#journals on biomedical science
Text
Efficacy of IV Immunoglobulins on Psychiatric Symptoms: A Case Report
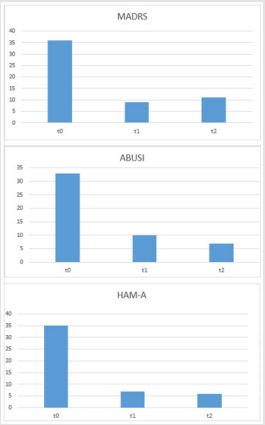
Efficacy of IV Immunoglobulins on Psychiatric Symptoms: A Case Report in Biomedical Journal of Scientific & Technical Research
https://biomedres.us/fulltexts/BJSTR.MS.ID.006058.php
Borderline personality disorder (BPD) is a fairly common psychiatric illness with a prevalence between 1.8% and 2% in the general population [1]. Diagnostic Criteria in the DSM-5 [2]: BPD is a pervasive pattern of instability in interpersonal relationships, self-image, and mood and marked impulsivity that begins by early adulthood and is present in a variety of contexts, as indicated by five (or more) of the following: a) Desperate efforts to avoid real or imagined abandonment (do not include behaviours indicated in criterion 5). A pattern of unstable and intense interpersonal relationships, characterized by the alternating between extremes of hyper-idealisation and devaluation. b) Altered identity: markedly and persistently unstable selfimage or self-perception. c) Impulsivity in at least two areas that are potentially harmful to the subject (e.g. reckless spending, promiscuous sex, substance abuse, reckless driving, binge drinking,). d) Recurrent suicidal behaviour, gestures or threats, or self-mutilating behaviour (self-harm, cuts on arms and legs, cigarette burns, etc.). e) Affective instability due to marked mood reactivity (e.g., episodic intense dysphoria, irritability or anxiety, usually lasting a few hours, and only rarely more than a few days). f) Chronic feelings of emptiness. g) Inappropriate, intense anger or difficulty controlling anger (e.g., frequent bouts of anger or constant rage, recurrent physical confrontations). h) Transient paranoid ideation, associated with stress, or severe dissociative symptoms.
For more articles in Journals on Biomedical Sciences click here bjstr
Follow on Twitter : https://twitter.com/Biomedres01
Follow on Blogger :https://biomedres01.blogspot.com/
Like Our Pins On : https://www.pinterest.com/biomedres/
#Biomedical Journal Impact Factor#Journals on Biomedical Science#medical journal in usa#Journal on medical science#Free medical journal
0 notes
Text
Biomed Grid | New Understanding of Fanconi Anemia Signaling Network upon Studying FANCD2
Abstract
The Fanconi Anemia (FA) pathway is activated upon replication stress and DNA damage. With the accumulated studies, this pathway has emerged as a fundamental signaling network to defend genome stability. The Fanconi Anemia complementation group D2 protein (FANCD2) sits at the center of the pathway, orchestrating many players to prevent our genome from going awry, leading to diseases including cancer. Here, we highlight recent advances in our understanding of FA signaling, emphasizing on a rarely known form of FANCD2, FANCD2-V2.
Fanconi Anemia
Fanconi anemia is a rare genetic disease, characterized by developmental and physical abnormalities, bone marrow failure and increased cancer susceptibility [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]. The majority of children with FA are likely to develop myelodysplastic syndrome or acute myeloid leukemia (AML), while adults are predisposed to head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, hepatocellular carcinoma, gynecological, and gastrointestinal cancers [1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 10, 11]. FA is caused by germline mutations in any of the 22 FA genes (FANCA/B/C/D1/ D2/E/F/G/I/J/L/M/N/O/P/Q/R/S/T/U/V/W). FA gene products maintain genomic integrity and participate in a common DNA repair pathway- the FA/BRCA pathway [2, 4, 12, 14]. Proteins involved are specialized more in resolving DNA interstrand cross-links (ICL), a lesion that blocks both DNA replication and transcription [2, 5, 14]. Patients suffering from FA display high frequencies of chromosomal abnormalities and are hypersensitive to DNA crosslinking agents (i.e. mitomycin C, cisplatin, diepoxybutane) [1, 3, 5, 6, 8]. If DNA is not properly repaired it can lead to genomic instability, apoptosis, senescence and tumorigenesis [4, 7].
