#run docker on mongodb container
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Docker Tutorial for Beginners: Learn Docker Step by Step
What is Docker?
Docker is an open-source platform that enables developers to automate the deployment of applications inside lightweight, portable containers. These containers include everything the application needs to run—code, runtime, system tools, libraries, and settings—so that it can work reliably in any environment.
Before Docker, developers faced the age-old problem: “It works on my machine!” Docker solves this by providing a consistent runtime environment across development, testing, and production.
Why Learn Docker?
Docker is used by organizations of all sizes to simplify software delivery and improve scalability. As more companies shift to microservices, cloud computing, and DevOps practices, Docker has become a must-have skill. Learning Docker helps you:
Package applications quickly and consistently
Deploy apps across different environments with confidence
Reduce system conflicts and configuration issues
Improve collaboration between development and operations teams
Work more effectively with modern cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, and GCP
Who Is This Docker Tutorial For?
This Docker tutorial is designed for absolute beginners. Whether you're a developer, system administrator, QA engineer, or DevOps enthusiast, you’ll find step-by-step instructions to help you:
Understand the basics of Docker
Install Docker on your machine
Create and manage Docker containers
Build custom Docker images
Use Docker commands and best practices
No prior knowledge of containers is required, but basic familiarity with the command line and a programming language (like Python, Java, or Node.js) will be helpful.
What You Will Learn: Step-by-Step Breakdown
1. Introduction to Docker
We start with the fundamentals. You’ll learn:
What Docker is and why it’s useful
The difference between containers and virtual machines
Key Docker components: Docker Engine, Docker Hub, Dockerfile, Docker Compose
2. Installing Docker
Next, we guide you through installing Docker on:
Windows
macOS
Linux
You’ll set up Docker Desktop or Docker CLI and run your first container using the hello-world image.
3. Working with Docker Images and Containers
You’ll explore:
How to pull images from Docker Hub
How to run containers using docker run
Inspecting containers with docker ps, docker inspect, and docker logs
Stopping and removing containers
4. Building Custom Docker Images
You’ll learn how to:
Write a Dockerfile
Use docker build to create a custom image
Add dependencies and environment variables
Optimize Docker images for performance
5. Docker Volumes and Networking
Understand how to:
Use volumes to persist data outside containers
Create custom networks for container communication
Link multiple containers (e.g., a Node.js app with a MongoDB container)
6. Docker Compose (Bonus Section)
Docker Compose lets you define multi-container applications. You’ll learn how to:
Write a docker-compose.yml file
Start multiple services with a single command
Manage application stacks easily
Real-World Examples Included
Throughout the tutorial, we use real-world examples to reinforce each concept. You’ll deploy a simple web application using Docker, connect it to a database, and scale services with Docker Compose.
Example Projects:
Dockerizing a static HTML website
Creating a REST API with Node.js and Express inside a container
Running a MySQL or MongoDB database container
Building a full-stack web app with Docker Compose
Best Practices and Tips
As you progress, you’ll also learn:
Naming conventions for containers and images
How to clean up unused images and containers
Tagging and pushing images to Docker Hub
Security basics when using Docker in production
What’s Next After This Tutorial?
After completing this Docker tutorial, you’ll be well-equipped to:
Use Docker in personal or professional projects
Learn Kubernetes and container orchestration
Apply Docker in CI/CD pipelines
Deploy containers to cloud platforms
Conclusion
Docker is an essential tool in the modern developer's toolbox. By learning Docker step by step in this beginner-friendly tutorial, you’ll gain the skills and confidence to build, deploy, and manage applications efficiently and consistently across different environments.
Whether you’re building simple web apps or complex microservices, Docker provides the flexibility, speed, and scalability needed for success. So dive in, follow along with the hands-on examples, and start your journey to mastering containerization with Docker tpoint-tech!
0 notes
Text
Using Docker in Software Development

Docker has become a vital tool in modern software development. It allows developers to package applications with all their dependencies into lightweight, portable containers. Whether you're building web applications, APIs, or microservices, Docker can simplify development, testing, and deployment.
What is Docker?
Docker is an open-source platform that enables you to build, ship, and run applications inside containers. Containers are isolated environments that contain everything your app needs—code, libraries, configuration files, and more—ensuring consistent behavior across development and production.
Why Use Docker?
Consistency: Run your app the same way in every environment.
Isolation: Avoid dependency conflicts between projects.
Portability: Docker containers work on any system that supports Docker.
Scalability: Easily scale containerized apps using orchestration tools like Kubernetes.
Faster Development: Spin up and tear down environments quickly.
Basic Docker Concepts
Image: A snapshot of a container. Think of it like a blueprint.
Container: A running instance of an image.
Dockerfile: A text file with instructions to build an image.
Volume: A persistent data storage system for containers.
Docker Hub: A cloud-based registry for storing and sharing Docker images.
Example: Dockerizing a Simple Python App
Let’s say you have a Python app called app.py: # app.py print("Hello from Docker!")
Create a Dockerfile: # Dockerfile FROM python:3.10-slim COPY app.py . CMD ["python", "app.py"]
Then build and run your Docker container: docker build -t hello-docker . docker run hello-docker
This will print Hello from Docker! in your terminal.
Popular Use Cases
Running databases (MySQL, PostgreSQL, MongoDB)
Hosting development environments
CI/CD pipelines
Deploying microservices
Local testing for APIs and apps
Essential Docker Commands
docker build -t <name> . — Build an image from a Dockerfile
docker run <image> — Run a container from an image
docker ps — List running containers
docker stop <container_id> — Stop a running container
docker exec -it <container_id> bash — Access the container shell
Docker Compose
Docker Compose allows you to run multi-container apps easily. Define all your services in a single docker-compose.yml file and launch them with one command: version: '3' services: web: build: . ports: - "5000:5000" db: image: postgres
Start everything with:docker-compose up
Best Practices
Use lightweight base images (e.g., Alpine)
Keep your Dockerfiles clean and minimal
Ignore unnecessary files with .dockerignore
Use multi-stage builds for smaller images
Regularly clean up unused images and containers
Conclusion
Docker empowers developers to work smarter, not harder. It eliminates "it works on my machine" problems and simplifies the development lifecycle. Once you start using Docker, you'll wonder how you ever lived without it!
