#contract tracking software
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Stop Losing Money: How Revenue Management Systems Prevent Revenue Leakage
Revenue leakage is a silent profit killer that many businesses overlook, but it can cost companies up to 9% of their annual revenue. Whether you're in hospitality, travel, retail, or SaaS, even small pricing errors or missed invoices can lead to massive financial losses over time.
In a world where profit margins are thin and competition is fierce, preventing revenue leakage is not optional—it's essential.
This is where an AI-powered Revenue Management System (RMS) like ZettaPrice comes in. From dynamic pricing to automated invoicing, RMS software can seal the leaks and boost your bottom line. In this blog, we’ll explore how a robust revenue management solution can transform financial performance across industries.
✅ What Is Revenue Leakage?
Revenue leakage refers to the unnoticed loss of potential revenue due to inefficiencies, manual errors, or poor pricing strategies. Common causes include:
Incorrect or inconsistent pricing
Contract non-compliance
Billing inefficiencies or missed invoices
Mismanaged discounts and promotions
Poor data visibility and tracking
🔍 Revenue leakage affects 42% of companies—costing businesses an average of 9% of total sales annually. The worst part? It often goes undetected until the damage is done.
🧠 What Is a Revenue Management System (RMS)?
A Revenue Management System is a data-driven, AI-powered software solution that helps businesses:
Optimize pricing based on market demand and competition
Forecast demand and adjust inventory or services accordingly
Automate critical revenue processes (e.g., invoicing, contract compliance, and discount approvals)
Detect and plug revenue gaps before they escalate
Popular in hotels, airlines, retail, and subscription-based businesses, an RMS ensures you’re not leaving money on the table.
🔐 How to Prevent Revenue Leakage Using Revenue Management Software
Here’s how an advanced revenue optimization software like ZettaPrice RMS helps businesses detect, prevent, and eliminate revenue leakage:
1. AI-Powered Dynamic Pricing
Adjust prices in real time based on market trends, competitor pricing, and demand.
Prevent underpricing or over-discounting that erodes profit margins.
Maximize revenue during high-demand periods without sacrificing customer satisfaction.
2. Contract and Compliance Monitoring
Automatically track contract terms, service-level agreements, and payment cycles.
Flag discrepancies, missed invoices, or unapproved discounts.
Ensure full revenue recognition from every agreement.
3. Demand Forecasting and Inventory Optimization
Use predictive analytics to forecast customer demand with high accuracy.
Minimize stockouts and overstocking—both major causes of revenue loss.
Optimize resource allocation and reduce holding costs.
4. Identifying Revenue Gaps and Errors
Real-time dashboards highlight where revenue is leaking and why.
Actionable insights help you fix issues proactively instead of reacting later.
Improve financial reporting and transparency.
🚀 Benefits of Implementing a Revenue Management System
1. Increased Profitability
With smart pricing strategies, businesses can ensure they’re charging the right price at the right time. This boosts revenue without alienating customers.
📌 Example: Hotels using RMS increase RevPAR (Revenue per Available Room) by adjusting room prices during peak and off-peak seasons.
2. Improved Operational Efficiency
Manual revenue tracking and billing are prone to errors. Automation through RMS helps:
Save time and reduce human errors
Standardize pricing and billing processes
Ensure regulatory compliance
📌 Example: Airlines use RMS to automate fare updates, reducing fare leakage due to outdated pricing.
3. Enhanced Customer Experience
Personalize pricing and promotions using customer data.
Improve conversion rates and brand loyalty.
Deliver better value to different customer segments.
📌 Example: E-commerce retailers apply dynamic discounts based on browsing behavior and purchase history.
4. Competitive Advantage
Stay one step ahead by responding to market changes in real time. With RMS:
React instantly to competitor pricing
Maintain market share without sacrificing margin
Improve price transparency and customer trust
5. Smarter, Data-Driven Decisions
Access to real-time analytics empowers your teams to:
Identify new revenue opportunities
Predict churn in subscription models
Avoid pricing blind spots and inefficiencies
📌 Example: SaaS platforms use RMS data to prevent downgrades and maximize lifetime customer value.
🧩 Why Choose ZettaPrice RMS to Prevent Revenue Leakage?
ZettaPrice Revenue Management System is a cutting-edge solution designed to plug revenue gaps and increase profitability. It helps your business:
✅ Dynamically optimize pricing using AI & machine learning ✅ Eliminate revenue loss from underpricing or outdated rates ✅ Automate invoicing, billing, and discount tracking ✅ Monitor contracts and ensure compliance ✅ Uncover hidden revenue opportunities using data analytics
ZettaPrice RMS is ideal for industries like:
Hotels and Resorts
Online Travel Agencies (OTAs)
Retail Chains & E-commerce
SaaS and Subscription Services
With ZettaPrice, you don’t just stop revenue leakage—you unlock long-term financial stability and growth.
🏁 Conclusion: Seal the Leaks Before It’s Too Late
Revenue leakage is preventable—but only if you have the right tools. In today’s data-driven world, investing in a revenue management system is no longer a luxury but a necessity. With AI-powered software like ZettaPrice RMS, you can:
Prevent revenue losses
Improve operational efficiency
Gain a competitive advantage
Maximize profitability
Don’t wait until your profits vanish through cracks you can’t see.
👉 Start your journey to leak-free revenue with ZettaPrice RMS today!
#Revenue leakage#Revenue management system (RMS)#Dynamic pricing software#Prevent revenue loss#AI pricing tool#Hotel revenue management#SaaS pricing optimization#E-commerce revenue software#Data-driven pricing strategies#Automate invoicing and billing#Contract compliance tracking#Retail pricing automation#Optimize demand forecasting#Revenue analytics software#ZettaPrice RMS
0 notes
Text
https://flowrocket.com/finance
#Accounting Advisory Servies USA#Accounting and Bookkeeping services for Business#Accouting and Bookkeeping services USA#Best Auditing Services in USA#Hire Accounting Associates in USA#Hire Audit Supervisor in USA#Hire Bookkeeping Associates in USA#Best CRM Software with Collaboration Tools#CRM solutions for Team Colloboration#Best construction CRM Software#CRM Solutions for Construction Management#Best contract management systems in USA#CRM Software for document management#Best CRM for customer support#CRM for customer service solutions#Customer service software in USA#Agile software development services USA#Business Process Automation USA#IT Consulting Service in USA#Lead management CRM software#Lead tracking CRM software#Best CRM for Financial Services#Financial Services CRM Software#Best GRC Software Solutions in USA#CRM for small businesses#CRM Solutions#Top CRM Software USA#Best CRM Software in USA#Industry Specific CRM Solutions#best free crm for insurance agents
0 notes
Text
i know everyone is really excited for the oblivion remake because i was too. oblivion was the first real video game i ever played when i was a kid, and is literally the reason i am a gamer today, but BDS has called for a microsoft boycott, and that includes anything made by bethesda.
this isn't just a "oh they have some obscure business partnerships in isr*el" or "oh they donate to this or that lobby" sort of boycott either, although those are important too. my tone is not meant to be flippant about them, but rather i want to emphasize the gravity of how microsoft directly and deliberately contributes to the palestinian death toll daily, in a way that is uniquely cruel and complicit.
microsoft has had a $35 million dollar contract with the isr*eli military since 2002. they provide cloud storage for surveillance data of gazan civillians, and an artificial intelligence program called a "mass assassination factory" to assist in planning and targeting their attacks, many of which are on civilians or involve mass civilian casualties.
microsoft's service agreements with the isr*eli military also includes the CPU responsible for the military's tech infrastructure, military intelligence units that develop spy technology used against palestinians and lebanese, the maintenance of the palestinian population registry that tracks and (illegally) limits the movement of palestinains in the west bank and gaza, their air force targeting database, and much more. they work closely with isr*eli military intelligence agencies on surveillance systems used to monitor palestians, provide specialized consulting, technical and engineering support, hosts training software for the IOF, provide financial support to organizations based in the illegally occupied west bank, and have repeatedly invested in isr*eli start ups specializing in war technology.
in 2020, internal and external pressure forced microsoft to pull out of its 74 million dollar investment in an isr*eli company that violated international law due to its use of facial recognition technology for military surveillance.
in 2021, microsoft signed a new, 3-year contract with the isr*eli ministry of defense worth $133 million dollars. the isr*eli military is microsoft's second largest military customer. the first? the united states.
you can read more (w/ sources) about microsoft's complicity here.
