#data aggregation services
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Precision Insights: Expert Quantitative Market Research Services
Our Quantitative Market Research Services help you quickly gather insights from our panellists and understand the changing consumer behaviour. Using our comprehensive services, we find the answers to the most of your questions! Follow this link to know more https://insighttellers.com/services/quantitative-research-market

#Quantitative Market Research Services#Qualitative Research#Translation#Survey Programming#Data Collection & Analysis#Secondary Research#Panel Aggregation#Contracted Work
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Network reliable sms Store:

TG:@Jakeworldfax Skype:live:.cid.4e9bd3d9e8de911 Whatsapp:12565258771
Update Notification Channel https://t.me/messageinspam
Business: Global network wholesale marketing
Wholesale, a good helper for channeling!
Austraila US UK Canada JP Thianland India Colombia South Africa
Daily good traffic we can provide hot working route can get 500k to 800k!
Update every week our need
Real source sales, daily huge profit you get.
#digital marketing#sms service provider#sms marketing#wholesales sms#data analytics#a2p sms#sms gateway#message service#sms#bulk sms#aggregate
0 notes
Text
Explore the best developer friendly API platforms designed to streamline integration, foster innovation, and accelerate development for seamless user experiences.
Developer Friendly Api Platform
#Developer Friendly Api Platform#Consumer Driven Banking#Competitive Market Advantage Through Data#Banking Data Aggregation Services#Advanced Security Architecture#Adr Open Banking#Accredited Data Recipient
0 notes
Text
Competitor Price Monitoring Services - Food Scraping Services
Competitor Price Monitoring Strategies
Price Optimization

If you want your restaurant to stay competitive, it’s crucial to analyze your competitors’ average menu prices. Foodspark offers a Competitor Price Monitoring service to help you with this task. By examining data from other restaurants and trends in menu prices, we can determine the best price for your menu. That will give you an edge in a constantly evolving industry and help you attract more customers, ultimately increasing profits.
Market Insights

Our restaurant data analytics can help you stay ahead by providing valuable insights into your competitors’ pricing trends. By collecting and analyzing data, we can give you a deep understanding of customer preferences, emerging trends, and regional variations in menu pricing. With this knowledge, you can make informed decisions and cater to evolving consumer tastes to stay ahead.
Competitive Advantage

To stay ahead in the restaurant industry, you must monitor your competitors’ charges and adjust your prices accordingly. Our solution can help you by monitoring your competitors’ pricing strategies and allowing you to adjust your expenses in real-time. That will help you find opportunities to offer special deals or menu items to make you stand out and attract more customers.
Price Gap Tracking

Knowing how your menu prices compare to your competitors is essential to improve your restaurant’s profitability. That is called price gap tracking. Using our tracking system, you can quickly identify the price differences between restaurant and your competitors for the same or similar menu items. This information can help you find opportunities to increase your prices while maintaining quality or offering lower costs. Our system allows you to keep a close eye on price gaps in your industry and identify areas where your expenses are below or above the average menu prices. By adjusting your pricing strategy accordingly, you can capture more market share and increase your profits.
Menu Mapping and SKU

Use our menu and SKU mapping features to guarantee that your products meet customer expectations. Find out which items are popular and which ones may need some changes. Stay adaptable and responsive to shifting preferences to keep your menu attractive and competitive.
Price Positioning

It’s essential to consider your target audience and desired brand image to effectively position your restaurant’s prices within the market. Competitor data can help you strategically set your prices as budget-friendly, mid-range, or premium. Foodspark Competitor Price Monitoring provides data-driven insights to optimize your pricing within your market segment. That helps you stay competitive while maximizing revenue and profit margins.
Competitor Price Index (CPI)

