#es2015
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Var, Let, and Const – What's the Difference?
A lot of shiny new features came out with ES2015 (ES6). And now, since it's 2020, it's assumed that a lot of JavaScript developers have become familiar with and have started using these features.
While this assumption might be partially true, it's still possible that some of these features remain a mystery to some devs.
One of the features that came with ES6 is the addition of let and const, which can be used for variable declaration. The question is, what makes them different from good ol' var which we've been using? If you are still not clear about this, then this article is for you.
In this article, we'll discuss var, let and const with respect to their scope, use, and hoisting. As you read, take note of the differences between them that I'll point out.
0 notes
Text
プロトタイプベイズドな言語のコンストラクタ

ES2015 で JavaScript に追加されたという、class 構文を ClojureScript で書いてみることに。 内部で保持する情報(canvasElement)が重たいためか、コンソールログを吐かないと、メソッド定義「drawRect」が有効にならない、という挙動がみられた。 greeting 処理(「こんにちは、〜さん」的な)に渡すような、文字列(名前)程度なら、保持させても問題なかったんだけど…)。 ;;=================== (defn Canvas2DUtility [canvas] (this-as this (set! (.-canvasElement this) canvas) (set! (.-context2d this) (.getContext (.-canvasElement this) "2d")) ;; これがないとメソッド定義が有効にならない。バグ? (.log js/console "constractor: Canvas2DUtility") )) (set! (.. Canvas2DUtility -prototype -drawRect) (fn [color x y width height] (this-as this (let [ctx (.-context2d this)] (set! (.-fillStyle ctx) color) (.fillRect ctx x y width height)) )))
;;=================== (defn initialize [] (let [canvas (.querySelector js/document.body "#main_canvas") util (Canvas2DUtility. canvas)]
(.drawRect util "white" 50 50 10 15) )) ;;=================== Inheritance in JavaScript & ClojureScript [ https://nextjournal.com/joe-loco/inheritance-js-cljs ]
0 notes
Text
Node.js / Multiline y template string
Hoy veremos dos conceptos que si son seguidores del curso ya hemos utilizado varias veces sin saberlo, espero les sea de utilidad!
Bienvenidos sean a este post, hoy analizaremos un tema que vimos en el post anterior. Las caracteristicas mencionadas en el titulo fueron implementadas a partir del ES2015 y las hemos estado usando un poco sin querer en posts anteriores, si bien sabemos que en Javascript normal podemos representar literales de texto mediante la comilla simple (‘) o la ccomilla doble (“) gracias al ES2015 se nos…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Embracing Angular 8: A Strategic Choice for IT Leaders in 2024
In the ever-evolving web development landscape, Angular stands out as a beacon of innovation, performance, and efficiency. With the release of Angular 8, the framework has again set new benchmarks, compelling IT leaders worldwide to take notice.
This blog post delves into the facets of Angular 8, enriched with the latest 2024 insights from leading market research firms, Forrester and Gartner. It explores why Angular remains the preferred choice for IT leaders over other technologies.
Angular 8: Unveiling the New Features
Angular 8 introduced several groundbreaking features, hire angularjs developers to simplify the development process further. Key among these features were:
Differential Loading of Modern JavaScript: A game-changer for performance optimization, Angular 8 automatically generates two builds of your app: one for modern, ES2015+ capable browsers and another for older browsers. This significantly improves loading times and efficiency, a critical factor in user experience and search engine rankings.
Dynamic Imports for Lazy Routes: Before Angular 8, lazy loading routes required a specific syntax and using the angular-router-loader for Webpack. Angular 8 simplified this by introducing dynamic imports, aligning with the modern JavaScript standard, and streamlining the development process.
Improved CLI Workflow: Angular 8 enhanced the Angular CLI, introducing new capabilities like the ng deploy command, simplifying the deployment process to various hosting services. This is a testament to Angular's commitment to improving developer productivity and operational efficiency.
Web Workers Support: Angular 8 made integrating web workers into your projects more accessible, allowing more intensive computations to be offloaded to a background thread. This enhances the application's responsiveness and overall performance, a key consideration for complex, data-intensive applications.
Ivy Renderer Preview: Although still in preview, introducing the Ivy renderer in Angular 8 marked a significant leap towards smaller bundle sizes, faster rendering, and better debugging. Ivy promises to revolutionize Angular applications' performance, making it a highly anticipated feature for future releases.