0 notes
Text
Let's Build a Full-Stack App Using the MERN Stack! Part 1: Mongo DB
Where Are We Storing Stuff? Before we code our full-stack MERN (MongoDB, Express, React, and Node.js) application, we need a place to store our data. The best way to do this is to set up a MongoDB instance. We’ll run MongoDB inside a Docker container to keep things simple and easily manageable. Setting Up MongoDB with Docker We’ll use the official MongoDB image from Docker Hub. To pull and run…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Essential Tools to Take Your Web Development to the Next Level
To take your web development skills to the next level, here are some essential tools that can help:
1. Code Editors and IDEs:
VS Code: A powerful, extensible code editor that supports a wide range of languages, extensions, and debugging tools.
Sublime Text: A fast and feature-rich editor with support for multiple programming languages and a sleek interface.
Atom: An open-source, customizable text editor, ideal for web development.
2. Version Control Systems:
Git: A version control tool to track changes in code and collaborate efficiently with other developers.
GitHub/GitLab/Bitbucket: Platforms for hosting Git repositories and collaborating with teams.
3. Front-End Frameworks:
React.js: A JavaScript library for building dynamic and interactive user interfaces.
Vue.js: A progressive JavaScript framework for building web interfaces.
Angular: A robust framework for creating scalable and structured web apps.
Tailwind CSS: A utility-first CSS framework for building custom designs quickly.
Bootstrap: A popular CSS framework for building responsive and mobile-first websites.
4. Back-End Frameworks:
Node.js: A JavaScript runtime for building scalable server-side applications.
Express.js: A minimal web framework for Node.js, often used for building APIs and web apps.
Django: A high-level Python web framework for building secure and maintainable websites.
Ruby on Rails: A full-stack framework built on Ruby, known for rapid development and ease of use.
5. Database Management:
MySQL: A widely used relational database management system.
MongoDB: A NoSQL database that's flexible and scalable.
PostgreSQL: A powerful, open-source object-relational database system.
Firebase: A cloud-based real-time database with simple authentication and data synchronization.
6. Package Managers:
npm: Node.js package manager for managing JavaScript libraries and dependencies.
Yarn: An alternative package manager for JavaScript with a focus on performance and reliability.
7. API Tools:
Postman: A powerful tool for testing and interacting with APIs.
Swagger: An open-source framework for API documentation, design, and testing.
8. Task Runners & Module Bundlers:
Webpack: A static module bundler for JavaScript, CSS, and other assets.
Gulp: A task runner used for automating repetitive development tasks.
Parcel: A zero-config bundler that is easy to use and fast.
9. CSS Preprocessors:
Sass: A CSS preprocessor that extends CSS with variables, nested rules, and functions.
Less: A preprocessor with features like variables and functions to make CSS more manageable.
10. Testing Tools:
Jest: A testing framework for JavaScript, commonly used for testing React apps.
Mocha: A flexible JavaScript testing framework for Node.js.
Cypress: An end-to-end testing framework for web applications.
Selenium: A tool for automating web browsers, useful for functional and UI testing.
11. Containerization & Deployment:
Docker: A platform for building, running, and shipping applications inside containers.
Kubernetes: An orchestration platform for automating the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications.
Netlify: A platform for continuous deployment of web apps with automatic scaling.
Vercel: A platform that provides serverless deployment and front-end hosting.
12. UI/UX Design Tools:
Figma: A collaborative interface design tool for creating web and app prototypes.
Adobe XD: A vector-based tool for designing and prototyping user experiences.
Sketch: A design tool for web and mobile interfaces, available for macOS.
13. Collaboration Tools:
Slack: A messaging platform for team communication and collaboration.
Trello: A task management tool for organizing and prioritizing tasks in a project.
Asana: A work management platform that helps teams plan, organize, and execute projects.
Using these tools effectively can streamline your workflow, help you collaborate better with teams, and enhance the quality of your web development projects.
0 notes
Text
Essential Tools and Frameworks Every Computer Science Engineer Should Know
The right tools can empower engineers to work more efficiently and develop innovative solutions. Just as a skilled artist has a preferred set of brushes and colors, a computer science engineer has essential tools that help in coding, data analysis, AI development, and more.
At St. Mary’s Group of Institutions, Hyderabad, we prepare our students with practical knowledge in computer science engineering, CSE-AIML, and diploma programs in computer engineering and embedded systems. Here are some of the top tools and frameworks that every budding computer science engineer should be familiar with.
Git and GitHub
One of the first tools every CS engineer needs is Git, a version control system that tracks changes to code over time. Git helps developers work collaboratively, manage large projects, and maintain a history of changes. GitHub takes this to the next level by offering an online platform for storing and sharing code repositories. It’s especially useful for team projects, where multiple contributors may be working on the same codebase.
Why It’s Important:
Allows collaboration across teams
Keeps track of code changes
Enables seamless rollback to previous versions
Visual Studio Code (VS Code)
A powerful yet lightweight code editor, VS Code supports numerous programming languages and is highly customizable with plugins for different coding needs. Whether it’s debugging, syntax highlighting, or version control integration, VS Code provides a well-rounded environment that streamlines coding tasks.
Why It’s Important:
Supports multiple languages (Java, Python, C++)
Easy to customize with extensions
Strong integration with Git for version control
Docker
Docker has revolutionized software development by allowing applications to run in isolated environments known as containers. It’s essential for engineers working on large-scale projects because it ensures code works consistently across different machines, making it a favorite for deployment.
Why It’s Important:
Promotes consistent development environments
Simplifies application deployment
Essential for modern DevOps practices
4. TensorFlow and PyTorch – Machine Learning Frameworks
For students interested in AI and machine learning, TensorFlow and PyTorch are must-have frameworks. TensorFlow, developed by Google, and PyTorch, developed by Facebook, provide a comprehensive suite of tools for building, training, and deploying machine learning models.
Why They’re Important:
Simplify complex ML and AI model development
Provide pre-built models for quick deployment
Widely used in AI research and industry projects
5. Jupyter Notebook – Data Science Tool
For anyone working with data, Jupyter Notebook is an invaluable tool that supports data analysis, visualization, and exploration within a single environment. With Jupyter, students can write and execute Python code in blocks, making it ideal for prototyping and exploring data.
