#alligatoridae
Text

A young American alligator (Alligator mississippiensis) rides on the back of its mother in Brazos Bend State Park, Texas, USA
by Rick Dunlap
#american alligator#alligators#crocodilians#reptiles#alligator mississippiensis#alligator#alligatoridae#crocodilia#reptilia#chordata#wildlife: texas#wildlife: usa#wildlife: north america
24K notes
·
View notes
Text
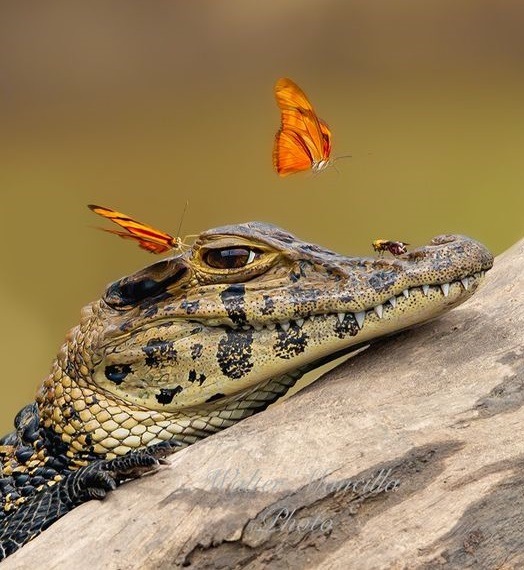

Black Caiman (Melanosuchus niger), juvenile with Julia butterlfies, family Alligatoridae, Manu National Park, Peru
photograph by Walter Mancilla Huaman
803 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Mun Alligator
Somehow 2023 felt like a slow year for new croc taxa, but I'm happy to report that a new one just dropped yesterday.
This new crocodilian is a member of the genus Alligator, which today only includes two living species, the American Alligator and the Chinese Alligator. This new species, Alligator munensis, lived during the Quaternary in what is now Thailand and may be an important species for understanding Asian alligators.
Art by Márton Szabó and size chart by yours truly


Before we go into the mystery of the Asian alligators and their origin, lets just take a moment to appreciate how weird this guy is. The skull is very short and very deep (altirostral), it was obviously small like its modern relative the Chinese Alligator and its nostrils were weirdly pulled back, with a huge bony element separating them externally. The later looks especially weird when you know alligator skulls, where the nasals do extend over the nares, but never this much. For comparisson, below is an image of the Mun Alligator in a, Chinese Alligator in e and American Alligator in i, as well as a close up.

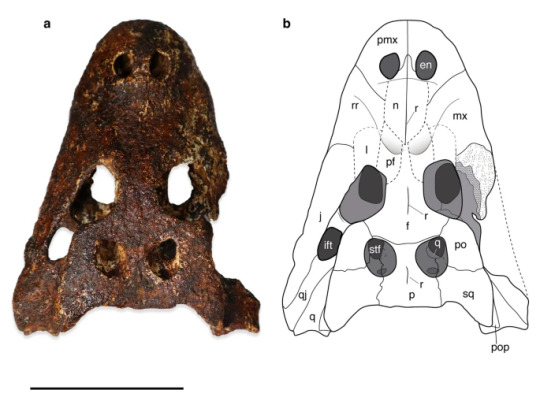
As you can see in the close up, the skull was also adorned by various ridges, both across the snout and the skulltable. Now the ridges beofre the eyes aren't unique to Alligator munensis, but I still want to highlight them as they are called spectacles. Just think that's something people should know (it's also what gives Spectacled Caimans their name).
What is sadly missing is the dentition, the teeth. This of course leaves out a big indicator of the diet. Which all in all leaves the ecology a bit unknown (we don't know why it has those weird nostrils either). However, Darlim and colleagues still found some clues. Notably, the tooth sockets in the back of the jaw are enlarged, something that's usually seen with globular teeth or teeth that are blunt and sideways flattened. Alligators actually derive from ancestors with globular teeth, which then became more generalized. Well, Alligator munensis may have done another switcheroo and gone back to that. Combining globular teeth with strong jaw muscles (check) and robust skulls (double check) could indicate that it could have fed on hard-shelled prey items. Now this doesn't mean it was specialised per say. Big turtles have big heads and do seasonally feed on snails, but are otherwise omnivores. Multiple alligatorids on the other hand lack globular teeth, but that doesn't stop them from taking hard-shelled prey regardless.
Images showing Caimans feeding on apple snails by Paul Williams and the BBC as well as an American Alligator eating a turtle by Okreb.