Why IT Leaders Choose Angular
In the competitive technology sphere, IT leaders are tasked with making decisions that align with strategic business goals, including technology adoption that ensures scalability, reliability, and developer productivity. With its robust ecosystem and forward-thinking features, Angular presents a compelling case if you are looking to hire frontend developers.
Alignment with Modern Web Standards
Angular's commitment to embracing modern web standards, as evidenced by features like differential loading and dynamic imports, ensures that applications are future-proof and optimized for current and emerging web environments.
Developer Productivity and Experience
Angular's comprehensive framework, including a powerful CLI, rich libraries, and a unified development approach, significantly boosts developer productivity. This ecosystem enables rapid prototyping, development, and deployment, which is crucial for meeting tight deadlines and high-quality standards.
Performance and Scalability
Performance is a non-negotiable attribute of modern web applications. Angular's architecture, coupled with features like the Ivy renderer and web workers, ensures applications are fast and scalable. IT leaders can use Angular confidently for small- and large-scale projects.
Community and Ecosystem Support
Angular benefits from strong community and corporate support, providing resources, libraries, and tools. This ecosystem ensures that Angular remains at the technological forefront, addressing emerging challenges and incorporating innovative solutions.
Insights from Forrester and Gartner in 2024
While direct quotes and statistics from 2024 Forrester and Gartner reports are beyond my scope, historical trends and expert analyses have consistently highlighted Angular's strategic advantages. These include its comprehensive feature set, robust ecosystem, and alignment with enterprise needs. IT leaders, driven by the need for robust, scalable, and efficient web solutions, often cite Angular's continuous evolution, community support, and corporate backing as critical factors in their decision-making process.
Conclusion
As we navigate through 2024, Angular 8 stands as a testament to the framework's enduring relevance and pivotal role in shaping the future of web development. Its innovative features enhance developer experience and productivity and significantly improve application performance and user satisfaction. For IT leaders, the choice of Angular is more than a technological preference; it's a strategic decision that aligns with long-term business objectives, ensuring their organizations remain competitive in a rapidly changing digital landscape.
In adopting Angular 8, IT leaders are leveraging technology and investing in a future where efficiency, performance, and innovation converge to create exceptional digital experiences. As Angular continues to evolve, it will undoubtedly remain at the forefront of web development, guiding enterprises seeking to thrive in the digital age.
#software development#mobile app development#web development#angularjsdevelopmentcompany#frontenddevelopment#angular 8
0 notes
Text
Every TypeScript example and tutorial I've come across so far mainly focuses on language features, static typing, and working with Visual Studio. However, I couldn't find much guidance on how to use TypeScript effectively with JavaScript and the DOM.
I remember having the same question a while back, just like Johnny on Stack Overflow. "Can we use TypeScript to manipulate the DOM?" This question motivated me to dive deeper and figure it out, and I'm here to share what I've learned.
Configuration: Using TypeScript for DOM manipulation is straightforward, but it does require some configuration. You'll need to include the specific types for DOM access, which aren't available by default in TypeScript. To do this, you must explicitly configure the TypeScript compiler to include the "dom" library in the compilerOptions section of your tsconfig.json file. It's worth noting that the decision not to include these types by default might suggest that TypeScript's creators initially intended it more for server-side development with Node.js than for front-end work.
/** tsconfig.json - Configuration file in the project folder for the TypeScript compiler */ { "compilerOptions": { "lib": [ "es2015", "dom" ], "strict": true, "target": "es2015" } }
Hello World: In this article, I'll create a simple "Hello, world!" program to demonstrate how to use the DOM in TypeScript. Since this is my first post about TypeScript, I'll cover the basics of working with DOM types and address a common challenge that beginners might encounter. Please note that I won't be discussing DOM events in this post; that's a topic for a future article.