FA Signaling
Proteins implicated in the FA/BRCA pathway coordinate nearly all known DNA repair mechanisms in order to resolve ICLs [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]. Given accumulated studies showing much crosstalk between FA and other important DNA damage repair proteins, FA signaling pathway emerges as a significant signaling network, responding to a variety of genotoxic stresses. This network is activated upon replication stress or DNA damage. FANCM is a DNA translocase and forms a protein complex with FAAP24 (FA-associated protein 24) and others. FANCM-FAAP24 recognizes stalled replication forks due to the ICL [1, 2]. Histone-fold containing kinetochore protein MHF1- MHF2 allow for the stable association of FANCM to chromatin [5]. ATR checkpoint kinase phosphorylates FANCM proceeding its recruitment to the site of damage [3]. Eight FA proteins assemble and form the FA core complex (FANCA, B, C, E, F, G, L, M) in addition to FAAP100, FAAP20, and FAAP24 to act as E3 ubiquitin ligase. Similarly, to FANCM, FANCD2 and FANCI are phosphorylated in an ATR-dependent manner. FANCT acts as an E2 together with the FA complex E3 responsible for monoubiquitinating FANCD2 and FANCI at Lys 561 and Lys 523, respectively [15]. The monoubiquitination of FANCD2-FANCDI (ID2) complex is a key step, representing FA signaling network activation. Therefore, FANCD2 must be tightly regulated to maintain DNA repair. The ID2 complex moves to the DNA lesion and recruits’ nucleases (FANCP/SLX4 and ERCC1/ FANCQ/XPF) to unhook the ICL [2, 16]. The incision is converted to a double strand break (DSB) and translesion synthesis (TLS) allows for continued replication of the leading strand, while the lagging strand is mediated by homologous recombination (HR) [3, 5, 14, 17, 18, 19, 20]. However, it remains largely unclear as to how each individual DNA damage repair mechanism works in concert to fully repair the damage within the expanded FA signaling network, including many FA and non-FA proteins that are yet to be identified.
FA Signaling and Cancer
Therefore, if the FA pathway is impaired due to mutations in involved genes, DNA remains damaged, promoting genotoxic stress, genomic instability, and tumorigenesis [3, 21, 22]. For instance, unresolved ICLs cause DNA breakage and chromosomal rearrangement, leading to cancer development [4]. Mutations or epigenetic silencing of FA genes are found in breast, ovarian and pancreatic cancers, and heterozygous germline mutations in BRCA2/FANCD1, BRIP1/FANCJ, PALB2/FANCN, RAD51C/FANCO, and BRCA1/FANCS are important cancer risk alleles [6, 12, 23, 24, 25]. Recently, researchers performed whole genome sequencing on three patients presented with three up to five primary cancers. Interestingly, the varied genes in each patient are part of the FA pathway [26]. FA gene defects are found in a variety of human cancers. Of the FA genes, FANCA has the highest mutation rate and is associated with AML, pancreatic, cervical, oral and prostate cancers [1, 27]. An elevated FANCA expression determines a worse outcome for patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and is due to a reduction of p53 genes, p21 and ΔNp73 [28]. Another group found FANCA amplification correlates with reduced progression-free survival in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma after radiotherapy [27]. FANCC has the next highest mutation rate and is similarly associated with pancreatic, cervical and oral cancers in addition to breast cancer [1, 6, 29]. Like any other FA gene, mutations in FANCD2 gene are involved in a variety of malignancies, including testicular and esophageal squamous cell carcinoma [1]. However, its importance is far beyond cancer implications, as FANCD2 sits at the center of the FA signaling network, and its activation/monoubiquitination represents the activation of FA signaling. With our recent studies on FANCD2, the previous unrecognized variant of FANCD2, FANCD2-V2 appears to be a more potent tumor suppressor than the commonly known form of FANCD2, FANCD2-V1. This review will focus on our current knowledge of FANCD2-V2. The related studies will aid in further understanding the roles that FANCD2 and/or FA signaling play in the development of human cancer and other diseases.
Overlooked FANCD2 Variant
Previously, our lab reported the first study on an alternate variant of FANCD2, named FANCD2-V2 (NCBI RefSeq accession#NM_033084.4) [30]. We refer to the long-known form as FANCD2-V1. FANCD2-V2’s cDNA is 60 bp longer than FANCD2-V1, encoding a 1471 amino acid (aa) transcript compared to FANCD2-V1 at 1451 aa. Both variants share 1427 aa at the N-terminus, resulting in 95% aa identity. We checked the expression of both FANCD2 variants in human lung tumor and matched normal samples. Interestingly, V2/V1 (ratio of V2 to V1) expression is higher in normal/non-malignant tissue compared to malignant tissues. We further assessed a panel of normal (CRL-1790, HEK293, WI-38) and tumor (HEK293T, PA-1, U2OS, HCT116, HT-29, RKO, LoVo) cell lines, which demonstrate the same trend.
In examining FANCD2 gene structure, we found a proximal and distal polyadenylation site (PAS). When the proximal PAS is used the FANCD2-V2 transcript loses the last intron; however, this intron is incorporated in the FANCD2-V1 transcript. We learned through RNA polymerase II ChIP that more DNA fragments were pulled down at the distal PAS in malignant cells compared to nonmalignant cells. U2 snRNP RNA Immunoprecipitation (RIP) showed SF3A1 antibody, a component of U2 snRNP, pulled down fragments representing the last FANCD2-V1 intron with greater binding in malignant cells than non-malignant cells. This finding suggests FANCD2-V1 transcripts are more prevalent in malignant cells. Additionally, human bladder and ovarian cancer samples present an increased V2/V1 expression in lower stage cancers. These data demonstrate FANCD2-V2 could be a more potent tumor suppressor as its expression is high in non-malignant cells and tissues.
