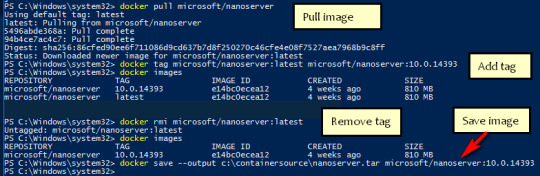
#install mongodb docker ubuntu
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Graylog Docker Compose Setup: An Open Source Syslog Server for Home Labs
Graylog Docker Compose Install: Open Source Syslog Server for Home #homelab GraylogInstallationGuide #DockerComposeOnUbuntu #GraylogRESTAPI #ElasticsearchAndGraylog #MongoDBWithGraylog #DockerComposeYmlConfiguration #GraylogDockerImage #Graylogdata
A really great open-source log management platform for both production and home lab environments is Graylog. Using Docker Compose, you can quickly launch and configure Graylog for a production or home lab Syslog. Using Docker Compose, you can create and configure all the containers needed, such as OpenSearch and MongoDB. Let’s look at this process. Table of contentsWhat is Graylog?Advantages of…

View On WordPress
#Docker Compose on Ubuntu#docker-compose.yml configuration#Elasticsearch and Graylog#Graylog data persistence#Graylog Docker image#Graylog installation guide#Graylog REST API#Graylog web interface setup#log management with Graylog#MongoDB with Graylog
0 notes
Text
PROJETO
Passo a Passo da Implementação da NeoSphere
1. Configuração do Ambiente de Desenvolvimento
Ferramentas Necessárias:
Python 3.10+ para backend Web2 (FastAPI, Redis).
Node.js 18+ para serviços Web3 e frontend.
Solidity para smart contracts.
Docker para conteinerização de serviços (Redis, MongoDB, RabbitMQ).
Truffle/Hardhat para desenvolvimento de smart contracts.
# Instalação de dependências básicas (Linux/Ubuntu) sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install -y python3.10 nodejs npm docker.io
2. Implementação da API Web2 com FastAPI
Estrutura do Projeto:
/neosphere-api ├── app/ │ ├── __init__.py │ ├── main.py # Ponto de entrada da API │ ├── models.py # Modelos Pydantic │ └── database.py # Conexão com MongoDB └── requirements.txt
Código Expandido (app/main.py):
from fastapi import FastAPI, Depends, HTTPException from pymongo import MongoClient from pymongo.errors import DuplicateKeyError from app.models import PostCreate, PostResponse from app.database import get_db import uuid import datetime app = FastAPI(title="NeoSphere API", version="0.2.0") @app.post("/posts/", response_model=PostResponse, status_code=201) async def create_post(post: PostCreate, db=Depends(get_db)): post_id = str(uuid.uuid4()) post_data = { "post_id": post_id, "user_id": post.user_id, "content": post.content, "media_urls": post.media_urls or [], "related_nft_id": post.related_nft_id, "created_at": datetime.datetime.utcnow(), "likes": 0, "comments_count": 0 } try: db.posts.insert_one(post_data) except DuplicateKeyError: raise HTTPException(status_code=400, detail="Post ID já existe") return post_data @app.get("/posts/{post_id}", response_model=PostResponse) async def get_post(post_id: str, db=Depends(get_db)): post = db.posts.find_one({"post_id": post_id}) if not post: raise HTTPException(status_code=404, detail="Post não encontrado") return post
3. Sistema de Cache com Redis para NFTs
Implementação Avançada (services/nft_cache.py):
import redis from tenacity import retry, stop_after_attempt, wait_fixed from config import settings class NFTCache: def __init__(self): self.client = redis.Redis( host=settings.REDIS_HOST, port=settings.REDIS_PORT, decode_responses=True ) @retry(stop=stop_after_attempt(3), wait=wait_fixed(0.5)) async def get_metadata(self, contract_address: str, token_id: str) -> dict: cache_key = f"nft:{contract_address}:{token_id}" cached_data = self.client.get(cache_key) if cached_data: return json.loads(cached_data) # Lógica de busca na blockchain metadata = await BlockchainService.fetch_metadata(contract_address, token_id) if metadata: self.client.setex( cache_key, settings.NFT_CACHE_TTL, json.dumps(metadata) ) return metadata def invalidate_cache(self, contract_address: str, token_id: str): self.client.delete(f"nft:{contract_address}:{token_id}")
4. Smart Contract para NFTs com Royalties (Arquivo Completo)
Contrato Completo (contracts/NeoSphereNFT.sol):
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT pragma solidity ^0.8.20; import "@openzeppelin/contracts/token/ERC721/ERC721.sol"; import "@openzeppelin/contracts/access/Ownable.sol"; import "@openzeppelin/contracts/interfaces/IERC2981.sol"; contract NeoSphereNFT is ERC721, Ownable, IERC2981 { using Counters for Counters.Counter; Counters.Counter private _tokenIdCounter; struct RoyaltyInfo { address recipient; uint96 percentage; } mapping(uint256 => RoyaltyInfo) private _royalties; mapping(uint256 => string) private _tokenURIs; event NFTMinted( uint256 indexed tokenId, address indexed owner, string tokenURI, address creator ); constructor() ERC721("NeoSphereNFT", "NSPH") Ownable(msg.sender) {} function mint( address to, string memory uri, address royaltyRecipient, uint96 royaltyPercentage ) external onlyOwner returns (uint256) { require(royaltyPercentage <= 10000, "Royalties max 100%"); uint256 tokenId = _tokenIdCounter.current(); _tokenIdCounter.increment(); _safeMint(to, tokenId); _setTokenURI(tokenId, uri); _setRoyaltyInfo(tokenId, royaltyRecipient, royaltyPercentage); emit NFTMinted(tokenId, to, uri, msg.sender); return tokenId; } function royaltyInfo( uint256 tokenId, uint256 salePrice ) external view override returns (address, uint256) { RoyaltyInfo memory info = _royalties[tokenId]; return ( info.recipient, (salePrice * info.percentage) / 10000 ); } function _setTokenURI(uint256 tokenId, string memory uri) internal { _tokenURIs[tokenId] = uri; } function _setRoyaltyInfo( uint256 tokenId, address recipient, uint96 percentage ) internal { _royalties[tokenId] = RoyaltyInfo(recipient, percentage); } }
5. Sistema de Pagamentos com Gateway Unificado
Implementação Completa (payment/gateway.py):
from abc import ABC, abstractmethod from typing import Dict, Optional from pydantic import BaseModel class PaymentRequest(BaseModel): amount: float currency: str method: str user_metadata: Dict payment_metadata: Dict class PaymentProvider(ABC): @abstractmethod def process_payment(self, request: PaymentRequest) -> Dict: pass class StripeACHProvider(PaymentProvider): def process_payment(self, request: PaymentRequest) -> Dict: # Implementação real usando a SDK do Stripe return { "status": "success", "transaction_id": "stripe_tx_123", "fee": request.amount * 0.02 } class NeoPaymentGateway: def __init__(self): self.providers = { "ach": StripeACHProvider(), # Adicionar outros provedores } def process_payment(self, request: PaymentRequest) -> Dict: provider = self.providers.get(request.method.lower()) if not provider: raise ValueError("Método de pagamento não suportado") # Validação adicional if request.currency not in ["USD", "BRL"]: raise ValueError("Moeda não suportada") return provider.process_payment(request) # Exemplo de uso: # gateway = NeoPaymentGateway() # resultado = gateway.process_payment(PaymentRequest( # amount=100.00, # currency="USD", # method="ACH", # user_metadata={"country": "US"}, # payment_metadata={"account_number": "..."} # ))
6. Autenticação Web3 com SIWE
Implementação no Frontend (React):
import { useSigner } from 'wagmi' import { SiweMessage } from 'siwe' const AuthButton = () => { const { data: signer } = useSigner() const handleLogin = async () => { const message = new SiweMessage({ domain: window.location.host, address: await signer.getAddress(), statement: 'Bem-vindo à NeoSphere!', uri: window.location.origin, version: '1', chainId: 137 // Polygon Mainnet }) const signature = await signer.signMessage(message.prepareMessage()) // Verificação no backend const response = await fetch('/api/auth/login', { method: 'POST', headers: { 'Content-Type': 'application/json' }, body: JSON.stringify({ message, signature }) }) if (response.ok) { console.log('Autenticado com sucesso!') } } return ( <button onClick={handleLogin}> Conectar Wallet </button> ) }
7. Estratégia de Implantação
Infraestrutura com Terraform:
# infra/main.tf provider "aws" { region = "us-east-1" } module "neosphere_cluster" { source = "terraform-aws-modules/ecs/aws" cluster_name = "neosphere-prod" fargate_capacity_providers = ["FARGATE"] services = { api = { cpu = 512 memory = 1024 port = 8000 } payment = { cpu = 256 memory = 512 port = 3000 } } } resource "aws_elasticache_cluster" "redis" { cluster_id = "neosphere-redis" engine = "redis" node_type = "cache.t3.micro" num_cache_nodes = 1 parameter_group_name = "default.redis6.x" }
Considerações Finais
Testes Automatizados:
Implementar testes end-to-end com Cypress para fluxos de usuário
Testes de carga com k6 para validar escalabilidade
Testes de segurança com OWASP ZAP
Monitoramento:
Configurar Prometheus + Grafana para métricas em tempo real
Integrar Sentry para captura de erros no frontend
CI/CD:
Pipeline com GitHub Actions para deploy automático
Verificação de smart contracts com Slither
Documentação:
Swagger para API REST
Storybook para componentes UI
Archimate para documentação de arquitetura
Este esqueleto técnico fornece a base para uma implementação robusta da NeoSphere, combinando as melhores práticas de desenvolvimento Web2 com as inovações da Web3.