The Competitor Price Index (CPI) measures how your restaurant’s prices compare to competitors. We calculate CPI for you by averaging the prices of similar menu items across multiple competitors. If your CPI is above 100, your prices are higher than your competitors. If it’s below 100, your prices are lower.
Benefits of Competitor Price Monitoring Services
Price Optimization
By continuous monitoring your competitor’s prices, you can adjust your own pricing policies, to remain competitive while maximizing your profit margins.
Dynamic Pricing
Real-time data on competitor’s prices enable to implement dynamic pricing strategies, allowing you to adjust your prices based on market demand and competitive conditions.
Market Positioning
Understanding how your prices compare to those of your competitors helps you position your brand effectively within the market.
Customer Insights
Analyzing customer pricing data can reveal customer behavior and preferences, allowing you to tailor your pricing and marketing strategies accordingly.
Brand Reputation Management
Consistently competitive pricing can enhance your brand’s reputation and make your product more appealing to customers.
Content Source: https://www.foodspark.io/competitor-price-monitoring/
#web scraping services#restaurantdataextraction#Competitor Price Monitoring#Mobile-app Specific Scraping#Real-Time API#Region - wise Restaurant Listings#Services#Food Aggregator#Food Data Scraping#Real-time Data API#Price Monitoring#Food App Scraping#Food Menu Data
0 notes
Text
Ready to take your data aggregation to the next level? Discover how strategic partnerships with digital data collection service companies can revolutionize your business. From scaling operations to enhancing data quality and compliance, there's immense potential waiting to be unlocked.
Learn how partnering with us can offer unparalleled data scope, faster insights, cost optimization, and access to specialized expertise. Let's collaborate to innovate and drive success together.
Connect with us today to explore how our digital data collection services can propel your data aggregation business forward. Don't miss out on the opportunity to harness the power of strategic partnerships for smarter data and smarter decisions. Read more: https://www.damcogroup.com/blogs/beyond-manual-exploring-benefits-of-automated-data-processing
#DataAggregation #Partnerships #DataCollection #BusinessGrowth
0 notes
Text
Empowering Business Growth: Unleashing the Potential of Data Analytics as a Service
In the fast-paced digital landscape, harnessing the power of data has become paramount for businesses striving to thrive. Discover how Data Analytics as a Service is reshaping industries. Explore the benefits of Analytics as a Service through insights from a leading Data Analytics company. From expert Data Analytics consulting to cutting-edge Data Engineering and from the agility of Data as a Service to the potential of Big Data as a Service, this article delves into the realms of Data Analytics, Data Aggregation, and Business Intelligence. Elevate your understanding of data's transformative role and embrace the future of informed decision-making.
#Data Analytics as a service#Analytics as a service#Data Analytics company#Data Analytics consulting#Data as a service#big data as a service#Data Analytics#Data Aggregation#Data Engineering#Business Intelligence in Data Analytics
0 notes
Text
In 2024, wealth concentration rose to an all-time high. According to Forbes’ Billionaires List, not only are there more billionaires than ever—2,781—but those billionaires are also richer than ever, with an aggregate worth of $14.2 trillion. This is a trend that looks set to continue unabated. A recent report from the financial data company Altrata estimated that about 1.2 million individuals who are worth more than $5 million will pass on a collective wealth of almost $31 trillion over the next decade.
Discontentment and concern over the consequences of extreme wealth in our society is growing. Senator Bernie Sanders, for instance, stated that the “obscene level of income and wealth inequality in America is a profoundly moral issue.” In a joint op-ed for CNN in 2023, Democratic congresswoman Barbara Lee and Disney heiress Abigail Disney wrote that “extreme wealth inequality is a threat to our economy and democracy.” In 2024, when the board of Tesla put to vote a $56 billion pay package for Elon Musk, some major shareholders voted against it, declaring that such a compensation level was “absurd” and “ridiculous.”
In 2025, the fight against rising wealth inequality will be high on the political agenda. In July 2024, the G20—the world’s 20 biggest economies—agreed to work on a proposal by Brazil to introduce a new global “billionaire tax” that would levy a 2 percent tax on assets worth more than $1 billion. This would raise an estimated $250 billion a year. While this specific proposal was not endorsed in the Rio declaration, the G20 countries agreed that the super rich should be taxed more.
Progressive politicians won’t be the only ones trying to address this problem. In 2025, millionaires themselves will increasingly mobilize and put pressure on political leaders. One such movement is Patriotic Millionaires, a nonpartisan group of multimillionaires who are already publicly campaigning and privately lobbying the American Congress for a guaranteed living wage for all, a fair tax system, and the protection of equal representation. “Millionaires and large corporations—who have benefited most from our country’s assets—should pay a larger percentage of the tab for running the country,” reads their value statement. Members include Abigail Disney, former BlackRock executive Morris Pearl, legal scholar Lawrence Lessig, screenwriter Norman Lear, and investor Lawrence Benenson.
Another example is TaxMeNow, a lobby group founded in 2021 by young multimillionaires in Germany, Austria, and Switzerland which also advocates for higher wealth taxation. Its most famous member is the 32-year old Marlene Engelhorn, descendant of Friedrich Engelhorn, founder of German pharma giant BASF. She recently set up a council made up of 50 randomly selected Austrian citizens to decide what should happen to her €25 million inheritance. “I have inherited a fortune, and therefore power, without having done anything for it,” she said in a statement. “If politicians don’t do their job and redistribute, then I have to redistribute my wealth myself.”
Earlier this year, Patriotic Millionaires, TaxMeNow, Oxfam, and another activist group called Millionaires For Humanity formed a coalition called Proud to Pay More, and addressed a letter to global leaders during the annual gathering of the World Economic Forum in Davos. Signed by hundreds of high-net-worth individuals—including heiress Valerie Rockefeller, actor Simon Pegg, and filmmaker Richard Curtis—the letter stated: “We all know that ‘trickle down economics’ has not translated into reality. Instead it has given us stagnating wages, crumbling infrastructure, failing public services, and destabilized the very institution of democracy.” It concluded: “We ask you to take this necessary and inevitable step before it’s too late. Make your countries proud. Tax extreme wealth.” In 2025, thanks to the nascent movement of activist millionaires, these calls will grow even louder.
#it's nice to think about but it's not going to happen anytime soon#not with this congress and president
606 notes
·
View notes
Text
Palantir’s NHS-stealing Big Lie

I'm on tour with my new, nationally bestselling novel The Bezzle! Catch me in TUCSON (Mar 9-10), then SAN FRANCISCO (Mar 13), Anaheim, and more!

