#spacetech
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text


1st commercial company in history completed a moon landing – Blue Ghost lunar lander from Firefly 🚀🌕👏
https://blog.adafruit.com/2025/03/02/1st-commercial-company-in-history-completed-a-moon-landing-blue-ghost-lunar-lander/
youtube
#moonlanding#fireflyaerospace#blueghost#lunarmission#spaceexploration#nasaclps#marecrisium#spacetech#commercialspace#lunarlanding#scienceonmoon#spaceinnovation#ghostriders#nasa#moonmission#spacehistory#astroscience#moonresearch#moondata#eclipseobservation#lunarhorizon#apollo17#spaceengineering#moonexploration#spacetravel#lunartech#scientificdiscovery#earthfrommoon#highdefinitionimagery#Youtube
51 notes
·
View notes
Text
How AI Is Revolutionizing Space Exploration: AI in Detecting New Planets and Cosmic Phenomena
AI in detect new planets is transforming space science, helping astronomers find exoplanets, black holes, and cosmic events rapidly. Artificial Intelligence (AI) in detect new planets is pushing space exploration boundaries for NASA, ESA, and global astronomers in advanced nations. AI is significantly improving detection techniques for new planets, cosmic phenomena, and black holes. By…
6 notes
·
View notes
Video
youtube
Blue Ghost Moon Landing - 4 Incredible Angles of Firefly's Lunar Touchdown
I was very excited during the BlueGhost Mission, It was amazing! Here is some background on Blue Ghost ands the mission:
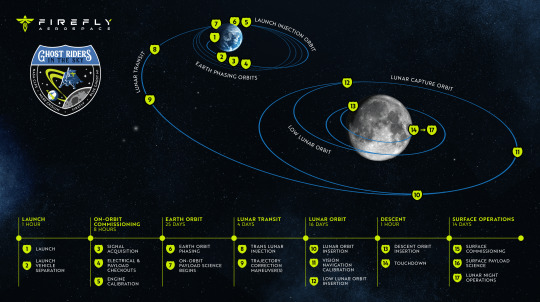
Blue Ghost Mission 1: Firefly’s Historic Lunar Landing
Firefly Aerospace’s Blue Ghost Mission 1, dubbed "Ghost Riders in the Sky," marked the first fully successful commercial soft landing on the Moon. Launched on January 15, 2025, and landing on March 2, 2025, it delivered 10 NASA payloads to Mare Crisium under the CLPS program. Here’s the scoop!
Mission Highlights
Launch: Jan 15, 2025, via SpaceX Falcon 9 from Kennedy Space Center.
Landing: Mar 2, 2025, at Mons Latreille, Mare Crisium.
Duration: ~60 days, with 14+ days of surface ops, surviving 5 hours into lunar night.
Data: Transmitted 119 GB, including 51 GB of science data.
The Lander
Named after the Phausis reticulata firefly, Blue Ghost is a 2m-tall, 3.5m-wide lander with:
Carbon composite structure for lightweight durability.
Three solar panels (400W) and robust X/S-band antennas for HD video.
1,000N main engine + eight 200N thrusters for precise landing.
Payloads
Carried 10 NASA payloads (94 kg), including:
RAC: Studied regolith stickiness.
NGLR: Enabled precise Earth-Moon distance measurements.
Lunar PlanetVac: Collected and sorted lunar soil.
LISTER: Drilled 3ft into the subsurface (hit hard rock).
SCALPSS 1.1: Captured 3D plume-surface imagery.
Eight payloads met objectives by Mar 6, 2025, supporting Artemis goals.
Cool Moments
Lunar Sunset: HD imagery of dust levitation on Mar 16, 2025.
Solar Eclipse: Captured a “diamond ring” effect on Mar 13-14, 2025.
First Images: Sent lunar surface pics 40 mins after landing.
Why It Matters
Blue Ghost’s upright landing and extended ops set a new bar for commercial lunar missions, paving the way for Artemis and future exploration. Firefly plans more missions in 2026 and 2028.