0 notes
Text
How to Install MongoDB on Docker Container linux.
How to Install MongoDB on Docker Container linux.
Hi Guys! Hope you are doing well. Let’s Learn about “How to Install MongoDB on Docker Container Linux”. The Docker is an open source platform, where developers can package there application and run that application into the Docker Container. So It is PAAS (Platform as a Service), which uses a OS virtualisation to deliver software in packages called containers. The containers are the bundle of…

View On WordPress
#docker hub#install mongodb#install mongodb docker#install mongodb docker container#install mongodb docker image#install mongodb docker linux#install mongodb docker ubuntu#install mongodb on docker container#mongodb docker install#mongodb docker tutorial#run docker on mongodb container
0 notes
Text
In this article we provide the steps for installing UniFi Network Application / UniFi Controller on Ubuntu 18.04 / Debian 9 Linux system. Ubiquiti offers a wide range of Access Points, Switches, Firewall devices, Routers, Cameras, among many other appliances which are managed from a single point. The commonly used management interface is provided by UniFi Dream Machine Pro. The UniFi Network Application (formerly UniFi Controller), is a wireless network management software solution from Ubiquiti Networks™. This tools provides the capability to manage multiple UniFI networks devices from a web browser. UniFi Network Application can be installed on Windows, macOS and Linux operating systems. In the guide that we did earlier, we covered installation process on macOS: Install UniFi Network Application on macOS For running in Docker see guide in the link below: How To Run UniFi Controller in Docker Container Below are the installation requirements for UniFi Network Application; A DHCP-enabled network Linux, Mac OS X, or Microsoft Windows 7/8 – Running controller software. Java Runtime Environment 8 Web Browser: Mozilla Firefox, Google Chrome, or Microsoft Internet Explorer 8 (or above) For UniFi Network Application installation on Linux, supported operating systems as of this article update are; Ubuntu 18.04 and 16.04 Debian 9 / Debian 8 Software versions requirements: Java 8 (My test with Java 17 and Java 11 failed). MongoDB =3.6 (We’ll install MongoDB 4.0) Before you proceed further query OS details through contents in /etc/os-release file to ensure OS version requirement is met. $ cat /etc/os-release NAME="Ubuntu" VERSION="18.04.6 LTS (Bionic Beaver)" ID=ubuntu ID_LIKE=debian PRETTY_NAME="Ubuntu 18.04.6 LTS" VERSION_ID="18.04" HOME_URL="https://www.ubuntu.com/" SUPPORT_URL="https://help.ubuntu.com/" BUG_REPORT_URL="https://bugs.launchpad.net/ubuntu/" PRIVACY_POLICY_URL="https://www.ubuntu.com/legal/terms-and-policies/privacy-policy" VERSION_CODENAME=bionic UBUNTU_CODENAME=bionic From the output we can see this installation is on Ubuntu 18.04 (Bionic Beaver), which is supported. Add UniFi and MongoDB APT repositories It’s always a good recommendation to keep your system updated. Run the commands below to update your OS. sudo apt update && sudo apt -y full-upgrade After the update perform a reboot if it’s required. [ -f /var/run/reboot-required ] && sudo reboot -f Install software packages required to configure UniFi and MongoDB APT repositories. sudo apt install curl gpg gnupg2 software-properties-common apt-transport-https lsb-release ca-certificates Add UniFi APT repository Import repository GPG key used in signing UniFi APT packages. sudo wget -O /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/unifi-repo.gpg https://dl.ui.com/unifi/unifi-repo.gpg Add UniFi APT repository by executing commands below in your terminal. echo 'deb https://www.ui.com/downloads/unifi/debian stable ubiquiti' | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/ubnt-unifi.list Add MongoDB APT repository Start by adding GPG key to your system keyring. wget -qO - https://www.mongodb.org/static/pgp/server-4.0.asc | sudo apt-key add - You should get a message in the output that says “OK” if this was successful. Next add repository to your system. ### Ubuntu 18.04 ### echo "deb https://repo.mongodb.org/apt/ubuntu bionic/mongodb-org/4.0 multiverse" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/mongodb-org-4.0.list ### Debian 9 ### echo "deb https://repo.mongodb.org/apt/debian stretch/mongodb-org/4.0 multiverse" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/mongodb-org-4.0.list Once all the repositories have beed added, test if they are functional. ### Ubuntu 18.04 ### $ sudo apt update Get:1 http://mirrors.digitalocean.com/ubuntu bionic InRelease [242 kB] Ign:2 https://repo.mongodb.org/apt/ubuntu bionic/mongodb-org/4.0 InRelease Hit:3 https://repos-droplet.digitalocean.com/apt/droplet-agent main InRelease Get:4 https://repo.mongodb.org/apt/ubuntu bionic/mongodb-org/4.0 Release [2989 B]
Hit:6 http://mirrors.digitalocean.com/ubuntu bionic-updates InRelease Hit:7 http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu bionic-security InRelease Get:8 https://repo.mongodb.org/apt/ubuntu bionic/mongodb-org/4.0 Release.gpg [801 B] Hit:9 http://mirrors.digitalocean.com/ubuntu bionic-backports InRelease Get:5 https://dl.ubnt.com/unifi/debian stable InRelease [3038 B] Get:10 https://repo.mongodb.org/apt/ubuntu bionic/mongodb-org/4.0/multiverse amd64 Packages [18.4 kB] Get:11 https://dl.ubnt.com/unifi/debian stable/ubiquiti amd64 Packages [732 B] Fetched 268 kB in 1s (319 kB/s) Reading package lists... Done Building dependency tree Reading state information... Done ### Debian 9 ### $ sudo apt update Hit:1 http://security.debian.org stretch/updates InRelease Ign:2 http://mirrors.digitalocean.com/debian stretch InRelease Hit:3 http://mirrors.digitalocean.com/debian stretch-updates InRelease Hit:4 http://mirrors.digitalocean.com/debian stretch Release Ign:5 https://repo.mongodb.org/apt/debian stretch/mongodb-org/4.0 InRelease Hit:6 https://repos-droplet.digitalocean.com/apt/droplet-agent main InRelease Get:8 https://repo.mongodb.org/apt/debian stretch/mongodb-org/4.0 Release [1490 B] Get:9 https://repo.mongodb.org/apt/debian stretch/mongodb-org/4.0 Release.gpg [801 B] Get:7 https://dl.ubnt.com/unifi/debian stable InRelease [3038 B] Get:11 https://dl.ubnt.com/unifi/debian stable/ubiquiti amd64 Packages [732 B] Fetched 6061 B in 1s (5707 B/s) Reading package lists... Done Building dependency tree Reading state information... Done Install Java 8 on Ubuntu 18.04 / Debian 9 Restrict Ubuntu and your Debian system from automatically installing Java 11 / Java 17: sudo apt-mark hold openjdk-11-* sudo apt-mark hold openjdk-17-* Install Java 8 from OS default APT repositories. sudo apt install openjdk-8-jdk openjdk-8-jre Remove any newer version of Java installed – Java 11 or Java 17. sudo apt remove openjdk-11-* openjdk-17-* sudo apt install openjdk-8-jdk openjdk-8-jre Confirm installed Java version with the command java -version , it should show openjdk 1.8 $ java -version openjdk version "1.8.0_312" OpenJDK Runtime Environment (build 1.8.0_312-8u312-b07-0ubuntu1~18.04-b07) OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM (build 25.312-b07, mixed mode) Install UniFi Network Application on Ubuntu 18.04 / Debian 9 We can now install UniFi Network Application on Ubuntu 18.04 / Debian 9 once Java 8 is confirmed to be the default Java version in the system. Run the commands below to install the latest release of UniFi Network Application (UniFi Controller). sudo apt install unifi Accept installation prompt as requested. Reading package lists... Done Building dependency tree Reading state information... Done The following additional packages will be installed: binutils binutils-common binutils-x86-64-linux-gnu ca-certificates-java fontconfig-config fonts-dejavu-core java-common jsvc libasound2 libasound2-data libavahi-client3 libavahi-common-data libavahi-common3 libbinutils libboost-filesystem1.65.1 libboost-iostreams1.65.1 libboost-program-options1.65.1 libboost-system1.65.1 libcommons-daemon-java libcups2 libfontconfig1 libgoogle-perftools4 libgraphite2-3 libharfbuzz0b libjpeg-turbo8 libjpeg8 liblcms2-2 libnspr4 libnss3 libpcrecpp0v5 libpcsclite1 libsnappy1v5 libstemmer0d libtcmalloc-minimal4 libyaml-cpp0.5v5 mongo-tools mongodb-clients mongodb-server mongodb-server-core openjdk-17-jre-headless Suggested packages: binutils-doc default-jre libasound2-plugins alsa-utils java-virtual-machine cups-common liblcms2-utils pcscd libnss-mdns fonts-dejavu-extra fonts-ipafont-gothic fonts-ipafont-mincho fonts-wqy-microhei | fonts-wqy-zenhei fonts-indic The following NEW packages will be installed: binutils binutils-common binutils-x86-64-linux-gnu ca-certificates-java fontconfig-config fonts-dejavu-core java-common jsvc libasound2 libasound2-data libavahi-client3 libavahi-common-data libavahi-common3 libbinutils libboost-filesystem1.