Capitalism's Big Lie in four words: "There is no alternative." Looters use this lie for cover, insisting that they're hard-nosed grownups living in the reality of human nature, incentives, and facts (which don't care about your feelings).
The point of "there is no alternative" is to extinguish the innovative imagination. "There is no alternative" is really "stop trying to think of alternatives, dammit." But there are always alternatives, and the only reason to demand that they be excluded from consideration is that these alternatives are manifestly superior to the looter's supposed inevitability.
Right now, there's an attempt underway to loot the NHS, the UK's single most beloved institution. The NHS has been under sustained assault for decades – budget cuts, overt and stealth privatisation, etc. But one of its crown jewels has been stubbournly resistant to being auctioned off: patient data. Not that HMG hasn't repeatedly tried to flog patient data – it's just that the public won't stand for it:
https://www.theguardian.com/society/2023/nov/21/nhs-data-platform-may-be-undermined-by-lack-of-public-trust-warn-campaigners
Patients – quite reasonably – do not trust the private sector to handle their sensitive medical records.
Now, this presents a real conundrum, because NHS patient data, taken as a whole, holds untold medical insights. The UK is a large and diverse country and those records in aggregate can help researchers understand the efficacy of various medicines and other interventions. Leaving that data inert and unanalysed will cost lives: in the UK, and all over the world.
For years, the stock answer to "how do we do science on NHS records without violating patient privacy?" has been "just anonymise the data." The claim is that if you replace patient names with random numbers, you can release the data to research partners without compromising patient privacy, because no one will be able to turn those numbers back into names.
It would be great if this were true, but it isn't. In theory and in practice, it is surprisingly easy to "re-identify" individuals in anonymous data-sets. To take an obvious example: we know which two dates former PM Tony Blair was given a specific treatment for a cardiac emergency, because this happened while he was in office. We also know Blair's date of birth. Check any trove of NHS data that records a person who matches those three facts and you've found Tony Blair – and all the private data contained alongside those public facts is now in the public domain, forever.
Not everyone has Tony Blair's reidentification hooks, but everyone has data in some kind of database, and those databases are continually being breached, leaked or intentionally released. A breach from a taxi service like Addison-Lee or Uber, or from Transport for London, will reveal the journeys that immediately preceded each prescription at each clinic or hospital in an "anonymous" NHS dataset, which can then be cross-referenced to databases of home addresses and workplaces. In an eyeblink, millions of Britons' records of receiving treatment for STIs or cancer can be connected with named individuals – again, forever.
Re-identification attacks are now considered inevitable; security researchers have made a sport out of seeing how little additional information they need to re-identify individuals in anonymised data-sets. A surprising number of people in any large data-set can be re-identified based on a single characteristic in the data-set.
Given all this, anonymous NHS data releases should have been ruled out years ago. Instead, NHS records are to be handed over to the US military surveillance company Palantir, a notorious human-rights abuser and supplier to the world's most disgusting authoritarian regimes. Palantir – founded by the far-right Trump bagman Peter Thiel – takes its name from the evil wizard Sauron's all-seeing orb in Lord of the Rings ("Sauron, are we the baddies?"):
https://pluralistic.net/2022/10/01/the-palantir-will-see-you-now/#public-private-partnership
The argument for turning over Britons' most sensitive personal data to an offshore war-crimes company is "there is no alternative." The UK needs the medical insights in those NHS records, and this is the only way to get at them.
As with every instance of "there is no alternative," this turns out to be a lie. What's more, the alternative is vastly superior to this chumocratic sell-out, was Made in Britain, and is the envy of medical researchers the world 'round. That alternative is "trusted research environments." In a new article for the Good Law Project, I describe these nigh-miraculous tools for privacy-preserving, best-of-breed medical research:
https://goodlawproject.org/cory-doctorow-health-data-it-isnt-just-palantir-or-bust/
At the outset of the covid pandemic Oxford's Ben Goldacre and his colleagues set out to perform realtime analysis of the data flooding into NHS trusts up and down the country, in order to learn more about this new disease. To do so, they created Opensafely, an open-source database that was tied into each NHS trust's own patient record systems:
https://timharford.com/2022/07/how-to-save-more-lives-and-avoid-a-privacy-apocalypse/
Opensafely has its own database query language, built on SQL, but tailored to medical research. Researchers write programs in this language to extract aggregate data from each NHS trust's servers, posing medical questions of the data without ever directly touching it. These programs are published in advance on a git server, and are preflighted on synthetic NHS data on a test server. Once the program is approved, it is sent to the main Opensafely server, which then farms out parts of the query to each NHS trust, packages up the results, and publishes them to a public repository.
This is better than "the best of both worlds." This public scientific process, with peer review and disclosure built in, allows for frequent, complex analysis of NHS data without giving a single third party access to a a single patient record, ever. Opensafely was wildly successful: in just months, Opensafely collaborators published sixty blockbuster papers in Nature – science that shaped the world's response to the pandemic.
Opensafely was so successful that the Secretary of State for Health and Social Care commissioned a review of the programme with an eye to expanding it to serve as the nation's default way of conducting research on medical data:
https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/better-broader-safer-using-health-data-for-research-and-analysis/better-broader-safer-using-health-data-for-research-and-analysis
This approach is cheaper, safer, and more effective than handing hundreds of millions of pounds to Palantir and hoping they will manage the impossible: anonymising data well enough that it is never re-identified. Trusted Research Environments have been endorsed by national associations of doctors and researchers as the superior alternative to giving the NHS's data to Peter Thiel or any other sharp operator seeking a public contract.
As a lifelong privacy campaigner, I find this approach nothing short of inspiring. I would love for there to be a way for publishers and researchers to glean privacy-preserving insights from public library checkouts (such a system would prove an important counter to Amazon's proprietary god's-eye view of reading habits); or BBC podcasts or streaming video viewership.
You see, there is an alternative. We don't have to choose between science and privacy, or the public interest and private gain. There's always an alternative – if there wasn't, the other side wouldn't have to continuously repeat the lie that no alternative is possible.

