#portuguese government
Text
Language schools listing the courses they offer are like:
English A1
English A2
English B1
ENGLISH CAMBRIDGE EXAM PREPARATIONS
Calls for the official English accreditation exams
English B2 (FIRST)
English C1 (ADVANCED)
English C2 (PROFICIENCY)
English intensive summer courses
English for business
ENGLISH ONLINE
English semi-online
Other special English courses
*in tiny minuscule letters*: (We also offer French, Chinese, etc)
#i'm on the mailing list for my uni's modern languages school because years ago I did italian there#and every time they send me an email it's like this#today's email has a total of 26 lines:#2 are saying hello dear (name)#17 are about english courses and exams#1 is saying ''besides English we also have FRENCH CHINESE ITALIAN and PORTUGUESE!'' in smaller letters at the end#3 more lines are saying you can fracture the payment and the last 3 are signing with the name and address#they offer more languages than english chinese italian french and portuguese btw. they just didn't bother including them#i went to their site to see if they do C2 Italian but I had a hard time finding the sections for things that aren't english#turns out they've stopped doing any Italian course besides A1 (the most basic) 🤦#then i looked at the government's official language school and the index on their website had 3 sections: English (and a list of many#English courses of many different levels and topics) then German (and a list of about as half) and then Special Courses#(which once again starts with English special courses and then lists French Chinese Italian)#I understand that English is mandatory for going to uni and for most jobs but 😭#💬
10 notes
·
View notes
Text

april 25, 1974.
lisbon, portugal.
0 notes
Text
"The settler such as one finds in Algeria, in Angola, in Kenya, in Rhodesia and in the Union of South Africa is obstinately hostile to any attack on his supremacy.
We do not say to the settler: ‘You are a stranger, go away.’ We do not say to him: ‘We will take over the leadership of the country and make you pay for your crimes and those of your ancestors.’ We do not tell him that ‘to the past hatred of the Black we will oppose the present and future hatred of the white man’. We say to him: ‘We are Algerians, banish all racism from our land, all forms of oppression and let us work for man, for the flourishing of man and for the enrichment of humanity.’
The settler replies, and the French government supports him: ‘Algeria is French.’ In Angola: Angola is Portuguese. In the Union of South Africa: The Union of South Africa is a white state.
... No, the violence of the Algerian people is neither a hatred of peace nor a rejection of human relations, nor a conviction that only war can put an end to the colonial regime in Algeria. The Algerian people have chosen the unique solution that was left to them and this choice will hold firm for us.
General de Gaulle said: ‘We must break the Algerian people.’ We reply: ‘Let us negotiate, find a solution that is commensurate with contemporary history. But know that if you want to break the Algerian people, you will have to accept seeing your armies break themselves against the rampart of the glorious Algerian soldiers.’"
Frantz Fanon, "Why We Use Violence," Address to the Accra Positive Action Conference, April 1960, trans. Robert JC Young in Alienation and Freedom, 2018
987 notes
·
View notes
Text
Denmark returns iconic indigenous cloak to Brazil

The National Museum of Denmark is handing over an iconic cloak belonging to an indigenous group in Brazil at a ceremony being attended by President Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva.
Considered sacred by the indigenous Tupinambá people, the garment was taken from Brazil during the Portuguese colonial period and has been on display in Copenhagen since 1689.
The 1.8m-long cloak is made of 4,000 red feathers from the scarlet ibis bird.
Brazil’s government has been trying to recover artefacts taken during the colonial period from around the world.
Continue reading.
#brazil#politics#denmark#indigenous rights#anthropology#museums#brazilian politics#tupinamba people#danish politics#international politics#image description in alt#mod nise da silveira
396 notes
·
View notes
Text
that kind of love never dies | chapter one

summary: the one where barbara thinks about an act of rebellion.
pairing: jake x mc
word count: 1.3K
warnings: tkolnd takes place after the events of episode 10; cover images found on pinterest; english is not my first language.
author’s note: even though she lives in the usa, my main character, barbara, is brazilian. i added terms and expressions that we use in our country, as well as cultural elements, to this fanfic. the words that appear in portuguese are highlighted and you can contact me if you have any questions.
masterlist

Barbara was sprawled out on the dorm carpet, reading a Lucy Maud Montgomery novel she found by chance in the university library, when her cell phone began vibrating on the nightstand. Without wasting time, she closed the book and got up, waiting to hear from her roommate, Meera, but, when Barbara swiped her finger across the lock screen, she found some text messages from an unknown number.
i would like to invite you again to eat something at that chinese restaurant
if you want to meet me, just show up there tomorrow
i'll be waiting for you :)
Her head started to throb just at the possibility of it being who she was imagining, but she quickly pushed the thought away.
Jake wouldn't put himself in danger like that.
After everything that happened in Grimrock, Duskwood's chief of police, Alan Bloomgate, personally went after her to conduct the interrogation, and, more than once, made it very clear that it was best for her to stay away from her new friends for a while. He didn't go into detail when he told her about what happened at the Ironsplinter Mine, but he confirmed that Richy was alive — despite having some serious injuries — and that Jake had fled from the FBI agents during the confusion caused by the explosion.
All the messages she sent and received during that time became evidence. Barbara had what it took to close Hannah Donfort's case literally in the palm of her hand, including the kidnapper's confession.
Consequently, she also had the means that could lead the people who were after Jake straight to him.
She was interrogated by the FBI countless times for months, until Alan decided to intervene and convinced her to hand over her cell phone to them in exchange for her old life. Since then, Barbara has not been part of the joint investigation. Or at least that's what they say — she's too smart to really believe that.
For a few seconds, she considered the chance that it was someone trying to play a trick on her. The video Lilly Donfort posted accusing her of kidnapping had gone viral across the Columbia University campus. Even her grandmother, who lived in the interior of Brazil, found out about her involvement with a hacker wanted by the North American government. However, no one else knew about the brief conversation they had about the chinese restaurant.
Except, of course, the FBI.
Without a doubt, it was a trap. Barbara felt her face turn red. It seemed that solving an old international murder case, giving up her privacy, being forced to abandon her group of friends and possibly cheating on the guy she was in love with was not enough. She also needed to act as bait when it was convenient.
Barbara huffed, irritated. Little did they know that Jake had no contact. Their partnership in crime had ended almost a year ago.
Still, there was no reason to decline the invitation. She could very well take advantage of the opportunity to tell some truths to those nosy agents, and as a bonus she would have an excuse to go to Germany without Alan being able to question her too openly.
Her lips lifted into a smile as the plan emerged in her mind.

