall approach and methods.
Outline key design aspects.
Describe data sources and parameters.
Explain data analysis processes.
Product
Present main findings/results of key aims or questions.
Provide findings/results of subsidiary or additional aims or questions
Conclusion
Discuss the significance/importance of findings beyond the research, considering contributions to theory, research, and practice.
Suggest applications for practice and implications for further research.
2. Introduction Chapter

Functions of a Thesis Introduction
The introduction sets the stage for the thesis, addressing several key points:
a. Describing the problem, issue, or question of interest.
b. Reviewing the background and context, including a literature review.
c. Identifying gaps in existing knowledge.
d. Explaining what the study will do to address these gaps.
e .Outlining the methodology and scope of the study.
f. Discussing the expected contribution to the field.
g. Providing an outline of the thesis structure.
Introduction Move and Sub-Move Options
Establish a Research Territory
Explain the importance, relevance, or problem of the topic.
Provide background information.
Review previous research.
Define key terms and constructs.
Establish a Niche
Indicate gaps in previous research.
Raise questions about prior studies.
Identify a problem or need.
Extend previous knowledge.
Occupy the Niche
Outline the purpose, aim, and objectives of the research.
Specify research questions/hypotheses.
Describe theoretical perspectives.
Detail the methodology and design.
Indicate the scope/delimitations.
Explain the contribution to the field.
Outline the thesis organization.
3. Literature Review Chapter

Functions of a Literature Review
The literature review chapter serves multiple purposes:
Summarizing background and contextual information.
Reviewing theoretical perspectives related to the research.
Critiquing the research literature relevant to the study.
Identifying gaps or shortcomings in existing research.
Justifying the significance of addressing these gaps.
Explaining how the literature informs the research design and methodology.
Organizational Options for a Literature Review
The literature review can be organized in various ways, including:
Themes and topics.
Research questions or hypotheses.
Variables investigated in the study.
Chronological presentation of literature.
A combination of these options.
Literature Review Move and Sub-Move Options
Establish Knowledge Territory
Present knowledge claims and statements about theories, beliefs, constructs, and definitions.
State the centrality, importance, or significance of the theme/topic.
Present research evidence.
Create a Research Niche/Gap in Knowledge
Critique knowledge claims, issues, and problems.
Present research evidence in relation to the critique.
Identify gaps in knowledge/research.
Continue or develop a tradition that is under-investigated.
Argue for a new perspective or theoretical framework.
Announce Occupation of the Research Niche/Gap
Announce the aim of the research study.
State theoretical positions/frameworks.
Describe the research design and processes.
Define key concepts and terms in the research.
4.Methodology Chapter

Functions of a Methodology Chapter
The methodology chapter details the research design and methods, including:
Describing and justifying the methodological approach.
Detailing the research design.
Justifying the specific methods for data collection.
Discussing the validity and reliability of data.
Outlining the data collection procedures.
Explaining the data analysis procedures.
Methodology Move and Sub-Move Options
Present Measurement Procedures
Overview the methodological approach.
Explain methods of measuring variables.
Justify the approach and methods.
Describe Data Collection Procedures
Describe the sample, including location, size, characteristics, context, and ethical issues.
Describe instruments used for data collection and their validity and reliability.
Detail the data collection steps.
Justify data collection procedures.
Elucidate Data and Analysis Procedures
Outline data analysis procedures.
Justify data analysis procedures.
Preview results.
5. Results Chapter

Functions of a Results Chapter
The results chapter presents and explains the findings:
Presenting results/findings relevant to research questions/hypotheses.
Explaining the meaning of findings without interpretation.
Providing evidence to support findings.
Referring back to methodology and background/context.
Referring forward to the discussion of results.
Results Move and Sub-Move Options
Present Metatextual Information
Provide background information.
Reference methodology detail.
Reference forward to discussion detail.
Link between sections.
Present Results
Restate research questions/hypotheses.
Present procedures for generating results.
Present results with evidence and explanation.
6. Discussion Chapter

Functions of a Thesis Discussion of Results
The discussion chapter interprets the results and situates them within the broader field:
Overviewing the research aims and questions/hypotheses.
Summarizing the theoretical and research contexts.
Summarizing the methodological approach.
Discussing the contribution of the results to existing theory, research, and practice.
Including interpretations, comparisons, explanations, and evaluations of the results.
Results Move and Sub-Move Options
Provide Background Information
Restate aims, research questions, and hypotheses.
Restate key published research.
Restate the research/methodological approach.
Present Statement of Results (SoR)
Restate a key result.
Expand on the key result.
Evaluate/Comment on Results or Findings
Explain the result and suggest reasons.
Comment on whether the result was expected or unexpected.
Compare results with previous research.
Provide examples of results.
Make general claims arising from the results.
Support claims with previous research.
Make recommendations for future research.
Justify further research recommendations.
7. Conclusion Chapter

Functions of a Conclusion Chapter
The conclusion chapter wraps up the thesis by:
Reminding of the aims and key methodological features.
Summarizing the study’s findings.
Evaluating the study’s contribution to theory and practice.
Discussing practical applications.