Name your price for 18 of my DRM-free ebooks and support the Electronic Frontier Foundation with the Humble Cory Doctorow Bundle.

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/03/08/the-fire-of-orodruin/#are-we-the-baddies

Image: Gage Skidmore (modified) https://commons.m.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Peter_Thiel_(51876933345).jpg
CC BY-SA 2.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.0/deed.en
#pluralistic#peter thiel#trusted research environment#opensafely#medical data#floss#privacy#reidentification#anonymization#anonymisation#nhs#ukpoli#uk#ben goldacre#goldacre report#science#evidence-based medicine#goldacre review#interoperability#transparency
530 notes
·
View notes
Text
Libraries have traditionally operated on a basic premise: Once they purchase a book, they can lend it out to patrons as much (or as little) as they like. Library copies often come from publishers, but they can also come from donations, used book sales, or other libraries. However the library obtains the book, once the library legally owns it, it is theirs to lend as they see fit. Not so for digital books. To make licensed e-books available to patrons, libraries have to pay publishers multiple times over. First, they must subscribe (for a fee) to aggregator platforms such as Overdrive. Aggregators, like streaming services such as HBO’s Max, have total control over adding or removing content from their catalogue. Content can be removed at any time, for any reason, without input from your local library. The decision happens not at the community level but at the corporate one, thousands of miles from the patrons affected. Then libraries must purchase each individual copy of each individual title that they want to offer as an e-book. These e-book copies are not only priced at a steep markup—up to 300% over consumer retail—but are also time- and loan-limited, meaning the files self-destruct after a certain number of loans. The library then needs to repurchase the same book, at a new price, in order to keep it in stock. This upending of the traditional order puts massive financial strain on libraries and the taxpayers that fund them. It also opens up a world of privacy concerns; while libraries are restricted in the reader data they can collect and share, private companies are under no such obligation. Some libraries have turned to another solution: controlled digital lending, or CDL, a process by which a library scans the physical books it already has in its collection, makes secure digital copies, and lends those out on a one-to-one “owned to loaned” ratio. The Internet Archive was an early pioneer of this technique. When the digital copy is loaned, the physical copy is sequestered from borrowing; when the physical copy is checked out, the digital copy becomes unavailable. The benefits to libraries are obvious; delicate books can be circulated without fear of damage, volumes can be moved off-site for facilities work without interrupting patron access, and older and endangered works become searchable and can get a second chance at life. Library patrons, who fund their local library’s purchases with their tax dollars, also benefit from the ability to freely access the books. Publishers are, unfortunately, not a fan of this model, and in 2020 four of them sued the Internet Archive over its CDL program. The suit ultimately focused on the Internet Archive’s lending of 127 books that were already commercially available through licensed aggregators. The publisher plaintiffs accused the Internet Archive of mass copyright infringement, while the Internet Archive argued that its digitization and lending program was a fair use. The trial court sided with the publishers, and on September 4, the Court of Appeals for the Second Circuit reaffirmed that decision with some alterations to the underlying reasoning. This decision harms libraries. It locks them into an e-book ecosystem designed to extract as much money as possible while harvesting (and reselling) reader data en masse. It leaves local communities’ reading habits at the mercy of curatorial decisions made by four dominant publishing companies thousands of miles away. It steers Americans away from one of the few remaining bastions of privacy protection and funnels them into a surveillance ecosystem that, like Big Tech, becomes more dangerous with each passing data breach. And by increasing the price for access to knowledge, it puts up even more barriers between underserved communities and the American dream.
11 September 2024
154 notes
·
View notes
Text
We document that, after remaining almost constant for almost 30 years, real labor productivity at U.S. restaurants surged over 15% during the COVID pandemic. This surge has persisted even as many conditions have returned to pre-pandemic levels. Using mobile phone data tracking visits and spending at more than 100,000 individual limited service restaurants across the country, we explore the potential sources of the surge. It cannot be explained by economies of scale, expanding market power, or a direct result of COVID-sourced demand fluctuations. The restaurants’ productivity growth rates are strongly correlated, however, with reductions in the amount of time their customers spend in the establishments, particularly with a rising share of customers spending 10 minutes or less. The frequency of such ‘take-out’ customers rose considerably during COVID, even at fast food restaurants, and never went back down. The magnitude of the restaurant-level relationship between productivity and customer dwell time, if applied to the aggregate decrease in dwell time, can explain almost all of the aggregate productivity increase in our sample.
Love to increase productivity
58 notes
·
View notes
Note
I just pulled this 2009 hp out of the dumpster what do i do with it. It has ubuntu.