65.1 libboost-iostreams1.65.1 libboost-program-options1.65.1 libboost-system1.65.1 libcommons-daemon-java libcups2 libfontconfig1 libgoogle-perftools4 libgraphite2-3 libharfbuzz0b libjpeg-turbo8 libjpeg8 liblcms2-2 libnspr4 libnss3 libpcrecpp0v5 libpcsclite1 libsnappy1v5 libstemmer0d libtcmalloc-minimal4 libyaml-cpp0.5v5 mongo-tools mongodb-clients mongodb-server mongodb-server-core openjdk-17-jre-headless unifi 0 upgraded, 41 newly installed, 0 to remove and 57 not upgraded. Need to get 280 MB of archives. After this operation, 724 MB of additional disk space will be used. Do you want to continue? [Y/n] y Manually installing UniFi Network Application on Ubuntu 18.04 / Debian 9 If you prefer to manually download a .deb package, visit the download the UniFi Controller software from the Ubiquiti Networks website. Choose “Debian / Ubuntu Linux and UniFi Cloud Key” from software list. Click the “Download” button that shows up after selecting. Use “Download File” button or copy Direct URL and use command line downloaders to get the file in your local system. Downloading the file with wget: wget https://dl.ui.com/unifi//unifi_sysvinit_all.deb Installation of .deb package can be done with apt while passing dowloaded file path as an argument. $ sudo apt install ./unifi_sysvinit_all.deb Reading package lists... Done Building dependency tree Reading state information... Done Note, selecting 'unifi' instead of './unifi_sysvinit_all.deb' The following additional packages will be installed: binutils binutils-common binutils-x86-64-linux-gnu ca-certificates-java fontconfig-config fonts-dejavu-core java-common jsvc libasound2 libasound2-data libavahi-client3 libavahi-common-data libavahi-common3 libbinutils libboost-filesystem1.65.1 libboost-iostreams1.65.1 libboost-program-options1.65.1 libboost-system1.65.1 libcommons-daemon-java libcups2 libfontconfig1 libgoogle-perftools4 libgraphite2-3 libharfbuzz0b libjpeg-turbo8 libjpeg8 liblcms2-2 libnspr4 libnss3 libpcrecpp0v5 libpcsclite1 libsnappy1v5 libstemmer0d libtcmalloc-minimal4 libyaml-cpp0.5v5 mongo-tools mongodb-clients mongodb-server mongodb-server-core openjdk-17-jre-headless Suggested packages: binutils-doc default-jre libasound2-plugins alsa-utils java-virtual-machine cups-common liblcms2-utils pcscd libnss-mdns fonts-dejavu-extra fonts-ipafont-gothic fonts-ipafont-mincho fonts-wqy-microhei | fonts-wqy-zenhei fonts-indic The following NEW packages will be installed: binutils binutils-common binutils-x86-64-linux-gnu ca-certificates-java fontconfig-config fonts-dejavu-core java-common jsvc libasound2 libasound2-data libavahi-client3 libavahi-common-data libavahi-common3 libbinutils libboost-filesystem1.65.1 libboost-iostreams1.65.1 libboost-program-options1.65.1 libboost-system1.65.1 libcommons-daemon-java libcups2 libfontconfig1 libgoogle-perftools4 libgraphite2-3 libharfbuzz0b libjpeg-turbo8 libjpeg8 liblcms2-2 libnspr4 libnss3 libpcrecpp0v5 libpcsclite1 libsnappy1v5 libstemmer0d libtcmalloc-minimal4 libyaml-cpp0.5v5 mongo-tools mongodb-clients mongodb-server mongodb-server-core openjdk-17-jre-headless unifi 0 upgraded, 41 newly installed, 0 to remove and 57 not upgraded. Need to get 280 MB of archives. After this operation, 724 MB of additional disk space will be used. Do you want to continue? [Y/n] y Successful installation output; Note, selecting 'unifi' instead of './unifi_sysvinit_all.deb' unifi is already the newest version (7.1.66-17875-1). 0 upgraded, 0 newly installed, 0 to remove and 57 not upgraded. Access UniFi Network Application on Web browser To restart the service run the following commands: sudo systemctl restart unifi.service Confirm that the status is running: $ systemctl status unifi.service ● unifi.service - unifi Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/unifi.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled) Active: active (running) since Mon 2022-07-11 23:46:08 UTC; 18s ago Process: 12237 ExecStop=/usr/lib/unifi/bin/unifi.init stop (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Process: 12307 ExecStart=/usr/lib/unifi/bin/unifi.init start (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) Main PID: 12375 (jsvc) Tasks: 101 (limit: 2314) CGroup: /system.slice/unifi.service ├─12375 unifi -cwd /usr/lib/unifi -home /usr/lib/jvm/java-8-openjdk-amd64 -cp /usr/share/java/commons-daemon.jar:/usr/lib/unifi/lib/ace.jar -pidfile /var/run/unifi.pid -procname unifi -ou ├─12377 unifi -cwd /usr/lib/unifi -home /usr/lib/jvm/java-8-openjdk-amd64 -cp /usr/share/java/commons-daemon.jar:/usr/lib/unifi/lib/ace.jar -pidfile /var/run/unifi.pid -procname unifi -ou ├─12378 unifi -cwd /usr/lib/unifi -home /usr/lib/jvm/java-8-openjdk-amd64 -cp /usr/share/java/commons-daemon.jar:/usr/lib/unifi/lib/ace.jar -pidfile /var/run/unifi.pid -procname unifi -ou ├─12397 /usr/lib/jvm/java-8-openjdk-amd64/jre/bin/java -Dfile.encoding=UTF-8 -Djava.awt.headless=true -Dapple.awt.UIElement=true -Dunifi.core.enabled=false -Xmx1024M -XX:+ExitOnOutOfMemor └─12449 bin/mongod --dbpath /usr/lib/unifi/data/db --port 27117 --unixSocketPrefix /usr/lib/unifi/run --logRotate reopen --logappend --logpath /usr/lib/unifi/logs/mongod.log --pidfilepath Jul 11 23:45:51 unifi-controller systemd[1]: Stopped unifi. Jul 11 23:45:51 unifi-controller systemd[1]: Starting unifi... Jul 11 23:45:51 unifi-controller unifi.init[12307]: * Starting Ubiquiti UniFi Network application unifi Jul 11 23:46:08 unifi-controller unifi.init[12307]: ...done. Jul 11 23:46:08 unifi-controller systemd[1]: Started unifi. Services should be available on port 8080 and port 8443. jmutai@unifi-controller:~$ ss -tunelp | egrep '8080|8443' tcp LISTEN 0 100 *:8443 *:* uid:112 ino:47897 sk:a v6only:0 tcp LISTEN 0 100 *:8080 *:* uid:112 ino:47891 sk:e v6only:0 Access UniFi Network Application on a web browser using the server IP address an port 8443. https://172.20.30.20:8443/ You’ll get SSL warnings while trying to access the portal. Click “Advanced” and “Proceed” to the portal. From your clients (UniFi devices), ping UniFi controller IP address to validate network connectivity. U6-LR-BZ.6.0.21# ping 172.20.30.20 -c 2 PING 172.20.30.20 (172.20.30.20): 56 data bytes 64 bytes from 172.20.30.20: seq=0 ttl=63 time=0.883 ms 64 bytes from 172.20.30.20: seq=1 ttl=63 time=0.885 ms --- 172.20.30.20 ping statistics --- 2 packets transmitted, 2 packets received, 0% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max = 0.883/0.884/0.885 ms Pointing UniFi Devices to new Network Application (UniFi Controller) if this setup is new, your Network Application will discover all UniFi network devices in your network. Check out initial UniFi Network Application configuration in our recent macOS guide: Configure UniFi Network Application If you’re replacing an old Controller, then login to your UniFi devices and set inform address to the new server address and port. See below example. set-inform http://172.20.30.20:8080/inform Give it sometime and status should reflect the recent update we populated. US-16-150W-US.6.2.14# info Model: US-16-150W Version: 6.2.14.13855 MAC Address: 98:8a:20:fd:ea:94 IP Address: 192.168.1.116 Hostname: US-16-150W Uptime: 992330 seconds Status: Connected (http://172.20.30.20:8080/inform) Your uniFi devices will be available for administration from Web browser once they’re enrolled / imported for management via UniFi Network Application. Log Files Location UniFi Network Application have log files that are essential for any troubleshooting required. Logs files available are; /usr/lib/unifi/logs/server.log /usr/lib/unifi/logs/mongod.log We’re working on more articles around UniFi network infrastructure and other integrations. Stay tuned for updates.