After going through customs at Zurich Airport, picking up luggage and going to an exchange office to exchange some notes, only an hour and fifteen minutes by car separated Barbara from Duskwood. Luckily, there were several yellow taxis forming a line next to the sidewalk, because it would be a nightmare to have to deal with someone trying to compete for the same vehicle as her.
She walked out of the lounge, pulling her hot pink rolling suitcase, and turned on her smartphone to announce on the family's group chat that she had arrived safely. But before she could check her contact list to see if her parents were online, she collided with a young man's broad chest.
She jumped away from him, apologizing — or at least trying to — in german. He laughed softly, grabbing her arm to stop her from tripping over herself, and for a moment, Barbara forgot to even breathe. The young man seemed to be a few years older than her, he was tall, had dark hair and prominent round eyes that resembled the curve of a teardrop, he was wearing a white sweatshirt with a hood and black jeans.
“I'm sorry, I didn't see you.” He spoke in english, with a slight accent.
“No problem, it was my fault.” Barbara quickly straightened up, realizing that she had somehow stared too long.
The young man analyzed her from head to toe with amusement before bending down and picking up the cell phone that had flown out of her hand during the impact.
“I believe this is yours.” He joked, handing the device to her.
“Thank you.”
He nodded curtly and turned, making his way through the travelers entering and exiting the airport, as silent as a wraith.
She was inexplicably disappointed to see him leave, however she had more important things to deal with. Then, she handed the luggage to the driver to put in the trunk and got into the taxi, giving the address of the Gates Hotel, on the outskirts of Duskwood.

Barbara ran across the room, feeling the cold floor beneath her feet. She was considerably late, but as far as she remembered, she had never arrived on time to participate in the interrogations, so whoever was waiting for her at the restaurant wouldn't mind too much. She put on a black strapless dress, put on her highest heels and curled her wet hair with her fingers, leaving a small trail of water on the floor.
Through an opening in the peach curtains, she noticed that the rain had picked up outside, beating violently against the window pane. She cursed under her breath, hoping someone at the front desk could lend her an umbrella, and before Barbara could procrastinate her meeting with the FBI Special Agent any further, she took one last look at the floor mirror near the entrance hall, realizing that she was dressed for revenge.
“Someone would definitely approve of that.”
Smiling to herself, she went down a small flight of stairs to the ground floor, where the girl at the reception was reading a magazine with Nicholas Galitzine's photo on the cover.
“How can I help you?” She asked in english, without taking her eyes off the celebrity gossip.
“Hey, how you doin'? Could you lend me an umbrella, please?”
“Of course.” She said, reaching for the object under the counter and handing it to her. “A fee of two euros will be added to your room bill.” Barbara sighed, surprised, as she mentally converted the currency. “What?” The receptionist looked up, frowning. “Did you think it would be free?”
“No, obviously not.” Barbara lied, smiling politely.
“Return it by midnight or I will have to charge the full value of the item.” The girl announced, turning her attention to the magazine. Then she added: “Nice dress.”
“Okay, I'll pay when I check out.” She assured, walking towards the glass doors while opening her rented umbrella. “And thank you.”
“Have fun, Cinderella!”
Barbara regretted walking out the door as soon as she set foot on the sidewalk. Not just because of the rain, but because of the wind blowing your hair back. In any case, she had come too far to give up, and despite the storm, she could see the lights of the chinese restaurant through the blue haze a few meters ahead, on the other side of the street.
Before she could take another step, someone grabbed her arm and turned her around.
“What?” She blinked in amazement at the handsome young man she had met at the airport.
“Come with me.” He said, pulling her away from the hotel entrance.
“You are crazy? I do not know you!” Barbara shouted, dropping the umbrella near her feet. The rain completely drenched them both in moments. “Me solta!”
“Barbara, please.” He asked, breathing short.
The sadness in his voice stopped her struggling.
“How do you…?” She gasped, eyes wide. “Jake?”