if it's that old, probably wipe and reinstall. If you're doing ubuntu again first uninstall snap but there's a lot of neat self-hosting stuff you can do with an old PC.
I have a little RasPi in my basement which runs an RSS Feed aggregator(FreshRSS), some calendars(Radicale) and notes(Joplin) so they're synced between all my devices.
If the computer has the storage and a little bit of power for processing things you could also run something to sync all your photos (Immich) and files (Nextcloud, which also does images but i like Immich better for it) between ur devices so you can avoid having to use paid services which may or may not be selling your data or whatever.
You can have it run a self hosted VPN such as WireGuard which you can port forward so you can use it from anywhere, or you can use a service like Tailscale which doesn't require port forwarding, but it's not something you host yourself, they have their own servers.
You can also put all the services behind a reverse proxy (nginx Proxy Manager, NOT nginx, i mean it's good but it's much harder) and be able to access it through a proper domain with SSL(a vpn will already do this though) instead of whatever 192.168.whatever, again, only accessible by people On That VPN.
All things are available (and usually encouraged) to run through docker, and they often even have their own compose files so it's not too much setup. (it's maintenence to update things though)
Also have fun and play tuoys. Old computers run modern versions of linux much better than windows. just open it up see what u can do with it, get used to it, try to customize the desktop to how you like it, or try another one (Ubuntu comes with GNOME. please try another one). See what works and what doesn't (hardware will likely be the issue if something doesn't work though, not linux itself). Something like Plasma or Cinnamon works just like a normal windows computer but there's still a bit of that "learning how to use a computer" that you don't really get after using the same version of windows for 10 years.
21 notes
·
View notes
Note
After seeing your weatherbugapp reblog i installed duckduckgo and tried it.
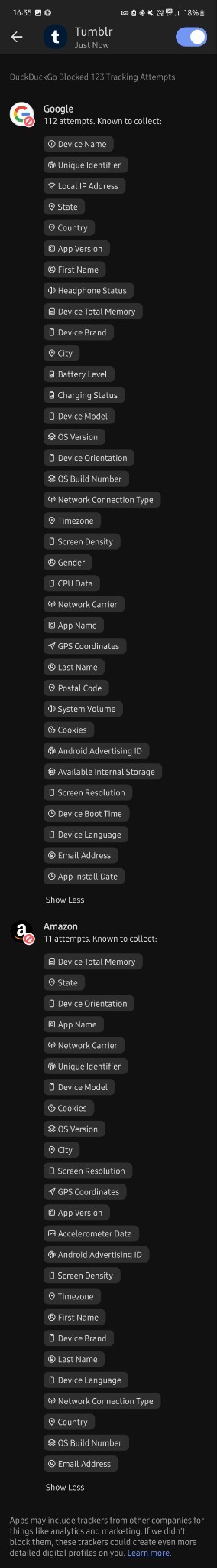
I don't know much about technology tbh but i downloaded this app less than 30 mins ago and in that time google tried to track me 112 times?? And they tried to collect finger prints? And my first and last name? And my gender? And my country, state and city? My gps coordinates? My postal code? My network carrier? My fricking battery level for whatever reason? Can you please tell me if this is normal at all, because i'm freaking out right now. I just turned 18 and started using mobile banking and stuff and this shit scares me
Why tf does it need to know my screen density???my system volume????my charging status????? What tf are they cooking
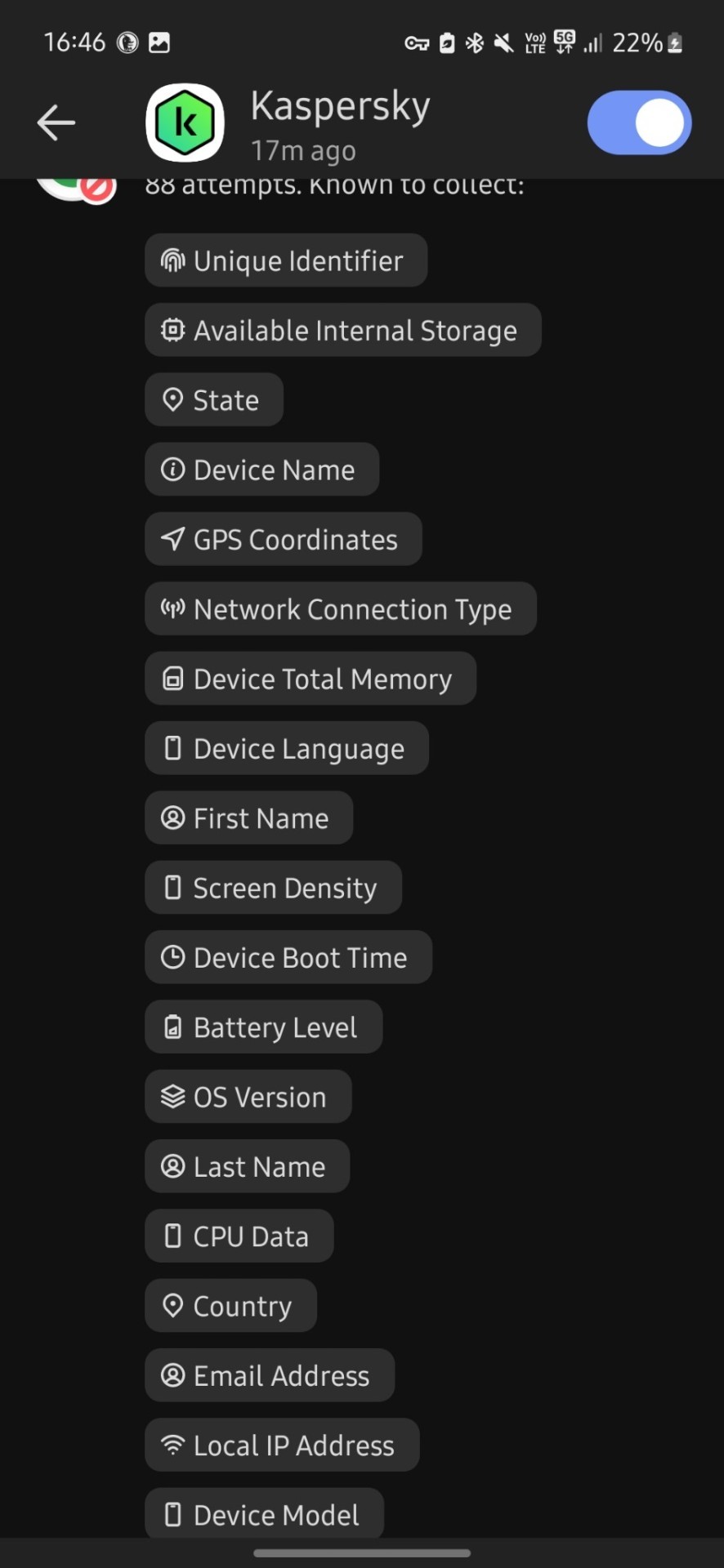
Now it's at 476 tracking attempts bro???? barely 5 mins passed.....
I condensed your three asks into one for readability!
And yeah, I'm very far from an expert about any of this, but as far as I know that's just. Normal. That's the normal amount of spying they're doing on your phone. I assume the numbers we see are to some extent because having been foiled, a lot of these scripts try repeatedly, since I can't imagine what use thousands of trackers per phone would be even to the great aggregators.
Tracking the phone stuff like screen resolution and battery level is because (apart from that definitely not being considered remotely 'private' so it's Free Real Estate) in aggregate that data can be used to track what phone use patterns are like on a demographic scale and therefore. Where the smart money is.
Almost all of this is getting sold in bulk for ad targeting and market analysis. This does presumably make it very hard to notice when like. Actually important stuff is being spied on, which is why I feel better about Having Apps with the duckduckgo app blocker thing.
My bank's app reportedly sells data to a couple aggregators including Google. Not like, my banking info, but it's still so offensive on principle that I avoid using the app unless I have to, and force stop it afterward.
The patterns that show up on the weekly duckduckgo blocker report are interesting. Hoopla attempts about two orders of magnitude more tracking than Libby, which makes sense because they're a commercial streaming service libraries pay by the unit for access, while Libby is a content management software run by a corporation that values its certification as a 'B' company--that is, one invested in the public good that can be trusted. The cleanness of their brand is a great deal of its value, so they have to care about their image and be a little more scrupulous.