Check out more at Firefly Aerospace or NASA. Pics and videos on Firefly’s Flickr!
#youtube#blueghost#firefly#space m o o n that spells moon#moon#space#m o o n that spells moon#BlueGhostMission#Blue Ghost Mission#FireflyAerospace#Firefly Aerospace#MoonLanding#Moon Landing#NASACLPS#NASA CLPS#ArtemisProgram#Artemis Program#SpaceExploration#Space Exploration#LunarScience#Lunar Science#CommercialSpace#Commercial Space#MareCrisium#Mare Crisium#SpaceX#Space X#LunarLander#Lunar Lander#SpaceTech
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Texas senators: Move space shuttle Discovery from Smithsonian to Houston
NASA’s retired space shuttle Discovery may be removed from the Smithsonian and put on display in Houston, if two lawmakers from Texas get their way. U.S. Senators John Cornyn (R-TX) and Ted Cruz (R-TX) on Thursday (April 10) introduced the “Bring the Space Shuttle Home Act

#SpaceShuttleDiscovery#TexasSenators#HoustonSpaceCenter#Smithsonian#SpaceExploration#NASA#SpaceHistory#HoustonSpaceMuseum#ShuttleDiscovery#SpaceScience#NASAHistory#SpaceNews#MuseumExhibits#SpaceTech#TexasNews#AstronomyNews#SpaceHeritage#SpaceShuttle#HoustonSpaceNews
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
"🌕🚀 Moon GPS is on the way! By 2030, navigating the lunar surface will be as easy as using GPS on Earth. Are you ready for a coffee run to LunaBucks? ☕ #SpaceExploration just got a whole lot more exciting! 🚀✨"
"The future of space travel
instagram
#MoonGPS#LunarExploration#SpaceTech#NASA#LunarEconomy#FutureTech#SpaceRace#Astronomy#MoonMission#TechInnovation#SpaceExploration just got a whole lot more exciting#InstaTech#instagram#InnovationUnleashed#instagrowth#explore#Instagram
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Space Tech: Private Ventures and Mars Exploration

Space Tech
Beyond intrepid exploration, space technology has advanced to address pressing issues on Earth. It is becoming more and more essential to the effective operation of contemporary societies and their economic growth. Space has the potential to directly affect billions of people’s lives and open up large-scale, highly impactful solutions.
A broad term for satellites, space stations, ground stations, tracking and monitoring centers, downstream analytics and artificial intelligence, software, and other technologies, SpaceTech offers innovative ways to solve global concerns. Satellites increase communication, navigation, and earth observation capacity at low cost even in remote locations. Satellite-based earth observation data is vital, accurate, and reliable for data-driven decision-making by businesses and governments.
The underserved and otherwise unprofitable regions can benefit from high-speed connectivity thanks to the satellites. The application of action plans for intelligent agriculture, resource management (land and water), infrastructure development (urban and rural), climate and weather monitoring, environmental protection (including reducing the risk of disaster), and other purposes can all benefit from the use of satellite data.
Aerospace Innovation
The space industry is predicted to increase in value from USD 360 billion in 2018 to USD 558 billion by 2026 and roughly USD 1 trillion by 2040. Even though the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) is one of the world’s top space agencies and is working on projects like the Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (NavIC) and the Mars Orbiter Mission (MOM), India currently only makes up 2%, or USD 7 Bn, of this market value.
One reason could be that the private sector’s contribution to the Indian space industry has primarily consisted of ISRO subcontracting, with ISRO historically handling the crucial value addition activities internally. Because of this, Indian private companies have lagged behind other world leaders in SpaceTech in terms of end-to-end capabilities.