Studies propose more than 50% of mammalian genes have multiple PAS [30]. How are sites of polyadenylation determined? A possible cause is DNA methylation. We recently reported, treating HEK293 with DNA methyltransferases reduced FANCD2-V2 expression and DNA methylation intensity near the proximal APS by methylated DNA immunoprecipitation (MeDIP) [31]. Our findings were validated with publicly available datasets (TCGA) in lung, ovarian, kidney, endometrial, colon and breast cancer, displaying an elevated methylated distal to methylated proximal APS ratio (Me-D/Me-P) is associated with malignancy. A high level of DNA methylation in the distal APS promotes FANCD2-V1 expression. Conversely, a high level of DNA methylation in the proximal APS results in FANCD2-V2 expression. To this end, we identified how two forms of FANCD2 are differentially expressed and connected with human tumorigenesis. However, it is largely unknown as to which traits in contributing to the functions are common or different between them. Simply, we would also ask; do additional FANCD2 variants exist? How are they expressed and/or function?
Conclusion and Prospective
In this short review, we aimed to update our understanding of FA signaling network with a focus on the center player, FANCD2. We described a recent recognized form of FANCD2, FANCD2-V2. This variant is expressed higher in non-malignant cell lines and tissues comparing to the corresponding malignant ones, due to proximal APS usage. These data suggest the long-known form FANCD2-V1 may be rather oncogenic compared to FANCD2-V2, which is more tumor suppressive. Of note, another group identified an alternatively splice isoform of FANCE, FANCEΔ4, which is expressed in breast cancer patients without BRCA1/2 mutations [32]. FANCEΔ4 blocked cells into G2/M phase after MMC treatment, reduced cell survival, and restricted FANCD2 and FANCI from monoubiquitination. Perhaps additional FA genes rely on alternative splicing for proper expression and gene regulation. More studies are needed to define the function(s) of alternative isoforms as wild-type protein function maybe disrupted or the isoform could gain new functions. These studies will allow for further characterization of FA genes and a deeper understanding of the FA signaling network.

Read More About this Article: https://biomedgrid.com/fulltext/volume7/new-understanding-of-fanconi-anemia-signaling-network-upon-studying-fancd2.001130.php
For more about: Journals on Biomedical Science :Biomed Grid | Current Issue
#biomedgrid#american journal of biomedical science & research#open access medical journal#journals on biomedical science
0 notes
Text


week one 🦡
i had a great week 😊 yesterday i extracted blood from someone for the first time. i don't think clinical analysis is the field for me but i'll try to keep my options open.
here's some adhd note taking for you (kinda attempting a cornell style here) and also a yummy bowl of frozen açaí!
#studybrl#studies#study#diary#journal#biomed#biomedicine#biomedical#biomedical science#stem#note taking#heartystudies
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
An Elusive Diagnosis - Posterior Cortical Atrophy: OAJBS Publishers
An Elusive Diagnosis - Posterior Cortical Atrophy by Asia Filatov* in Open Access Journal of Biomedical Science (OAJBS)

Posterior Cortical Atrophy (PCA) is a neurodegenerative syndrome characterized by progressive apraxia, dyslexia and most strikingly, loss of visual perceptual and visuospatial ability. In most cases, neurodegeneration of the occipital, parietal, and posterior temporal cortices occur as a consequence of the Visual Variant of Alzheimer disease (AD). Less frequent etiologies include Corticobasal Degeneration, Dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB), and the Heidenhain variant of prion disease. It is unknown what predisposes these conditions to present as PCA. Given its rarity and variable presentations, misdiagnosis is common. We present a case of a 60-year-old woman with PCA who was initially undiagnosed. She measurably improved on donepezil and memantine suggesting AD as its pathogenesis.
https://biomedscis.com/fulltext/an-elusive-diagnosis-posterior-cortical-atrophy.ID.000386.php
To Know More About Open Access Journal of Biomedical Science Please Visit: Biomedscis
Are Click on: https://Biomedscis.Com/
1 note
·
View note
Text
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL ON BIOMEDICAL RESEARCH AND TECHNOLOGY
About Us
The only motto of International Journal on Biomedical Research and Technology (IJBRT) Publishers is accelerating the scientific and technical research papers, reflecting the standards of technology and the human health in the progressive levels and several emergency medical and clinical issues associated with it, the key attention is given towards biomedical research. Thus, asserting the requirement of a common evoked and enriched information sharing platform for the craving readers.
IJBRT is such a unique platform to gather and expose scientific knowledge on science and related discipline. This multidisciplinary open access publisher is rendering a global podium for the professors, academicians, researchers and students of the relevant disciplines to share their scientific excellence in the form of an original research article, review article, case reports, short communication, e-books, video articles, etc.
IJBRT Publishers are self-supporting, with no dependance on any other external sources (like universities, centers) for funds and strives for the best and enhanced quality publications competes the worldwide open access publishing market.
We always rely on the support from the members of our IJBRT family that is relevantly our Authors, Editorial Committee members, advisory board, Reviewers Board, and all the technical support teams all over the globe. We trust in the communal coordination and collaboration in terms of communicating the scientific knowledge of persons and Groups of Research centers/areas will in turn educates and elicits in innovative research.
In this case we would like to act as a media that anchors in the transformation of information in the form of global online publication.