Now to discuss the history of Asian alligator species. It does seem rather strange that all extant alligatorids are from the Americas with the exception of the Chinese Alligator and it has been a long mystery how and when they got there. This isn't helped by the fact that alligator fossils from Asia are very much understudied. The Mun Alligator however shows what is to be expected, that diversity was a lot higher in prehistory than it is today. And it wasn't even that long ago, with the deposits dating to the Pleistocene or maybe even Holocene.
However, it doesn not solve the mystery entirely. While both the Chinese Alligator and the Mun Alligator are thought to be closely related, they are not ancestor and descendent. Instead, they seem to have diverged quite some time ago and evolved isolated from one another. That is still an interesting thought tho.
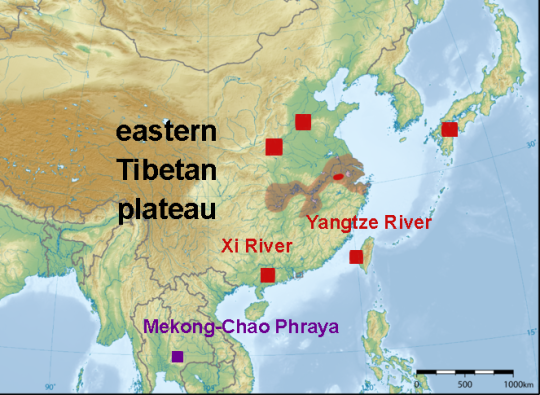
Darlim and colleagues suggest that this could all date back to the Miocene, when the ancestor of these two species inhabited the wetlands of eastern Asia. When plate tectonics caused the Himalayas to form and the Tibetan Plateau to be lifted up, both appear to have been split into distinct river systems. The ancestor of the Chinese Alligator into the Xi and Yangtze river systems and the Mun Alligator into the Mekong and Chao Phraya river systems.
Based on this hypothesis, and figures by Iijima, Takahashi, & Kobayashi (2016) chronicling the fossil record and distribution of Chinese Alligators, I put together this handy-dandy map that should illustrate the whole affair. Red for A. sinensis, purple for A. munensis. The red and transparent red areas are the formers current and former range, whereas squares represent fossil discoveries.
For any wanting to look deeper, there is of course the Wikipedia page Alligator munensis - Wikipedia or the paper, which is open access.
An extinct deep-snouted Alligator species from the Quaternary of Thailand and comments on the evolution of crushing dentition in alligatorids | Scientific Reports (nature.com)
#paleontology#crocodile#palaeoblr#prehistory#croc#long post#alligator#alligator munensis#chinese alligator#mun alligator#pleistocene#holocene#asia#fossils#crocodilia#alligatoridae#science
64 notes
·
View notes
Photo

American alligator (Alligator mississippiensis) hatchlings at Wakodahatchee Wetlands in Florida, U.S.
Pedro Lastra
219 notes
·
View notes
Text

Eurycephalosuchus
Eurycephalosuchus — вимерлий рід орієнталозухієвих алігатороїдів з пізньої крейди провінції Цзянсі в Китаї. Відомий за добре збереженим черепом і нижньою щелепою, а також різними посткраніальними рештками, Eurycephalosuchus мав короткий і широкий череп з дуже короткою черепною коробкою. Рід монотипний, містить лише вид Eurycephalosuchus gannanensis.
Повний текст на сайті "Вимерлий світ":
https://extinctworld.in.ua/eurycephalosuchus/
#eurycephalosuchus#art#alligator#late cretaceous#cretaceous#alligatoridae#china#jiangxi#ua#reptilia#cretaceous period#paleontology#paleoart#prehistoric#animals#палеоарт#палеонтологія#ukraine#ukrainian#українська мова#арт#мова#україна#digital art#daily#extinct#illustration#тварини#китай#український тамблер
23 notes
·
View notes
Note
So, I don't know who to ask this...
It occurred to me that bison used to be *Very* populous, and that they migrated, and crossed rivers to do so.
So, extrapolating from Africa, we have a vast water born bounty, floating downstream. What took advantage of this?
I am guessing wolves, bears, fish, birds.... In Africa there are crocodiles. Who sometimes get very little food the rest of the year.
Did alligators come north?
Are alligator Snapping Turtles big enough to feast for a while year(, or just pack on weight while the food lasted.)
Can that be one reason they get so darn big?
Has anyone else thought of this?
Hi there! This is a really interesting question, although the answer might not be what you think.
You're correct that, in Africa, there are crocodiles that regularly take advantage of larger prey like antelope and zebra as they attempt to cross rivers. However, all these rivers are major bodies of water, like the Nile, the Okavango Delta, or the Congo river. They're big, so they provide enough room for crocodiles to compete for food and mates, and attract a lot of prey via migration and the necessity of drinking. These rivers are also ideal temperatures for crocodiles, who are cold-blooded and need to bask in the sun to maintain their body temperatures.
In North America, there aren't many rivers that meet those qualifications. There are some alligators in the southeast end of the Rio Grande, where it runs into the Gulf of Mexico, but father north both it and the Colorado River are too cold for big reptiles. Other rivers that cross bison country are both too cold and too small. Alligator snapping turtles do have a mean bite, but they aren't nearly big enough to bring down a bison-- some of the largest have weighed over 100kg (close to 300lbs) but the average adult bison weighs at least 300kg (something like 700 lbs). The range of bison and alligator snapping turtles also don't overlap much; snapping turtles live generally east of the Mississippi River, while bison live to the west of it. So unfortunately there weren't really any big aquatic predators of bison.
However, wolves, cougars, and bears will all hunt bison, especially the old, young, or sick. Another important predator for bison were people: in fact, some historians believe now that the 'vast seas of bison herds' were actually a result of the decline of Native American populations due to disease and conflict with colonizers, which then allowed the bison population to spread unchecked.
#american bison#Artiodactyla#Bovidae#bovines#even toed ungulates#ungulates#mammals#alligator snapping turtle#Testudines#Chelydridae#snapping turtles#turtles#reptiles#american alligator#nile crocodile#Crocodilia#Crocodylidae#Alligatoridae#crocodiles#alligators#crocodilians#north america#africa#answered#asks#jack speaks
28 notes
·
View notes
Note
Are all crocodilians crocodiles?
I got asked if a tomistoma was an alligator or crocodile the other day (I work at a zoo) and it’s been bugging me. I’m pretty sure they were asking in terms of the species name not taxonomic specificity, so I said it was a tomistoma, but then realized in hindsight that I’m not actually sure what the classification is for this particular animal, so any insight would be appreciated.
(I think I may be misremembering but it might be a type of alligator or crocodile or something? But again I’m not sure and I realized that the term crocodilians can be confusing, hence the question)
Great question! You were right, tomistoma aren't considered crocodiles or alligators, they are gavialids. They're actually most closely related to gharials.
Here's crocodile taxonomy 101. Crocodiles are split into two families, Alligatoridae and Longirostres.
Alligatoridae includes true alligators:

