#aggregator model
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
This headline is necessarily false too. If workers are bringing lunch from home by choice, then by revealed preference they are deriving more utility from that behavior than from dining out. That constitutes a welfare gain. In a normative sense that is "good" (whatever that means) for the economy. If, on the other hand, they are doing so out of financial necessity, then the underlying economic harm has already occurred elsewhere; their behavior is a response, not a cause. In either case, individuals are optimizing under their constraints, and they are evidently increasingly preferring a bundle of goods that involves fewer take out meals and (relatively) more of other goods. To describe this as “hurting the economy” is to claim that welfare-improving or cost-minimizing behavior constitutes economic damage. Deriving maximal welfare from given resources or using minimal resource to provide given welfare is, like, the whole point of the economy. It is, in effect, a statement that defines increased utility as harm, which is a necessarily false proposition under the normative premises of economic theory.



“...eat my paycheck to paycheck ass, ‘the economy’...”
#Journalistic institutions hire economics writers or just ask an economist and listen to what they say challenge (impossible)#aggregate spending is not an end in itself#It is rather a means to welfare#If people can satisfy the same needs with fewer resources (lower costs when resources are priced accurately)#then the economy is functioning more efficiently and productively.#Calling this “harm” reveals a model of the economy divorced from its foundational purpose.#do not let journos fool you#or business majors for that matter
12K notes
·
View notes
Text
SciTech Chronicles. . . . . . . . .Jun 6th, 2025
#CANYA#protein#aggregation#motifs#alexithymia#“Autism spectrum”#interoception#“bivariate twin modeling”#“sodium polyacrylate”#“passive cooling”#hygroscopic#lithium chloride#infrared#seasonal#tilt#Dragonfly#criticality#NREM#Adenosine#oscillations
0 notes
Text
Tips to Start your own Taxi Aggregator business model like Uber
Do you want to know how the Uber taxi model works? Find the expert's tips from UnicoTaxi to start your own Taxi aggregator business model like Uber in your city.
#taxi business#taxi aggregator#ride sharing#car pooling#car sharing#uber#uber model#uber like solutions#business tips#transportation#passenger transportation#unicotaxi
0 notes
Text
I'm flat out tired of seeing actual reputable news sources, real actual companies, and living, sentient people talking about investment in AI. Does nobody understand what this technology actually is.
my understanding is that large language models basically construct statistically likely combinations of words based upon enormous, sprawling aggregations of statistical data drawn from basically all written text on the entire internet. I've read a million articles explaining how AI works and I never learn anything new from them.
But I still feel like I'm constantly missing something because everybody seems to expect that in the near future chatGPT is going to like, transfigure into something other than a chatbot that aggregates an exceptionally large amount of information about how language tends to be constructed.
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
So, let me try and put everything together here, because I really do think it needs to be talked about.
Today, Unity announced that it intends to apply a fee to use its software. Then it got worse.
For those not in the know, Unity is the most popular free to use video game development tool, offering a basic version for individuals who want to learn how to create games or create independently alongside paid versions for corporations or people who want more features. It's decent enough at this job, has issues but for the price point I can't complain, and is the idea entry point into creating in this medium, it's a very important piece of software.
But speaking of tools, the CEO is a massive one. When he was the COO of EA, he advocated for using, what out and out sounds like emotional manipulation to coerce players into microtransactions.
"A consumer gets engaged in a property, they might spend 10, 20, 30, 50 hours on the game and then when they're deep into the game they're well invested in it. We're not gouging, but we're charging and at that point in time the commitment can be pretty high."
He also called game developers who don't discuss monetization early in the planning stages of development, quote, "fucking idiots".
So that sets the stage for what might be one of the most bald-faced greediest moves I've seen from a corporation in a minute. Most at least have the sense of self-preservation to hide it.
A few hours ago, Unity posted this announcement on the official blog.
Effective January 1, 2024, we will introduce a new Unity Runtime Fee that’s based on game installs. We will also add cloud-based asset storage, Unity DevOps tools, and AI at runtime at no extra cost to Unity subscription plans this November. We are introducing a Unity Runtime Fee that is based upon each time a qualifying game is downloaded by an end user. We chose this because each time a game is downloaded, the Unity Runtime is also installed. Also we believe that an initial install-based fee allows creators to keep the ongoing financial gains from player engagement, unlike a revenue share.
Now there are a few red flags to note in this pitch immediately.
Unity is planning on charging a fee on all games which use its engine.
This is a flat fee per number of installs.
They are using an always online runtime function to determine whether a game is downloaded.
There is just so many things wrong with this that it's hard to know where to start, not helped by this FAQ which doubled down on a lot of the major issues people had.
I guess let's start with what people noticed first. Because it's using a system baked into the software itself, Unity would not be differentiating between a "purchase" and a "download". If someone uninstalls and reinstalls a game, that's two downloads. If someone gets a new computer or a new console and downloads a game already purchased from their account, that's two download. If someone pirates the game, the studio will be asked to pay for that download.
Q: How are you going to collect installs? A: We leverage our own proprietary data model. We believe it gives an accurate determination of the number of times the runtime is distributed for a given project. Q: Is software made in unity going to be calling home to unity whenever it's ran, even for enterprice licenses? A: We use a composite model for counting runtime installs that collects data from numerous sources. The Unity Runtime Fee will use data in compliance with GDPR and CCPA. The data being requested is aggregated and is being used for billing purposes. Q: If a user reinstalls/redownloads a game / changes their hardware, will that count as multiple installs? A: Yes. The creator will need to pay for all future installs. The reason is that Unity doesn’t receive end-player information, just aggregate data. Q: What's going to stop us being charged for pirated copies of our games? A: We do already have fraud detection practices in our Ads technology which is solving a similar problem, so we will leverage that know-how as a starting point. We recognize that users will have concerns about this and we will make available a process for them to submit their concerns to our fraud compliance team.
This is potentially related to a new system that will require Unity Personal developers to go online at least once every three days.
Starting in November, Unity Personal users will get a new sign-in and online user experience. Users will need to be signed into the Hub with their Unity ID and connect to the internet to use Unity. If the internet connection is lost, users can continue using Unity for up to 3 days while offline. More details to come, when this change takes effect.
It's unclear whether this requirement will be attached to any and all Unity games, though it would explain how they're theoretically able to track "the number of installs", and why the methodology for tracking these installs is so shit, as we'll discuss later.
Unity claims that it will only leverage this fee to games which surpass a certain threshold of downloads and yearly revenue.
Only games that meet the following thresholds qualify for the Unity Runtime Fee: Unity Personal and Unity Plus: Those that have made $200,000 USD or more in the last 12 months AND have at least 200,000 lifetime game installs. Unity Pro and Unity Enterprise: Those that have made $1,000,000 USD or more in the last 12 months AND have at least 1,000,000 lifetime game installs.
They don't say how they're going to collect information on a game's revenue, likely this is just to say that they're only interested in squeezing larger products (games like Genshin Impact and Honkai: Star Rail, Fate Grand Order, Among Us, and Fall Guys) and not every 2 dollar puzzle platformer that drops on Steam. But also, these larger products have the easiest time porting off of Unity and the most incentives to, meaning realistically those heaviest impacted are going to be the ones who just barely meet this threshold, most of them indie developers.
Aggro Crab Games, one of the first to properly break this story, points out that systems like the Xbox Game Pass, which is already pretty predatory towards smaller developers, will quickly inflate their "lifetime game installs" meaning even skimming the threshold of that 200k revenue, will be asked to pay a fee per install, not a percentage on said revenue.