The publication of SpaceCom Policy 2020, Space RS Policy 2020, Geospatial Policy 2021, and other policies, along with the creation of organizations like NewSpace India Ltd (NSIL) and the Indian National Space Promotion and Authorization Centre (IN–SPACe), have created a national push to expedite the private sector’s involvement in the Indian space area. The Department of Space is also working on a comprehensive Space Act and other policies, including launch vehicle and space exploration policies.
Because of our natural curiosity and desire to understand the universe, space travel has long fascinated people.
Recently, private enterprise and international cooperation have transformed space exploration.
This article will explore the changing face of space exploration and emphasize the importance of international collaboration and private industry.
New Space Technologies
Pioneers of Personal Space Travel
NASA, Roscosmos, and ESA were the only government space agencies allowed to explore space. However, private companies leading space innovation changed everything:
SpaceX since 2002 has resupplied the ISS, developed reusable rocket technology, and prepared to colonize Mars.
Jeff Bezos’ Blue Origin offers professional and recreational suborbital and orbital spaceflight.
Rick Branson’s suborbital space tourism company, Virgin Galactic.
Innovating, competing, and seeking commercial opportunities beyond Earth are redefining space exploration in private space ventures.
Space Exploration Companies
International Space Cooperation
Space exploration requires international cooperation even as private businesses grow:
The Earth-orbiting International Space Station (ISS) is a global collaboration marvel. European, Japanese, Canadian, Russian, and US space agencies participate.
Mars exploration: NASA, ESA, and others work on Curiosity and Mars Sample Return.
The Artemis Accords outlines global cooperation on the Moon and beyond, inviting international partners to lunar exploration.
Global Collaboration and Private Enterprises Benefits
Space exploration benefits from private sector involvement and international cooperation in a number of ways.
Innovation: By bringing in competition and innovation, private endeavors lower costs and advance technology.
Commercialization: Businesses worldwide can take advantage of commercial endeavors to expand their satellite deployment, space tourism, and resource exploitation capabilities.
Shared Resources: Working together, nations can pool resources, exchange knowledge, and take on challenging projects.
Scientific Discovery: Across national boundaries, international cooperation increases the possibility of scientific discovery and exploration.
Difficulties and Things to Think About
Although private and international partnerships present notable benefits, they also present certain challenges.
Regulation: To address new challenges, the framework governing international cooperation and private space endeavors needs to change.
Resource Management: A complex ethical and legal challenge is the responsible use of space resources, such as lunar mining.
Space Debris: Coordinated actions ought to tackle the expanding problem of space debris and environmentally friendly space operations.
Space Travel Prospects
Future space exploration could lead to asteroid mining, planet colonization, and scientific breakthroughs.
Space exploration is entering a new era as private companies and multinational partnerships change the space environment.
Space exploration is more accessible, sustainable, and transformative than ever thanks to private innovation and international collaboration. It shows our willingness to push the limits and our enduring spirit of exploration.
Mars Rover
What is Mars Rover?
A robotic vehicle that investigates the surface of Mars is called a rover. Rovers are long-range, remotely controlled vehicles that gather data and take images while traveling great distances. They have found evidence of water, ancient life, and possible resources on Mars, among many other significant discoveries.
Six Mars rovers have been successful so far:
In 1997, Sojourner became the first rover to set foot on Mars. During 83 days, it investigated the Ares Vallis region. The twin rovers Spirit (2004) and Opportunity (2004) touched down on Mars in 2004. For many years, they investigated the Gusev Crater and Meridiani Planum, respectively. Opportunity stopped operating in 2018 and Spirit became stuck in 2010.
Gale Crater is presently being explored by Curiosity (2012). It has found evidence of ancient lakes and rivers, among many other significant discoveries.
The Jezero Crater region is being explored in Perseverance (2021). In addition to gathering samples of rock and regolith broken rock and soil for potential return to Earth, it is searching for indications of prehistoric life.
The first Chinese rover to set foot on Mars is Zhurong (2021). It is investigating the area of Utopia Planitia.
An essential component of our Mars exploration are the Mars rovers. They have made significant contributions to our understanding of the Red Planet’s potential for habitability.