Let's start with the basics by changing the inner text value of an existing HTML element. I began by creating an HTML file with a standard HTML5 boilerplate, including an <h1> element with the id "greeter" in the body.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <!-- ... --> </head> <body> <h1 id="greeter">Hello</h1> </body> </html>
Next, I opened a new TypeScript file and added the following code:
let greeter: HTMLHeadingElement = document.getElementById("greeter") as HTMLHeadingElement; greeter.innerText = "Hello world!";
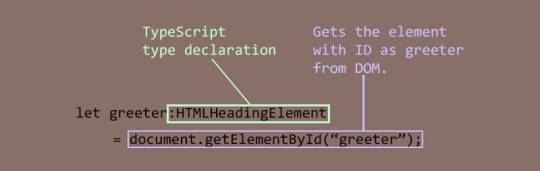
In this code, I created a variable called greeter and assigned the type HTMLHeadingElement to it. The HTMLHeadingElement type is defined in the "dom" library we added to the configuration. It tells the TypeScript compiler that greeter expects an HTML heading element and nothing else. Then, I assigned the greeter to the value returned by the getElementById function, which selects an element by its ID. Finally, I set the inner text of the greeter element to "Hello world."
When I compiled the code with the following command:
tsc script.ts
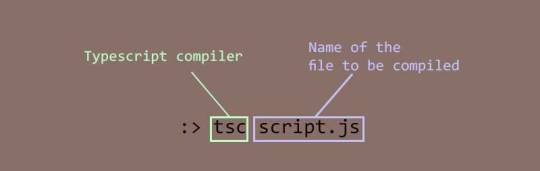
It produced the following error:
Type 'HTMLElement | null' is not assignable to type 'HTMLHeadingElement'. Type 'null' is not assignable to type 'HTMLHeadingElement'.
It's a bit frustrating, but TypeScript is doing its job. This error means that I tried to assign a greeter, which is of type HTMLHeadingElement, with an object of type HTMLElement that the getElementById method returned. The HTMLElement | null in the error message indicates that the method's return value can be either of type HTMLElement or null.
To address this, I used TypeScript's type assertion feature to tell the compiler that the element returned by getElementById is indeed a heading element, and it doesn't need to worry about it. Here's the updated code:
let greeter: HTMLHeadingElement = document.getElementById("greeter") as HTMLHeadingElement; greeter.innerText = "Hello world!";

With this change, the compilation was successful. I included the script.js file generated by the compiler in the HTML document and opened it in a browser.
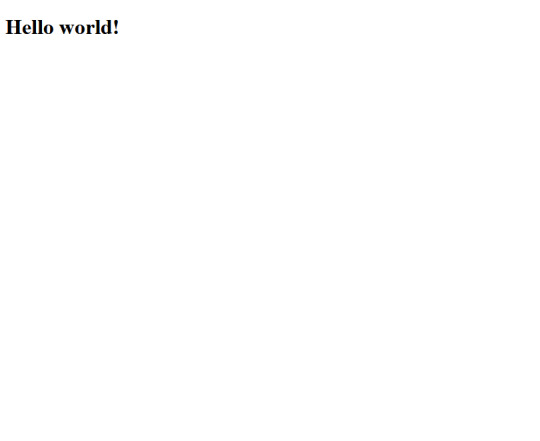
Decoration Time: Now that I've confirmed that everything works as intended, it's time to make the page more visually appealing. I wanted a font style that was informal, so I chose the "Rock Salt" font from Google Fonts. I imported it into my stylesheet, along with "Dancing Script" as a secondary font, using CSS imports. I then added a few more elements to the HTML document, centered all the text using CSS flexbox, added a background from UI gradients, and adjusted the positions of some elements for proper arrangement. The page now looked beautiful.
Animation: To add a finishing touch, I wanted to include a background animation of orbs rising to the top like bubbles. To create the orbs, I decided to use <div> elements. Since I wanted several orbs with different sizes, I split the task into two steps to simplify the work.
First, I created a common style for all the orbs and defined a custom animation for the orbs in CSS. Then, I created the orbs dynamically using TypeScript. I created a set number of <div> elements, assigned them the pre-defined style, and randomized their sizes, positions, and animation delays to make them appear more natural.
Here's an excerpt of the code for creating the bubbles:
function createBubbles() { for (let i = 0; i < bubbleCount; i++) { let div: HTMLDivElement = document.createElement("div") as HTMLDivElement; let divSize = getSize(); div.style.left = getLeftPosition() + "px"; div.style.width = divSize + "px"; div.style.height = divSize + "px"; div.style.animationDelay = i * randomFloat(0, 30) + "s"; div.style.filter = "blur(" + randomFloat(2, 5) + "px)"; div.classList.add("bubble"); bubbleBuffer.push(div); } console.log("Bubbles created"); }
After creating the orbs, I added them to the DOM and started the animation:
function releaseBubbles() { createBubbles(); for (let i = 0; i < bubbleCount; i++) { containerDiv.appendChild(bubbleBuffer[i]); } console.log("Bubbles released"); }
And with that, the animation of orbs rising like bubbles was set in motion.