To know more about our Journal: https://ijbiomed.com/
#International Journal on Biomedical Research and Technology#Biomedical Research#Biomedical Science#Open access Journals#Open access publishers
1 note
·
View note
Text
Eight Columbia Engineering Professors Win NSF CAREER Awards
Eight Columbia Engineering Professors Win NSF CAREER Awards
Newswise — Eight professors from Columbia Engineering are among this year’s recipients of the National Science Foundation’s (NSF) Early Career Development (CAREER) awards, one of the most prestigious recognitions for junior researchers. Their areas of expertise will contribute to gains in personalized cancer treatment, the analysis of cellular processes, distributed control in large-scale…

View On WordPress
#All Journal News#Columbia University School of Engineering and Applied Science#engineering#Newswise#NSF CAREER Awards;BioMedical Engineering and Imaging Institute;Chemical Engineering;Electrical Engineering;Computer Science#Technology
0 notes
Text
Researchers have found a correlation between flavonoids, a compound found in fruits and vegetables, and a reduction in the symptoms of endometriosis.
In the study, published in the journal Endocrinology, the researchers outline how flavonoids may be able to help suppress the symptoms of inflammatory diseases like endometriosis. In endometriosis, cells similar to those in the lining of the uterus begin growing in other places in the body, causing inflammation.
The painful condition affects millions of women, and there is no cure.
Flavonoids have been associated with anticancer, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antiviral medical benefits, but the details of how they work have remained a mystery.
“Scientists have known for a while that people who eat more fruits and vegetables tend to live longer and have lower risk for many types of diseases, including Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s diseases,” says Stephen Safe, a professor in the veterinary physiology and pharmacology department at the School of Veterinary Medicine and Biomedical Sciences at Texas A&M University.
Continue Reading.
119 notes
·
View notes
Note
hiya :D
i love ur headcannons they always make me laugh reading them!
do u think u could do some on what subjects u think the mercs would teach if they were teachers?
What Subjects Would The TF2 Mercs Teach?
————————————————————
Awe, thank you, Anon, that's so sweet 💖 I can definitely write this, it seems like a lot of fun! UH going to just assume that these guys are teaching at a college, so they get specialized fields to teach!
This is probably going to be very similar to "What Jobs Would The TF2 Mercs Have If They Weren't Mercenaries" post, so I'll probably keep this shorter so I don't end up repeating myself, uh I also added how the classes would like them as a teacher!
————————————————————
Demo would teach chemistry, trying very hard not to dabble with anything too illegal in his classroom. He loves the way science almost works like magic when it comes to chemistry. Loves the bearly visible bridge between a perfect result and utter chaos. His students are both deeply terrified and greatly inspired by Demo. He's a genius when it comes to science, and it shows through the times he's deeply concentrated while teaching. May or may not have "accidentally" shown the class how to make explosives. Oops.
————————————————————
Engie is a fan of biomedical engineering regardless of if it's his job or just something he'd be asked to teach to people who were curious about it. He has such a passion for the mix of two things he loves, helping people and making things. He will go on for hours, showing examples of how important biomedical engineering is, how impactful even one person in the field can be. His students would love the passion he speaks on the subject with and how willing he is to make sure everyone in his class understands the material.
————————————————————
Heavy would teach Russian literature after being inspired by his teachers. The passion they showed in their teachings and how willing they were to prioritize helping students evoked feelings in him that he never known. He does everything for his students, making sure that everyone is supported. He tries his hardest to give his all to make these students feel the same passion he has for it. His students love him, and his class is one of the most popular, has made large impacts on every student that's came into his class.
————————————————————
Medic teaches, shock of all shocks, medical classes! I know, I know, but what can I say? He lives for the medical field. Keeps his class ethical enough, stating multiple times that as doctors, their job is to heal and save lives. However, some of his students who share the same, uh, curious shine in their eyes are more than welcome to attend a class that dips into the unethical side of medical practices. He's a good teacher, and his students are fond of him for his unsettling aura and passion.
(Can you tell I know jack all about medicine and how it's taught lmao)
————————————————————
Scout is a teacher in sports journalism, and his class both loves and loathes him as a teacher. He loves sports, so writing about them is super easy! He has a lot of fun teaching other people the best way to describe things and how to put their feelings on the page, but he's also horrendous at spelling and writing in general. His class understands his struggles but gets rather annoyed when Scout pulls up an article he wrote and can't understand any of it. He's trying his best, and he makes a half decent teacher.
————————————————————
Sniper is a photography teacher, and honestly? His class isn't for everyone. In Snipers mind through every picture he takes he's expressing a deep feeling or trying to invoke an emotion in the viewer, which he succeeds in most of the time, but it's hard for other people to replicate that when you, don't. Talk. To. Them. Some people just pick up photography and understand exactly how to do what Sniper expects without guidance, others can't understand at all. Basically, not a teacher, teacher.
————————————————————
Spy is teaching political science, hoping he can somehow subtly influence a few students into using the knowledge he provided to find a profession in espionage. He's definitely a teacher who would make you nervous, kind of a mean teacher, but he never let's a student fall behind. Subtly offering help or an extension to make sure his students succeed. Claiming he doesn't do it out of love for his students, just so he isn't known for having any failures in his class.