Why It’s Important:
Great for visualizing data in real time
Simplifies data analysis workflows
Supports inline visualization with libraries like Matplotlib and Seaborn
Kubernetes
As software systems become more complex, Kubernetes offers a solution for managing clusters of containers, automating deployment, and scaling applications. It’s a powerful tool that helps engineers manage containerized applications across multiple servers.
Why It’s Important:
Essential for managing large-scale, containerized applications
Automates deployment, scaling, and maintenance
Vital in cloud-native development environments
SQL and NoSQL Databases – Data Management
Database management is a core aspect of computer science, and knowledge of both SQL (Structured Query Language) and NoSQL (Non-relational) databases is essential. MySQL and PostgreSQL are popular SQL databases, while MongoDB and Cassandra are prominent NoSQL databases.
Why They’re Important:
Allow efficient data storage, retrieval, and management
Enable flexible data structuring with NoSQL
Important for back-end development and data-driven applications
Linux
While not a specific tool, knowledge of Linux and its command-line interface is crucial for any CS engineer. Linux is widely used in servers and development environments due to its stability, security, and customization options. Being familiar with Linux commands can improve productivity and help with server management.
Why It’s Important:
Provides a stable, secure platform for development
Widely used in enterprise and cloud environments
Essential for understanding system-level operations
Ansible – Configuration Management
Ansible is an open-source tool for configuration management, automation, and orchestration. It allows engineers to manage IT infrastructure, set up software environments, and handle deployment, all from one platform. It’s particularly useful for system administrators and DevOps engineers.
Why It’s Important:
Simplifies repetitive tasks like setting up servers
Increases productivity in managing infrastructure
Widely used for automating configurations in cloud computing
MATLAB – For Mathematical Computing
MATLAB is a high-level language and environment for numerical computation, visualization, and programming. It’s especially popular in fields that require complex mathematical computations, like embedded systems and engineering.
Why It’s Important:
Supports extensive mathematical functions and plotting
Useful for simulation and prototyping
Essential in fields that require intensive numerical analysis
Apache Spark – Big Data Processing
Apache Spark is a powerful tool for handling and processing large datasets, especially in real-time. It’s highly efficient and is used for tasks like data cleaning, machine learning, and stream processing. For students interested in big data, learning Spark can open doors to data engineering and data science careers.
Why It’s Important:
Enables real-time data processing
Handles large volumes of data with speed and efficiency
Important for big data and data analytics projects
Postman – API Testing Tool
APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) are critical for building modern applications. Postman is a tool that allows engineers to design, test, and document APIs. It’s essential for back-end and full-stack developers to ensure that their APIs function correctly before deploying them.
Why It’s Important:
Simplifies API testing and development
Supports automated testing with scripting
Enhances collaboration with team features
Preparing Students with Industry-Relevant Skills
At St. Mary’s Group of Institutions, Hyderabad, we understand the importance of practical experience in learning. By introducing students to these tools and frameworks, we prepare them for careers in software development, data science, AI, and more.
Through hands-on labs, projects, and collaborative exercises, our curriculum ensures students are ready to tackle real-world challenges with the confidence and skills that top companies seek in computer science professionals.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Tools for Your Path
Each of these tools plays a significant role in various areas of computer science engineering. Whether you’re passionate about data science, AI, software development, or system administration, mastering these tools can give you a strong foundation and a competitive edge.
For students at St Mary's Group of Institutions, Best Engineering College in Hyderabad, these tools aren’t just names on a syllabus—they’re powerful resources that open doors to innovation, allowing them to become the engineers who shape tomorrow’s technology
1 note
·
View note
Text
What Are the Tools Used to Develop Software?
Software development is a complex process that involves various tools tailored for different stages and tasks. Here’s a comprehensive overview of the key tools commonly used in software development:

1. Integrated Development Environments (IDEs)
IDEs are essential for writing, testing, and debugging code. Some popular options include:
Visual Studio: Great for .NET applications.
Eclipse: Widely used for Java development.
IntelliJ IDEA: Preferred by many for its smart coding assistance.
2. Version Control Systems
Version control systems help developers manage changes to the codebase, facilitating collaboration. Key tools include:
Git: The most widely used system, often paired with platforms like GitHub and GitLab.
Subversion (SVN): An older but still utilized version control system.
3. Build Tools
These tools automate the process of compiling source code into binary code. Notable examples are:
Maven: Primarily for Java projects, it manages project dependencies and builds.
Gradle: An advanced build tool that is versatile and used for various languages.
4. Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) Tools
CI/CD tools streamline the integration and deployment of code changes, ensuring that software is delivered reliably. Popular options include:
Jenkins: An open-source automation server.
CircleCI: Known for its ease of use and flexibility.
5. Testing Frameworks
Automated testing is crucial for ensuring software quality. Common testing frameworks include:
JUnit: For unit testing in Java.
Selenium: For web application testing.
PyTest: A robust framework for Python.
6. Containerization and Virtualization Tools
These tools help in creating isolated environments for development and deployment:
Docker: Simplifies the process of running applications in containers.
Kubernetes: Used for automating the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications.
7. Collaboration and Project Management Tools
Effective teamwork and project management are key to successful software development. Some popular tools include:
Jira: For issue tracking and agile project management.
Trello: A visual tool for organizing tasks.
Slack: For team communication.
8. Database Management Systems
Databases are crucial for storing and managing data. Commonly used systems include:
MySQL: A popular relational database.
MongoDB: A leading NoSQL database, favored for its flexibility.
Conclusion
Choosing the right tools depends on the specific needs of your project, team size, and technology stack. By leveraging these tools effectively, developers can enhance productivity, improve collaboration, and deliver high-quality software.
Further Reading
For those looking to dive deeper into software development tools, consider exploring resources like:
0 notes
Text
Ansible and Docker: Automating Container Management
In today's fast-paced tech environment, containerization and automation are key to maintaining efficient, scalable, and reliable infrastructure. Two powerful tools that have become essential in this space are Ansible and Docker. While Docker enables you to create, deploy, and run applications in containers, Ansible provides a simple yet powerful automation engine to manage and orchestrate these containers. In this blog post, we'll explore how to use Ansible to automate Docker container management, including deployment and orchestration.
Why Combine Ansible and Docker?