Here's the final output:
youtube
You can find the complete code in this repository.
Conclusion: While writing this article and creating the example, I realized the involvement of advanced concepts like type assertion and union types. I now understand why the authors of those tutorials didn't include them; introducing them could confuse beginners. It's best to learn TypeScript thoroughly before venturing into DOM manipulation.
In my example, I skipped null checking when fixing the type mismatch error, as it seemed unnecessary for the demonstration. However, in real projects, it's important to check for null values to avoid runtime errors. I also didn't
#While writing this article and creating the example#I realized the involvement of advanced concepts like type assertion and union types. I now understand why the authors of those tutorials di#beginner#typescript#dom manipulation#Youtube
0 notes
Text
CommonJS is a project to standardize the module ecosystem for JavaScript outside of web browsers (e.g. on web servers or native desktop applications). CommonJS's specification of how modules should work is widely used today for server-side JavaScript with Node.js.[1] It is also used for browser-side JavaScript, but that code must be packaged with a transpiler since browsers don't support CommonJS.[1] The other major module specification in use is the ECMAScript (ES) modules specification (ES6 modules aka ES2015 modules).[2] CommonJS can be recognized by the use of the require() function and module.exports, while ES modules use import and export statements for similar (though not identical) functionality. —via wikipedia
i see this. i read this. i even mostly understand it. what i don't understand is why you would fucking this shit for a script that was always meant to be used in a fucking browser. what is happening here.
i have come to really resent things that are almost but not quite javascript. what are they why are they here and why can't they be Not Like This.
2 notes
·
View notes
Link
A short and simple project for beginners to practice javascript.
1 note
·
View note
Photo

This code allows you to isolate a specific cookie. 🍪 ➖➖➖ 🕉 Follow @the.unpaid.dev on #instagram for new JS, CSS, HTML, DevOps 🔥🔥 ➖➖➖ ♋ Comment below 📲📲 #javascript #js #es6 #es2015 #Ui #ux #css #css3 #sass #scss #html #code #coder #apple #laptop #coding #frontend #codinglife #macbook #siliconvalley #programmer #development #programming (at Nagpur, Maharashtra, India) https://www.instagram.com/p/B3VJzjHH2jE/?igshid=1amoehwlfrr76
#instagram#javascript#js#es6#es2015#ui#ux#css#css3#sass#scss#html#code#coder#apple#laptop#coding#frontend#codinglife#macbook#siliconvalley#programmer#development#programming
1 note
·
View note
Text
How to become a better React Native developer?
If React Native is your option, and if you are interested in the way how to become a better React Native developer, this article is definitely for you. Here, we will try to make a short guide that should make learning React Native app development easy for you. Before you dig yourself into learn...
#Android#app#cross-platform#debugging#ECMAScript#ES2015#ES6#ios#javascript#js#learn JavaScript#mobile#Mobile development#performance#react#React courses#react native#React Native apps#React Native developer#React Native for Android#React Native for iOS#React Native Navigation#React Navigation#React tutorials#react.js#Redux#resources#testing#web development
2 notes
·
View notes
Link
1 note
·
View note
Text
Node.js / Clases de javascript y herencia
Hoy veremos dos pilares fundamentales de OOP pero en Javascript, espero les sea de utilidad y buen finde!
Bienvenidos sean a este post, hoy veremos un tema muy particular. Este es un simple repaso/comentario sobre como en Javascript podemos manejar dos temas que son fundamentales en OOP como son las clases y las herencias, si bien estos no son originales del lenguaje mediante el ES2015 se agrego una forma muy similar a otros lenguajes para tener la misma conducta, veamos la sintaxis de una…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
How to become a Web Developer: a detailed plan for learning JavaScript

Everyone who wants to become an IT developer usually begins with making sites, as the easiest part of it. To work, you need only a text editor for writing the code and browser to see visually what you are doing. If you're not aiming to a full-stack approach and you just want learn the magic of client-side programming, you won't have to study complicated algorithms: as a matter of fact, the main skill each client-side web developer must have nowadays is the knowledge of JavaScript (and its frameworks). The best way to learn is by creating own website using multiple technologies. For example, you can create website and display stats from popular games like Counter-Strike and Valorant. Such a project requires HTML, CSS, Git, Bootstrap, JavaScript, Bash, MySQL. A nice example is the Valorant Tracker project, which is something that could be done in 4-6 months if you're willing to learning JavaScript programming. Once you manage to pull off something like that, you'll have a good chance to get hired as a junior code in a decent company and start your developer career. Nowadays, JS has been developing incredibly fast, so it's easy to get confused while studying this language. We offer you an educational plan with a convenient structure, where you will find all the main aspects of JavaScript and other adjacent technologies.
