#webb space telescope
Text
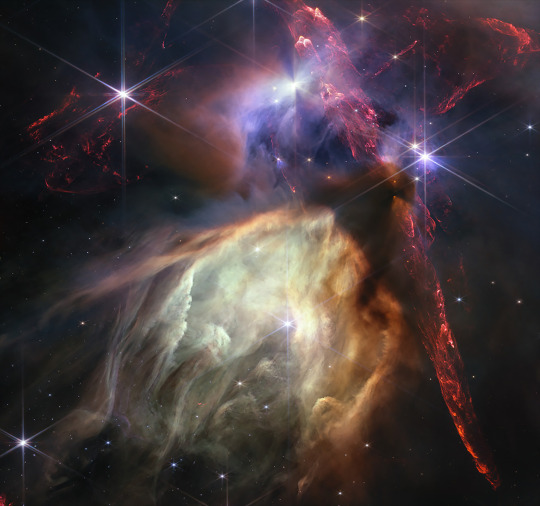


Rho Ophiuchi cloud cluster
~Happy anniversary to the James Webb Space Telescope~
27K notes
·
View notes
Text

#james webb telescope#lgbtq community#lesbian#lgbtq#lgbt pride#nonbinary#lgbtqia#sapphic#nonbinary lesbian#queer#gay girls#james webb update#james webb deepest sharpest view of universe#james webb space telescope#jwst#james webb images#james webb photos#webb space telescope#southern ring nebula#planet#space#solar system#galaxy#telescope#galaxies#quran#queer artist#queer pride
2K notes
·
View notes
Photo

Significant discovery from the Webb Telescope.
552 notes
·
View notes
Text
Supernova 1987A's Rings of Power

Here's a Hubble photo - that's the supernova remnant embedded in the center of the image.

A Hubble close-up.
Now the Webb Space Telescope crew has released a new photo, bringing out incredible detail using the instrument's infrared camera:
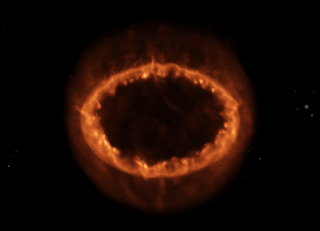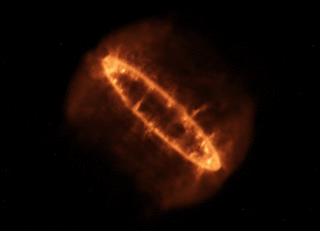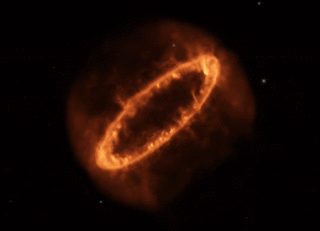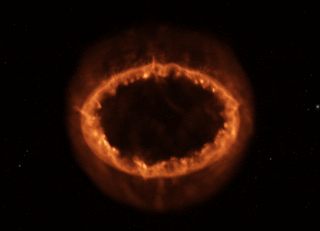
The center of the remnant is packed with clumpy gas and dust ejected by the supernova explosion, first seen lighting up the Large Magellanic Cloud in February, 1987. The dust is so dense that even the near-infrared light Webb can detect can't penetrate, shaping the dark spot at the center of what looks like a keyhole.
A bright, equatorial ring surrounds all this, forming a band around the waist from material ejected tens of thousands of years before the supernova explosion. This ring contains bright hot spots that appeared as the supernova's shock wave hit the ring. Two faint arms of hourglass-shaped outer rings surround it.
Webb reveals spots throughout the ring, where supernova shocks crash into exterior material:

We'll close with NASA's animated model of Supernova 1987A's Ring of Power.
Imagine what it would be like to live on an alien world in the Large Magellanic Cloud when this beautiful monster popped off just down the street, briefly brighter than all the other stars in this companion galaxy - even brighter than our huge Milky Way Galaxy, the huge city right next door. Our potential alien neighbor can probably still see the glowing remnant in the night sky with naked eyes, decades after the star's brilliant demise. But when it exploded, it would have been visible there in broad daylight.
66 notes
·
View notes
Text