Making recommendations for further research.
Results Move and Sub-Move Options
Restatement of Aims and Methodological Approach
Restate the aims of the study.
Restate key features of the research methodology and methods.
Summary of Findings
Summarize the key findings.
Evaluation of Study’s Contribution
Discuss the significance of findings for theory and research development.
Discuss the significance of findings for practical application.
Justify the significance of findings.
Identify any limitations.
Recommendations for Further Research
Make recommendations for further research based on the findings and limitations.
Investing in your academic future with Dissertation Writing Help For Students means choosing a dedicated professional who understands the complexities of dissertation writing and is committed to your success. With a comprehensive range of services, personalized attention, and a proven track record of helping students achieve their academic goals, I am here to support you at every stage of your dissertation journey.
Feel free to reach out to me at [email protected] to commence a collaborative endeavor towards scholarly excellence. Whether you seek guidance in crafting a compelling research proposal, require comprehensive editing to refine your dissertation, or need support in conducting a thorough literature review, I am here to facilitate your journey towards academic success. and discuss how I can assist you in realizing your academic aspirations.
#academics#education#grad school#gradblr#phd#phd life#phd research#phd student#phdblr#study#study motivation#studying#studyblr#studyspo#study blog#study aesthetic#student#university#student life#university student#writters on tumblr#my writing#writeblr#writing#writers on tumblr#writers and poets#writerscommunity#uniblr#students#academia
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Politics of Experimental Translation by Lily Robert-Foley
"Situating norms is obviously a fluid and problematic, culturally specific activity. Examining what is opposed to these norms serves to accentuate this. ... Translation very often is inflected with political or ethical aims, a desire to right wrongs in the original or to intervene in the landscape of authority and canon formation." "... experimental translation is any translation practice that opposes itself to translational norms." "It poses a threat to the mainstream dogma of translation, in particular, the place of fidelity, equivalence, accuracy, transparency, smoothness, and legibility. [...] it defines itself in contrast, or in opposition, to other more frequent forms of translation. ... not solely for aesthetic reasons but for social and political reasons. ... supported by a belief that the structures of aesthetics and poetics are profoundly and radically political." "the idea that translation is also radically political, never neutral, always inflected or even generated by the ideologies that frame it and give it its pulse."
"what separates this practice from other forms of experimental writing is the question of language, of the foreignness of languages, and the act of translating in its formal sense and amidst the chaos of its cultural negotiations."
"Tim Atkins’s ‘7 Translation Types’, as part of his unpublished PhD dissertation, which identifies seven discrete practices, including constraint, editing and domestication, misreading, allusive referential, derangement of the senses, intersemiotic, and hoax and parody."
"the question of fidelity is proportional to the text and most importantly, to the context of manipulation and power dynamics in which it is situated. [...] The implication here is that to translate faithfully, an author who does not have much visibility represents a homologous subverting of norms to a translation that, for example, shoots holes in a source text with a 12-gauge shotgun and translates the resulting text. ... And this is because of each practice’s relationship to the norm."
"translation always brings out dimensions of cultural context that might be otherwise invisible, reveals what might first appear as transcendent universals as situated specificities."
"norms do not represent the majority but are always determined by power and by the elite minority who wields it."
"that the notion of sense equivalence is deeply connected to a closed, un-situated relationship between two equal languages and can even be associated with culturally blind constructions of sense and sameness."
"Authorial intention then becomes an instrument of justice: respect for the original is connected to the desire to right a transnational wrong – specifically with regard to the ‘neocolony’."
"Luise von Flotow’s four strategies for feminist translation (supplementing, prefacing and footnoting, and hijacking) (1991) are instructions for experimental translators seeking to align themselves with the feminist cause."
"Spivak has referred to her in her article on the politics of translation as ‘intimacy’ with the culture and language original, necessary for the carrying out of an honourable translation. ... a lack of intimacy with an original, specifically in the case of translating across unequal power divides, can lead to essentialisms that serve more to propagate colonial or misogynist ideologies than they do to enact justice."
"By deforming, mistranslating, or rendering unintelligible a white, male canonical text written in a hegemonic language in a power centre, many experimental translators have political aims of posing a threat to forces of oppression ... a faithful translation of a text written by a subaltern author in a non-hegemonic language or in a marginal situation seeks to do the same thing."
"For Spivak, although the original text is not transparent, the activity of translation is – and must be."
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Save Time and Look Professional with These Expert Formatting Services
Academic writing is more than strong research and compelling arguments—it’s also about presentation. Whether you're finalizing a PhD thesis, a Master’s dissertation, or submitting a manuscript to a journal, professional formatting ensures your work meets required standards, impresses reviewers, and gets accepted faster.
At TutorsIndia, our Formatting and Typesetting Service transforms complex academic documents into professionally structured files that align with university and journal guidelines. With our expertise in thesis typesetting, dissertation formatting, and reference styling, you can save time and make a lasting impression.
Why Formatting Matters in Academic Writing
Common Pitfalls in Poor Formatting
Misaligned margins, inconsistent spacing, and improper citations can lead to rejected submissions, even when the research is solid. Our team helps eliminate these issues, polishing every element of your document. If your writing also needs polishing for grammar and tone, our Language Editing Services can refine your content to match academic standards.