And caimans:

And Longirostres includes true crocodiles:

And gavialids, which are gharials and tomistoma.

So tomistoma are more closely related to crocodiles than they are to alligators, but they're considered an entirely separate thing!

237 notes
·
View notes
Text
Animal of the Day!
Yacare Caiman (Caiman yacare)

(Photo from Animalia)
Conservation Status- Least Concern
Habitat- Northern Argentina; Bolivia; Southern Brazil; Paraguay
Size (Weight/Length)- 58 kg; 3 m
Diet- Fish; Crustaceans; Snails; Mollusks; Mammals; Birds
Cool Facts- Nicknamed the piranha caiman, the yacare caiman sports an impressive 74 teeth. These caiman live in slow moving rivers and wetlands with plentiful vegetation along the banks. While yacare caiman prefer cracking open snails, large males are capable of taking down prey as large as capybaras. Most Alligatoridae have a large amount of parental care towards their offspring, yet yacare caiman moms ditch the nest as soon as her babies hatch. In the 1980’s, it was believed these caiman were on track for extinction due to overhunting for their skin. Luckily, in 1992 a ban was placed on trading crocodilian skins and over 10 million individuals survive in the wild today.
Rating- 12/10 (Escargot to go.)
#animal of the day#animals#reptiles#caiman#alligator#saturday#june 17#yacare caiman#biology#science#conservation#the more you know
190 notes
·
View notes
Note
more jaunger and snake ememei and neo
I'm just gonna do one of them for now.
Ruby: What are you doing?
Jaguar!Faunus Emerald: Hunting. Be quiet.
Ruby: What are you hunting?
Emerald: There! *Leaps*
Gator!Faunus Yang: HELPHELPEHELP!
Emerald: *Pins Yang* I Win!
Yang: Yeah! By Being a cheater!
Emerald: Actually, I'm a Jaguar.
Yang: ... Fine. I forgive you because of that Pun.
Fun Fact! Jaguars are Obligate Carnivores, meaning they can only eat meat. Some of their more common prey, especially in Flood seasons, are Turtles and Caimans, Caimans are a member of the Family Alligatoridae.
#rwby#ruby rose#yang xiao long#rwby shitpost#emerald sustrai#jaguar!faunus emerald#alligator!faunus yang#asks and answers#saiyukirp
34 notes
·
View notes
Text
metazooa PLAYS 65 WINS 62 STREAK 14
WOO

[ID: Metazooa, the cladistics puzzle tree, solved in three guesses. First guess: Swan, related at archosauria. Second guess, caiman, related at alligatoridae. Next guess and final answer under the same: Alligator. END]
GET FUCKEDDDDD
#some shit#wifi at the zoo#okay now to get my ass handed to me at metaflora. metafloora. [<-not what its called]
11 notes
·
View notes
Text