0 notes
Text
Docker Commands Windows

Docker Commands Windows
Docker Commands Windows Server 2016
MongoDB document databases provide high availability and easy scalability. You do not need to push your certificates with git commands. When the Docker Desktop application starts, it copies the /.docker/certs.d folder on your Windows system to the /etc/docker/certs.d directory on Moby (the Docker Desktop virtual machine running on Hyper-V). Docker Desktop for Windows can’t route traffic to Linux containers. However, you can ping the Windows containers. Per-container IP addressing is not possible. The docker (Linux) bridge network is not reachable from the Windows host. However, it works with Windows containers. Use cases and workarounds.
Estimated reading time: 15 minutes
Welcome to Docker Desktop! The Docker Desktop for Windows user manual provides information on how to configure and manage your Docker Desktop settings.
For information about Docker Desktop download, system requirements, and installation instructions, see Install Docker Desktop.
Settings
The Docker Desktop menu allows you to configure your Docker settings such as installation, updates, version channels, Docker Hub login,and more.
This section explains the configuration options accessible from the Settings dialog.
Open the Docker Desktop menu by clicking the Docker icon in the Notifications area (or System tray):
Select Settings to open the Settings dialog:
General
On the General tab of the Settings dialog, you can configure when to start and update Docker.
Start Docker when you log in - Automatically start Docker Desktop upon Windows system login.
Expose daemon on tcp://localhost:2375 without TLS - Click this option to enable legacy clients to connect to the Docker daemon. You must use this option with caution as exposing the daemon without TLS can result in remote code execution attacks.
Send usage statistics - By default, Docker Desktop sends diagnostics,crash reports, and usage data. This information helps Docker improve andtroubleshoot the application. Clear the check box to opt out. Docker may periodically prompt you for more information.
Resources
The Resources tab allows you to configure CPU, memory, disk, proxies, network, and other resources. Different settings are available for configuration depending on whether you are using Linux containers in WSL 2 mode, Linux containers in Hyper-V mode, or Windows containers.
Advanced
Note
The Advanced tab is only available in Hyper-V mode, because in WSL 2 mode and Windows container mode these resources are managed by Windows. In WSL 2 mode, you can configure limits on the memory, CPU, and swap size allocatedto the WSL 2 utility VM.
Use the Advanced tab to limit resources available to Docker.
CPUs: By default, Docker Desktop is set to use half the number of processorsavailable on the host machine. To increase processing power, set this to ahigher number; to decrease, lower the number.
Memory: By default, Docker Desktop is set to use 2 GB runtime memory,allocated from the total available memory on your machine. To increase the RAM, set this to a higher number. To decrease it, lower the number.
Swap: Configure swap file size as needed. The default is 1 GB.
Disk image size: Specify the size of the disk image.
Disk image location: Specify the location of the Linux volume where containers and images are stored.
You can also move the disk image to a different location. If you attempt to move a disk image to a location that already has one, you get a prompt asking if you want to use the existing image or replace it.
Download Apple MacOS High Sierra for Mac to get a boost with new technologies in the latest Mac OS update coming fall 2017. Apple download sierra.
File sharing
Note
The File sharing tab is only available in Hyper-V mode, because in WSL 2 mode and Windows container mode all files are automatically shared by Windows.
Use File sharing to allow local directories on Windows to be shared with Linux containers.This is especially useful forediting source code in an IDE on the host while running and testing the code in a container.Note that configuring file sharing is not necessary for Windows containers, only Linux containers. If a directory is not shared with a Linux container you may get file not found or cannot start service errors at runtime. See Volume mounting requires shared folders for Linux containers.
File share settings are:
Add a Directory: Click + and navigate to the directory you want to add.
Apply & Restart makes the directory available to containers using Docker’sbind mount (-v) feature.
Tips on shared folders, permissions, and volume mounts
Share only the directories that you need with the container. File sharing introduces overhead as any changes to the files on the host need to be notified to the Linux VM. Sharing too many files can lead to high CPU load and slow filesystem performance.
Shared folders are designed to allow application code to be edited on the host while being executed in containers. For non-code items such as cache directories or databases, the performance will be much better if they are stored in the Linux VM, using a data volume (named volume) or data container.
Docker Desktop sets permissions to read/write/execute for users, groups and others 0777 or a+rwx.This is not configurable. See Permissions errors on data directories for shared volumes.
Windows presents a case-insensitive view of the filesystem to applications while Linux is case-sensitive. On Linux it is possible to create 2 separate files: test and Test, while on Windows these filenames would actually refer to the same underlying file. This can lead to problems where an app works correctly on a developer Windows machine (where the file contents are shared) but fails when run in Linux in production (where the file contents are distinct). To avoid this, Docker Desktop insists that all shared files are accessed as their original case. Therefore if a file is created called test, it must be opened as test. Attempts to open Test will fail with “No such file or directory”. Similarly once a file called test is created, attempts to create a second file called Test will fail.
Shared folders on demand

You can share a folder “on demand” the first time a particular folder is used by a container.
If you run a Docker command from a shell with a volume mount (as shown in theexample below) or kick off a Compose file that includes volume mounts, you get apopup asking if you want to share the specified folder.
You can select to Share it, in which case it is added your Docker Desktop Shared Folders list and available tocontainers. Alternatively, you can opt not to share it by selecting Cancel.
Proxies
Docker Desktop lets you configure HTTP/HTTPS Proxy Settings andautomatically propagates these to Docker. For example, if you set your proxysettings to http://proxy.example.com, Docker uses this proxy when pulling containers.
Your proxy settings, however, will not be propagated into the containers you start.If you wish to set the proxy settings for your containers, you need to defineenvironment variables for them, just like you would do on Linux, for example:
For more information on setting environment variables for running containers,see Set environment variables.
Network
Note
The Network tab is not available in Windows container mode because networking is managed by Windows.
You can configure Docker Desktop networking to work on a virtual private network (VPN). Specify a network address translation (NAT) prefix and subnet mask to enable Internet connectivity.
DNS Server: You can configure the DNS server to use dynamic or static IP addressing.
Note
Some users reported problems connecting to Docker Hub on Docker Desktop. This would manifest as an error when trying to rundocker commands that pull images from Docker Hub that are not alreadydownloaded, such as a first time run of docker run hello-world. If youencounter this, reset the DNS server to use the Google DNS fixed address:8.8.8.8. For more information, seeNetworking issues in Troubleshooting.