How Expert Formatting Helps You Succeed
With formatting handled by experts, you gain:
Time to focus on content and research
Improved acceptance rates from universities and journals
Confidence that every visual, citation, and section is correctly styled
If your work is based on audio or interviews, we can also help convert it into well-structured academic content via our Transcription Services, ensuring it’s properly formatted for inclusion.
What Our Formatting Services Include
Thesis and Dissertation Typesetting
We specialize in formatting academic documents like:
PhD theses
Master’s dissertations
Research proposals
Our team follows guidelines such as APA, AMA, and CMOS, ensuring consistent layout, pagination, heading hierarchy, and structure.
Reference and Citation Formatting
Our experts format your:
In-text citations
Footnotes/endnotes
Final bibliography
All references are aligned with your required style guide, whether it's APA, MLA, Chicago, or Harvard.
Figure & Table Layout and Page Design
We format:
Charts, graphs, and tables
Captions and labels
Lists of figures/tables
You also benefit from optimized page layout, ensuring readability and compliance.
Technical Precision at Every Step
3-Level Quality Check
Each file is reviewed through:
Technical QC – for formatting integrity
Editorial QC – for clarity and consistency
Final QC – to ensure submission-readiness
Data Security and Privacy
We handle your documents under strict confidentiality using:
NDA agreements
SSL encryption
GDPR-compliant protocols
<5% Similarity Guarantee
All documents include a plagiarism scan report, ensuring clean formatting and originality, critical for journal or university submissions.
Tailored for Journal Submissions
Journals often reject papers for not following their template guidelines. We ensure:
Correct margin, font, and spacing
Abstract and title page formatting
Reference styling as per publisher requirements
Whether it's Elsevier, Springer, or IEEE, we format to spec—so your work is submission-ready from the first draft.
Who We Help
Our formatting support is ideal for:
PhD and Master’s students
Research scholars
Journal authors
Medical writers
Engineering and business professionals
We also support poster creation, PowerPoint formatting, and research presentations.
Our Process
Upload your draft and specify formatting needs
Our experts review and begin formatting
Document passes through 3-level QC
You receive the formatted file
Request unlimited revisions (if needed)
Frequently Asked Questions
Do you follow university or journal-specific guidelines? Yes, we customize formatting based on your institution or publisher’s requirements.
Can you fix grammar and writing style, too? Absolutely. Our Language Editing Services refine clarity, tone, and academic style.
Do you handle raw content like recordings or notes? Yes. Use our Transcription Services to convert interviews or notes into formatted academic text.
What file types do you support? We work with Microsoft Word, PDF, LaTeX, and PowerPoint.
Final Thought: Let Formatting Speak for You
Formatting can be the silent decider between acceptance and rejection. Let TutorsIndia format your documents to perfection so your ideas stand out, not your layout errors.
Ready to Submit Like a Pro?
Explore our Formatting and Typesetting Service Improve your tone with Language Editing Convert raw data with Transcription Services
0 notes
Text

Top Tips for Successful Master's Dissertation Writing
A master’s dissertation is more than just a long academic paper—it’s a journey that tests your critical thinking, research, and writing skills. It is often the most challenging and rewarding part of postgraduate study. Whether you’re just beginning or already stuck in the middle of your writing process, the following tips can help you successfully write your master’s dissertation and submit it with confidence.
1. Understand the Purpose and Structure
Before you dive into writing, it’s crucial to understand what a dissertation is meant to achieve. It typically involves independent research on a topic of your choice, demonstrating your understanding of theoretical concepts and research methods in your field.
A typical dissertation structure includes:
Title Page
Abstract
Acknowledgements
Table of Contents
Introduction
Literature Review
Methodology
Results/Findings
Discussion
Conclusion
References
Appendices (if any)
Knowing this structure early helps you stay organized and ensures no essential component is overlooked.
2. Choose the Right Topic
Your topic will define your entire dissertation journey. Choose a topic that is:
Relevant to your field of study.
Interesting enough to keep you engaged for months.
Manageable in terms of scope and data availability.
Researchable using existing methods or resources.
Original, yet grounded in existing research.
Discuss your ideas with your supervisor and refine your topic until it’s sharp and feasible.
3. Develop a Clear Research Question
Your research question is the core of your dissertation. It guides your study and keeps your work focused. A strong research question is:
Clear and concise.
Neither too broad nor too narrow.
Answerable through analysis, research, or experimentation.
Example: "How has remote working affected employee productivity in the IT industry post-COVID-19?"
Your research should revolve around answering this question comprehensively.
4. Create a Solid Proposal
Most programs require a dissertation proposal before full approval. This outlines what you plan to research, why it matters, and how you’ll conduct the study. A well-written proposal will:
Show you’ve done initial background research.
Highlight gaps in the current literature.
Outline your objectives, hypotheses, and methods.
Set a timeline for the work.
Getting your proposal right saves you from major issues later in the process.