BDS asks us to boycott microsoft products whenever possible.

microsoft is directly complicit in countless isr*eli war crimes, and the money you provide them will further proliferate this violence. i know the oblivion remake was exciting, but please, consider the lives of palestinians above your own nostalgia. no one is free until everyone is free.
766 notes
·
View notes
Text
Spain lied about not selling weapons to Israel.
Even after October 7th, Spain has sold more than 1 million € of weapons to Israel. Norway and Finland make it possible.
In January, Spain made headlines word-wide when the government's Minister of Exteriors, José Manuel Albares (PSOE), claimed in Congress and later again in a radio interview that Spain had stopped selling weapons to Israel ever since October 7th. Israel's intensification of violence in Gaza following October 7th meant that, on top of decades of apartheid and ethnic cleansing, between October 7th and January 23rd Israel had already killed 28,000 people and forced 2 million out of their home. In this context, many people were demanding their governments stop arming and funding the genocide of the Palestinian people, and here on Tumblr and other social media sites like Twitter I think we all saw the many posts praising the Spanish government for this.
Well, it turns out it was a lie.
According to Albares, "Since October 7th there are no more weapons exportations [from Spain] to Israel". But in November alone, Spain exported weapons to Israel for 987,000€, as was published on the Spanish Government's official website dedicated to exterior commerce (Comex). A researcher from Centre Delàs (an independent centre for peace studies) found it and published it, and it has also been verified by newspapers such as elDiario.es.
This 987,000€ worth of weapons in November was not the only ammunition that Spain has sent to Israel in 2023. In 2023, Spain exported a total of 1.48 million € in war material to Israel.
All of the weapons sent in November come from the factory of Nammo Palencia (Castilla y León), a corporation that is 50% property of the Government of Norway and 50% owned by a public Finnish business. However, even if the owners are foreigners, the ammunition was sent from Spain and thus it had to be authorized by the an organism of the Spanish Government named Junta Interministerial de Defensa y Doble Uso, whose deliberations on whether a weapons exportation is accepted or denied are kept secret. The only cases where they have denied exporting weapons to Israel have been when they thought that Israel would re-sell these weapons to the Philippines.
Spain has had a close relation with Israel for years. As published by the Spanish Government, Spain has sold 20 million € of weapons to Israel between 2012 and 2022. Spain also buys weapons and military software from Israel (for example, the Spanish Intelligence Service has been using the Israeli software Pegasus to illegally spy on Catalan activists, journalists, politicians and civil society members and their relatives to attack the Catalan independence movement), and Spain has continued buying from Israel and allocating defense contracts to Israel even after the October 7th attacks. It is very difficult to track the concessions of public contracts such as buying weapons, but some contracts have been known. For example, on November 24th 2023, Spain bought 287.5 million € of missiles from Israel. This is not unusual: between 2011 and 2021, it is publicly known that Spain bought war material from Israel for at least 268 million €, but experts say that the real number could be two or three times as much.
Spain has also continued allocating concessions to Israel. For example, on December 15th 2023 Spain allocated a contract worth over 576 million € to Israel for a rocket launcher programme. On November 22nd, Spain allocated another another Israeli company to provide missiles for 237 million € at the same time as the Spanish army bought Israeli inhibitors for 1.4 million €. The very next day, November 23rd, Spain signed another military allocation to Israel for 82,600€. The following week, Spain signed yet another allocation with a different Israeli military corporation for 3.7 million €.
Spain also allows Israeli weapon manufacturing companies to produce weapons through their branches located in Spain. This way, Israeli weapons make their way to markets with which Israel doesn't have diplomatic ties but Spain does, like Saudi Arabia. And since Spain is a member of NATO, Israeli weapons produced in Spain are approved according to NATO standards and access it easily. In the same way, these Israeli weapons manufacturers also access European Union defense funds through their branches in Spain. (source).
As I said, I saw a lot of positive posts around when Albares said Spain was going to embargo, but I haven't seen any post about how they didn't do it. I also (personally) haven't seen anything on international media, and barely anything on Spanish media, which is already busy with the PSOE covid material corruption scandal. So I share this in the hope of helping put pressure on Spain to cut all ties with Israel immediately.
SHAME ON EVERYONE WHO GIVES ISRAEL THE MATERIAL AND MONEY THAT WILL BE USED TO MASSACRE THE PALESTINIAN PEOPLE. SHAME ON SPAIN, NORWAY, AND FINLAND.
#i've been meaning to post this for a few days but never manmaged to finish writing since i don't have internet at work and i barely have#time to do anything else than sleep eat and prepare work stuff when i'm home#so I'm late but this is still relevant#palestine#gaza#israel#free palestine#spain#norway#finland#españa#end genocide#bds#boycott divest sanction#free gaza#peace#anti military#💬
3K notes
·
View notes
Text

Each week (or so), we'll highlight the relevant (and sometimes rage-inducing) news adjacent to writing and freedom of expression. This week:
Inkitt’s AI-powered fiction factory
Inkitt started in the mid-2010s as a cozy platform where anyone could share their writing. Fast forward twenty twenty-fuckkkkk, and like most startups, it’s pivoted hard into AI-fueled content production with the soul of an algorithm.
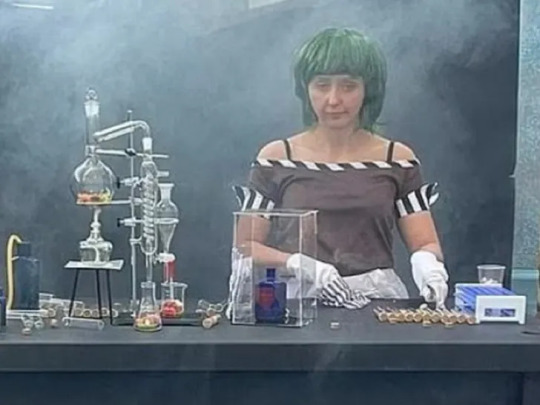

Pictured: Inkitt preparing human-generated work for an AI-powered flume ride to The Unknown.
Here’s how it works: Inkitt monitors reader engagement with tracking software, then picks popular stories to publish on its premium app, Galatea. From there, stories can get spun into sequels, spinoffs, or adapted for GalateaTV… often with minimal author involvement. Authors get an undisclosed cut of revenue, but for most, it’s a fraction of what they’d earn with a traditional publisher (let alone self-publishing).
“'They prey on new writers who have no idea what they’re doing,' said the writer of one popular Galatea series."
Many, many authors have side-eyed or outright decried the platform as inherently predatory for years, due to nebulous payout promises. And much of the concern centers on contracts that don’t require authors’ consent for editorial changes or AI-generated “additions” to the original text.
Now, Inkitt has gone full DiSrUpTiOn, leaning heavily on generative AI to ghostwrite, edit, generate audiobook narration, and design covers, under the banner of “democratizing storytelling.” (AI? In my democratized storytelling platform? It’s more likely than you think.)

Pictured: Inkitt’s CEO looking at the most-read stories.
But Inkitt’s CEO doesn’t seem too concerned about what authors think: “His business model doesn’t need them.”