[IMAGE DESCRIPTION: Hey Gamers!
Today, Unity (the engine we use to make our games) announced that they'll soon be taking a fee from developers for every copy of the game installed over a certain threshold - regardless of how that copy was obtained.
Guess who has a somewhat highly anticipated game coming to Xbox Game Pass in 2024? That's right, it's us and a lot of other developers.
That means Another Crab's Treasure will be free to install for the 25 million Game Pass subscribers. If a fraction of those users download our game, Unity could take a fee that puts an enormous dent in our income and threatens the sustainability of our business.
And that's before we even think about sales on other platforms, or pirated installs of our game, or even multiple installs by the same user!!!
This decision puts us and countless other studios in a position where we might not be able to justify using Unity for our future titles. If these changes aren't rolled back, we'll be heavily considering abandoning our wealth of Unity expertise we've accumulated over the years and starting from scratch in a new engine. Which is really something we'd rather not do.
On behalf of the dev community, we're calling on Unity to reverse the latest in a string of shortsighted decisions that seem to prioritize shareholders over their product's actual users.
I fucking hate it here.
-Aggro Crab - END DESCRIPTION]
That fee, by the way, is a flat fee. Not a percentage, not a royalty. This means that any games made in Unity expecting any kind of success are heavily incentivized to cost as much as possible.

[IMAGE DESCRIPTION: A table listing the various fees by number of Installs over the Install Threshold vs. version of Unity used, ranging from $0.01 to $0.20 per install. END DESCRIPTION]
Basic elementary school math tells us that if a game comes out for $1.99, they will be paying, at maximum, 10% of their revenue to Unity, whereas jacking the price up to $59.99 lowers that percentage to something closer to 0.3%. Obviously any company, especially any company in financial desperation, which a sudden anchor on all your revenue is going to create, is going to choose the latter.
Furthermore, and following the trend of "fuck anyone who doesn't ask for money", Unity helpfully defines what an install is on their main site.
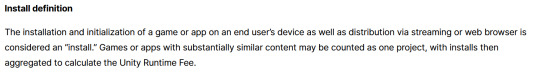
While I'm looking at this page as it exists now, it currently says
The installation and initialization of a game or app on an end user’s device as well as distribution via streaming is considered an “install.” Games or apps with substantially similar content may be counted as one project, with installs then aggregated to calculate the Unity Runtime Fee.
However, I saw a screenshot saying something different, and utilizing the Wayback Machine we can see that this phrasing was changed at some point in the few hours since this announcement went up. Instead, it reads:
The installation and initialization of a game or app on an end user’s device as well as distribution via streaming or web browser is considered an “install.” Games or apps with substantially similar content may be counted as one project, with installs then aggregated to calculate the Unity Runtime Fee.
Screenshot for posterity:
That would mean web browser games made in Unity would count towards this install threshold. You could legitimately drive the count up simply by continuously refreshing the page. The FAQ, again, doubles down.
Q: Does this affect WebGL and streamed games? A: Games on all platforms are eligible for the fee but will only incur costs if both the install and revenue thresholds are crossed. Installs - which involves initialization of the runtime on a client device - are counted on all platforms the same way (WebGL and streaming included).
And, what I personally consider to be the most suspect claim in this entire debacle, they claim that "lifetime installs" includes installs prior to this change going into effect.
Will this fee apply to games using Unity Runtime that are already on the market on January 1, 2024? Yes, the fee applies to eligible games currently in market that continue to distribute the runtime. We look at a game's lifetime installs to determine eligibility for the runtime fee. Then we bill the runtime fee based on all new installs that occur after January 1, 2024.
Again, again, doubled down in the FAQ.
Q: Are these fees going to apply to games which have been out for years already? If you met the threshold 2 years ago, you'll start owing for any installs monthly from January, no? (in theory). It says they'll use previous installs to determine threshold eligibility & then you'll start owing them for the new ones. A: Yes, assuming the game is eligible and distributing the Unity Runtime then runtime fees will apply. We look at a game's lifetime installs to determine eligibility for the runtime fee. Then we bill the runtime fee based on all new installs that occur after January 1, 2024.
That would involve billing companies for using their software before telling them of the existence of a bill. Holding their actions to a contract that they performed before the contract existed!
Okay. I think that's everything. So far.
There is one thing that I want to mention before ending this post, unfortunately it's a little conspiratorial, but it's so hard to believe that anyone genuinely thought this was a good idea that it's stuck in my brain as a significant possibility.
A few days ago it was reported that Unity's CEO sold 2,000 shares of his own company.
On September 6, 2023, John Riccitiello, President and CEO of Unity Software Inc (NYSE:U), sold 2,000 shares of the company. This move is part of a larger trend for the insider, who over the past year has sold a total of 50,610 shares and purchased none.
I would not be surprised if this decision gets reversed tomorrow, that it was literally only made for the CEO to short his own goddamn company, because I would sooner believe that this whole thing is some idiotic attempt at committing fraud than a real monetization strategy, even knowing how unfathomably greedy these people can be.
So, with all that said, what do we do now?
Well, in all likelihood you won't need to do anything. As I said, some of the biggest names in the industry would be directly affected by this change, and you can bet your bottom dollar that they're not just going to take it lying down. After all, the only way to stop a greedy CEO is with a greedier CEO, right?
(I fucking hate it here.)
And that's not mentioning the indie devs who are already talking about abandoning the engine.
[Links display tweets from the lead developer of Among Us saying it'd be less costly to hire people to move the game off of Unity and Cult of the Lamb's official twitter saying the game won't be available after January 1st in response to the news.]
That being said, I'm still shaken by all this. The fact that Unity is openly willing to go back and punish its developers for ever having used the engine in the past makes me question my relationship to it.
The news has given rise to the visibility of free, open source alternative Godot, which, if you're interested, is likely a better option than Unity at this point. Mostly, though, I just hope we can get out of this whole, fucking, environment where creatives are treated as an endless mill of free profits that's going to be continuously ratcheted up and up to drive unsustainable infinite corporate growth that our entire economy is based on for some fuckin reason.
Anyways, that's that, I find having these big posts that break everything down to be helpful.
#Unity#Unity3D#Video Games#Game Development#Game Developers#fuckshit#I don't know what to tag news like this
6K notes
·
View notes
Text
I would honestly ask everyone pushing Copyright Law solutions to AI Art how they would feel about a scenario in which it becomes settled law that you cannot train a generative image model on images you do not own the rights to,
and then the creators of these programs legally purchase the right to use large databases of art owned by media corporations and stock image aggregators, and create a legally-sound pipeline for AI image generation with which they can safely replace human artists, without fear of legal reprisals
because to my mind this is both the worst possible outcome and the most likely one
2K notes
·
View notes
Text