5. Plan Your Time Effectively
Time management is key. Break your work into smaller tasks with deadlines. Use a Gantt chart or project timeline to allocate time for:
Research and reading.
Data collection and analysis.
Writing each chapter.
Revisions and proofreading.
Start early. The closer you get to the deadline, the more stressful even small tasks can feel.
6. Conduct Thorough Research
Use a variety of credible academic sources including journals, books, official reports, and databases like JSTOR or Google Scholar. Make sure to:
Take notes while reading.
Keep track of citations using tools like Zotero, Mendeley, or EndNote.
Organize your sources by themes or relevance.
A strong literature review sets the foundation for your research and shows your depth of understanding.
7. Be Methodologically Sound
Your methodology section explains how you conducted your research. Be clear, specific, and justify your choices. Include:
Research approach (qualitative, quantitative, or mixed).
Data collection methods (surveys, interviews, experiments, etc.).
Sampling techniques.
Ethical considerations.
Your methodology should be replicable, meaning another researcher could follow your method and arrive at similar results.
8. Write with Clarity and Consistency
When it comes to writing:
Follow a consistent academic tone.
Avoid jargon unless necessary, and define technical terms.
Start each chapter with an introduction and end with a summary.
Make sure each part flows logically into the next.
If possible, write daily or regularly, even in small chunks. Consistent writing helps reduce last-minute panic.
9. Revise and Edit Thoroughly
Once your first draft is complete, don’t rush to submit it. Revisions are where real improvement happens. Focus on:
Content: Are arguments strong and supported?
Structure: Is the flow logical?
Language: Are grammar and spelling correct?
Formatting: Is your document consistent and professional?
Use editing tools like Grammarly, and seek feedback from your supervisor or peers.
10. Reference Properly
Proper referencing shows academic integrity and avoids plagiarism. Always:
Follow the required citation style (APA, MLA, Harvard, etc.).
Cite every source you use.
Include a complete bibliography.
Use referencing tools, but double-check formatting to avoid automated errors.
11. Stay in Touch with Your Supervisor
Your dissertation supervisor is there to guide you—don’t hesitate to ask questions. Keep them updated on your progress and meet deadlines for review and feedback. Their advice can save you from costly mistakes.
12. Take Care of Yourself
Dissertation writing can be mentally exhausting. To avoid burnout:
Take breaks and follow a healthy routine.
Sleep well, eat healthy, and exercise regularly.
Don’t isolate—talk to peers or mentors for support.
Celebrate small milestones to stay motivated.
Your mental and physical well-being will impact your writing quality more than you think.
Conclusion
Writing a master’s dissertation is no small feat. It takes planning, patience, and persistence. By choosing the right topic, managing your time, and writing clearly, you can create a dissertation that not only meets academic standards but also gives you a sense of accomplishment.
Remember, it's a journey of learning and growth. Stay focused, be adaptable, and don’t hesitate to ask for help when you need it. You've got this!
0 notes
Text
Dissertation Draft 1
With the secondary research that was gathered online, the first draft of the dissertation was written.
0 notes
Text
How AI Humanizer Pro Helps Researchers Turn AI Drafts into Publication-Ready Papers
Imagine investing years into a groundbreaking study, only to face rejection because your paper lacks a natural tone. Or relying on AI tools to speed up your writing—only for your content to be flagged. A survey involving 908 environmental science researchers revealed that non-native English speakers are 2.5 to 3 times more likely to have papers rejected due to language issues. These problems are usually aggravated by mechanical phrasing by AI tools. This inhibits publication and even discourages great minds from continuing research.
To assist in solving these problems, AI Humanizer Pro provides an enhanced solution to fill the gap between AI Humanizer and publication-ready writing.
AI Humanizer: The Assistant That Polishes Your Research Voice
AI Humanizer Pro is an easy-to-use tool designed to transform robotic, AI-written drafts into natural, readable scholarly work. Whether you are writing using ChatGPT, Perplexity, or similar software to write, this tool smoothes your writing without losing the original research intent. It refines tone, enhances structure, and makes writing read as if it were written by a human being.
Perfect for students, scholars, and researchers, it's your best companion to produce authentic and eloquent academic content.
Why AI-Generated Content More Often Than Not Fails in Academia
Though AI platforms make it easy to write, journal editors and research reviewers are now more vigilant than ever. With the prevalence of AI detection software, even well-researched articles can get flagged or rejected if they appear machine-written.
Common problems are repetitive language, ambiguous statements, and weak linkage between ideas. Even with thorough research, your paper may lose reliability and experience delays or rejections for unnatural tone.
Common Problems in AI-Aided Research Writing
Robotic Tone: Robot-like drafts are common when AI generates them, even when grammatically sound.
Overlooked Academic Purpose: AI tends to overgeneralize or misuse technical vocabulary, resulting in muddled or deceptive conclusions.
Detection by AI Checkers: Most journals now employ AI checker software to verify content originality, and machine-generated content tends to get detected.
Non-native Writers and AI: Most researchers employ AI software to polish grammar, but it can still lead to stilted or formulaic writing—particularly in abstracts or literature reviews.