taglist: @daniiiworlds; @labemquarts; @deinily

550 notes
·
View notes
Text
“This raises the question: if industrial production is necessary to meet decent-living standards today, then perhaps capitalism—notwithstanding its negative impact on social indicators over the past five hundred years—is necessary to develop the industrial capacity to meet these higher-order goals. This has been the dominant assumption in development economics for the past half century. But it does not withstand empirical scrutiny. For the majority of the world, capitalism has historically constrained, rather than enabled, technological development—and this dynamic remains a major problem today.
It has long been recognized by liberals and Marxists alike that the rise of capitalism in the core economies was associated with rapid industrial expansion, on a scale with no precedent under feudalism or other precapitalist class structures. What is less widely understood is that this very same system produced the opposite effect in the periphery and semi-periphery. Indeed, the forced integration of peripheral regions into the capitalist world-system during the period circa 1492 to 1914 was characterized by widespread deindustrialization and agrarianization, with countries compelled to specialize in agricultural and other primary commodities, often under “pre-modern” and ostensibly “feudal” conditions.
In Eastern Europe, for instance, the number of people living in cities declined by almost one-third during the seventeenth century, as the region became an agrarian serf-economy exporting cheap grain and timber to Western Europe. At the same time, Spanish and Portuguese colonizers were transforming the American continents into suppliers of precious metals and agricultural goods, with urban manufacturing suppressed by the state. When the capitalist world-system expanded into Africa in the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries, imports of British cloth and steel destroyed Indigenous textile production and iron smelting, while Africans were instead made to specialize in palm oil, peanuts, and other cheap cash crops produced with enslaved labor. India—once the great manufacturing hub of the world—suffered a similar fate after colonization by Britain in 1757. By 1840, British colonizers boasted that they had “succeeded in converting India from a manufacturing country into a country exporting raw produce.” Much the same story unfolded in China after it was forced to open its domestic economy to capitalist trade during the British invasion of 1839–42. According to historians, the influx of European textiles, soap, and other manufactured goods “destroyed rural handicraft industries in the villages, causing unemployment and hardship for the Chinese peasantry.”
The great deindustrialization of the periphery was achieved in part through policy interventions by the core states, such as through the imposition of colonial prohibitions on manufacturing and through “unequal treaties,” which were intended to destroy industrial competition from Southern producers, establish captive markets for Western industrial output, and position Southern economies as providers of cheap labor and resources. But these dynamics were also reinforced by structural features of profit-oriented markets. Capitalists only employ new technologies to the extent that it is profitable for them to do so. This can present an obstacle to economic development if there is little demand for domestic industrial production (due to low incomes, foreign competition, etc.), or if the costs of innovation are high.
Capitalists in the Global North overcame these problems because the state intervened extensively in the economy by setting high tariffs, providing public subsidies, assuming the costs of research and development, and ensuring adequate consumer demand through government spending. But in the Global South, where state support for industry was foreclosed by centuries of formal and informal colonialism, it has been more profitable for capitalists to export cheap agricultural goods than to invest in high-technology manufacturing. The profitability of new technologies also depends on the cost of labor. In the North, where wages are comparatively high, capitalists have historically found it profitable to employ labor-saving technologies. But in the peripheral economies, where wages have been heavily compressed, it has often been cheaper to use labor-intensive production techniques than to pay for expensive machinery.
Of course, the global division of labor has changed since the late nineteenth century. Many of the leading industries of that time, including textiles, steel, and assembly line processes, have now been outsourced to low-wage peripheral economies like India and China, while the core states have moved to innovation activities, high-technology aerospace and biotech engineering, information technology, and capital-intensive agriculture. Yet still the basic problem remains. Under neoliberal globalization (structural adjustment programs and WTO rules), governments in the periphery are generally precluded from using tariffs, subsidies, and other forms of industrial policy to achieve meaningful development and economic sovereignty, while labor market deregulation and global labor arbitrage have kept wages extremely low. In this context, the drive to maximize profit leads Southern capitalists and foreign investors to pour resources into relatively low-technology export sectors, at the expense of more modern lines of industry.
Moreover, for those parts of the periphery that occupy the lowest rungs in global commodity chains, production continues to be organized along so-called pre-modern lines, even under the new division of labor. In the Congo, for instance, workers are sent into dangerous mineshafts without any modern safety equipment, tunneling deep into the ground with nothing but shovels, often coerced at gunpoint by U.S.-backed militias, so that Microsoft and Apple can secure cheap coltan for their electronics devices. Pre-modern production processes predicated on the “technology” of labor coercion are also found in the cocoa plantations of Ghana and Côte d’Ivoire, where enslaved children labor in brutal conditions for corporations like Cadbury, or Colombia’s banana export sector, where a hyper-exploited peasantry is kept in line by a regime of rural terror and extrajudicial killings overseen by private death squads.
Uneven global development, including the endurance of ostensibly “feudal” relations of production, is not inevitable. It is an effect of capitalist dynamics. Capitalists in the periphery find it more profitable to employ cheap labor subject to conditions of slavery or other forms of coercion than they do to invest in modern industry.”
Capitalism, Global Poverty, and the Case for Democratic Socialism by Jason Hickle and Dylan Sullivan
595 notes
·
View notes
Text
Fish and Chips’ Surprising Jewish History. Jamie Oliver confirmed it!
You may be surprised to learn that fish and chips, though wildly popular in England for what seems like eternity, was actually a specialty of the Portuguese Sephardic Jews who fled the Inquisition in the 16th century and found refuge in the British Isles. Celebrity Chef Jamie Oliver referred to this recently in an article in the New York Times, adding that, “Dishes evolve, impacted by trade, war, famine and a hundred other forces.”

Among those “other forces” are dishes born of religious ritual. For observant Jews, fish is pareve, a neutral food in kosher terms, thus an easy way to avoid treyf (non-kosher food) and possibly include dairy in the same meal. It was especially important for Marranos, the so-called crypto-Jews, who pretended to be Christian during the Inquisition. They ate fish on Fridays, when meat was forbidden by the Church, and also saved some to eat cold the next day at lunch, to avoid cooking on Shabbat.
Frying was natural for Jewish home cooks — think of latkes and sufganyiot — and as the Jewish community began to flourish in England, it spurred a taste for its beloved fried, battered fish throughout the country. According to Claudia Roden’s The Book of Jewish Food, Thomas Jefferson tried some on a trip to London and noted that he ate “fish in the Jewish fashion” during his visit. Alexis Soyer, a French cook who became a celebrated chef in Victorian England included a recipe for “Fried Fish, Jewish Fashion” in the first edition of his cookbook A Shilling Cookery for the People (1845). Soyer’s recipe notes that the “Jewish manner” includes using oil rather than meat fat (presumably lard), which made the dish taste better, though also made it more expensive.
There’s some dispute about the where and when of “chips” (what we Americans call French fries and the French call pommes frites). Many historians say that deep-fried, cut-up potatoes were invented in Belgium and, in fact, substituted for the fish during hard times. The first time the word “chips” was used was in Charles Dickens’ A Tale of Two Cities in 1859: “husky chips of potato, fried with some reluctant drops of oil.”
The official pairing of fish and chips didn’t happen until a few years later, though. Although there are some who dispute it, most authorities say that it is thanks to a Jewish cook, this time a young Ashkenazi immigrant named Joseph Malin, who opened the first British chippy, AKA fish and chip shop, in London in 1863. The shop was so successful it remained in business until the 1970s.
Who could foresee that fearful Jewish immigrants hiding their true religion and practicing in secret would be responsible for creating one of the most iconic dishes in the U.K.? The down-home dish that Winston Churchill claimed help the British defeat the Nazis, the comfort food that George Orwell said helped keep the masses happy and “averted revolution.” The dish, by the way, that was among the only foods never rationed during wartime because the British government believed that preserving access to it was a way of keeping up morale. A dish that continues to be a mainstay of the British diet.
Think about that the next time you find yourself feasting on this centuries-old — Jewish? British? — recipe.
These days, some restaurants are putting a new spin on fish and chips. Almond crusted. Baked instead of fried. Quinoa coated. Sweet potato fries instead of regular. And those are all fine; as Oliver says, “Dishes evolve.” But plain old fish and chips endures and probably always will. Good recipes usually do.
H/T : @scartale-an-undertale-au
Naveed Anjum
#Jews#crypto jews#jewish cuisine#fish and chips#israel#secular-jew#jewish#judaism#israeli#jerusalem#diaspora#secular jew#secularjew#islam#global cuisine#global foods#cooking#home cooking#history of food#fish n chips#marrano#jamie oliver#chippy#England#London#Britain
273 notes
·
View notes
Text