An American alligator (Alligator mississippiensis) in Birmingham Zoo, Alabama, USA
by Dystopos
#american alligator#crocodilians#reptiles#alligator mississippiensis#alligator#alligatoridae#crocodilia#reptilia#chordata#captive animal#birmingham zoo
885 notes
·
View notes
Text

Smooth-fronted Caiman aka Schneider’s Dwarf Caiman (Paleosuchus trigonatus), family Alligatoridae, Peru
photograph by Andres Novales Aguirrezabal
#dwarf caiman#caiman#paleosuchus#alligatoridae#crocodilian#reptile#herpetology#south america#animals#nature
424 notes
·
View notes
Text

prompt 1: american alligator
my favorite animal of all time; that makes it one of the most important animals ever
American alligators are one of two alligator species in the world, the other being the Chinese alligator. The reason the only two alligator species live literally across the world is because of the Bering Land Bridge that existed 33 million years ago.
They're in the familiy Alligatoridae, which includes alligators and caimans. True alligators are in the subfamiliy Alligatorinae.
They, like all crocodilians, are pretty much the closest thing you can get to a dinosaur that isn't an actual dinosaur. They're more related to birds than lizard
#digital art#art#doodle#drawing#illustration#alligator#crocodilian#croctober#october#drawing challenge
11 notes
·
View notes
Photo
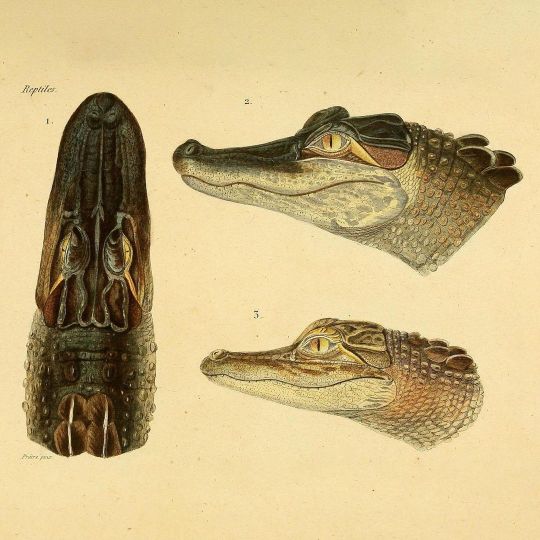
Head of the caiman and alligator. A caiman is an alligatorid belonging to the subfamily Caimaninae, one of two primary lineages within Alligatoridae, the other being alligators. Caimans inhabit Mexico, Central and South America from marshes and swamps to mangrove rivers and lakes. Caimans have scaly skin and live a fairly nocturnal existence.
45 notes
·
View notes
Text

Necrosuchus
Necrosuchus — вимерлий рід кайманів з території сучасної Аргентини, що жив в епоху палеоцену (селандський вік, близько 60 мільйонів років тому). Він мешкав у річково-озерному середовищі патагонської формації Саламанка. Типовий вид — Necrosuchus ionensis.
Повний текст на сайті "Вимерлий світ":
https://extinctworld.in.ua/necrosuchus/
#necrosuchus#caiman#lake#river#art#argentina#patagonia#alligatoridae#reptilia#paleocene#paleoart#paleontology#prehistoric#animals#illustration#digital art#extinct#animal art#fossils#image#daily#ua#палеоарт#палеонтологія#україна#мова#арт#ukraine#ukrainian#creatures
18 notes
·
View notes
Text

🐊 AMERICAN ALLIGATOR 🐊
Scientific Name: Alligator mississippiensis
Family: Alligatoridae
Class: Reptile
Length: 8.5-15 ft. (260-457 cm)
Weight (males): 500 lbs (227 kg)
Weight (females): 200 lbs (91 kg)
Number of Teeth: 80

Top Speed: 35 mph (56 km/h) on land, 20 mph in water (32 km/h)
Lifespan: 30-50 years in the wild, 65-80 years in captivity
Location: In the United States from North Carolina to the Rio Grande in Texas
Diet: Fish, snakes, turtles, small mammals, and birds




Behavior: Larger alligators are territorial and solitary while smaller ones stay closer to one another, they hunt at random intervals mostly at night. Not typically aggressive towards humans, but approaching one is strongly discouraged.
Offspring: 35-50 eggs are laid at a time, though some have up to 90. When the babies hatch, they're about 6-8 in. (2.4-3.1 cm) 🥺



ANIMAL REQUESTS OPEN
#agere animal cards#agere#age regression#petre#pet regression#agedre#petdre#cglre#aminals#mine#my post#crocs & gators#card: american alligator#class: reptiles
29 notes
·
View notes