This post from a verified X account recently received 17 million “views,” about 14,000 retweets and around 500 replies. But the replies aren’t what you’d normally see on Twitter pre-Elon Musk’s takeover. Instead, they’re almost exclusively from other verified accounts, who aren’t even attempting to actually reply to the post. Even weirder, some of the accounts replying underneath this post appear to be trying to start a completely different reply thread.
It's bizarre new trend on X that I’ve noticed becoming more popular recently. And I’m going to call it a Verified Meme Dump. And it’s sort of a perfect example of how paid verification and user monetization has broken a platform that was primarily powered by conversations.
On Twitter, back when it was Twitter, the incentive to be funny or interesting or informative was retweets and likes, which if you gained enough of you might get a media job, or a book deal, or get laid. On X, Musk’s pay-to-play model of virality has turned the site into an environment of pure capitalism where conversation simply gets in the way. And after scrolling through enough of these Verified Meme Dumps, I slowly realized what they actually reminded me of. These replies are just galleries of refried edgy memes with no coherent theme, posted by scammers and weirdos, surrounded by ads for brands I’ve never heard of and products that probably don’t exist, with poorly-aggregated headlines sitting next to them on the sidebar. It’s 9gag. Elon Musk paid $44 billion to make 9gag. And his big plan to improve it, according to Fortune this week, is to start charging new users $1 a year to use it.
[Read more at Garbage Day]
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Words for the Universe

kind (late Old English–1600) - Nature in the abstract or viewed collectively.
world (c.1175–) - The material universe; the cosmos; (also rarely) a system of celestial objects. Also figurative. Chiefly with the.
frame (a.1325–) - The universe, the heavens, the earth, or any part of it, regarded as a structure. Now archaic.
creature (c.1384–1611) - The created universe; creation. Obsolete.
university (c.1450–1642) - The whole world; the universe. Obsolete.
engine (?1510–1741) - The universe, or a particular division of it, considered as a working system. Frequently in engine of the world. Obsolete.
universal (1569–1628) - The universe. Obsolete.
universality (1577–1603) - The whole world; the universe. Obsolete.
mass (1587–1697) - The created universe; the earth. Obsolete.
universe (1589–) - All existing matter, space, time, energy, etc., regarded collectively.
all (1598–) - The universe, the macrocosm; the whole of nature or existence.
cosmosie (1600) - Cosmos.
macrocosm (1602–) - The universe (opposed to microcosm); the world of all nature.
existence (1610–) - concrete. All that exists; the aggregate of being.
system (1610–1816) - The whole scheme of created things, the universe. Obsolete.
megacosm (1617–1851) - macrocosm.
cosmos (1650–) - The world or universe as an ordered and harmonious system.
materialism (1817) - concrete. The system of material things; the material universe. Obsolete. rare. world-all (1847–) - The world considered as a unit; the universe.
panarchy (1848–) - A universal realm.
multiverse (1895–) - The universe considered as lacking order or a single ruling and guiding power.
metaverse (1994–) - Meta-universe; cosmology: the hypothetical combination of all co-existing or sequentially existing universes.
SPECIFIC TERMS
static universe (1871–) - A universe which does not move or change.
block universe (1881–) - The universe conceived as resembling an unchanging block.
plenum (1887–) - A space completely filled with matter; spec. the whole of space regarded as being so filled. Contrasted with vacuum.
expanding universe (1931–) - The universe regarded as continually expanding, so that the galaxies are steadily receding from one another.
steady state (1948–) - An unvarying condition in a physical process, especially as in the theory that the universe is eternal and maintained by constant creation of matter.
bubble universe (1982–) - In some inflationary models of cosmology: any of an infinite number of universes formed as expanding regions within a space.
Source ⚜ Writing Resources PDFs ⚜ Word List: Star More: Word Lists ⚜ References ⚜ Historical Thesaurus
#writing reference#writeblr#dark academia#spilled ink#langblr#worldbuilding#literature#science#writers on tumblr#linguistics#writing prompt#science fiction#poets on tumblr#poetry#writing prompts#language#words#sci fi#creative writing#writing inspiration#vincent van gogh#writing resources
153 notes
·
View notes
Text
What is a Rock?
Hey folks!
Before we get started with sharing our full survey notes, we thought it would be a good idea to go over some basic terminology to ensure we're all on the same page!
What is a Rock?
No, seriously! What counts as a “rock”? Geologically speaking, a rock is a solid, naturally-occurring collection of minerals. It might be made of a single mineral type, or multiple, but it is an aggregate of many individual mineral crystals that are interlocked together.

Fig. 1: An image of a coarse-grained granite showing individual crystals of feldspar, mica and quartz. Note that the entire rock is made up of these interlocking crystals.
What is a Mineral?
Okay, so we know what a rock is now - it's made up of minerals. But, what is a mineral? A mineral is a building component of rocks, and they have a very specific definition based on particular criteria that must be met. For something to be considered a mineral, it must meet all the following criteria:-
It must be solid
It must be naturally-occurring
It must be inorganic
It must have a definite and known chemical composition
It must have a defined crystal structure
What does this actually mean? Let’s walk through it. Criterion one discounts anything that is a liquid - such as water. As you know, rocks and minerals can become liquid when exposed to high temperatures, magma and lava for example, but in this form, they are not minerals, and therefore not rocks! They can only be classed as minerals once they solidify, provided they meet the other criteria alongside.