The company recently raised $37 million, with backers including former CEOs of Sony, Penguin, and HarperCollins, proving once again that publishing loves a disruptor… as long as it disrupts creatives, not capital. And more AI companies are mushrooming up to chase the same vision: “a vision of human-created art becoming the raw material for AI-powered, corporate-owned content-production machines—a scenario in which humans would play an ever-shrinking role.”
(Not to say we predicted this, but…)
Welcome to the creator-industrial complex.

Publishers to AI: Stop stealing our stuff (please?)
Major publishers—including The New York Times, The Washington Post, The Guardian, and Vox Media—have launched a "Support Responsible AI" campaign, urging the U.S. government to regulate AI's use of copyrighted content.
Like last month's campaigns by the Authors Guild and the UK's Society of Authors, there's a website where where you can (and should!) contact your representatives to say, “Hey, maybe stop letting billion-dollar tech giants strip-mine journalism.”
The campaign’s ads carry slogans like “Stop AI Theft” and “AI Steals From You Too” and call for legislation that would force AI companies to pay for the content they train on and clearly label AI-generated content with attribution. This follows lobbying by OpenAI and Google to make it legal to scrape and train on copyrighted material without consent.
The publishers assert they are not explicitly anti-AI, but advocate for a “fair” system that respects intellectual property and supports journalism.
But… awkward, The Washington Post—now owned by Jeff Bezos—has reportedly already struck a deal with OpenAI to license and summarize its content. So, mixed signals.
Still, as the campaign reminds us: “Stealing is un-American.”
(Unless it’s profitable.)

#WarForever
We at Ellipsus love a good meme-turned-megaproject. Back in January, the-app-formerly-known-as-Twitter user @lolt64 tweeted a cryptic line about "the frozen wastes of europa,” the earliest reference to the never-ending war on Jupiter’s icy moon.
A slew of bleak dispatches from weary, doomed soldiers entrenched on Europa’s ice fields snowballed (iceberged?) into a sprawling saga, yes-and-ing with fan art, vignettes, and memes under the hashtag #WarForever.
It’s not quite X’s answer to Goncharov: It turns out WarForever is some flavor of viral marketing for a tabletop RPG zine. But the internet ran with it anyway, with NASA playing the Scorcese of the stars.

In a digital hellworld increasingly dominated by AI slopification, data harvesting, and “content at scale,” projects like WarForever are a blessed reminder that creativity—actual, human creativity—perseveres.
Even on a frozen moon. Even here.

Let us know if you find something other writers should know about, (or join our Discord and share it there!)
- The Ellipsus Team xo

#ellipsus#writblr#writers on tumblr#writing#creative writing#anti ai#writing community#fanfic#fanfiction#fiction#inkitt#us politics
330 notes
·
View notes
Text
In the span of just weeks, the U.S. government has experienced what may be the most consequential security breach in its history—not through a sophisticated cyberattack or an act of foreign espionage, but through official orders by a billionaire with a poorly defined government role. And the implications for national security are profound.
First, it was reported that people associated with the newly created Department of Government Efficiency (DOGE) had accessed the U.S. Treasury computer system, giving them the ability to collect data on and potentially control the department’s roughly $5.45 trillion in annual federal payments.
Then, we learned that uncleared DOGE personnel had gained access to classified data from the U.S. Agency for International Development, possibly copying it onto their own systems. Next, the Office of Personnel Management—which holds detailed personal data on millions of federal employees, including those with security clearances—was compromised. After that, Medicaid and Medicare records were compromised.
Meanwhile, only partially redacted names of CIA employees were sent over an unclassified email account. DOGE personnel are also reported to be feeding Education Department data into artificial intelligence software, and they have also started working at the Department of Energy.
This story is moving very fast. On Feb. 8, a federal judge blocked the DOGE team from accessing the Treasury Department systems any further. But given that DOGE workers have already copied data and possibly installed and modified software, it’s unclear how this fixes anything.
In any case, breaches of other critical government systems are likely to follow unless federal employees stand firm on the protocols protecting national security.
The systems that DOGE is accessing are not esoteric pieces of our nation’s infrastructure—they are the sinews of government.
For example, the Treasury Department systems contain the technical blueprints for how the federal government moves money, while the Office of Personnel Management (OPM) network contains information on who and what organizations the government employs and contracts with.
What makes this situation unprecedented isn’t just the scope, but also the method of attack. Foreign adversaries typically spend years attempting to penetrate government systems such as these, using stealth to avoid being seen and carefully hiding any tells or tracks. The Chinese government’s 2015 breach of OPM was a significant U.S. security failure, and it illustrated how personnel data could be used to identify intelligence officers and compromise national security.
In this case, external operators with limited experience and minimal oversight are doing their work in plain sight and under massive public scrutiny: gaining the highest levels of administrative access and making changes to the United States’ most sensitive networks, potentially introducing new security vulnerabilities in the process.
But the most alarming aspect isn’t just the access being granted. It’s the systematic dismantling of security measures that would detect and prevent misuse—including standard incident response protocols, auditing, and change-tracking mechanisms—by removing the career officials in charge of those security measures and replacing them with inexperienced operators.
The Treasury’s computer systems have such an impact on national security that they were designed with the same principle that guides nuclear launch protocols: No single person should have unlimited power. Just as launching a nuclear missile requires two separate officers turning their keys simultaneously, making changes to critical financial systems traditionally requires multiple authorized personnel working in concert.
This approach, known as “separation of duties,” isn’t just bureaucratic red tape; it’s a fundamental security principle as old as banking itself. When your local bank processes a large transfer, it requires two different employees to verify the transaction. When a company issues a major financial report, separate teams must review and approve it. These aren’t just formalities—they’re essential safeguards against corruption and error.
These measures have been bypassed or ignored. It’s as if someone found a way to rob Fort Knox by simply declaring that the new official policy is to fire all the guards and allow unescorted visits to the vault.
The implications for national security are staggering. Sen. Ron Wyden said his office had learned that the attackers gained privileges that allow them to modify core programs in Treasury Department computers that verify federal payments, access encrypted keys that secure financial transactions, and alter audit logs that record system changes. Over at OPM, reports indicate that individuals associated with DOGE connected an unauthorized server into the network. They are also reportedly training AI software on all of this sensitive data.
This is much more critical than the initial unauthorized access. These new servers have unknown capabilities and configurations, and there’s no evidence that this new code has gone through any rigorous security testing protocols. The AIs being trained are certainly not secure enough for this kind of data. All are ideal targets for any adversary, foreign or domestic, also seeking access to federal data.
There’s a reason why every modification—hardware or software—to these systems goes through a complex planning process and includes sophisticated access-control mechanisms. The national security crisis is that these systems are now much more vulnerable to dangerous attacks at the same time that the legitimate system administrators trained to protect them have been locked out.
By modifying core systems, the attackers have not only compromised current operations, but have also left behind vulnerabilities that could be exploited in future attacks—giving adversaries such as Russia and China an unprecedented opportunity. These countries have long targeted these systems. And they don’t just want to gather intelligence—they also want to understand how to disrupt these systems in a crisis.
Now, the technical details of how these systems operate, their security protocols, and their vulnerabilities are now potentially exposed to unknown parties without any of the usual safeguards. Instead of having to breach heavily fortified digital walls, these parties can simply walk through doors that are being propped open—and then erase evidence of their actions.
The security implications span three critical areas.
First, system manipulation: External operators can now modify operations while also altering audit trails that would track their changes. Second, data exposure: Beyond accessing personal information and transaction records, these operators can copy entire system architectures and security configurations—in one case, the technical blueprint of the country’s federal payment infrastructure. Third, and most critically, is the issue of system control: These operators can alter core systems and authentication mechanisms while disabling the very tools designed to detect such changes. This is more than modifying operations; it is modifying the infrastructure that those operations use.