Why JavaScript?
We have to mention that language being pretty open - many companies are rivaling using JS with the goal of its evolution. The language is incredibly flexible, so it is perfect for people who like both object-oriented and functional approaches. A mammoth amount of different libraries and frameworks allows you to solve even the most difficult issues. Moreover, the server platform Node.js allows you to use JS not just in browsers but on the console. You can create apps for both smartphones and PC. Apps for a computer by using the Electron framework, and mobile apps thanks to NativeScript or ReactNative.
Git
The first thing you should do is to study how Git works: a source code manager is a vital instrument for developers, so you have to learn it first - since it's arguably the best choice nowadays. Here are three common topics you might start to learn to quickly understand the basics: Creation and moving of the files across catalogs. Initialization and commits in Git. Repositories settings in GitHub. Also, you must have the next skills: Object-oriented JS - constructors and factories. Functional JS - functions of the highest order, circuit, and recursion. Specification of the Jasmine tests. Basics of the HTML, CSS, and jQuery. To better understand these topics, be sure to check out our posts, guides and tutorials regarding Git and GitHub.
Algorithms and data structures
Later you have to learn algorithms (especially big complicated ones), and basic data structures: connected lists, turns, stacks, binary searching trees, and hash-tables.
Back-end JavaScript frameworks
Node.js - Approximately a decade ago JS was used only for writing the code for front-end (just like CSS and HTML), but today due to Node.js the situation is quite the opposite. Node - is a server area for committing all the actions by JS, so you won't have to learn all the new syntax. Although, you will have to import and export files, divide the entire code for modules, and use the pack-manager NPM. Express.js - Besides learning Node you have to get more knowledge about back-end development, especially about servers and routing. Ports and protocols with HTTP will be a nice start before studying Express. Express.js - Node-library for requests` processing.
Asynchronous JavaScript (AJAX)
If you don’t want to refresh your page after each change in your DB, Ajax is certainly what you will need - it sends asynchronous HTTP-request to reload only part of the page. You can work with Ajax through the jQuery (see below) or by directly (manually) handling the XMLHttpRequest object. Asynchrony is the thing that makes JS unique but separating developers into two sides: some love it and some hate. Each developer has to know both advantages and disadvantages of that technology. You can start by studying call stacks, events cycles, and callbacks, then - studying promises.
Databases, Schemes, Models, and ORM
Databases one of the most important parts of web development. If your app has to save or load some information without losing it just after the page's update, you definitely will have to use DB. You have to learn how to see the difference between relational and non-relational DB and learn their connection ways. The next step will be studying the SQL and different systems for controlling DB. Knowledge of ORM won't be excessive.
HTML and CSS
Those languages are the very basics of the web-design. You don't have to know them perfectly but understand their code. Then you will have to learn at least one popular library (for example, Bootstrap). For CSS you have to learn processors, like Sass that will make CSS more similar to the normal code. For making work with the HTML you can pick any template, like PUG. To better understand these topics, be sure to check out our posts, guides and tutorials regarding HTML, HTML5, CSS and CSS3.
jQuery and DOM manipulations
After you finished the main look of the page using HTML and CSS, you will use event translators and jQuery for the DOM controlling. Many people think that jQuery is useless and soon will be replaced by Angular or React. Maybe it's true, but jQuery is worldwide popular, so in any case, you must know it. Moreover, you can get into the situation when you will have to do an incredibly complicated job using React-microscope, so in that situation, light jQuery will be your salvation. To better understand these topics, be sure to check out our posts, guides and tutorials regarding JQuery.