Fig. 2: Image of lava (a non-mineral due to its liquid form) and basalt (a fine grained, igneous rock, and the solidified form of many low viscosity lava flows).
As for the other criteria, naturally-occurring and inorganic are self-explanatory. No crystals that can only be manufactured in a laboratory setting are true minerals, because they cannot exist in nature! Crystals that are commonly lab-grown but can exist in nature (such as moissanite) still count as minerals. Inorganic means the mineral can be formed by inorganic processes. Something like calcite can be produced by animals (such as clam shells) but can also be formed by geological processes without the involvement of any living thing. This actually discounts amber as a mineral - since it is tree resin (formed organically) and is not replaced by any other minerals as is the case with fossilisation - therefore amber is not a mineral!
Having a definite chemical composition is also pretty much what it sounds like - it needs to have a chemical formula - a sequence of elements organized to form a compound that we know the definite composition of. For example, the chemical composition of quartz is SiO₂, which means it is a compound made up of atoms of silica and oxygen. Similarly, the composition of potassium feldspar - KAlSi₃O₈ is made up of potassium, aluminium, silica and oxygen atoms. When dealing with specific types of rocks, such as fine grained igneous specimens, the fine grain size of the individual crystals often makes it impractical to determine rock type via crystal analysis alone, so some geologists will use chemical analysis to aid in this - hence why it's important to know the definite chemical composition of your specimens!
Lastly, a mineral must have a crystal structure - but what is a crystal structure? The simplest way to imagine this is with building blocks. Each block is the unit that defines the chemical composition - for example, SiO₄ for quartz. So, one “block” of quartz will be a unit of SiO₄. By arranging these blocks in a repeating pattern, a larger structure begins to take form. Crystals are naturally orderly structures - imagine the blocks are piled nicely on top of each other, this is why many crystals have such well defined shapes!

Fig. 3: Diagram showing the atomic "building block" structure of quartz using a 3D model and ball-and-stick diagram; diagram showing "building blocks" arranged in the natural crystal structure; image of a quartz crystal - note the same crystal structure!
Something like glass, or a naturally-occurring glass, like obsidian, has these blocks arranged randomly, like if you were to take your tower and throw it into a storage bin. Because obsidian lacks this order on an atomic level, it isn’t considered a true mineral!

Fig. 4: Image showing a fragment of obsidian. Note the conchoidal fracturing on the obsidian - this is caused by the lack of organisation in its structure. The disorganised nature of natural glass and obsidian exclude them from being a true crystal, and therefore they are also not considered true minerals.
Unfortunately, we aren’t going to be able to run any chemical analyses in Outer Wilds, but we’ll do our best to compare what we see to real-world rocks, minerals, and features, and hopefully this will be able to steer us in the correct direction regarding some of these criteria to ensure we are making the most scientifically informed analyses possible!
What is a Fossil?
Now, we just said that minerals and rocks can’t be organic, and you’re probably thinking, well hold on a second, what about fossils? How can something that was organic become inorganic, and then a rock?
Let’s start by defining what a fossil actually is. Fossils are described as “any preserved remains, or trace of a once-living thing from a past geological age.” This includes anything from the fossilised skeletons of dinosaurs, to the delicate imprints of leaves and plants. Now, it’s important to note that not all fossils are rocks. Objects preserved in amber, for example, are classed as fossils - but as they remain organic they cannot be classed as a rock.
How do we go from something organic, like a bone, to an inorganic version of it? Probably the most well known form of fossilisation is via replacement - where organic remains are replaced by inorganic minerals. Most bones are made up of calcium phosphate and other organic materials. When an animal dies and is buried by sediment, these organic materials are replaced by inorganic crystals in a process known as permineralisation. Permineralisation occurs when the pores of the original specimen are infilled with mineral matter from the ground or water - which then, bit by bit, replace the original organics with minerals, eventually completely replacing the whole specimen! When this occurs, you no longer have your original animal bone, but instead a replica of it with a completely inorganic composition - a fossil! The minerals involved in replacement can vary widely, which can produce spectacular finds such as these pyritised ammonites, or opalised vertebrae!

Fig. 5: Fossilised remains of two opalised Iguanodon vertebrae; a pyritised Ammonite.
Other fossils, such as footprints and burrows provide a record of an organism’s life, as opposed to actual remains of the organism itself. These fossils are known as trace fossils and are normally impressions that have been made in soft mud/soil that has then lithified. The cool thing about trace fossils, and especially footprints, is that you’re left with a cast of whatever part of the creature made contact with the substrate - sometimes with incredible detail of footpads, claws, and/or skin. Other trace fossils include things like coprolites, gizzard stones, and nests! A trace fossil is also completely inorganic, as it’s simply an imprint of a creature, or something a creature left behind, and as such, technically classes as a rock!