Updating these settings requires a reconfiguration and reboot of the Linux VM.
WSL Integration
In WSL 2 mode, you can configure which WSL 2 distributions will have the Docker WSL integration.
By default, the integration will be enabled on your default WSL distribution. To change your default WSL distro, run wsl --set-default <distro name>. (For example, to set Ubuntu as your default WSL distro, run wsl --set-default ubuntu).
You can also select any additional distributions you would like to enable the WSL 2 integration on.
For more details on configuring Docker Desktop to use WSL 2, see Docker Desktop WSL 2 backend.
Docker Engine
The Docker Engine page allows you to configure the Docker daemon to determine how your containers run.
Type a JSON configuration file in the box to configure the daemon settings. For a full list of options, see the Docker Enginedockerd commandline reference.
Click Apply & Restart to save your settings and restart Docker Desktop.
Command Line
On the Command Line page, you can specify whether or not to enable experimental features.
You can toggle the experimental features on and off in Docker Desktop. If you toggle the experimental features off, Docker Desktop uses the current generally available release of Docker Engine. Final cut pro mac app store.
Experimental features
Experimental features provide early access to future product functionality.These features are intended for testing and feedback only as they may changebetween releases without warning or can be removed entirely from a futurerelease. Experimental features must not be used in production environments.Docker does not offer support for experimental features.
For a list of current experimental features in the Docker CLI, see Docker CLI Experimental features.
Run docker version to verify whether you have enabled experimental features. Experimental modeis listed under Server Adobe photoshop 2020 patcher windows. data. Sonos controller mac 10.6.8 download. If Experimental is true, then Docker isrunning in experimental mode, as shown here:
Kubernetes
Note
The Kubernetes tab is not available in Windows container mode.
Docker Desktop includes a standalone Kubernetes server that runs on your Windows machince, sothat you can test deploying your Docker workloads on Kubernetes. To enable Kubernetes support and install a standalone instance of Kubernetes running as a Docker container, select Enable Kubernetes.
For more information about using the Kubernetes integration with Docker Desktop, see Deploy on Kubernetes.
Reset
The Restart Docker Desktop and Reset to factory defaults options are now available on the Troubleshoot menu. For information, see Logs and Troubleshooting.
Troubleshoot
Visit our Logs and Troubleshooting guide for more details.
Log on to our Docker Desktop for Windows forum to get help from the community, review current user topics, or join a discussion.
Log on to Docker Desktop for Windows issues on GitHub to report bugs or problems and review community reported issues.
For information about providing feedback on the documentation or update it yourself, see Contribute to documentation.
Switch between Windows and Linux containers

From the Docker Desktop menu, you can toggle which daemon (Linux or Windows)the Docker CLI talks to. Select Switch to Windows containers to use Windowscontainers, or select Switch to Linux containers to use Linux containers(the default).
For more information on Windows containers, refer to the following documentation:
Microsoft documentation on Windows containers.
Build and Run Your First Windows Server Container (Blog Post)gives a quick tour of how to build and run native Docker Windows containers on Windows 10 and Windows Server 2016 evaluation releases.
Getting Started with Windows Containers (Lab)shows you how to use the MusicStoreapplication with Windows containers. The MusicStore is a standard .NET application and,forked here to use containers, is a good example of a multi-container application.
To understand how to connect to Windows containers from the local host, seeLimitations of Windows containers for localhost and published ports
Settings dialog changes with Windows containers
When you switch to Windows containers, the Settings dialog only shows those tabs that are active and apply to your Windows containers:
If you set proxies or daemon configuration in Windows containers mode, theseapply only on Windows containers. If you switch back to Linux containers,proxies and daemon configurations return to what you had set for Linuxcontainers. Your Windows container settings are retained and become availableagain when you switch back.
Dashboard
The Docker Desktop Dashboard enables you to interact with containers and applications and manage the lifecycle of your applications directly from your machine. The Dashboard UI shows all running, stopped, and started containers with their state. It provides an intuitive interface to perform common actions to inspect and manage containers and Docker Compose applications. For more information, see Docker Desktop Dashboard.
Docker Hub
Docker Commands Windows
Select Sign in /Create Docker ID from the Docker Desktop menu to access your Docker Hub account. Once logged in, you can access your Docker Hub repositories directly from the Docker Desktop menu.
For more information, refer to the following Docker Hub topics:
Two-factor authentication
Docker Desktop enables you to sign into Docker Hub using two-factor authentication. Two-factor authentication provides an extra layer of security when accessing your Docker Hub account.
You must enable two-factor authentication in Docker Hub before signing into your Docker Hub account through Docker Desktop. For instructions, see Enable two-factor authentication for Docker Hub.
Docker Desktop for Windows user manual. Estimated reading time: 17 minutes. Welcome to Docker Desktop! The Docker Desktop for Windows user manual provides information on how to configure and manage your Docker Desktop settings. The fastest and easiest way to get started with Docker on Windows. Docker Desktop is an application for MacOS and Windows machines for the building and sharing of containerized applications and microservices. Docker Desktop delivers the speed, choice and security you need for designing and delivering containerized applications on your desktop. I have the same thing, but I also noticed that Hyper-V has to be enabled. As in, if your copy of Windows 10 has Hyper-V, you can install it by simply enabling it because it’s already there. On Windows 10 Home, though, there is no Hyper-V to enable. I also have Windows 10 Home. The only option for Home edition users is to use Docker. Docker supports Docker Desktop on Windows for those versions of Windows 10 that are still within Microsoft’s servicing timeline. What’s included in the installer The Docker Desktop installation includes Docker Engine, Docker CLI client, Docker Compose, Notary, Kubernetes, and Credential Helper. https://luckyloading560.tumblr.com/post/653769899713380352/docker-windows-home-edition.
After you have enabled two-factor authentication:
Docker Commands Windows Server 2016
Go to the Docker Desktop menu and then select Sign in / Create Docker ID.
Enter your Docker ID and password and click Sign in.
After you have successfully signed in, Docker Desktop prompts you to enter the authentication code. Enter the six-digit code from your phone and then click Verify.
After you have successfully authenticated, you can access your organizations and repositories directly from the Docker Desktop menu.
Adding TLS certificates
You can add trusted Certificate Authorities (CAs) to your Docker daemon to verify registry server certificates, and client certificates, to authenticate to registries.
How do I add custom CA certificates?
Docker Desktop supports all trusted Certificate Authorities (CAs) (root orintermediate). Docker recognizes certs stored under Trust RootCertification Authorities or Intermediate Certification Authorities.
Docker Desktop creates a certificate bundle of all user-trusted CAs based onthe Windows certificate store, and appends it to Moby trusted certificates. Therefore, if an enterprise SSL certificate is trusted by the user on the host, it is trusted by Docker Desktop.
To learn more about how to install a CA root certificate for the registry, seeVerify repository client with certificatesin the Docker Engine topics.
How do I add client certificates?
You can add your client certificatesin ~/.docker/certs.d/<MyRegistry>:<Port>/client.cert and~/.docker/certs.d/<MyRegistry>:<Port>/client.key. You do not need to push your certificates with git commands.
When the Docker Desktop application starts, it copies the~/.docker/certs.d folder on your Windows system to the /etc/docker/certs.ddirectory on Moby (the Docker Desktop virtual machine running on Hyper-V).
You need to restart Docker Desktop after making any changes to the keychainor to the ~/.docker/certs.d directory in order for the changes to take effect.
The registry cannot be listed as an insecure registry (seeDocker Daemon). Docker Desktop ignorescertificates listed under insecure registries, and does not send clientcertificates. Commands like docker run that attempt to pull from the registryproduce error messages on the command line, as well as on the registry.
To learn more about how to set the client TLS certificate for verification, seeVerify repository client with certificatesin the Docker Engine topics.
Where to go next
Try out the walkthrough at Get Started.
Dig in deeper with Docker Labs example walkthroughs and source code.
Refer to the Docker CLI Reference Guide.
windows, edge, tutorial, run, docker, local, machine

0 notes
Text
How to Install Docker on Linux Mint 20.
How to Install Docker on Linux Mint 20.