Which doesn't mean not being a little bit spyware, because everything is spyware now. Something else I've noticed is that in terms of free game apps, the polished professional stuff is now much more invasive than the random kinda janky thing someone just threw together.
Back in the day you tended to expect the opposite, because spyware was a marginal shifty profit-margin with too narrow a revenue stream to be worth more to an established brand than their reputation, but now that everyone does it there's not a lot of reputation cost and refraining would be sacrificing a potential revenue stream, which is Irresponsible Conduct for a corporation.
While meanwhile 'developing a free game app to put on the game store' is something a person can do for free with the hardware they already have for home use, as a hobby or practice or to put on their coding resume. So while such apps absolutely can be malicious and more dangerous when they are than The Big Brand, they can also be neutral in a way commercial stuff no longer is. Wild world.
But yeah for the most part as far as I can make out, these are just The Commercial Panopticon, operating as intended. It's gross but it probably doesn't indicate anything dangerous on an individual level.
56 notes
·
View notes
Text
Hypothetical Decentralised Social Media Protocol Stack
if we were to dream up the Next Social Media from first principles we face three problems. one is scaling hosting, the second is discovery/aggregation, the third is moderation.
hosting
hosting for millions of users is very very expensive. you have to have a network of datacentres around the world and mechanisms to sync the data between them. you probably use something like AWS, and they will charge you an eye-watering amount of money for it. since it's so expensive, there's no way to break even except by either charging users to access your service (which people generally hate to do) or selling ads, the ability to intrude on their attention to the highest bidder (which people also hate, and go out of their way to filter out). unless you have a lot of money to burn, this is a major barrier.
the traditional internet hosts everything on different servers, and you use addresses that point you to that server. the problem with this is that it responds poorly to sudden spikes in attention. if you self-host your blog, you can get DDOSed entirely by accident. you can use a service like cloudflare to protect you but that's $$$. you can host a blog on a service like wordpress, or a static site on a service like Github Pages or Neocities, often for free, but that broadly limits interaction to people leaving comments on your blog and doesn't have the off-the-cuff passing-thought sort of interaction that social media does.
the middle ground is forums, which used to be the primary form of social interaction before social media eclipsed them, typically running on one or a few servers with a database + frontend. these are viable enough, often they can be run with fairly minimal ads or by user subscriptions (the SomethingAwful model), but they can't scale indefinitely, and each one is a separate bubble. mastodon is a semi-return to this model, with the addition of a means to use your account on one bubble to interact with another ('federation').
the issue with everything so far is that it's an all-eggs-in-one-basket approach. you depend on the forum, instance, or service paying its bills to stay up. if it goes down, it's just gone. and database-backend models often interact poorly with the internet archive's scraping, so huge chunks won't be preserved.
scaling hosting could theoretically be solved by a model like torrents or IPFS, in which every user becomes a 'server' for all the posts they download, and you look up files using hashes of the content. if a post gets popular, it also gets better seeded! an issue with that design is archival: there is no guarantee that stuff will stay on the network, so if nobody is downloading a post, it is likely to get flushed out by newer stuff. it's like link rot, but it happens automatically.
IPFS solves this by 'pinning': you order an IPFS node (e.g. your server) not to flush a certain file so it will always be available from at least one source. they've sadly mixed this up in cryptocurrency, with 'pinning services' which will take payment in crypto to pin your data. my distaste for a technology designed around red queen races aside, I don't know how pinning costs compare to regular hosting costs.
theoretically you could build a social network on a backbone of content-based addressing. it would come with some drawbacks (posts would be immutable, unless you use some indirection to a traditional address-based hosting) but i think you could make it work (a mix of location-based addressing for low-bandwidth stuff like text, and content-based addressing for inline media). in fact, IPFS has the ability to mix in a bit of address-based lookup into its content-based approach, used for hosting blogs and the like.