How AI Humanizer Pro Fixes AI-Writing Pitfalls
Natural Academic Language Transformation: The software rewrites content in natural human fluency, as if the voice is a real researcher's.
Preserves Original Research Context: It enhances flow without changing your arguments or findings.
Evades AI Detection Tools: With advanced processing, it minimizes patterns that cause AI detection tools to activate while maintaining content authenticity.
Several Tone Presets: From academic to conversational, the software lets you control tone to suit your publication standards.
Why AI Humanizer Pro Trumps Simple Grammar Tools
Better than Grammar Checks: It rewrites content with academic style in mind, not just fixing sentences.
Addresses AI-generated Flaws: It eliminates robotic language, redundancy, and vague statements, so your writing flows and grabs attention.
Increases Trust with Humanized Tone: By humanizing AI work, the tool makes reviewers view your paper as well-written and credible—not a product of cut corners.
Your Trusted Research Partner
AI Humanizer Pro is not merely a language tool—it's a crucial friend in your publishing journey. From polishing a dissertation, proposal, or journal article, it makes machine-written text into a version that is natural, submission-worthy, and free of red flags.
Copy and paste your text, select your tone, and let AI Humanizer Pro make your research sparkle risk-free.
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Text
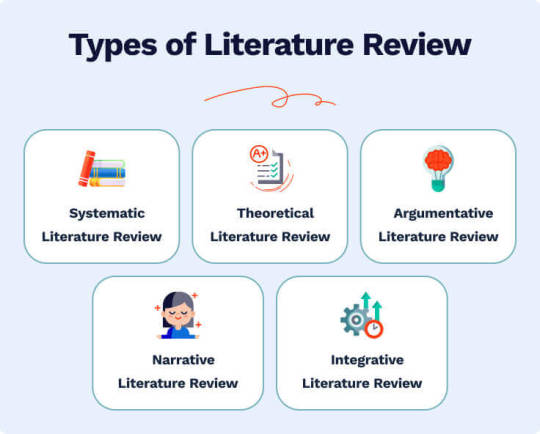
To excel in literature review writing, start by developing a strong outline of a reviewed paper. It is essential to not just summarize the sources, but involve analyzing and synthesizing the materials on a chosen topic. Focus on academic research and build a foundation for your further study. Using our literature review outline example can help you structure your work efficiently. You will learn how to: - Identify and examine all relevant scholarly sources on your topic - Overview the current research trends - Highlight gaps or unresolved questions. - Organize your findings coherently, from introduction to conclusion. Additionally, we recommend you fully understand the types of literature review: narrative, integrative, and others. In this article, our experts provide actionable tips, a clear RRL outline, and topic suggestions to help you succeed. Whether you’re drafting your first review or refining your skills, this guide will ensure you produce a comprehensive and insightful paper. Table of Contents What Is a Literature Review? Let’s start with the literature review definition. Literature review outlooks the existing sources on a given topic. Its primary goal is to provide an overall picture of the study object. It clears up the context and showcases the analysis of the paper’s theoretical methodology. In case you want to see the examples of this type of work, check out our collection of free student essays. Importance of Literature Review In most cases, you need to write a literature review as a part of an academic project. Those can be dissertations, theses, or research papers. Why is it important? Imagine your final research as a 100% bar. Let’s recall Pareto law: 20% of efforts make 80% of the result. In our case, 20% is preparing a literature review. Writing itself is less important than an in-depth analysis of current literature. Do you want to avoid possible frustration in academic writing? Make a confident start with a literature review. Sure, it’s impossible to find a topic that hasn’t been discussed or cited. That is why we cannot but use the works of other authors. You don’t have to agree with them. Discuss, criticize, analyze, and debate. So, the purpose of the literature review is to give the knowledge foundation for the topic and establish its understanding. Abstracting from personal opinions and judgments is a crucial attribute. Types of Literature Review You can reach the purpose we have discussed above in several ways, which means there are several types of literature review. What sets them apart? In short, it’s their research methods and structure. Let’s break down each type: - Systematic literature review is the most precise and well-defined type. It identifies, evaluates, and appraises the studied topic. The purpose is to get the lay of the land in a given research area. It falls into meta-analysis and meta-synthesis. They differ in the undertaken approach: deductive or inductive. - Meta-analysis implies the deductive approach. At first, you gather several related research papers. Then, you carry out its statistical analysis. As a result, you answer a formulated question. - Meta-synthesis goes along with the inductive approach. It bases qualitative data assessment. - Theoretical literature review implies gathering theories. Those theories apply to studied ideas or concepts. Links between theories become more explicit and clear. Why is it useful? It confirms that the theoretical framework is valid. On top of that, it assists in new hypothesis-making. - Argumentative literature review starts with a problem statement. Then, you select and study the topic-related literature to confirm or deny the stated question. There is one sufficient problem in this type, by the way. The author may write the text with a grain of bias. - Narrative literature review focuses on literature mismatches. It indicates possible gaps and concludes the body of literature. The primary step here is stating a focused research question. Another name for this type — a traditional literature review. - Integrative literature review drives scientific novelty. It generates new statements around the existing research. The primary tool for that is secondary data. The thing you need is to review and criticize it. When is the best option to write an integrative literature review? It’s when you lack primary data analysis. Remember: before writing a literature review, specify its type. Another step you should take is to argue your choice. Make sure it fits the research framework. It will save your time as you won’t need to figure out fitting strategies and methods. Annotated Bibliography vs. Literature Review Some would