————————————————————
Soldier is the worlds best american history teacher, hands down. You want to talk about passion? He loves American history and will go on the longest rants and makes all of them entertaining. His class is never dull or boring. He's another prime example of a teacher who will do anything for his students and make sure they understand everything going on. No man left behind and all that. His students love him :)
————————————————————
Pyro is a teacher of fire science (I didn't even know that was a thing, but apparently it is, who knew?) Pyro, being obsessed with lighting fires, knows quite a bit about all types of fire is more than happy to share their knowledge about flames. While their students can barely understand them, they don't call Pyro out on it as their passion for the subject transcends words. Pyro's class is less of a class than a period of entertainment, but somehow everyone comes away from the class knowing everything they needed, and even somethings they didn't.
————————————————————
Short and sweet little headcanons, how fun! Sorry if it's actually too short! Thank you again for the ask anon, super fun to write :)
I'm just now realizing that there's a chance that this won't make sense because I'm a little tired while writing this, so I hope it turned out well. Sorry if it didn't, Anon 😭
#tf2#team fortress 2#tf2 headcanons#team fortress headcanons#tf2 hcs#tf2 demoman#tf2 engineer#tf2 heavy#tf2 medic#tf2 scout#tf2 sniper#tf2 spy#tf2 soldier#tf2 pyro
65 notes
·
View notes
Note
original anon here tysm for the recs ! if the marxist frameworks was too limiting im also completely fine w general postcolonial botany readings on the topic :0
A Spiteful Campaign: Agriculture, Forests, and Administering the Environment in Imperial Singapore and Malaya (2022). Barnard, Timothy P. & Joanna W. C. Lee. Environmental History Volume: 27 Issue: 3 Pages: 467-490. DOI: 10.1086/719685
Planting Empire, Cultivating Subjects: British Malaya, 1786–1941 (2018). Lynn Hollen Lees
The Plantation Paradigm: Colonial Agronomy, African Farmers, and the Global Cocoa Boom, 1870s--1940s (2014). Ross, Corey. Journal of Global History Volume: 9 Issue: 1 Pages: 49-71. DOI: 10.1017/S1740022813000491
Cultivating “Care”: Colonial Botany and the Moral Lives of Oil Palm at the Twentieth Century’s Turn (2022). Alice Rudge. Comparative Studies in Society and History Volume: 64 Issue: 4 Pages: 878-909. DOI: 10.1017/S0010417522000354
Pacific Forests: A History of Resource Control and Contest in Solomon Islands, c. 1800-1997 (2000). Bennett, Judith A.
Thomas Potts of Canterbury: Colonist and Conservationist (2020). Star, Paul
Colonialism and Green Science: History of Colonial Scientific Forestry in South India, 1820--1920 (2012). Kumar, V. M. Ravi. Indian Journal of History of Science Volume: 47 Issue 2 Pages: 241-259
Plantation Botany: Slavery and the Infrastructure of Government Science in the St. Vincent Botanic Garden, 1765–1820 (2021). Williams, J'Nese. Berichte zur Wissenschaftsgeschichte Volume: 44 Issue: 2 Pages: 137-158. DOI: 10.1002/bewi.202100011
Angel in the House, Angel in the Scientific Empire: Women and Colonial Botany During the Eighteenth and Nineteenth Centuries (2020). Hong, Jiang. Notes and Records: The Royal Society Journal of the History of Science Volume: 75 Issue: 3 Pages: 415-438. DOI: 10.1098/rsnr.2020.0046
From Ethnobotany to Emancipation: Slaves, Plant Knowledge, and Gardens on Eighteenth-Century Isle de France (2019). Brixius, Dorit. History of Science Volume: 58 Issue: 1 Pages: 51-75. DOI: 10.1177/0073275319835431
African Oil Palms, Colonial Socioecological Transformation and the Making of an Afro-Brazilian Landscape in Bahia, Brazil (2015). Watkins, Case. Environment and History Volume: 21 Issue: 1 Pages: 13-42. DOI: 10.3197/096734015X14183179969700
The East India Company and the Natural World (2015). Ed. Damodaran, Vinita; Winterbottom, Anna; Lester, Alan
Colonising Plants in Bihar (1760-1950): Tobacco Betwixt Indigo and Sugarcane (2014). Kerkhoff, Kathinka Sinha
Science in the Service of Colonial Agro-Industrialism: The Case of Cinchona Cultivation in the Dutch and British East Indies, 1852--1900 (2014). Hoogte, Arjo Roersch van der & Pieters, Toine. Studies in History and Philosophy of Science Part C: Studies in History and Philosophy of Biological and Biomedical Sciences Volume: 47 Issue: Part A Pages: 12-22
Trading Nature: Tahitians, Europeans, and Ecological Exchange (2010). Newell, Jennifer
The Colonial Machine: French Science and Overseas Expansion in the Old Regime (2011). McClellan, James E. & Regourd, François
Colonial Botany: Science, Commerce, and Politics in the Early Modern World (2005). Ed. Schiebinger, Londa L. & Swan, Claudia
Plants and Empire: Colonial Bioprospecting in the Atlantic World (2004). Schiebinger, Londa L.