Combining Ansible and Docker offers several benefits:
Consistency and Reliability: Automating Docker container management with Ansible ensures consistent and reliable deployments across different environments.
Simplified Management: Ansible’s easy-to-read YAML playbooks make it straightforward to manage Docker containers, even at scale.
Infrastructure as Code (IaC): By treating your infrastructure as code, you can version control, review, and track changes over time.
Scalability: Automation allows you to easily scale your containerized applications by managing multiple containers across multiple hosts seamlessly.
Getting Started with Ansible and Docker
To get started, ensure you have Ansible and Docker installed on your system. You can install Ansible using pip: pip install ansible
And Docker by following the official Docker installation guide for your operating system.
Next, you'll need to set up an Ansible playbook to manage Docker. Here’s a simple example:
Example Playbook: Deploying a Docker Container
Create a file named deploy_docker.yml:
---
- name: Deploy a Docker container
hosts: localhost
tasks:
- name: Ensure Docker is installed
apt:
name: docker.io
state: present
become: yes
- name: Start Docker service
service:
name: docker
state: started
enabled: yes
become: yes
- name: Pull the latest nginx image
docker_image:
name: nginx
tag: latest
source: pull
- name: Run a Docker container
docker_container:
name: nginx
image: nginx
state: started
ports:
- "80:80"
In this playbook:
We ensure Docker is installed and running.
We pull the latest nginx Docker image.
We start a Docker container with the nginx image, mapping port 80 on the host to port 80 on the container.
Automating Docker Orchestration
For more complex scenarios, such as orchestrating multiple containers, you can extend your playbook. Here’s an example of orchestrating a simple web application stack with Nginx, a Node.js application, and a MongoDB database:
---
- name: Orchestrate web application stack
hosts: localhost
tasks:
- name: Ensure Docker is installed
apt:
name: docker.io
state: present
become: yes
- name: Start Docker service
service:
name: docker
state: started
enabled: yes
become: yes
- name: Pull necessary Docker images
docker_image:
name: "{{ item }}"
tag: latest
source: pull
loop:
- nginx
- node
- mongo
- name: Run MongoDB container
docker_container:
name: mongo
image: mongo
state: started
ports:
- "27017:27017"
- name: Run Node.js application container
docker_container:
name: node_app
image: node
state: started
volumes:
- ./app:/usr/src/app
working_dir: /usr/src/app
command: "node app.js"
links:
- mongo
- name: Run Nginx container
docker_container:
name: nginx
image: nginx
state: started
ports:
- "80:80"
volumes:
- ./nginx.conf:/etc/nginx/nginx.conf
links:
- node_app
Conclusion
By integrating Ansible with Docker, you can streamline and automate your container management processes, making your infrastructure more consistent, scalable, and reliable. This combination allows you to focus more on developing and less on managing infrastructure. Whether you're managing a single container or orchestrating a complex multi-container environment, Ansible and Docker together provide a powerful toolkit for modern DevOps practices.
Give it a try and see how much time and effort you can save by automating your Docker container management with Ansible!
For more details click www.qcsdclabs.com
#redhatcourses#information technology#containerorchestration#container#linux#docker#kubernetes#containersecurity#dockerswarm#aws
0 notes
Text
Essential Tools for High-Quality Web Development Services

For web development services, having the right set of tools is crucial to streamline the development process, enhance productivity, and ensure top-quality outputs. Here are some recommended tools across different aspects of website development services:
1. Code Editors and IDEs
Visual Studio Code (VS Code): A lightweight yet powerful code editor with built-in Git support and a wide range of extensions.
Sublime Text: A fast, feature-rich code editor with extensive customization options.
JetBrains WebStorm: A robust IDE specifically designed for JavaScript development, offering powerful features for modern frameworks.
2. Version Control
Git: A distributed version control system essential for tracking changes and collaborating on code.
GitHub: A platform for hosting Git repositories, code collaboration, and project management.
GitLab: A comprehensive DevOps platform offering Git repository management, CI/CD, and more.
3. Front-end Development
React: A popular JavaScript library for building user interfaces.
Angular: A powerful framework for building dynamic web applications.
Vue.js: A progressive JavaScript framework for building user interfaces.
Bootstrap: A front-end framework for developing responsive and mobile-first websites, crucial for any website development service.
4. Back-end Development
Node.js: A JavaScript runtime for building scalable server-side applications.
Django: A high-level Python web framework that encourages rapid development and clean, pragmatic design.
Laravel: A PHP framework known for its elegant syntax and extensive feature set.
5. Database Management
MySQL: A widely-used relational database management system.
PostgreSQL: An advanced open-source relational database system with a strong reputation for reliability and feature robustness.
MongoDB: A popular NoSQL database for storing and retrieving large volumes of data, often used in web development services.
6. API Development
Postman: A collaboration platform for API development, testing, and documentation.
Swagger: Tools for designing, building, documenting, and consuming RESTful web services.
7. Containerization and Orchestration
Docker: A platform for developing, shipping, and running applications in containers.
Kubernetes: An open-source system for automating deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications.
8. CI/CD Tools
Jenkins: An open-source automation server for continuous integration and delivery.
CircleCI: A CI/CD service that supports rapid software development and publishing.
Travis CI: A CI/CD service used to build and test software projects hosted on GitHub.
9. Project Management and Collaboration
Jira: A project management tool for planning, tracking, and managing agile software development projects.
Trello: A visual collaboration tool that creates a shared perspective on any project.
Slack: A messaging app for teams that supports collaboration through channels, direct messages, and integrations with other tools.
10. Design and Prototyping
Adobe XD: A vector-based tool for designing and prototyping user experiences for web and mobile apps.
Figma: A collaborative interface design tool that allows multiple designers to work simultaneously.
Sketch: A digital design toolkit for macOS focused on UI/UX design.
11. Performance and Testing
Selenium: A suite of tools for automating web browsers for testing purposes.
Lighthouse: An open-source tool for auditing web performance, accessibility, SEO, and more.
Jest: A JavaScript testing framework designed to ensure the correctness of any JavaScript codebase, important for website development services.
12. Security
OWASP ZAP: An open-source web application security scanner to find security vulnerabilities in web applications.
Burp Suite: A suite of tools for testing web security, including a proxy, scanner, and intruder.
13. Monitoring and Analytics
Google Analytics: A powerful tool for tracking and analyzing website traffic and user behavior.