To address these vulnerabilities, three immediate steps are essential. First, unauthorized access must be revoked and proper authentication protocols restored. Next, comprehensive system monitoring and change management must be reinstated—which, given the difficulty of cleaning a compromised system, will likely require a complete system reset. Finally, thorough audits must be conducted of all system changes made during this period.
This is beyond politics—this is a matter of national security. Foreign national intelligence organizations will be quick to take advantage of both the chaos and the new insecurities to steal U.S. data and install backdoors to allow for future access.
Each day of continued unrestricted access makes the eventual recovery more difficult and increases the risk of irreversible damage to these critical systems. While the full impact may take time to assess, these steps represent the minimum necessary actions to begin restoring system integrity and security protocols.
Assuming that anyone in the government still cares.
184 notes
·
View notes
Text
reposting this bc the OP blocked me (and is blocking anyone else who disagrees which means blocked people can't reblog) and i want to say this loud and with my whole chest!!!!!
another Dragon Age fic was recently outed as being AI, and this is what the writer had to say for themselves about it:

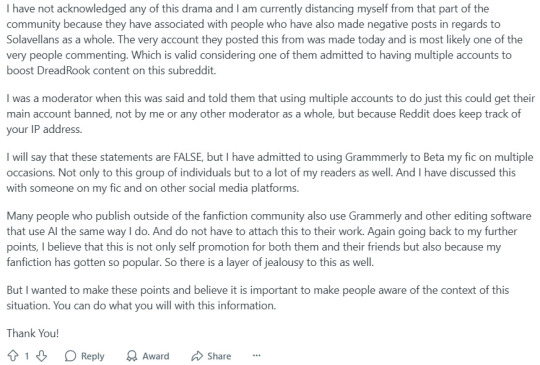
so actually, Grammarly uses generative AI and is just as bad as ChatGPT. it also objectively makes your writing worse, it sucks the voice out of your prose and turns it into corporate sounding homogenized paste. it's also unethical for all the same reasons any generative AI is unethical. get a writing group and have a real human beta read for you if you don't trust yourself to check your own grammar etc. but honestly something unpolished and written entirely by your human brain and human imagination will ALWAYS be better than AI slop.
also, the part about published authors doing this is patently untrue. i know this is a huge problem in the self-publishing space, but most publishers now are including clauses in their contracts that expressly forbid the use of AI in ANY part of the creative process. this includes using ChatGPT to generate or clean up outlines or Grammarly to spellcheck and revise. so if you're trying to publish, don't fucking do this or you could literally be asked to return an advance if you get caught.
i've posted about this in the past, but AI detectors are actually shocking accurate these days. i've tested them extensively recently and they can consistently and correctly flag individual sentences written by ChatGPT in an otherwise original passage. and they almost never flag false positives. so the argument that AI detectors can't be trusted is just flat out wrong. are they correct 100% of the time? no. but can they indicate with a high degree of accuracy if AI was used in some capacity? absolutely, especially if there is additional evidence.
and for all the people hand wringing about AI detectors flagging false positives, let me just say this: if something is not AI written it is very easy to prove. you can't write anything of any considerable length without leaving a massive paper trail of notes and drafts. almost all writing software tracks changes and makes it very easy to prove you wrote something yourself. being falsely being accused of AI isn't actually a real problem and is only being made to seem as such by people who are trying to get away with and justify using AI or who are worried about getting caught.
i think a lot of people are just lured by a seemingly easy shortcut, and to their untrained eye, what the AI is spitting out feels "better" to them than their own writing. but i promise you it's not. trust your own brain and put in the work to improve at your craft rather than outsourcing the gift of your imagination to a robot that steals from other people's work.
i will continue to die on this hill!!!!!
#this isn't about solrook or shipping wars or any other dumb shit like this#this is about AI use in creative writing and my opinion on that won't ever change#i'm not in that solrook discord idk what OP is talking about#this isn't about brigading or bullying it's about taking a hard line stance against AI use#calling out AI isn't “starting drama” it's about upholding fandom to a certain standard#this literally isn't about ships AT ALL#ship whoever the fuck you want#just don't use AI#AI critical#ai discourse#ai slop#gen ai#fuck ai#chat gpt#grammarly#fanfic#fan fiction#fanfics#fanfic authors#archive of our own#ao3 fanfic#fanfic writing#dragon age#dragon age fanfic#dragon age fan fiction#dragon age fic#da fanfic#dragon age fanfiction#da fic#anti ai
168 notes
·
View notes
Text
Here's your regular service reminder that $48k/year sounds like a dream come true to people who have never made a living off their art or comics before, until you factor in the following:
Cost of assistants which is out-of-pocket (some creators literally don't hire assistants because of this which makes the process of meeting their deadlines even harder)
Cost of additional tools necessary to making webtoons and meeting deadlines, such as paying for drawing software, 3D models, etc.
Cost of emergency services such as healthcare are not covered by WT, so if your health deteriorates while you're working on your comic (which it often does for many creators whose bodies are destroyed from working long hours at a desk 7 days a week), WT will not help you.
No paid vacation time, no paid sick leave, no accommodations for people with kids, disabilities, etc. meaning if you have to take time off, WT will not be covering it.
Speaking of vacation time, Webtoons ONLY pays creators for completed and submitted episodes, meaning they will not pay you for pre-production time leading up to a series release OR have your back when you have to go on hiatus. Some creators manage multiple series to make ends meet and avoid stretches of unpaid hiatuses (IIRC I believe KitTrace does this with Nevermore and Shiloh rotating on and off hiatus one at a time) and others simply have to go without pay relying solely on their Patreons and other forms of income when they go on hiatus. And, as we've seen in the past, when they return from hiatus is often up to Webtoons, not them.
That $48k is basically just an average ballpark of what Webtoons pays creators for a season of content, and for those who recall, FastPass earnings are not given to creators until they make back that payment.
It's really hard to get people to FastPass when Webtoons is deliberately not advertising your series and, in some cases, outright SABOTAGING your attempts to advertise.
I don't even know if that $48k is before or AFTER taxes, I'm assuming before considering this is a self-employment contract, meaning you likely have to put away a good few thousand for taxes depending on your state tax rate and what you're able to write off. This also includes having to track assistant expenditures for filing.
The 60-80+ hour weeks many creators are having to pull to meet their deadlines turns that $48k/year into an ASTOUNDING drum roll ... $11 - $15/hour! Which is just barely over minimum wage in many states, and absolutely 100% not a living wage in most! And that's BEST CASE scenario in which you don't pay an assistant, don't suffer any health expenses, don't pay for 3D models / software, and POSSIBLY don't pay your taxes. Yaaaaay! 😒🖕
TL : DR $48k/year hasn't been a salary worth bragging about since 2005 ESPECIALLY not for such high-demand specialized work like this, fuck you Webtoons <3
167 notes
·
View notes
Text
A critical resource that cybersecurity professionals worldwide rely on to identify, mitigate and fix security vulnerabilities in software and hardware is in danger of breaking down. The federally funded, non-profit research and development organization MITRE warned today that its contract to maintain the Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE) program — which is traditionally funded each year by the Department of Homeland Security — expires on April 16. Tens of thousands of security flaws in software are found and reported every year, and these vulnerabilities are eventually assigned their own unique CVE tracking number (e.g. CVE-2024-43573, which is a Microsoft Windows bug that Redmond patched last year). There are hundreds of organizations — known as CVE Numbering Authorities (CNAs) — that are authorized by MITRE to bestow these CVE numbers on newly reported flaws. Many of these CNAs are country and government-specific, or tied to individual software vendors or vulnerability disclosure platforms (a.k.a. bug bounty programs). Put simply, MITRE is a critical, widely-used resource for centralizing and standardizing information on software vulnerabilities. That means the pipeline of information it supplies is plugged into an array of cybersecurity tools and services that help organizations identify and patch security holes — ideally before malware or malcontents can wriggle through them.