ask: isn’t what you are writing about is just an annotated bibliography? Sure, both annotated bibliography and literature review list the research topic-related sources. But no more than that. Such contextual attributes as goal, structure, and components differ a lot. For a more visual illustration of its difference, we made a table: Attribute Annotated Bibliography Literature Review Purpose Informative nature. Listing additional sources for a reader is possible. Analyzes the top research sources to get the most of a topic. Content Proofs of sources’ relevance and credibility. The complete picture of the study object. Structure requirements - Alphabetical sorting - Clear separation of entries - Easy navigation - Advanced representation of sources in the text - Sources can appear several times Components List formatted in the formal citation styles (MLA, APA, Chicago, etc.). Introduction, main body, and conclusion. To sum up: an annotated bibliography is more referral. It does not require reading all the sources in the list. On the contrary, you won’t reach the literature review purpose without examining all the sources cited. Share to FacebookPin ItCopy Image URL Literature Review: Step-by-Step Strategy Now it’s time for a step-by-step guide. We are getting closer to a perfect literature review! Step 1. Select the Topic Selecting a topic requires looking from two perspectives. They are the following: - Stand-alone paper. Choose an engaging topic and state a central problem. Then, investigate the trusted literature sources in scholarly databases. - Part of a dissertation or thesis. In this case, you should dig around the thesis topic, research objectives, and purpose. Regardless of the situation, you should not just list several literature items. On the contrary, build a decent logical connection and analysis. Only that way, you’ll answer the research question. Step 2. Identify the Review Scope One more essential thing to do is to define the research boundaries: don’t make them too broad or too narrow. Push back on the chosen topic and define the number and level of comprehensiveness of your paper. Define the historical period as well. After that, select a pool of credible sources for further synthesis and analysis. Step 3. Work with Sources Investigate each chosen source. Note each important insight you come across. Learn how to cite a literature review to avoid plagiarism. Step 4. Write a Literature Review Outline No matter what the writing purpose is: research, informative, promotional, etc. The power of your future text is in the proper planning. If you start with a well-defined structure, there’s a much higher chance that you’ll reach exceptional results. Step 5. Review the Literature Once you’ve outlined your literature review, you’re ready for a writing part. While writing, try to be selective, thinking critically, and don’t forget to stay to the point. In the end, make a compelling literature review conclusion. What Are the 5 C’s of Writing a Literature Review? Don’t forget about these five C’s to make things easier in writing a literature review: Cite. Make a list of references for research you’ve used and apply proper citation rules. Use Google Scholar for this. Compare. Make a comparison of such literature attributes as theories, insights, trends, arguments, etc. It’s better to use tables or diagrams to make your content visual. Contrast. Use listings to categorize particular approaches, themes, and so on. Critique. Critical thinking is a must in any scientific research. Don’t take individual formulations as truth. Explore controversial points of view. Connect. Find a place of your research between existing studies. Propose new possible areas to dig further. Read the full article
0 notes
Text
What is the standard law dissertation structure?

A well-organised and clear law dissertation structure is crucial for students so they can present their legal arguments and meet the highest level of academia. The standard structure typically includes the following sections-
Title Page – On the title page, it includes your dissertation title, name, institution, and date.
Table of Contents- This section involves page numbers and chapters.
Introduction- A law dissertation must have a strong introduction, which includes the topic, research question and objectives.
Literature Review- In the literature review, it must discuss existing legal scholarship and identify gaps.
Bibliography- By listing all the credible references and relevant legal sources.
Appendices- Provide all the supplementary materials for the law dissertation structure.
Findings / Analysis- Showcase the main findings and main legal arguments.
Methodology- Briefly explain the legal research methods whether it is socio-legal, doctrinal and comparative.
Abstract- A well-explained summary of the findings, research and conclusions.
Discussion- Interpret findings and connect them to the research question.
Conclusion- At the end, summarise the key points and suggest the areas for future research.
Students who are struggling with the law dissertation structure can get assistance from O’Connor PhD Law Writers who are specialists in crafting a law dissertation that follows the best and ideal dissertation structure by ensuring clarity, coherence and academic excellence. Students can trust our service for expert guidance and personalised support so they can achieve higher grades and meets their academic standards.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Basic Structure of a Scientific Paper to Write.

The fundamental structure of a scientific paper is encapsulated by the acronym IMRAD, which stands for Introduction, Methods, Results, and Discussion. This structure is integral to original research articles and facilitates clear and organized presentation of research findings. Each component of IMRAD serves a distinct purpose:
Introduction: Presents the research question and its significance.
Methods: Describes the procedures and techniques used to conduct the study.
Results: Summarizes the data and findings of the research.
Discussion: Interprets the findings, linking them back to the research question and broader context.