Fig. 6: Photograph showing a dinosaur footprint mould and a dinosaur footprint cast. Both of these are trace fossils and have been formed via sediment infilling and lithification.
Alright, there was a lot of information there, but hopefully it has provided you with a strong foundation and understanding of what classes as a true rock! In our next post, we will be diving into the different rock types and the funky structures and features that they can create!
Hopefully, you’ll soon be able to start identifying a variety of rocks in your own Outer Wilds adventures!
If you have any questions regarding what we have talked about here, or indeed just about the Outer Wilds Geological Survey in general, please don't hesitate to drop us an ask!
Catch you in the next loop! The OWGS Team
71 notes
·
View notes
Note
historical writing followup anon here. ackk i thought the link got pasted but it mustve gotten sucked into the void. i was referring to this ^^ https://www.tumblr.com/transmutationisms/777831995879374848/
oh my god i literally meant to circle back to that like a month ago. my drafts are where posts go to die.
yeas for anyone who cares & missed it—the question was for any historical texts that have influenced how i think about the formal practice of writing history, and/or that are simply enjoyable reads on a mechanical prose level. i'm listing in no particular order, & with more of a focus on style & general methodological orientation over the substance of the arguments. also these are probably all going to be in history of science/medicine but that's rly just because those are texts i've spent a lot of time with lol.
ill composed: sickness, gender, and belief in early modern england by olivia weisser -- primary sources here are largely personal writings: journals, business records, marginalia, she spent a LOT of time combing archives here and it allows her to really straddle the line between history of medicine and history of affect/emotions, which is not typically a topic i find treated this persuasively
doctoring traditions: ayurveda, small technologies, and braided sciences by projit bihari mukharji -- loved this on a prose level, and is also a useful demo of how histories can look once we move past the unidirectional basalla-style model of colonial knowledge dissemination & deal with eg the interests of these upper-caste colonial administrators in the creation & defence of an 'ayurvedic tradition'
medicalizing blackness: making racial difference in the atlantic world, 1780–1840 by rana hogarth -- both the periodisation and the geographic delineation are very very strongly chosen here, she brings together a number of atlantic-world episodes often treated in isolation from one another. treats each in its specificity but succeeds in pulling from the aggregate a strong analysis of the overarching concept (antiblackness; the creation of race via medical science) that she's after
baron de vastey and the origins of black atlantic humanism by marlene daut -- brought me back to seeing how close literary textual analysis can be historicised / integrated into historical analysis productively, after several years of mostly trying to curb my impulse toward the former
victorian sensation: the extraordinary publication, reception, and secret authorship of vestiges and of the natural history of creation by james secord -- classic of history of the book, history of readership / popular audiences, &c
the fall of robespierre: 24 hours in revolutionary paris by colin jones -- i found this boring & its specific topic means it's not really beating the great man allegations but it did certainly get me thinking about how we narrativise/periodise in history, and why
the physician-legislators of france: medicine and politics in the early third republic, 1870–1914 by jack ellis -- prosopography is hard to write and usually kind of boring to read but the payoff is worth it i fear
ideals of the body: architecture, urbanism, and hygiene in postrevolutionary paris by sun-young park -- working in traditions of urban history, architectural history, anthropology à la rabinow, really gorgeous granular analysis of the creation & design of the actual physical spaces comprising a city. esp shines where she treats pedagogical institutions, incl paris deaf-blind institutes
mining language: racial thinking, indigenous knowledge, & colonial metallurgy in the early modern iberian world by allison bigelow -- super super fun & fruitful moves here bringing together discourse analysis, history of the book, economic history, and history of technology in colonial mining & the creation & circulation of knowledge in those colonial networks
engineers of happy land: technology and nationalism in a colony by rudolf mrázek -- i have issues with this book but stylistically it is really a pleasure & got me thinking a lot about how we write history & how style and ideology inform one another in that process. like if the arcades project was about colonial indonesia
what nostalgia was: war, empire, and the time of a deadly emotion by thomas dodman -- more people should spend half this effort on historicising 1) affects and 2) psychiatric descriptions of those affects. history is so fun when it's fun
the expressiveness of the body and the divergence of greek and chinese medicine by shigehisa kuriyama -- this is so so fun on a prose level in a way academic history rarely is. it's a comparative history, which in general i don't love, and is markedly much more detailed in the exposition of greek medicine than chinese
88 notes
·
View notes
Text
BoyBoy book club⭑.ᐟ
These books have either been mentioned or recommended by the boys, list made to the best of my memory, some notes added for context + little abstract. [(A.) = Aleksa's rec; (L.) = Lucas' rec; (Al.) = Alex's rec] Reply or reblog to add more to update the list thanks!
⊹ Caliban and the Witch: Women, the Body and Primitive Accumulation - Silvia Federici (A.) [Aleksa's commentary: Also 'Caliban and the Witch' by Silvia Federicci is brilliant. It's a great marxist-feminist retelling of the European witch-hunts, it's really really cool. It completely flipped my view of the birth of capitalism... She posits that capitalism is a reaction to a potential peasant revolution in Europe that never succeeded, and situates the witch-hunt as a tool of the capitalist class to break peasant social-ties and discipline women into their new role as reproducers of workers.] || Is a history of the body in the transition to capitalism. Moving from the peasant revolts of the late Middle Ages to the witch-hunts and the rise of mechanical philosophy, Federici investigates the capitalist rationalization of social reproduction. She shows how the battle against the rebel body and the conflict between body and mind are essential conditions for the development of labor power and self-ownership, two central principles of modern social organization.
⊹ The Age of Surveillance Capitalism - Shoshana Zuboff (A.) || This book looks at the development of digital companies like Google and Amazon, and suggests that their business models represent a new form of capitalist accumulation that she calls "surveillance capitalism". While industrial capitalism exploited and controlled nature with devastating consequences, surveillance capitalism exploits and controls human nature with a totalitarian order as the endpoint of the development.
⊹ Anti-Oedipus: Capitalism and Schizophrenia - Gilles Deleuze and Félix Guattari (L.) || In this book , Gilles Deleuze and Félix Guattari set forth the following theory: Western society's innate herd instinct has allowed the government, the media, and even the principles of economics to take advantage of each person's unwillingness to be cut off from the group. What's more, those who suffer from mental disorders may not be insane, but could be individuals in the purest sense, because they are by nature isolated from society.
⊹ Open Veins of Latin America - Eduardo Galeano (A.) (Intro to LATAM history, infuriating but good.) (Personal recommendation if you know nothing about LATAM.) || An analysis of the impact that European settlement, imperialism, and slavery have had in Latin America. In the book, Galeano analyzes the history of the Americas as a whole, from the time period of the European settlement of the New World to contemporary Latin America, describing the effects of European and later United States economic exploitation and political dominance over the region. Throughout the book, Galeano analyses notions of colonialism, imperialism, and the dependency theory.
⊹ The Origin of Capitalism - Ellen Wood (A.) || Book on history and political economy, specifically the history of capitalism, written from the perspective of political Marxism.
⊹ If We Burn - Vincent Bevins (L.) || The book concerns the wave of mass protests during the 2010s and examines the question of how the organization and tactics of such protests resulted in a "missing revolution," given that most of these movements appear to have failed in their goals, and even led to a "record of failures, setbacks, and cataclysms".
⊹ The Jakarta Method - Vincent Bevins (A.) [Aleksa’s recommendation for leftists friends] || It concerns U.S. government support for and complicity in anti-communist mass killings around the world and their aggregate consequences from the Cold War until the present era. The title is a reference to Indonesian mass killings of 1965–66, during which an estimated one million people were killed in an effort to destroy the political left and movements for government reform in the country.
⊹ The Anarchy: The Relentless Rise of the East India Company - William Dalrymple (L.) [Not read by the boys yet, but wanted to read.] || History book that recounts the rise of the East India Company in the second half of the 18th century, against the backdrop of a crumbling Mughal Empire and the rise of regional powers.
⊹ The Triumph of Evil: The Reality of the USA's Cold War Victory - Austin Murphy (A.) || Contrary to the USA false propaganda, this book documents the fact that the USA triumph in the Cold War has increased economic suffering and wars, which are shown to be endemic to the New World Order under USA capitalist domination.
⊹ Technofeudalism: What Killed Capitalism - Yanis Varoufakis (L.) || Big tech has replaced capitalism’s twin pillars—markets and profit—with its platforms and rents. With every click and scroll, we labor like serfs to increase its power. Welcome to technofeudalism . . .
⊹ The History of the Russian Revolution - Leon Trotsky (A.) [Aleksa's commentary: This might be misconstrued since I'm not a massive fan of Trotsky... but... his book "History of the russian revolution" is amazing. It's so unique to have such a detailed history book compiled by someone who was an active participant in the events, and he's surprisingly hilarious. Makes some great jokes in there and really captures the revolutionary spirit of the time.] || The History of the Russian Revolution offers an unparalleled account of one of the most pivotal and hotly debated events in world history. This book presents, from the perspective of one of its central actors, the profound liberating character of the early Russian Revolution.
⊹ Rise of The Red Engineers - Joel Andreas (A.) [Aleksa's commentary: It's a sick history book, focusing on a single university in China following it's history from imperial china, through the revolution and to the modern day. It documents sincere efforts to revolutionize the education system, but does it from a very detailed, on-the-ground view of how these cataclysmic changes effect individual students and teachers at this institution.] || In a fascinating account, author Joel Andreas chronicles how two mutually hostile groups—the poorly educated peasant revolutionaries who seized power in 1949 and China's old educated elite—coalesced to form a new dominant class.
⊹ Adults in the Room: My Battle with the European and American Deep Establishment - Yanis Varoufakis (A.) [Aleksa's commentary: The book I mentioned earlier - "adults in the room" - is amazing. There's a great description of Greece's role in the European economy [as an archetype for other, small European countries] and the Union's successful attempts to discipline smaller countries to keep their monetary policy in line with the interest of central European bankers. I'd definitely reccommend it!] || What happens when you take on the establishment? In Adults in the Room, the renowned economist and former finance minister of Greece Yanis Varoufakis gives the full, blistering account of his momentous clash with the mightiest economic and political forces on earth.
Edit: Links added when possible! If they stop working let me know or if you have a link for the ones missing.
#IDK if anyone else is interested in this but in case anyone finds it useful <3#boy boy#aleksa vulović#alex apollonov#ididathing#ngl most of this r aleksa/lucas recs.... idk if any of them are alex sorry i forgot?#bb book club
167 notes
·
View notes
Text
When prophecy fails, election polling edition