Arkanis starts TODAY at 2pm PST / 5pm EST! (18:00 BRT)
"The city of Valigma is on the verge of collapse after the exhaustive exploitation of its mines. With depleted resources, a sick population, crumbling structures and a government in crisis, hope seems lost. In a last-ditch effort, Mayor Jota calls experts to revive the city's former glory. However, in Valigma, not everything is as it seems..."
Arkanis is a lore-based Minecraft RP server featuring Brazilian and Portuguese-speaking creators. QSMP members Pac, Mike, Bagi, and Felps are participating, and several familiar faces from Purgatory will also be there (JVNQ, Febatista, Guaxinim, Wuant, and more)! Pac is one of the main creators in charge of the project, so let's show him our support!
Want to learn more about the server?
Check out the official Arkanis website.
Follow @arkanis-englishupdates for translations, news, and updates.
Watch the official Arkanis trailer!
Follow the official Arkanis Twitch account.
#Arkanis#I'm hyped!#There was clearly a lot of thought and love put into this so I'm excited to see what they do#Am I biased because Pac is in this / is part of the leadership? Yes absolutely#Oh Tumblr just completely botched the formatting of this. Cool. Great. Love to see that
151 notes
·
View notes
Text


Welcome to Diphylleia, your new populated neighborhood!
Diphylleia is a neighborhood formed by two large islands connected by a bridge. One island is more residential, which the majority of the population lives and has a few community lots. The other island is where only the richest families lives and has most of the community lots. Both have beach lots.
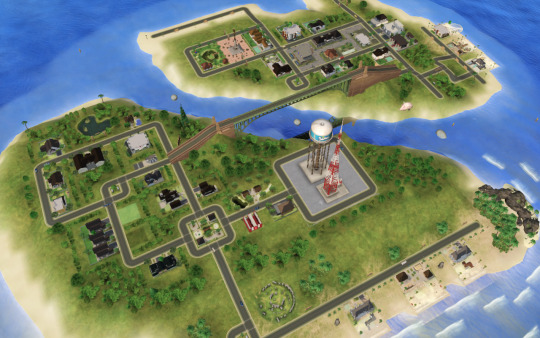
✿ Neighborhood Info:
This neighborhood requires all EPs & SPs or Ultimate Collection. It also does not needs a camera mod, you can see all lots in the vanilla game. All lots are compressed with Mootilda's LotCompressor.
This neighborhood comes in three versions: a Normal one, a No CC one and an Empty one. The Normal version needs custom content, and is avaiable in ModTheSims. Both Normal and No CC uses the NID "LEIA", the Empty version uses the NID "LEI4", so you can have a populated version and a no populated at the same time!
✿ Installation guide:
Once you download the version you wish of the neighborhood, you will extract the .zip file and put the LEIA folder (or LEI4 folder) into "Documents/EA Games/The Sims 2/Neighborhoods". There is an English and Brazilian Portuguese instructions file in the .zip.
✿ Main Story:
The Aurora family, founders of the neighborhood, live on the richest island. (...) The election day is set and Charlotte, Aurora's oldest daughter, got elected as mayor! In the celebration party, someone unexpected came… It was Elisa, Charlotte's evil sister, who decided to return home just to ruin her sister government.
During the party, Elisa met Nicolas, the son of Christtoper Walls, the richest men in Diphylleia. She had an affair with Christtopher but since he is far away from Diphylleia, she feels somehow attracted to Nicolas… After all, he looks a lot like his father… Well, Elisa just does not know that Christtopher never left. (...)
Can Zuri Okanlawon, a sucessful journalist, catch this love triangle and ruin Charlotte's image - as Elisa wishes?
✿ Sims pictures:


✿ You can download and see more information of Diphylleia HERE!
#ts2#sims 2#the sims 2#neighborhood#custom hood#sims 2 custom hood#custom neighborhood#sims 2 screenshots#sims 2 stories#sims 2 bacc#sims 2 download#ts2 custom hood#ts2 hood#diphylleia#sims 2 hood#mine#mine:hood
197 notes
·
View notes
Text

50 ANOS 🌹🇵🇹 25 de Abril Sempre 💕
O povo unido jamais será vencido!
For those who don't know, the 25th of April is the date of the Carnation Revolution, in which the Portuguese people came together to overthrow the oppressive f𝗮scist government. This year marks the 50-year anniversary of that achievement! Here's to 50 more years of freedom!
#self portrait#oc#my oc#my art#artists on tumblr#digital art#オリキャライラスト#25 de abril#portugal#portuguese#carnation revolution#grândola vila morena#zeca afonso#josé afonso
241 notes
·
View notes
Note
(To wit: this is why I have a problem with the people who want to dismantle Israel with no plan or regard for Israeli and/or Jewish safety.)
After Mozambique and Angola's independence, the Portuguese were not kicked out contrary to popular belief. Most chose to leave on their own (so-called "returnados"), while the others who chose to stay were allowed (especially those who supported independence + joined MLPA/FRELIMO and opposed colonialism) as long as they did not own weapons and supported the government. While the situation was more complex, in South Africa while whites still hold most financial power, after Apartheid many white decided to leave on their own.
In regards to your previous point on the UNRWA post, I don't see why Jewish citizens couldn't stay as long as they supported the new government and stood against colonialism and ethnic cleasing.
If you don't see the problem, you are not educated enough about this topic to weigh in. Please talk to even one (1) Mizrahi Israeli Jew about how they/their family came to be in Israel. Then consider (1) reading what the existing political entities in the Palestinian territories have to say about Jews, and (2) stop comparing this situation to historical cases of post-colonialism and start comparing it to historical cases of Arab/Muslim majority countries with Jewish citizens. Then consider how Jews the world over have fared under the rule of foreign powers, without self-determination, for the last 2000 years: (this post is a great place to start; read ALL of it + I will know if you skim)
Anyway, until you can explain to me correctly what the Farhud was and what happened to the 1000+ year old Jewish communities across the Middle East that no longer exist, as well as demonstrate a real understanding of what dhimmi status was and meant at a practical level for Jews, I am unwilling to continue this conversation.
373 notes
·
View notes
Text
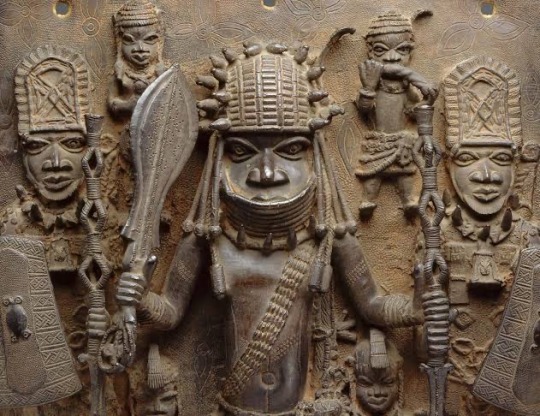