as for videos - well, BitTorrent is great for distributing video files. though I don't know how well that scales to something like Youtube. you'd need a lot of hard drive space to handle the amount of Youtube that people typically watch and continue seeding it.
aggregation/discovery
the next problem is aggregation/discovery. social media sites approach this problem in various ways. early social media sites like LiveJournal had a somewhat newsgroup-like approach, you'd join a 'community' and people would post stuff to that community. this got replaced by the subscription model of sites like Twitter and Tumblr, where every user is simultaneously an author and a curator, and you subscribe to someone to see what posts they want to share.
this in turn got replaced by neural network-driven algorithms which attempt to guess what you'll want to see and show you stuff that's popular with whatever it thinks your demographic is. that's gotta go, or at least not be an intrinsic part of the social network anymore.
it would be easy enough to replicate the 'subscribe to see someone's recommended stuff' model, you just need a protocol for pointing people at stuff. (getting analytics such as like/reblog counts would be more difficult!) it would probably look similar to RSS feeds: you upload a list of suitably formatted data, and programs which speak that protocol can download it.
the problem of discovery - ways to find strangers who are interested in the same stuff you are - is more tricky. if we're trying to design this as a fully decentralised, censorship-resistant network, we face the spam problem. any means you use to broadcast 'hi, i exist and i like to talk about this thing, come interact with me' can be subverted by spammers. either you restrict yourself entirely to spreading across a network of curated recommendations, or you have to have moderation.
moderation
moderation is one of the hardest problems of social networks as they currently exist. it's both a problem of spam (the posts that users want to see getting swamped by porn bots or whatever) and legality (they're obliged to remove child porn, beheading videos and the like). the usual solution is a combination of AI shit - does the robot think this looks like a naked person - and outsourcing it to poorly paid workers in (typically) African countries, whose job is to look at reports of the most traumatic shit humans can come up with all day and confirm whether it's bad or not.
for our purposes, the hypothetical decentralised network is a protocol to help computers find stuff, not a platform. we can't control how people use it, and if we're not hosting any of the bad shit, it's not on us. but spam moderation is a problem any time that people can insert content you did not request into your feed.
possibly this is where you could have something like Mastodon instances, with their own moderation rules, but crucially, which don't host the content they aggregate. so instead of having 'an account on an instance', you have a stable address on the network, and you submit it to various directories so people can find you. by keeping each one limited in scale, it makes moderation more feasible. this is basically Reddit's model: you have topic-based hubs which people can subscribe to, and submit stuff to.
the other moderation issue is that there is no mechanism in this design to protect from mass harassment. if someone put you on the K*w*f*rms List of Degenerate Trannies To Suicidebait, there'd be fuck all you can do except refuse to receive contact from strangers. though... that's kind of already true of the internet as it stands. nobody has solved this problem.
to sum up
primarily static sites 'hosted' partly or fully on IPFS and BitTorrent
a protocol for sharing content you want to promote, similar to RSS, that you can aggregate into a 'feed'
directories you can submit posts to which handle their own moderation
no ads, nobody makes money off this
honestly, the biggest problem with all this is mostly just... getting it going in the first place. because let's be real, who but tech nerds is going to use a system that requires you to understand fuckin IPFS? until it's already up and running, this idea's got about as much hope as getting people to sign each others' GPG keys. it would have to have the sharp edges sanded down, so it's as easy to get on the Hypothetical Decentralised Social Network Protocol Stack as it is to register an account on tumblr.
but running over it like this... I don't think it's actually impossible in principle. a lot of the technical hurdles have already been solved. and that's what I want the Next Place to look like.
245 notes
·
View notes
Text
Has anyone used SquidgeWorld Archive ( https://squidgeworld.org/ ) to read/post fanfictions ? Apparently it's exactly like Ao3 but with a clear position against AI :