New Relic: A suite of performance monitoring tools to observe application performance, infrastructure, and user experience.
Datadog: A monitoring and security platform for cloud applications, essential for maintaining professional web development services.
These tools can help streamline your web development services, improve productivity, ensure high-quality outputs, and maintain secure and efficient applications. Depending on your specific project requirements and team preferences, you can choose the tools that best fit your web development service workflow. For those looking to enhance their website development services, these tools are indispensable in creating robust, high-performing websites that meet client needs and industry standards.
0 notes
Text
Top Software Tools and Technologies for MCA Students
The Master of Computer Applications (MCA) program is designed to equip students with the skills and knowledge needed to excel in the IT industry. To succeed in this dynamic field, it’s essential for MCA students to be proficient in a range of software tools and technologies. Here’s a look at some of the top software tools and technologies that MCA students should familiarize themselves with to stay competitive and industry-ready.

Integrated Development Environments (IDEs) Visual Studio Code: A versatile, open-source IDE developed by Microsoft, ideal for web development and supporting numerous extensions for various programming languages. Eclipse: Popular for Java development, Eclipse offers extensive plugins that cater to other languages and development needs. PyCharm: Specifically designed for Python, PyCharm enhances productivity with features like code completion, inspections, and a powerful debugger.
Version Control Systems Git: An essential tool for source code management, Git allows multiple developers to work on a project simultaneously. Platforms like GitHub, GitLab, and Bitbucket provide cloud repositories and collaboration tools. SVN (Apache Subversion): Though less common today, SVN is still used in some organizations and is good to know for understanding different version control methodologies.
Database Management Systems MySQL: A widely used relational database management system, MySQL is crucial for understanding SQL and handling large datasets. PostgreSQL: Known for its advanced features and compliance with standards, PostgreSQL is another critical tool for database management. MongoDB: A NoSQL database that’s perfect for working with unstructured data, MongoDB is increasingly relevant in the era of big data.
Programming Languages Java: A foundational language for many MCA programs, Java is essential for learning object-oriented programming. Python: Renowned for its simplicity and versatility, Python is extensively used in web development, data science, and AI. JavaScript: Essential for web development, JavaScript enables dynamic and interactive user experiences.
Web Development Frameworks React.js: A JavaScript library for building user interfaces, React.js is maintained by Facebook and widely used in the industry. Angular: Developed by Google, Angular is a robust framework for building web applications. Django: Framework for rapid development and clean, pragmatic web design based on Python.
Data Science and Machine Learning TensorFlow: An open-source platform for machine learning, TensorFlow is developed by the Google Brain team. SciPy and NumPy: Python libraries for scientific computing and numerical operations, essential for data analysis. Pandas: Python library for manipulating and analyzing data.
Project Management and Collaboration Tools Jira: A tool for agile project management, Jira helps in tracking bugs, tasks, and project progress. Trello: A flexible project management tool that uses boards, lists, and cards to organize tasks and collaborate with team members. Slack: A communication platform that integrates with other tools, facilitating seamless team collaboration.
Cloud Platforms Amazon Web Services (AWS): A comprehensive cloud platform offering a range of services from computing power to storage. Microsoft Azure: Another leading cloud platform, Azure supports a variety of cloud services and integrates well with Microsoft tools. Google Cloud Platform (GCP): Known for its strong data and machine learning services, GCP is a valuable tool for cloud-based projects.
DevOps Tools Docker: A tool for creating, deploying, and running applications in containers, Docker ensures that software runs consistently across different environments. Kubernetes: Automates application container deployment, scaling, and operation using open-source code. Jenkins: A continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) tool that automates parts of the software development process.
Cybersecurity Tools Wireshark: A network protocol analyzer that helps in troubleshooting and analyzing network traffic. Nmap: A network scanning tool used for security auditing and network discovery. Burp Suite: A set of tools for testing web application security. Conclusion Mastering these tools and technologies will provide MCA students with a strong foundation to build successful careers in the IT industry. Keeping up with the latest developments and continuously honing technical skills is crucial in this fast-evolving field. By integrating these tools into their education and projects, MCA students can ensure they are well-prepared for the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead. Know more visit : Best MCA Course in Kerala
0 notes
Text
10 Full Stack Development Tools
Visual Studio Code: A lightweight, yet powerful source code editor developed by Microsoft. It supports syntax highlighting, debugging, and extensions for various programming languages.
Node.js: An open-source, server-side JavaScript runtime environment that allows developers to build scalable and fast network applications. It's commonly used for building the backend of web applications.
React.js: A JavaScript library for building user interfaces, particularly for single-page applications. It's maintained by Facebook and a community of developers and is known for its component-based architecture.
Angular: A TypeScript-based open-source web application framework led by the Angular Team at Google. It's used for building dynamic web applications with features like data binding, dependency injection, and modular development.
Express.js: A minimal and flexible Node.js web application framework that provides a robust set of features for web and mobile applications. It's often used as the backend framework in the MEAN stack (MongoDB, Express.js, Angular, Node.js).
MongoDB: A NoSQL database program that uses a document-oriented data model. It's known for its flexibility and scalability and is commonly used in full stack development for storing and managing data.
MySQL: An open-source relational database management system that uses Structured Query Language (SQL). It's a popular choice for full stack developers due to its reliability, scalability, and wide support.
Git: A distributed version control system used for tracking changes in source code during software development. It allows multiple developers to collaborate on projects efficiently and is essential for managing code in full stack development.
Docker: A platform for developing, shipping, and running applications in containers. Docker containers provide a consistent environment for applications to run in, making it easier to deploy and manage software across different environments.
Webpack: A module bundler for JavaScript applications. It's commonly used in full stack development to bundle JavaScript files for usage in a browser, along with other assets like CSS, images, and fonts
1 note
·
View note
Video
youtube
Run Nestjs Microservices & Mongo Database in Docker Containers | #docker...Full Video Link - https://youtu.be/g3pRQZSP1rU Check out new video about Running Nestjs #Microservices in Docker Container with #Mongo DB on the #CodeOneDigest YouTube channel! Learn to setup #nestjs project with dependencies. Learn to create #docker image of nestjs project. Learn to connect nestjs application with mongo database. #mongodb #dockerimage #dockerfile@nestframework @nodejs @typescript @Docker @MongoDB @JavaScript @dotenvx @npmjs @vscodetips @getpostman #nestjs
1 note
·
View note
Text
A Comprehensive Guide to Essential Tools for Full Stack Developers
In the ever-evolving world of web development, full stack developers play a pivotal role. They are responsible for both the front-end and back-end of web applications, requiring a versatile set of tools to excel in their roles. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore a wide range of common tools that every full stack developer should consider using to build robust, efficient, and scalable applications. We will delve deep into each tool category, offering insights and recommendations to help you make informed choices in your development journey.