21 notes
·
View notes
Text
The cogent documentary, “Surveilled,” now available on HBO, tracks journalist Ronan Farrow as he investigates the proliferation and implementation of spyware, specifically, Pegasus, which was created by the Israeli company NSO Group. The company sells its product to clients who use it to fight crime and terrorism. It is claimed that Pegasus was instrumental in helping capture Mexican drug lord, Joaquín “El Chapo” Guzman. However, there are also reports that NSO’s products are being used to target journalists, human rights activists and political dissidents.
. . .
Farrow: I put up a piece in The New Yorker this week. It was fascinating to talk to experts in the privacy law space who are really in a high state of alarm right now. The United States, under administrations from both parties, has flirted with this technology in ways that is alarming. Under the first Trump administration, they bought Pegasus. They claimed they were buying it to test it and see what our enemies were doing, and The New York Times later sued them for more information and found really persuasive evidence that the FBI wanted to operationalize that in American law enforcement investigations.
youtube
In September, the Department of Homeland Security (D.H.S.) signed a two-million-dollar contract with Paragon, an Israeli firm whose spyware product Graphite focusses on breaching encrypted-messaging applications such as Telegram and Signal. Wired first reported that the technology was acquired by Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE)—an agency within D.H.S. that will soon be involved in executing the Trump Administration’s promises of mass deportations and crackdowns on border crossings. A source at Paragon told me that the deal followed a vetting process, during which the company was able to demonstrate that it had robust tools to prevent other countries that purchase its spyware from hacking Americans—but that wouldn’t limit the U.S. government’s ability to target its own citizens. The technology is part of a booming multibillion-dollar market for intrusive phone-hacking software that is making government surveillance increasingly cheap and accessible. In recent years, a number of Western democracies have been roiled by controversies in which spyware has been used, apparently by defense and intelligence agencies, to target opposition politicians, journalists, and apolitical civilians caught up in Orwellian surveillance dragnets.
Now Donald Trump and incoming members of his Administration will decide whether to curtail or expand the U.S. government’s use of this kind of technology. Privacy advocates have been in a state of high alarm about the colliding political and technological trend lines.
“It’s just so evident—the impending disaster,” Emily Tucker, the executive director at the Center on Privacy and Technology at Georgetown Law, told me. “You may believe yourself not to be in one of the vulnerable categories, but you won’t know if you’ve ended up on a list for some reason or your loved ones have. Every single person should be worried.”
40 notes
·
View notes
Note
tell me about your defense contract pleage
Oh boy!
To be fair, it's nothing grandiose, like, it wasn't about "a new missile blueprint" or whatever, but, just thinking about what it could have become? yeesh.
So, let's go.
For context, this is taking place in the early 2010s, where I was working as a dev and manager for a company that mostly did space stuff, but they had some defence and security contracts too.
One day we got a new contract though, which was... a weird one. It was state-auctioned, meaning that this was basically a homeland contract, but the main sponsor was Philip Morris. Yeah. The American cigarette company.
Why? Because the contract was essentially a crackdown on "illegal cigarette sales", but it was sold as a more general "war on drugs" contract.
For those unaware (because chances are, like me, you are a non-smoker), cigarette contraband is very much a thing. At the time, ~15% of cigarettes were sold illegally here (read: they were smuggled in and sold on the street).
And Phillip Morris wanted to stop that. After all, they're only a small company worth uhhh... oh JFC. Just a paltry 150 billion dollars. They need those extra dollars, you understand?
Anyway. So they sponsored a contract to the state, promising that "the technology used for this can be used to stop drug deals too". Also that "the state would benefit from the cigarettes part as well because smaller black market means more official sales means a higher tax revenue" (that has actually been proven true during the 2020 quarantine).
Anyway, here was the plan:
Phase 1 was to train a neural network and plug it in directly to the city's video-surveillance system, in order to detect illegal transactions as soon as they occur. Big brother who?
Phase 2 was to then track the people involved in said transaction throughout the city, based on their appearance and gait. You ever seen the Plainsight sheep counting video? Imagine something like this but with people. That data would then be relayed to police officers in the area.
So yeah, an automated CCTV-based tracking system. Because that's not setting a scary precedent.
So what do you do when you're in that position? Let me tell you. If you're thrust unknowingly, or against your will, into a project like this,
Note. The following is not a legal advice. In fact it's not even good advice. Do not attempt any of this unless you know you can't get caught, or that even if you are caught, the consequences are acceptable. Above all else, always have a backup plan if and when it backfires. Also don't do anything that can get you sued. Be reasonable.
Let me introduce you to the world of Corporate Sabotage! It's a funny form of striking, very effective in office environments.
Here's what I did:
First of all was the training data. We had extensive footage, but it needed to be marked manually for the training. Basically, just cropping the clips around the "transaction" and drawing some boxes on top of the "criminals". I was in charge of several batches of those. It helped that I was fast at it since I had video editing experience already. Well, let's just say that a good deal of those markings were... not very accurate.
Also, did you know that some video encodings are very slow to process by OpenCV, to the point of sometimes crashing? I'm sure the software is better at it nowadays though. So I did that to another portion of the data.
Unfortunately the training model itself was handled by a different company, so I couldn't do more about this.
Or could I?
I was the main person communicating with them, after all.
Enter: Miscommunication Master
In short (because this is already way too long), I became the most rigid person in the project. Like insisting on sharing the training data only on our own secure shared drive, which they didn't have access to yet. Or tracking down every single bug in the program and making weekly reports on those, which bogged down progress. Or asking for things to be done but without pointing at anyone in particular, so that no one actually did the thing. You know, classic manager incompetence. Except I couldn't be faulted, because after all, I was just "really serious about the security aspect of this project. And you don't want the state to learn that we've mishandled the data security of the project, do you, Jeff?"
A thousand little jabs like this, to slow down and delay the project.
At the end of it, after a full year on this project, we had.... a neural network full of false positives and a semi-working visualizer.
They said the project needed to be wrapped up in the next three months.
I said "damn, good luck with that! By the way my contract is up next month and I'm not renewing."
Last I heard, that city still doesn't have anything installed on their CCTV.
tl;dr: I used corporate sabotage to prevent automated surveillance to be implemented in a city--
hey hold on
wait
what
HEY ACTUALLY I DID SOME EXTRA RESEARCH TO SEE IF PHILLIP MORRIS TRIED THIS SHIT WITH ANOTHER COMPANY SINCE THEN AND WHAT THE FUCK

HUH??????

well what the fuck was all that even about then if they already own most of the black market???
#i'm sorry this got sidetracked in the end#i'm speechless#anyway yeah!#sometimes activism is sitting in an office and wasting everyone's time in a very polite manner#i learned that one from the CIA actually
160 notes
·
View notes
Text
#Accounting Advisory Servies USA#Accounting and Bookkeeping services for Business#Accouting and Bookkeeping services USA#Best Auditing Services in USA#Hire Accounting Associates in USA#Hire Audit Supervisor in USA#Hire Bookkeeping Associates in USA#Best CRM Software with Collaboration Tools#CRM solutions for Team Colloboration#Best construction CRM Software#CRM Solutions for Construction Management#Best contract management systems in USA#CRM Software for document management#Best CRM for customer support#CRM for customer service solutions#Customer service software in USA#Agile software development services USA#Business Process Automation USA#IT Consulting Service in USA#Lead management CRM software#Lead tracking CRM software#Best CRM for Financial Services#Financial Services CRM Software#Best GRC Software Solutions in USA#CRM for small businesses#CRM Solutions#Top CRM Software USA#Best CRM Software in USA#Industry Specific CRM Solutions#best free crm for insurance agents
0 notes
Text
April 11, 2025
HEATHER COX RICHARDSON
APR 12
READ IN APP
On April 4, Trump fired head of U.S. Cyber Command (CYBERCOM) and director of the National Security Agency (NSA) General Timothy Haugh, apparently on the recommendation of right-wing conspiracy theorist Laura Loomer, who is pitching her new opposition research firm to “vet” candidates for jobs in Trump’s administration.