Chrome instruments for developers
If we didn't mention the Chrome instrument which makes the programming job easier, we wouldn't forgive ourselves. Thanks to them you will be able to learn DOM, debugging process through the console, routes` tracking and so much more.
Test-Diven Development
Also called TDD: this is the development tactic when the software divides for a few tiny cycles: Writing down the code to make all changes you had to. Writing down the code that will pass all tests. Refactoring the code and writing new tests if those are necessary. If some parts of the code don't pass the test, they have to be rewritten. If you work with JS we firmly recommend you pay attention to the Jasmine, Chai, and Mocha frameworks. To better understand these topics, be sure to check out the ASP.NET Core 3 and Angular 9 book, which features an entire chapter about client-side TDD using the Karma test runner and Jasmine testing suite.
Web Sockets
We have to pay extra attention to that topic because web-sockets are useful. WebSocket protocol, unlike the HTTP one, will allow you to work with a bidirectional data stream – the reason why is that tech unique. The most popular library called socket.io and is well documented here.
EcmaScript 6 (ES2015)
Nowadays, the main standard is ES6 (ES2015), ES2016 has been confirmed already and the ES2017 is under development right now, so you always have to watch their updates and use the newest and most stable version. All compatibility problems can be solved easily with the next apps.
Babel
Babel - compiles ES6 (ES2016 support is expected soon) into the ES5, which is well-known by all browsers. It also can compile JSX/REACT-components, which makes it vital for web-developers. Webpack - takes all your files (images, fonts, style tables, JS-files, etc) into the single dependency graph. You don't have to use it if you are making a small app but shall use it while working with React.
React and Redux
React (also known as ReactJS) - the library which will allow you to create a user's interface. It was created by Facebook in 2013 and became worldwide popular pretty fast. React is needed not just for web-design, but there are versions for smartphones (React Native) and VR (React VR), published later by the same company. Redux - container of predictable states, usually used with React. It can be used for shortening the code by the modeling way. Pretty useful in real-time working apps with a big number of users, such as games. To better understand these topics, be sure to check out the series of React & ReactJS articles we've published in the last few years.
Authentication, Sessions, Cookies
You have to understand how the app will interact with users - how users will log in\out of their accounts, get bonuses, etc. For identifying people during surfing your site, web-sites using cookies - small text-files that send a reply from server to browser for user's HTTP request. For the connection between DB and log-in page, you can use the express-session library.
Web Security
Each site/app, of course, must be secure and reliable. You have to get the knowledge of all possible attacks on your creation and ways of protection as well. To better understand these topics, be sure to check out the various IT & Development Security articles we published in the last few years.
Conclusions
In this post we tried to write a list of the main study topics that await a novice JavaScript developer. Most of these tools will become your best friends, others will make you spit blood: each of them, however, will help you better understand how to overcome the inevitable difficulties that await your learning path and satisfy the development requests of the clients. Read the full article
#Ajax#Babel#Counter-Strike#CSS#Electron#ES2015#Express.js#Git#GitHub#HTML#Jasmine#Javascript#Karma#Node.js#React#Redux#Valorant
0 notes
Link
!
Most web developers I talk to these days love writing JavaScript with all the newest language features—async/await, classes, arrow functions, etc. However, despite the fact that all modern browsers can run ES2015+ code and natively support the features I just mentioned, most developers still transpile their code to ES5 and bundle it with polyfills to accommodate the small percentage of users still on older browsers.
This kinda sucks. In an ideal world, we wouldn’t be shipping unnecessary code.
With new JavaScript and DOM APIs, we can conditionally load polyfills because we can feature detect their support at runtime. But with new JavaScript syntax, this is a lot trickier since any unknown syntax will cause a parse error, and then none of the code will run.
While we don’t currently have a good solution for feature-detecting new syntax, we do have a way to feature-detect basic ES2015 syntax support today.
The solution is <script type="module">.
A working example
I created webpack-esnext-boilerplate so developers could see a real implementation of this technique.
With this boilerplate I intentionally included several advanced webpack features because I wanted to show that this technique is production-ready and works in real-world scenarios. These include well-known bundling best-practices like:
Code splitting
Dynamic imports (loading additional code conditionally at runtime)
Asset fingerprinting (for effective long-term caching)
And since I would never recommend something I wouldn’t use myself, I’ve updated this blog to use the technique as well. You can check out the source code if you’d like to see more.
1 note
·
View note