Black history is not slavery
Slavery is not the only history of black Black history goes deeper than slave trade
This is a message for my black brothers and sisters
Today I will be talking about the people of benin
The historical kingdom of Benin was established in the forested region of West Africa in the 1200s C.E. According to history, the Edo people of southern Nigeria founded Benin. They no longer wanted to be ruled by their kings, known as the ogisos. They asked a prince from Ife, an important West African kingdom, to take control. The first oba, or king, in Benin was Eweka. He was the son of the prince from Ife.The kingdom reached its greatest power and size under Oba Ewuare the Great. He expanded the kingdom and improved the capital, present-day Benin City; the city was defined by massive walls. The height of power for Benin’s monarchs began during this period. To honor the powerful obas, the people of Benin participated in many rituals that expressed their devotion and loyalty, including human sacrifices.Artists of the Benin Kingdom were well known for working in many materials, particularly brass, wood, and ivory. They were famous for their bas-relief sculptures, particularly plaques, and life-size head sculptures. The plaques typically portrayed historical events, and the heads were often naturalistic and life size. Artisans also carved many different ivory objects, including masks and, for their European trade partners, salt cellars.The success of Benin was fueled by its lively trade. Tradesmen and artisans from Benin developed relationships with the Portuguese, who sought after the kingdom’s artwork, gold, ivory, and pepper. In the early modern era, Benin was also heavily involved in the West African slave trade. They would capture men, women, and children from rival peoples and sell them into slavery to European and American buyers. This trade provided a significant source of wealth for the kingdom.Benin began to lose power during the 1800s, as royal family members fought for power and control of the throne. Civil wars broke out, dealing a significant blow to both Benin’s administration as well as its economy. In its weakened state, Benin struggled to resist foreign interference in its trading network, particularly by the British. A desire for control over West African trade and territory ultimately led to a British invasion of Benin in 1897. Benin City was burned by the British, who then made the kingdom part of British Nigeria (which became Nigeria after the country gained independence in 1960). After that time, the kingdom no longer played a governing role in West Africa. However, even today, the oba still serves in Benin City as a government advisor.

#life#culture#black history#history#blm blacklivesmatter#aesthetic#generations from exile tribe#genshin fanart#sculpture#nigeria#heritage#transgender#traditional media
730 notes
·
View notes
Text
Sorrow and struggle in the Amazon: Tuíre Kayapó, the Indigenous Brazilian woman who postponed the end of the world, dies
Every time the state tried to silence Indigenous peoples in Brazil, the late Tuíre raised her voice

Tuíre Kayapó, one of the most important Indigenous leaders in Brazil, died on Saturday (10) at a hospital in the town of Redenção, in the state of Pará. She was 57 and battled uterine cancer. Her death ended an outstanding story of defending the rights of Indigenous and Amazonian peoples. From the disputes about the Belo Monte Hydroelectric Plant up to the legal argument known as “marco temporal” (usually translated into English as "Time Frame Law"), Tuíre has always taken a stance about government attacks against forest peoples.
Tuíre raised international attention in 1989. That year, the city of Altamira, Pará, was home to the First Meeting of Xingu Indigenous Peoples. The event, which gathered 600 Indigenous individuals all painted for war, aimed at discussing the Kararaô Hydroelectric Plant, later renamed Belo Monte Hydroelectric Plant.
At a certain point, the then 19-year-old Tuíre put her machete on the face of the president of the Eletronorte company, José Antônio Muniz Lopes. According to her recollections of the episode in an interview with the Socio-environmental Institute (ISA, in Portuguese), Tuíre said to the man: “White man, you have no forest. This land isn’t yours. You were born in the city and came here to attack our forests and rivers. You won’t do this.”
The photograph of her action became known worldwide and drew the attention of authorities, activists and international artists, postponing the construction of the power plant for 20 years. After finished, Belo Monte was dubbed “the end of the world” among people in Volta Grande do Xingu. Tuíre was, in Aílton Krenak’s words, the woman who postponed the end of the world.
Continue reading.
#brazil#brazilian politics#politics#environmental justice#indigenous rights#tuire kayapo#kayapo people#image description in alt#mod nise da silveira
225 notes
·
View notes
Text
Shōgun Historical Shallow-Dive: the Final Part - The Samurai Were Assholes, When 'Accuracy' Isn't Accurate, Beautiful Art, and Where to From Here