89 notes
·
View notes
Text
given that he grew up a normal life…
also these jobs are general examples, i dont know entirely enough if they are accurate
#dean winchester#supernatural#dean#spn#winchester#sam winchester#dean headcanons#dean fanfiction#fanfiction#supernatural x reader#college#stanford era#dean au#spn au#dean college#au#dean headcanon
21 notes
·
View notes
Text
A Brief Overview on the Methods of Impact Evaluation of Public Policies

A Brief Overview on the Methods of Impact Evaluation of Public Policies in Biomedical Journal of Scientific & Technical Research
https://biomedres.us/fulltexts/BJSTR.MS.ID.006047.php
Impact assessment is an important tool for the formulation and implementation of evidence-informed public policies. The primary objective of this article is to present a brief review of the methods most commonly used in evaluating the impact of public policies, and the secondary objective is to present examples of the application of these methods in the evaluation of programs to promote physical activity. Quasi-experimental methods are configured as an important alternative for the construction of causal inferences about the impact of policies and programs, especially when it is not possible to participate in these interventions and do not happen randomly. In this sense, we highlight the propensity score matching method and the difference-in-differences estimator, which can be used alone, combined with each other or with other methods to generate valid and robust estimates of the causal effect. At the end of the article, the application of these methods in evaluating the impact of physical activity programs in Brazil and the United States is presented, emphasizing the versatility of these methods to assess the impact by comparing groups of aggregated units (such as municipalities), either to verify the effect of an intervention on groups of individuals.
For more articles in Journals on Biomedical Sciences click here bjstr
Follow on Twitter : https://twitter.com/Biomedres01
Follow on Blogger :https://biomedres01.blogspot.com/
Like Our Pins On : https://www.pinterest.com/biomedres/
#American medical journal#Journals on Biomedical Engineering#Journals on Biomedical Science#Journal of Biomedical Research and Review#Biomedical Open Access Journals
0 notes
Text
Biomed Grid | Bio Polymerization as One of The Stimulation Cause of The Cancer Cell Multiplication
Introduction
As it is known one of the general properties of the carcinogen materials and other influencers on the cancer evolution is their polymerizing properties. Therefore, we can assume that one of the factors stimulating the process of blocking of intercellular feedback is the bio polymerization process. Carcinogenic materials and other factors contribute to the blocking of intercellular metabolism and exchange of genetic information what complicates the genetic balance of biological processes [1] . As a result, the management of genetic processes by the central nervous system is weakened. After a certain concentration of carcinogenic substances and other factors acting on the cells, an uncontrolled polymerization process occurs, for example, of the membrane system between cells, and an uncontrolled process of cell reproduction begins, that is, cancer growth and the appearance of metastases. So, one of the important mechanisms of the cancer generation must be uncontrolled additional process of bio polymerization in the organism [2] .
Overview
Let’s list of the some carcinogens - substances of various chemical structures that can cause malignant tumors (cancer) and/ or benign neoplasms: Aflatoxins; Benzene; Benz (a) pyrenes; Vinyl chloride; Dioxins; Nitrates, nitrites; Cadmium and its compounds; Peroxides; Formaldehyde and so on. All of these materials are activators of polymerization processes.
Most chemical carcinogens are organic compounds, only a small number of inorganic substances have this ability [3] . According to Miller, all carcinogens are, to one degree or another, electrophiles that easily interact with nucleophilic groups of nitrogenous bases of nucleic acids, in particular DNA, forming strong covalent bonds with them. The negative effects of carcinogens are manifested in the chemical modification of nucleic acids [4] . The consequences of such modifications are manifested in the impossibility of the proper course of DNA transcription and replication, which leads to the formation of the so-called DNA adducts associated with it. For example, in the replication of modified DNA, nucleotides that are associated with a carcinogen may not be read correctly by DNA polymerase, resulting in mutations. The accumulation of a large number of mutations in the genome leads to the transformation of normal cells into tumor cells, which is carcinogenesis.
Chemical carcinogens can be divided into two large groups:
a) Genotoxical
b) Non-genotoxical
Genotoxic carcinogens are chemical compounds in the interaction of which with DNA components can cause damage and mutations of the cell genome [5] . Mutations in turn can lead to the formation of tumor cells. Non-toxic carcinogens are chemicals that can cause damage to the genome only in high concentrations, with a very long and almost continuous exposure [6] . They cause uncontrolled cell proliferation, inhibit apoptosis, disrupt the interaction between cells (cell adhesion). Most non-genotoxic carcinogens are carcinogenesis promoters, such as organochlorine pesticides, hormones, fibrous materials, asbestos, especially dust.
According to the mode of action, genotoxic carcinogens can be divided into:
i. Substances containing alkyl and acetylating substances- N-nitrosyl alkylurea (NAM), epoxides (especially PAHs), ethyleneimine and its derivatives, chloroethylamine, etc.).
ii. indirect - low-activity substances that form covalently bound DNA adducts only after enzymatic activation, which occurs with the formation of highly active electrophilic metabolites that can interact with nucleophilic DNA groups (PAHs and their derivatives).
The most famous physical carcinogens are various types of ionizing radiation (α, β, γ radiation, x-ray x radiation, neutron radiation, proton radiation, cluster radioactivity, ion fluxes, fission fragments), although they are also used to treat cancer. Ultraviolet is completely absorbed by the skin, and therefore can only cause melanoma. Whereas ionizing radiation, freely penetrating into the body, can cause radiogenic tumors of any tissues and organs of the body (quite often hematopoietic, due to high sensitivity). Microwave radiation.