Read more on Govindhtech.com
#Space Tech#MarsExploration#Ventures#SpaceTech#satellites#AI#Aerospace#NASA#technews#technology#govindhtech
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Lonesome and Poor
Who is your favorite historical figure? Lucky Luke is the man on earth….Lonesome SpaceWalker in Space….
#dailyprompt#dailyprompt-1975#Little Astronaut#Lonesome Spacewalker#LoSW#my universe#on Facebook#on Tumblr#Spacetech#Work in deep Space
0 notes
Text
#SpaceTech#RadarSystems#SatelliteInnovation#Aerospace#DefenseTech#powerelectronics#powermanagement#powersemiconductor
0 notes
Text
🌞 Science Just Got Cooler: Artificial Solar Eclipses Are Now a Thing! 🛰️ The ESA's Proba-3 mission is creating unprecedented solar observations by using two precisely positioned satellites. We break down this groundbreaking technique in our latest episode. Listen & be amazed at astronomydaily.io #SolarScience #SpaceTech
0 notes
Text
Small Satellite Market Drivers Include Demand for Earth Observation and Low-Cost Launch Solutions
The Small Satellite Market is experiencing a paradigm shift, primarily driven by the soaring need for Earth observation capabilities and the emergence of low-cost launch options. This combination is making space more accessible, allowing government agencies, private firms, and research institutions to capitalize on the advantages of compact satellite technologies. With the increasing affordability and technical feasibility, small satellites are disrupting traditional satellite development cycles and reshaping the future of global satellite services.

Surge in Earth Observation Applications
Earth observation has emerged as one of the most critical uses of small satellites. Whether monitoring climate change, analyzing agricultural productivity, or managing natural disasters, small satellites provide high-resolution imagery and data in near real-time. This capability allows for data-driven decision-making across sectors such as:
Agriculture: Monitoring crop health and predicting yields
Urban Planning: Tracking infrastructure development
Environmental Monitoring: Assessing deforestation, pollution, and water cycles
Disaster Management: Supporting emergency response during floods, wildfires, and hurricanes
Governments and commercial enterprises alike are leveraging small satellites to achieve these outcomes with unprecedented frequency and geographic coverage.
Cost Reduction and Miniaturization
Historically, space missions were prohibitively expensive and monopolized by national space agencies. Today, miniaturization and advances in electronics have reduced payload sizes without compromising performance. These compact payloads drastically lower the cost per mission and allow for more frequent launches.
Several contributing cost drivers include:
Standardized CubeSat architectures
Commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) components
Shared launch services (ride-sharing missions)
Reusable launch vehicles (e.g., by SpaceX and Rocket Lab)
By lowering the financial barrier to entry, small satellites are attracting a wide array of stakeholders, from startups to universities.
Enabling Commercial and Defense Capabilities
Commercial organizations are deploying satellite constellations for services ranging from broadband internet to global asset tracking. Notable developments include:
Communications: Providing global internet connectivity to underserved regions
Logistics: Tracking containers, cargo, and vehicles in real-time
Insurance: Monitoring assets for risk evaluation and loss mitigation
On the defense front, countries are investing in small satellites to bolster surveillance, intelligence, and navigation capabilities. These satellites are often easier to launch and replace, enhancing operational agility during geopolitical conflicts or emergencies.
Integration With Ground Infrastructure
The usability of small satellite data depends heavily on ground-based processing and communications infrastructure. Market drivers are amplified by developments in:
Ground stations: More numerous and interconnected stations allow for faster data downlink.
Data analytics platforms: AI and machine learning help in processing the deluge of incoming satellite data.
Cloud-based storage and delivery: Seamlessly integrating satellite imagery with end-user platforms like GIS systems.
These developments ensure that the advantages gained in orbit are fully realized on Earth, enhancing the overall efficiency of satellite applications.