Former secretary of the Air Force Frank Kendall wrote in Newsweek yesterday that the position Haugh held is “one of the most sensitive and powerful jobs in America.” Kendall writes that NSA and CYBERCOM oversee the world’s most sophisticated tools and techniques to penetrate computer systems, monitor communications around the globe, and, if national security requires it, attack those systems. U.S. law drastically curtails how those tools can be used in the U.S. and against American citizens and businesses. Will a Trump loyalist follow those laws? Kendall writes: “Every American should view this development with alarm.”
Just after 2:00 a.m. eastern time this morning, the Senate confirmed Retired Air Force Lieutenant General John Dan Caine, who goes by the nickname “Razin,” for chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff by a vote of 60–25. U.S. law requires the chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff to have served as the vice chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff, the chief of staff of the Army, the chief of naval operations, the chief of staff of the Air Force, the commandant of the Marine Corps, or the commander of a unified or specified combatant command.
Although Caine has 34 years of military experience, he did not serve in any of the required positions. The law provides that the president can waive the requirement if “the President determines such action is necessary in the national interest,” and he has apparently done so for Caine. The politicization of the U.S. military by filling it with Trump loyalists is now, as Kendall writes, “indisputable.”
The politicization of data is also indisputable. Billionaire Elon Musk’s “Department of Government Efficiency” (DOGE) claims to be saving Americans money, but the Wall Street Journal reported today that effort has been largely a failure (despite today’s announcement of devastating cuts to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration that monitors our weather). But what DOGE is really doing is burrowing into Americans’ data.
The first people to be targeted by that data collection appear to be undocumented immigrants. Jason Koebler of 404 Media reported on Wednesday that Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE) has been using a database that enables officials to search for people by filtering for “hundreds of different, highly specific categories,” including scars or tattoos, bankruptcy filings, Social Security number, hair color, and race. The system, called Investigative Case Management (ICM), was created by billionaire Peter Thiel’s software company Palantir, which in 2022 signed a $95.9 million contract with the government to develop ICM.
Three Trump officials told Sophia Cai of Politico that DOGE staffers embedded in agencies across the government are expanding government cooperation with immigration officials, using the information they’re gleaning from government databases to facilitate deportation. On Tuesday, DOGE software engineer Aram Moghaddassi sent the first 6,300 names of individuals whose temporary legal status had just been canceled. On the list, which Moghaddassi said covered those on “the terror watch list” or with “F.B.I. criminal records,” were eight minors, including one 13-year-old.
The Social Security Administration worked with the administration to get those people to “self-deport” by adding them to the agency's “death master file.” That file is supposed to track people whose death means they should no longer receive benefits. Adding to it people the administration wants to erase is “financial murder,” former SSA commissioner Martin O’Malley told Alexandra Berzon, Hamed Aleaziz, Nicholas Nehamas, Ryan Mac, and Tara Siegel Bernard of the New York Times. Those people will not be able to use credit cards or banks.
On Tuesday, Acting Internal Revenue Service (IRS) Commissioner Melanie Krause resigned after the IRS and the Department of Homeland Security agreed to share sensitive taxpayer data with immigration authorities. Undocumented immigrants pay billions in taxes, in part to demonstrate their commitment to citizenship, and the government has promised immigrants that it would not use that information for immigration enforcement. Until now, the IRS has protected sensitive taxpayer information.
Rene Marsh and Marshall Cohen of CNN note that “[m]ultiple senior career IRS officials refused to sign the data-sharing agreement with DHS,” which will enable HHS officials to ask the IRS for names and addresses of people they suspect are undocumented, “because of grave concerns about its legality.” Ultimately, Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent signed the agreement with Secretary of Homeland Security Kristi Noem.
Krause was only one of several senior career officials leaving the IRS, raising concerns among those staying that there is no longer a “defense against the potential unlawful use of taxpayer data by the Trump administration.”
Makena Kelly of Wired reported today that for the past three days, DOGE staffers have been working with representatives from Palantir and career engineers from the IRS in a giant “hackathon.” Their goal is to build a system that will be able to access all IRS records, including names, addresses, job data, and Social Security numbers, that can then be compared with data from other agencies.
But the administration’s attempt to automate deportation is riddled with errors. Last night the government sent threatening emails to U.S. citizens, green card holders, and even a Canadian (in Canada) terminating “your parole” and giving them seven days to leave the U.S. One Massachusetts-born immigration lawyer asked on social media: “Does anyone know if you can get Italian citizenship through great-grandparents?”
The government is not keen to correct its errors. On March 15 the government rendered to prison in El Salvador a legal U.S. resident, Kilmar Armando Abrego Garcia, whom the courts had ordered the U.S. not to send to El Salvador, where his life was in danger. The government has admitted that its arrest and rendition of Abrego Garcia happened because of “administrative error” but now claims—without evidence—that he is a member of the MS-13 gang and that his return to the U.S. would threaten the public. Abrego Garcia says he is not a gang member and notes that he has never been charged with a crime.
On April 4, U.S. District Court Judge Paula Xinis ordered the government to return Abrego Garcia to the U.S. no later than 11:59 pm on April 7. The administration appealed to the Supreme Court, which handed down a 9–0 decision yesterday, saying the government must “facilitate” Abrego Garcia’s release, but asked the district court to clarify what it meant by “effectuate,” noting that it must give “due regard for the deference owed to the Executive Branch in the conduct of foreign affairs.”
The Supreme Court also ordered that “the Government should be prepared to share what it can concerning the steps it has taken and the prospect of further steps.”
Legal analyst Joyce White Vance explained what happened next. Judge Xinis ordered the government to file an update by 9:30 a.m. today explaining where Abrego Garcia is, what the government is doing to get him back, and what more it will do. She planned an in-person hearing at 1:00 p.m.
The administration made clear it did not intend to comply. It answered that the judge had not given them enough time to answer and suggested that it would delay over the Supreme Court’s instruction that Xinis must show deference to the president’s ability to conduct foreign affairs. Xinis gave the government until 11:30 and said she would still hold the hearing. The government submitted its filing at about 12:15, saying that Abrego Garcia is “in the custody of a foreign sovereign,” but at the 1:00 hearing, as Anna Bower of Lawfare reported, the lawyer representing the government, Drew Ensign, said he did not have information about where Abrego Garcia is and that the government had done nothing to get him back. Ensign said he might have answers by next Tuesday. Xinis says they will have to give an update tomorrow.
As Supreme Court Justice Sonia Sotomayor recently warned, if the administration can take noncitizens off the streets, render them to prison in another country, and then claim it is helpless to correct the error because the person is out of reach of U.S. jurisdiction, it could do the same thing to citizens. Indeed, both President Trump and White House press secretary Karoline Leavitt have proposed that very thing.
Tonight, Trump signed a memorandum to the secretaries of defense, interior, agriculture, and homeland security calling for a “Military Mission for Sealing the Southern Border of the United States and Repelling Invasions.” The memorandum creates a military buffer zone along the border so that any migrant crossing would be trespassing on a U.S. military base. This would allow active-duty soldiers to hold migrants until ICE agents take them.
By April 20, the secretaries of defense and homeland security are supposed to report to the president whether they think he should invoke the 1807 Insurrection Act to enable him to use the military to aid in mass deportations.