Integrated Development Environments (IDEs)
Visual Studio Code (VS Code): VS Code is a highly popular, free, and open-source code editor developed by Microsoft. Its extensive library of extensions makes it a versatile choice for working with various programming languages. Whether you're coding in JavaScript, Python, Java, or any other language, VS Code offers an excellent development experience.
WebStorm: WebStorm, developed by JetBrains, is an ideal choice for JavaScript and Node.js development. It excels in providing code completion, intelligent code analysis, and robust debugging features. For full stack developers working extensively with JavaScript, WebStorm is a powerful ally.
Front-End Development
HTML/CSS/JavaScript: These fundamental technologies form the core of front-end development. HTML is used for structuring web content, CSS for styling, and JavaScript for interactivity.
React, Angular, or Vue.js: Full stack developers often rely on popular JavaScript libraries/frameworks to build dynamic and responsive user interfaces. React, Angular, and Vue.js are among the top choices, each offering its unique strengths.
Back-End Development:
Node.js: Node.js is a server-side runtime that enables you to use JavaScript on the server. It is known for its non-blocking, event-driven architecture, making it suitable for building scalable and high-performance applications.
Python, Ruby, Java, or PHP: Depending on your project's requirements and your personal preferences, you can choose from a variety of programming languages for back-end development. Python, Ruby, Java, and PHP are common choices, each with its ecosystem and strengths.
Databases
MySQL, PostgreSQL, MongoDB: These relational and NoSQL databases offer flexibility in data modeling and are commonly used for various web applications.
Redis: Redis is a powerful in-memory data store that is often used for caching frequently accessed data. It can significantly improve the performance of web applications by reducing database load.
Containerization and Orchestration
Docker: Docker is a leading containerization tool that packages applications and their dependencies into isolated containers. This approach ensures consistency across different environments and simplifies deployment.
Kubernetes: Kubernetes is an orchestration platform that automates the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications. It is highly valuable when dealing with complex, containerized microservices architectures.
Testing and Debugging
Jest, Mocha, Chai (for JavaScript): These testing frameworks help you write and run automated tests for your code, ensuring that it functions as expected.
Postman: Postman is a popular tool for testing APIs. It allows you to create and execute API requests, automate testing, and perform detailed response validation.
Debugging tools in IDEs: Integrated debugging features in IDEs like VS Code and WebStorm make it easier to identify and resolve issues in your code during development.
Deployment and Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD)
Jenkins, Travis CI, GitLab CI/CD: These tools enable you to automate building, testing, and deploying your applications, ensuring code changes are integrated and deployed smoothly.
Heroku, AWS, Azure, Google Cloud Platform: Cloud providers offer robust infrastructure and hosting services that simplify deployment and scaling of web applications. Choosing the right provider depends on your project's requirements and budget.
Package Managers
npm (Node Package Manager): npm is the go-to package manager for JavaScript and Node.js projects. It simplifies dependency management and facilitates the installation of packages and libraries.
pip (Python Package Installer): Python developers rely on pip to manage Python package dependencies. It streamlines the process of installing and maintaining libraries.
Collaboration and Communication
Slack, Microsoft Teams: These communication platforms enable seamless communication within development teams. They provide channels for discussions, file sharing, and integrations with other development tools.
JIRA, Trello: Project management and issue tracking tools like JIRA and Trello help teams organize tasks, track progress, and manage project workflows efficiently.
Monitoring and Logging
Prometheus, Grafana: Prometheus is an open-source monitoring and alerting toolkit, while Grafana is a visualization and dashboarding platform. Together, they provide a powerful solution for monitoring application metrics and visualizing data.
ELK Stack (Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana): The ELK Stack is a popular choice for centralized logging and analysis. It helps you collect, store, and analyze logs generated by your applications, aiding in debugging and performance optimization.

In conclusion, full stack developers require a diverse toolkit to navigate the multifaceted world of web development successfully. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced developer, the tools mentioned in this guide are essential for building robust, efficient, and scalable applications. By carefully selecting the right tools for your specific project requirements, you can streamline your development workflow and deliver high-quality software.
To further enhance your skills and stay up-to-date with the latest industry trends, consider exploring Full Stack Developer courses offered by ACTE Technologies. ACTE Technologies provides comprehensive programs designed to empower developers with the knowledge and expertise needed to excel in their careers. With a strong foundation in these tools and continuous learning, you can become a proficient full stack developer ready to tackle complex web development challenges.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Control-Alt-Delete
Last night's breakdown was the best one yet, I've been holding in so many feelings hehe who knew I had it in me to say such things... there's just so much to do, and thats never been a problem.
But god damn, those were some really sad things that were in my mind, things I thought I'd moved on from and things I thought were okayl
I am just going to take a break from chatting to people, maybe thats getting to me. I'm just going to do my other practicals and then focus on the project, I'll try to put in some studying for security but hey we'll see how it goes.
By the end of today I should be an expert in:
Neo4j
MongoDB
Fortran
COBOL
Computer Security
From tomorrow I'll see in developing the Orcust system for the app, thats literally my last wish for the project. What's the Orcust system you ask? Well think of it as a service that allows for user submitted code to be included into the app's system, and this is accomplished through an orchestration of docker containers.
So we're taking your code, creating a docker image from it using a template and then running it as a container on its assigned port, and the running.
The orcust system is built using python and making use of docker library for this orchestration (I think management is a better word but I like the word "orchestrate") and making use of mysql for managing each container along with their assigned ports.
You'll be able to update, each version before being accepted is tested to ensure it meets the requirements which are as follows:
The running of the app shouldn't exceed the TIMEOUT of 10 seconds
Must be able to process images of different sizes
No viruses detected in images
I'll
0 notes
Text
How to Install MongoDB on Docker Container linux.