Growing Support From Governments and Agencies
Global governments are stepping in to support small satellite missions through:
Funding: Subsidies, grants, and public-private partnerships
Regulations: Streamlining licensing and orbital assignment procedures
Infrastructure: Investing in spaceports and testbeds
Agencies like NASA, ESA, ISRO, and JAXA are integrating small satellite missions into their strategic goals, further validating their critical role in space innovation.
The Domino Effect of Launch Service Providers
Low-cost launch providers are the backbone of the small satellite boom. Companies such as Rocket Lab, Firefly Aerospace, and Virgin Orbit are offering tailored solutions for smaller payloads. Their entry has intensified competition and driven launch prices downward. Additionally, these providers offer more flexible scheduling, enabling organizations to plan launches without waiting for larger missions to align.
Strategic Collaborations and Ecosystem Expansion
The collaborative ecosystem around small satellites is robust. Manufacturers, component suppliers, launch firms, and analytics companies are increasingly forming joint ventures to offer end-to-end solutions. Strategic partnerships allow:
Faster time-to-market
Integrated data delivery solutions
Broader international market access
This ecosystem is especially advantageous for new entrants lacking in-house technical or financial resources.
Conclusion: Transitioning Into Trend-Driven Development
As demand for Earth observation and cost-effective launch continues to intensify, the Small Satellite Market is poised for sustained growth. The convergence of affordability, accessibility, and application diversity is making these systems indispensable. Looking ahead, market trends such as satellite miniaturization, rapid deployment, and AI-driven analytics will further shape the competitive landscape—topics we’ll explore in the next article of this series.
#SmallSatelliteMarket#EarthObservation#LowCostLaunch#CubeSats#SatelliteTechnology#SpaceInnovation#MiniSatellites#RemoteSensing#DefenseSatellites#NewSpace#SatelliteLaunch#SpaceTech
0 notes
Link
#Baltictech#biotech#deeptech#IronWolfCapital#NorthernEurope#spacetech#startup-funding#venturecapital
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Text
🌌 AI in Space Exploration: Transforming Satellite Data and Planetary Science
AI in space exploration is revolutionizing satellite data and planetary science. Discover how artificial intelligence powers modern space missions and data analysis. The integration of AI in space exploration has revolutionized how scientists analyze satellite data and understand distant planetary environments. With increasing volumes of cosmic data, artificial intelligence is enabling faster…
0 notes
Text
🌌 trendsofgalaxies.com is available!
The perfect domain for astronomy blogs, sci-fi fashion brands, or futuristic tech startups. Where cosmic wonder meets cutting-edge trends!
🔗 Claim this stellar domain: www.godaddy.com/en-uk/domainsearch/find?domainToCheck=trendsofgalaxies.com
0 notes
Text

Designing and building reliable hardware systems takes more than just great ideas—it demands a clear process. At Auckam, we break it down into a proven path that helps you go from concept to production with confidence. This infographic walks you through every critical phase: defining requirements and system architecture, creating effective schematics and PCB layouts, prototyping and rigorous testing, and finally optimizing for production and long-term reliability. Whether you're developing advanced deep tech, space tech, or scalable industrial hardware, following this process ensures your product is built to last. Discover how we engineer reliability into every step at www.auckam.com.
#HardwareDesign#ElectronicsEngineering#ProductDevelopment#DeepTech#SpaceTech#MadTech#Prototyping#EngineeringInnovation#ReliableHardware#TechDevelopment#IoTHardware#ManufacturingExcellence#Auckam#FutureTech
0 notes
Text
GrowX reaps a bonanza from space-tech agency Pixxel
MUMBAI : GrowX Ventures Fund, an early-stage B2B-focused enterprise capital agency, partially exited its stake in space-tech startup Pixxel, delivering a 17x return, a prime govt stated. Present buyers, together with Athera Enterprise Companions and Sparta, purchased growX’s stake in a secondary transaction final month, the chief added. “We have now half exited put up the sequence B spherical,…
0 notes