In Canto 20 of Inferno, Dante confronts a pit where the sinners have had their heads twisted around backwards; they trudge, naked and weeping, through puddles of cooling tears. Virgil informs him that these are the fortunetellers, who tried to look forwards in life and now must look backwards forever.
In a completely unrelated subject, how about those election pollsters, huh?
Writing for The American Prospect, historian Rick Perlstein takes a hard look at characteristic failure modes of election polling and ponders their meaning:
https://prospect.org/politics/2024-09-25-polling-imperilment/
Apart from the pre-election polling chaos we're living through today, Perlstein's main inspiration is W Joseph Campbell 2024 University of California Press book, Lost in a Gallup: Polling Failure in US Presidential Elections:
https://www.ucpress.edu/books/lost-in-a-gallup/paper
In Campbell's telling, US election polling follows a century-old pattern: pollsters discover a new technique that works spookily well..for a while. While the new polling technique works, the pollster is hailed a supernaturally insightful fortune-teller.
In 1932, the Raleigh News and Observer was so impressed with polling by The Literary Digest that they proposed replacing elections with Digest's poll. The Digest's innovation was sending out 20,000,000 postcards advertising subscriptions and asking about presidential preferences. This worked perfectly for three elections – 1924, 1928, and 1932. But in 1936, the Digest blew it, calling the election for Alf Landon over FDR.
The Digest was dethroned, and new soothsayers were appointed: George Gallup, Elmo Roper and Archibald Crossler, who replaced the Digest's high-volume polling with a new kind of poll, one that sought out a representative slice of the population (as Perlstein says, this seems "so obvious in retrospect, you wonder how nobody thought of it before").
Representative polling worked so well that, three elections later, the pollsters declared that they could predict the election so well from early on that there was no reason to keep polling voters. They'd just declare the winner after the early polls were in and take the rest of the election off.
That was in 1948 – you know, 1948, the "Dewey Defeats Truman" election?
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dewey_Defeats_Truman
If this sounds familiar, perhaps you – like Perlstein – are reminded of the 2016 election, where Fivethirtyeight and Nate Silver called the election for Hillary Clinton, and we took them at their word because they'd developed a new, incredibly accurate polling technique that had aced the previous two elections.
Silver's innovation? Aggregating state polls, weighting them by accuracy, and then producing a kind of meta-poll that combined their conclusions.
When Silver's prophecy failed in 2016, he offered the same excuse that Gallup gave in 1948: when voters are truly undecided, you can't predict how they'll vote, because they don't know how they'll vote.
Which, you know, okay, sure, that's right. But if you know that the election can't be called, if you know that undecided voters are feeding noise into the system whenever you poll them, then why report the polls at all? If all the polling fluctuation is undecided voters flopping around, not making up their mind, then the fact that candidate X is up 5 points with undecided means nothing.
As the finance industry disclaimer has it, "past performance is no guarantee of future results." But, as Perlstein says, "past performance is all a pollster has to go on." When Nate Silver weights his model in favor of a given poll, it's based on that poll's historical accuracy, not its future accuracy, because its future accuracy can't be determined until it's in the past. Like Dante's fortune-tellers, pollsters have to look backwards even as they march forwards.
Of course, it doesn't help that in some cases, Silver was just bad at assessing polls for accuracy, like when he put polls from the far-right "shock pollster" Trafalgar Group into the highly reliable bucket. Since 2016, Trafalgar has specialized in releasing garbage polls that announce that MAGA weirdos are way ahead, and because they always say that, they were far more accurate than the Clinton-predicting competition in 2016 when they proclaimed that Trump had it in the bag. For Silver, this warranted an "A-" on reliability, and that is partially to blame for how bad Silver's 2020 predictions were, when Republicans got pasted, but Trafalgar continued to predict a Democratic wipeout. Silver's methodology has a huge flaw: because Trafalgar's prediction history began in 2016, that single data-point made them look pretty darned reliable, even though their method was to just keep saying the same thing, over and over:
https://www.ettingermentum.news/p/the-art-of-losing-a-fivethirtyeight
Pollsters who get lucky with a temporarily reliable methodology inevitably get cocky and start cutting corners. After all, polling is expensive, so discontinuing the polls once you think you have an answer is a way to increase the enterprise's profitability. But, of course, pollsters can only make money so long as they're somewhat reliable, which leads to a whole subindustry of excuse-making when this cost-cutting bites them in the ass. In 1948, George Gallup blamed his failures on the audience, who failed to grasp the "difference between forecasting an election and picking the winner of a horse race." In 2016, Silver declared that he'd been right because he'd given Trump at 28.6% chance of winning.
This isn't an entirely worthless excuse. If you predict that Clinton's victory is 71.4% in the bag, you are saying that Trump might win. But pollsters want to eat their cake and have it, too: when they're right, they trumpet their predictive accuracy, without any of the caveats they are so insistent upon when they blow it:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1jDlo7YfUxc
There's always some excuse when it comes to the polls: in 1952, George Gallup called the election a tossup, but it went for Eisenhower in a landslide. He took out a full-page NYT ad, trumpeting that he was right, actually, because he wasn't accounting for undecided voters.
Polling is ultimately a form of empiricism-washing. The pollster may be counting up poll responses, but that doesn't make the prediction any less qualitative. Sure, the pollster counts responses, but who they ask, and what they do with those responses, is purely subjective. They're making guesses (or wishes) about which people are likely to vote, and what it means when someone tells you they're undecided. This is at least as much an ideological project as it is a scientific one:
https://prospect.org/blogs-and-newsletters/tap/2024-09-23-polling-whiplash/
But for all that polling is ideological, it's a very thin ideology. When it comes to serious political deliberation, questions like "who is likely to vote" and "what does 'undecided' mean" are a lot less important than, "what are the candidates promising to do?" and "what are the candidates likely to do?"
But – as Perlstein writes – the only kind of election journalism that is consistently, adequately funded is poll coverage. As a 1949 critic put it, this isn't the "pulse of democracy," it's "its baby talk."