How to Install MongoDB on Docker Container linux.
Hi Guys! Hope you are doing well. Let’s Learn about “How to Install MongoDB on Docker Container Linux”. The Docker is an open source platform, where developers can package there application and run that application into the Docker Container. So It is PAAS (Platform as a Service), which uses a OS virtualisation to deliver software in packages called containers. The containers are the bundle of…

View On WordPress
#docker hub#install mongodb#install mongodb docker#install mongodb docker container#install mongodb docker image#install mongodb docker linux#install mongodb docker ubuntu#install mongodb on docker container#mongodb docker install#mongodb docker tutorial#run docker on mongodb container
0 notes
Text
UYPP: Ben Ruel's Garage Garden

Back in March, we announced the winners for our Unleash Your Potential Program, in which six participants got to configure their own System76 computer to use for their awesome projects. This first awesome project is the Garage Garden, helmed by awesome project-er, engineer, and mighty green thumb Ben Ruel. We sat down with Ben to see how his project has been growing on the Meerkat.
Can you tell us about the Garage Garden project? What's it all about?
I spent a career with the Coast Guard and came up here—my final tour with the Coast Guard was in Juneau. Being in southeast Alaska, we’re constrained with what they call off-the-road systems, and the only way in or out of town is by boat or by plane. So all of our food comes up here by barge for a small nominal fee, or by aircraft for an incredibly large fee.
When I came up to Juneau with my wife and kids 11 years ago, we noticed that by the time our produce gets up here, it’s lived on a barge a week, two weeks out of Seattle, and you have no shelf life left on them. We started trying to grow food within the first year of getting here, and we came to the conclusion pretty quickly that with 300 days plus of rain every year, outdoor growing wasn’t really a viable option. That’s when we started a hobby farm in a garage growing some stuff in soil under fluorescent lights, as odd as that sounds.
Since then, we’ve progressed into hydroponics, but we’ve done it very manually. We go out every other day and take readings by hand, so I’ve been doing some research about building IOT devices that will talk back and automate some of the readings. My dream would be using it to actually control the concentration of nutrient solutions that we use. The overall goal is we’re going to build the hydroponic monitoring network of IOT devices, and use the Meerkat as a control center for the devices and a repository for all the data. We’ve also been doing some investigating behind the scenes into whether or not it could grow enough legs to become a business.

Is there a specific type of produce that you’re starting with?
We’ve been all over the road. Right now we’ve got lettuce. We’ve always got some kind of green leafy vegetables whether it’s any variety of lettuce that will grow hydro, some bok choy and tatsoi, and we’re growing kale like it’s going out of style. We’ve grown cucumbers to the point where I think I’ve harvested 65 pounds of cucumbers off of 4 plants over the last couple of months, but we’re really constrained by our size.
I live in a relatively small 3-bedroom house, and we’re just using a one-and-a-half car garage as our grow area. Right now I’ve got two tents. As funny as it sounds, cannabis is legal in Alaska and has been forever—my wife and I don’t touch the stuff, but because it’s been legalized, the infrastructure and the supplies that we need are freely available. We’re growing tomatoes in a tent that’s designed for marijuana growth. It works really well. It helps to maintain efficient temperature control; you can maintain temperature and humidity, block out extraneous light if you don’t want it, and cycle the lights on and off.
Depending on whether it’s too hot in the summer we’ll run the lights at night, and in the wintertime we’re looking for extra warmth, we can shift the cycle and run the lights during the day. Our big benefit up here is that, because Juneau’s all on hydroelectric power, electricity is really cheap.
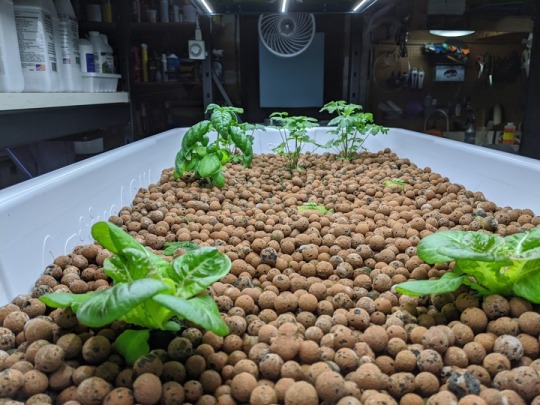

What variables are being monitored?
With hydroponics, there’s a good number of parameters that you’ve got to try and keep track of. You’re basically diluting nutrients in a solution of as pure water as you can get. You want to keep track of things—your pH can’t be too acidic or too alkaline, for example.
The other big parameter is the electrical conductivity, or total dissolved solids. You want to make sure you’ve got the right concentration of nutrients, and that your nutrient solution isn’t salting up. As you’re adjusting pH back and forth, it’ll start demineralizing salt, so tracking that data gives you a good indication for when it’s time to dump the reservoir and start over.
We’re doing it manually now. I go out every couple of days and we take samples, and sit down and log it into a spreadsheet. The Meerkat acts as a control center for programming devices, keeping a repository of the programming for the IOT devices that we’re using (Arduinos with the esp8266 chips) as well as running different database programs as Docker containers, so that they can be spun up and knocked down fast enough as we try and figure out what the best way to move forward is. We’ve got a couple of database servers that I’ve been playing around with, trying to break from traditional SQL and looking at NoSQL type of databases.
I’m not an IT guy by trade. I’m more of an electronics guy, so I’m kind of doing it as a study-by-night type of project.
What has your experience been like with the Meerkat so far?
I’m actually completely blown away by the Meerkat’s performance. It’s astounding what that small form factor and footprint is able to do. I’ve used Linux for a number of years, and basically everybody’s heard of System76. I’ve seen Pop!_OS before and never really played with it all that much, but I’ve actually grown to love it. The feel, the ergonomics, the interface, and even down to the color schemes that come bone-stock right out of the box. They just make more sense to me. I’m looking forward to the COSMIC update after researching that to see how the differences in the workflow will affect things.

What software are you using for this project?
Right now we’re writing in Docker containers and running the Tick Stack from Influx. We’re also running Telegraf, Protograph, Capacitor, playing around with the Time Series Database, I’ve got a container running MongoDB I run with SQLite, and there’s a couple different IDEs I’ve got loaded on there as well for programming Arduinos or esp8266 chip flashing.