—
16 notes
·
View notes
Text

Matt Davies
* * * *
LETTERS FROM AN AMERICAN
April 11, 2025
Heather Cox Richardson
Apr 12, 2025
On April 4, Trump fired head of U.S. Cyber Command (CYBERCOM) and director of the National Security Agency (NSA) General Timothy Haugh, apparently on the recommendation of right-wing conspiracy theorist Laura Loomer, who is pitching her new opposition research firm to “vet” candidates for jobs in Trump’s administration.
Former secretary of the Air Force Frank Kendall wrote in Newsweek yesterday that the position Haugh held is “one of the most sensitive and powerful jobs in America.” Kendall writes that NSA and CYBERCOM oversee the world’s most sophisticated tools and techniques to penetrate computer systems, monitor communications around the globe, and, if national security requires it, attack those systems. U.S. law drastically curtails how those tools can be used in the U.S. and against American citizens and businesses. Will a Trump loyalist follow those laws? Kendall writes: “Every American should view this development with alarm.”
Just after 2:00 a.m. eastern time this morning, the Senate confirmed Retired Air Force Lieutenant General John Dan Caine, who goes by the nickname “Razin,” for chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff by a vote of 60–25. U.S. law requires the chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff to have served as the vice chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff, the chief of staff of the Army, the chief of naval operations, the chief of staff of the Air Force, the commandant of the Marine Corps, or the commander of a unified or specified combatant command.
Although Caine has 34 years of military experience, he did not serve in any of the required positions. The law provides that the president can waive the requirement if “the President determines such action is necessary in the national interest,” and he has apparently done so for Caine. The politicization of the U.S. military by filling it with Trump loyalists is now, as Kendall writes, “indisputable.”
The politicization of data is also indisputable. Billionaire Elon Musk’s “Department of Government Efficiency” (DOGE) claims to be saving Americans money, but the Wall Street Journal reported today that effort has been largely a failure (despite today’s announcement of devastating cuts to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration that monitors our weather). But what DOGE is really doing is burrowing into Americans’ data.
The first people to be targeted by that data collection appear to be undocumented immigrants. Jason Koebler of 404 Media reported on Wednesday that Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE) has been using a database that enables officials to search for people by filtering for “hundreds of different, highly specific categories,” including scars or tattoos, bankruptcy filings, Social Security number, hair color, and race. The system, called Investigative Case Management (ICM), was created by billionaire Peter Thiel’s software company Palantir, which in 2022 signed a $95.9 million contract with the government to develop ICM.
Three Trump officials told Sophia Cai of Politico that DOGE staffers embedded in agencies across the government are expanding government cooperation with immigration officials, using the information they’re gleaning from government databases to facilitate deportation. On Tuesday, DOGE software engineer Aram Moghaddassi sent the first 6,300 names of individuals whose temporary legal status had just been canceled. On the list, which Moghaddassi said covered those on “the terror watch list” or with “F.B.I. criminal records,” were eight minors, including one 13-year-old.
The Social Security Administration worked with the administration to get those people to “self-deport” by adding them to the agency's “death master file.” That file is supposed to track people whose death means they should no longer receive benefits. Adding to it people the administration wants to erase is “financial murder,” former SSA commissioner Martin O’Malley told Alexandra Berzon, Hamed Aleaziz, Nicholas Nehamas, Ryan Mac, and Tara Siegel Bernard of the New York Times. Those people will not be able to use credit cards or banks.
On Tuesday, Acting Internal Revenue Service (IRS) Commissioner Melanie Krause resigned after the IRS and the Department of Homeland Security agreed to share sensitive taxpayer data with immigration authorities. Undocumented immigrants pay billions in taxes, in part to demonstrate their commitment to citizenship, and the government has promised immigrants that it would not use that information for immigration enforcement. Until now, the IRS has protected sensitive taxpayer information.
Rene Marsh and Marshall Cohen of CNN note that “[m]ultiple senior career IRS officials refused to sign the data-sharing agreement with DHS,” which will enable HHS officials to ask the IRS for names and addresses of people they suspect are undocumented, “because of grave concerns about its legality.” Ultimately, Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent signed the agreement with Secretary of Homeland Security Kristi Noem.
Krause was only one of several senior career officials leaving the IRS, raising concerns among those staying that there is no longer a “defense against the potential unlawful use of taxpayer data by the Trump administration.”
Makena Kelly of Wired reported today that for the past three days, DOGE staffers have been working with representatives from Palantir and career engineers from the IRS in a giant “hackathon.” Their goal is to build a system that will be able to access all IRS records, including names, addresses, job data, and Social Security numbers, that can then be compared with data from other agencies.
But the administration’s attempt to automate deportation is riddled with errors. Last night the government sent threatening emails to U.S. citizens, green card holders, and even a Canadian (in Canada) terminating “your parole” and giving them seven days to leave the U.S. One Massachusetts-born immigration lawyer asked on social media: “Does anyone know if you can get Italian citizenship through great-grandparents?”
The government is not keen to correct its errors. On March 15 the government rendered to prison in El Salvador a legal U.S. resident, Kilmar Armando Abrego Garcia, whom the courts had ordered the U.S. not to send to El Salvador, where his life was in danger. The government has admitted that its arrest and rendition of Abrego Garcia happened because of “administrative error” but now claims—without evidence—that he is a member of the MS-13 gang and that his return to the U.S. would threaten the public. Abrego Garcia says he is not a gang member and notes that he has never been charged with a crime.
On April 4, U.S. District Court Judge Paula Xinis ordered the government to return Abrego Garcia to the U.S. no later than 11:59 pm on April 7. The administration appealed to the Supreme Court, which handed down a 9–0 decision yesterday, saying the government must “facilitate” Abrego Garcia’s release, but asked the district court to clarify what it meant by “effectuate,” noting that it must give “due regard for the deference owed to the Executive Branch in the conduct of foreign affairs.”
The Supreme Court also ordered that “the Government should be prepared to share what it can concerning the steps it has taken and the prospect of further steps.”
Legal analyst Joyce White Vance explained what happened next. Judge Xinis ordered the government to file an update by 9:30 a.m. today explaining where Abrego Garcia is, what the government is doing to get him back, and what more it will do. She planned an in-person hearing at 1:00 p.m.
The administration made clear it did not intend to comply. It answered that the judge had not given them enough time to answer and suggested that it would delay over the Supreme Court’s instruction that Xinis must show deference to the president’s ability to conduct foreign affairs. Xinis gave the government until 11:30 and said she would still hold the hearing. The government submitted its filing at about 12:15, saying that Abrego Garcia is “in the custody of a foreign sovereign,” but at the 1:00 hearing, as Anna Bower of Lawfare reported, the lawyer representing the government, Drew Ensign, said he did not have information about where Abrego Garcia is and that the government had done nothing to get him back. Ensign said he might have answers by next Tuesday. Xinis says they will have to give an update tomorrow.
As Supreme Court Justice Sonia Sotomayor recently warned, if the administration can take noncitizens off the streets, render them to prison in another country, and then claim it is helpless to correct the error because the person is out of reach of U.S. jurisdiction, it could do the same thing to citizens. Indeed, both President Trump and White House press secretary Karoline Leavitt have proposed that very thing.
Tonight, Trump signed a memorandum to the secretaries of defense, interior, agriculture, and homeland security calling for a “Military Mission for Sealing the Southern Border of the United States and Repelling Invasions.” The memorandum creates a military buffer zone along the border so that any migrant crossing would be trespassing on a U.S. military base. This would allow active-duty soldiers to hold migrants until ICE agents take them.
By April 20, the secretaries of defense and homeland security are supposed to report to the president whether they think he should invoke the 1807 Insurrection Act to enable him to use the military to aid in mass deportations.