Thinking about the Webb Space pictures...
89 notes
·
View notes
Photo

‘THE UNIVERSE AS NOBODY HAS SEEN IT YET’
IMAGES BY NASA, ESA, CSA, AND STSCI
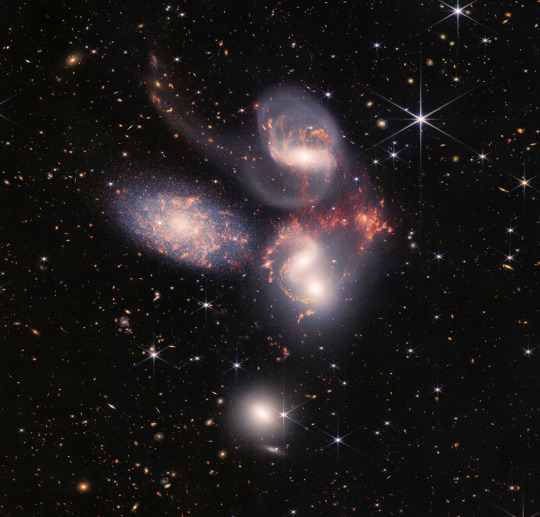

Pictured at top, the “mountains” and “valleys” speckled with glittering stars are actually the edge of a nearby, star-forming region called NGC 3324 in the Carina Nebula. Above, Stephan’s Quintet, a visual grouping of five galaxies, is Webb’s largest image to date.

Above, a side-by-side comparison shows the Southern Ring Nebula in near-infrared light, at left, and mid-infrared light.
#space#universe#astronomy#astrophotography#nasa#esa#casa#stsci#carina nebula#stephan's quintet#galaxy#southern ring nebula#webb space telescope#national geographic
88 notes
·
View notes
Text
Webb Space Telescope captures clearest view of Neptune’s rings in decades

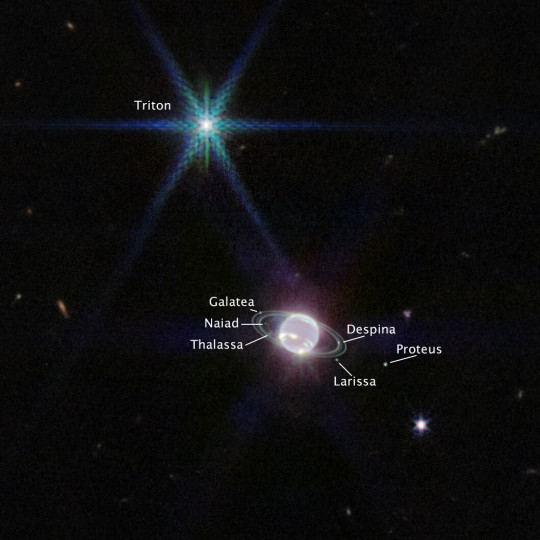
Neptune has 14 known satellites, and seven of them are visible in this image (labeled in the second one)
Triton, the bright light with diffraction spikes in the upper left, outshines Neptune because, while methane in the planet’s atmosphere absorbs wavelengths imaged by Webb, Triton is covered in a frozen sheen of nitrogen, reflecting 70% of sunlight that hits it
Triton orbits Neptune backwardsly - astronomers suspect it was originally a Kuiper Belt object the planet gravitationally captured long ago
(also I hold great fondness for Triton, and it's an important setting in my novel Transcendence)
read more about Webb's atmospheric discoveries about Neptune on the NASA page: X
144 notes
·
View notes
Photo