How was the setup process for the machine?
It was up and running within 10–15 minutes of pulling it out of the box. I actually took it to work, too. We do a lot of work with government agencies, and I’ve been doing a lot of microwave radio repair. I’ve got a pretty small workbench at our shop here in Juneau, so using the Meerkat to drive all of our test equipment to control the radio while logging data coming out of the radio, it was perfect. It had enough horsepower to remotely control the test equipment. I wasn’t pushing it all that hard, but setting it up and going back and forth between having it at home or at work, it was negligible to get it up and running.
Stay tuned for further updates from Ben Ruel’s Garage Garden and cool projects from our other UYPP winners!
#system76#meerkat#desktop#mini#minicomputer#computers#desktops#laptops#servers#keyboards#NoSQL#Pop!_OS#Ubuntu#Linux#Alaska#Juneau#hydroponics#farming#vegetables#produce#cucumbers#totsui#bok choy#Arduino#Mongodb#IOT#iot solutions#automation#harvest#garage
19 notes
·
View notes
Text
6 ESSENTIAL SKILLS FOR AWS DEVELOPERS
AWS is the 500-pound gorilla in the room of cloud stages. Regarding piece of the pie, AWS claims a greater amount of the cloud market than its nearest four rivals joined. The pervasiveness of a solitary stage implies that when engineers are on the lookout for a new position, there's an amazingly decent possibility that they'll discover "AWS" under the ideal abilities for designer jobs. By having a firm comprehension of AWS improvement, you'll separate yourself and become profoundly esteemed in your group or organization. The measure of administrations and usefulness in AWS can be overpowering; this article reduces the most fundamental abilities you should know as an AWS designer.

1. Deployment
So you've composed a web application, presently what? Sending web applications to AWS is perhaps the most essential, and probably the most profound expertise to know as an AWS engineer. There are different approaches to convey to AWS, yet they keep on developing as new strategies arise and more established ones are the sunset. On account of this advancement, the accompanying outline of AWS arrangement strategies ought to be checked to ensure there aren't fresher techniques recommended.
In the first place, you ought to be agreeable to physically convey a web application to an EC2 occurrence. Understanding this establishment will permit you to expand on it and conceivably make your own mechanized sending scripts.
Then, you should know CloudFormation well and see how to utilize that to send an application, yet in addition, stand up your application framework. You ought to likewise be acquainted with Elastic Beanstalk and the work it accomplishes for you. The jury is as yet out on whether EB is the awesome most exceedingly terrible help for conveying applications to AWS, yet it is utilized at a ton of organizations so realizing it is a smart thought.
At last, compartments are turning out to be increasingly mainstream, so realizing how to convey applications with Elastic Container Service (ECS) for Docker or Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS) for Kubernetes is getting increasingly fundamental.
2. Security
The force of AWS is at times a two-sided deal. In spite of the fact that it permits you to do a ton, it likewise doesn't hold your hand. Acting naturally dependent and understanding the intricate details of the AWS Security Model and IAM is fundamental. Regularly, the most well-known bugs and issues that emerge in AWS come from a misconception of IAM by engineers. Getting very acquainted with how Roles and Policies work will upgrade all aspects of your AWS work.
Privileged insights the board is likewise another interesting subject that emerges regularly. AWS dispatched another assistance a year ago—properly called Secrets Manager—that truly removes the intricacy from overseeing and recovering any insider facts (like API keys, passwords, and so on) in your web applications.
3. AWS SDK
The AWS Software Development Kit (SDK) is the manner by which your application will communicate with AWS in the code. The API layer is totally gigantic in the SDK; even as an expert, you will continually discover new things that can be cultivated with it. Being acquainted with the SDK will deliver profits, on the grounds that interfacing with AWS won't be new to you. It's regular for engineers to not realize where to begin when pulling down an article from an S3 pail or associating with a DynamoDB table. Try not to be that designer. Get some involvement in SDK and perceive that it is so natural to utilize perhaps the most impressive advancements on the planet.
4. Databases
Data sets are a fundamental piece of each web application and AWS has various choices for fulfilling that utilization case. The issue is sorting out which information base assistance is ideal for your application. Without seeing every one of the alternatives and a portion of the advantages and disadvantages, you risk picking some unacceptable choice and blocking your application's development.
Investigate the current alternatives accessible in RDS. Aurora proceeds to improve and add new layers of similarity with MySQL and PostgreSQL. Attempt to comprehend why you should utilize Aurora rather than different alternatives. DynamoDB keeps on being a well-known decision for fast and straightforward NoSQL data set requirements. Perhaps the best part is its REST-based API, which implies no long-running data set association is required. At last, DocumentDB is the new child on the AWS information base scene, giving MongoDB similarity. Assuming DynamoDB doesn't work for your archive data set requirements, DocumentDB may get the job done.
5. Debugging
Assuming you're a designer, you know how baffling hitting a detour can be. However, you additionally likely ability a lot simpler it will manage barriers after you have some experience defeating them. AWS is the same in such a manner. Each time you conquer an issue in AWS, it just makes investigating and fixing the following issue that a lot simpler. Tragically, there's no guide to troubleshooting. It truly takes getting in there and acquiring experience with AWS. Albeit most issues you'll experience will probably be either identified with IAM consents or VPC bases access rules (for example Security Groups), there's simply no substitution for getting into the stage and creating. You'll run into issues and uncover yourself. Consider that experience when you experience your next issue to have the option to investigate it successfully.
6. Serverless
Serverless administrations in AWS, like Lambda and API Gateway, are taking care of an ever-increasing number of designer's issues nowadays. Getting when and for what reason to utilize them is a fundamental ability for each AWS engineer. Serverless engineering is extraordinary for specific sorts of usefulness and you ought to do research and evaluate this kind of design. Since Serverless is a new methodology, it's not generally comprehended by more prepared designers. By acquiring some involvement in this new innovation worldview, you can separate yourself in your group and in your organization. An open-source structure that makes building applications on Serverless engineering such a ton simpler is the Serverless Framework. By using Cloud Formation and the AWS SDK, this system permits you to utilize straightforward design records to construct incredible Serverless innovations. Perceive how your AWS consultant in India abilities stacks up.
1 note
·
View note