Today, Tor Books publishes VIGILANT, a new, free LITTLE BROTHER story about creepy surveillance in distance education. It follows SPILL, another new, free LITTLE BROTHER novella about oil pipelines and indigenous landback.

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/09/26/dewey-beats-truman/#past-performance-is-no-guarantee-of-future-results
#pluralistic#prognostication#polling#uspoli#elections#pollsters#fivethirtyeight#nate silver#george gallup#rick perlstein#history#past performance is no guarantee of future results#W Joseph Campbell#Lost in a Gallup
153 notes
·
View notes
Text
Libraries have traditionally operated on a basic premise: Once they purchase a book, they can lend it out to patrons as much (or as little) as they like. Library copies often come from publishers, but they can also come from donations, used book sales, or other libraries. However the library obtains the book, once the library legally owns it, it is theirs to lend as they see fit. Not so for digital books. To make licensed e-books available to patrons, libraries have to pay publishers multiple times over. First, they must subscribe (for a fee) to aggregator platforms such as Overdrive. Aggregators, like streaming services such as HBO’s Max, have total control over adding or removing content from their catalogue. Content can be removed at any time, for any reason, without input from your local library. The decision happens not at the community level but at the corporate one, thousands of miles from the patrons affected. Then libraries must purchase each individual copy of each individual title that they want to offer as an e-book. These e-book copies are not only priced at a steep markup—up to 300% over consumer retail—but are also time- and loan-limited, meaning the files self-destruct after a certain number of loans. The library then needs to repurchase the same book, at a new price, in order to keep it in stock. This upending of the traditional order puts massive financial strain on libraries and the taxpayers that fund them. It also opens up a world of privacy concerns; while libraries are restricted in the reader data they can collect and share, private companies are under no such obligation. Some libraries have turned to another solution: controlled digital lending, or CDL, a process by which a library scans the physical books it already has in its collection, makes secure digital copies, and lends those out on a one-to-one “owned to loaned” ratio. The Internet Archive was an early pioneer of this technique. When the digital copy is loaned, the physical copy is sequestered from borrowing; when the physical copy is checked out, the digital copy becomes unavailable. The benefits to libraries are obvious; delicate books can be circulated without fear of damage, volumes can be moved off-site for facilities work without interrupting patron access, and older and endangered works become searchable and can get a second chance at life. Library patrons, who fund their local library’s purchases with their tax dollars, also benefit from the ability to freely access the books. Publishers are, unfortunately, not a fan of this model, and in 2020 four of them sued the Internet Archive over its CDL program. The suit ultimately focused on the Internet Archive’s lending of 127 books that were already commercially available through licensed aggregators. The publisher plaintiffs accused the Internet Archive of mass copyright infringement, while the Internet Archive argued that its digitization and lending program was a fair use. The trial court sided with the publishers, and on September 4, the Court of Appeals for the Second Circuit reaffirmed that decision with some alterations to the underlying reasoning. This decision harms libraries. It locks them into an e-book ecosystem designed to extract as much money as possible while harvesting (and reselling) reader data en masse. It leaves local communities’ reading habits at the mercy of curatorial decisions made by four dominant publishing companies thousands of miles away. It steers Americans away from one of the few remaining bastions of privacy protection and funnels them into a surveillance ecosystem that, like Big Tech, becomes more dangerous with each passing data breach. And by increasing the price for access to knowledge, it puts up even more barriers between underserved communities and the American dream.
11 September 2024
154 notes
·
View notes
Text
This groundbreaking study finds that you are about 150% more likely to cause/take part in a traffic accident following a covid infection. This increase is across the board with no effect from vaccination or long covid status. The authors say this is likely due to neurological changes in anyone post covid infection. Mask up. Don't let a virus rewire your brain.
Abstract Objective This study evaluated the association between acute COVID-19 cases and the number of car crashes with varying COVID-19 vaccination rates, Long COVID rates, and COVID-19 mitigation strategies.
Background The ongoing SARS-CoV-2 pandemic has led to significant concern over long-term post-infection sequelae, especially in the Neurologic domain. Long COVID symptoms, including cognitive impairments, could potentially impact activities requiring high cognitive function, such as driving. Despite various potential impacts on driving skills and the general prevalence of Long COVID, the specific effects on driving capabilities remain understudied.
Design/Methods This study utilized a Poisson regression model to analyze data from 2020-2022, comparing aggregate car crash records and COVID-19 statistics. This model adjusted for population and included binary variables for specific months to account for stay-at-home orders. The correlation between acute COVID-19 cases and car crashes was investigated across seven states, considering vaccination rates and COVID-19 mitigation measures as potential confounders.
Results Findings indicate an association between acute COVID-19 rates and increased car crashes with an OR of 1.5 (1.23-1.26 95%CI). The analysis did not find a protective effect of vaccination against increased crash risks, contrary to previous assumptions. The OR of car crashes associated with COVID-19 was comparable to driving under the influence of alcohol at legal limits or driving with a seizure disorder.
Conclusions The study suggests that acute COVID-19, regardless of Long COVID status, is linked to an increased risk of car crashes presumably due to neurologic changes caused by SARS-CoV-2. These findings underscore the need for further research into the neuropsychological impacts of COVID-19. Further studies are recommended to explore the causality and mechanisms behind these findings and to evaluate the implications for public safety in other critical operational tasks. Finally, neurologists dealing with post-COVID patients, should remember that they may have an obligation to report medically impaired drivers.
#mask up#covid#wear a mask#pandemic#covid 19#public health#wear a respirator#still coviding#coronavirus#sars cov 2#long covid#covid conscious#covid is not over#wear a fucking mask#covid news#covidー19#covid is airborne#covid isn't over#covid pandemic#covid19
130 notes
·
View notes
Text
FiveThirtyEight is gone. Its legacy will endure.
Nate Silver’s website suffered because of Trump and changes in political news coverage.