“Two of the farthest galaxies seen to date are captured in these Webb Space Telescope pictures of the outer regions of the giant galaxy cluster Abell 2744. The galaxies are not inside the cluster, but many billions of light-years farther behind it. The galaxy labeled (1) existed only 450 million years after the big bang. The galaxy labeled (2) existed 350 million years after the big bang.”
These galaxies discovered by Webb just a few days after it has begun science operations are already forcing scientists to rethink their theories on the evolution of the universe, pushing back the birth of the first galaxies to just 100 million years after the big bang, and possibly providing our first known glimpse of the to-this-point only theorized “Population III” stars: “the first stars ever born, blazing at blistering temperatures and made up only of primordial hydrogen and helium.”
#webb space telescope#james webb#telescope#space telescope#webb#galaxies#universe#science#astronomy#nasa#population iii#stars#big bang#galaxy formation#oldest galaxies#oldest stars#first stars#abell 2744
69 notes
·
View notes
Text


Webb telescope shows the Pillars of Creation in near-infrared (top, and right). Visible light image from Hubble made in 2014 on the left. The red glowing points are newly-formed stars.
#webb space telescope#nircam#space!#science!#nasa#eagle nebula#pillars of creation#hubble#my beloved#breathtaking
50 notes
·
View notes
Text
the hubble and webb telescopes are girlfriends stop comparing them. they are both good
#hubble space telescope#webb space telescope#webb telescope#hubble telescope#lesbian#gay#space#nasa#galax speaks but probably shouldn't
32 notes
·
View notes
Photo



More Webb Space Telescope inspired resin panels © Peter Solarz
After one layer of resin out of five layers for finished piece.
#paintings#abstract painting#abstract sculpture#webb space telescope#artists on tumblr#artists studio
32 notes
·
View notes
Photo


#magic school bus#out of context#ms frizzle#carlos#you sure this is gonna work#it better#bob#webb space telescope#jwst#outer space#asteroid#comet#Out of This World
24 notes
·
View notes
Text








31 notes
·
View notes
Text

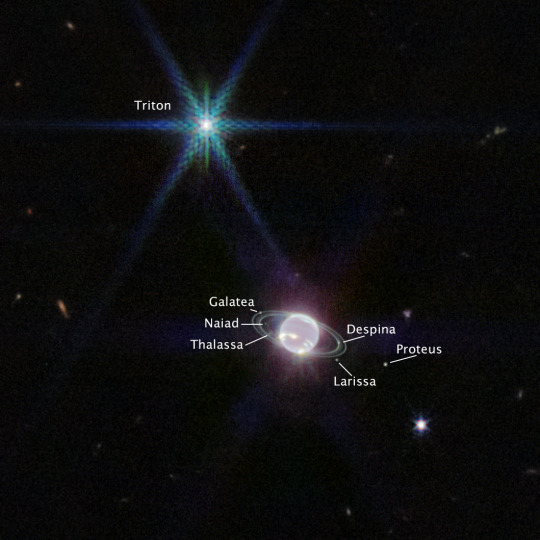

No one talk to me I'm in love
Webb Telescope Captures Clearest View of Neptune's Rings in Decades
#patch posts#space#james webb telescope#webb space telescope#neptune#this isnt sponsored#i just love space so much
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
Deep Extragalactic Survey reveals more than 45,000 ancient galaxies

And hundreds of these were fully formed before the universe was less than 600 million years old - the Epoch of Reionization, when the baby universe transformed from opaque to transparent.
Imagine what it must have been like to look up and see a hot, glowing sky instead of blackness.
The sheer number of these galaxies was far beyond predictions from before Webb’s launch.
Check out NASA's Webb Space Telescope page for far higher resolution images: X
60 notes
·
View notes
Text

Looking at infrared wavelengths beyond Hubble’s deepest fields, Webb’s sharp near-infrared view reveals thousands of galaxies—including the faintest objects ever observed in the infrared—in the most detailed view of the early universe to date. We can now see tiny, faint structures we’ve never seen before, like star clusters and diffuse features and soon, we’ll begin to learn more about the galaxies’ masses, ages, histories, and compositions.
These images and data are just the beginning of what the observatory will find. It will study every phase in the history of our Universe, ranging from the first luminous glows after the Big Bang, to the formation of solar systems capable of supporting life on planets like Earth, to the evolution of our own Solar System. Via @nasa
12 notes
·
View notes