Final part. There is an enormous cancer attached to the samurai mythos and James Clavell's orientalism that I need to address. Well, I want to, anyway. In acknowledging how great the 2024 adaptation of Shōgun is, it's important to engage with the fact that it's fiction, and that much of its marketed authenticity is fake. That doesn't take away from it being an excellent work of fiction, but it is a very important distinction to me.
If you want to engage with the cool 'honourable men with swords' trope without thinking any deeper, navigate away now. Beyond here, there are monsters - literal and figurative. If you're interested in how different forms of media are used to manufacture consent and shape national identity, please bear with me.
I think the makers of 2024's Shōgun have done a fantastic job. But there is one underlying problem they never fully wrestled with. It's one that Hiroyuki Sanada, the leading man and face of the production team, is enthusiastically supportive of. And with the recent announcement of Season 2, it's likely to return. You may disagree, but to me, ignoring this dishonours the millions of people who were killed or brutalised by either the samurai class, or people in the 20th century inspired by a constructed idea of them.
Why are we drawn to the samurai?
A pretty badly sourced, but wildly popular history podcast contends that 'The Japanese are just like everybody else, only more so.' I saw a post on here that tried to make the assertion that the show's John Blackthorne would have been exposed to as much violence as he saw in Japan, and wouldn't have found it abnormal.
This is incorrect. Obviously 16th and 17th century Europe were violent places, but they contained violence familiar to Europeans through their cultural lens. Why am I confidently asserting this? We have hundreds of letters, journals and reports from Spaniards, Portuguese, Dutch and English expressing absolute horror about what they encountered. Testing swords on peasants was becoming so common that it would eventually become the law of the land. Crucifixion was enacted as a punishment for Christians - first by the Taiko, then by the Tokugawa shogunate - for irony's sake.
Before the end of the feudal period, battles would end with the taking of heads for washing and display. Depending on who was viewing them, this was either to honour them, or to gloat: 'I'm alive, you're dead.' These things were ritualised to the point of being codified when real-life Toranaga took control. Seppuku started as a cultural meme and ended up being the enforced punishment for any minor mistake for the 260 years the ruling samurai class acted as the nation's bureaucracy. It got more and more ritualised and flowery the more it got divorced from its origin: men being ordered by other men to kill themselves during a period of chaotic warfare. I've read accounts of samurai 'warriors' during the Edo period committing seppuku for being late for work. Not life-and-death warrior work - after Sekigahara, they were just book-keepers. They had desk jobs.
Since Europe's contact with Japan, the samurai myth has fascinated and appalled in equal measure. As time has gone on, the fascination has gone up and the horror has been dialled down. This is not an accident. This isn't just a change in the rest of the world's perception of the samurai. This is the result of approximately 120 years of Japanese government policies. Successive governments - nationalist, military authoritarian, and post-war democratic - began to lionize the samurai as the perfect warrior ideal, and sanitize the history of their origin and their heydey (the period Shōgun covers). It erases the fact that almost all of the fighting of the glorious samurai Sengoku Jidai was done by peasant ashigaru (levies), who had no choice.
It is important to never forget why this was done initially: to form an imagined-historical ideal of a fighting culture. An imagined fighting culture that Japanese invasion forces could emulate to take colonies and subdue foreign populations in WWI, and, much more brutally, in WWII. James Clavell came into contact with it as a Japanese Prisoner of War.
He just didn't have access to the long view, or he didn't care.
The Original Novel - How One Ayn Rand Fan Introduced Japan to America
There's a reason why 1975's Shogun novel contains so many historical anachronisms. James Clavell bought into a bunch of state-sanctioned lies, unachored in history, about the warring states period, the concept of bushido (manufactured after the samurai had stopped fighting), and the samurai class's role in Japanese history.
For the novel, I could go into great depth, but there are three things that stand out.
Never let the truth get in the way of a good story. He's a novelist, and he did what he liked. But Clavell's novel was groundbreaking in the 70's because it was sold as a lightly-fictionalised history of Japan. The unfortunate fact is the official version that was being taught at the time (and now) is horseshit, and used for far-right wing authoritarian/nationalist political projects. The Three Unifiers and the 'honour of the samurai' magnates at the time is a neat package to tell kids and adults, but it was manufactured by an early-20th century Japanese Imperial Government trying to harness nationalism for building up a war-ready population. Any slightly critical reading of the primary sources shows the samurai to be just like any ruling class - brutal, venal, self-interested, and horrifically cruel. Even to their contemporary warrior elites in Korea and China.
Fake history as propraganda. Clavell swallowed and regurgitated the 'death before dishonour', 'loyalty to the cause above all else', 'it's all for the Realm' messages that were deployed to justify Imperial Japanese Army Class-A war crimes during the war in the Pacific and the Creation of the Greater East Asian Co-Properity Sphere. This retroactive samurai ethos was used in the late Meiji restoration and early 20th century nationalist-military governments to radicalise young Japanese men into being willing to die for nothing, and kill without restraint. The best book on this is An Introduction to Japanese Society by Sugimoto Yoshio, but there is a vast corpus of scholarship to back it up.
Clavell's orientalism strays into outright racism. Despite the novel Shōgun undercutting John Blackthorne as a white savior in its final pages - showing him as just a pawn in the game - Clavell's politics come into play in every Asia Saga novel. A white man dominates an Asian culture through the power of capitalism. This is orthagonal to points 1 and 2, but Clavell was a devotee of Ayn Rand. There's a reason his protagonists all appear cut from the same cloth. They thrust their way into an unfamiliar society, they use their knowledge of trade and mercantilism to heroically save the day, they are remarked upon by the Asian characters as braver and stronger, and they are irresistible to the - mostly simpering, extremely submissive - caricatures of Asian women in his novels. Call it a product of its times or a product of Clavell's beliefs, I still find it repulsive. Clavell invents (nearly from whole cloth, actually) the idea that samurai find money repulsive and distasteful, and his Blackthorne shows them the power of commerce and markets. Plus there are numerous other stereotypes (Blackthorne's massive dick! Japanese men have tiny penises! Everyone gets naked and bathes together because they're so sexually free! White guys are automatically cool over there!) that have fuelled the fantasies of generations of non-Japanese men, usually white: Clavell's primary audience of 'dad history' buffs.
2024's Shōgun, as a television adaptation, did a far better job in almost every respect
But the show did much better, right? Yes. Unquestionably. It was an incredible achievement in bringing forward a tired, stereotypical story to add new themes of cultural encounter, questioning one's place in the broader world, and killing your ego. In many ways, the show was the antithesis to Clavell's thesis.
It drastically reigned in the anachronistic, ahistorical referencees to 'bushido' and 'samurai honor', and showed the ruling class of Japan in 1600 much more accurately. John Blackthorne (William Adams) was shown to be an extraordinary person, but he wasn't central to the outcome of the Eastern Army-Western Army civil war. There aren't scenes of him being the best lover every woman he encounters in Japan has ever had (if you haven't read the book, this is not an exaggeration). He doesn't teach Japanese warriors how to use matchlock rifles, which they had been doing for two hundred years. He doesn't change the outcome of enormous events with his thrusting, self-confident individualism. In 2024's Shōgun, Blackthorne is much like his historical counterpart. He was there for fascinating events, but not central. He wasn't teaching Japanese people basic concepts like how to make money or how to make war.
On fake history - the manufactured samurai mythos - it improved on the novel, but didn't overcome the central problems. In many ways, I can't blame the showrunners. Many of the central lies (and they are deliberate lies) constructed around the concept of samurai are hallmarks of the genre. But it's still important to me to notice when it's happening - even while enjoying some of the tropes - without passively accepting it.
'Authenticity' to a precisely manufactured story, not to history
There's a core problem surrounding the promotion and manufactured discussion surrounding 2024's Shōgun. I think it's a disconnect between the creative and marketing teams, but it came up again and again in advertising and promotion for the show: 'It's authentic. It's as real as possible.'
I've only seen this brought up in one article, Shōgun Has a Japanese-Superiority Complex, by Ryu Spaeth:
'The show also valorizes a supreme military power that is tempered by the pursuit of beauty and the highest of cultures, as if that might be a formula for peace. Shōgun displays these two extremes of the Japanese self, the savagery and the refinement, but seems wholly unaware that there may be a connection between them, that the exquisite sensibility Japan is famous for may flow from, and be a mask for, its many uses of atrocious domination.'
Here we come to authenticity.
'The publicity surrounding the series has focused on its fidelity to authenticity: multiple rounds of translation to give the dialogue a “classical” feel; fastidious attention to how katana swords should be slung, how women of the nobility should fold their knees when they sit, how kimonos should be colored and styled; and, crucially, a decentralization of the narrative so that it’s not dominated by the character John Blackthorne.'
It's undeniable that the 2024 production spent enormous amounts of energy on authenticity. But authenticity to what? To traditional depictions of samurai in Japanese media, not to history itself. The experts hired for gestures, movement, costumes, buildings, and every other aspect of the show were experts with decades in experience making Japanese historical dramas 'look right', not experts in Japanese history. But this appeal to 'Japanese authenticity' was made in almost every piece of promotional material.
The show had only one historical advisor on staff, and he was Dutch. The numerous Japanese consultants, experts and specialists brought on board (talked about at length in the show's marketing and behind the scenes) were there to assist with making an accurate Japanese jidaigeki. It's the difference between hiring an experienced BBC period drama consultant, and a historian specialising in the Regency. One knows how to make things look 'right' to a British audience. The other knows what actually happened.
That's fine, but a critical viewing of the show needs to engage with this. It's a stylistically accurate Japanese period drama. It is not an accurate telling of Japanese history around the unification of Japan. If it was, the horses would be the size of ponies, there would be far more malnourished and brutalised peasants, the word samurai would have far less importance as it wasn't yet a rigidly enforced caste, seppuku wouldn't yet be ritualised and performed with as much frequency, and Toranaga - Tokugawa - would be a famously corpulently obese man, pounding the saddle of his horse in frustration at minor setbacks, as he was in history.
The noble picture of restraint, patience, refinement and honour presented by Hiroyuki Sanada as Toranaga/Tokugawa is historical sanitation at its most extreme. Despite being Sanada's personal hero, Tokugawa Ieyasu was a brutal warlord (even for the standards of the time), and he committed acts of horrific cruelty. He ordered many more after gaining ultimate power. Think a miniseries about the Founding Fathers of the United States that doesn't touch upon slavery - I'm sure there have been plenty.
The final myth that 2024's Shōgun leaves us with is that it took a man like Toranaga - Tokugawa Ieyasu - to bring peace to a land ripped assunder by chaos. This plays into 19th century notions of Great Man History, and is a neat story, but the consensus amongst historians is if it wasn't Tokugawa, it would have been some other cunt. In many cases, it very nearly was. His success was historical contingency, not 5D chess.
So how did this image get manufactured, to the point where the Japanese populace - by and large - believes it to be true? Very long story short: after a period of rapid modernisation, Japan embraced nationalism in the late 19th century. It was all the rage. Nationalism depends on a glorified past. The samurai (recently the pariahs of Japanese history) were repurposed as Japan's unique warrior heroes, and woven into state education. This was especially heated in the 1920s and 30s in the lead up to the invasion of Manchuria and Japan's war of aggression in the Pacific. Nationalism + militarism = the modern Japanese samurai myth, to prepare men to obey orders unquestioningly from a military dictatorship.
This persists in the postwar period. Every year since 1963, Japan's state broadcaster NHK commissions a historical drama - a Taiga Drama, where many of this show's actors got their starts - that manufactures and re-enforces the idea of samurai as noble, artful, honourable people. Read a book - read a Wikipedia article! - and you'll see that most of it stems from Tokugawa-shogunate era self-propaganda. It's much like the European re-interpretation of chivalry. In Europe's case, chivalry in actual history was a set of guidelines that allowed for the sanctioned mass-rape and murder of civilians, with a side of rules regarding the ransoming of nobles in scorched-earth military campaigns. In Japan's case, historical figures that regularly backstabbed each other, tortured rival warriors and their lessers, and inflicted horrific casualties on the peasants that they owned (we have a term for that) are cast as noble, honourable, dedicated servants of the Empire.
Why does this matter to me? Samurai movies and TV shows are just media, after all. The issue, for me, is that the actors, the producers - including Hiroyuki Sanada - passionately extoll 'accuracy' as if they genuinely believe they're telling history. They talk emotionally about bushido and its special place in Japanese society.
But the entire concept of bushido is a retroactive, post-conflict, samurai construction. Bushio is bullshit. Despite being spoken of as the central tenet of 2024's Shōgun by actors like Hiroyuki Sanada, Tadanobu Asano, and Tokuma Nishioka, it simply didn't exist at the time. It was made up after the advent of modern nationalism.
It was used to justify horrendous acts during the late Edo period, the Meiji restoration, and the years leading up to the conclusion of Japan's war of aggression in the Pacific. It's still used now by Japan's primarily right-wing government to deny war crimes and justify the horrors unleashed on Asia and the Pacific during World War II as some kind of noble warrior crusade. If you ever want your stomach turned, visit the museum attached to Yasukuni Shrine. It's a theme park dedicated to war crimes denial, linked intimately to Japan's imagined warrior past. Whether or not the production staff, cast, and marketing team of 2024's Shōgun knew they were engaging with a long line of ahistorical bullshit is unknown, but it is important.
It's also important to acknowledge that, having listened to many interviews with Rachel Kondo and Justin Marks, they were acutely aware that they weren't Japanese, to claim to be telling an authentically Japanese story would be wrong, and that all they could do was do their best to make an engaging work that plays on ideas of cultural encounter and letting go. I think the 'authenticity!' thing is mostly marketing, and judicious editing of what the creators and writers actually said in interviews.
So... you hate the show, then? What the hell is this all about?
No, I love the show. It's beautiful. But it's a beautiful artwork.