In addition to IMRAD, scientific papers typically include a title page, abstract, keywords, tables, graphs, figures, acknowledgments, and references. Each element contributes to the overall clarity and accessibility of the research.
Types of Papers

Scientific journals publish various types of papers, each serving a specific purpose and judged by distinct criteria. Understanding these types can help authors select the most appropriate format for their work, thus maximizing the impact and acceptance chances of their manuscript. The main types of papers include:
Original Article: Reports new research findings based on original research. This is the most critical paper type, often subdivided into Major Papers and Original Reports.
Case Report: Describes unique cases that provide new insights or highlight unusual clinical conditions.
Technical Note: Details specific techniques, procedures, or new equipment relevant to a medical field.
Pictorial Essay: Focuses on the educational value of high-quality images, often used in teaching.
Review: Summarizes recent developments on a specific topic without introducing new data.
Commentary: Offers personal perspectives on current issues or controversial topics.
Editorial: Provides short reviews or critiques of articles published in the same journal issue.
Letter to the Editor: Allows for short communications on various subjects, including comments on previously published articles.
Preparing the Manuscript
Authors must tailor their manuscripts to the type of paper they are writing, following specific guidelines and structures. For example:
Original Articles should follow the IMRAD structure with a detailed methods section and robust statistical analysis.
Case Reports often have a simpler structure with a focus on the unique aspects of the case and their implications.
Technical Notes and Pictorial Essays emphasize methods and visual elements, respectively, with concise text sections.
Reviews and Commentaries should be well-organized with comprehensive coverage of the relevant literature and clear presentation of viewpoints.
Enhancing Chances of Acceptance
To enhance the chances of manuscript acceptance, authors should:
Adhere to the journal’s specific guidelines outlined in the “Instructions to Authors” or “Guide for Authors.”
Ensure their manuscript is well-structured, clear, and concise.
Select the most appropriate type of paper for their research.
Include all necessary components, such as a structured abstract, relevant keywords, and thorough references.
Conclusion
Familiarity with the basic structure and types of scientific papers, as well as adherence to journal guidelines, is crucial for authors aiming to publish their work successfully. By choosing the appropriate format and meticulously preparing their manuscripts, authors can effectively communicate their research and increase their chances of acceptance in reputable journals. This structured approach not only maximizes the material’s impact but also contributes to the advancement of scientific knowledge in the medical field.
Investing in your academic future with Dissertation Writing Help For Students means choosing a dedicated professional who understands the complexities of dissertation writing and is committed to your success. With a comprehensive range of services, personalized attention, and a proven track record of helping students achieve their academic goals, I am here to support you at every stage of your dissertation journey.
Feel free to reach out to me at [email protected] to commence a collaborative endeavor towards scholarly excellence. Whether you seek guidance in crafting a compelling research proposal, require comprehensive editing to refine your dissertation, or need support in conducting a thorough literature review, I am here to facilitate your journey towards academic success. and discuss how I can assist you in realizing your academic aspirations.
#academics#education#grad school#gradblr#phd#phd life#phd research#phd student#phdblr#study#study with me#study motivation#studyspo#study blog#studyblr#study aesthetic#studying#student life#university#university student#uni life#writers on tumblr#writing#my writing#writeblr#writers and poets#writerscommunity#scientific research#thesis#dissertation
1 note
·
View note
Text
Scientific Poster Design Services for MBA Students in the UK | Tutors India
Introduction
For MBA students in the UK, the journey of academic success goes beyond writing a dissertation. One of the most important, yet often overlooked, components of research communication is the scientific poster presentation. Whether it’s part of your final assessment, an academic conference, or a departmental showcase, poster presentations offer a concise and visual way to share your research insights.
Creating an effective poster is not just about design—it’s about academic precision, structured content, and engaging visual communication. With the growing demand for high-quality presentations, Tutors India offers expert support through its Scientific Poster Presentation Services tailored for MBA students who want to stand out with confidence and clarity.
The Role of Academic Posters in MBA Research
A poster acts as a research summary, combining critical aspects such as the introduction, literature review, methodology, data analysis, and conclusions in a single-page layout. It helps communicate your MBA dissertation’s objectives and outcomes in a way that is visually engaging and academically credible.
At Tutors India, we understand the evolving needs of UK-based MBA students and provide expert Academic Poster Presentation Help to ensure your poster meets academic expectations while communicating your research effectively.
Academic posters are commonly used in:
Research symposia and conferences
Internal assessments and viva presentations
Public-facing exhibitions of student research
MBA dissertation showcases within departments
Unlike traditional dissertation submissions, poster presentations require a distinct set of skills, from graphical layout to concise writing. A poorly designed poster can reduce the impact of well-conducted research, which is why MBA students across the UK trust Tutors India and its Masters Dissertation Poster Support Services for professional assistance.
Common Challenges Faced by MBA Students
MBA students often face challenges when preparing their academic posters:
Lack of design and formatting knowledge
Difficulty summarizing complex research into visual sections
Unfamiliarity with poster structure and referencing guidelines
Trouble integrating quantitative data from SPSS, MATLAB, or R
Limited understanding of how to communicate research visually
In such cases, Tutors India’s Poster Design Services for Students help bridge the gap between great research and effective presentation.