Hi hope you are doing well, lets learn about “How to Setup and Install Docker on Linux Mint 20”, the Docker is the fastest growing technology in the IT market. Docker is the container technology. Many industries are moving towards docker from the normal EC2 instances. It is PAAS (Platform as a Service), which uses a OS virtualisation to deliver software in packages called containers. The…

View On WordPress
#docker hub#docker install rocky linux#install docker ce on Linux Mint 20#Install Docker CE on Rocky Linux#install docker engine on ubuntu#Install docker in rocky linux 8#install docker on Linux Mint 20#Install docker on rocky linux 8#Install docker on ubuntu#Install docker on ubuntu 20.04#install mongodb docker
0 notes
Text
All applications generate information when running, this information is stored as logs. As a system administrator, you need to monitor these logs to ensure the proper functioning of the system and therefore prevent risks and errors. These logs are normally scattered over servers and management becomes harder as the data volume increases. Graylog is a free and open-source log management tool that can be used to capture, centralize and view real-time logs from several devices across a network. It can be used to analyze both structured and unstructured logs. The Graylog setup consists of MongoDB, Elasticsearch, and the Graylog server. The server receives data from the clients installed on several servers and displays it on the web interface. Below is a diagram illustrating the Graylog architecture Graylog offers the following features: Log Collection – Graylog’s modern log-focused architecture can accept nearly any type of structured data, including log messages and network traffic from; syslog (TCP, UDP, AMQP, Kafka), AWS (AWS Logs, FlowLogs, CloudTrail), JSON Path from HTTP API, Beats/Logstash, Plain/Raw Text (TCP, UDP, AMQP, Kafka) e.t.c Log analysis – Graylog really shines when exploring data to understand what is happening in your environment. It uses; enhanced search, search workflow and dashboards. Extracting data – whenever log management system is in operations, there will be summary data that needs to be passed to somewhere else in your Operations Center. Graylog offers several options that include; scheduled reports, correlation engine, REST API and data fowarder. Enhanced security and performance – Graylog often contains sensitive, regulated data so it is critical that the system itself is secure, accessible, and speedy. This is achieved using role-based access control, archiving, fault tolerance e.t.c Extendable – with the phenomenal Open Source Community, extensions are built and made available in the market to improve the funmctionality of Graylog This guide will walk you through how to run the Graylog Server in Docker Containers. This method is preferred since you can run and configure Graylog with all the dependencies, Elasticsearch and MongoDB already bundled. Setup Prerequisites. Before we begin, you need to update the system and install the required packages. ## On Debian/Ubuntu sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade sudo apt install curl vim git ## On RHEL/CentOS/RockyLinux 8 sudo yum -y update sudo yum -y install curl vim git ## On Fedora sudo dnf update sudo dnf -y install curl vim git 1. Install Docker and Docker-Compose on Linux Of course, you need the docker engine to run the docker containers. To install the docker engine, use the dedicated guide below: How To Install Docker CE on Linux Systems Once installed, check the installed version. $ docker -v Docker version 20.10.13, build a224086 You also need to add your system user to the docker group. This will allow you to run docker commands without using sudo sudo usermod -aG docker $USER newgrp docker With docker installed, proceed and install docker-compose using the guide below: How To Install Docker Compose on Linux Verify the installation. $ docker-compose version Docker Compose version v2.3.3 Now start and enable docker to run automatically on system boot. sudo systemctl start docker && sudo systemctl enable docker 2. Provision the Graylog Container The Graylog container will consist of the Graylog server, Elasticsearch, and MongoDB. To be able to achieve this, we will capture the information and settings in a YAML file. Create the YAML file as below: vim docker-compose.yml In the file, add the below lines: version: '2' services: # MongoDB: https://hub.docker.com/_/mongo/ mongodb: image: mongo:4.2 networks: - graylog #DB in share for persistence volumes: - /mongo_data:/data/db # Elasticsearch: https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/7.10/docker.html
elasticsearch: image: docker.elastic.co/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-oss:7.10.2 #data folder in share for persistence volumes: - /es_data:/usr/share/elasticsearch/data environment: - http.host=0.0.0.0 - transport.host=localhost - network.host=0.0.0.0 - "ES_JAVA_OPTS=-Xms512m -Xmx512m" ulimits: memlock: soft: -1 hard: -1 mem_limit: 1g networks: - graylog # Graylog: https://hub.docker.com/r/graylog/graylog/ graylog: image: graylog/graylog:4.2 #journal and config directories in local NFS share for persistence volumes: - /graylog_journal:/usr/share/graylog/data/journal environment: # CHANGE ME (must be at least 16 characters)! - GRAYLOG_PASSWORD_SECRET=somepasswordpepper # Password: admin - GRAYLOG_ROOT_PASSWORD_SHA2=e1b24204830484d635d744e849441b793a6f7e1032ea1eef40747d95d30da592 - GRAYLOG_HTTP_EXTERNAL_URI=http://192.168.205.4:9000/ entrypoint: /usr/bin/tini -- wait-for-it elasticsearch:9200 -- /docker-entrypoint.sh networks: - graylog links: - mongodb:mongo - elasticsearch restart: always depends_on: - mongodb - elasticsearch ports: # Graylog web interface and REST API - 9000:9000 # Syslog TCP - 1514:1514 # Syslog UDP - 1514:1514/udp # GELF TCP - 12201:12201 # GELF UDP - 12201:12201/udp # Volumes for persisting data, see https://docs.docker.com/engine/admin/volumes/volumes/ volumes: mongo_data: driver: local es_data: driver: local graylog_journal: driver: local networks: graylog: driver: bridge In the file, replace: GRAYLOG_PASSWORD_SECRET with your own password which must be at least 16 characters GRAYLOG_ROOT_PASSWORD_SHA2 with a SHA2 password obtained using the command: echo -n "Enter Password: " && head -1 1514/tcp, :::1514->1514/tcp, 0.0.0.0:9000->9000/tcp, 0.0.0.0:1514->1514/udp, :::9000->9000/tcp, :::1514->1514/udp, 0.0.0.0:12201->12201/tcp, 0.0.0.0:12201->12201/udp, :::12201->12201/tcp, :::12201->12201/udp thor-graylog-1 1a21d2de4439 docker.elastic.co/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-oss:7.10.2 "/tini -- /usr/local…" 31 seconds ago Up 28 seconds 9200/tcp, 9300/tcp thor-elasticsearch-1 1b187f47d77e mongo:4.2 "docker-entrypoint.s…" 31 seconds ago Up 28 seconds 27017/tcp thor-mongodb-1 If you have a firewall enabled, allow the Graylog service port through it. ##For Firewalld sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=9000/tcp --permanent sudo firewall-cmd --reload ##For UFW sudo ufw allow 9000/tcp 5. Access the Graylog Web UI Now open the Graylog web interface using the URL http://IP_address:9000. Log in using the username admin and SHA2 password(StrongPassw0rd) set in the YAML. On the dashboard, let’s create the first input to get logs by navigating to the systems tab and selecting input. Now search for Raw/Plaintext TCP and click launch new input Once launched, a pop-up window will appear as below. You only need to change the name for the input, port(1514), and select the node, or “Global” for the location for the input. Leave the other details as they are. Save the file and try sending a plain text message to the Graylog Raw/Plaintext TCP input on port 1514. echo 'First log message' | nc localhost 1514 ##OR from another server##
echo 'First log message' | nc 192.168.205.4 1514 On the running Raw/Plaintext Input, show received messages The received message should be displayed as below. You can as well export this to a dashboard as below. Create the dashboard by providing the required information. You will have the dashboard appear under the dashboards tab. Conclusion That is it! We have triumphantly walked through how to run the Graylog Server in Docker Containers. Now you can monitor and access logs on several servers with ease. I hope this was significant to you.
0 notes
Text
flask docker vagrant mac inceptions
First, some vagrant preparation stuff, cos I docker doesn't play well on mac.
$ vagrant up $ vagrant plugin install vagrant-vbguest $ vagrant ssh $ sudo apt-get install -y virtualbox-guest-dkms virtualbox-guest-utils virtualbox-guest-x11 $ sudo apt-get install linux-image-extra-$(uname -r) linux-image-extra-virtual
The Vagrantfile I used looks like this.