The role of biological factors in carcinogenesis is not as great as that of chemical and physical factors, but in the etiology of some malignant tumors it is very significant [7] . So, up to 25% of cases of primary liver cancer in Asia and Africa are associated with hepatitis B virus infection. About 300,000 cases of cervical cancer per year and a significant proportion of cases of cancer of the penis are associated with sexually transmitted papillomaviruses (primarily HPV-16, HPV-18, HPV-33). Approximately 30-50% of cases of Hodgkin’s lymphoma are associated with damage to the human body by the Epstein-Barr virus.
In the 1990s, convincing data were obtained on the dependence of most varieties of gastric cancer on infection with the bacterium Helicobacter pylori [8] . In any case, all processes of initiation and propagation of cancer cells can be associated with uncontrolled processes of bio polymerization.
Conclusion
According to the author, the role of polymerization processes in the body should be taken into account when studying and treating cancer [9] . From this point of view, one should look for ways to slow down or reverse the polymerization processes in the body. Based on the author’s many years of experience, one of the most effective ways to prevent and treat cancer is the effects of passive radiation on the body in the optical range of 0.6-0.90.6-0.9μm of the corresponding lasers or LED which increase the activity of weak intermolecular bonds.

Read More About this Article: https://biomedgrid.com/fulltext/volume7/bio-polymerization-as-one-of-the-stimulation-cause-of-the-cancer-cell-multiplication.001125.php
For more about: Journals on Biomedical Science :Biomed Grid | Current Issue
#biomedgrid#american journal of biomedical science & research#american medical journal#journals on biomedical science
0 notes
Text
Which search engine is best for academic research? Hint: It's not Wikipedia

PubMed
PubMed is a free resource supporting the search and retrieval of biomedical and life sciences literature with the aim of improving health–both globally and personally.
The PubMed database contains more than 34 million citations and abstracts of biomedical literature. It does not include full-text journal articles; however, links to the full text are often present when available from other sources, such as the publisher's website or PubMed Central (PMC).
Available to the public online since 1996, PubMed was developed and is maintained by the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI), at the U.S. National Library of Medicine (NLM), located at the National Institutes of Health (NIH).
Google Scholar
Google Scholar provides a simple way to broadly search for scholarly literature. From one place, you can search across many disciplines and sources: articles, theses, books, abstracts, and court opinions, from academic publishers, professional societies, online repositories, universities, and other websites. Google Scholar helps you find relevant work across the world of scholarly research.
Semantic Scholar
Semantic Scholar provides free, AI-driven search and discovery tools, and open resources for the global research community. With Semantic Scholar, researchers can understand a paper at a glance. Our system extracts meaning and identifies connections from within papers, then surfaces these insights to help Scholars discover and understand research.
Connected Papers
Connected Papers is a unique, visual tool to help researchers and applied scientists find and explore papers relevant to their field of work.

Research Rabbit
Research Rabbit is starting with our Discovery app which unlocks a completely novel way to search for papers and authors, monitor new literature, visualize research landscapes, and collaborate with colleagues.
#pubmed#google scholar#semanticscholar#research rabbit#connected papers#researchers#research paper#research#biotechnology#biotech#science#biology#biochemistry#studyblr#molecularbiology#notes#class notes#students#biotechnology science#useful information#search engines & search marketing#search engine#phd scholar#phd#phd candidate#thesis#university#grad school#phd topics#wikipedia
993 notes
·
View notes
Text
Facile Synthesis of Chitosan Nanoparticle with Different Features and Histopathological Ultrastructural Study on the Effect of its Bio-complex with Bovine Serum Albumin in Mice Liver
Facile Synthesis of Chitosan Nanoparticle with Different Features and Histopathological Ultrastructural Study on The Effect of Its Bio-complex with Bovine Serum Albumin in Mice Liver by Maged El-Kemary* in Open Access Journal of Biomedical Science (OAJBS)

We have synthesized chitosan nanoparticles (CS-NPs) with different characteristics using ionic gelation method. Results showed that the synthesized CS-NPs with different concentrations of trisodium polyphosphate (TPP) are irregular – spherical shaped with narrow size distribution and high stability. The microporous chitosan was also synthesized with new features characterized with different techniques as SEM, EDX, FTIR and BET. The synthesized microporous chitosan has a surface area and pore volume of 245.571m2/g and 0.155cm3/g respectively. Its microporous surface is functionalized with carboxyl and amine groups. Histopathological and ultrastructural studies of mice liver were performed using optical and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) by intraperitoneal (IP) injection of male mice to evaluate toxicity of free and BSA-CS-NPs inside the body after three, six and nine days. However, no pathological or illness signs were observed in mice throughout the in vivo experiment with non-significant changes on body and relative weight of liver in compared to the negative control group. In addition, biochemical parameters exhibited a normal functionality of liver after BSA-CS-NPs administration. Accordingly, mild histopathological or ultrastructural alterations were observed in the liver of treated mice in all groups with respect with the negative controls. Activated Kupffer cells and leukocytes were observed due to the synergism of adjuvant effect of CS-NPs and antigenic peptides involved in BSA. Herein, we opened new direction for synthesis of different forms of CS-NPs and providing an obvious insight on histopathological and ultrastructural changes after administration of CS-NPs and its protein bio-complexes.