Just as the noh theatre in the show was a twisting of events within the show, so are all works of fiction that take inspiration from history. Some do it better than others. And on balance, in the show, Shōgun did it better than most. But so much of the marketing and the discussion of this adaptation has been on its accuracy. This has been by design - it was the strategy Disney adopted to market the show and give it a unique viewing proposition.
'This time, Shōgun is authentic!*
*an authentic Japanese period drama, but we won't mention that part.
And audiences have conflated that with what actually happened, as opposed to accuracy to a particular form of Japanese propaganda that has been honed over a century. This difference is crucial.
It doesn't detract from my enjoyment of it. Where I view James Clavell's novel as a horrid remnant of an orientalist, racist past, I believe the showrunners of 2024's Shōgun have updated that story to put Japanese characters front and centre, to decentralise the white protagonist to a more accurate place of observation and interest, and do their best to make a compelling subversion of the 'stranger in a strange land' tale.
But I don't want anyone who reads my words or has followed this series to think that the samurai were better than the armed thugs of any society. They weren't more noble, they weren't more honourable, they weren't more restrained. They just had 260 years in which they worked desk-jobs while wearing two swords to write stories about how glorious the good old days were, and how great people were.
Well... that's a bleak note to end on. Where to from here?
There are beautiful works of fiction that engage much closer with the actual truth of the samurai class that I'd recommend. One even stars Hiroyuki Sanada, and is (I think) his finest role.
I'd really encourage anyone who enjoyed Shōgun to check out The Twilight Samurai. That was the reality for the vast majority of post-Sekigahara samurai
For something closer to the period that Shogun is set, the best film is Seppuku (Hara-Kiri in English releases). It is a post-war Japanese film that engages both with the reality of samurai rule, and, through its central themes, how that created mythos was used to radicalise millions of Japanese into senseless death during the war. It is the best possible response to a romanticisation of a brutal, hateful period of history, dominated by cruel men who put power first, every single time.
I want to end this series, if I can, with hope. I hope that reading the novel or watching the 1980 show or the 2024 show has ignited in people an interest in Japanese culture, or society, or history. But don't let that be an end. Go further. There are so many things that aren't whitewashed warlords nobly killing - the social history of Japan is amazing, as is the women's history. A great book for getting an introduction to this is The Japanese: A History in 20 Lives.
And outside of that, there are so many beautiful Japanese movies and shows that don't deal with glorified violence and death. In fact, it makes up the vast majority of Japanese media! Who would have thought! Your Name was the first major work of art to bridge some of the cultural animosity between China and Japan stemming from WW2, and is a goofy time travel love story. Perfect Days is a beautiful movie about the simple joy of living, and it's about the most Tokyo story you can get.
Please go out, read more, watch more. If you can, try and find your way to Japan. It's one of the most beautiful places on earth. The people are kind, the food is delicious, and the culture is very welcoming to foreigners.
2024's Shōgun was great, but please don't let that be the end. Let it be the beginning, and I hope it serves as a gateway for you.