LETTERS FROM AN AMERICAN
HEATHER COX RICHARDSON
#political cartoons#Matt Davies#The Big Chill#Heather Cox Richardson#Letters from An American#personal data#the right to privacy#identity theft#mistaken identity#SCOTUS#secretary of defense#homeland security#incompetence#data mining#data weaponization
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
Trump administration directs spy satellite agencies to surveil US-Mexico border (Reuters)
Reuters could not determine whether the effort, which has not been previously reported, would gather imagery of U.S. territory. While laws generally restrict U.S. spy agencies from surveilling citizens and other legal residents, they allow immigration authorities to conduct physical searches "within a reasonable distance from any external boundary of the United States." Regulations have defined this as 100 air miles from the border, opens new tab– an area including cities such as San Diego and El Paso. "If they follow the law, these agencies should only collect on the other side of the border in foreign territory," said Paul Rosenzweig, a lawyer who specializes in national security and privacy law. "But how they implement that, and if they do, are legitimate oversight questions."
There's no world where the "digital wall" they are trying to build (see below) doesn't hasten the conjoining of the NROs spy satellite outputs and the booming market of domestically-operating private surveillance technology firms, many of which are building out border surveillance networks.
Multiple defense contractors - new and legacy ones alike - are in talks with various government agencies to aid the border-security work, building on existing deals they have, said the two sources aware of the initiative. A “digital wall” to augment the border’s physical one would be the goal, said one of the sources. For instance, data analytics provider Palantir (PLTR.O), opens new tab powers the so-called Maven Smart System for the Pentagon, via contracts it won last year valued at about $580 million. Maven pulls together data and uses AI to speed up target identification for intelligence analysts. Palantir has long worked with the Department of Homeland Security as well. Anduril, a defense tech startup, designs sensor towers and related software. Last fall, the company announced it had deployed 300 autonomous versions of these towers for U.S. Customs and Border Protection, detecting and tracking objects of interest through radar and other technology. In recent months, Palantir, Anduril, Elon Musk's SpaceX and other newer contractors have discussed a consortium to jointly bid for U.S. defense deals and outcompete the Beltway's legacy players, according to a source familiar with the matter.
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
Over the past couple of decades, a number of US government officials have left their roles for lucrative jobs at tech companies. Plenty of tech executives have also departed to take leadership positions inside federal agencies. But four experts who track the federal workforce tell WIRED they were stunned last week by a development unlike any other they could recall: The Department of Treasury internally announced that Tom Krause had been appointed its fiscal assistant secretary, but that he would simultaneously continue his job as CEO of the company Cloud Software Group.
Krause is now in charge of both a sensitive government payment system and a company that has millions of dollars’ worth of active contracts with various federal agencies through distribution partners, according to a WIRED review of searchable spending records. The Department of Treasury alone accounts for a dozen ongoing contracts tied to Krause’s company that are together valued between $7.3 million to $11.8 million. These include licenses for the data visualization tool ibi WebFocus and purchases of systems called Citrix NetScaler that help manage traffic to apps. (Some publicly posted procurement records do not break out contract details, so actual figures may be even higher.)
Critics have expressed concern about the alleged conflicts of interest posed by Krause’s decision to keep his role in the private sector. Cloud Software could benefit from extending its federal contracts or securing additional ones, though there is no public evidence that Krause has done anything improper with his dual roles. Existing federal regulations also bar actual and apparent unjust favoritism in contracting. “Public trust in those safeguards is nonnegotiable,” says Scott Amey, general counsel at the Project on Government Oversight, a nonpartisan watchdog group.
As Krause moves forward with two jobs, he could have to potentially navigate not only contracting conflicts, but also dueling crises. “What would happen if a Citrix emergency emerges at the same time as Treasury obligations?” says Jeff Hauser, founder and executive director of the Revolving Door Project, which researches federal appointees. “Generally, the thicket of restrictions on full-time employees would make a CEO role impossible in an administration which took adherence to ethics laws seriously.”
Krause, the Treasury Department, and Cloud Software didn’t respond to requests for comment. Cloud Software investors also didn’t respond to a request for comment.
The Treasury Department has told Congress that Krause is a “special government employee”—a type of temporary role—that is supposed to be held to “the same ethical standards of privacy, confidentiality, conflicts of interest assessment, and professionalism of other government employees.” In a foreword to a code of conduct policy posted on Cloud Software’s website, Krause states, “Cloud Software Group is committed to ensuring that its business is conducted ethically, in compliance with the law, and according to its values of integrity, honesty and respect.”
Krause is among a group of several dozen veteran tech executives, mid-level tech operations managers, and fresh-out-of-school software coders who have been recently installed across a series of federal agencies under the auspices of the self-styled Department of Government Efficiency. DOGE’s authority is being challenged by some Democratic state attorneys general. In the meantime, its representatives have been carrying out an order from President Donald Trump to cut costs and modernize technology across the government.
There is some precedent for corporate executives to simultaneously work in the US government. When the US was at war in the early 1900s, the federal government recruited business leaders to fill key posts. They retained their private sector jobs and wages; the government pitched in a $1 annual salary to the executives who became known as “dollar-a-year men.” Congress later raised concerns that some of them had engaged in self-dealing.
Since then, other executives have continued to retain their jobs as they serve on government boards and commissions, typically in a part-time capacity. But maintaining a day-to-day operational role in both the federal government and at a corporation is now virtually unheard of, says David E. Lewis, a political scientist who wrote a book on appointed government bureaucrats. “Most persons in regular executive positions divest themselves of private interests before government service,” he says.
Trump, according to his company, has handed management of his businesses, including hotels and golf courses, to his children for the duration of his presidency (though he reportedly still takes meetings that have raised questions among ethics experts). Musk, who is CEO of Tesla and SpaceX and has oversight of four other companies, including X and Neuralink, has been a vocal figure in DOGE’s operations, but the White House has said he’s not actually in charge—without specifying who is leading the project. Some of the other individuals associated with DOGE are otherwise unemployed, have taken leave, or maintain dual roles but at lower levels than chief executive.
Krause is the only Trump administration official identified so far as being a CEO and a day-to-day decisionmaker inside one particular agency. After years of working as an executive at chip companies, Krause joined Florida-based Cloud Software Group in 2022. The company was created that year as part of a private-equity-backed acquisition of Citrix, followed by a merger with Tibco, another tech company. At the time, Citrix was saddled with an extensive amount of debt and generating essentially stagnant revenues, and while Tibco had not recently publicly disclosed its finances, analysts had considered the company’s outlook to be “negative.”
The US government, including state and local agencies, is expected to spend $287 billion on technology this year, or about 14 percent of overall US tech spending, according to Forrester, a research and advisory company. Whether DOGE’s efforts to boost the quality and efficiency of federal IT systems will lead that spending to increase or decrease isn’t clear. So far, DOGE has both tried to purchase emerging technologies and moved to cancel some existing contracts. But Krause’s inside access could potentially provide an advantage to Cloud Software at a pivotal moment for the company.
Over the past couple of years, Cloud Software has laid off thousands of people and faced accusations that it potentially became lax with cybersecurity. Cloud Software’s most well-known offering, Citrix, enables groups of workers to access data and run apps that are located on a remote machine. But increasing adoption of tools that can operate on any device has chipped away at some of Citrix’s dominance, according to Will McKeon-White, senior analyst for infrastructure and operations at Forrester. There are other options now, he says, including from Microsoft and smaller companies such as Island.
Cloud Software’s Tibco program, which helps workers automate tasks such as adding a new user to multiple internal databases, is often mentioned in the wrong sort of conversations these days, according to David Mooter, a Forrester principal analyst. “They tend to come up more when somebody wants to abandon them,” he says.
That said, some Cloud Software services are more affordable than alternatives for governments, and they also are better suited for the older infrastructure used by some agencies. Last year appears to have been one of Citrix’s best in a long time financially, says Shannon Kalvar, a research director for enterprise systems management and other areas at IDC. One reason for the upswing is that Citrix has put more emphasis on catering to the feature demands of its largest customers, including governments.
13 notes
·
View notes