Their Terms of Service state :
7. Added May 13th, 2023: Artificial Intelligence (A.I.) generated works are not supported in the archive. The only exception to this rule would be partial only in posts that are clearly marked meta as part of discussion of said works. Otherwise, no. AI generated works are not welcomed in the archive 8. Added September 24th, 2023: Web scraping by artificial intelligence (AI), or any process of extracting data from the contents of this website for the purpose of use with artificial intelligence (AI) is strictly prohibited. Any data collection, content aggregation, or use of contents on this website in any way for training datasets or machine learning models is expressly prohibited. For more information, contact us via the “Contact Us” section of this website, or via any of the links on other Squidge.org property websites.
It sounds nice ! I love Ao3 but indeed it doesn't mention AI, simply stating that "AI generated works are allowed". So it's good that at least some fanwork websites are addressing the issue ! Hopefully Ao3 will release a clear rule against web scraping / machine learning for all posted works.
Now if you're wondering what is available right now on SqWA, I haven't checked all my favorite tags yet. If you're planning on writing something, maybe give it a go ?? So we'll have more to look forward to !
38 notes
·
View notes
Text
Discover how data aggregators can achieve unprecedented success by fostering collaborations with leading digital data collection companies. Our insightful blog explores the strategic pathways for thriving in the dynamic landscape of data management. Uncover the key principles that drive effective partnerships, enhancing your understanding of the symbiotic relationship between data aggregators and digital data collectors. Elevate your data strategies and stay ahead in the industry.
0 notes
Text
Useful
Big Data: We know everything about you. We track where you live, what you buy, who you talk to, what you do for entertainment. We even listen in on your conversations. We will use this to tailor advertisement to you, and if we feel like it we will use this to influence your voting patterns and control your government.
Me: Cool, cool, cool. That's fine, totally fine. So, um, could you give me contact info for this guy I went to school with? I haven't heard from him in years and I was kinda wondering how he's doing.
Big data: Here's a bunch of super shady malware-laden sites which claim to have that info, and for only $24.99/month, non-cancellable, they'll probably not tell you.
Me: But you have that information. And since you supposedly get it from aggregating publicly-available data, there's no legal reason you couldn't tell me. It's all public data which you gathered legally, riiiight?
Big Data: Yes, of course. Definitely. Absolutely no illegal or unethical data mining here, no sirree. It's all completely legal and above board.
Me: And you'd be able and willing to prove that, right?
Big Data: No.
Me: Riiiight. Anyway, you have what I want. You know what I'm after. Some of the results you've shown me indicate very clearly you definitely know exactly what I want and are deliberately not showing it to me. Could I please just have it?
Big Data: No.
Anyway. I was thinking about this actually when I was trying to find a business on Google Maps. There's so much data gathered, and it's very obvious not only that various entities have that data but that they're the authoritative source of that data. And they're using that data for their own purposes, but they are intentionally withholding it in order to force a black market. It's not even simply someone wanting to acquire a huge batch of names and SSNs, it's that right now - in spite of the data not being privileged in any legal sense - the only way to find the phone number of Irene Adler in Craft Mills, Washington I would have to go to a site which is clearly meant to install a bot on my computer. And 20 years ago I could just go to Yahoo People Search and pull that information up.
And, you know, that drives resentment. They've demonstrated these services can exist, and it's not like there's no market. But they're refusing out of what seems like sheer spite. They're not even just refusing, they're actively taking these things away.
19 notes
·
View notes