# -*- mode: ruby -*- # vi: set ft=ruby : Vagrant.configure(2) do |config| config.vm.provider :virtualbox do |provider| provider.check_guest_additions = false provider.functional_vboxsf = false provider.memory = 1024 provider.cpus = 1 end config.vm.define "pewpew" do |pewpew| pewpew.vm.box = "ubuntu/trusty64" pewpew.vm.box_check_update = false pewpew.vm.box_download_insecure = true pewpew.vm.network "private_network", ip: "192.168.50.14", netmask: "255.255.255.0" pewpew.vm.hostname = "pewpew.mydomain.com" pewpew.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 80, host: 8080, auto_correct: true# <-- nginx pewpew.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 443, host: 8082, auto_correct: true# <-- nginx pewpew.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 5000, host: 5000, auto_correct: true# <-- flask / gunicorn pewpew.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 27017, host: 27017, auto_correct: true# <-- mongodb pewpew.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 2376, host: 2376, auto_correct: true# <-- docker-machine pewpew.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 8081, host: 8081, auto_correct: true# <-- image-generator pewpew.vm.synced_folder "~/Vagrant/docker/", "/srv/", owner: "root", group: "root" # add swap space pewpew.vm.provision :shell, inline: "fallocate -l 2G /swapfile && chmod 0600 /swapfile && mkswap /swapfile && swapon /swapfile && echo '/swapfile none swap sw 0 0' >> /etc/fstab" pewpew.vm.provision :shell, inline: "echo vm.swappiness = 10 >> /etc/sysctl.conf && echo vm.vfs_cache_pressure = 50 >> /etc/sysctl.conf && sysctl -p" end config.ssh.username = "vagrant" config.ssh.pty = true config.vm.provision "shell" do |shell| shell.privileged = true shell.inline = "sudo sed -i '/tty/!s/mesg n/tty -s \\&\\& mesg n/' /root/.profile" end end
My /etc/hosts file contains this line:
192.168.50.14 pewpew.mydomain.com
My working directory on my mac looks like this:
$ tree . ├── Vagrantfile ├── app │ ├── Dockerfile │ ├── index.py │ └── pewpew.wsgi ├── db │ └── Dockerfile └── rp ├── Dockerfile └── site.conf
This directory is mounted into the Vagrant vm at /srv.
Let's go through each file:
--- /srv/app/Dockerfile --- FROM python:2.7 RUN pip install --no-cache-dir Flask==0.10.1 RUN pip install --no-cache-dir gunicorn==19.3.0 RUN pip install --no-cache-dir eventlet==0.17.4 RUN pip install --no-cache-dir pymongo==3.4.0 COPY index.py /app/ COPY pewpew.wsgi /app/ EXPOSE 5000 WORKDIR /app CMD ["gunicorn", "-k", "eventlet", "-b", "0.0.0.0:5000", "-w", "1", "index:app"] --- /srv/app/index.py --- import os from flask import Flask from pymongo import MongoClient app = Flask(__name__) db = "mongodb" client = MongoClient(db, 27017) @app.route("/") def hello(): try: server_info = client.server_info() db_names = client.database_names() client.close() return "Pew Pew!\n%s\n%s\n" % (server_info, db_names) except: return "Pew Pew! DB failing...\n" if __name__ == '__main__': app.run() --- /srv/app/pewpew.wsgi --- import sys PROJECT_DIR = '/app/' sys.path.append(PROJECT_DIR) from pewpew import app as application --- /srv/db/Dockerfile --- FROM mongo EXPOSE 27017 --- /srv/rp/Dockerfile --- FROM nginx COPY site.conf /etc/nginx/conf.d/site.conf EXPOSE 80 443 --- /srv/rp/Dockerfile --- server { listen 80; server_name pewpew.mydomain.com; access_log /var/log/nginx/nginx_access_myapp.log; error_log /var/log/nginx/nginx_error_myapp.log; location / { proxy_pass http://flaskapp:5000/; } }
Ok let's start. ssh into the vagrant box and check the kernel. To use docker you need 3.10+ or sum chit...
$ vagrant ssh $ uname -r 3.13.0-98-generic
Ok cool, install the docker daemon.
$ sudo curl -sSL https://get.docker.com/ | sh
Now let's build these images from the three Dockerfiles we have.
$ sudo docker build -t reverseproxy /srv/rp/ $ sudo docker build -t flaskapp /srv/app/ $ sudo docker build -t mongodb /srv/db/ $ docker images REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE reverseproxy latest fa2ead9fdb67 11 minutes ago 107MB flaskapp latest 48ce64a24bea About an hour ago 681MB nginx latest b8efb18f159b 12 days ago 107MB python 2.7 fa8e55b2235d 13 days ago 673MB mongo latest b39de1d79a53 13 days ago 359MB
Start the database container first.
$ docker run -d -e DB_PORT_27017_TCP_ADDR='0.0.0.0' -v /srv/db:/data -p 27017:27017 --name mongodb mongo $ docker ps -a CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES c610b1a11752 mongo "docker-entrypoint..." 3 seconds ago Up 1 second 0.0.0.0:27017->27017/tcp mongodb
Then start the flask application container.
$ docker run -d -p 5000:5000 --name flaskapp --link mongodb:mongodb flaskapp $ docker ps -a CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES ebf6ba70b2f8 flaskapp "gunicorn -k event..." 2 seconds ago Up 1 second 0.0.0.0:5000->5000/tcp flaskapp c610b1a11752 mongo "docker-entrypoint..." 24 seconds ago Up 23 seconds 0.0.0.0:27017->27017/tcp mongodb
Send a request to the app
$ curl http://127.0.0.1:5000 Pew Pew! {u'storageEngines': [u'devnull', u'ephemeralForTest', u'mmapv1', u'wiredTiger'], u'maxBsonObjectSize': 16777216, u'ok': 1.0, u'bits': 64, u'modules': [], u'openssl': {u'compiled': u'OpenSSL 1.0.1t 3 May 2016', u'running': u'OpenSSL 1.0.1t 3 May 2016'}, u'javascriptEngine': u'mozjs', u'version': u'3.4.6', u'gitVersion': u'c55eb86ef46ee7aede3b1e2a5d184a7df4bfb5b5', u'versionArray': [3, 4, 6, 0], u'debug': False, u'buildEnvironment': {u'cxxflags': u'-Woverloaded-virtual -Wno-maybe-uninitialized -std=c++11', u'cc': u'/opt/mongodbtoolchain/v2/bin/gcc: gcc (GCC) 5.4.0', u'linkflags': u'-pthread -Wl,-z,now -rdynamic -Wl,--fatal-warnings -fstack-protector-strong -fuse-ld=gold -Wl,--build-id -Wl,-z,noexecstack -Wl,--warn-execstack -Wl,-z,relro', u'distarch': u'x86_64', u'cxx': u'/opt/mongodbtoolchain/v2/bin/g++: g++ (GCC) 5.4.0', u'ccflags': u'-fno-omit-frame-pointer -fno-strict-aliasing -ggdb -pthread -Wall -Wsign-compare -Wno-unknown-pragmas -Winvalid-pch -Werror -O2 -Wno-unused-local-typedefs -Wno-unused-function -Wno-deprecated-declarations -Wno-unused-but-set-variable -Wno-missing-braces -fstack-protector-strong -fno-builtin-memcmp', u'target_arch': u'x86_64', u'distmod': u'debian81', u'target_os': u'linux'}, u'sysInfo': u'deprecated', u'allocator': u'tcmalloc'} [u'admin', u'local']
Nice! Now let's try with the nginx container.
$ docker run -d -p 80:80 --name reverseproxy --link flaskapp:flaskapp reverseproxy $ sudo docker ps -a CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 716f3c7c321c reverseproxy "nginx -g 'daemon ..." 1 second ago Up Less than a second 0.0.0.0:80->80/tcp, 443/tcp reverseproxy ebf6ba70b2f8 flaskapp "gunicorn -k event..." 19 seconds ago Up 18 seconds 0.0.0.0:5000->5000/tcp flaskapp c610b1a11752 mongo "docker-entrypoint..." 41 seconds ago Up 39 seconds 0.0.0.0:27017->27017/tcp mongodb
Send a request to the nginx vhost.