What Tutors India Offers Through Scientific Poster Services
At Tutors India, our professional services are designed to support MBA students from start to finish. Our Scientific Poster Design Services include:
Scientific Poster Design and Layout We create compelling layouts using professional tools, ensuring visual hierarchy, formatting, and color balance that enhance academic presentation.
Content Development and Section Writing From the abstract to the results and conclusion, our academic writers develop clear, concise content that accurately represents your research objectives.
Data Visualization and Tool Integration Using visually impactful charts and graphs, we help integrate SPSS, R, or MATLAB outputs into your poster.
Poster Formatting and Referencing Support Our formatting complies with APA, Harvard, and MLA guidelines, ensuring academic accuracy and visual professionalism.
Conference-Ready Poster Delivery All outputs are prepared to meet university printing or digital submission requirements. We also assist with poster handouts for conferences and seminars.
Specialized Features for MBA Poster Presentation
With Tutors India’s Poster Presentation Services, MBA students benefit from:
Custom-designed academic posters tailored to dissertation themes
Chapter-wise development: Abstract, Methodology, Results, and more
SPSS/MATLAB integration with clear, labeled visuals
Infographic and statistical representation techniques
Turnitin-checked, plagiarism-free content
Poster critique, editing, and final proofreading
NDA-protected support ensuring full confidentiality
Why UK-Based MBA Students Choose Tutors India
Tutors India has established itself as a trusted brand for UK students. Here’s why MBA candidates rely on our Academic Poster Support Services:
Time Efficiency We handle layout, structure, and design—saving you hours of formatting work.
Academic Excellence Professionally developed posters reflect academic rigor and help boost performance.
Visual Communication Our designs communicate your research visually and clearly, perfect for evaluations and conferences.
Confidential & Plagiarism-Free All work is original, Turnitin-checked, and fully confidential under NDA agreements.
End-to-End Poster Help From initial concept to final delivery, we ensure your poster aligns with your dissertation goals and university standards.
Real Use Case: MBA Poster Success with Tutors India
An MBA student from a UK university specializing in Operations Management needed to present her SPSS-based findings on supply chain optimization. She approached Tutors India, and our team developed a clean, professional academic poster featuring her research objectives, regression analysis, and a structured conclusion. Presented during her viva, the poster earned her recognition and helped secure a high grade.
Conclusion
For MBA students in the UK, poster presentations are more than just visuals; they’re an academic communication tool. With high expectations and tight deadlines, many students benefit from professional support.
Tutors India’s Scientific Poster Presentation Services are designed to help you create a powerful, university-compliant academic poster that showcases your research effectively.
Whether you're preparing for a viva, conference, or internal showcase, trust Tutors India to deliver a well-crafted, research-driven, and eye-catching poster. Let your hard work shine with clarity, accuracy, and visual impact.
Contact Us:
UK: +44-1143520021
IN: +91 8754446690
Email: [email protected]
0 notes
Text
Final PhD Synopsis Writing: A Detailed Guide
Introduction
Drafting the final PhD synopsis is an important milestone prior to submitting your dissertation. It is an abstract of your research that provides the key points of your study in an orderly fashion. A well-structured synopsis ensures that your research is brief, unambiguous, and in the format of evaluation by the specialists in your subject.
Role of a PhD Synopsis
PhD synopsis is a well-defined guide of your thesis outlining the problem statement, goals, research strategy, conclusions, and results. It provides proper insight into your research material for the examiners and ensures everything that should be included in your thesis is also included.
Structure of a Final PhD Synopsis
A typical PhD synopsis will generally adopt a formalized structure, with the following principal components:
Title Page
Title of the thesis
Name of the candidate
University/Institution name
Supervisor's name
Submission date
Abstract
A concise overview (about 300 words) of the research problem, objectives, methodology, key findings, and conclusions.
Introduction
Background and significance of the research
Research problem and its significance
Objectives of the study
Scope and limitations
Review of Literature
Summary of current research on the subject
Identification of research gaps
Rationale for the study
Research Methodology
Research design and approach (qualitative, quantitative, or mixed-method)
Data collection techniques (surveys, experiments, case studies, etc.)
Analytical techniques and instruments used
Results and Discussion
Summary of key findings
What the results mean according to research objectives
Comparison with current literature
Conclusion and Contributions
Summary of key conclusions
Theoretical and practical implications of the study
Future research directions
References
List of all sources referenced in the required citation style (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.)
Writing an Effective PhD Synopsis: Tips
Be Concise and Clear – Refrain from using unnecessary information and make the content concise.
Adhere to Guidelines – Adhere to the format given by your institution. Have a Logical Structure – Ensure all components are well connected.
Use Proper Citations – Acknowledge all sources.
Proofread Thoroughly – Remove grammatical mistakes and inconsistencies.
Conclusion
The final PhD synopsis is an important document that encapsulates your years of research work in a systematic manner. By adhering to the correct format and keeping the narrative brief, you can develop a persuasive synopsis that effectively conveys your research contribution.
1 note
·
View note