And I hope our little fandom on here remembers this show as a special time, where we came together to talk about something we loved. I'll miss you all.
#shōgun#shogun#shogun fx#toda mariko#john blackthorne#anjin#adaptationsdaily#perioddramasource#hiroyuki sanada#yoshii toranaga#akechi mariko#history#history lesson#japan#world war ii#japanese culture#tokugawa ieyasu#hosokowa gracia#william adams#sengoku jidai#writer stuff#book adaptation#women in history#social history#period drama
107 notes
·
View notes
Photo

The Habsburg Empire, 16th-17th centuries
« Atlas historique », Nathan, 1982
by cartesdhistoire
In 1519, Charles Quint found himself virtually the master of Europe. However, instead of viewing his role as a spiritual mission, he felt a deep sense of duty to his lineage. This obligation drove him to perpetuate, and if possible, enhance, what he had inherited for his successors. This principle, deeply ingrained in the tradition of the House of Burgundy, became a cornerstone of Habsburg governance, with each possession managed as if he were the sole monarch of each one.
In 1556, Philippe II inherited the ancient estates of Burgundy, the Spanish Monarchy (including its Italian dependencies), and the Duchy of Milan. Throughout his foreign policy, the sense of dynasty always took precedence: the Dutch were treated more as rebels than heretics; the incorporation of Portugal in 1580 was driven by the defense of succession rights rather than expansionism. Similarly, interventions in the French civil war and the Armada against England in 1588 aimed more at defending the integrity of heritage than pursuing a crusade.
Under Philippe III (1598-1621), signs of decline began to emerge within the Hispanic monarchy. The reign of Philippe IV (1621-1665) was marked by continual unrest, with no respite for a year of peace. Involvement in the Thirty Years War strained the Castilian Treasury, leading to economic crises in the 1630s and subsequent anti-tax revolts. The dissatisfaction of peripheral elites culminated in secessionist revolts in Catalonia and Portugal in 1640, while nobles conspired against the Crown. In Italy, revolts in Naples and Sicily in 1647 further exacerbated the crisis. Amid internal opposition, economic depression, and military setbacks, the Hispanic Monarchy struggled for survival, with only the Portuguese secession achieving success.
106 notes
·
View notes