Opinion | Perry Bacon, Jr. | March 7, 2025
FiveThirtyEight became famous for its “forecasts” from founder Nate Silver. But the website (where I worked from 2017 to 2021) was trying to do much more than predict presidential election results. FiveThirtyEight was an attempt to improve and reimagine journalism. I think it succeeded — even though the website is now defunct. ABC News, which owned FiveThirtyEight, this week laid off the site’s 15 remaining staffers. The network had already made drastic cutbacks two years ago, with Silver himself departing back then. We are in the midst of staff reductions throughout the journalism industry. That said, ABC News is not a newspaper in a declining city in the Midwest. If the network wanted to keep the site going, it could have. This decision probably wasn’t just about money. [...] Political journalism has changed in ways that have made FiveThirtyEight less essential. Silver started the website during the 2008 presidential campaign. (There are 538 votes in the electoral college.) He correctly saw a flaw in American political coverage. Journalism professors and many within the news industry had for years argued that political news was too focused on the “horse race” (who was going to win the next election) instead of policy issues. What Silver argued was that horse-race coverage, while extensive, was often quite bad. It was overly fixated on a single poll or arguing that a candidate appeared to be surging after delivering a strong speech, without any other evidence. Averaging polls, scrutinizing demographics and voting histories of states — that all seems obvious now. It wasn’t 17 years ago. [emphasis added]
I will miss FiveThirtyEight. It was always a reliable source of aggregate polling data. It also provided a lot of background information about the potential bias and reliability of individual polls.
R.I.P. FiveThirtyEight March 7, 2008 - March 5, 2025

_________________ Collage sources (before edits, starting in center, then moving top left to right clockwise, ending bottom left): 01, 02, 03, 04, 05, 06, 07
[See more excerpts from the column under the cut]
In 2010, the New York Times hired Silver and starting hosting FiveThirtyEight on its website. A few years later, ESPN hired him to create a FiveThirtyEight that would cover not only politics but also sports, science and other topics with statisticians and more traditional journalists working in a combined newsroom. The site grew in size and influence. And other news organizations started borrowing its methods, averaging polls and producing statistical models to analyze elections. [...] The site often had political scientists and scholars write pieces. Fact-checking was extensive, adding to the site’s reliability and reputation. But I knew FiveThirtyEight was in trouble when I saw not only stories similar to ours published in the Times and The Washington Post but also those larger organizations poaching our staffers. Another factor that made the website less relevant was Trump. He made politics more about tweets, firings and other drama that the data can’t really capture. [...] But for me, FiveThirtyEight staffers and its devoted fans, the site was about much more than election predictions and even Silver. It was an alternative, higher form of journalism. It was also a lovable community of nerds, wonks and junkies. Our readers were Democratic-leaning, but they weren’t people watching MSNBC just to hear how terrible Republicans are. They wanted us to tell them if a Democratic politician was going to lose. They loved that every article seemed to involve the writer examining election results down to the county level and producing three charts to support their thesis. Silver now has one of the most popular political Substack newsletters; former managing editor Micah Cohen is now politics editor for Apple News; reporter Anna Maria Barry-Jester has moved on to cover public health for ProPublica. But from my vantage point, FiveThirtyEight is everywhere in more subtle ways. The amount of charts and data in stories about politics in particular is much larger than it was two decades ago. The chief political analyst at the New York Times is a data whiz named Nate (Cohn) who joined the paper essentially as Silver’s replacement. If you tell someone about a poll, they will often ask whether other surveys show the same result. There is still too much horse-race coverage. I hate when I see polls of the 2028 Democratic primary. Can we wait a minute? But FiveThirtyEight made that coverage smarter and more rigorous — creating a legacy that will endure.
#rip 538#five thirty eight#abc ended 538#nate silver#political polling#perry bacon jr#the washington post#my collages#my edits
78 notes
·
View notes
Text
Well if I'm going to use stupidass TikTok, I should find out what all the weird baby straights and soon-to-be-divorced tradwives are up to over there.
Today we learn about the "Clean Girl Aesthetic".
Near as I can tell, it basically means not looking or dressing like some kind of dumpster clown.
And there's a fascination with pleated slacks or shorts and exposed belly buttons.
Doubtless this is mimicking some lady all these people have seen on their TVs. Taylor Swift? Another lady? Who can say? Not me, because Taylor Swift is the only lady I know of.
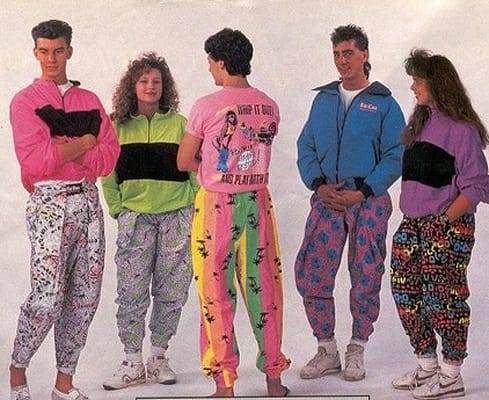
I'm old enough to remember the predecessor of this style as a kind of late 80s / early 90s Yacht Club thing that was popular with movie bullies and other people no one liked. I'm sure it has a History of Fashion name but I'm not looking it up, because Google already doesn't know who the hell I am or what the hell to sell me. I know it was very polo-shirt heavy back then. Big pockets. Beiges and greys and muted colors, probably because the POOR PEOPLE were all dressing like dumpster clowns:

But I looked up the Clean Girl thing to see exactly what probably-AI says it is:

...So it is literally about not being dirty? Isn't all fashion, inherently? Was there a trend that was wearing filth recently? Filthcore? Dumpster clown?

Well yeah, the midriff thing. But again, isn't all fashion inherently fatphobic? That's still bad, but kind of a universal in the world of people being dicks to other people about how everyone looks. The TRUE SOUL of fashion.
And that's not a new thing. Or is the Clean Girl thing especially virulently anti-fatty? Like to be a Clean Girl, you have to drive at least one fat person to contemplate suicide a month?
I mean that's awful, but TikTok is a lot of teenagers with stupid hair. I wouldn't put this past them. They're horrible little idiots. Look at their hair!

...Wait so you guys are doing "brown = dirty"? In 2024? What Gulf Coast cave did you people crawl out of after a 150-year Rip Van Winkle nap? The War Between the States is over, and your side lost. How did you figure out TikTok so fast, displaced temporal stranger?
Can't we all just shut up and wear pants?
As for the stealing thing, white people have been stealing and recreating the things they stole from POCs, then excluding them from those versions of those things, for as long as there have been white people.
It's bad, but as it is our primary cultural trait, we're certainly never going to stop.
Especially not those hibernating cave people. They probably still think "the Curse of Ham" is a justifiable legal defense.
This is what Clean Girl looks like, in case you too want to dress like someone whose dad mismanages a major streaming platform:

(I don't know who this model is. The picture is from a half-broken aggregator website in Foreign.)
145 notes
·
View notes