$ curl http://127.0.0.1/ Pew Pew! {u'storageEngines': [u'devnull', u'ephemeralForTest', u'mmapv1', u'wiredTiger'], u'maxBsonObjectSize': 16777216, u'ok': 1.0, u'bits': 64, u'modules': [], u'openssl': {u'compiled': u'OpenSSL 1.0.1t 3 May 2016', u'running': u'OpenSSL 1.0.1t 3 May 2016'}, u'javascriptEngine': u'mozjs', u'version': u'3.4.6', u'gitVersion': u'c55eb86ef46ee7aede3b1e2a5d184a7df4bfb5b5', u'versionArray': [3, 4, 6, 0], u'debug': False, u'buildEnvironment': {u'cxxflags': u'-Woverloaded-virtual -Wno-maybe-uninitialized -std=c++11', u'cc': u'/opt/mongodbtoolchain/v2/bin/gcc: gcc (GCC) 5.4.0', u'linkflags': u'-pthread -Wl,-z,now -rdynamic -Wl,--fatal-warnings -fstack-protector-strong -fuse-ld=gold -Wl,--build-id -Wl,-z,noexecstack -Wl,--warn-execstack -Wl,-z,relro', u'distarch': u'x86_64', u'cxx': u'/opt/mongodbtoolchain/v2/bin/g++: g++ (GCC) 5.4.0', u'ccflags': u'-fno-omit-frame-pointer -fno-strict-aliasing -ggdb -pthread -Wall -Wsign-compare -Wno-unknown-pragmas -Winvalid-pch -Werror -O2 -Wno-unused-local-typedefs -Wno-unused-function -Wno-deprecated-declarations -Wno-unused-but-set-variable -Wno-missing-braces -fstack-protector-strong -fno-builtin-memcmp', u'target_arch': u'x86_64', u'distmod': u'debian81', u'target_os': u'linux'}, u'sysInfo': u'deprecated', u'allocator': u'tcmalloc'} [u'admin', u'local']
Awesome, we can also go to our http://pewpew.mydomain.com URL in a browser on our mac, as we have forwarded the port on our Vagrant box and added a local DNS entry in /etc/hosts remember?
0 notes
Text
DevOps Engineer job at Camdy Global Sdn Bhd Malaysia
CAMDY is a market place for personalized gifts. Our mission is to revolutionize the gift industry by providing the widest variety of unique & customize-able products using cutting edge technology.
· Installation, testing the operation server software, hardware and firmware
· Setup of Virtual Private Cloud, Network ACLs, Security Groups and route tables
· Plan, manage, document and perform installations and upgrades of servers
· Configuration and administration of Load Balancers, Network and Auto scaling for high availability
· Design, implement and maintain system security
· Installing and configuring operating systems in adherence to specification
· Develop, review, and modify changes to the schedule of operation to ensure systems, servers, workstations, peripherals, communications devices, and software is on-line, patched and supported.
· Configure and manage system backups and restores
· Provide UNIX-based application support
· Managing Application Security such as creating/managing users’ responsibilities
· Analyze failure trends and provide recommendations on future design
· Ensure policies, procedures, and strategies are optimize and integrated into the installation, configuration, and maintenance of the operating environment
· Operating Systems: UNIX, Linux Ubuntu.
· Cloud technologies: AWS, Docker.
· Database: MySQL,MongoDB.
· Version Control Systems: Git, GitHub
· Languages/Scripting: Various shell flavors ksh, csh, bash, JSON, Amazon Web Services Scripting, PHP, Javascript.
· Development Environments and Tools: Docker, Virtualbox.
· Web/App Servers: Apache, NGINX.
· Monitoring: Nagios, Nagios Log server, Centreon, ELK, Grafana.
Others
· At least 3 to 5 years of experience in the relevant field.
· Good to have CCNP and LPIC-2 certificate
· Knowledge and experience with large-scale systems integration involving private, hybrid, and public cloud platforms.
· Advanced knowledge of large-scale server architecture & database administration and monitoring tools
· Must be willing to be on call especially during emergency
· Excellent communication skills
· Able to work with minimal supervision.
From http://www.startupjobs.asia/job/26400-devops-engineer-it-job-at-camdy-global-sdn-bhd-malaysia
from https://startupjobsasiablog.wordpress.com/2017/03/22/devops-engineer-job-at-camdy-global-sdn-bhd-malaysia/
0 notes
Text
DevOps Engineer job at Camdy Global Sdn Bhd Malaysia
CAMDY is a market place for personalized gifts. Our mission is to revolutionize the gift industry by providing the widest variety of unique & customize-able products using cutting edge technology.
· Installation, testing the operation server software, hardware and firmware
· Setup of Virtual Private Cloud, Network ACLs, Security Groups and route tables
· Plan, manage, document and perform installations and upgrades of servers
· Configuration and administration of Load Balancers, Network and Auto scaling for high availability
· Design, implement and maintain system security
· Installing and configuring operating systems in adherence to specification
· Develop, review, and modify changes to the schedule of operation to ensure systems, servers, workstations, peripherals, communications devices, and software is on-line, patched and supported.
· Configure and manage system backups and restores
· Provide UNIX-based application support
· Managing Application Security such as creating/managing users’ responsibilities
· Analyze failure trends and provide recommendations on future design
· Ensure policies, procedures, and strategies are optimize and integrated into the installation, configuration, and maintenance of the operating environment
· Operating Systems: UNIX, Linux Ubuntu.
· Cloud technologies: AWS, Docker.
· Database: MySQL,MongoDB.
· Version Control Systems: Git, GitHub
· Languages/Scripting: Various shell flavors ksh, csh, bash, JSON, Amazon Web Services Scripting, PHP, Javascript.
· Development Environments and Tools: Docker, Virtualbox.
· Web/App Servers: Apache, NGINX.
· Monitoring: Nagios, Nagios Log server, Centreon, ELK, Grafana.
Others
· At least 3 to 5 years of experience in the relevant field.
· Good to have CCNP and LPIC-2 certificate
· Knowledge and experience with large-scale systems integration involving private, hybrid, and public cloud platforms.
· Advanced knowledge of large-scale server architecture & database administration and monitoring tools
· Must be willing to be on call especially during emergency
· Excellent communication skills
· Able to work with minimal supervision.
StartUp Jobs Asia - Startup Jobs in Singapore , Malaysia , HongKong ,Thailand from http://www.startupjobs.asia/job/26400-devops-engineer-it-job-at-camdy-global-sdn-bhd-malaysia Startup Jobs Asia https://startupjobsasia.tumblr.com/post/158692489734
0 notes
Text
DevOps Engineer job at Camdy Global Sdn Bhd Malaysia
CAMDY is a market place for personalized gifts. Our mission is to revolutionize the gift industry by providing the widest variety of unique & customize-able products using cutting edge technology.
· Installation, testing the operation server software, hardware and firmware
· Setup of Virtual Private Cloud, Network ACLs, Security Groups and route tables
· Plan, manage, document and perform installations and upgrades of servers
· Configuration and administration of Load Balancers, Network and Auto scaling for high availability
· Design, implement and maintain system security
· Installing and configuring operating systems in adherence to specification
· Develop, review, and modify changes to the schedule of operation to ensure systems, servers, workstations, peripherals, communications devices, and software is on-line, patched and supported.
· Configure and manage system backups and restores
· Provide UNIX-based application support
· Managing Application Security such as creating/managing users’ responsibilities
· Analyze failure trends and provide recommendations on future design
· Ensure policies, procedures, and strategies are optimize and integrated into the installation, configuration, and maintenance of the operating environment
· Operating Systems: UNIX, Linux Ubuntu.
· Cloud technologies: AWS, Docker.
· Database: MySQL,MongoDB.
· Version Control Systems: Git, GitHub
· Languages/Scripting: Various shell flavors ksh, csh, bash, JSON, Amazon Web Services Scripting, PHP, Javascript.
· Development Environments and Tools: Docker, Virtualbox.
· Web/App Servers: Apache, NGINX.
· Monitoring: Nagios, Nagios Log server, Centreon, ELK, Grafana.
Others
· At least 3 to 5 years of experience in the relevant field.
· Good to have CCNP and LPIC-2 certificate
· Knowledge and experience with large-scale systems integration involving private, hybrid, and public cloud platforms.
· Advanced knowledge of large-scale server architecture & database administration and monitoring tools
· Must be willing to be on call especially during emergency
· Excellent communication skills
· Able to work with minimal supervision.
StartUp Jobs Asia - Startup Jobs in Singapore , Malaysia , HongKong ,Thailand from http://www.startupjobs.asia/job/26400-devops-engineer-it-job-at-camdy-global-sdn-bhd-malaysia
0 notes
Text
How to Install Docker on Ubuntu 20.04.
How to Install Docker on Ubuntu 20.04.
Hi hope you are doing well, lets learn about “How to Setup and Install Docker on Ubuntu 20.04”, the Docker is the fastest growing technology in the IT market. Docker is the container technology. Many industries are moving towards docker from the normal EC2 instances. It is PAAS (Platform as a Service), which uses a OS virtualisation to deliver software in packages called containers. The…

View On WordPress
#docker hub#docker install rocky linux#Install Docker CE on Rocky Linux#install docker engine on ubuntu#Install docker in rocky linux 8#Install docker on rocky linux 8#Install docker on ubuntu#Install docker on ubuntu 20.04#install mongodb docker#setup docker on rocky linux
0 notes