https://biomedscis.com/fulltext/facile-synthesis-of-chitosan-nanoparticle-with-different-features-and-histopathological-ultrastructural-study.ID.000402.php
To Know More About Open Access Journal of Biomedical Science Please Visit: Biomedscis
Are Click on: https://Biomedscis.Com/
#OAJBS#Open Access Journal of Biomedical Science#Open Access Journal of Biomedical Science and Research#Biomedscis#OAJBSPublishers
0 notes
Note
Tumblr keeps crashing each time I send this so I gotta be quick: do have any tips on how to study biology (college is not an option atm)
Oh boy! I will do my best!
I've listed the basic irl resources for biological information first, followed by some online resources.
I've got a strong Animalia bias, so apologies that I don't have any botany-specific sites for you. 😔
I'm sure there's some stuff I'm forgetting. I'll add on to this if I think of anything!
If there's anything specific you need help finding a reliable biological resource for, let me know and I will try my best to help find you something!
•••
Finding primary sources (stuff written by the scientists who did the research [i.e. a journal article]) is always very good, but reliable secondary resources (someone else summarizing other people's research [i.e. Wikipedia page, book]) can be very valuable as well.
•••
Meatspace Resources
-
I would highly recommend checking to see if there is a Nature Park in your area! Nature parks often have volunteer programs and/or free educational opportunities. In my experience, naturalists are always very excited to meet new people interested in learning about local ecology!
-
There's also Zoos and Aquariums of course, although I know they cost money and are typically geared more towards kids. I'm lucky to live near some nice ones. Maybe check if there are any special programs happening at Zoos/Aquariums in your area (by checking their website[s]), where you might learn more than you would on a normal day trip.
-
Plus natural history museums, which usually have rotating exhibits so that you can keep learning new things when you come back! They also have more of an all-ages vibe than Zoos in my experience. Once again dependant on if there's one near you, and not free.
-
Last but not least: the local library, although obviously not every published book is a flawless resource. Still, might be interesting to poke around! There's usually some sort of digital search catalogue to make finding things easier. Libraries are fun :)
•••
Online Resources
-
Jstor is GREAT. Not all jstor articles are open access/free, but some are! And you can set a search filter to show you only things you can access.
One good way to find out what experts have written for other experts about biology: search a species name or biological concept or type of experimental study, etc. etc., in jstor's journal articles. I've linked a search for journal articles "I can access" containing the word "biology" as an example.
The website layout can feel a little obtuse at first but I think if you fiddle around with it a bit, it's not too bad to figure out? Feel free to kick my ass if I'm wrong djgjkeg
-
Wikipedia is actually a very good place to introduce yourself to a lot of biological concepts. I would recommend checking out some of the sources yourself if you can-- usually at least some of them are free, and that can introduce you to new free resources for learning more (today I discovered bugguide.net!). Often they will link you to jstor.
But biology-focused wiki pages have a pretty good track record for Correct Information in my experience. The only issue I've run into is there being too little information sometimes.
-
Pubmed is a really good resource to read biomedical scientific papers for free if that interests you at all! Reading scientific papers is a really important skill and I think you can pick up a lot just by diving in and googling words you don't know.
A well-designed experiment is replicable (that is, you can understand from the paper how they set things up to the point that you could do it yourself, given the resources). It's also important to pay attention to sample size. The more times you replicate any process in an experiment, the more likely you will be able to identify what the most common result really is, and why.
-
Fishbase is a website I was introduced to in my icthyology class to find info about different fish species :) It kind of just dumps all the info on you in a big text wall, but many pages include great details about life cycle and diet that might go unmentioned on wiki pages.
-
I've never used bugguide.net before today, but so far it seems solid and like it has a lot of good info. I assume it is similar to fishbase but for bugs
-
EDIT: FREE ONLINE TEXTBOOKS I FORGOT ABOUT!!!
I used both of these for university classes at some point. I didn't use them much, so there may be issues I don't know about.
In my experience though they were solid resources, if a little confusingly worded at times. Bouncing between the textbooks and wikipedia tended to help me.
125 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Transparent wood could soon replace plastics
Transparent wood promises to be an environmentally friendly substitute for glass or plastic used for making car windshields, see-through packaging and biomedical devices, according to a study.
Published in the journal Science of The Total Environment, the study said transparent wood reduced ecological impacts on the environment because of its renewable and biodegradable properties. It is also said to be cost-efficient as it is five times more efficient than glass thus cutting energy cost significantly.
The world currently produces around 400 million tons of plastic waste each year, with increasing levels of single-use plastic which is used and then discarded, according to the UN Environment Program. Now, transparent wood is emerging as one of the most promising substitute materials of the future.
"Transparent wood as a material can replace the environmentally harmful petroleum-based plastics such as polypropylene, polyvinyl chloride (PVC), acrylic, polyethylene, etc.," said Prodyut Dhar, an author of the study and assistant professor at the Indian Institute of Technology's biochemical engineering school.
Read more.
158 notes
·
View notes